Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide
|
|
|
- Clinton Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S A N D T H E C H E S T F O U N D A T I O N
2 Controlling Your Asthma Patient Education Guide Single copies are free. Additional copies are available from: American College of Chest Physicians 3300 Dundee Road Northbrook, IL PHONE: (800) or (847) FAX: (847) or (847) Home page: Asthma Action Plan reprinted from: National Asthma Education and Prevention Program; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; NIH Publication No Rules of Two Dallas Asthma Consortium This patient education booklet has been published by the American College of Chest Physicians and is made possible by an unrestricted educational grant from GlaxoSmithKline. This publication s content does not replace professional medical care and physician advice, which always should be sought. Medical treatments vary based on individual facts and circumstances. The information provided herein is not intended to be medical advice. The American College of Chest Physicians specifically disclaims all responsibility for any liability, loss or risk, personal or otherwise, which is incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and application of any of the material herein. 2 Copyright 2004 by the American College of Chest Physicians
3 Table of Contents This booklet will help you and your health-care provider (doctor, nurse practitioner, or physician assistant) plan ways to control your asthma. Why? Because with good treatment, almost all people with asthma can live normal, active lives. Prevention is the key. With a few lifestyle changes and medicine, you can learn to prevent serious asthma problems. Together with your provider, you will learn how to reach this goal. 4 What Is Asthma? 6 Why Does Asthma Happen? 13 Work With Your Health-care Provider 14 How To Use a Peak Flow Meter 17 Asthma Action Plan 18 Asthma Medicine 25 How To Take Asthma Medicines 3
4 What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) disease of the airways in the lungs. It can t be spread to others, and it has nothing to do with how you were raised or your relationships. Asthma is often hereditary, meaning it is passed through families. Sometimes, more than one person in the same family has asthma. Understanding how your lungs work will help you understand more about asthma. Inside Your Lungs Lungs Trachea Windpipe Bronchial tubes Air passages of the lungs 4
5 When You Have Asthma Normal Airway Inflamed Airway Airway Under Attack Bronchial tube Bronchiole - Smaller branches of the bronchial tubes Muscles - The bronchial tubes are wrapped with muscles Tight muscle Extra mucus Alveoli - Balloonlike sacs through which air passes Mucus lines the bronchial tubes Inflamed airway Alveoli with trapped air Inflamed swollen airway NORMAL INFLAMED AIRWAYS DURING AN ATTACK When asthma is under control, the linings of the airways (bronchial tubes) are smooth, clear, and air flows easily in and out. With asthma, your airways are super sensitive. When asthma is not controlled, the airways become inflamed and swollen. The airways then are made smaller, but air can still flow. When this happens, you may have a cough, chest tightness, wheezing, shortness of breath, or you may feel tired. During an attack, the airways swell up even more and make extra mucus (phlegm). Also, the muscles around the airways become tight, and air gets trapped in the alveoli (the small sacs at the end of the bronchial tubes). All of this makes it very hard for air to pass through your airways and can even block them. You may wheeze, cough, and have trouble breathing. 5
6 Why Does Asthma Happen? Sensitive airways can become affected by many things. These are called asthma triggers. The first important step in controlling your asthma is to discover what allergens trigger your asthma, and stay away from them! If you can control your triggers, you can help keep your airways from becoming inflamed and swollen. Common Allergens That Trigger Asthma House Dust Mites Dust mites are tiny insects found in house dust in almost all parts of the United States. They live on human dander (skin flakes shed by all people), and they increase with moisture in the air. Dust mites are plentiful on mattresses, pillows, carpets, bed covers, and upholstered furniture. S O L U T I O N You can control dust mites by washing the bed pillows, sheets, and covers every week in hot water (130 o F). Use a special allergy-proof mattress and pillow covers. If possible, get rid of carpets, extra pillows, and upholstered furniture, especially in the bedroom. Limit stuffed animals in children s rooms, and wash them weekly in hot water (130 o F). Dust and vacuum often. Use a dehumidifier in damp areas, such as basements dust mites need moist air to live. 6
7 Common Allergens That Trigger Asthma Animals All warm-blooded animals, including birds and small rodents, produce dander (shedded skin, fur, and feathers), urine, saliva, and droppings to which you may be sensitive. S O L U T I O N Don t have furry pets in your home. Your pet will increase asthma symptoms, either immediately or over time. If that s not an option, keep pets out of your bedroom. Keep your bedroom door closed, and consider using dense filters or tape double-thickness cheesecloth over forced-air outlets. Keep pets away from carpet and upholstered furniture as much as possible. Molds Molds can grow in many homes and apartments, especially if you have a damp environment. S O L U T I O N Repair leaks and clean with fungicide or bleach and water solutions where mold is visible. Keep humidity at less than 50%, using a dehumidifier if necessary, especially in basements. 7
8 Common Allergens That Trigger Asthma Cockroach Droppings You can breathe in the droppings of cockroaches and become sensitive to it. This is a concern in big cities and areas of the country with cockroach problems. S O L U T I O N Keep food in tight containers. Repair water leaks. Use traps and poison baits to control cockroaches. Sprays can be irritating to your airways. If spraying is necessary, people with asthma must leave the home until the odor has cleared. Outdoor Triggers Tree, grass, and weed pollens and outdoor mold can also be a problem. Air pollution, smoke, and car exhaust can affect you as well. S O L U T I O N Keep your doors and windows shut, when possible, during times when outdoor triggers are present. Avoid outdoor activity during high pollen or ozone hours, or premedicate prior to activity. Shower and shampoo after being outside. 8
9 Common Irritants That Trigger Asthma Strong Smells Strong smells from painting, spraying, cleaning fluids, garden chemicals, perfumes, lotions, hair sprays, and deodorants can trigger asthma problems. S O L U T I O N Stay away from the house or apartment when these chemicals and sprays are in use, and stay away until the smell clears. Smoking Cigarette, pipe, and cigar smoke are triggers that can affect asthma severely. Children in homes with adults who smoke are far more likely to have asthma problems and ear infections. S O L U T I O N If possible, smokers in families with asthma should quit. Smokers should never smoke indoors, in cars, or around people with asthma. Smokers should wear a removable shirt or jacket while smoking that can be taken off upon returning inside. 9
10 Additional Asthma Triggers Infections Viruses and infections of the sinuses can also make asthma worse. Viral infections are the most common triggers in young children and also cause attacks in adults. S O L U T I O N Get your flu shot every year. See your provider for proper treatment. Often, you will need more of your regular asthma medicines until the infection clears. Ask your provider for asthma medicine prior to flu season to prevent an asthma attack if your child gets a viral infection every year. Drainage From Colds and Sinus Problems Drainage from colds and other sinus problems can make asthma worse. S O L U T I O N Don t ignore a drippy nose. Talk to your provider about medicines you can take to reduce the drainage. Wash hands frequently. Don t share toothbrushes or toothpaste when you have a cold. 10
11 Additional Asthma Triggers Food and Medicine Allergies Many people with asthma report problems with eating certain types of food, especially those that contain sulfites, such as beer, wine, shrimp, and processed potatoes. Some medicines, especially aspirin and beta-blockers (contained in some heart medicines and eye drops), cause problems. Check with your provider. S O L U T I O N Be careful to avoid eating foods that contain sulfites. Read food labels, and use substitute medicines, such as Tylenol or Advil, instead of aspirin. Stay away from any food or medicine that makes your asthma worse. Weather Changes Weather changes can affect the lungs and airways of people with asthma usually very hot, humid weather or very cold, dry weather. S O L U T I O N Avoid doing much outdoors when the weather is very hot or cold. Wear a scarf around your mouth and nose to protect your airways when you must be out in cold, dry weather. 11
12 Additional Asthma Triggers Exercise and Stress Many people with asthma can have attacks during exercise or during times of high stress. S O L U T I O N If exercise is one of your triggers, your provider can give you medicine to take 15 to 30 minutes before exercising to prevent an asthma attack. Do warm-up exercises 6 to 10 minutes prior to exercise. If you are still experiencing asthma symptoms, see your provider, as you may need additional medicine. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD Heartburn) GERD occurs when a muscle in the esophagus (food pipe) relaxes and opens at the wrong time, allowing food or stomach fluids to splash up into the esophagus. You experience a burning sensation (heartburn) because of this occurrence. This is present in children and adults with asthma more than other people. S O L U T I O N You may need to make some lifestyle changes, such as avoiding certain foods, alcohol, or tobacco, or take medicine. You may need to take medication to control acid in your stomach. Ask your provider for guidance. R E M E M B E R Even though asthma can affect exercise, you should not avoid it. Regular exercise can improve your lungs and overall health. It s an important part of controlling your asthma. Ask your provider to help you plan a safe exercise program. Controlling your asthma triggers is the first important step in keeping your airways open and in controlling your asthma. 12
13 Work With Your Health-care Provider The second important step in controlling your asthma is to work with your provider to form an asthma action plan. You may be asked to keep an asthma diary to help you do this. The action plan will tell you what medicines to take and when. As part of your asthma action plan, your provider will teach you how to use a peak flow meter. Keep regular appointments with your provider, even when you are feeling fine. Well visits will help you keep your asthma under control. Keep an accurate diary, as your provider will use this as part of your assessment to help direct your asthma management. Lung Function Testing Spirometry The National Asthma Guidelines recommend a breathing test on the initial visit, every 1 to 2 years, or as often as your provider feels it is necessary. This test, called spirometry, measures how air is moving through your lungs. Ask your provider about this test. Peak Flow Meter A peak flow meter can be used at a clinic or at home to measure how well you are breathing. Peak flow can be useful in identifying triggers. If a peak flow meter is used every day at home, you can find breathing problems even before you start to wheeze or cough. A drop in peak flow is a good way to recognize early signs of a coming asthma attack. Peak flow and the symptoms you are having help your provider decide if you are having an asthma flare. It helps to see how severely an asthma attack is affecting you. It helps the provider see how your asthma can be controlled over time. There are many kinds of peak flow meters. 13
14 How To Use a Peak Flow Meter Your asthma is not like anyone else s, so you will need to discover your own personal best peak flow. STEP 1: Slide the marker down as far as it will go. This sets the meter at zero. STEP 2: Stand up. Take a deep breath in, and blow all the way out as far as possible. STEP 3: Then take as deep a breath in as possible with your mouth open. STEP 4: Place the meter in your mouth and close your lips around it to form a seal. Your tongue should be away from the hole. Keep your fingers away from the markings. Blow out once as hard and fast as you can. STEP 5: Don t touch the marker, and write down the number you get. STEP 6: Repeat twice. Reset the marker to zero each time. Write down the number each time. Your peak flow is the highest of these three numbers. 14
15 How To Use a Peak Flow Meter Find your peak flow number in the morning and evening. Hold the meter next to the chart each time you blow to make it easier to record the number. Circle the highest number of three blows. This is your peak flow. SAMPLE DAY SAMPLE DAY 1DAY DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY NIGHT DAY NIGHT DAY NIGHT DAY NIGHT How To Establish Your Personal Best Peak Flow: When your asthma is under control, record your peak flow twice daily for 2 weeks. Measure your peak flow at the same time of day, as peak flow is lowest in the early morning and highest between 12:00 noon and 5:00 PM. The highest number during those 2 weeks will be your personal best peak flow. Reestablish your personal best peak flow with new peak flow meters. Children need to reestablish their personal best peak flow every 6 months to allow for lung growth changes. 15
16 Asthma Diary With your provider s help, use this diary. Keep it up to date and always on hand. In an emergency, it s an important record of your medicines, triggers, and peak flow. Your provider will use this as part of your assessment. RANGE NAME (emergency information) 16
17 Trouble walking and talking due to shortness of breath Lips or fingernails are blue Take 4 or 6 puffs of your quick-relief medicine AND Go to the hospital or call for an ambulance N O W! (emergency information) DANGER SIGNS! Peak flow: less than (50% of my best peak flow) You are still in the RED ZONE after 15 minutes AND You have not reached your doctor. - O R - Then call your doctor NOW! Go to the hospital or call for an ambulance if: Very short of breath, or Quick-relief medicines have not helped, or Cannot do usual activities, or Symptoms are same or get worse after 24 hours in YELLOW ZONE mg per day (oral steroid) 4 or 6 puffs or Nebulizer (short-acting beta 2 -agonist) RED ZONE: Medical Alert! Take this medicine: Add: mg per day for (3 to 10) days. (oral steroid) Call the doctor within hours after taking the oral steroid. Take: 2 or 4 puffs or Nebulizer (short-acting beta 2 -agonist) Peak flow: to (50% to 80% of my best peak flow) - O R - If your symptoms (and peak flow, if used) do not return to GREEN ZONE after 1 hour of above treatment: - O R - Take the quick-relief medicine every 4 hours for 1 to 2 days. Double the dose of your inhaled steroid for (7 to 10) days. S E C O N D If your symptoms (and peak flow, if used) return to GREEN ZONE after 1 hour of above treatment: Cough, wheeze, chest tightness, or shortness of breath or Waking at night due to asthma, or Can do some, but not all, usual activities YELLOW ZONE: Asthma is Getting Worse F I R S T Add: quick-relief medicine and keep taking your GREEN ZONE medicine. 2 or 4 puffs, every 20 minutes for up to 1 hour (short-acting beta 2 -agonist) Nebulizer, once B E F O R E E X E R C I S E 2 or 4 puffs 5 to 60 minutes before exercise My best peak flow is: More than: (80% or more of my best peak flow) And, if a peak flow meter is used, peak flow: No cough, wheeze, chest tightness, or shortness of breath during the day or night Can do usual activities MEDICINE HOW MUCH TO TAKE WHEN TO TAKE IT GREEN ZONE: Doing Well Take these long-term control medicines each day (includes an antiinflammatory): PROVIDER S PHONE NUMBER HOSPITAL/EMERGENCY ROOM PHONE NUMBER ASTHMA ACTION PLAN FOR Provider s Name Date 17
18 Asthma Medicine If you regulate your triggers and use long-term control medicines correctly, your asthma can be very well controlled. Long-term Control Medicines They reduce and help prevent the inflammation and swelling of your airways. If inflammation is controlled, your chances of having an asthma attack are low. Remember, managing your triggers, along with using long-term medicines, will give you good control of inflammation. Inhaled corticosteroids are the preferred medicine for persistent asthma (National Asthma Education and Prevention Program 2002). They must be used regularly to be effective, usually every day. You cannot become addicted to them, even if you use them for many years. Most will be inhaled, some are swallowed. With each new inhaler, especially the corticosteroid inhaler, check the number of doses in the canister. Count the number of doses you will be using each day and divide that number into the total number in the canister. This will tell you how long the medicine will last. Write the date to call for a refill on the canister. DO NOT USE BEYOND THE NUMBER OF DOSES ON THE CANISTER. DO NOT DROP THE CANISTER INTO WATER. Inhaled Corticosteroids T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D Below are examples of the most common medicines used for controlling inflammation and swelling of the airways. They are not the same as muscle-building steroids that are misused by athletes. FLUTICASONE/SALMETEROL FLUTICASONE BUDESONIDE (Flovent/Serevent) (Flovent) (Pulmicort Turbuhaler) Combination Therapy (Advair Diskus) 18
19 Long-term Control Medicines Inhaled Corticosteroids TRIAMCINOLONE (Azmacort) FLUNISOLIDE (Aerobid) BECLOMETHASONE DIPROPRIONATE (Qvar) BUDESONIDE (Pulmicort) Nebulized form (Pulmicort Respules) T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S Oral thrush (fungal infection in mouth) Dysphonia (hoarseness) Minimum growth delay in first year of treatment with children. Research shows these children attain their normal height. Your provider will keep your child on the lowest maintenance dose possible. Uncontrolled asthma may cause more development problems than long-term medicine. 19
20 Long-term Control Medicines Oral Corticosteroids PREDNISONE - Deltasone - Prednisone METHYLPREDNISOLONE - Medrol - Methylprednisolone PREDNISOLONE - Prelone Syrup - Pediapred P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S You may notice after a few days: Fluid retention Increased appetite You may experience after several months of use: Adrenal suppression (less able to handle stress) Decreased resistance to infection (get infections more easily) T H E S E A R E S W A L L O W E D You may experience after several months or years of use: Moon face Cataracts Excess facial hair Osteoporosis Non-Steroid Medicine T H I S I S A L W A Y S I N H A L E D Protects the airways from some asthma triggers. Can help prevent asthma attacks due to exercise. Must take at least three times a day to be effective. P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T Dry mouth CROMOLYN SODIUM (Intal) 20
21 Long-term Control Medicines Long-Acting Inhaled Beta 2 -Agonists T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D Can be used to prevent asthma problems, especially at night. Can help prevent asthma attacks due to exercise. Should not be used during an attack. Should not exceed more than 2 doses a day, 12 hours apart. P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S Racing heart Tremors (shaking) Nervousness SALMETEROL (Serevent Discus) FORMOTEROL FUMERATE (Foradil) FLUTICASONE/SALMETEROL COMBINATION (Advair) Long-Acting Oral Beta 2 -Agonists T H E S E A R E S W A L L O W E D These medicines have a slower onset of action than the inhaled albuterol. Not a preferred therapy. ALBUTEROL SULFATE - Proventil Tablets P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S Racing heart Tremors (shaking) Nervousness ALBUTEROL SULFATE - Ventolin Syrup ALBUTEROL SULFATE - Volmax Tablets 21
22 Long-term Control Medicines Methylxanthines Theophylline, sustained release tablets and capsules. Used especially for nighttime asthma symptoms. Check with your provider if you have any of the side effects. Check with your provider about taking a blood test to make sure that the treatment dose is correct. Examples: Slo-bid Theo-dur Theo-24 Uni-Dur T H E S E A R E S W A L L O W E D P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S Racing heart Tremors (shaking) Nervousness Nausea Headaches Insomnia (sleeplessness) Heartburn Seizures (rarely) Leukotriene Modifiers T H E S E A R E S W A L L O W E D Can be used in combination with inhaled corticosteroids for people with mild asthma. Can help reduce the amount of steroids taken. Singulair can help with allergic asthma. ZAFIRLUKAST (Accolate) POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS MONTELUKAST SODIUM (Singulair) POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS Headache Infection Stomach pain or upset Generalized pain Dizziness Fever Weakness Tiredness Stomach pain or upset Dizziness Rash Cough Stuffy nose 22
23 Quick-Relief Medicines The long-term control medicines, on pages 20 to 24, are used to prevent asthma attacks from happening in the first place, but if asthma is severe, asthma attacks can still happen. Your provider will provide quick-relief medicines that usually relieve an asthma attack once it starts or keep it from getting worse. The medicines quickly relax the muscles around your airways so you can breathe easier. These medicines can also be used to prevent attacks if used before you exercise. No matter what kind of quick-relief medicine you use, always carry it with you. Never leave home without it! Make sure you know how to use it the correct way. Check expiration dates regularly to make sure it is still effective. B E C A R E F U L You can use quick-relief medicines too often. They make you feel better for a little while, but will not help if you need to use them every day. You may need long-term control medicines if you: Need quick-relief medicine more than twice a week. Wake up at night more than twice a month with asthma symptoms. Need a refill more than twice a year. (Baylor s Rules of Two ) With good control, you should not need quick-relief medicines very often. Short-Acting Beta 2 -Agonists T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D Below examples are used most often. P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T S Racing heart Nervousness and tremors (shaking) ALBUTEROL SULFATE ALBUTEROL SULFATE ALBUTEROL SULFATE (Proventil) (Proventil HFA) (Ventolin) Also available in nebulized form 23
24 Quick-Relief Medicines Short-Acting Beta 2 -Agonists T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D PIRBUTEROL ACETATE METAPROTERENOL SULFATE LEVALBUTEROL HCI INHALATION SOLUTION (Maxair) (Alupent) (Xopenex) Anticholinergics Most often used together with short-acting beta 2 -agonists in the emergency room. Acts as a booster for the short-acting beta 2 -agonists. IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE (Atrovent) IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE/ALBUTEROL (Combivent) Combination Therapy T H E S E A R E I N H A L E D P O S S I B L E S I D E E F F E C T Dry mouth R E M E M B E R Set aside money for asthma medicine. Buy more before you run out. Ask your provider any questions you have about medicines. Asthma may get better or worse over the years. Your provider may need to change your medicines over time. Always check expiration dates. 24
25 How To Take Asthma Medicines Many asthma medicines come as sprays and powders that are used in an inhaler. When you breathe in the medicine through the inhaler, it goes right to the airways in the lungs where it is needed. Ask your provider to help you learn how to use an inhaler. How to use a metered-dose inhaler (MDI) STEP 1: Take off the cap, and shake the inhaler with the metal canister inserted. STEP 2: Hold the inhaler like this stand up, take a deep breath, and breathe out as much as you can. Tilt head back slightly. STEP 3: Hold the inhaler in your mouth or 2 fingers away from your mouth (the best method). As you start to breathe in, push down on the top of the inhaler, and keep breathing in slowly and deeply, keeping mouth open until breathing is complete. STEP 4: Hold your breath for 5 to 10 seconds with your mouth closed, then breathe out slowly. If you use more than one puff, wait 1 minute before inhaling again. STEP 5: If using inhaled corticosteroids, rinse your mouth with water, but don t swallow. STEP 6: Once a day, remove the cap and the canister from plastic holder, and wash them with mild soap and water. Rinse with running water. Let dry. 25
26 Turbuhaler Technique and Tips Follow the manufacturer s instructions to load your dose of medication. Hold inhaler upright after loading medicine. Hold the inhaler away from the mouth, take a deep breath in, and blow out slowly and completely. Put your mouth around the mouthpiece and inhale deeply and forcefully. Hold your breath and count to 10. Breathe out slowly. Repeat these steps for the number of doses that your doctor has prescribed. Rinse your mouth with water, but don t swallow. The red line appearing on the window of your turbuhaler indicates only 20 doses left. Order refill at this time. Diskus Technique and Tips Hold Diskus in left hand and place thumb on the thumb grip, pushing it forward away from you as far as it will go. Holding the Diskus in a level horizontal position, push the lever forward away from you until it clicks or as far as it can go. Holding the Diskus level but away from your mouth, take a deep breath, and blow out as deeply and completely as possible. Put the mouthpiece to your lips and breathe in steadily and deeply through your mouth. Remove the Diskus from your mouth. Hold your breath and count to 10. Breathe out slowly. To close Diskus, put your thumb on the thumb piece and slide the thumb grip back toward you until it clicks shut. The lever will automatically return with the thumb grip and reset itself. Repeat procedure for the number of doses the doctor has prescribed. If using inhaled corticosteroids, rinse your mouth with water, but don t swallow. 26 Never wash the mouthpiece or any part of the Diskus device. It must always be kept dry.
27 Spacers and Holding Chambers Some people, especially children, have trouble using an inhaler the right way. Using a spacer helps deliver more medicine to the lungs and helps decrease hoarseness that may occur with inhaled corticosteroids. Holding chambers allow you to breathe in and out more than once per puff of medicine. Wash the plastic spacer or chamber with soap and water when it is new to cut down on the electrostatic field that is inside the chamber. STEP 1: The holding chamber or spacer attaches to the inhaler. STEP 2: Shake well. R E P E A T T H E S E S T E P S T W I C E STEP 3: Breathe all the way out. Place the mouthpiece in your mouth, then press the inhaler button to release a puff of medicine into the spacer or chamber. STEP 4: Breathe in slow and deep, keeping the mouthpiece in place until finished. STEP 5: Hold your breath and count to 10, then relax and breathe out. If you need more than one puff of medicine, wait at least a minute before using the spacer again. STEP 6: Young children may require a chamber with a mask. It is necessary for the mask to fit securely against the face for the child to receive maximum dose. No matter what medicines you take and when, use your asthma diary and asthma action plan that you ve created with your provider. Always follow your plan, and your asthma can be controlled. 27
28 Using a Nebulizer If using a face mask, the mask must fit properly (right size) and tightly over nose and mouth. If using a mouthpiece, it must be between the teeth with lips closed tightly around it. Waving the mouthpiece or mask in front of the mouth will NOT get the medicine into the lungs. Rinse out mouth after nebulizing Budesonide (Pulmicort Respules). Give infants a drink of water. If a face mask was used, wash face with soap and water to avoid skin irritation. The cup, mouthpiece, or mask should be washed daily with mild soap and water, rinsed in a vinegar and water solution, and dried. Never wash the tubing. Change filter on nebulizer compressor according to manufacturer s recommendations. 28
29 Asthma Attacks Can Be Dangerous It helps to know when an asthma attack may be starting. You may be able to prevent it before it starts. D A N G E R S I G N S Can t talk well or walk/gasping for air Lips or fingernails turn blue YOU ARE HAVING A MAJOR ATTACK. IF YOU HAVE THESE SIGNS, GO TO THE EMERGENCY ROOM OR CALL 911 IMMEDIATELY! Know Your Signs and Symptoms Coughing, sneezing, itchy throat Tight chest, wheeze Shortness of breath Wake up at night Fast heartbeat and breathing Headache Take Action Work with your provider to develop an action plan. Learn what your warning signs are. When you feel an attack coming: 1. Get away from the trigger that started your attack. 2. Take a quick-relief medicine, up to 3 treatments of 2 to 4 puffs, 20 minutes apart. Check your peak flow first and before each additional dose. 3. If you still have wheezing and shortness of breath, get emergency help from your provider. 29
30 Follow Your Asthma Action Plan Controlling your asthma may seem like a lot of work, but taking steps now can help you live a normal life. Find ways to control your asthma triggers. Keep your asthma diary up-to-date and follow your asthma action plan. Take your long-term control medicines daily or as prescribed. Always carry your quick-relief medicine with you. All of these steps together can greatly reduce your chances of having asthma attacks. Prevention is the key. All it takes is good information and a working partnership with your provider. 30
31 Controlling Your Asthma is also available in Spanish. Other patient education guides available from the ACCP in print and on the ACCP Web site ( are: Living Well With COPD Flexible Bronchoscopy Cough: Understanding and Treating a Problem With Many Causes Mechanical Ventilation: Beyond the Intensive Care Unit Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A Team Approach To Improving Quality of Life 31
32 Printing of this patient education booklet was made possible by an unrestricted educational grant from: American College of Chest Physicians 3300 Dundee Road Northbrook, IL Product Code: 5024
Kickin Asthma. Workbook for Children with Asthma. Name:
 Kickin Asthma Workbook for Children with Asthma Name: Why Have You Been Invited to Kickin Asthma? You have been invited to Kickin Asthma because you have asthma. Asthma is a disease of your air tubes that
Kickin Asthma Workbook for Children with Asthma Name: Why Have You Been Invited to Kickin Asthma? You have been invited to Kickin Asthma because you have asthma. Asthma is a disease of your air tubes that
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA. A guide for parents. childrensmn.org
 CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Breathe Easy ACTIVITIES. A Family Guide to Living with Asthma F O R T H E K ! I D S
 Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
ASTHMA CONTROL. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms.
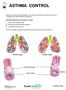 ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Home Management Plan. Cover Page
 Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD
 How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
Asthma Education. The Keys to Asthma Prevention and Control. what to do when one s asthma is flared! Lucile Packard Children s Hospital.
 Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Welcome to our Asthma Program
 Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
Welcome to our Asthma Program We re here to help you be your healthiest through information, education and support for your asthma. We ll work with you by: Partnering with your health care team to make
PATIENT INFORMATION FORM
 PATIENT INFORMATION FORM "I am going to ask you a number of questions about your asthma. The set of questions is somewhat long, but I will try to move through it fairly quickly so that we can complete
PATIENT INFORMATION FORM "I am going to ask you a number of questions about your asthma. The set of questions is somewhat long, but I will try to move through it fairly quickly so that we can complete
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Breathe Easy. Tips for controlling your Asthma
 Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma. January 2011
 Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
Asthma Triggers. It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them.
 Asthma s It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them. With asthma, your child s airways are very sensitive. Things, called triggers, may
Asthma s It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them. With asthma, your child s airways are very sensitive. Things, called triggers, may
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Sources. Taking Charge of Your Asthma. Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company
 Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Asthma Action Plan (to be completed with your doctor) Green Zone: (80 to 00% of my personal best) Peak Flow between and (00% = personal best) You can do all the things you usually do. Your asthma medicine
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING Presented by:
 MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
Living Well with Asthma
 Living Well with Asthma Understanding Asthma Monitoring Your Breathing Using an Inhaler Reducing Triggers Staying Active Living with Asthma If you have asthma, there s good news. Today, people with asthma
Living Well with Asthma Understanding Asthma Monitoring Your Breathing Using an Inhaler Reducing Triggers Staying Active Living with Asthma If you have asthma, there s good news. Today, people with asthma
Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families. What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma
 Page 1 of 8 PED-ALL-005-1992 Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma What Medicines Are used to Treat Asthma? There are two kinds of medicines:
Page 1 of 8 PED-ALL-005-1992 Asthma Medications: Information for Children and Families What You Need to Know about Medicines for Asthma What Medicines Are used to Treat Asthma? There are two kinds of medicines:
How to Manage Asthma
 How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol
![MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol MEDICATION GUIDE. ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol](/thumbs/78/76835983.jpg) MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol ADVAIR HFA 115/21 (fluticasone propionate 115 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation
MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR [ad vair] HFA 45/21 (fluticasone propionate 45 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation Aerosol ADVAIR HFA 115/21 (fluticasone propionate 115 mcg and salmeterol 21 mcg) Inhalation
ASTHMA. Disclaimer. Multimedia Health Education
 ASTHMA Disclaimer This film is an educational resource, and should not be used for decisions about asthma treatment. All such decisions must be made in consultation with a physician or a healthcare provider.
ASTHMA Disclaimer This film is an educational resource, and should not be used for decisions about asthma treatment. All such decisions must be made in consultation with a physician or a healthcare provider.
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation
![PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation PATIENT INFORMATION. ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation](/thumbs/74/71128680.jpg) PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
PATIENT INFORMATION ADVAIR DISKUS [AD vair DISK us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is ADVAIR DISKUS? ADVAIR DISKUS combines the inhaled corticosteroid
Staying Healthy. with Asthma. Illustrations by paulsharp.com
 Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Taking Care of Your Child s Asthma. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
Clear and Easy. Skypark Publishing. Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line
 Clear and Easy #5 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Clear and Easy #5 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
LivingWith Asthma. A Guide to Understanding Asthma...
 A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
Clear and Easy #12. Skypark Publishing. Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line
 Clear and Easy #12 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Clear and Easy #12 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Asthma. Basic Information About Asthma. What is asthma? Who is at risk? What are the most common triggers for asthma symptoms?
 In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
Asthma 101. Introduction
 TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
Appendix E: Device Technique
 Adult Asthma Care Guidelines for Nurses: Promoting Control of Asthma Appendix E: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Adapted with permission from The Lung Association: www.lung.ca/asthma/manage/devices.html
Adult Asthma Care Guidelines for Nurses: Promoting Control of Asthma Appendix E: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Adapted with permission from The Lung Association: www.lung.ca/asthma/manage/devices.html
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather
 Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Ohio Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes swelling
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Ohio Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes swelling
Asthma symptoms are usually more active at night, when waking up in the early morning or after exercise. The asthma symptoms are:
 Health Bites - Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a long-term disease that affects the air passages in the lungs. Air passages are tiny breathing tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs. People who
Health Bites - Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a long-term disease that affects the air passages in the lungs. Air passages are tiny breathing tubes that carry air in and out of the lungs. People who
B.R.E.A.T.H.E. Bringing Reduction and Education of Asthma Triggers to the Home Environment
 B.R.E.A.T.H.E. Bringing Reduction and Education of Asthma Triggers to the Home Environment A collaborative project of HDHHS and the EPA Bureau of Community and Children s Environmental Health Acknowledgements
B.R.E.A.T.H.E. Bringing Reduction and Education of Asthma Triggers to the Home Environment A collaborative project of HDHHS and the EPA Bureau of Community and Children s Environmental Health Acknowledgements
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:
 (pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma
 Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma Table of Contents 1 What is Asthma?... 2 2 What causes asthma?... 2 2.1 Triggers... 2 3 Signs and Symptoms... 2 4 Treatment... 2 4.1 Relievers... 2 4.2 Preventers...
Complex Care Hub Manual Section: Asthma Table of Contents 1 What is Asthma?... 2 2 What causes asthma?... 2 2.1 Triggers... 2 3 Signs and Symptoms... 2 4 Treatment... 2 4.1 Relievers... 2 4.2 Preventers...
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Washington Fall 2012 Importance of Controller Medicines Asthma is a disease that causes
Asthma (Short wind) in Children
 In partnership: Asthma (Short wind) in Children The lungs You have two lungs. They sit inside your chest, above your stomach and surround your heart. The lungs have a very important job inside your body.
In partnership: Asthma (Short wind) in Children The lungs You have two lungs. They sit inside your chest, above your stomach and surround your heart. The lungs have a very important job inside your body.
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma and the things you can do every day to help control symptoms. As always, talk to your
You Can Control Your Asthma
 asthma_brochureprint_v2.qxd 9/5/06 9:54 AM Page 2 For More Information on Controlling Asthma: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health, MS F52 4770 Buford Highway,
asthma_brochureprint_v2.qxd 9/5/06 9:54 AM Page 2 For More Information on Controlling Asthma: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health, MS F52 4770 Buford Highway,
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
MY ASTHMA BOOKLET. Name: Date: / /
 MY ASTHMA BOOKLET Name: Date: / / 1 2 WHAT IS ASTHMA? WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma is a lung disease. The airways in the lungs get very small. It is hard for air to move through very small airways. It is hard
MY ASTHMA BOOKLET Name: Date: / / 1 2 WHAT IS ASTHMA? WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma is a lung disease. The airways in the lungs get very small. It is hard for air to move through very small airways. It is hard
Medications. prescribed. Use as. A s t h m a B a s i c s # 3
 Medications A s t h m a B a s i c s # 3 Use as prescribed The Asthma Basics Booklet Series was developed to provide Canadians with asthma, current and accurate information about asthma management. This
Medications A s t h m a B a s i c s # 3 Use as prescribed The Asthma Basics Booklet Series was developed to provide Canadians with asthma, current and accurate information about asthma management. This
ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1. Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis
 ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1 Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis OBJECTIVES By the end of training, participants will:
ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1 Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis OBJECTIVES By the end of training, participants will:
Appendix M: Device Technique
 Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Breezhaler. Open to see clear capsule. How do I use my Breezhaler? Care of my Breezhaler
 Breezhaler 3 Pull cap off Press buttons once and release Breathe in rapidly and steadily. Hold. Open. Place capsule in chamber. Close (click). Breathe out 4 Open to see clear capsule. If not all clear
Breezhaler 3 Pull cap off Press buttons once and release Breathe in rapidly and steadily. Hold. Open. Place capsule in chamber. Close (click). Breathe out 4 Open to see clear capsule. If not all clear
Asthma. If an Ambulance is required - call immediately - do not delay. H & A Training PL RTO No:90871
 Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Asthma Action Plan and Education
 Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Acute Services Division Asthma Action Plan and Education Name: Date: Index What is Asthma? Page 4 Asthma Triggers Page 5 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (Peak Flow) Page 6 Asthma Treatments Page 7 Asthma Action
Asthma. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know
 1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
What You Need to Know about Metered-Dose Inhalers and the HFA Propellant
 What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
Teacher Training on Asthma
 Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Michigan Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Michigan Newsletter Spring 2012 Getting Rid of Mold There are many types of molds. Molds will not grow without water
Medications. prescribed. Use as. Your Asthma Basics series: Asthma Basics #3. Diagnosis Triggers Medications Kids
 Medications Asthma Basics #3 Your Asthma Basics series: 1 2 3 Diagnosis Triggers Medications Kids Use as prescribed Supported by unrestricted educational grants from: For more information from the Asthma
Medications Asthma Basics #3 Your Asthma Basics series: 1 2 3 Diagnosis Triggers Medications Kids Use as prescribed Supported by unrestricted educational grants from: For more information from the Asthma
your breathing problems worsen quickly. you use your rescue inhaler, but it does not relieve your breathing problems.
 MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
MEDICATION GUIDE ADVAIR DISKUS [ad vair disk us] (fluticasone propionate and salmeterol inhalation powder) for oral inhalation What is the most important information I should know about ADVAIR DISKUS?
Helping Your Child Stay Healthy & Active
 Helping Your Child Stay Healthy & Active 11480 1401 Taking Control of Your Child s Asthma Learning that your child has asthma can be overwhelming. Asthma is a chronic (ongoing) disease of the airways in
Helping Your Child Stay Healthy & Active 11480 1401 Taking Control of Your Child s Asthma Learning that your child has asthma can be overwhelming. Asthma is a chronic (ongoing) disease of the airways in
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Because the more you know, the better you ll feel.
 ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
ABOUT ASTHMA Because the more you know, the better you ll feel. What You ll Find Attitudes and Beliefs Asthma What Is It? Where You ll Find It Page 4-5 This booklet is designed to help you understand asthma
Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma
 Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma Lesson 2: What causes asthma? Identifying Asthma Triggers Teacher Instructions, Introduction, and Student Worksheets Objectives for Lesson 2: After completing
Learners Take Action to Reduce the Risk of Asthma Lesson 2: What causes asthma? Identifying Asthma Triggers Teacher Instructions, Introduction, and Student Worksheets Objectives for Lesson 2: After completing
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan - Spring 2014 Asthma and Your Home Asthma is one of our nation s most common chronic
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Michigan - Spring 2014 Asthma and Your Home Asthma is one of our nation s most common chronic
Asthma Management. Photo from
 Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
Asthma Management 1 Photo from www.nhlbi.nih.gov Course Overview 1. Recognition of the symptoms and signs Basic Knowledge of asthma Recognition of common symptoms Recognition of the signs of asthma including
A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Table of Contents What is COPD? 2 How the Lungs Work 2 Lungs with Chronic Bronchitis 3 Lungs with Emphysema 4 Causes of COPD 4 COPD Symptoms
A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Table of Contents What is COPD? 2 How the Lungs Work 2 Lungs with Chronic Bronchitis 3 Lungs with Emphysema 4 Causes of COPD 4 COPD Symptoms
Asthma. What Is Asthma? Overview. Asthma
 Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Provided as an educational resource by Merck. A Guide to Living With Asthma
 Provided as an educational resource by Merck A Guide to Living With Asthma Table of Contents 1. Introduction...2 7 fast facts about asthma...2 2. Asthma Basics...3 6 What happens during an asthma attack?...3
Provided as an educational resource by Merck A Guide to Living With Asthma Table of Contents 1. Introduction...2 7 fast facts about asthma...2 2. Asthma Basics...3 6 What happens during an asthma attack?...3
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
Asthma and COPD Awareness breathe with ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Texas Newsletter Spring 2011 Asthma Warning Signs In This Issue Asthma Warning Signs pg 1 Working with the Provider
Asthma Friendly School Environments
 Asthma Friendly School Environments Our Mission Prevent lung disease and promote lung health in Mississippi through: Education Advocacy Research What is Asthma? Asthma: Is a life-long disease found in
Asthma Friendly School Environments Our Mission Prevent lung disease and promote lung health in Mississippi through: Education Advocacy Research What is Asthma? Asthma: Is a life-long disease found in
Asthma Basic Facts. Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers.
 Asthma Basic Facts Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers. Asthma App Contact your local Asthma Foundation asthmaaustralia.org.au Breathing Breathing is how we get air
Asthma Basic Facts Staying safe and well with asthma. For people with asthma and their carers. Asthma App Contact your local Asthma Foundation asthmaaustralia.org.au Breathing Breathing is how we get air
My Asthma Log. Tommy Traffic Light. NHS Number: Name:
 My Asthma Log Tommy Traffic Light NHS Number: Name: My Asthma Log Book This book is designed to help you understand and learn about managing your asthma. You should take your book with you to all your
My Asthma Log Tommy Traffic Light NHS Number: Name: My Asthma Log Book This book is designed to help you understand and learn about managing your asthma. You should take your book with you to all your
Your Child and Asthma
 Understanding Your Child and Asthma An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best
Understanding Your Child and Asthma An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Web E-Mial Registration Form. Med practitioner s name. Med practitioner s phone. Name/location of the clinic
 AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Asthma Management Protocol
 Asthma Management Protocol USC School of Pharmacy Updated October 2012 08/24/18 USC School of Pharmacy 1 I. Goals and Objectives The goal of the pharmacist-managed Asthma Management Program (AMP) is to
Asthma Management Protocol USC School of Pharmacy Updated October 2012 08/24/18 USC School of Pharmacy 1 I. Goals and Objectives The goal of the pharmacist-managed Asthma Management Program (AMP) is to
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol)
 Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Asthma and COPD Awareness
 Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Texas Summer 2013 Asthma Triggers You may not always know when an asthma attack will
Asthma and COPD Awareness Molina Breathe with Ease sm and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Molina Healthcare of Texas Summer 2013 Asthma Triggers You may not always know when an asthma attack will
Understanding. Asthma. An educational health series from
 Understanding Asthma An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Understanding Asthma An educational health series from Our Mission since 1899 is to heal, to discover, and to educate as a preeminent healthcare institution. We serve by providing the best integrated and
Asthma and IAQ. Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst
 Asthma and IAQ Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst Division of Adolescent and School Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Asthma is a Major Public Health Problem
Asthma and IAQ Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst Division of Adolescent and School Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Asthma is a Major Public Health Problem
ESSENTIAL STANDARD. 6.PCH.1 Understand wellness, disease prevention, and recognition of symptoms.
 PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
PRE-TEST 1.What are the basic functions of the respiratory system? 2.Describe five symptoms of asthma. 3.How can asthma be controlled? 4.What are some common asthma triggers? ESSENTIAL STANDARD 6.PCH.1
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
How to Use Inhaled Medications
 How to Use Inhaled Medications FOR ASTHMA AND COPD introduction Inhaled medications are an important part of controlling and treating asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The medication
How to Use Inhaled Medications FOR ASTHMA AND COPD introduction Inhaled medications are an important part of controlling and treating asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The medication
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING
 UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
Cough Associated with Bronchitis
 Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
A patient educational resource provided by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
9/30/2013. Asthma in the Classroom: What do teachers need to know? Asthma Impact. Asthma is Common
 Asthma in the Classroom: What do teachers need to know? Pulmonary Rehabilitation Asthma Impact Asthma affects over twenty five million people nationwide causes 10.5 million lost school days annually third-ranking
Asthma in the Classroom: What do teachers need to know? Pulmonary Rehabilitation Asthma Impact Asthma affects over twenty five million people nationwide causes 10.5 million lost school days annually third-ranking
