Chapter 10 Respiration
|
|
|
- Reginald Hicks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically. Respiration Cellular respiration All organisms respire, or exchange gases with their environment Respiratory system in humans is closely linked with the circulatory system and the digestive system. Section 10.1 The Respiratory System Outcomes: I can explain the need for a respiratory surface in humans I am able to identify and state the function of the following respiratory structures: nasal cavity, epiglottis, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, diaphragm The basic function of the respiratory system is to distribute oxygen to each cell and allow carbon dioxide to leave each cell. This gas exchange helps to maintain homeostasis in the body. All respiratory systems share certain requirements for gas exchange (regardless of the type of organism): The surface through which gas exchange takes place must be: large to allow for efficient gas exchange thin walled so diffusion can occur rapidly moist - O 2 and CO 2 need to dissolve in contact with a source of O 2 in contact with a transport system that carries dissolved materials to and from the cells The Human Respiratory System
2 2 Lungs Gas exchange organs in air-breathing vertebrates and some other animals The lungs fill a large area of the human s chest cavity Each lung is divided into lobes; three on the right and two on the left (to make room for the heart) and enclosed by a two-layered membrane called the pleura. Visceral pleura inner pleura directly surrounding the lungs Parietal pleura outer pleura surrounding the lungs and which is in contact with the diaphragm and other organs of the chest cavity In between the pleural membranes is a lubricating fluid which allows the lungs to move freely during breathing. The lungs are separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm - large muscle that forms the floor of the chest cavity and plays a role in breathing. The Pathway of Air The respiratory system is broken down into two parts: 1. The Upper Respiratory Tract 2. The Lower Respiratory Tract The Upper Respiratory Tract Air may be taken in through the mouth or the nose. Inhaling through the nose is more beneficial; Nasal cavity Air usually enters the respiratory system through the nostrils which lead to the hollow nasal passages. Hairs at the opening of the nostrils help keep foreign particles from entering. The air passageway (except mouth) has cilia and mucus secreting membranes which help trap unwanted particles from the air. Mucus also moistens the air As air passes through the nose, the air is warmed by the capillaries that lie below the mucus membrane. They also increase the humidity of the air. When you breathe through your mouth, you lose the advantages of filtering, warming and moistening the air before it enters the lungs Pharynx The section where the mouth and nasal cavity connect to the larynx and the esophagus. Also known as the throat Larynx Composed of cartilage Also known as the voice box The vocal cords are two pairs of membranes stretched across the inside of the larynx As air is breathed out the vocal cords vibrate allowing you to speak The larynx runs directly into the
3 3 Glottis Opening of the trachea. It is protected by the epiglottis a flap like structure that prevents food from entering the lungs by closing over the glottis when you swallow. Trachea Also known as the windpipe. It is kept open by cartilage. The trachea connects the air to the lungs The trachea is supported with horse shoe cartilage rings which prevent the trachea from collapsing. Foreign particles are removed by sweeping cilia. They sweep the mucus and trapped foreign particles to the nose and throat area where it can be removed by sneezing, swallowing, coughing, or spitting. The Lower Respiratory Tract Bronchi, Bronchial tubes, Bronchioles In the middle of the chest, the trachea divide into two bronchi (singular bronchus). One of these cartilage lined tubes enters each lung. Also lined with ciliated cells In the lungs the bronchi branch in a tree like fashion into bronchial tubes Bronchial tubes divide and divide into bronchioles Walls become thinner and thinner and are lined with ciliated mucus membranes. Alveoli At the end of each bronchiole tubule is a grape-like cluster of tiny sacs known as alveoli (singular alveolus). These structures are the respiratory surface where actual gas exchange occurs. The total surface area of the alveoli is about 40 times that of the surface area of the skin. These sacs are surrounded by a network of capillaries that deliver O 2 and remove CO 2 from the blood stream. Most gas exchange happens through simple diffusion but facilitated diffusion delivers a portion of O 2 to the bloodstream (allows more, faster) Section The Mechanics of Breathing Outcomes I can explain the mechanics of breathing (inhaling and exhaling), and gas exchange Gas exchange in humans is divided into four stages: 1. Breathing 2. External Respiration 3. Internal Respiration 4. Oxygen Transport
4 4 1. Breathing The movement of air in and out of the lungs. This is an involuntary process controlled by the respiratory center in the brain (medulla oblongata). Chemoreceptors in the blood sense elevated levels of CO 2 and stimulating an increase in breathing rate. Two phases of breathing: Inhalation (Inspiration) The active phase of breathing that draws air into the lungs. It is controlled through the action of the ribs, the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. The lungs themselves are not muscular, but elastic and respond to the contractions and relaxations of the associated structures. Inhalation begins as the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm contract. This moves the rib cage out and up, diaphragm down, expanding the chest cavity. This causes a decrease in air pressure, creating a vacuum and air rushes into the lungs. Exhalation (Expiration) The passive phase of breathing that forces air out of the lungs. As the intercostal muscles relax and move inward, the diaphragm moves upward creating an increase in pressure which forces air out of the lungs. 2. External Respiration (between air and blood) The exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between the inhaled air and the alveoli of the lungs. Oxygen from the alveoli (region of higher concentration) diffuses to the blood (region of lower concentration) AND at the same time carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and into the alveoli (according to the concentration of CO 2
5 5 3. Internal Respiration (between blood and cells) The exchange of O 2 and CO 2 between the blood in the capillaries and the body cells. O 2 diffuses out of the blood and into the cells and CO 2 diffuses out of the body cells and into the bloodstream. 4. Oxygen Transport O 2 is carried by hemoglobin (Hb). This respiratory pigment is a red, iron-containing protein that holds O 2 loosely. O 2 combines with Hb to form HbO (oxyhemoglobin), which is bright red. o 1 hemoglobin molecule can transport 4 oxygen molecules HbO travels to cells, breaks down into Hb and O 2 allowing the O 2 to diffuse into the cells to be used during cellular respiration. CO 2 diffuses out of the cells, into the blood and is carried back to the lungs in three ways; - 70% is carried away in the plasma as an acid (in the form of bicarbonate ions) - 20% combines loosely with Hb to become HbCO 2 (carboxyhemoglobin) and - 10% is dissolved directly into the plasma Composition of Air Air In 21% O 2 16% O 2 79% N 2 79% N % CO % CO 2 Air Out Section 10.3 Respiratory Health Outcomes I can identify how respiratory diseases affect an organism I can predict the impact of environmental factors on an organism The Effects of Smoking Smoking stops the movement of cilia in the respiratory tract for up to 20 minutes (therefore unable to filter) Increases mucus production in response to the foreign particles. When smokers cough, they are trying to rid their body of excess mucus. Cigarette smoke contains carbon monoxide (CO) which prevents O 2 from bonding with Hb, therefore less O 2 reaches the body cells. This leaves smokers chronically short of breathe. When cigarette smoke is inhaled, about 1/3 of the particles remain on the alveoli Smoking can lead to emphysema
6 6 Lung Cancer A disease in which tumors form in the lungs as a result of an uncontrolled cell growth. The carcinoma takes over the healthy tissue and interferes with normal cell activity. Death is usually not caused by difficulty breathing but by the spread of cancer to other regions of the body. Most cases are caused by smoking where substances contained in cigarette smoke irritate the lining of the lungs and cancerous tumors form. Stopping smoking can reduce the risk of cancer as it allows normal cells to take over and replace cancerous cells. Other causes include exposure to radioactive chemicals like radon. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Irritation of the lungs that can lead to asthma, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. And, in fact, many people develop two or three of these together. This group is known as COPD. It is caused most often by smoking, and rarely by cystic fibrosis. Asthma A severe allergic reaction that causes wheezing, coughing and breathing difficulty. During an asthma attack, the bronchioles go into spasms, which squeeze the air passages. Some children outgrow this condition Common triggers include: cold and chest infections, exercise and sports, and allergens (pollen, smoke, pollution, mould, pets) Treatments: removal of triggers, medication (anti-inflammatory agents, and bronchodilators) Bronchitis A condition in which the linings of the bronchial tubes become irritated and swollen due to an infection (acute) or an irritant (chronic). Passageways to the alveoli may swell and clog with mucus. Very common in smokers Emphysema A chronic condition in which the lungs lose their elasticity, and the walls of the alveoli become damaged (making the respiratory surface smaller). This results in a shortness of breath. Common in smokers The damage is irreversible Treatments only slow the progression of the disease, and include: eliminating smoking, exercise, drugs to aid with alveoli work, and supplemental oxygen. Pneumonia A condition in which the alveoli become filled with fluid and prevents the exchange of gases in the lungs. Caused by: bacterial infection, viruses, fungi, and some chemicals. Treatment: antibiotics
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
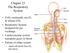 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
The Respiratory System
 I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure
![Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure Bronchioles. Bronchi. Pharynx epiglottis. (bronchus) Nose mouth. Diaphragm. Alveoli [alveolus] Larynx Trachea. Respiratory Structure](/thumbs/83/88046543.jpg) Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
Respiratory Structure Nose mouth Function Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchi (bronchus) Bronchioles Alveoli [alveolus] Diaphragm Jan 13 1:28 PM 1 NOSE Pharynx LUNGS Larynx/Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results
 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
The respiratory system
 Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Inspiration: Inhalation or breathing in air. The respiratory system Expiration: Exhalation or breathing out of air Ventilation (both) CVS carry the O2 to cells where Cellular respiration is taking place
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1
 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Write It! Station Directions
 Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Write It! Station Directions It is recommended that you have completed at least two of the following stations before working at this station. -Read It! -Explore It! -Watch It! -Research It! Answer each
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
