Pulmonary function in healthy young adult
|
|
|
- Cody Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax 1990;45: Pulmonary function in healthy young adult Indians in Madras 611 Cardiopulmonary Medicine Unit, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Indian Council of Medical Research, Madras, India V K Vijayan K V Kuppurao P Venkatesan K Sankaran R Prabhakar Address for reprint requests: Dr V K Vijayan, Cardiopulmonary Medicine Unit, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Indian Council of Medical Research, Madras , India. Accepted 25 April 1990 V K Vijayan, K V Kuppurao, P Venkatesan, K Sankaran, R Prabhakar Abstract Forced vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in one second, functional residual capacity, residual volume, total lung capacity, and single breath diffusing capacity measurements (effective alveolar volume, carbon monoxide transfer factor, and transfer coefficient) were measured in 247 young healthy adults (130 male, 117 female) aged years living in Madras. Subjects were of Dravidian stock, living at sea level with rice as their staple diet. Regression equations were derived for men and women for predicting normal pulmonary function for young adults in South India. The values were similar to those reported for subjects from Western India and lower than those reported for North Indians and caucasians. Differences in pulmonary function in normal people may be due to ethnic origin, physical activity, environmental conditions, altitude, tobacco smoking, age, height, sex, and socioeconomic status.' The wide range of geographical and climatic conditions in a large country such as India may be associated with regional differences in lung function in healthy individuals, as shown in previous studies.2' We have measured pulmonary function, including spirometric indices, static lung volumes, and diffusing capacity indices, in healthy young adults in South India. Methods SUBJECTS We studied 247 ethnic South Indians living in Madras and aged years. They included relatives of patients attending the Tuberculosis Research Centre, staff members, manual workers, students, and executives, to obtain a cross section of the normal inhabitants of Madras city. The proportions of subjects in the different income groups were: low (less than 500 rupees a month) 49%, middle ( rupees) 38%, and high (more than 1500 rupees) 13%, similar to the proportions seen in the general population in Madras city (data obtained from Madras Municipal Corporation on the basis of the 1981 government census). The proportion of subjects who declined to take part in this study was less than 10%. Subjects were eligible for the study if they were ethnic South Indians, had no structural deformity of the thoracic cage, and were free from respiratory infections and had been so for at least three months before the tests. None of the subjects had any cardiorespiratory disease, as assessed by detailed history, physical examination, chest radiography, and 12 lead electrocardiography. Symptomless smokers were included. TESTS Pulmonary function tests were carried out with transfer test model C (P K Morgan, Chatham, UK), readings being obtained from a Data Dec computer. Sex, ethnic identity, standing height to the nearest centimetre without shoes, weight in kilograms, age, smoking habit, occupation, and spirometer temperature were recorded for all subjects before testing. The tests were carried out with the subject seated and with a nose clip applied. The equipment was calibrated fully every day. The coefficient of variation for six subjects studied over a year was less than 1% for forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEVy), less than 2% for total lung capacity (TLC), alveolar volume (VA), carbon monoxide transfer factor (TLCO), and transfer coefficient (Kco), less than 2-5% for functional residual capacity (FRC), and less than 5% for residual volume (RV). All volumes were expressed in BTPS. Spirometry At least three forced vital capacity manoeuvres7 were obtained for each subject; for FVC and FEVy the best two of three tracings had to be within + 50%. The largest of three FVC and FEVy values was accepted even if the two volumes did not come from the same curve. The ratio of FEVy to FVC was expressed as a percentage. Static lung volumes Functional residual capacity, residual volume, and total lung capacity were measured by the closed circuit helium dilution method.8 Duplicate measurements of FRC were made for each patient and the mean value was used for analysis.' Residual volume and total lung capacity were calculated from the kymograph tracing. Single breath carbon monoxide transferfactor The single breath carbon monoxide transfer factor78 was measured with a gas mixture containing helium 14%, carbon monoxide 0-288%, and oxygen 18%, the rest being
2 612 Vijayan, Kuppurao, Venkatesan, Sankaran, Prabhakar Table 1 nitrogen (P K Morgan). All subjects attended the clinic at hours and the single breath measurements were performed after 1200 hours to make sure that none of the smokers had smoked tobacco for at least four hours before the test. This was performed at least in duplicate and values were accepted if the duplicate determinations did not vary by more than 5%. The highest value (expressed in mmol/kpa/min) was used for the analysis. A value for alveolar volume was obtained during the single breath TLCO measurement. Kco was calculated as the ratio of TLCO to VA and expressed in mmol/kpa/min/litre. Measured TLCo and Kco were corrected to a standard haemoglobin (Hb) concentration of 14-6 g/dl by means of the following equation9: TLCO corrected for Hb concentration (CTLco) = TLcoobserved x (14-6 a + Hb)/(l + a)hb, where Hb is the actual haemoglobin concentration in g/dl and a is 0 7. The Kco corrected for haemoglobin (CKco) was calculated from CTLCO. STATISTICAL MIETHODS Best fitting cross sectional equations were derived separately for men and women by multiple linear regression analysis. As there was an increase in spirometric and static lung volumes from 15 to 25 years, a plateau from 25 to 35 years, and a decline from 35 years onwards, a quadratic term (age squared) was included in the prediction model. Age2 and height were entered into the equation for all pulmonary function measurements; age'- height interactions were tested for significance by means of a stepwise regression procedure. Residuals were calculated and tested for each of these best fitting models for each sex. The goodness of fit of the models was also tested by examining the correlations of residuals with age2 and height and by inspecting graphs of residuals versus predicted values to confirm the absence of a curvilinear pattem. A dummy variable for smoking (non-smokers = 0, smokers = 1) was introduced into the regression equations to test the effect of smoking in men. All analyses were performed with the SPSS/PC statistical computing package on an IBM/XT compatible personal computer. Unless otherwise specified, the term significant is used to imply a p value of less than Results The mean (SD) height was 166 (7 6) cm in men and 152 (5 3) cm in women, and weight was 53-4 (11 6) and 44 7 (9 3) kg. The mean haemoglobin concentration in men was 14-3 (1 7) g/dl and only two had values below 11 g/dl. In women, however, it was 10-8 (1 6) g/dl and 27 (23 %) had a concentration of less than 10 g/dl. All women were non-smokers. Among the 45 male smokers eight had stopped smoking at least one year before the tests; 26 had smoked three to 10 cigarettes or bidis (sun cured tobacco packed loosely inside a vegetable leaf) a day for less than five years, and 11 had smoked more than 20 cigarettes or bidis a day for more than five years. In men the mean FVC was 3-53 (0-68) litres, TLC 4 76 (0 86) 1, and TLCO 9 40 (2 00) mmol/ kpa/min; in women the mean FVC was 2-37 (0 36)1, TLC 3.43 (0-45) 1, and TLCO 6-34 (1 10) mmol/kpa/min. Almost all measurements reached a peak in the age group, remained at that level up to the age of years, and then showed a mild decline. RV and RV/TLC%, however, showed a small rise in the year age group. FEVI/FVC% showed a gradual decline with increasing age in both sexes. Additional data are available on request. Both age and height in men showed a significant positive correlation with FVC, FRC, RV, TLC and VA; the correlations were stronger with height (table 1). FEVy and TLCO were significantly correlated with height; Kco showed a significant negative correlation with age. In women FVC, FEV, FRC, TLC, and VA showed a significant positive correlation with height (table 2). There was a negative Regression relationships for predicting indices of lungfunction from age2 (y) and height (cm) in healthy young adult South Indian men Regression coefficientst Correlation coefficients Standard Measurement Mean SD Constant Age2 Height Multiple R error Age Height FVC * 0-692** FEV, ** FEV0O FVC /O ** FRC ** 0-621** RV ** 0-533** TLC ** 0-736** RVLC% ** VA ** 0-688** TLCO ** Kco * CTLCO ** CKco ** ** tsmoking coefficient for Kco = ; smoking coefficient for CKco = *p < 0-01; **p < FVC-forced vital capacity; FEV,-forced expiratory volume in one second; FRC-functional residual capacity; RV-residual volume; TLC-total lung capacity; VA-alveolar volume; TLco-carbon monoxide transfer factor; Kco-transfer coefficient.
3 Pulmonary function in healthy young adult Indians in Madras 613 Table 2 Regression relationships for predicting indices of lung function from age2 (y) and height (cm) in healthy young adult South Indian women (non-smokers) Regression coefficient Correlation coefficients Standard Measurement Mean SD Constant Age2 Height Multiple R error Age Height FVC ** FEV, ** FVCEYO ** FRC ** RV TLC ** TLC VA ** TLCO * Kco * * CTLCO ** *CKco *p < 0-01; **p < Table 3 correlation between TLCO and age, and be- 155 cm for women) are compared with those tween Kco and age and height. from other studies in tables 3 and 4. As the addition of a dummy variable for smoking did not have any significant effect on Discussion any of the pulmonary function measurements Establishig regression equations to predict except Kco and CKco, the coefficients for various measurements ofnormallungfunction smok.g were io te pon a regional basis in a smoking were introduced into the prediction country like India, with equations for measure- wide variations in geography, climate, food mequaonts only.for Kco and CKcohabits, and ethnic groups, is important for the ments. The multiple regression equations for men management of patients with various cardioand women based on age2 and height are shown pulmonary diseases. Results of comprehensive in tables 1 and 2. Predicted values are derived lung function studies in normal subjects are from these regression equations as follows: available jects."31 for There North have and West not, Indian however, been sub- any Predicted value = K + (age' in 'rears x age' coefficient) comparable studies of lung function, including + (standing height in cm x height coefficient), lung volumes and diffusing capacity measurements, in South Indians of Dravidian where K is the constant. Smoking coefficients stock living in a tropical climate at sea level with are added for Kco and CKco to derive the rice as their staple food. Previous studies of predicted values in smokers. ventilatory capacity in South Indians had The predicted values of various pulmonary shown that the subjects had lower values for function measurements obtained from these ventilatory capacity and expiratory flow451' regression equations for subjects of specified than subjects from the Western world and age (30 years) and height (165 cm for men, North Indians. Predicted pulmonary function valuesfrom various studies in men of specified age (30y) and height (165 cm) TLCO Kco CTLco CKco (mmol/ (mmol/ (mmol/ (mmol/ Location and reference FVC (1) FEV, (1) RV (1) FRC (1) TLC (1) VA (1) kpa/min) kpalmin/l) kpa/min) kpa/min/l) Indians Jain' (N India) Udwadia6 (W India) Kamat" (S India) Vijayan (this study) Caucasions Cotes Goldman" Chinese DaCosta' Others Wcolcock' (New Guinea coast) Miller" Guyanan Indians Guyanan Negroes Highlanders Woolcock'
4 614 Vijayan, Kuppurao, Venkatesan, Sankaran, Prabhakar Table 4 Predicted pulmonary function valuesfrom various studies in women of specified age (30y) and height (155 cm) TLCO Kco CTLco CKco (mmol/ (mmol/ (mmol/ (nmol/ Location and reference FVC (1) FEV, (1) RV (1) FRC (1) TLC (1) VA (1) kpalmin) kpalmin/l) kpa/min) kpalminll) Indian Jain' (N India) Udwadia6 (W India) Kamat" (S India) Vijayan (this study) Caucasians Goldman1l Hall et al" Chinese DaCosta' Others Woolcock' (New Guinea coast) Miller"5 New Guyanan Indians New Guyanan Negroes Highlanders Woolcock' The positive and strong correlations between various indices of lung size (FVC, FRC, TLC, and VA) and height in both sexes in this study are similar to those reported in previous studies.'26 "-'3 There was no age related decline in FVC in either sex in this study but FEV1 showed an age related decline in men, though not in women. In a study of 250 non-smoking healthy Pakistanis from an area with extremely low levels of air pollution Ayub et al found that in men age made only a slight contribution to change in FVC and FEVI.'4 The absence of any age related decline in FVC has also been observed in North Indians.2 FVC, FEV1, and FEV,/FVC% in both sexes in our study are similar to values reported by Udwadia et al in West Indians6 and by Kamat et al in South Indians." They are also similar to those of Guyanan Indians,'5 coastal dwellers of New Guinea,' and Chinese,'6 but are lower than those reported from North India23 and from Western countries Static lung volumes (TLC and FRC) in both sexes were similar to those seen in West Indians,6 but lower than those of North Indians.23 Lung volumes are about 1520% lower in South Indians than in Western subjects.'3 17 Age was associated with an increase in TLC in men but had a minimal effect in women. Our findings are similar to those of other studies from India26 and in highlanders from New Guinea.' Earlier observations suggested that RV may not show ethnic variability8 and, in keeping with this, RV in our study was similar to values reported from studies of Indian,26 Western,'3 and Chinese subjects.'6 The early closure of peripheral airways in subjects with small lungs may be responsible for the similar RV values in the various groups despite different lung volumes. The single breath transfer factor (TLCO) in men in our study was similar to values seen in West Indians6 and similar to2l or slightly less (6%) than European values.8 Though TLCO values in South Indian and British men were similar,8 the British subjects had a higher alveolar volume and hence lower Kco values. Previous reports found no difference in Kco between the sexes2223 and we may reasonably assume that the gas transfer per unit lung volume is similar in men and women. The fact that Kco was 10% lower in women in our study than in men may be due to the fact that more women (23%) had a haemoglobin concentration below 10 g/dl, only two men having a concentration less than 11 g/dl. Kco values were similar in men and women after correction for haemoglobin concentration. The finding of similar TLCO values in men in the present study and in Western studies, despite 15-20% lower values for lung volumes, points to the need for further study. I Woolcock JA, Colman MH, Blackburn CRB. Factors affecting normal values for ventilatory lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis 1972;106: Jain SK, Ramaiah TJ. Normal standards of pulmonary function tests for healthy Indian Men years old. Comparison of different regression equations (prediction formulae). Indian J Med Res 1969;57: Jain SK, Ramaiah TJ. Influence of age, height and body surface area on lung functions in healthy women years old. Indian J Chest Dis 1967;9: Milledge JB. Vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in South Indian men. Indian J Chest Dis 1965;7: Kamat SR, Thiruvengadam KV, Rao TL. A study of pulmonary functions among Indians and assessment ofthe Wright's peak flow meter in relation to spirometry for field use. Am Rev Respir Dis 1967;96: Udwadia FE, Sunavala JD, Shetye VM. Lung function studies in healthy Indian subjects. J Ass Physicians India 1987;35: Ferris BG, ed. Epidemiology standardisation project. Am Rev Respir Dis 1978;118(part 2): Cotes JE. Lung function: assessment and applications in medicine. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell, 1975:113-7, , Cotes JE, Dabbs JM, Elwood PC, Hall AM, McDonald A, Saunders MJ. Iron deficiency anemia: its effects on transfer factor for the lung (diffusing capacity) and ventilation and cardiac frequency during submaximal exercise. Clin Sci 1972;42: Guleria JS, Sharma MP, Pande JN, Ramachandran K. Pulmonary dfusing capacity in normal Indian subjects. Indian J Physiol Pharmac 1970;14: Kamat SR, Tyagi NK, Rashid SSA. Lung functions in Indian adult subjects. Lung India 1982;1:
5 Pulmonary function in healthy young adult Indians in Madras 12 Grimby G, Soderholm B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. III. Static lung volumes and maximum voluntary ventilation in adults with a note on physical fitness. Acta Med Scand 1963;173: Goldman HI, Becklake MR. Respiratory function tests: Normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc 1959;79: Ayub M, Zaidi SH, Burki NK. Spirometry and flow-volume curves in healthy normal Pakistanis. Br J Dis Chest 1987;81: Miller GJ, Aschcroft MT, Swan AV, Beadnell HMSG. Ethnic variation in forced expiratory volume and forced vital capacity of African and Indian adults in Guyana. Am Rev Respir Dis 1970;102: DaCosta JL. Pulmonary function studies in healthy chinese adults in Singapore. Am Rev Respir Dis 1971;104: Cotes JE, Rossiter CE, Higgins ITT, Gibon JC. Average normal values for the forced expiratory volume in white 615 caucasian males. Br Med J 1966;i: Hall AM, Heywood C, Cotes JE. Lung function in healthy British Women. Thorax 1979;34: Kory RC, Callahan R, Boren HG, Syner JC. The veterans administration army co-operative study of pulmonary functions 1-Clinical spirometry in men. Am J Med 1961;30: Ferris BG Jr, Anderson DO, Zickmantel R. Prediction values for screening tests of pulmonary function. Am Rev Respir Dis 1965;91: Cotes JE, Malhotra MS. Differences in lung function between Indians and Europeans. JPhysiol 1965;177: Burrows B, Kasik JE, Niden AH, Barclary WR. Clinical usefulness of the single-breath pulmonary diffusing capacity test. Am Rev Respir Dis 1961;84: Bradley J, Bye C, Hayden SP, Hughes DTD. Normal values for transfer factor and transfer coefficients in healthy males and females. Respiration 1979;38: Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 August Downloaded from on 28 March 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; September 2013: Issue-8, Vol.-2, P
 Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
MEASUREMENTS LN ADULT CHINESE
 Vol. 12. No. 4. SINGAPORE MEDICAL IOGILNA1. 193 Augu=t. 1971. PREDICTION NOMOGRAMS FOR LUNG FUNCTION MEASUREMENTS LN ADULT CHINESE fiv J. L. Da Costa and B. K. Goh SYNOPSIS Increasing utilization of lung
Vol. 12. No. 4. SINGAPORE MEDICAL IOGILNA1. 193 Augu=t. 1971. PREDICTION NOMOGRAMS FOR LUNG FUNCTION MEASUREMENTS LN ADULT CHINESE fiv J. L. Da Costa and B. K. Goh SYNOPSIS Increasing utilization of lung
DIFFUSING CAPACITY IN ACUTE UNTREATED TROPICAL EOSINOPHILIA
 Indian J Chest Dis & Alli Sci Vol. 30 No.2 pp 71-77 (1988) DIFFUSING CAPACITY IN ACUTE UNTREATED TROPICAL EOSINOPHILIA V.K. VIJAYAN, K.V. KUPPU RAO, K. SANKARAN, P. VENKATESAN and R. PRABHAKAR Cardio-pulmonary
Indian J Chest Dis & Alli Sci Vol. 30 No.2 pp 71-77 (1988) DIFFUSING CAPACITY IN ACUTE UNTREATED TROPICAL EOSINOPHILIA V.K. VIJAYAN, K.V. KUPPU RAO, K. SANKARAN, P. VENKATESAN and R. PRABHAKAR Cardio-pulmonary
normal and asthmatic males
 Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Prasad B K
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5E):1854-1858 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5E):1854-1858 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children Aged 6 to 17 Years in Delhi Region
 Short Communication Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children Aged 6 to 17 Years in Delhi Region S.K. Chhabra 1, V.K. Vijayan 2, M. Rahman 3, V. Mittal 1 and P.D. Singh 1 Departments of Cardio-respiratory
Short Communication Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children Aged 6 to 17 Years in Delhi Region S.K. Chhabra 1, V.K. Vijayan 2, M. Rahman 3, V. Mittal 1 and P.D. Singh 1 Departments of Cardio-respiratory
PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION
 Prediction Equations for Lung Function in Healthy, Non-smoking Malaysian Population PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION Justin Gnanou, Brinnell
Prediction Equations for Lung Function in Healthy, Non-smoking Malaysian Population PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION Justin Gnanou, Brinnell
PULMONARY FUNCTION STUDIES IN GUJARATI SUBJECfS
 Indian J Physiol I'harmacol 1992; 36(1) : 55-59 PULMONARY FUNCTION STUDIES IN GUJARATI SUBJECfS N. MOHA.N RAO. M. G. MAVLANKAR, P. K. KULKARNI AND S. K. KASHYAP Department of Respiratroy Physiology, National
Indian J Physiol I'harmacol 1992; 36(1) : 55-59 PULMONARY FUNCTION STUDIES IN GUJARATI SUBJECfS N. MOHA.N RAO. M. G. MAVLANKAR, P. K. KULKARNI AND S. K. KASHYAP Department of Respiratroy Physiology, National
Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
/FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan
 Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
residual volume calculated from radiographs in a random sample of the Michigan population
 Thorax 1992;47:519-523 University of Southern California, School of Medicine, Los Angeles, California K H Kilburn Worker's Disease Detection Services, San Dimas, California R H Warshaw Thornton Associates,
Thorax 1992;47:519-523 University of Southern California, School of Medicine, Los Angeles, California K H Kilburn Worker's Disease Detection Services, San Dimas, California R H Warshaw Thornton Associates,
EFFECTS OF INACTIVITY, WEIGHT GAIN AND ANTITUBERCULAR CHEMOTHERAPY UPON LUNG FUNCTION IN WORKING COAL-MINERS
 Ann. Occup. Hyg: Vol. 10, pp. 327-335. Pergamon Press Ltd., 1967. Printed in Great Britain EFFECTS OF INACTIVITY, WEIGHT GAIN AND ANTITUBERCULAR CHEMOTHERAPY UPON LUNG FUNCTION IN WORKING COAL-MINERS J.
Ann. Occup. Hyg: Vol. 10, pp. 327-335. Pergamon Press Ltd., 1967. Printed in Great Britain EFFECTS OF INACTIVITY, WEIGHT GAIN AND ANTITUBERCULAR CHEMOTHERAPY UPON LUNG FUNCTION IN WORKING COAL-MINERS J.
pulmonary dysfunction in chronic alcoholics
 Thorax 1986;41:197-202 Contribution of ethanol and cigarette smoking to pulmonary dysfunction in chronic alcoholics DJ LYONS, SUSANNAH V HOWARD, JS MILLEDGE, TJ PETERS From the Divisions ofanaesthetics
Thorax 1986;41:197-202 Contribution of ethanol and cigarette smoking to pulmonary dysfunction in chronic alcoholics DJ LYONS, SUSANNAH V HOWARD, JS MILLEDGE, TJ PETERS From the Divisions ofanaesthetics
Pulmonary involvement in ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1986, 45, 736-74 Pulmonary involvement in ankylosing spondylitis NILS FELTELIUS,1 HANS HEDENSTROM,2 GUNNAR HILLERDAL,3 AND ROGER HALLGREN' From the Departments of 'Internal
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1986, 45, 736-74 Pulmonary involvement in ankylosing spondylitis NILS FELTELIUS,1 HANS HEDENSTROM,2 GUNNAR HILLERDAL,3 AND ROGER HALLGREN' From the Departments of 'Internal
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values
 PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
PFT Interpretation and Reference Values September 21, 2018 Eric Wong Objectives Understand the components of PFT Interpretation of PFT Clinical Patterns How to choose Reference Values 3 Components Spirometry
Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia
 Indian J Med Res 134, November 2011, pp 653-657 Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia Amit Bandyopadhyay * School of Health Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Kelantan,
Indian J Med Res 134, November 2011, pp 653-657 Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia Amit Bandyopadhyay * School of Health Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Kelantan,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. Purposes of Pulmonary Tests. General Categories of Lung Diseases. Types of PF Tests
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
Ashok Fulambarker, MD, FCCP; Ahmet Sinan Copur, MD; Asavari Javeri, MD; Sujata Jere, MD; and Mark E. Cohen, PhD
 Reference Values for Pulmonary Function in Asian Indians Living in the United States* Ashok Fulambarker, MD, FCCP; Ahmet Sinan Copur, MD; Asavari Javeri, MD; Sujata Jere, MD; and Mark E. Cohen, PhD Objective:
Reference Values for Pulmonary Function in Asian Indians Living in the United States* Ashok Fulambarker, MD, FCCP; Ahmet Sinan Copur, MD; Asavari Javeri, MD; Sujata Jere, MD; and Mark E. Cohen, PhD Objective:
Effects of mitral valve surgery on static lung function
 Thorax 1985;40:107-112 Effects of mitral valve surgery on static lung function and exercise performance KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Regional Cardiothoracic Centre, Freeman Hospital,
Thorax 1985;40:107-112 Effects of mitral valve surgery on static lung function and exercise performance KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Regional Cardiothoracic Centre, Freeman Hospital,
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing
 In the Clinic Pulmonary Function Testing Hawa Edriss MD, Gilbert Berdine MD The term PFT encompasses three different measures of lung function: spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity. In this
In the Clinic Pulmonary Function Testing Hawa Edriss MD, Gilbert Berdine MD The term PFT encompasses three different measures of lung function: spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity. In this
MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME LOOP IN SOUTHERN INDIAN COLLEGE SPORTSMEN
 MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME LOOP IN SOUTHERN INDIAN COLLEGE SPORTSMEN K. V. KUPPU RAO AND V. K. VIJA YAN Cardio-Pulmonary Medicine Unit, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Indian Council of Medical Research,
MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME LOOP IN SOUTHERN INDIAN COLLEGE SPORTSMEN K. V. KUPPU RAO AND V. K. VIJA YAN Cardio-Pulmonary Medicine Unit, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Indian Council of Medical Research,
Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement
 Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology
 Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Pulmonary function in advanced pulmonary hypertension
 Pulmonary function in advanced pulmonary hypertension Thorax 1987;42:131-135 CONOR M BURKE, ALLAN R GLANVILLE, ADRIAN J R MORRIS, DANIEL RUBIN, JAMES A HARVEY, JAMES THEODORE, EUGENE D ROBIN From the Division
Pulmonary function in advanced pulmonary hypertension Thorax 1987;42:131-135 CONOR M BURKE, ALLAN R GLANVILLE, ADRIAN J R MORRIS, DANIEL RUBIN, JAMES A HARVEY, JAMES THEODORE, EUGENE D ROBIN From the Division
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY. Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0099111 -Session-1989-90 -Superclass- PB -Title- PRINCIPLES
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0099111 -Session-1989-90 -Superclass- PB -Title- PRINCIPLES
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Lung function in the elderly
 Thorax 1985;40:54-59 Lung function in the elderly MCHAEL L BURR, KARN M PHLLPS, DANE N HURST From the Medical Research Council, Epidemiology Unit, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, Penarth ABSTRACT Data
Thorax 1985;40:54-59 Lung function in the elderly MCHAEL L BURR, KARN M PHLLPS, DANE N HURST From the Medical Research Council, Epidemiology Unit, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, Penarth ABSTRACT Data
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
Chapter 3. Pulmonary Function Study Assessments. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Lung function in textile workers
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1975, 32, 283-288 Lung function in textile workers EUGENIJA ZUSKIN', F. VALIC', D. BUTKOVIC', and A. BOUHUYS2 Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1975, 32, 283-288 Lung function in textile workers EUGENIJA ZUSKIN', F. VALIC', D. BUTKOVIC', and A. BOUHUYS2 Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India
 Original Article Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India S.K. Chhabra 1, R. Kumar 3, U. Gupta 1, M. Rahman 2 and D.J. Dash 1 Department of Cardiorespiratory Physiology 1 and Biostatistics
Original Article Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India S.K. Chhabra 1, R. Kumar 3, U. Gupta 1, M. Rahman 2 and D.J. Dash 1 Department of Cardiorespiratory Physiology 1 and Biostatistics
Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers
 Thorax 1982;37:751-755 Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Cardiothoracic Centre,
Thorax 1982;37:751-755 Relation between severity of mitral valve disease and results of routine lung function tests in non-smokers KM RHODES, K EVEMY, S NARIMAN, GJ GIBSON From the Cardiothoracic Centre,
Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged years
 Research Article Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged 18 25 years Prakash Kumar Nayak 1, Sudeep Satpathy 1, Magna Manjareeka 1, Priyadarsini Samanta 1, Jayanti Mishra
Research Article Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged 18 25 years Prakash Kumar Nayak 1, Sudeep Satpathy 1, Magna Manjareeka 1, Priyadarsini Samanta 1, Jayanti Mishra
Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children
 Original Article Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children G Liyanage 1 *, BDW Jayamanne 2, Aaqiff M 3 1 Department of Paediatrics
Original Article Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children G Liyanage 1 *, BDW Jayamanne 2, Aaqiff M 3 1 Department of Paediatrics
Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District
 Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal G. B. Nepal 1, P. K. L. Das 2, A. Bhaila 3 1,3 Lecturer, Department of Physiology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal G. B. Nepal 1, P. K. L. Das 2, A. Bhaila 3 1,3 Lecturer, Department of Physiology,
Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide. (DLco) in healthy adolescents ABSTRACT
 Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide (DLco) in healthy adolescents AMJAD F. AHMADP P ABSTRACT In pulmonary function tests (PFT), the selection of prediction equation for lung diffusing
Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide (DLco) in healthy adolescents AMJAD F. AHMADP P ABSTRACT In pulmonary function tests (PFT), the selection of prediction equation for lung diffusing
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
INDICES OF VENTILATORY MEASUREMENTS
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1971), 25, 203-209 INDICES OF VENTILATORY MEASUREMENTS T. KHOSLA* Department of Medical Statistics, Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Single breath pulmonary function
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1971), 25, 203-209 INDICES OF VENTILATORY MEASUREMENTS T. KHOSLA* Department of Medical Statistics, Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff Single breath pulmonary function
Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung
 Thorax (1969X, 24, 374. Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung P. DINDA, S. S. CHATTERJEE, AND W. D. RIDING From Baguley Hospital, Manchester Pulmonary function studies were performed at the
Thorax (1969X, 24, 374. Pulmonary function studies in bird breeder's lung P. DINDA, S. S. CHATTERJEE, AND W. D. RIDING From Baguley Hospital, Manchester Pulmonary function studies were performed at the
Interpreting pulmonary function tests: Recognize the pattern, and the diagnosis will follow
 REVIEW FEYROUZ AL-ASHKAR, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, The Cleveland Clinic REENA MEHRA, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University Hospitals, Cleveland PETER J. MAZZONE,
REVIEW FEYROUZ AL-ASHKAR, MD Department of General Internal Medicine, The Cleveland Clinic REENA MEHRA, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University Hospitals, Cleveland PETER J. MAZZONE,
Physiology lab (RS) First : Spirometry. ** Objectives :-
 Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Body mass, fat percentage, and fat free mass as reference variables for lung function: evects on terms for age and sex
 Thorax 2001;56:839 844 839 Respiration and Exercise Laboratory, Department of Physiological Sciences, Medical School, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, UK J E Cotes D J Chinn J W Reed *Present address: Postgraduate
Thorax 2001;56:839 844 839 Respiration and Exercise Laboratory, Department of Physiological Sciences, Medical School, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, UK J E Cotes D J Chinn J W Reed *Present address: Postgraduate
public health exhibition
 Thorax (1972), 27, 557. Peak flow measurements among visitors to a public health exhibition A. G. F. BROOKS and R. E. WALLER MRC Air Pollution Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College, London ECIM
Thorax (1972), 27, 557. Peak flow measurements among visitors to a public health exhibition A. G. F. BROOKS and R. E. WALLER MRC Air Pollution Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College, London ECIM
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL
 Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
polyvinylchloride dust
 Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
Thorax 1983;38:834-839 Clinical studies of workers exposed to polyvinylchloride dust CA SOUTAR, S GAULD From the Institute of Occupational Medicine, Edinburgh ABsTRAcr A previous study showed that exposure
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Lung function after exposure to barley dust
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine 1 985; 4: 106-1 1 0 Lung function after exposure to barley dust P E MCCARTHY, A E COCKCROFT, AND M MCDERMOTT From the MRC Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital,
British Journal of Industrial Medicine 1 985; 4: 106-1 1 0 Lung function after exposure to barley dust P E MCCARTHY, A E COCKCROFT, AND M MCDERMOTT From the MRC Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital,
Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 401-405 Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows P. W. LORD AND J. M. EDWARDS From the MRC Toxicology Unit, Clinical Section, St. Bartholomew's Hlospital
Thorax, 1978, 33, 401-405 Variation in airways resistance when defined over different ranges of airflows P. W. LORD AND J. M. EDWARDS From the MRC Toxicology Unit, Clinical Section, St. Bartholomew's Hlospital
Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh
 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
SPIROMETRY METHOD. COR-MAN IN / EN Issue A, Rev INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark
 SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
Lung mechanics in subjects showing increased residual volume without bronchial obstruction
 Lung mechanics in subjects showing increased residual volume without bronchial obstruction S VULTERINI, M R BIANCO, L PELLICCIOTTI, AND A M SIDOTI From the Divisione di Medicina Generale, Ospedale Fatebenefratelli,
Lung mechanics in subjects showing increased residual volume without bronchial obstruction S VULTERINI, M R BIANCO, L PELLICCIOTTI, AND A M SIDOTI From the Divisione di Medicina Generale, Ospedale Fatebenefratelli,
PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA
 Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA Sukhsohale D Neelam 1, Narlawar W Uday 2, Thakre S Sushama 1 and Ughade
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA Sukhsohale D Neelam 1, Narlawar W Uday 2, Thakre S Sushama 1 and Ughade
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Spirometric studies on normal Turkish subjects aged 8 to 20 years
 Thorax (1969), 24, 714. Spirometric studies on normal Turkish subjects aged 8 to 20 years NECATI AKGUN AND HAMIT OZGONUL From the Departmenit of Physiology, Ege University Medical Faculty, Izmir, Turkey
Thorax (1969), 24, 714. Spirometric studies on normal Turkish subjects aged 8 to 20 years NECATI AKGUN AND HAMIT OZGONUL From the Departmenit of Physiology, Ege University Medical Faculty, Izmir, Turkey
industrial population
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 210-214 A consideration of risk factors and development of chronic bronchitis in a five-year follow-up study of an industrial population WIESLAW
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 210-214 A consideration of risk factors and development of chronic bronchitis in a five-year follow-up study of an industrial population WIESLAW
Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Lung function testing
 ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 3/12/2018
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
How to Perform Spirometry
 Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans
 The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans A. Neuhaus, M.D., D. Markowitz, M.D., H. H. Rotman, M.D., and John G. Weg, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
The Effects of Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy With Ad Without Atropine Prernedication on Pulmonary Function in Humans A. Neuhaus, M.D., D. Markowitz, M.D., H. H. Rotman, M.D., and John G. Weg, M.D. ABSTRACT Pulmonary
Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function
 Thorax (1972), 27, 454. Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function changes in relation to length of exposure to cotton dust E. ZUgKIN and F. VALIC Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
Thorax (1972), 27, 454. Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function changes in relation to length of exposure to cotton dust E. ZUgKIN and F. VALIC Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
#7 - Respiratory System
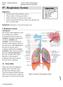 #7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
#7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
Clinical pulmonary physiology. How to report lung function tests
 Clinical pulmonary physiology or How to report lung function tests Lung function testing A brief history Why measure? What can you measure? Interpretation/ reporting Examples and case histories Exercise
Clinical pulmonary physiology or How to report lung function tests Lung function testing A brief history Why measure? What can you measure? Interpretation/ reporting Examples and case histories Exercise
D.J. Chinn, J.E. Cotes, R. Flowers, A-M. Marks, J.W. Reed
 Eur Respir J, 199, 9, 129 1277 DOI: 1.1183/93193.9.9129 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 199 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-193 Transfer factor (diffusing capacity)
Eur Respir J, 199, 9, 129 1277 DOI: 1.1183/93193.9.9129 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 199 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-193 Transfer factor (diffusing capacity)
Pulmonary Function Studies of Healthy Nonsmoking Male University Students of Kolkata, India Revisited
 Original Article Pulmonary Function Studies of Healthy Nonsmoking Male University Students of Kolkata, India Revisited Amit Bandyopadhyay, Ishita Bhattacharjee, Rishna Dalui, Sangita Pal Submitted: 17
Original Article Pulmonary Function Studies of Healthy Nonsmoking Male University Students of Kolkata, India Revisited Amit Bandyopadhyay, Ishita Bhattacharjee, Rishna Dalui, Sangita Pal Submitted: 17
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Domestic Cooking Fuel and Lung Functions in Healthy Non-smoking Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Domestic Cooking Fuel and Lung Functions in Healthy Non-smoking Women T.S. Reddy, R. Guleria, Sanjeev Sinha, S.K. Sharma and J.N. Pande Department of Medicine, All India Institute of Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Domestic Cooking Fuel and Lung Functions in Healthy Non-smoking Women T.S. Reddy, R. Guleria, Sanjeev Sinha, S.K. Sharma and J.N. Pande Department of Medicine, All India Institute of Medical
In order to diagnose lung diseases doctors
 You Take My Breath Away Activity 5C NOTE: This activity is designed to follow You Really Are Full of Hot Air! Activity Objectives: After completing You Really Are Full of Hot Air! Activity 5B, students
You Take My Breath Away Activity 5C NOTE: This activity is designed to follow You Really Are Full of Hot Air! Activity Objectives: After completing You Really Are Full of Hot Air! Activity 5B, students
Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics
 8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Serial pulmonary function tests in progressive systemic sclerosis
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 224-228 Serial pulmonary function tests in progressive systemic sclerosis L R BAGG AND D T D HUGHES From the Pulmonary Research Unit, Departnment of Chest Medicine, London Hospital, London,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 224-228 Serial pulmonary function tests in progressive systemic sclerosis L R BAGG AND D T D HUGHES From the Pulmonary Research Unit, Departnment of Chest Medicine, London Hospital, London,
Effect of change of reference standard to NHANES III on interpretation of spirometric abnormality
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of change of reference standard to NHANES III on interpretation of spirometric abnormality Akshay Sood Beth K Dawson Joseph Q Henkle Patricia Hopkins-Price Clifford Qualls Department
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effect of change of reference standard to NHANES III on interpretation of spirometric abnormality Akshay Sood Beth K Dawson Joseph Q Henkle Patricia Hopkins-Price Clifford Qualls Department
EVect of breathing circuit resistance on the measurement of ventilatory function
 9 Department of Respiratory Medicine, The Alfred Hospital and Monash University Medical School, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 311 D P Johns C M Ingram S Khov P D Rochford E H Walters Correspondence to:
9 Department of Respiratory Medicine, The Alfred Hospital and Monash University Medical School, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia 311 D P Johns C M Ingram S Khov P D Rochford E H Walters Correspondence to:
Pulmonary Function Testing
 Pulmonary Function Testing Let s catch our breath Eddie Needham, MD, FAAFP Program Director Emory Family Medicine Residency Program Learning Objectives The Astute Learner will: Become familiar with indications
Pulmonary Function Testing Let s catch our breath Eddie Needham, MD, FAAFP Program Director Emory Family Medicine Residency Program Learning Objectives The Astute Learner will: Become familiar with indications
Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing. Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum deflation. Total lung capacity at maximum inflation
 r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
r Total lung capacity at maximum inflation Variation in lung with normal, quiet breathing Volume of lungs at end of normal inspiration (average 2,200 ml) Minimal lung volume (residual volume) at maximum
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Lung function prediction equations derived from healthy South African gold miners
 698 National Centre for Occupational Health, Johannesburg 2000, South Africa E Hnizdo Arum Health Research, Welkom, South Africa G Churchyard Precious Metal Refiners, PO Box 331, Kroonsdal 0, South Africa
698 National Centre for Occupational Health, Johannesburg 2000, South Africa E Hnizdo Arum Health Research, Welkom, South Africa G Churchyard Precious Metal Refiners, PO Box 331, Kroonsdal 0, South Africa
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Pulmonary Function Test
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel GMC Spirometry Pulmonary Function Test! Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel GMC Spirometry Pulmonary Function Test! Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after
Regional lung function in ankylosing
 Regional lung function in ankylosing RUSSELL M. STEWART', JOHN B. RIDYARD, and JOHN D. PEARSON Regional Cardio-Thoracic Centre, Broadgreen Hospital, Liverpool L14 3LB Thorax (1976), 31, 433. Stewart, R.
Regional lung function in ankylosing RUSSELL M. STEWART', JOHN B. RIDYARD, and JOHN D. PEARSON Regional Cardio-Thoracic Centre, Broadgreen Hospital, Liverpool L14 3LB Thorax (1976), 31, 433. Stewart, R.
Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation
 Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation Jennifer Hale, M.D. Valley Baptist Family Practice Residency Objectives Identify the components of PFTs Describe the indications Develop a stepwise
Pulmonary Function Testing The Basics of Interpretation Jennifer Hale, M.D. Valley Baptist Family Practice Residency Objectives Identify the components of PFTs Describe the indications Develop a stepwise
Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran Syad Saleh Tabatabaie 1, Mohammad Hossein Boskabady 1,2, Sakinah Shah Mohammadi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran Syad Saleh Tabatabaie 1, Mohammad Hossein Boskabady 1,2, Sakinah Shah Mohammadi
behaviour are out of scope of the present review.
 explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article
 Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article A STUDY OF CHANGES IN PULMONARY FUNCTION WITH ADVANCING AGE AND THE EFFECT OF SMOKING IN MALES OF NORTH KERALA
Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article A STUDY OF CHANGES IN PULMONARY FUNCTION WITH ADVANCING AGE AND THE EFFECT OF SMOKING IN MALES OF NORTH KERALA
Using spirometr. ometry results in occupational medicine and resear good practice in statistical analysis and repor. Review Article.
 Free full text available from www.ijoem.com Review Article Using spirometr ometry results in occupational medicine and resear esearch: Common errors and good practice in statistical analysis and repor
Free full text available from www.ijoem.com Review Article Using spirometr ometry results in occupational medicine and resear esearch: Common errors and good practice in statistical analysis and repor
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
COMPREHENSIVE RESPIROMETRY
 INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
ABNORMALITIES IN LUNG FUNCTION AMONG MULTIPLY- TRANSFUSED THALASSEMIA PATIENTS: RESULTS FROM A THALASSEMIA CENTER IN MALAYSIA
 ABNORMALITIES IN LUNG FUNCTION AMONG MULTIPLY- TRANSFUSED THALASSEMIA PATIENTS: RESULTS FROM A THALASSEMIA CENTER IN MALAYSIA R Jamal 1, J Baizura 1, A Hamidah 1, N Idris 2, AH Jeffrey 3 and H Roslan 3
ABNORMALITIES IN LUNG FUNCTION AMONG MULTIPLY- TRANSFUSED THALASSEMIA PATIENTS: RESULTS FROM A THALASSEMIA CENTER IN MALAYSIA R Jamal 1, J Baizura 1, A Hamidah 1, N Idris 2, AH Jeffrey 3 and H Roslan 3
LONGITUDINAL STUDY OF LUNG FUNCTION DEVELOPMENT IN A COHORT OF INDIAN MEDICAL STUDENTS: INTERACTION OF RESPIRATORY ALLERGY AND SMOKING
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1991; 35(1): 44-48 LONTUDINAL STUDY OF LUNG FUNCTION DEVELOPMENT IN A COHORT OF INDIAN MEDICAL STUDENTS: INTERACTION OF RESPIRATORY ALLERGY AND SMOKING S. WALTER* AND J. RICHARD**
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1991; 35(1): 44-48 LONTUDINAL STUDY OF LUNG FUNCTION DEVELOPMENT IN A COHORT OF INDIAN MEDICAL STUDENTS: INTERACTION OF RESPIRATORY ALLERGY AND SMOKING S. WALTER* AND J. RICHARD**
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 2/5/2019
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Shape of small opacities and lung function in coalworkers
 Thorax 98;7:765-769 Shape of small opacities and lung function in coalworkers A COCKCROFT, G BERRY, JE COTES, JP LYONS From the Medical Research Council Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth,
Thorax 98;7:765-769 Shape of small opacities and lung function in coalworkers A COCKCROFT, G BERRY, JE COTES, JP LYONS From the Medical Research Council Pneumoconiosis Unit, Llandough Hospital, Penarth,
To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry
 Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 34(2), September October 2015; Article No. 24, Pages: Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases
 Review Article Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases Dipti Mohapatra 1, Tapaswini Mishra 1, Manasi Behera 1, Nibedita Priyadarsini 1, Arati Mohanty 1, *Prakash Kumar Sasmal 2 1 Department
Review Article Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases Dipti Mohapatra 1, Tapaswini Mishra 1, Manasi Behera 1, Nibedita Priyadarsini 1, Arati Mohanty 1, *Prakash Kumar Sasmal 2 1 Department
