Emergency Medical Services. Pharmacology Reference Guide
|
|
|
- Claribel Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas BioTel EMS System Emergency Medical Services Pharmacology Reference Guide January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2008 (subject to revision prior to the end of this period, as authorized by the Medical Director)
2 This page intentionally blank
3 UTSW/BioTel EMS System Pharmacology Table of Contents Medication Page Medication Page Adenosine (Adenocard ) 5 Glucose (Oral Glucose) 20 Albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin ) 6 Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent ) 21 Amiodarone HCl (Cordarone ) 7 Lidocaine HCl 23 Aspirin (Acetylsalicylate Acid) 8 Magnesium Sulfate 25 Atropine Sulfate 9 Midazolam (Versed ) 26 Calcium Chloride 10 Morphine Sulfate 27 Dextrose 50% 11 Naloxone HCl (Narcan ) 28 Diazepam (Valium ) 12 Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat ) 29 Diphenhydramine HCl (Benadryl ) 13 Nitrous Oxide (Nitronox ) 30 Dopamine HCl (Inotropin ) 14 Norepinephrine bitartrate (Levophed ) 31 Epinephrine 1:1, Pralidoxime Chloride 32 Epinephrine 1:10, Promethazine HCl (Phenergan ) 33 Etomidate 17 Proparacaine HCl (Alcaine ) 34 Fentanyl 18 Sodium Bicarbonate 35 Glucagon 19 Page 3 of 35
4 This page intentionally blank Page 4 of 35
5 Adenosine (Adenocard ) Route: Atrial Antiarrhythmic Rapid IV push at the insertion site (antecubital space) Rapid intraosseous push (alternative site) First Dose: 12mg rapid push followed immediately by a rapid 20mL NS flush - standing order Second Dose: 12mg rapid push followed immediately by a rapid 20mL NS flush - standing order First Dose: 0.1 mg/kg rapid push (max 6mg) followed immediately by a rapid 5mL NS flush - BioTel authorization only Second Dose: 0.2 mg/kg rapid push (max 12mg) followed immediately by a rapid 5mL NS flush - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Slows conduction through AV node thereby terminating reentrant tachycardia Causes transient AV block Vasodilation Indications: Immediate 10 seconds Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Standing order administration for stable adults only, BioTel must authorize administration in unstable adults and in the pediatric patient. Precautions: Assure rhythm is not ventricular in origin Explain expected side effects to patient Monitor patient and ECG continuously Use with caution: COPD, CHF, CAD Contact BioTel for the following prior to administration: Asthma patient taking bronchodilators (theophylline class) Seizure patient taking carbamazepine (Tegretol ) Recent caffeine ingestion Side Effects: Flushing Sweating Chest Pain Nausea/Vomiting Lightheadedness Transient Arrhythmias Transient Asystole Contraindications: 2 or 3 heart block Atrial fibrillation or flutter Sick Sinus Syndrome Dipyridamole (Persantine ) Organophosphate ingestion Poisoning/Drug-induced tachycardia Special: Record rhythm strip during administration Page 5 of 35
6 Albuterol (Ventolin, Proventil ) Sympathomimetic Route: Inhalation Endotracheal administration (alternative route) 2.5mg given via nebulizer over 5-15 minutes. If the patient is improving after the first dose, two additional doses may be given. If there is NO improvement after the first dose, combine the 2 nd and 3 rd doses with Ipratropium (Atrovent ) 0.5 mg. - standing order. BioTel must authorize any additional doses. 2.5mg given via nebulizer over 5-15 minutes. If the patient is improving after the first dose, two additional doses may be given. If there is NO improvement after the first dose, combine the 2 nd and 3 rd doses with Ipratropium (Atrovent ) 0.5 mg. - standing order. BioTel must authorize any additional doses. Drug Action: Indications: Precautions: Bronchodilation (beta-two adrenergic) 5-15 minutes after inhalation 3-4 hours after inhalation Bronchospasm associated with: Asthma and COPD Chemical toxins: nerve agents, cyanide, blistering agents, choking agents Allergic reaction unresponsive to epinephrine and diphenhydramine CHF - BioTel authorization only Known heart disease Side Effects: Restlessness Hypertension Tachycardia - palpitations Contraindications: Pregnancy, except in life-threatening situations Page 6 of 35
7 Amiodarone HCL (Cordarone ) Route: Antiarrhythmic IV or intraosseous push only Ventricular fibrillation, pulseless ventricular tachycardia First Dose mg - standing order Second Dose mg - standing order Stable or unstable, sustained ventricular tachycardia with pulse 150 mg - over 10 minutes - BioTel authorization only Ventricular fibrillation, pulseless ventricular tachycardia 5 mg/kg in 100mL NS slow push over 30 minutes. - BioTel authorization only Stable or unstable, sustained or non-sustained ventricular tachycardia with pulse 5 mg/kg in 100mL NS slow push over 30 minutes. - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Alters the movement of sodium, potassium and calcium through normal channels; These actions: increase the refractory period of all cardiac tissues slow repolarization decrease automaticity Alpha and beta blocker Within minutes Variable Indications: Ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia that does not respond to initial defibrillation attempts Sustained ventricular tachycardia with a pulse Precautions: Do not shake (prevents foaming); draw-up with large gauge needle Protect from light Avoid contact with plastic; administer at closest IV port Use with caution in renal failure patients Side Effects: Bradycardia Hypotension Contraindications: Trauma patients Not to be administered via ETT Page 7 of 35
8 Aspirin (Acetylsalicylate Acid) Route: Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, anti-platelet aggregator Orally (chewed) One (325mg) adult aspirin or four (81 mg) baby aspirin - standing order regardless of whether the patient has taken any aspirin within the previous 24 hours. Not normally given to pediatric patients by EMS - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Blocks pain impulses in the CNS Dilates peripheral vessels Reduces platelet stickiness Reduces coronary artery vasoconstriction Indications: Precautions: Side Effects: Contraindications: minutes 4-6 hours Chest pain believed to be of cardiac origin Any significant bleeding None for pre-hospital Aspirin allergy Aspirin-induced asthma Page 8 of 35
9 Atropine Sulfate Anticholinergic/Parasympatholytic agent Route: Rapid IV or intraosseous push Endotracheal administration (alternative route) May be administered deep IM in nerve agent exposure PEA or Asystole: standing order 1 mg rapid push every three (3) to five (5) minutes (max total dose 0.04mg/kg) 2 mg via endotracheal tube Symptomatic Bradycardia: standing order 0.5mg - 1.0mg push - Additional doses must be approved by BioTel Organophosphate poisoning: BioTel authorization only 2mg push every 5-15 minutes until excessive secretions are diminished Nerve agent exposure: BioTel authorization only 2mg - 20mg IM, IV, intraosseous PEA or Asystole: - Atropine not administered for these conditions Symptomatic Bradycardia: standing order 0.02mg/kg, (minimum single dose 0.1 mg) IV or intraosseous. May repeat once 0.04mg/kg via endotracheal tube Organophosphate poisoning: BioTel authorization only 0.05mg/kg push every 20 minutes until excessive secretions are diminished Premedication in Pharmacologically-Assisted Intubation: standing order 0.01mg/Kg push two minutes prior to intubation Drug Action: Reverses suspected vagal tone in bradycardias, asystole and PEA Blocks acetylcholine in organophosphate poisonings; Reverses effects of nerve agents Rapid 2-6 hours Indications: Symptomatic bradycardia Asystole PEA with ECG rate < 60 per min Organophosphate poisoning Chemical exposure due to nerve agent Pharmacologically-Assisted Intubation Precautions: If given too slowly, can cause transient bradycardias Administer into medication port closest to IV site Notify BioTel before giving to patients with glaucoma Side Effects: Tachycardia; Dilated pupils (may make pupil assessment unreliable) Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, blurred vision Contraindications: Hypothermic bradycardia, PEA, and asystole Page 9 of 35
10 Calcium Chloride Route: Electrolyte IV or intraosseous push; slow push (in live patients) - 1mL/minute mg/kg of a 10% solution - BioTel authorization only mg/kg of a 10% solution - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Balances hyperkalemia Increases myocardial contractile force and ventricular automaticity Aids in the re-entry of calcium into muscle when given for calcium channel blocker or magnesium sulfate toxicity 5-15 minutes Dose dependent (effects may persist fo 4 hours after IV administration) Indications: Known or suspected hyperkalemic cardiac arrest (renal failure) Calcium channel blocker toxicity (bradycardia or hypotension) Beta-blocker toxicity (bradycardia or hypotension) Magnesium sulfate toxicity Precautions: Start IV s in the antecubital fossa to lower risk of infiltration, and while administering, continually check IV site for patency and signs/symptoms of infiltration Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate; flush tubing well between drugs Inform BioTel (prior to administration) if patient taking digitalis preparation Side Effects: Tissue necrosis if CaCl 2 infiltrates Forms precipitate if given with sodium bicarbonate Causes digitalis toxicity if administered to patient on digitalis With rapid infusion or overdose: bradycardia, hypotension and asystole Contraindications: None Page 10 of 35
11 Dextrose 50% Route: Drug Action: Carbohydrate Slow IV or intraosseous push (to prevent infiltration) 25 grams - 50 grams - standing order 0.5 grams per kilogram of body weight - standing order, diluted as follows Newborn-1 month: dilute D50 1:4, administer 5mL/kg of the new D10 solution 1 Month-12 years: dilute D50 1:1, administer 2mL/kg of the new D25 solution Increases blood glucose levels 1 minute Depends on the degree of hypoglycemia Indications: Altered mental status or seizure caused by hypoglycemia; hypoglycemia defined as; Adults: Diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 110mg/dL Non-diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 80mg/dL Children: Diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 90mg/dL Non-diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 60mg/dL Coma of unknown cause Precautions: Start IV s in the antecubital fossa to lower risk of infiltration, and while administering, continually check IV site for patency and signs/symptoms of infiltration Contact BioTel (prior to drug administration) for hypoglycemia in the patient with head trauma or increased intracranial pressure Side Effects: Contraindications: Tissue necrosis with infiltration None Page 11 of 35
12 Diazepam (Valium ) Benzodiazepine Route: Slow IV or intraosseous push IM (alternate route) Rectal (preferred route for pediatric patients and alternate route for adults) Titrate doses of 2.5mg (up to a maximum of 10 mg) to achieve: Standing Order sedation prior to TCP relief of cocaine-induced chest pain and/or tachycardia relief of seizure including those related to eclampsia sedation prior to cardioversion BioTel authorization only relief of extreme agitation in psychiatric or behavioral emergencies sedation to facilitate endotracheal intubation chemical restraint for patients who continue to struggle against physical restraint relief of stimulant- or hallucinogen-induced tachycardia or agitation in AMS BioTel may order additional doses beyond 10 mg. 0.5 mg/kg per rectum (PR) for relief of seizure or relief of stimulant- or hallucinogeninduced tachycardia or agitation, up to a maximum of 10 mg - standing order Drug Action: Central nervous system depressant that causes: Amnesia Sedation Muscle relaxation Onset (IV) 1 min - 5 min (IM) 15 min - 30 min (Rectal) 5 min - 15 min (IV, IM) 15 min - 60 min (Rectal) 2 hours - 4 hours Indications: Active seizure/status epilepticus Sedation prior to cardioversion or transcutaneous pacing in conscious patients Chest pain or tachycardia following an overdose or ingestion of a stimulant or hallucinogen (cocaine, amphetamine, ecstacy, LSD, PCP, ketamine) Sedation in struggling patients when medical restraints are applied Precautions: Monitor respiratory status closely Give at site closest to IV catheter and avoid mixing with any other drugs and solutions; flush well before and after use Titrate in small boluses to avoid side effects Side Effects: Respiratory depression Hypotension Confusion Contraindications: Pregnancy only with BioTel permission Alcohol or other sedative drug use Stupor Vein irritation, phlebitis and sclerosis Nausea Head injury Hypersensitivity Page 12 of 35
13 Diphenhydramine HCl (Benadryl ) Antihistamine Route: IV push (25mg/minute) IM Intraosseous (alternative route) Pediatric Dose 25mg - 50mg - standing order 1mg/kg - 2mg/kg - standing order Drug Action: Blocks histamine receptor sites in allergic reactions Reverses side effects of dystonic reactions caused by phenothiazines Maximum effects seen in 1 hour - 3 hours 6 hours - 12 hours Indications: Allergic reactions - standing order Dystonic reactions - BioTel authorization only Precautions: Acute asthma attack Side Effects: Drowsiness Sedation Disturbed coordination hypotension Palpitations Tachycardia Bardycardia Thickening of bronchial secretions Dry mouth and throat Paradoxical excitement in children Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to diphenhydramine Page 13 of 35
14 Dopamine HCL (Intropin ) Route: Sympathomimetic IV or intraosseous piggyback 2-10mcg/kg/minute - BioTel authorization only, as follows 400mg dopamine in 250mL NS (1600mcg/mL) 800mg dopamine in 500mL NS (1600mcg/mL) Refer to the Drug Drip Chart in Protocol Appendix for the number of drops per minute to deliver the BioTel authorized order Pediatric Dose 2-10mcg/kg/minute - BioTel authorization only, as follows 400mg dopamine in 250mL NS (1600mcg/mL) 800mg dopamine in 500mL NS (1600mcg/mL) Refer to the Drug Drip Chart in Protocol Appendix for the number of drops per minute to deliver the BioTel authorized order Drug Action: At low doses, increases perfusion to kidneys and abdominal organs At moderate doses, increases force and rate of ventricular contractions At high doses, peripheral vasoconstrictor 2 minutes - 4 minutes 10 minutes - 15 minutes Indications: Cardiogenic shock with systolic blood pressure between 70mmHg-90mmHg Symptomatic bradycardia unresponsive to atropine or TCP Precautions: Start IV s in the antecubital fossa to lower risk of infiltration, and while administering, continually check IV site for patency and signs/symptoms of infiltration. Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate; flush tubing well between drugs Continually monitor ECG, heart rate and blood pressure. Side Effects: Tissue necrosis with infiltration Hypertension Tachycardia Arrhythmias Contraindications: Hypovolemic shock Page 14 of 35
15 Epinephrine 1:1,000 Sympathomimetic Route: Subcutaneous Endotracheal administration (alternative route) in pediatric patients Allergic reaction/anaphylactic shock: 0.3mg - 0.5mg SQ - standing order Bronchospasm unresponsive to inhaled beta-agonists: 0.3mg mg SQ - standing order Allergic reaction/anaphylactic shock: 0.01mg/kg (max 0.3mg per dose) - standing order Bronchospasm unresponsive to inhaled beta-agonists: 0.01mg/kg (max 0.3mg per dose) SQ - BioTel authorization only Cardiac arrest: 0.1mg/kg via endotracheal tube followed by 5 ml NS flush - standing order Drug Action: Alpha effects produce peripheral vasoconstriction which: Increases coronary and cerebral perfusion Increases blood pressure in anaphylaxis Beta 1 effects: Increases heart rate Improves force of ventricular contractions Beta 2 effects produce bronchodilation 5 minutes - 10 minutes 5 minutes - 10 minutes Indications: Allergic reaction/anaphylactic shock Bronchospasm unresponsive to inhaled beta-agonists Pediatric cardiac arrest Precautions: CPR: None Allergic reaction/anaphylactic shock/refractory bronchospasm: Monitor ECG closely Patients on beta blockers may need glucagon or higher doses of epinephrine Side Effects: CPR: None Anaphylaxis: Tachycardia Ventricular arrhythmias Headache Flushing Nausea/vomiting Chest Pain Contraindications: CPR: None Allergic reaction: None Refractory bronchospasm: Heart disease, History of AMI, Age > 45 years, Arrhythmia, Labor Page 15 of 35
16 Epinephrine 1:10,000 Sympathomimetic Route: IV or intraosseous push Endotracheal administration (alternative route) Cardiac arrest: 1mg push - standing order 2mg - 2.5mg via endotracheal tube - standing order Anaphylaxis: 0.1mg - 0.2mg slow push (over 1 minute) - standing order Cardiac arrest: 0.01mg/kg rapid push - standing order Anaphylaxis: 0.01mg/kg slow push (maximum is 0.3mg per dose) - standing order Drug Action: Alpha effects produce peripheral vasoconstriction which: Increases coronary and cerebral perfusion Increases blood pressure in anaphylaxis Beta 1 effects: Increases heart rate Improves force of ventricular contractions Beta 2 effects produce bronchodilation 1 minute - 2 minutes 5 minutes - 10 minutes Indications: Cardiac arrest Anaphylaxis Pediatric bradycardias unresponsive to other treatment Precautions: CPR: None Anaphylaxis: Monitor ECG closely Patients on beta blockers may need glucagon or higher doses of epinephrine. Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate; flush tubing well between drugs. Side Effects: CPR: None Anaphylaxis: Tachycardia Ventricular arrhythmias Headache Flushing Nausea/vomiting Chest Pain Contraindications: None Page 16 of 35
17 Etomidate short-acting intravenous anesthetic hypnotic sedative Route: Drug Action: Indications: IV or IO push 0.3 mg/kg slow push 0.3 mg/kg slow push Suppresses central nervous system activity thereby inducing rapid unconsciousness 1 minute - 2 minute Dose dependent, but usually 3-5 minutes Sedation to provide pharmacologically-assisted intubation Precautions: May cause myoclonic activity (e.g., coughing, hiccups) May exacerbate focal seizure disorder Side Effects: Nausea and/or vomiting Temporary involuntary muscle contractions Contraindications: For EMS use, no contraindications. Relative contraindication known adrenal insufficiency (known to suppress cortisol production) known history of focal seizure disorder (may exacerbate condition) pregnancy Use with caution hypotension severe asthma Not recommended in children under the age of 10 years (safety and efficacy have not been established) Page 17 of 35
18 Fentanyl Route: Drug Action: Indications: Opiate narcotic analgesic slow IV or IO push For pain relief unresponsive or untreatable with nitrous oxide - standing order: 1 mcg/kg to 2 mcg/kg slow IVP - Do not exceed 100 mcg per dose. May repeat every 15 minutes. For pain relief unresponsive or untreatable with nitrous oxide - standing order: 1 mcg/kg to 2 mcg/kg slow IVP - Do not exceed 100 mcg per dose. May repeat every 15 minutes. Produces analgesic effects similar to but about 50 to 100 times stronger than morphine, although the two medications are not chemically related. Immediate, however maximal analgesia may not occur for several minutes 30 to 60 minutes Relief of pain Precautions: May produce respiratory depression May produce bradycardia Use with caution in patients with liver and kidney dysfunction Side Effects: Respiratory depression Temporary involuntary muscle contractions Bradycardia Contraindications: Severe Hemorrhage Shock Known hypersensitivity MAO inhibitor use within the previous 14 days. Antidote: Actions of fentanyl may be reversed by naloxone Page 18 of 35
19 Glucagon Pancreatic Hormone Insulin Antagonist Route: IM or subcutaneous) for hypoglycemia IM or slow IV push (over 2-5 minutes) for bradycardia due to beta-blocker or calciumchannel blocker toxicity Rapid IV push for cardiac arrest due to beta-blocker or calcium-channel toxicity Hypoglycemia - 1mg - standing order. If no response, additional doses may be authorized by BioTel at 15 minute intervals if necessary. Bradycardia (beta-blocker or calcium-channel blocker toxicity) - 1mg - BioTel authorization only Cardiac arrest (beta-blocker or calcium-channel toxicity) - 1mg-5mg - standing order Pediatric Dose Hypoglycemia - 1mg - standing order. If no response, additional doses may be authorized by BioTel at 15 minute intervals if necessary. Beta-blocker or calcium-channel toxicity - 1mg - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Converts stored glycogen to glucose, increasing blood glucose levels Improves cardiac contractility and increases heart rate Within 1 minute, however it may be 15 minutes before any response is observed minutes Indications: Hypoglycemia when no IV is obtainable and gag reflex is absent (should not be considered a first-line choice for hypoglycemia) Beta blocker and calcium channel blocker toxicity Precautions: Administer cautiously to: Patients with cardiovascular disease Patients with kidney or liver dysfunction Side Effects: Hypotension Nausea Vomiting Tachycardia Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to proteins Page 19 of 35
20 Glutose (Oral Glucose) Route: Drug Action: Indications: Carbohydrate Oral Full tube given in small doses (25-50 gm) - standing order 0.5 gm/kg in small doses - standing order Increases blood glucose level 1 minute Depends on the degree of hypoglycemia Altered mental status caused by hypoglycemia defined as; Adults: Diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 110mg/dL Non-diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 80mg/dL Children: Diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 90mg/dL Non-diabetics = fingerstick blood glucose analysis less than 60mg/dL Precautions: Side Effects: Assure gag reflex is present Aspiration Contraindications: Absent gag reflex Patients who are unable to protect their own airway Patients who are unable to swallow Page 20 of 35
21 Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent ) Topical Anticholinergic/Parasympatholytic Route: Inhalation Endotracheal administration (alternative route) Standing order - 0.5mg mixed with 2.5mg albuterol given via nebulizer over 5-15 minutes if the patient is not improving after a single albuterol-only nebulized treatment. A second 0.5 mg dose mixed with 2.5mg albuterol may be given standing order, if needed. BioTel must authorize any additional doses. If less than 1 year old Standing order mg mixed with 2.5mg albuterol given via nebulizer over 5-15 minutes if the patient is not improving after a single albuterol-only nebulized treatment. A second 0.25 mg dose mixed with 2.5mg albuterol may be given standing order, if needed. BioTel must authorize any additional doses. If 1 year or older Standing order - 0.5mg mixed with 2.5mg albuterol given via nebulizer over 5-15 minutes if the patient is not improving after a single albuterol-only nebulized treatment. A second 0.5 mg dose mixed with 2.5mg albuterol may be given standing order, if needed. BioTel must authorize any additional doses. Drug Action: Bronchodilation Dries respiratory tract secretions 5-15 minutes 4-6 hours Indications: Bronchospasm associated with asthma or COPD that does not respond to the first dose of albuterol Bronchospasm from chemical toxins: nerve agents, cyanide, blistering agents, choking agents Precautions: Notify BioTel (prior to administration) if patient has: Narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy (enlarged prostate), bladder-neck obstruction Side Effects: Tachycardia/Palpitations Restlessness/Nervousness Blurred vision Dizziness, Headache Dry mouth Cough, worsening of symptoms Skin rash Contraindications: Sensitivity to soy lecithin products (soybeans, peanuts) Sensitivity to Atropine Bronchoconstriction that is caused by allergic reaction Page 21 of 35
22 This page intentionally blank Page 22 of 35
23 Lidocaine HCL (Xylocaine ) Ventricular Antiarrhythmic Local Anesthetic Route: IV or intraosseous push (no faster than 50 mg/minute in conscious patients) IV or intraosseous piggyback Ventricular fibrillation - standing order which converts with the initial shock 1.5mg/kg push Lidocaine drip 1-4 mg/minute that does not respond to amiodarone or when amiodarone cannot be used 1.5mg/kg push. May repeat once. Sustained ventricular tachycardia - standing order Stable patients - 1.0mg/kg push; if conversion occurs, begin infusion 1-4 mg/min Unstable patients following synchronized cardioversion - 1.5mg/kg push Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia or PVCs - BioTel authorization only Initial bolus - 1mg/kg push Repeat bolus - 0.5mg/kg push Infusion 1-4mg/minute piggyback Pain related to Intraosseous Access 40 mg IO prior to saline flush Ventricular fibrillation - standing order which converts with the initial stacked shocks 1.0mg/kg push Lidocaine drip 1-4 mg/minute that does not respond to amiodarone or when amiodarone cannot be used 1.0mg/kg push. May repeat once. Sustained ventricular tachycardia - BioTel authorization only Stable patients - 1.0mg/kg push Unstable patients following synchronized cardioversion - 1.0mg/kg push Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia or PVCs - BioTel authorization only Initial bolus - 1mg/kg push Drug Action: Suppresses ventricular ectopy Blocks conduction of pain impulses 30 seconds - 90 seconds 10 minutes - 20 minutes Indications: Ventricular fibrillation Sustained ventricular tachycardia Nonsustained ventricular tachycardia or PVCs Pain related to Intraosseous Access Page 23 of 35
24 Precautions: Contact BioTel in patients over 65, history of liver disease, or CHF Contact BioTel prior to administration if patient has any "caine" allergy Short half-life; bolus may need repeating, and if bolus converts rhythm, it is followed by a lidocaine drip Continually monitor ECG, blood pressure and level of consciousness Maximum total dose of lidocaine is 3mg/kg Side Effects: Initially: drowsy, lightheadedness, blurred vision Toxicity: hypotension, change in level of consciousness, seizures, cardiovascular collapse, bradycardia Contraindications: Life-sustaining ventricular escape rhythms associated with bradycardia or 2 or 3 heart blocks Hypersensitivity Page 24 of 35
25 Magnesium Sulfate Electrolyte Anticonvulsant Smooth Muscle Relaxer Route: Refractory bronchospasm: IV or intraosseous piggyback over 6-10 minutes Pulseless Torsade de Pointes: Slow IV or intraosseous push over 6-10 minutes Torsade de Pointes with a pulse: Slow IV or intraosseous piggyback over 6-10 minutes Pulseless Torsade de Pointes - Standing order - 2 grams magnesium sulfate slow IV or intraosseous push over 6-10 minutes Refractory bronchospasm or Torsade de Pointes with a pulse - BioTel authorization only - Mix 2 grams of magnesium sulfate into a 250mL bag of saline and infuse piggyback wide open via microdrip tubing. (6-10 minutes) Not administered to pediatric patients Drug Action: Reverses magnesium deficiency Calcium-channel blocker Increases intracellular potassium Central nervous system depressant Relaxes smooth muscle Immediate following IV infusion 30 minutes Indications: Torsades de pointes (antiarrhythmic of choice) Bronchospasm in asthma or COPD that is not responsive to other therapy Precautions: Inform BioTel prior to administration when hypomagnesmia is suspected patients are on digitalis preparations Continually monitor blood pressure, respirations, ECG, LOC and muscle strength Side Effects: Diaphoresis Facial flushing Hypotension Depressed reflexes Hypothermia Bradycardia Circulatory collapse Respiratory depression Muscle weakness/paralysis CNS depression Contraindications: Shock or systolic blood pressure <110mmHg Heart block Respiratory depression Chronic kidney disease/dialysis Antidote: Calcium Chloride Page 25 of 35
26 Midazolam (Versed ) Route: Benzodiazepine IV or intraosseous push 0.1 mg/kg IVP to a maximum single dose of 5 mg - standing order 0.1 mg/kg IVP to a maximum single dose of 5 mg - standing order Drug Action: Central nervous system depressant that causes: Amnesia Sedation Muscle relaxation Highly variable, however usually 1-5 minutes Variable however, usually 15 minutes to 1 hour Indications: Active seizure/status epilepticus Sedation prior to cardioversion or transcutaneous pacing in conscious patients Chest pain or tachycardia following an overdose or ingestion of a stimulant or hallucinogen (cocaine, amphetamine, ecstacy, LSD, PCP, ketamine) Sedation in struggling patients when medical restraints are applied Precautions: Monitor respiratory status closely Give at site closest to IV catheter and avoid mixing with any other drugs and solutions; flush well before and after use Titrate in small boluses to avoid side effects Side Effects: Respiratory depression Hypotension Confusion Stupor Nausea Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity Acute narrow-angle glaucoma Antidote: Page 26 of 35
27 Morphine Sulfate Route: Narcotic Analgesic Slow IV or intraosseous push 2mg - 4mg increments to a maximum of 10mg - standing order If patient is > 65 yr of age, debilitated, has altered mental status, or SBP < 110mmHg, BioTel must authorize administration. 0.1mg/kg to a maximum of 10mg - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Alleviates pain Decreases peripheral vascular resistance - vasodilator Decreases cardiac workload and oxygen demand on the heart 1 minute - 2 minutes following IV administration 2 hours - 7 hours Indications: Chest pain unresponsive to nitroglycerin Moderate to acute pain secondary to amputations, fractures, or other situations that cannot be controlled with nitrous oxide Precautions: Monitor respiratory status and blood pressure closely Have naloxone (Narcan ) readily available Side Effects: Hypotension Tachycardia Bradycardia Palpitations Syncope Facial flushing Respiratory depression Euphoria Bronchospasm Dry mouth Allergic reaction Contraindications: Systolic BP <110mmHg; BioTel may authorize administration in patients with systolic blood pressures less than 110mmHg but greater than 90mmHg. Head injury Severe respiratory depression Hypersensitivity Antidote: Naloxone (Narcan ) Page 27 of 35
28 Naloxone HCL (Narcan ) Narcotic Antagonist Route: Slow IV or intraosseous push IM (alternate route) Subcutaneous (alternative route - rare) Non-cardiac arrest - Standing order 0.4 mg every 5 minutes slow push until the respiratory rate improves and the patient can maintain a pulse oximetry reading of 96% OR until 2 mg has been given. Cardiac Arrest - Standing Order 2 mg IV or IO push Pediatric Dose Non-cardiac arrest - Standing order 0.1mg/kg slow push (maximum single dose 0.4mg) until the respiratory rate improves and the patient can maintain a pulse oximetry reading of 96% OR until 2 mg has been given. Cardiac Arrest - Standing order 0.1mg/kg slow push (maximum single dose 2.0 mg Drug Action: Reverses narcotic effects Within 2 minutes of IV administration 30 minutes - 60 minutes Indications: Narcotic overdose Coma of unknown origin Cardiac arrest with suspected narcotic overdose etiology Seizure with suspected narcotic overdose etiology Precautions: Effective for only minutes; repeat if LOC and/or respiratory status deteriorate Secure patient prior to administration Administration of naloxone is not recommended as part of initial resuscitative efforts for newborns with respiratory depression. It also should be avoided in babies whose mothers are suspected of having had long term exposure to opiods. Side Effects: Tachycardia Hypertension Diaphoresis Nausea Blurred vision Acute withdrawal syndrome (violent behavior) With rapid administration: Arrhythmia Projectile vomiting Contraindications: Hypersensitivity Page 28 of 35
29 Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat ) Route: Vasodilator Sublingual 1 spray (0.4mg) or tablet - standing order May be repeated twice at 5 minute intervals PRN - standing order Additional doses beyond the initial three must be authorized by BioTel 1 spray (0.4mg) or tablet - BioTel authorization only Drug Action: Coronary and systemic vasodilator - decreases peripheral vascular resistance and preload Decreases cardiac workload and oxygen demand on the heart 1 minute - 3 minutes 30 minutes - 60 minutes Indications: Chest pain of cardiac origin Pulmonary edema associated with congestive heart failure (may be administered without an IV if systolic blood pressure > 110mmHg) Precautions: For acute coronary syndrome, 12-lead must be performed prior to nitroglycerin administration Monitor blood pressure closely. If blood pressure falls below 110 mmhg resulting from nitroglycerin administration, DO NOT give any additional nitroglycerin. Assure patient is sitting or lying down during administration Active ingredient of nitroglycerin will sting when administered sublingually IV must be established prior to administration in patients with suspected inferior wall MI Side Effects: Hypotension Headache Postural hypotension/syncope Reflex tachycardia Nausea and vomiting Diaphoresis Contraindications: Systolic blood pressure <110 mmhg Increased intracranial pressure Viagra or similar drugs (Sildenafil, Cialis, Tadalafil, Levitra, Vardenafil) in the previous 24 hours Hypersensitivity Page 29 of 35
30 Nitrous Oxide (Nitronox ) Route: Gaseous Analgesic/Anesthetic Inhalation Instruct patient to inhale deeply through patient-held mask or mouthpiece Instruct patient to inhale deeply through patient-held mask or mouthpiece Drug Action: Depresses the central nervous system Increases oxygen tension in the blood thereby reducing hypoxia 2 minutes - 5 minutes 2 minutes - 5 minutes Indications: Adjunct analgesic for ischemic chest pain Severe pain or discomfort in all patients without contraindications Precautions: Must be self administered Check machine gauges daily for proper concentrations Monitor blood pressure and pulse oximetry values during administration Side Effects: Hypotension Dizziness Nausea and vomiting Contraindications: Any altered level of consciousness or head injury Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Chest trauma or actual/suspected pneumothorax Abdominal trauma Major facial trauma Acutely psychotic patients Pregnancy, other than active labor Any patient (adult or pediatric) unable to self-administer Decompression sickness Page 30 of 35
31 Norepinephrine bitartrate (Levophed ) Route: Sympathomimetic IV or intraosseous piggyback Post-resuscitation (medical) systolic blood pressures less than 90 mmhg - BioTel authorization only 8-12mcg/minute 4mg norepinephrine in 250mL NS (16mcg/mL) 8mg norepinephrine in 500mL NS (16mcg/mL) Cardiogenic shock with systolic blood pressures less than 70 mmhg - BioTel authorization only 8-12mcg/minute 4mg norepinephrine in 250mL NS (16mcg/mL) 8mg norepinephrine in 500mL NS (16mcg/mL) Refer to the Drug Drip Chart in Protocol Appendix for the number of drops per minute to deliver the BioTel authorized order Not administered to pediatric patients Drug Action: Potent peripheral vasoconstrictor Increases myocardial contractility 1 minute - 3 minute 5 minutes - 10 minutes Indications: Cardiogenic shock when systolic blood pressure is < 70mmHg Post resuscitation hypotension after medical CPR s when systolic BP < 90mmHg Precautions: Start IV s in the antecubital fossa to lower risk of infiltration. While administering continually check IV site for patency and signs/symptoms of infiltration Continually monitor blood pressure Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate; flush tubing well between drugs Side Effects: Tissue necrosis with infiltration Hypertension Headache Dysrhythmia Tachycardia Reflex bradycardia Chest pain Contraindications: Hypovolemia Page 31 of 35
32 Pralidoxime Chloride (Protopam Chloride, 2-PAM, 2-PAM Chloride) Route: Cholinesterase reactivator Deep IM 600mg (1 autoinjector) mg (3 autoinjectors) - standing order Not generally administered to pediatric patients Drug Action: Reactivates cholinesterase which has been deactivated by chemical nerve agents and organophospate poisons Relieves paralysis of the respiratory muscles following chemical nerve agent or organophospate exposure About 15 minutes About 1 hour Indications: Second drug given for the treatment of poisoning due to organophosphate pesticides and chemical nerve agents (First drug is atropine) Primary indication for pralidoxime administration is muscle weakness or respiratory depression in these patients Precautions: Not indicated for poisonings with carbamate pesticides Effects during pregnancy are unknown Safety and efficacy in children is unknown Do not administer more than 3 autoinjectors due to its hypertensive effects Side Effects: Tachycardia, laryngospasm, muscle rigidity if IV and infused too quickly Mild to moderate pain at injection site Blurred or double vision, dizziness, loss of coordination, headache drowsiness, hypertension, tachycardia Contraindications: No absolute contraindications Page 32 of 35
33 Promethazine HCl (Phenergan ) Antiemetic Phenothiazine Antihistamine Route: IV or intraosseous push slowly over 1 minute IM - deep into muscle Titrate doses of 12.5mg to achieve the desired effect, up to a maximum of 25mg - standing order Drug Action: Indications: Do not administer to pediatric patients Potent antiemetic Rapid with IV administration 4 hours - 6 hours Persistent vomiting due to gastrointestinal problems Precautions: Monitor LOC Avoid intra-arterial or subcutaneous administration Give slowly rapid administration can cause vein irritation, phlebitis and sclerosis Watch for signs/symptoms of excessive sedation and dystonic reaction Side Effects: Marked drowsiness/sedation Allergic reaction Dysrhythmia Nausea and vomiting Hyperexcitability Dystonic reaction Use in children may cause hallucinations, convulsions and sudden death Contraindications: Elderly >65 years of age Debilitated patients (signs of dehydration and weakness) Trauma Altered level of consciousness Pregnancy - only with BioTel permission Known sulfa allergy Hypersensitivity Antidote For dystonic reactions give diphenhydramine (Benadryl ) Page 33 of 35
34 Proparacaine HCL (Alcaine ) Route: Topical ophthalmic anesthetic Dropped into the affected eye 1-2 drops in affected eye. Repeat dose every 5 minutes up to a total of 3 applications - standing order 1-2 drops in affected eye. Repeat dose every 5 minutes up to a total of 3 applications - standing order Drug Action: Rapid, brief, superficial anesthesia; blocks nerve impulses from sensory nerves Within 30 seconds minutes Indications: Short-term relief from corneal burns or corneal abrasions Patient comfort prior to irrigation associated with chemical exposure, pepper spray, mace Precautions: Caution patient not to rub eye Side Effects: Burning or stinging sensation Irritation Contraindications: Eye avulsion Foreign bodies in the eyes Globe rupture Allergies to the "caine" drugs Page 34 of 35
35 Sodium Bicarbonate Electrolyte Alkalinizing Agent Route: IV or intraosseous push 1mEq/kg - standing order when indicated for cardiac arrest 1mEq/kg - BioTel authorization only when indicated for TCA toxicity 1mEq/kg - standing order when indicated for cardiac arrest 1mEq/kg - BioTel authorization only when indicated for TCA toxicity Drug Action: Drives serum potassium back into the cell Enhances urinary excretion of tricyclic antidepressants Neutralizes acidosis 2 minutes - 10 minutes 30 minutes - 60 minutes Indications: Altered Level of Consciousness and wide complex tachycardia resulting from tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) overdose or ingestion - BioTel authorization only Cardiac arrest associated with - Standing order Hyperkalemia renal failure dialysis Metabolic acidosis renal failure diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) methanol ingestion aspirin (ASA) overdose Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) overdose or ingestion Precautions: Flush IV line well between all drugs May inactivate epinephrine or dopamine Side Effects: Alkalosis Seizures Tissue sloughing at injection site Contraindications: Not recommended for routine use in cardiac arrest Page 35 of 35
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Drug Profiles Professional Responder
 Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
Intermediate Medications. Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol
 Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Management Of Medical Emergencies. Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS
 Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology
 ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALS MODULE 7 Pharmacology Relates to HLT404C Apply Advanced Resuscitation Techniques Introduction There are no studies that addressed the order of drug administration. There is inadequate evidence to define
ALBUTEROL. Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells
 ALBUTEROL Bronchodilator (Beta-2 specific) Actions: Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells Respiratory distress with wheezes/bronchospasm
ALBUTEROL Bronchodilator (Beta-2 specific) Actions: Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle Decreases airway resistance Promotes reuptake of potassium into cells Respiratory distress with wheezes/bronchospasm
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
CalvertHealth Medical Center s Moderate Sedation Competency Examination
 Medical Staff Office Use Only: Congratulations! You passed the Moderate Sedation Competency Examination. Enclosed is the test for your follow-up review. Test Results: % ( of 35 correct) Your test result
Medical Staff Office Use Only: Congratulations! You passed the Moderate Sedation Competency Examination. Enclosed is the test for your follow-up review. Test Results: % ( of 35 correct) Your test result
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS
 MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS
 THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Z19.2 Cross Reference to Patient Care Maps & Clinical Care Procedures
 2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013
 8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
8:41-7.1 Scope SUBCHAPTER 7. STANDING ORDERS FOR ADULT PATIENT Adopted 08/2011 Update 03/2013 The following treatment protocols shall be considered standing orders when treating adult patients. For the
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Conscious Sedation Permit Evaluation. General Comments Emergency Algorithms
 General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
Atrovent Administration
 Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Atrovent Administration ICEMA Training 2007 Sherri Shimshy RN OBJECTIVES Describe the pharmacology of Atrovent Identify the indications for use of Atrovent in the Adult Population Identify the indications
Chapter 26. Media Directory. Dysrhythmias. Diagnosis/Treatment of Dysrhythmias. Frequency in Population Difficult to Predict
 Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
Chapter 26 Drugs for Dysrythmias Slide 33 Slide 35 Media Directory Propranolol Animation Amiodarone Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Dysrhythmias Abnormalities of electrical
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
Creates a loss of Provide Used in EMS for sedation for cardioversion, RSI, and chemical restraint, Versed
 1 Chapter 6, Part 2 General Principles of Pharmacology 2 Drug Classifications There are numerous drug classifications in the medical field Most EMS medications are: medications medications Respiratory
1 Chapter 6, Part 2 General Principles of Pharmacology 2 Drug Classifications There are numerous drug classifications in the medical field Most EMS medications are: medications medications Respiratory
PBCFR ALS/BLS Protocols 2009 ALS Pretest
 1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
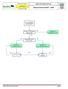 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose
 Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table
 2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
Chapter 23 Outline. Chapter 23: Emergency Drugs. General Measures. Categories of Emergencies. Preparation for Treatment 12/12/2011.
 Chapter 23 Outline Chapter 23: Emergency General measures Categories of emergencies Emergency kit for the dental office Emergency 2 Emergency General Measures Haveles (p. 290) Haveles (pp. 290-291) (Boxes
Chapter 23 Outline Chapter 23: Emergency General measures Categories of emergencies Emergency kit for the dental office Emergency 2 Emergency General Measures Haveles (p. 290) Haveles (pp. 290-291) (Boxes
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% Date of FAR:
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis
 Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis Antiallergics and drugs used in anaphylaxis The H 1 -receptor antagonists are generally referred to as antihistamines. They inhibit the wheal, pruritus, sneezing
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA
 1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
table of contents adult treatment guidelines
 table of contents adult treatment guidelines A1 ADULT PATIENT CARE... 3 A2 CHEST PAIN SUSPECTED ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME/STEMI...4 5 A3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...6 7 A4 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
table of contents adult treatment guidelines A1 ADULT PATIENT CARE... 3 A2 CHEST PAIN SUSPECTED ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME/STEMI...4 5 A3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...6 7 A4 VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
Unstable: Hypotension/Shock, Fever, Altered Mental Status, Chest discomfort, Acute Heart Failure Saturation <94%, Systolic BP < 90mmHg
 Bradycardia Heart Rate less than 50/min Stable: Monitor Seek expert help Treat Reversible Causes Unstable Signs and Symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, altered mental status, weak, Hypotension,
Bradycardia Heart Rate less than 50/min Stable: Monitor Seek expert help Treat Reversible Causes Unstable Signs and Symptoms: chest pain, shortness of breath, altered mental status, weak, Hypotension,
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
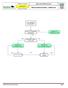 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV OBHG Education Subcommittee
 Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Chapter 8. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Anaphylaxis. List symptoms of anaphylactic shock
 Chapter 8 Anaphylaxis Learning Objectives List symptoms of anaphylactic shock Discuss role of immune system in fighting antigens Define allergic response Learning Objectives Describe body s response to
Chapter 8 Anaphylaxis Learning Objectives List symptoms of anaphylactic shock Discuss role of immune system in fighting antigens Define allergic response Learning Objectives Describe body s response to
Pain: 1-2µg/kg q30-60min prn. effects in 10 minutes. Contraindications: Morphine is preferred in. Duration of Action: minutes. renal failure.
 Procedural Sedation / Analgesia / Anaesthesia Chart - Page 1 Diazepam (Valium) Anxiolytic / Sedative Etomidate (Amidate) Hypnotic / Anesthetic Fentanyl Citrate (Sublimaze) Narcotic Analgesic Dose Pediatric:
Procedural Sedation / Analgesia / Anaesthesia Chart - Page 1 Diazepam (Valium) Anxiolytic / Sedative Etomidate (Amidate) Hypnotic / Anesthetic Fentanyl Citrate (Sublimaze) Narcotic Analgesic Dose Pediatric:
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT
 PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
PEDIATRIC SVT MANAGEMENT 1 INTRODUCTION Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) can be defined as an abnormally rapid heart rhythm originating above the ventricles, often (but not always) with a narrow QRS
Analgesic-Sedatives Drug Dose Onset
 Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
Table 4. Commonly used medications in procedural sedation and analgesia Analgesic-Sedatives Fentanyl Morphine IV: 1-2 mcg/kg Titrate 1 mcg/kg q3-5 minutes prn IN: 2 mcg/kg Nebulized: 3 mcg/kg IV: 0.05-0.15
POISON ANTIDOTE DOSE* COMMENTS
 Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Antidotes Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg initial oral dose, followed Most effective within 16 24 hr; may by 70 mg/kg every 4 hr 17 doses be useful after chronic intoxication or intravenously
Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS
 Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Essential Medical Training, LLC Providing Quality, Professional Training Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS Course Study Guide and Agenda 772-781-9249 office 772-382-0607 fax Email: treasurecoastcpr@gmail.com
Drug Reference Guidelines
 Adenosine Antiarrhythmic s Adenosine is a naturally occurring nucleoside that slows AV conduction through the AV node. It has an exceptionally short half-life and a relatively good safety profile. Adenosine
Adenosine Antiarrhythmic s Adenosine is a naturally occurring nucleoside that slows AV conduction through the AV node. It has an exceptionally short half-life and a relatively good safety profile. Adenosine
Algorithm Focus. Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
Norepinephrine (Levophed )
 Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
7/21/2017. Learning Objectives. Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology. Epinephrine. Cardiotonic Agents. Epinephrine. Epinephrine. Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT
 Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
Learning Objectives Current Cardiovascular Pharmacology Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Explain the actions, effects, indications, adverse effects, & precautions for agents from the following drug categories Cardiotonic
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
PM-03 PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS. Protocol SECTION: PM-03 PROTOCOL TITLE: PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS REVISED: 01MAY2018
 SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SAN FRANCISCO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY MEDICATION GLOSSARY
 MEDICATION GLOSSARY Adenosine (Adenocard)... 2 Albuterol (Ventolin or Proventil)... 3 Amiodarone... 4 Asprin (ASA)... 5 Atropine Sulfate... 6 CalciumChloride 10% [CaCl]... 7 Cetacain Spray... 8 Charcoal
MEDICATION GLOSSARY Adenosine (Adenocard)... 2 Albuterol (Ventolin or Proventil)... 3 Amiodarone... 4 Asprin (ASA)... 5 Atropine Sulfate... 6 CalciumChloride 10% [CaCl]... 7 Cetacain Spray... 8 Charcoal
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014
 Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
Rhythm Control: Is There a Role for the PCP? Blake Norris, MD, FACC BHHI Primary Care Symposium February 28, 2014 Financial disclosures Consultant Medtronic 3 reasons to evaluate and treat arrhythmias
POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION
 POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION Name: Date: Instructions: Complete the Post-Test (an 85% is required to pass). If there are areas that you are unsure of, please review the relevant portions of the learning
POST TEST: PROCEDURAL SEDATION Name: Date: Instructions: Complete the Post-Test (an 85% is required to pass). If there are areas that you are unsure of, please review the relevant portions of the learning
ANESTHESIA DRUG REVIEW
 ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES
 ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Prehospital Care Bundles
 Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
6 th Floor and 7 East Nurses Guide Intravenous Drip List Approved for RN Administration University of Kentucky Chandler Medical Center
 RATE Abciximab (Reopro) Alteplase (tpa, Activase) All units 6S and 6W ONLY Platelet aggregation inhibitor Thrombolytic agent Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg IV over 5 min Infusion: 0.125 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg); 10% of
RATE Abciximab (Reopro) Alteplase (tpa, Activase) All units 6S and 6W ONLY Platelet aggregation inhibitor Thrombolytic agent Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg IV over 5 min Infusion: 0.125 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg); 10% of
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
ILS Protocols Content Page
 Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
