Chronic Cough Due to Chronic Interstitial Pulmonary Diseases. ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
|
|
|
- Virginia Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chronic Cough Due to Chronic Interstitial Pulmonary Diseases ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Kevin K. Brown, MD, FCCP Objectives: To review the role of chronic interstitial pulmonary disease in the spectrum of causes of cough and its management. Design/methodology: A MEDLINE search (through May 2004) for studies published in the English language since 1980 on human subjects using the medical subject heading terms cough, causes of cough, etiology of cough, interstitial lung disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis was performed. Case series and prospective descriptive clinical trials were selected for review. Any references from these studies that were pertinent to the topic were also obtained. Results/conclusions: In patients with cough, chronic interstitial pulmonary disease should be considered as a primary cause only after more common causes, such as upper airway cough syndrome and gastroesophageal reflux, have been excluded. Successful management depends on identification of the specific disorder. (CHEST 2006; 129:180S 185S) Key words: hypersensitivity pneumonitis; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; interstitial lung disease; sarcoidosis Abbreviations: CXR chest radiograph; HP hypersensitivity pneumonitis; GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease; HRCT high-resolution CT; IPF idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; ILD interstitial lung diseases; UACS upper airway cough syndrome Reproduction of this article is prohibited without written permission from the American College of Chest Physicians ( org/misc/reprints.shtml). Correspondence to: Kevin K. Brown, MD, FCCP, National Jewish Center, 1400 Jackson St, Denver, CO 80206; brownk@njc.org While not as common as asthma or COPD, the chronic interstitial pulmonary diseases or interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) account for up to 15% of the patients seen by practicing pulmonologists. 1 The simple designation ILD is misleading, however, as the term combines a wide range of pulmonary disorders that diffusely affect the lung parenchyma with variable amounts of inflammation (ie, lymphocytic, neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and granulomatous), fibrosis, and architectural distortion. Chronic cough has been described as both a presenting and complicating clinical feature in essentially all of them. While we provide a general overview of ILD, because of the large number of diseases referred to under this heading, in this section we focus on three disorders, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), sarcoidosis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) as the more common and prototypic examples of diffuse parenchymal lung disease. A MEDLINE search (through May 2004) was conducted for studies published in the English language since 1980 on human subjects using the medical subject heading terms cough, causes of cough, etiology of cough, interstitial lung disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis was performed. Case series and prospective descriptive clinical trials were selected for review. Any references from these studies that were pertinent to the topic were also obtained. Definition Using strict terminology, the pulmonary interstitium is confined to the microscopic anatomic space bounded by the basement membranes of epithelial and endothelial cells. However, the pathologic fea- 180S Diagnosis and Management of Cough: ACCP Guidelines
2 tures of these diseases regularly include structures well beyond the interstitium, including the alveolar space, small airways, vessels, and even the pleura. 2 In any one disorder, one or more of these may contribute to the etiology of cough. The diseases can be generally classified as follows: those associated with an underlying systemic disorder (eg, autoimmune disease); those associated with an antigenic or toxic exposure (eg, drug ingestion, or avocational, occupational, or environmental exposure); and those associated with idiopathic disorders such as IPF. 3 Epidemiology Estimates of the overall prevalence of clinically significant ILD have ranged from 25 to 74 per 100,000 population, and up to 80.9 per 100,000 in men and 67.2 per 100,000 in women. The overall incidence of 31.5 per 100,000 in men and 26.1 per 100,000 in women with IPF and other pulmonary fibrotic diseases accounts for 45% of the diagnoses. 4 Clinically, significant cough occurs in 80% of IPF patients, 5,6 although the percentage of those in whom the symptom was solely or primarily due to IPF is unknown. Pathogenesis The pathogenesis of cough in the most common of the ILDs, IPF, has been investigated. In a wellconceived and well-performed study, nonsmoking patients with a confirmed diagnosis of IPF in whom airway hyperresponsiveness, chronic rhinitis, and gastroesophageal reflux were excluded, there was an increased sensitivity to substance P and capsaicin, and increased sputum levels of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor, suggesting a functional up-regulation of sensory neurons of the lung. 7 Restrictive physiology with increased deposition of aerosolized particles does not appear to play a role. 8 While the lack of control patients with other causes of cough may limit the specificity of these findings, they offer new insight with potential therapeutic implications. The pathogenesis of cough in other types of ILD are less well-understood; however, many of them appear to have predictable causes, for example, inflammatory changes of the airways both large and small are often affected in rheumatoid arthritis-related ILD, reversible airflow limitation is commonly seen in eosinophilic pneumonias, and chronic sinus and airways disease is a regular finding in Churg-Strauss vasculitis. Diagnosis A specific diagnosis of the ILD is required as therapeutic interventions and outcome may differ significantly based on the underlying disease. 9 A diagnosis may occasionally be made on the basis of characteristic findings on the necessarily comprehensive medical history, physical examination, pulmonary physiologic studies (eg, lung volumes, spirometry, and gas exchange), and radiographic studies (ie, chest radiographs [CXRs] and high-resolution CT (HRCT) scans). For example, there are particular clinical, physiologic, radiographic, and bronchoscopic features that when present provide a confident diagnosis of IPF without performing a surgical lung biopsy. 3,10 However, up to 10% of patients with ILD may have normal CXR findings 11 ; therefore, a normal CXR finding cannot rule out clinically significant disease. In contrast, with the technical resolution of the current generations of HRCT scans, it is unlikely that a patient with a truly normal scan finding will have clinically significant ILD. The greater problem is whether the radiographic abnormalities identified define a characteristic enough pattern to provide a diagnosis. 10 As most patterns are not diagnostic, a significant number of patients will require bronchoscopy (with endobronchial/transbronchial biopsy and/or BAL) and/or surgical lung biopsy for a definitive diagnosis. 10 Also, as the common causes of cough occur commonly, explanations other than the diagnosis of ILD should always be considered before ascribing a specific cause for the cough. A recent review 12 of the causes of chronic cough in patients with ILD at a center with a validated systematic diagnostic protocol has suggested that the cause of cough may be due to a diagnosis other than ILD at least 50% of the time. Also as part of their clinical syndrome, some cases of ILD may be specifically associated with one or more of the common causes such as chronic sinus disease and other upper airway abnormalities (eg, Wegener granulomatosis), 13 gastroesophageal reflux (eg, scleroderma), 14 or reactive airways disease (eg, chronic eosinophilic pneumonia). Therefore, a diagnosis of ILD as the sole cause of cough should be considered a diagnosis of exclusion. Specific Treatment No formal treatment trial in IPF has used reduction in cough as an end point. However, one small prospective controlled study 7 in nonsmoking IPF patients without reversible airflow limitation, chronic rhinitis, or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) showed that treatment with oral corticosteroids decreased cough severity and sensitivity to capsaicin and substance P in all patients. Given the dismal prognosis of IPF, the fact that corticosteroids have not been shown to prolong survival or quality of life CHEST / 129 / 1/ JANUARY, 2006 SUPPLEMENT 181S
3 in these patients, and that they are associated with significant side effects, 15 the use of corticosteroids requires an analysis of the benefit and risk in each individual. In other ILDs, as cough is often part and parcel of the clinical features of the disease, therapy that is directed at the underlying diagnosis is often beneficial. Recommendations 1. In patients with chronic cough, before diagnosing ILD as the sole cause, common etiologies such as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), which was previously referred to as postnasal drip syndrome, asthma, and GERD should be considered. As these common causes may also share clinical features with specific ILDs, a diagnosis of ILD as the cause of cough should be considered a diagnosis of exclusion. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 2. In patients with cough secondary to an ILD, because of the prognostic implications, primary treatment should be dictated by the specific disorder. Level of evidence, low; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, B 3. In patients with cough secondary to IPF, corticosteroids may lead to symptomatic improvement; however, as they have been shown to neither prolong survival nor improve quality of life and may be associated with significant side effects, their use requires an individualized analysis of the overall benefits and risks. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, intermediate; grade of recommendation, E/B Definition Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a chronic, multisystem, granulomatous disease of unknown cause, most commonly seen in young and middle-aged adults. It has protean clinical manifestations, although presentation with abnormalities of the lymphatic, pulmonary, ophthalmologic, or dermatologic systems are most common. Pulmonary manifestations generally dominate the presentation with 90% of all patients with sarcoidosis having identifiable lung involvement. 16 While the cause of sarcoidosis is unknown, essentially identical clinical and pathologic features can be seen in berylliosis and aluminosis, disorders with known etiologies, and these three should be considered as one for the purposes of this discussion. The systemic granulomatous disease that complicates common variable immunodeficiency, while superficially similar, appears to be a distinct clinical disorder. 17 Epidemiology All races, ages, and both sexes are affected. Prevalence rates range widely from 10 to 80 per 100,000 population, depending on the age, gender, ethnicity, geographic location, and method of diagnosis. 18 When a diagnosis is made by radiographic screening, 50% of patients will be asymptomatic. 18 Of those patients with symptoms, cough, with or without scant amounts of mucoid sputum, is seen in 40 to 80%. 19 Pathogenesis While the pathogenesis of cough in sarcoidosis is unknown, significant airway involvement with parenchymal distortion, endobronchial disease, and extrinsic airway compression is a characteristic of the disease. Small airway involvement detected by the presence of physiologic airflow limitation can be identified in well over half of patients, independent of smoking status, and bronchial hyperresponsiveness to challenge testing can be found in 50% of patients, depending on the stage of disease. 20 Pathologically, granulomatous inflammation is found in and around both the large and small airways, occasionally to the point of obstruction. The presence of airflow limitation, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and the anatomic location of inflammation likely plays a critical role in the development of cough. Diagnosis The diagnosis of sarcoidosis requires a comprehensive evaluation as noted above. A definite diagnosis requires a compatible clinical picture, a histologic demonstration of noncaseating granulomas, and the exclusion of alternative explanations for the abnormalities. 16 Often, strongly suggestive chest radiographic features are present at the time of presentation. 16 Prior to concluding that sarcoidosis is the sole cause of cough, other more common disorders such as UACS and GERD should be excluded as primary or contributing causes. Specific Treatment Despite a number of prospectively performed, randomized, controlled trials, 21 the role of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of sarcoidosis remains a subject of considerable debate. Differences in the stage and duration of disease, baseline symptoms, and level of physiologic impairment may account for some of the conflicting data. Based on an 182S Diagnosis and Management of Cough: ACCP Guidelines
4 analysis of seven randomized controlled trials, a Cochrane Database review 22 concluded that the use of therapy with oral corticosteroids was associated with an improvement in symptoms (including cough), spirometry findings, and chest radiographic abnormalities over a period of 6 to 24 months. A randomized controlled trial of inhaled corticosteroids after initial therapy with oral corticosteroids showed a nonstatistically significant improvement in cough. 23 Given that cough is but one feature of this systemic disease, that corticosteroids can be associated with significant side effects, and that there are few data beyond 2 years of therapy to indicate a beneficial effect on long-term disease progression, the use of corticosteroids requires an individualized analysis of the overall benefit and risk. Recommendations 4. In patients with cough and characteristic clinical and radiographic features, sarcoidosis should be considered as a cause. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 5. In patients with cough secondary to sarcoidosis, although therapy with oral corticosteroids may lead to symptomatic improvement, as they have not been proven to have a durable benefit and are associated with significant side effects, an individualized analysis of the overall benefit and risk is necessary. Level of evidence, fair; benefit, intermediate; grade of recommendation, B 6. In patients with cough secondary to sarcoidosis, therapy with oral corticosteroids followed by inhaled corticosteroids may improve symptoms. Level of evidence, fair; benefit, conflicting; grade of recommendation, I Definition HP HP, or extrinsic allergic alveolitis, is a diffuse parenchymal lung disease that is characterized by an immunologic reaction to the repeated inhalation of a finely dispersed allergen. The immunologic mechanism appears to be primarily a type IV (T-cellmediated) delayed type hypersensitivity reactions. 24 Histopathologically, this is generally identified by bronchiolocentric granulomatous inflammation. 25 From a clinical perspective, HP is not one disease but a complex group of syndromes that can be classified by the following characteristics: the temporal relationship between exposure and symptoms; occupation; or the type of antigen. While the types of allergens that can cause HP are vast and growing, they can be classified by type, as follows: organic particles (eg, mammalian and avian proteins, fungi, and thermophilic bacteria) make up the vast majority of clinically important antigens, and the inhalation of certain small molecular weight volatile and nonvolatile chemicals by a susceptible individual can cause the same syndrome. 26 The most common exposures include farming, direct or indirect contacts with birds, and aerosolized water contaminated with microbes. For those interested, more comprehensive lists of specific exposures, relevant occupations, and clinical scenarios are available. 26 HP is classically divided into acute disease (symptoms 4 to 8 h after exposure), subacute disease, and chronic (fibrotic) disease. All are commonly associated with cough as part of the clinical syndrome. Epidemiology The prevalence of HP varies by country, geography, climate, local customs, and occupational opportunities. For example, the prevalence of farmer s lung has been estimated to range from 11.5 to 192 per 100,000 population in England, 27 while the rate of clinical disease in pigeon breeders may be as high as 20% in patients with high levels of antigen exposure. 28 Up to two thirds or more of patients will have a clinically significant cough at presentation, 29 although the percentage of those in whom the symptom was solely or primarily due to the HP is unknown. Pathogenesis The pathogenesis of cough in HP is unknown. Pathologically, the small airways are affected by cellular granulomatous inflammatory change (a bronchiolitis), and physiologic airflow limitation, either with or without reversibility, is frequently identified. 29 This suggests that in at least a portion of patients, the mechanism may be similar to that of asthma. In the chronic or fibrotic form of the disease, airflow limitation is much less common 29 ; however, cough is at least as frequent, suggesting that additional mechanisms are also operative. Diagnosis The diagnosis of HP requires a comprehensive evaluation, as noted above. Often strongly suggestive historical evidence of exposure will be present. The appropriate history combined with typical radiographic, physiologic, and serologic precipitin features with a lymphocytic BAL sample and/or transbronchial lung biopsy findings of bronchiolocentric CHEST / 129 / 1/ JANUARY, 2006 SUPPLEMENT 183S
5 granulomatous inflammation are often adequate for diagnosis. 30 However, in order to attribute the cough solely or primarily to HP requires that cough go away with successful treatment for HP. Specific Treatment Therapy for patients with HP requires the elimination of the causative exposure with or without the use of corticosteroids. While therapy with corticosteroids is regularly recommended for acute disease, symptomatically and physiologically severe disease, and progressive disease, their long-term efficacy has yet to be proven. In patients with acute farmer s lung, pulmonary function and symptoms improve with 2 months of therapy with corticosteroids; however, this approach may not alter the long-term outcome. 31 The use of inhaled corticosteroids is theoretically useful; however, few data are available to support this approach. 32 Recommendations 7. In patients with cough, ILD, and a concerning environmental, occupational, or avocational exposure, HP should be considered as a potential cause. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 8. In patients with cough due to HP, treatment should include the removal of the offending exposure and systemic corticosteroid therapy in those with evidence of physiologic impairment. Level of evidence, low; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, B Summary of Recommendations 1. In patients with chronic cough, before diagnosing ILD as the sole cause, common etiologies such as upper airway cough syndrome (UACS), which was previously referred to as postnasal drip syndrome, asthma, and GERD should be considered. As these common causes may also share clinical features with specific ILDs, a diagnosis of ILD as the cause of cough should be considered a diagnosis of exclusion. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 2. In patients with cough secondary to an ILD, because of the prognostic implications, primary treatment should be dictated by the specific disorder. Level of evidence, low; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, B 3. In patients with cough secondary to IPF, corticosteroids may lead to symptomatic improvement; however, as they have been shown to neither prolong survival nor improve quality of life and may be associated with significant side effects, their use requires an individualized analysis of the overall benefits and risks. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, intermediate; grade of recommendation, E/B 4. In patients with cough and characteristic clinical and radiographic features, sarcoidosis should be considered as a cause. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 5. In patients with cough secondary to sarcoidosis, although therapy with oral corticosteroids may lead to symptomatic improvement, as they have not been proven to have a durable benefit and are associated with significant side effects, an individualized analysis of the overall benefit and risk is necessary. Level of evidence, fair; benefit, intermediate; grade of recommendation, B 6. In patients with cough secondary to sarcoidosis, therapy with oral corticosteroids followed by inhaled corticosteroids may improve symptoms. Level of evidence, fair; benefit, conflicting; grade of recommendation, I 7. In patients with cough, ILD, and a concerning environmental, occupational, or avocational exposure, HP should be considered as a potential cause. Level of evidence, expert opinion; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, E/A 8. In patients with cough due to HP, treatment should include the removal of the offending exposure and systemic corticosteroid therapy in those with evidence of physiologic impairment. Level of evidence, low; benefit, substantial; grade of recommendation, B References 1 Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. National Heart and Lung Institute Task Force on Respiratory Diseases. Washington, DC: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, October 1972; DHEW Publication No British Medical Association. The diagnosis, assessment and treatment of diffuse parenchymal lung disease in adults: introduction. Thorax 1999; 54(suppl):S1 S14 3 American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of 184S Diagnosis and Management of Cough: ACCP Guidelines
6 the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: Coultas DB, Zumwalt RE, Black WC, et al. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 150: Turner-Warwick M, Burrows B, Johnson A. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: clinical features and their influence on survival. Thorax 1980; 35: Crystal RG, Fulmer JD, Roberts WC, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med 1976; 85: Hope-Gill BD, Hilldrup S, Davies C, et al. A study of the cough reflex in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168: Doherty MJ, Mister R, Pearson MG, et al. Capsaicin induced cough in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Thorax 2000; 55: Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, et al. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: Hunninghake GW, Zimmerman MB, Schwartz DA, et al. Utility of a lung biopsy for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164: Epler GR, McLoud TC, Gaensler EA, et al. Normal chest roentgenograms in chronic diffuse infiltrative lung disease. N Engl J Med 1978; 298: Madison JM, Irwin RS. Chronic cough in adults with interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2005; 11: Hoffman GS, Kerr GS, Leavitt RY, et al. Wegener granulomatosis: an analysis of 158 patients. Ann Intern Med 1992; 116: Ferri C, Valentini G, Cozzi F, et al. Systemic sclerosis: demographic, clinical, and serologic features and survival in 1,012 Italian patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2002; 81: Westall GP, Stirling RG, Cullinan P, et al. Sarcoidosis. In: Schwartz MI, King TE Jr, eds. Interstitial lung disease. 4th ed. Hamilton, ON, Canada: BC Decker, 2003; American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, and World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders. Statement on sarcoidosis: joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: Bates CA, Ellison MC, Lynch DA, et al. Granulomatouslymphocytic lung disease shortens survival in common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: Westall GP, Stirling RG, Cullinan P, et al. Interstitial lung disease. 4th ed. Hamilton, ON, Canada: BC Decker, Sharma SK, Mohan A, Guleria JS. Clinical characteristics, pulmonary function abnormalities and outcome of prednisolone treatment in 106 patients with sarcoidosis. J Assoc Physicians India 2001; 49: Mihailovic-Vucinic V, Zugic V, Videnovic-Ivanov J. New observations on pulmonary function changes in sarcoidosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2003; 9: Gibson GJ, Prescott RJ, Muers MF, et al. British Thoracic Society sarcoidosis study: effects of long term corticosteroid treatment. Thorax 1996; 51: Paramothayan NS, Jones PW. Corticosteroids for pulmonary sarcoidosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (database online). Issue 4, Baughman RP, Iannuzzi MC, Lower EE, et al. Use of fluticasone in acute symptomatic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 2002; 19: Salvaggio JE, Millhollon BW. Allergic alveolitis: new insights into old mysteries. Respir Med 1993; 87: Coleman A, Colby TV. Histologic diagnosis of extrinsic allergic alveolitis. Am J Surg Pathol 1988; 12: Selman M. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In: Schwartz MI, King TE Jr, eds. Interstitial lung disease. 4th ed. Hamilton, ON, Canada: BC Decker, 2003; Staines F, Forman J. A survey of Farmer s lung. J Coll Gen Pract 1961; 4: Christensen LT, Schmidt CD, Robbins L. Pigeon breeders disease: a prevalence study and review. Clin Allergy 1975; 5: Vourlekis JS, Schwarz MI, Cherniack RM, et al. The effect of pulmonary fibrosis on survival in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Med 2004; 116: Lacasse Y, Selman M, Costabel U, et al. Clinical diagnosis of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 168: Kokkarinen JI, Tukiainen HO, Terho EO. Effect of corticosteroid treatment on the recovery of pulmonary function in farmer s lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 1992; 145: Carlsen KH, Leegaard J, Lund OD, et al. Allergic alveolitis in a 12-year-old boy: treatment with budesonide nebulizing solution. Pediatr Pulmonol 1992; 12: CHEST / 129 / 1/ JANUARY, 2006 SUPPLEMENT 185S
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Common Diagnostic and Treatment Dilemmas Rishi Raj MD Director, Interstitial Lung Diseases Program Clinical Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Stanford University
Chronic Cough Due to Nonbronchiectatic Suppurative Airway Disease (Bronchiolitis) ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Chronic Cough Due to Nonbronchiectatic Suppurative Airway Disease (Bronchiolitis) ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Kevin K. Brown, MD, FCCP Objectives: To review the role of nonbronchiectatic
Chronic Cough Due to Nonbronchiectatic Suppurative Airway Disease (Bronchiolitis) ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Kevin K. Brown, MD, FCCP Objectives: To review the role of nonbronchiectatic
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS
 HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
HYPERSENSITIVITY PNEUMONITIS A preventable fibrosis MOSAVIR ANSARIE MB., FCCP INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASES A heterogeneous group of non infectious, non malignant diffuse parenchymal disorders of the lower
CTD-related Lung Disease
 13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
13 th Cambridge Chest Meeting King s College, Cambridge April 2015 Imaging of CTD-related Lung Disease Dr Sujal R Desai King s College Hospital, London Disclosure Statement No Disclosures / Conflicts of
4/17/2010 C ini n ca c l a Ev E a v l a ua u t a ion o n of o ILD U dat a e t e i n I LDs
 Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Update in ILDs Diagnosis 101: Clinical Evaluation April 17, 2010 Jay H. Ryu, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN Clinical Evaluation of ILD Outline General aspects of ILDs Classification of ILDs Clinical evaluation
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Diffuse interstitial lung diseases (DILDs) are a heterogeneous group of non-neoplastic, noninfectious
 Focused Issue of This Month Diagnostic Approaches to Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases Dong Soon Kim, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine E -
Focused Issue of This Month Diagnostic Approaches to Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases Dong Soon Kim, MD Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine E -
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Epidemiology and classification of smoking related interstitial lung diseases
 Epidemiology and classification of smoking related interstitial lung diseases Šterclová M. Department of Respiratory Diseases, Thomayer Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic Supported by an IGA Grant No G 1207
Epidemiology and classification of smoking related interstitial lung diseases Šterclová M. Department of Respiratory Diseases, Thomayer Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic Supported by an IGA Grant No G 1207
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines
 Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
Diagnosing Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on Evidence-Based Guidelines Rebecca Keith, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine National Jewish Health, Denver, CO Objectives
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Case 4 History. 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar
 Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Definition, classification and epidemiology
 Interstitial Lung Diseases Definition, classification and epidemiology Haluk Türktaş Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Gazi University Ankara Interstitial Lung Diseases Definition of ILD A diverse group
Interstitial Lung Diseases Definition, classification and epidemiology Haluk Türktaş Professor of Pulmonary Medicine Gazi University Ankara Interstitial Lung Diseases Definition of ILD A diverse group
International consensus statement on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
Eur Respir J 2001; 17: 163 167 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 PERSPECTIVE International consensus statement on idiopathic
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf
 Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Indep Rev Jul-Dec 2018;20(7-12) Dr. Zulqarnain Ashraf IR-653 Abstract: ILD is a group of diseases affect interstitium of the lung. Repeated insult to the lung cause the interstitium to be damaged. Similarly
Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy
 Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy Jeff Swigris, DO, MS Director, ILD Program National Jewish Health Disclosures Speaker - Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech Objectives Describe
Overview of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Therapy Jeff Swigris, DO, MS Director, ILD Program National Jewish Health Disclosures Speaker - Boehringer Ingelheim and Genentech Objectives Describe
COI: no conflicts of interest to declare
 Idiopathic versus secondary Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) pattern in a series of 96 consecutive surgical lung biopsies: The value of histologic ancillary findings in a multidisciplinary discussion
Idiopathic versus secondary Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) pattern in a series of 96 consecutive surgical lung biopsies: The value of histologic ancillary findings in a multidisciplinary discussion
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment
 Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Prague, June 2014 Pulmonary manifestations of CTDs Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification Ulrich Costabel, MD University of Duisburg-Essen, Ruhrlandklinik Department of Pneumology/Allergy Objectives Definitions, Etiology Epidemiology
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Epidemiology and Classification Ulrich Costabel, MD University of Duisburg-Essen, Ruhrlandklinik Department of Pneumology/Allergy Objectives Definitions, Etiology Epidemiology
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Prognostic Significance of Histopathologic Subsets in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Prognostic Significance of Histopathologic Subsets in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis JULIE A. BJORAKER, JAY H. RYU, MARK K. EDWIN, JEFFREY L. MYERS, HENRY D. TAZELAAR, DARRELL R. SCHROEDER, and KENNETH
Prognostic Significance of Histopathologic Subsets in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis JULIE A. BJORAKER, JAY H. RYU, MARK K. EDWIN, JEFFREY L. MYERS, HENRY D. TAZELAAR, DARRELL R. SCHROEDER, and KENNETH
Interstitial Lung Disease
 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a broad category of lung diseases that includes more than 130 disorders which are characterized by scarring (i.e. fibrosis ) and/or inflammation
Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a broad category of lung diseases that includes more than 130 disorders which are characterized by scarring (i.e. fibrosis ) and/or inflammation
Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School, University of Crete Prague, June 2014
 Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Causes, clinical course, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Causes, clinical course, diagnosis and differential diagnosis, treatment Katerina M. Antoniou, MD, PhD As. Professor in Thoracic Medicine ERS ILD Group Secretary Medical School,
Déjà vu all over again
 Disclosures Déjà vu all over again None Jonathan Singer MD MS University of California, San Francisco HPI 49 y/o woman presents for lung transplant evaluation for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Exposures:
Disclosures Déjà vu all over again None Jonathan Singer MD MS University of California, San Francisco HPI 49 y/o woman presents for lung transplant evaluation for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Exposures:
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Spectrum of High-Resolution CT and Pathologic Findings
 CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
CT of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay C. Isabela S. Silva 1 ndrew Churg 2 Nestor L. Müller 1 Silva CIS, Churg, Müller NL Keywords: high-resolution CT, hypersensitivity pneumonitis,
Methodology and Grading of the Evidence for the Diagnosis and Management of Cough. ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Methodology and Grading of the Evidence for the Diagnosis and Management of Cough ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHS; and Sandra Zelman Lewis, PhD Objectives:
Methodology and Grading of the Evidence for the Diagnosis and Management of Cough ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Douglas C. McCrory, MD, MHS; and Sandra Zelman Lewis, PhD Objectives:
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Radiological Manifestations of Common Variable Immuodeficiency Sydrome (CVID) and associated complications
 Radiological Manifestations of Common Variable Immuodeficiency Sydrome (CVID) and associated complications Poster No.: P-0034 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Wallis, C. Ball, K.
Radiological Manifestations of Common Variable Immuodeficiency Sydrome (CVID) and associated complications Poster No.: P-0034 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Wallis, C. Ball, K.
CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD)
 CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD) David Northrop MBA, RRT Assistant Director of Respiratory Therapy Services The University of Kansas Health System Clinical Assistant
CLEARING THE AIR ON DIFFUSE PARENCHYMAL (INTERSTITIAL) LUNG DISEASE (ILD) David Northrop MBA, RRT Assistant Director of Respiratory Therapy Services The University of Kansas Health System Clinical Assistant
DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE
 DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE SOAP NOTE TEMPLATE WHEN CONSIDERING A DIAGNOSIS OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS (IPF) CHIEF COMPLAINT HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS Consider IPF as possible diagnosis if any of the
DIAGNOSTIC NOTE TEMPLATE SOAP NOTE TEMPLATE WHEN CONSIDERING A DIAGNOSIS OF IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS (IPF) CHIEF COMPLAINT HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS Consider IPF as possible diagnosis if any of the
Disclosures. Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting. Relevant financial relationships: None. Off-label usage: None
 Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona
Fibrotic lung diseases: Basic Principles, Common Problems, and Reporting Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates
 Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory. cells or cellular debris. Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases.
 Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory cells Pulmonary Edema Pneumonia Hemorrhage Diffuse alveolar
Parenchymal, Interstitial (Restrictive) and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Replacement of air with fluid, inflammatory cells Pulmonary Edema Pneumonia Hemorrhage Diffuse alveolar
Chronic Cough Due to Nonasthmatic Eosinophilic Bronchitis. ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Chronic Cough Due to Nonasthmatic Eosinophilic Bronchitis ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Christopher E. Brightling, MBBS, PhD, FCCP Objectives: Nonasthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis is
Chronic Cough Due to Nonasthmatic Eosinophilic Bronchitis ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Christopher E. Brightling, MBBS, PhD, FCCP Objectives: Nonasthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis is
Bronkhorst colloquium Interstitiële longziekten. Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog
 Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Bronkhorst colloquium 2013-2014 Interstitiële longziekten De pathologie achter de CT Katrien Grünberg, klinisch patholoog K.grunberg@vumc.nl Preparing: introduction and 3 cases The introduction on microscopic
Interstitial Lung Disease ILD: Definition
 Interstitial Lung Disease 2007 Paul F. Simonelli,, MD, PhD, FCCP Clinical Director Center for Interstitial Lung Disease Columbia University Medical Center 1. ILD is not one disorder ILD: Definition 2.
Interstitial Lung Disease 2007 Paul F. Simonelli,, MD, PhD, FCCP Clinical Director Center for Interstitial Lung Disease Columbia University Medical Center 1. ILD is not one disorder ILD: Definition 2.
Cough: Make It Easy. Kreetha Thammakumpee Respiratory and Respiratory Critical Care Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University
 Cough: Make It Easy Kreetha Thammakumpee Respiratory and Respiratory Critical Care Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Cough: definition Acute < 3 wk Subacute 3-8 wk Chronic cough
Cough: Make It Easy Kreetha Thammakumpee Respiratory and Respiratory Critical Care Medicine Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Cough: definition Acute < 3 wk Subacute 3-8 wk Chronic cough
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Diseases: Is There Really Anything New?
 : Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
: Is There Really Anything New? Sujal R. Desai, MBBS, MD ESTI SPEAKER SUNDAY Society of Thoracic Radiology San Antonio, Texas March 2014 Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease The State of Play DILDs Is There
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014
 Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries
 Eur Respir J 2001; 18: Suppl. 32, 114s 118s Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0904-1850 ISBN 1-904097-01-4 SELECTED REPORT Comparison
Eur Respir J 2001; 18: Suppl. 32, 114s 118s Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2001 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0904-1850 ISBN 1-904097-01-4 SELECTED REPORT Comparison
Bronchoalveolar lavage in fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
 Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 655 660 Bronchoalveolar lavage in fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Yon Ju Ryu a, Man Pyo Chung b,, Joungho Han c, Tae Sung Kim d, Kyung Soo Lee d, Eun-Mi Chun
Respiratory Medicine (2007) 101, 655 660 Bronchoalveolar lavage in fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Yon Ju Ryu a, Man Pyo Chung b,, Joungho Han c, Tae Sung Kim d, Kyung Soo Lee d, Eun-Mi Chun
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
Future Directions in the Clinical Management of Cough. ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines
 Future Directions in the Clinical Management of Cough ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Louis-Philippe Boulet, MD, FCCP Objectives: To impart a call for further research into the identified
Future Directions in the Clinical Management of Cough ACCP Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines Louis-Philippe Boulet, MD, FCCP Objectives: To impart a call for further research into the identified
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases. Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
IPF AND OTHER FIBROSING LUNG DISEASE: WHAT DRUGS MIGHT WORK AND ON WHOM DO THEY W ORK?
 IPF AND OTHER FIBROSING LUNG DISEASE: WHAT DRUGS MIGHT WORK AND ON WHOM DO THEY W ORK? KEVIN K. BROWN, MD PROFESSOR AND VICE CHAIRMAN, DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE NATIONAL JEWISH HEALTH DENVER, CO Kevin K.
IPF AND OTHER FIBROSING LUNG DISEASE: WHAT DRUGS MIGHT WORK AND ON WHOM DO THEY W ORK? KEVIN K. BROWN, MD PROFESSOR AND VICE CHAIRMAN, DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE NATIONAL JEWISH HEALTH DENVER, CO Kevin K.
Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Bronchoalveolar Lavage and Histopathologic Diagnosis Based on Biopsy JMAJ 46(11): 469 474, 2003 Yukihiko SUGIYAMA Professor, Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of
The diagnostic and prognostic utility of
 Eur Respir Rev 2010; 19: 117, 237 241 DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00005510 CopyrightßERS 2010 REVIEW: ENDOSCOPY The clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage in diffuse parenchymal lung disease A.U. Wells ABSTRACT:
Eur Respir Rev 2010; 19: 117, 237 241 DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00005510 CopyrightßERS 2010 REVIEW: ENDOSCOPY The clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage in diffuse parenchymal lung disease A.U. Wells ABSTRACT:
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review.
 Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
Imaging findings in Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - a pictorical review. Poster No.: C-1655 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Araujo, A. F. S. Simões, M. S. C. Rodrigues, J. Pereira;
Survival in Patients With Cryptogenic Fibrosing Alveolitis*
 Survival in Patients With Cryptogenic Fibrosing Alveolitis* A Population-Based Cohort Study Richard Hubbard, DM; Ian johnston, MD; and john Britton, MD Study objectives: To determine the median survival
Survival in Patients With Cryptogenic Fibrosing Alveolitis* A Population-Based Cohort Study Richard Hubbard, DM; Ian johnston, MD; and john Britton, MD Study objectives: To determine the median survival
Combination Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: Last Review: Origination: Next Review: Policy When Policy Topic is covered:
 Combina ation Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2014 Next Review: 07/2015 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for the combination beta2-agonist/corticosteroid
Combina ation Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2014 Next Review: 07/2015 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for the combination beta2-agonist/corticosteroid
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
Interstitial Lung Disease
 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a broad category of lung diseases that includes more than 130 disorders which are characterized by scarring (i.e. fibrosis ) and/or inflammation
Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a broad category of lung diseases that includes more than 130 disorders which are characterized by scarring (i.e. fibrosis ) and/or inflammation
T he terms interstitial lung disease (ILD) and
 494 REVIEW Interstitial lung disease: progress and problems S J Bourke... Interstitial lung disease involves all areas of medicine as it often occurs in patients with comorbidities or as a consequence
494 REVIEW Interstitial lung disease: progress and problems S J Bourke... Interstitial lung disease involves all areas of medicine as it often occurs in patients with comorbidities or as a consequence
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
COUGH Dr. A m A it i e t sh A g A garwa w l Le L ctu t rer Departm t ent t o f f M e M dic i in i e
 COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
R eview. Cough: Controversies and Consensus Brian s Case. Acute Cough
 R eview Cough: Controversies and Consensus 2011 Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution Irvin Mayers, MD, FRCPC Unauthorised use prohibited. Authorised users can download, display, view and print
R eview Cough: Controversies and Consensus 2011 Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution Irvin Mayers, MD, FRCPC Unauthorised use prohibited. Authorised users can download, display, view and print
A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases
 Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
Outline A Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases Paul J. Wolters, MD Associate Professor Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Overview of diagnosis in ILD Why it is important Definition/Classification
DIFFERENCES IN FIBROPROLIFERATIVE HEALING IN EXOGENEOUS AND IDIOPATHIC ILDs. ARE THERE ANY?
 NIHR Southampton Respiratory Biomedical Research Unit DIFFERENCES IN FIBROPROLIFERATIVE HEALING IN EXOGENEOUS AND IDIOPATHIC ILDs. ARE THERE ANY? Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases CPFS/WASOG/AIPO/ERS
NIHR Southampton Respiratory Biomedical Research Unit DIFFERENCES IN FIBROPROLIFERATIVE HEALING IN EXOGENEOUS AND IDIOPATHIC ILDs. ARE THERE ANY? Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases CPFS/WASOG/AIPO/ERS
Unpaid scientific collaborator & advisor with Veracyte, Inc.
 Diagnosis and Classification of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Role of Histopathology in the Golden Age of Consensus Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor of Diagnostic Pathology Vice Chair
Diagnosis and Classification of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Role of Histopathology in the Golden Age of Consensus Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor of Diagnostic Pathology Vice Chair
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases
 Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis Chair in Pulmonary Medicine Chief, Section on Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy & Immunologic Diseases
Eosinophilia Associated Lung Diseases Stephen P. Peters, MD, PhD, FAAAAI, FACP, FCCP, FCPP Thomas H. Davis Chair in Pulmonary Medicine Chief, Section on Pulmonary Critical Care, Allergy & Immunologic Diseases
Monday 10 September Interstitial lung disease 15:10 15:35. The uncommon interstitial lung diseases (ILD)
 Interstitial lung disease 15:10 15:35 The uncommon interstitial lung diseases (ILD) Dr Grant Griffiths, Cwm Taf University Health Board, Cardiff Be familiar with the Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic
Interstitial lung disease 15:10 15:35 The uncommon interstitial lung diseases (ILD) Dr Grant Griffiths, Cwm Taf University Health Board, Cardiff Be familiar with the Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION!
 UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
UIP OR NOT UIP PATTERN: THAT IS NOT THE ONLY QUESTION! STÉPHANE JOUNEAU 11 JULY 2014 Respiratory Medicine Department, Pontchaillou Hospital, Rennes, France CASE OVERVIEW This case highlights how a usual
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
OFEV MEDIA BACKGROUNDER
 OFEV MEDIA BACKGROUNDER 1 What is OFEV (nintedanib*)? 2 How does OFEV (nintedanib*) work? 3 Data overview 4 OFEV (nintedanib*) approval status 1 What is OFEV (nintedanib*)? OFEV (nintedanib*) is a small
OFEV MEDIA BACKGROUNDER 1 What is OFEV (nintedanib*)? 2 How does OFEV (nintedanib*) work? 3 Data overview 4 OFEV (nintedanib*) approval status 1 What is OFEV (nintedanib*)? OFEV (nintedanib*) is a small
Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases
 Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation II Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation
Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation II Parenchymal, Interstitial i (Restrictive) i and Vascular Diseases Alain C. Borczuk, M.D. Dept of Pathology Pulmonary Diseases: Structure-Function Correlation
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The Importance of Qualitative and Quantitative Phenotyping
 Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The Importance of Qualitative and Quantitative Phenotyping K. R. Flaherty Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor,
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: The Importance of Qualitative and Quantitative Phenotyping K. R. Flaherty Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor,
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS
 USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
USEFULNESS OF HRCT IN DIAGNOSIS AND FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY INVOLVEMENT IN SYSTEMIC SCLEROSIS Brestas P., Vergadis V., Emmanouil E., Malagari K. 2 nd Dept of Radiology, University of Athens, Greece ABSTRACT
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Study of 46 Patients from Western India: Clinical Presentations and Survival
 Turk Thorac J 205; 6:4-20 DOI: 0.552/ttd.205.4584 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Study of 46 Patients from Western India: Clinical Presentations and Survival Subramanian Natarajan,
Turk Thorac J 205; 6:4-20 DOI: 0.552/ttd.205.4584 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Study of 46 Patients from Western India: Clinical Presentations and Survival Subramanian Natarajan,
Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease
 Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Why? Much of interstitial lung disease biopsies
Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Why? Much of interstitial lung disease biopsies
C aring for patients with interstitial lung disease is an
 980 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK J Gribbin, R B Hubbard, I Le Jeune, C J P Smith, J West, L J Tata... See end of article
980 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK J Gribbin, R B Hubbard, I Le Jeune, C J P Smith, J West, L J Tata... See end of article
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis
 Original Article Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis Xia Li 1, Chang Chen 2, Jinfu Xu 1, Jinming Liu 1, Xianghua
Original Article Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia: comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis Xia Li 1, Chang Chen 2, Jinfu Xu 1, Jinming Liu 1, Xianghua
Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: review of the literature
 Eur Respir Rev 12; 21: 126, 355 361 DOI: 1.1183/95918.2512 CopyrightßERS 12 REVIEW Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: review of the literature Luba Nalysnyk*, Javier Cid-Ruzafa
Eur Respir Rev 12; 21: 126, 355 361 DOI: 1.1183/95918.2512 CopyrightßERS 12 REVIEW Incidence and prevalence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: review of the literature Luba Nalysnyk*, Javier Cid-Ruzafa
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Mushroom worker's lung
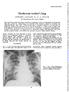 Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Mushroom worker's lung EDWARD JACKSON, K. M. A. WELCH The Royal Hospital, West Street, Sheffield Thorax (1970), 25, 25. Two cases of an acute chest illness occurring in mushroom workers are described.
Diagnostic challenges in IPF
 Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences Diagnostic challenges in IPF Dr Ian Glaspole Central and Eastern Clinical School, Alfred Hospital and Monash University March 2015 Disclosures Consultancy fees from
Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences Diagnostic challenges in IPF Dr Ian Glaspole Central and Eastern Clinical School, Alfred Hospital and Monash University March 2015 Disclosures Consultancy fees from
Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases
 Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases Dávid L. Tárnoki MD, PhD Ádám D. TárnokiMD, PhD Department of Radiology Semmelweis University Topics 1. Interstitial lung diseases 2. Occupational lung diseases
Chest imaging II. Interstitial lung diseases Dávid L. Tárnoki MD, PhD Ádám D. TárnokiMD, PhD Department of Radiology Semmelweis University Topics 1. Interstitial lung diseases 2. Occupational lung diseases
Bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy increases diagnostic confidence. in the multidisciplinary diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary
 Bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy increases diagnostic confidence in the multidisciplinary diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sara Tomassetti, Athol U Wells, Ulrich Costabel, Alberto Cavazza, Thomas
Bronchoscopic lung cryobiopsy increases diagnostic confidence in the multidisciplinary diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sara Tomassetti, Athol U Wells, Ulrich Costabel, Alberto Cavazza, Thomas
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP)
 Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) Information for patients and families UHN Read this handout to learn about: What hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis (HP) Information for patients and families UHN Read this handout to learn about: What hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you
Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis
 Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
11/15/2017. Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust) Causes of chronic cough
 A whistle stop of Chronic Cough For 10min consultations.. Dr Dean Creer Consultant Chest Physician (MBChB, FRCP) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust) E: drcreer.pa@gmail.com(secretary)
A whistle stop of Chronic Cough For 10min consultations.. Dr Dean Creer Consultant Chest Physician (MBChB, FRCP) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust) E: drcreer.pa@gmail.com(secretary)
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Diagnosing ILD. What is important in 2016? Chris Grainge
 Diagnosing ILD What is important in 2016? Chris Grainge Senior Staff Specialist Respiratory Medicine John Hunter Hospital Conjoint A/Prof University of Newcastle Conflict of interest I have acted as a
Diagnosing ILD What is important in 2016? Chris Grainge Senior Staff Specialist Respiratory Medicine John Hunter Hospital Conjoint A/Prof University of Newcastle Conflict of interest I have acted as a
