WANTED Manuscript supporting the prevailing paradigm of tuberculosis by any author DEAD or ALIVE $1,000 REWARD. 3 TB India HSCP
|
|
|
- Annabella Christal Bryant
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A New Paradigm for the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Bronchogenic tuberculosis The missing link between primary and post-primary disease Robert Hunter MD, PhD Dept. of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Texas-Houston Medical School Houston, TX77030 USA M. tuberculosis (MTB) an Obligate Human Parasite. MTB is a human pathogen because it can survive in humans and complete its life cycle, not because it is especially virulent for humans. The life cycle of MTB is to infect a person, remain dormant for decades and then induce a cavity that produces massive numbers of MTB to infect a new generation of people. PRIMARY TB Much is known about early tuberculosis and how it is localized and resolved. Very little is known on how MTB drives the late stage leading to transmission. 10th National Conference on Laboratory Aspects of TB Atlanta GA April 19, 2017 POST PRIMARY TB M. tuberculosis (MTB) an Obligate Human Parasite. The Current Paradigm Granulomas are the characteristic lesion of all tuberculosis. We need to better understand the delicate balance between the host and pathogen in the context of the entire biological system and this requires a radical and transformational approach Dr. Anthony Fauci, NIAID, NIH PRIMARY TB POST PRIMARY TB First Signs of Problems Mice are considered to be a poor model of tuberculosis because they don t make caseating granulomas. We found that mice could produce a spectrum of caseating granulomas simply by adjusting the protocol of injection of organisms and cord factor (Hunter et al 2006). This initiated a decade long investigation of the pathology and pathogenesis of human pulmonary tuberculosis. Surprisingly, we did not find any support for the current paradigm. WANTED Manuscript supporting the prevailing paradigm of tuberculosis by any author DEAD or ALIVE $1,000 REWARD For decades, most TB research has developed the paradigm that granulomas are the characteristic lesion of both primary and post-primary (adult type pulmonary) TB. We have not found any original papers that support this paradigm. Consequently, a reward of $1,000 is offered to the first person to produce a paper written by an investigator who personally studied the pathology of developing human post-primary pulmonary TB that supports the paradigm that granulomas are the characteristic lesion of both primary and post-primary TB and that cavities arise by erosion of granulomas in to bronchi. To claim reward, send reprint to Robert.L.Hunter@uth.tmc.edu Caseating granulomas in C57Bl/6 mice 3 TB India HSCP
2 Origin of the Current Paradigm. This paradigm dates from studies with M. bovis in rabbits in the late 20th century. Origin of the Current Paradigm. This paradigm dates from studies with M. bovis in rabbits in the late 20th century. Availability of human lung tissue with untreated tuberculosis plummeted with the introduction of antibiotics and decline in autopsies in the 1950s. Origin of the Current Paradigm. This paradigm dates from studies with M. bovis in rabbits in the late 20th century. Origin of the Current Paradigm. This paradigm dates from studies with M. bovis in rabbits in the late 20th century. Availability of human lung tissue with untreated tuberculosis plummeted with the introduction of antibiotics and decline in autopsies in the 1950s. Rabbits infected with M bovis were the only model that produced cavities and fibrocaseous disease. Availability of human lung tissue with untreated tuberculosis plummeted with the introduction of antibiotics and decline in autopsies in the 1950s. Rabbits infected with M bovis were the only model that produced cavities and fibrocaseous disease. In the absence of human tissues for study, this has become the nearly universally accepted paradigm. A 10 year Odyssey to Understand Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Humans Tissues for study have not been readily available since the 1950s. The literature in the pre-antibodies era, proved exceedingly difficult to find and read because the nomenclature had changed, there were very few images and many distractors. We began a search for microscope slides of untreated human pulmonary tuberculosis. The first cases came from medical examiners autopsies of people who died outside of healthcare system. We traveled to India twice and Russia three times seeking slides and blocks. We learned of the historic collections of Johns Hopkins Hospital. Finally, the pathology human tuberculosis has become quite clear. Literature from the Pre-antibiotic era. Studies published from the 1820s through the 1960 reported that human pulmonary TB has not just one, but two characteristic lesions: 1 The caseating granuloma (nodular tubercle or productive reaction), 2 Tuberculous pneumonia (infiltration or exudative reaction) Asymptomatic bronchogenic spread of pneumonia initiates postprimary tuberculosis. Granuloma 3 TB India HSCP
3 Literature from the Pre-antibiotic era. Studies published from the 1820s through the 1960 reported that human pulmonary TB has not just one, but two characteristic lesions: How Good is the Data It has been found by all who have studied early human pulmonary lesions that they represent areas of caseous pneumonia rather than nodular tubercles. [Rich, 1951] 1 The caseating granuloma (nodular tubercle or productive reaction), 2 Tuberculous pneumonia (infiltration or exudative reaction) Asymptomatic bronchogenic spread of pneumonia initiates post-primary tuberculosis. Granuloma Cornil and Ranvier 1880 (Levine, 1949) Supporting publications with more than 1,000 cases each. Laennec 1821 Virchow 1863 Powell 1876 Cornil and Ranvier, 1880 Hamilton 1883 Hektoen 1901 Osler 1921 Levine 1949 Canetti 1950 Rich 1951 Medlar 1955 Pagel 1960 CT Signs of Developing Post-Primary Tuberculosis The tree-in-bud sign is the method of choice to reveal early bronchogenic spread, with 2 to 4 mm centrilobular nodules and sharply marginated linear branching opacities around terminal and respiratory bronchioles (Sukora, 2015 ) CAT Scans of Early Post-Primary Tuberculosis Tree in Bud Sign Obstructive Lobular Cavity Tree in bud Tree in bud Tree-in-bud sign in an asymptomatic Sterioscopic person. xray of asymptomatic developing TB Hamilton 1883 Early Stage of Post-Primary TB Bronchogenic Spread Tree-in-Bud sign of Bronchogenic Spread of Tuberculosis TREE TREE in BUD Bronchial Obstruction CAVITY BUD Post Obstructive Lobular Tree in Bud 3 TB India HSCP
4 Formation of Cavities Cavities form by dissolution of the center of the caseous pneumonic mass Stages of Tuberculosis in Humans No Immunity. Induction of CMI. Effective Systemic Immunity. _Post-Primary Bronchogenic Disseminated Primary Obstructive Resolving (95%) 1883 (5%) Post-Primary Granulomas and Fibrocaseous TB Caseous Cavity Key Findings Supporting a New Paradigm of Post-Primary TB Post Obstructive due to Lung Cancer 1) Bronchogenic spread of obstructive lobular pneumonia is the early lesion of pulmonary TB. 1) Supported by publications from 1821 through ) Bronchial obstruction produces post-obstructive lipid pneumonia that has a propensity to cavitate. Cancer obstructing bronchus Post Obstructive Golden Post-Obstructive Lipid Foamy alveolar macrophages with apoptosis and interstitial lymphocytic inflammation. Cancer Tuberculosis Cavity produced by chemotherapy of post-obstructive pneumonia caused by cancer. Cavity formed in one week following initiation of chemotherapy 3 TB India HSCP
5 Cavity produced by chemotherapy of post-obstructive pneumonia caused by cancer. Key Findings Supporting a New Paradigm of Post-Primary TB 1) Bronchogenic spread of obstructive lobular pneumonia is the early lesion of pulmonary TB. 1) Bronchial obstruction produces post-obstructive lipid pneumonia that has a propensity to cavitate. 1) Apical localization facilitates obstructive lobular pneumonia. Apical Distribution of TB vs. 4dCT Lung Movement Key Findings Supporting a New Paradigm of Post-Primary TB 1) Bronchogenic spread of obstructive lobular pneumonia is the early lesion of pulmonary TB. 1) Bronchial obstruction produces post-obstructive lipid pneumonia that has a propensity to cavitate. 1) Apical localization facilitates obstructive lobular pneumonia. 1) Alveolar cells in developing tuberculosis asymptomatically produce and store large amounts of secreted mycobacterial antigens. Lowest movement, ventilation, blood flow, and lymph drainage in the apices facilitates obstructive lobular pneumonia. (Medlar EM, The pathogenesis of minimal pulmonary tuberculosis: a study of 1,225 necropsies in cases of sudden and unexpected death. Am Rev Tuberculosis 58, , 1948) Web site, René Werner, University Medical Center Hamburg- Eppendorf, Germany Key Feature of Developing Post-Primary TB MTB Antigen Accumulation in Alveolar Macrophages Key to Understanding Post-Primary TB Very few MTB produce and store secreted antigens and host lipids in alveolar macrophages asymptomatically for months behind an obstructed bronchus. They spread as bronchogenic tuberculosis. A B C D A. Immunocompetent person with developing post-primary TB B. Higher power of same section. AFB stain was negative C. AFB in a patient with HIV and disseminated TB D. IHC stain for MTB of SAME section 3 TB India HSCP
6 Key Findings Supporting a New Paradigm of Post-Primary TB 1) Obstructive lobular pneumonia is the early lesion of pulmonary TB. Untreated Human Tuberculosis with Early Cavitation Necrosis of tuberculous pneumonia occurs rapidly to produce cavities. 1) Bronchial obstruction produces post-obstructive lipid pneumonia that has a propensity to cavitate. 1) Apical localization facilitates obstructive lobular pneumonia. 1) Alveolar cells in developing tuberculosis asymptomatically produce and store large amounts of host lipid and secreted mycobacterial antigens ) After many months, the lesion suddenly undergoes caseous necrosis. The necrotic lung is coughed out to produce cavities or remains to become fibrocaseous disease. New Paradigm - Tuberculosis as a Three Act Play ACT 1 War of Attrition Immunity None Strong Lymphatic/Hematogenous spread Disseminated Caseating Granuloma Granulomas form, contain and kill MTB as CMI develops ACT 2 The Sneak Attack MTB antigens and host lipids accumulate in obstructive lobular Caseous pneumonia (5%) Sudden onset ACT 3 The Fallout Effective Systemic Immunity. Bronchial spread (tree-in-bud) No spread Obstructive Lipid Resolution (95%) remain as Fibrocaseous TB Paucibacillary Cavity Mature Cavity Caseating Granulomas of Human Tuberculosis Primary Post-Primary Earliest lesion: Obstructive Lobular pneumonia MTB Pellicle Homogeneous caseum with peripheral lipid. Found in all organs Ghosts of alveolar structures surrounded by granuloma. Found only in lung MTB antigens In cell Tree-in-Bud Obstructed bronchiole Primary Granuloma Pathology of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Caseating granulomas are characteristic only of primary tuberculosis. Post-primary (secondary) tuberculosis is an endogenous lipid pneumonia that characteristically develops in people with sufficient immunity to heal caseating granulomas (Tuberculosis (Edinb) Primary (Granuloma) Post-Primary () Post-Primary Granulomas 36 3 TB India HSCP
7 Obstructive Bronchiolar Obstructive Bronchiolar This lesions spontaneously resolve because of failure of obstruction, accumulation sufficient antigens or other. Obstructive Bronchiolar Obstructive Bronchiolar They have the strongest hypersensitivity when antigens are released. Obstruction of lobules starts the clock for storage of mycobacterial antigens and host lipids. That drives all the rest. Obstructive Bronchiolar Obstructive Bronchiolar Why does recovery from disease produce increased susceptibility to new disease? Damage to bronchi facilitates obstruction. Totally different mechanisms of protection. CMI vs. failure to obstruct and accumulate mycobacterial antigens. 3 TB India HSCP
8 Obstructive Bronchiolar Animal Models No animal develops TB like humans. However, The apices have the least ventilation, perfusion, lymph flow and movement. This facilitates obstructive lobular pneumonia. Several animals can develop parts of the human disease Must try to reproduce the conditions in animals that exist in people at different stages of disease. DO NOT only reproduce the route of infection. Measure pathologic effects, not just CFUs. A central problem in tuberculosis research is to explain why immunity to infection does not enable mice, guinea pigs, rabbits, or susceptible humans to resolve lung infection and thereby stop the development of disease. (North 2004) Acknowledgements Texas Medical Center, Houston C. Jagannath Jeffrey Actor ShenAn Hwang Grover Hutchins Nina Tatevian Vadim Karev Elena Fedotova 3 TB India HSCP
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis
 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
Pulmonary TB: HRCT findings
 Pulmonary TB: HRCT findings Tuberculosis: History BC 5000: Evidence of TB in neolithic man Jung-Gi Im, MD Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital BC 2900: Pyramid builders BC 1000 :
Pulmonary TB: HRCT findings Tuberculosis: History BC 5000: Evidence of TB in neolithic man Jung-Gi Im, MD Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital BC 2900: Pyramid builders BC 1000 :
Perspectives on Clinical and Preclinical Testing of New Tuberculosis Vaccines
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2010, p. 781 794 Vol. 23, No. 4 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00005-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Perspectives on
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2010, p. 781 794 Vol. 23, No. 4 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00005-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Perspectives on
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR November 30, 2011 Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR has the following disclosures to make: No
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas November 29-December 2, 2011 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR November 30, 2011 Michael McCarthy, MD, FACR has the following disclosures to make: No
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit
 MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology
 Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: An Update Review
 15 Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: An Update Review Devender Sharma *, Deepika Sarkar Hi Tech College of Pharmacy, Chandrapur, Maharashtra, India sdevender350@gmail.com ABSTRACT Tuberculosis is a hypersensitive
15 Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: An Update Review Devender Sharma *, Deepika Sarkar Hi Tech College of Pharmacy, Chandrapur, Maharashtra, India sdevender350@gmail.com ABSTRACT Tuberculosis is a hypersensitive
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system. Answer Sheet
 Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Lymphoid System: cells of the immune system Answer Sheet Q1 Which areas of the lymph node have most CD3 staining? A1 Most CD3 staining is present in the paracortex (T cell areas). This is towards the outside
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age.
 Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age. The vast majority of infected people (90%) the disease does not progress. Predicted by WHO in the next twenty years
Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age. The vast majority of infected people (90%) the disease does not progress. Predicted by WHO in the next twenty years
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining
 Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I
 BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
The diagnosis of active TB
 The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients
 Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Atypical radiologic appearances of pulmonary tuberculosis in non-hiv adult patients Poster No.: R-0200 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. N. Jeon, K. Bae, M. J. Park Keywords:
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
the bronchogenic spread of tuberculosis shown on high-resolution CT scans has been well documented by Murata et a! (6,7). However, the vanous
 Jung-Gi Irn, MD #{149}Harurni Itoh, MD #{149}Young-Soo Shim, MD #{149} Jeong Hun Lee, MD Joongmo Ahn, MD #{149}Man Chung Han, MD #{149}Satoshi Noma, MD Pulmonary Tuberculosis: CT Findings- Early Active
Jung-Gi Irn, MD #{149}Harurni Itoh, MD #{149}Young-Soo Shim, MD #{149} Jeong Hun Lee, MD Joongmo Ahn, MD #{149}Man Chung Han, MD #{149}Satoshi Noma, MD Pulmonary Tuberculosis: CT Findings- Early Active
Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia. Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia. Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia. Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia. 53 Year-Old Smoker
 Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia 53 Year-Old Smoker Emphysema Pink puffer Barrel chest Hyperinflation Trapped air
Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia 53 Year-Old Smoker Emphysema Pink puffer Barrel chest Hyperinflation Trapped air
Hypothesis on the Evolution of Cavitary Lesions in Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection: Thin-Section CT and Histopathologic Correlation
 CT of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Tae Sung Kim 1 Won-Jung Koh 2 Joungho Han 3 Myung Jin Chung 1 Ju Hyun Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 O Jung Kwon 2 Kim TS, Koh W-J, Han J, et al. Received
CT of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Tae Sung Kim 1 Won-Jung Koh 2 Joungho Han 3 Myung Jin Chung 1 Ju Hyun Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 O Jung Kwon 2 Kim TS, Koh W-J, Han J, et al. Received
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Mycobacteria. Introduction to the pathogen Transmission
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
TUBERCULOSIS. Famous victims in their intellectual prime: Chopin, Paganini, Thoreau, Keats, Elizabeth Browning, Brontës
 TUBERCULOSIS GENERAL Tuberculosis (TB) kills 1,700,000 annually worldwide. "The Captain of all the men of death that came to take him away was the consumption, for it was that which brought him down to
TUBERCULOSIS GENERAL Tuberculosis (TB) kills 1,700,000 annually worldwide. "The Captain of all the men of death that came to take him away was the consumption, for it was that which brought him down to
Radiological Features of Mycobacterium tuberculosis TUBERCULE BACILLUS TUBERCULE BACILLUS DIAGNOSIS. Guy Richards. PATHOGENESIS of TUBERCULOSIS
 Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
 Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Charles Daley, MD National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero Investigator Insmed Objectives After attending
Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Charles Daley, MD National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero Investigator Insmed Objectives After attending
TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008
 TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN, MPH November 7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN MPH Nurse Consultant Heartland National TB
TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN, MPH November 7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN MPH Nurse Consultant Heartland National TB
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis
 Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
HRCT in Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis. Where are the lymphatics? Anatomic distribution
 Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
Steps in High Resolution CT Diagnosis Pattern of abnormality Distribution of disease Associated findings Clinical history Tomás Franquet MD What is the diagnosis? Hospital de Sant Pau. Barcelona Secondary
HISTORY TB = 25% ADULT DEATHS EGYPTIAN MUMMIES: SPINAL TB. 17 th -18th CENTURIES- URBANIZATION MID 24
 HISTORY EGYPTIAN MUMMIES: SPINAL TB 17 th -18th CENTURIES- URBANIZATION 19th CENTURY INDUSTRIALIZATION TB = 25% ADULT DEATHS GERM THEORY OF DISEASE KOCH S BACILLUS-1883 PRE-ANTIBIOTIC ERA SANATORIUM REGIMENS
HISTORY EGYPTIAN MUMMIES: SPINAL TB 17 th -18th CENTURIES- URBANIZATION 19th CENTURY INDUSTRIALIZATION TB = 25% ADULT DEATHS GERM THEORY OF DISEASE KOCH S BACILLUS-1883 PRE-ANTIBIOTIC ERA SANATORIUM REGIMENS
Trehalose 6,6 -Dimycolate and Lipid in the Pathogenesis of Caseating Granulomas of Tuberculosis in Mice
 American Journal of Pathology, Vol. 168, No. 4, April 2006 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050848 Immunopathology and Infectious Diseases Trehalose 6,6 -Dimycolate
American Journal of Pathology, Vol. 168, No. 4, April 2006 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050848 Immunopathology and Infectious Diseases Trehalose 6,6 -Dimycolate
HISTORY TB = 25% ADULT DEATHS MID 24 PRE-ANTIBIOTIC ERA
 PRE-ANTIBIOTIC ERA SANATORIUM REGIMENS & REST CAVITARY DISEASE & COLLAPSE THERAPY FRESH AIR, SUNSHINE-ROOFTOPS SOLARIA HISTORY EGYPTIAN MUMMIES: SPINAL TB 17 th -18th CENTURIES- URBANIZATION 19th CENTURY
PRE-ANTIBIOTIC ERA SANATORIUM REGIMENS & REST CAVITARY DISEASE & COLLAPSE THERAPY FRESH AIR, SUNSHINE-ROOFTOPS SOLARIA HISTORY EGYPTIAN MUMMIES: SPINAL TB 17 th -18th CENTURIES- URBANIZATION 19th CENTURY
Leslie Case 4. Prac%cal Approach to Granulomatous Lung Disease. PRE-TEST Which of these images is more likely to have organisms on special stains?
 Leslie Case 4 Prac%cal pproach to Granulomatous Lung Disease Kevin O. Leslie, MD Professor and Consultant Mayo Clinic rizona PRE-TEST have organisms on special stains? PRE-TEST represent infection? PRE-TEST
Leslie Case 4 Prac%cal pproach to Granulomatous Lung Disease Kevin O. Leslie, MD Professor and Consultant Mayo Clinic rizona PRE-TEST have organisms on special stains? PRE-TEST represent infection? PRE-TEST
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE
 DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between
 In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease. Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015
 Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Pulmonary TB aspects
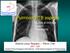 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي
 Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي Pathology sheet 5 Tuberculosis Done by: Ahmad Al-Sahele Introduction: as we know TB is caused by mycobacterium tubercolosis; now keep in your mind another microorganism
Respiratory System الفريق الطبي االكاديمي Pathology sheet 5 Tuberculosis Done by: Ahmad Al-Sahele Introduction: as we know TB is caused by mycobacterium tubercolosis; now keep in your mind another microorganism
Micronodular Lung Disease an algorithm
 Micronodular Lung Disease an algorithm H. Page McAdams, MD Department of Radiology Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC USA page.mcadams@duke.edu Question Which of the following lung diseases is MOST
Micronodular Lung Disease an algorithm H. Page McAdams, MD Department of Radiology Duke University Medical Center Durham, NC USA page.mcadams@duke.edu Question Which of the following lung diseases is MOST
Bronkhorst colloquium Interstitiële longziekten. Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog
 Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
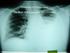 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Firm Texture. (chronic) Cut surface: purulent exudate in bronchi Sequels: Abscesses,
 2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
2008 Classification of Pneumonias in Domestic Animals There is no universal classification! Based on texture, distribution of lesions and type of exudate, pneumonias in domestic animals are currently classified
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
TUBERCULOSIS. Pathogenesis and Transmission
 TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
2018 Vindico Medical Education. Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria: Circumventing Difficulties in Diagnosis and Treatment
 Activity presentations are considered intellectual property. These slides may not be published or posted online without permission from Vindico Medical Education (cme@vindicocme.com). Please be respectful
Activity presentations are considered intellectual property. These slides may not be published or posted online without permission from Vindico Medical Education (cme@vindicocme.com). Please be respectful
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Tuberculosis Part 1. Some useful truths
 Tuberculosis Part 1 Some useful truths Tuberculosis will be dealt with in detail in chapter 9 in a few week s time when we deal with the air borne bacterial diseases and the diseases of the lower respiratory
Tuberculosis Part 1 Some useful truths Tuberculosis will be dealt with in detail in chapter 9 in a few week s time when we deal with the air borne bacterial diseases and the diseases of the lower respiratory
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis?
 Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Asthma. - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness.
 Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis
 Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Louis Joslyn Dept of Bioinformatics With Dr. Denise Kirschner and Dr. Jennifer Linderman
 Immunology of TB: insights from in vivo models and implications for prevention Louis Joslyn Dept of Bioinformatics With Dr. Denise Kirschner and Dr. Jennifer Linderman Dendritic cell (DC) DC responds to
Immunology of TB: insights from in vivo models and implications for prevention Louis Joslyn Dept of Bioinformatics With Dr. Denise Kirschner and Dr. Jennifer Linderman Dendritic cell (DC) DC responds to
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Use of High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) in Diagnosis of Sputum Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis
 Turk Thorac J 2016; 17: 59-64 DOI: 10.5578/ttj.17.2.012 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Use of High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) in Diagnosis of Sputum Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis Vandna Raghuvanshi
Turk Thorac J 2016; 17: 59-64 DOI: 10.5578/ttj.17.2.012 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Use of High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) in Diagnosis of Sputum Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis Vandna Raghuvanshi
(b) Describe the role of antigen presentation in the body s specific immune response to infection by viruses. (4)
 1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
1 The human body responds to infection by viruses in a number of ways. The non-specific response involves interferon. The specific immune response requires antigen presentation to the cells of the immune
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington
 Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ 2015 Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington Respiratory Infection: overview Influenza virus Clinical picture Emerging infection New Zealand Influenza
Emerging Respiratory Infections NZ 2015 Amanda McNaughton Respiratory Physician CCDHB Wellington Respiratory Infection: overview Influenza virus Clinical picture Emerging infection New Zealand Influenza
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
has the following disclosures to make:
 CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH September 22, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management September 22 24, 2015 San Antonio. TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Annie Kizilbash
CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH September 22, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management September 22 24, 2015 San Antonio. TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Annie Kizilbash
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM)
 Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) Bacteria, like plants and animals, have been classified into similar groups. The groups are called "families." One such family of bacteria is known as the Mycobacteriaceae.
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) Bacteria, like plants and animals, have been classified into similar groups. The groups are called "families." One such family of bacteria is known as the Mycobacteriaceae.
anys. Reinfection vs. Reactivation Is this the question?
 Reinfection vs. Reactivation Is this the question? Unitary Concept. Stead 1967. Infant and Adult TB is defined as Primary and Post-primary as a conclusion of the mass radiography campaings in Europe after
Reinfection vs. Reactivation Is this the question? Unitary Concept. Stead 1967. Infant and Adult TB is defined as Primary and Post-primary as a conclusion of the mass radiography campaings in Europe after
Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2010; 44: 56-62 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.56 Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Hye-Jong Song Jung Suk
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2010; 44: 56-62 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.56 Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Hye-Jong Song Jung Suk
