Outcomes: Initially, our primary definitions of pneumonia was severe pneumonia, where the subject was hospitalized
|
|
|
- Justin Valentine George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product. Before prescribing any product mentioned in this Register, healthcare professionals should consult prescribing information for the product approved in their country. GSK Medicine: Inhaled Corticosteroid (ICS-)-containing Medications as a class were examined in this study. Individual medications were not examined in the study. Medications included: Salmeterol/Fluticasone Propionate and Fluticasone Propionate. Study Number:e-track: WWE116952; protocol WEUSKOP6416 Title: WEUSKOP6416: Evaluating pneumonia events in patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) to inform risk minimization: A Retrospective Observational Study Rationale: Based on the increased risk of severe pneumonia observed in subjects randomized to Fluticasone furoate / vilanteral (FF/VI), GSK sought to gain a better understanding of the rates and risk factors for severe pneumonia in patients with COPD using retrospective observational studies of the class of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS)-containing medications. The results may be used to identify patients at greater risk of pneumonia requiring hospitalization and may identify where risk minimization and/or medical recommendations may be appropriate to prevent pneumonia or improve pneumonia treatment leading to reduced morbidity and mortality. Study Period: Final Protocol 27-JUN-2012; Final Study Report-2-MAY-2013 Objectives: The overall objectives of this retrospective observational COPD cohort study were: To estimate the magnitude of association between risk factors and pneumonia requiring hospitalization, including ICS-containing medications To evaluate if ICS-containing medications modify the effect of risk factors for severe pneumonia (i.e. evaluate statistical interaction between ICS other risk factors) To evaluate any differences in clinical characteristics between subjects who develop pneumonia or severe pneumonia vs. those who do not develop pneumonia in the one year period following new user cohort entry Indication: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Study Investigators/Centers: GSK-conducted database study Data Source: Clinical Practice Research Datalink s General Practitioner OnLine Database (CPRD-GOLD), with linked Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) and Vital Statistics Study Design: This was a retrospective observational study in the United Kingdom useing linked primary and secondary care data with vital statistics. Study Population: Subjects were required to be new users of of long-acting bronchodilator medications (LABD) or ICS-containing medications from January 2002-December 2010, 45 years of age or older, have one year or more of data prior to cohort entry for assessment of subject characteristics, and have the ability to link to Hospital Episode Statistics. Subjects had at least one prescription for LABD, including long-acting beta-agonists (LABA) and long-acting anti-muscarinics (LAMA), or ICS-containing medicine from January 2002 (the earliest use) until December 2010 preceded by a year of no use of either medicine.subjects with medical conditions potentially confounding the natural course of COPD were excluded (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis, bronchiectasis). Study Exposures, Outcomes: Exposures: The primary exposure of interest was ICS, evaluated in a new user cohort of ICS-containing medications. The comparator exposure group of interest was LABD. To account for poor adherence to respiratory medications, subjects were classified as exposed to study medication for the duration of prescribed therapy plus 60 days. Therefore, in the case of a single inhaler (30-days supplied), subjects were allowed for gaps of up to 90 days between prescriptions. To identify a study population of persistent users, we restricted to subjects on treatment for 6 months. To examine a potential dose-response relationship with ICS-containing medications, the strength of the prescribed ICS medication on the Cohort Entry Date was categorized into equipotent doses of low, medium, and high-dose ICS based on classification from the Global Initiative for Asthma [estimated equipotent daily doses to beclomethasone dipropinate CFC (BDP) low ( µg), medium (> µg), high (> µg)]. Outcomes: Initially, our primary definitions of pneumonia was severe pneumonia, where the subject was hospitalized 1
2 for pneumonia or died (for any reason) during their pneumonia episode. As a secondary outcome, any pneumonia (regardless of if it was recorded in primary care or HES) was examined. As 90% of pneumonia episodes resulted in hospitalization where pneumonia was listed as a primary or secondary cause during the hospitalization, additional post hoc analyses to assess sensitivity were added. Four pneumonia definitions (sensitive and specific) were therefore used in this study: Overall pneumonia: pneumonia regardless where it was recorded in the subject record, primary care or HES Severe pneumonia: pneumonia resulting in a hospitalization or death Hospitalized pneumonia: pneumonia resulting in hospitalization where pneumonia was listed as the primary cause for any episode of care during a hospitalization Hospitalized with pneumonia on the first episode: pneumonia resulting in hospitalization where pneumonia was listed as the primary cause for the first episode of care during a hospitalization Data Analysis Methods: This was a retrospective observational study in the United Kingdom using linked primary and secondary care data with vital statistics. Pneumonia and pneumonia hospitalization events in subjects with COPD were compared in new users defined as an initial prescription of ICS-containing medications (n=11,555; ICS, ICS/LABA combination) and inhaled LABD monotherapies (n=6,492; LABA, LAMA) using Cox models (hazard ratios [HR] and 95% confidence intervals [CI]) and propensity scores with inverse proportional treatment weighting (IPTW) to control for confounding. New users were censored at earliest of: pneumonia event, death, switching/stopping treatment, or end of study period. Sensitive and specific pneumonia outcomes were examined including any pneumonia and severe pneumonia resulting in hospitalization or death during the episode. Hospitalized pneumonia was examined further, as primary cause on any episode within a hospitalization and as a primary cause on the first episode within a hospitalization. Limitations: There are known limitations of non-randomized database analyses of medication safety, including the potential for confounding by severity. ICS-containing medications may have been dispensed to subjects who have more severe COPD or those at higher risk for exacerbation than subjects who are receiving long-acting bronchodilators alone per treatment guidelines. In this study, we adjusted for disease severity in the year prior to initiation using propensity scores, including adjustments for several confounders relating to the assignment to treatment (e.g., lung function, exacerbation history, pneumonia history, smoking status, and rescue medication use). Co-morbidities were also accounted for in the propensity score analysis using the entire subject record. We did note channelling of more severe subjects to ICS medications, as requiring 30 days of treatment and 6 months of treatment attenuated the observed HRs (ICS vs. LABD), though pneumonia was still associated with ICS exposure. In addition, there were higher rates of pneumonia observed among those patents prescribed the highest doses of ICS. Most of the prescribed high-dose ICS was fixed dose combination whereas low-dose was ICS-monotherapy, which could also reflect channelling of more severe subjects to higher dose ICS. There may be some differences in this observational study relative to clinical trials in terms of the diagnosis of pneumonia. When identifying pneumonia in databases, definitions are based upon existing information collected in routine healthcare which may not include all details measured in clinical trials. In addition, there is lack of agreement between pneumonia classification in the absence of chest x-rays, sputum, etc. Our definitions were based on using HES for hospitalization and built upon prior work (including validation of severe CAP). There may be some confusion between diagnoses of pneumonia versus influenza-related morbidity. However, most pneumonia events in the study were associated with an inpatient hospital admission where pneumonia was recorded as a primary or non-primary cause (95%, 631 of 702 pneumonia events). Therefore, it is likely that pneumonia was more rigorously diagnosed than pneumonia diagnosed in the primary care setting where chest x-rays may not be ordered. 2
3 Study Results: : The results of this new-user cohort study design are consistent with published findings that ICS use is associated with increased risk of pneumonia and hospitalized pneumonia in COPD patients treated in the UK. In addition, factors associated with pneumonia included known risk factors such as BMI, age, and co-morbidities. Unadjusted incidence rates of pneumonia were 48.7 per 1000 person years (PY) among the ICS-containing cohort and 30.9 per 1000 PY among the LABD cohort. Following propensity score adjustment, new use of ICS-containing mediations was associated with an increased risk of pneumonia hospitalization (n=18,047 at risk, n=322 events; HR= % CI: 1.14, 2.10) and overall pneumonia (n=18,047 at risk, n=702 events; HR=1.49, 95% CI: 1.22, 1.83). Excess ICS risk was reduced when requiring 1 month of new use (all pneumonia: n=17,287 at risk, n=614 events; HR=1.39, 95% CI: 1.12, 1.72) or 6 months (all pneumonia: 6 months; n= 9,396 at risk, n=507 events; HR=1.19, 95% CI: 0.93, 1.52). There was an apparent dose-response with greater risk at higher doses (>1000 mcg/day), however, confidence intervals were overlapping. There was some evidence of channeling bias, with more severe subjects being prescribed ICS, which may not have been fully adjusted in the analysis. Nevertheless, there was an increase in pneumonia associated with ICS. Demographics/Baseline Characteristics Cohort Variable ICS-Containing LABD Medicines Medicines p-value n=11,555 % n=6,492 % Male 6, , <0.01 Age at cohort entry date yrs 3, , < yrs 5, , >=80 yrs 2, , Clinically significant dyspnea diagnosis , <0.01 Asthma diagnosis prior to cohort entry date 2, <0.01 Pneumonia episode in year prior to cohort entry
4 Primary and Secondary Pneumonia Outcomes from IPTW propensity score model: ICS-containing vs. LABD Endpoint ICS- Containing New Users LABD New Users Pneumonia Events N= N= ICS LABD HR LL UL Primary Model Overall Pneumonia 11,555 6, Severe Pneumonia 11,555 6, Hospitalized Pneumonia 11,555 6, Hospitalized with Pneumonia on the First Episode 11,555 6, New use for at least 30 days Overall Pneumonia 11,333 5, Severe Pneumonia 11,333 5, Hospitalized Pneumonia 11,333 5, Hospitalized with Pneumonia on the First Episode 11,333 5, Persistent user (>6 mo) Overall Pneumonia 5,549 3, Severe Pneumonia 5,549 3, Hospitalized Pneumonia 5,549 3, Hospitalized with Pneumonia on the First Episode 5,549 3, IPTW 4
5 Logistic Regression: Adjusted Odds Ratios for Any Pneumonia in the Year following Cohort Entry (independent of treatment) Wald Confidence Interval for Adjusted Odds Ratios Effect Odds Ratio 95% Confidence Limits Age at Cohort Entry Baseline Pneumonia CHF in baseline CVD in Baseline Peripheral vascular disease Hemiplagia/Paraplegia diagnosis prior to cohort entry date Diabetes Cancer, Non-metastatic Anxiety diagnosis or Anxiety prescription prior to cohort entry date SABD in Baseline Period Statins in Baseline Period Gender : Male vs Female Cohort Entry Year 2003 vs Cohort Entry Year 2004 vs Cohort Entry Year 2005 vs Cohort Entry Year 2006 vs Cohort Entry Year 2007 vs Cohort Entry Year 2008 vs Cohort Entry Year 2009 vs Cohort Entry Year 2010 vs GOLD Stage 0 vs GOLD Stage 1 vs GOLD Stage 3 vs GOLD Stage 4 vs GOLD Stage Unknown vs BMI <18.5 vs BMI 21 - <25 vs BMI 25 - <30 vs BMI Unknown vs GERD Diagnosis or Medication in Baseline Count of emergency hospital admissions in the baseline period 1 vs Count of emergency hospital admissions in the baseline period 2+ vs Count of moderate COPD exacerbations during baseline period 1 vs Count of moderate COPD exacerbations during baseline period 2+ vs Number of severe exacerbations in baseline period 1 vs
6 Conclusions: Among new users, factors associated with pneumonia within the first year independent of treatment included known risk factors such as low BMI, advanced age, severe exacerbation, and co-morbidities. The strongest risk factor for pneumonia was 2 or more emergency hospital admissions in the prior year during baseline (OR=3.2, 95% CI: ). The results of this new-user cohort study design are consistent with published findings that ICS use is associated with increased risk of pneumonia and hospitalized pneumonia in COPD patients treated in the UK. New use of ICS-containing mediations was associated with an increased risk of pneumonia relative to LABD (n=18,047 at risk, n=702 events; HR=1.49, 95% CI: 1.22, 1.83) Excess ICS risk was attenuated somewhat when requiring 30 days of new use (n=17,287 at risk, n=614 events; HR=1.39, 95% CI: 1.12, 1.72) or persistent use ( 6 months; n= 9,396 at risk; n=507 events, HR=1.19, 95% CI: 0.93, 1.52); Results were robust and did not vary appreciably when examining more sensitive or more specific pneumonia hospitalization outcomes (e.g., pneumonia hospitalization, pneumonia as primary reason in any episode, pneumonia as a primary reason on the first episode of care) There was an apparent dose response, with an increase in risk of pneumonia observed with increasing doses of ICS; however, the confidence intervals between doses overlapped and residual confounding by severity cannot be ruled out as contributing to this trend. This risk must be weighed against the benefits when prescribing ICS to patients with COPD. 6
GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone
 GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone Study No.: WWE111984/WEUSRTP2640/EPI40528 Title: The Asthma Death Case Control Study (ADCCS): Association
GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone Study No.: WWE111984/WEUSRTP2640/EPI40528 Title: The Asthma Death Case Control Study (ADCCS): Association
Journal of the COPD Foundation. Journal Club. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases:
 85 Journal Club Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: inhaled corticosteroid, ICS; long acting β 2 -agonist,
85 Journal Club Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: inhaled corticosteroid, ICS; long acting β 2 -agonist,
Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets
 Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
The impacts of cognitive impairment on acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 The impacts of cognitive impairment on acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Dr. Lo Iek Long Department of Respiratory Medicine C.H.C.S.J. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
The impacts of cognitive impairment on acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Dr. Lo Iek Long Department of Respiratory Medicine C.H.C.S.J. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk. NICE All rights reserved.
 Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Online supplementary material
 Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled corticosteroids + long-acting beta agonists (ICS+LABA) for the treatment of asthma
 Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled corticosteroids + long-acting beta agonists (ICS+LABA) for the treatment of asthma Pharmacoepidemiology Unit July 10, 2014 30 Bond Street, Toronto ON, M5B 1W8 www.odprn.ca
Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled corticosteroids + long-acting beta agonists (ICS+LABA) for the treatment of asthma Pharmacoepidemiology Unit July 10, 2014 30 Bond Street, Toronto ON, M5B 1W8 www.odprn.ca
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]
![Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]](/thumbs/85/91889043.jpg) Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Co-Primary Outcomes/Efficacy Variables:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
April 10 th, Bond Street, Toronto ON, M5B 1W8
 Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs; long-acting anticholinergics) for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) April 10 th, 2014 30 Bond
Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs; long-acting anticholinergics) for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) April 10 th, 2014 30 Bond
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Decline In lung-function Among Patients with chronic obstructive Lung disease On maintenance therapy (DIAPLO)
 Version V1.4 Decline In lung-function Among Patients with chronic obstructive Lung disease On maintenance therapy (DIAPLO) An observational study evaluating the benefits of early intervention with maintenance
Version V1.4 Decline In lung-function Among Patients with chronic obstructive Lung disease On maintenance therapy (DIAPLO) An observational study evaluating the benefits of early intervention with maintenance
Decramer 2014 a &b [21]
![Decramer 2014 a &b [21] Decramer 2014 a &b [21]](/thumbs/90/101390504.jpg) Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
Buhl 2015 [19] Celli 2014 [20] Decramer 2014 a &b [21] D Urzo 2014 [22] Maleki-Yazdi 2014 [23] Inclusion criteria: Diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; 40 years of age or older; Relatively
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior Authorization of Combination Inhaled Corticosteroid / Long-Acting Beta-Agonists
 Drug Use Research & Management Program OHA Division of Medical Assistance Programs 500 Summer Street NE, E35; Salem, OR 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior
Drug Use Research & Management Program OHA Division of Medical Assistance Programs 500 Summer Street NE, E35; Salem, OR 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior
Pharmacotherapy for COPD
 10/3/2017 Topics to be covered Pharmacotherapy for chronic treatment Pharmacotherapy for COPD Dr. W C Yu 3rd September 2017 Commonly used drugs Guidelines for their use Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in
10/3/2017 Topics to be covered Pharmacotherapy for chronic treatment Pharmacotherapy for COPD Dr. W C Yu 3rd September 2017 Commonly used drugs Guidelines for their use Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in
Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year,
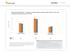 ASTHMA CHART 1 Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year, 215-216 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 Controller medication 1 Rescue medication
ASTHMA CHART 1 Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year, 215-216 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 Controller medication 1 Rescue medication
JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
 JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES Authors Dr Ian Benton Respiratory Consultant COCH Penny Rideal Respiratory Nurse COCH Kirti Burgul Respiratory Pharmacist COCH Pam
JOINT CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES Authors Dr Ian Benton Respiratory Consultant COCH Penny Rideal Respiratory Nurse COCH Kirti Burgul Respiratory Pharmacist COCH Pam
Potential risks of ICS use
 Potential risks of ICS use Randomised controlled trial Observational study Systematic review Pneumonia Tuberculosis Bone fracture Skin thinning/easy bruising Cataract Diabetes No effect on fracture risk
Potential risks of ICS use Randomised controlled trial Observational study Systematic review Pneumonia Tuberculosis Bone fracture Skin thinning/easy bruising Cataract Diabetes No effect on fracture risk
Research in Real Life
 Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
2/4/2019. GOLD Objectives. GOLD 2019 Report: Chapters
 GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
Type of intervention Treatment. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Cost-effectiveness of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate combination product 50/250 micro g twice daily and budesonide 800 micro g twice daily in the treatment of adults and adolescents with asthma Lundback
Cost-effectiveness of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate combination product 50/250 micro g twice daily and budesonide 800 micro g twice daily in the treatment of adults and adolescents with asthma Lundback
GSK Medicine: Study Number: Title: Rationale: Study Period: Objectives: Indication: Study Investigators/Centers: Research Methods: Data Source
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple. Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital
 Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital 1 Declaration of interests I have received speaker fees, sponsorship to attend conferences, and funding for research from companies
Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital 1 Declaration of interests I have received speaker fees, sponsorship to attend conferences, and funding for research from companies
UMEC/VI vs. UMEC in subjects who responded to UMEC UMEC/VI vs. VI in subjects who responded to VI
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Propensity Score Methods to Adjust for Bias in Observational Data SAS HEALTH USERS GROUP APRIL 6, 2018
 Propensity Score Methods to Adjust for Bias in Observational Data SAS HEALTH USERS GROUP APRIL 6, 2018 Institute Institute for Clinical for Clinical Evaluative Evaluative Sciences Sciences Overview 1.
Propensity Score Methods to Adjust for Bias in Observational Data SAS HEALTH USERS GROUP APRIL 6, 2018 Institute Institute for Clinical for Clinical Evaluative Evaluative Sciences Sciences Overview 1.
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center
 Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
Research in real life ltd study protocol for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
 Research in real life ltd study protocol for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. The use of a spacer in the delivery of large (Fluticasone Propionate) and small particle FP and Qvar Spacer vs Non-Spacer
Research in real life ltd study protocol for Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. The use of a spacer in the delivery of large (Fluticasone Propionate) and small particle FP and Qvar Spacer vs Non-Spacer
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 DRAFT NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary
DRAFT NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary
Bridges to Excellence Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Care Recognition Program Guide
 Bridges to Excellence Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Care Recognition Program Guide Altarum Bridges to Excellence 3520 Green Court, Suite 300 Ann Arbor, MI 48105 bte@altarum.org www.bridgestoexcellence.org
Bridges to Excellence Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Care Recognition Program Guide Altarum Bridges to Excellence 3520 Green Court, Suite 300 Ann Arbor, MI 48105 bte@altarum.org www.bridgestoexcellence.org
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Laventair (umeclidinium bromide and vilanterol)
 EMA/258177/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Laventair (umeclidinium bromide and vilanterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Laventair, which details the measures
EMA/258177/2014 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Laventair (umeclidinium bromide and vilanterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Laventair, which details the measures
SABA: VENTOLIN EVOHALER (SALBUTAMOL) SAMA: ATROVENT IPRATROPIUM. Offer LAMA (discontinue SAMA) OR LABA
 COPD GUIDELINES DIAGNOSIS >35 years of age Symptoms of cough, breathlessness, sputum, wheeze, Risk factor (SMOKING) Spirometry (post bronchodilator) FEV1/FVC = 0.7 ENCOURAGE PATIENTS TO BRING INHALERS
COPD GUIDELINES DIAGNOSIS >35 years of age Symptoms of cough, breathlessness, sputum, wheeze, Risk factor (SMOKING) Spirometry (post bronchodilator) FEV1/FVC = 0.7 ENCOURAGE PATIENTS TO BRING INHALERS
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) TREATMENT GUIDELINES Document Description Document Type Service Application Version Guidelines All healthcare professionals(hcps) caring for patients with asthma
Statistical Analysis Plan
 Drug utilisation study of new users of fluticasone furoate / vilanterol (FF/VI) in the primary care setting: UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) study Statistical Analysis Plan Subject: 205052:
Drug utilisation study of new users of fluticasone furoate / vilanterol (FF/VI) in the primary care setting: UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) study Statistical Analysis Plan Subject: 205052:
Airway Vista Background
 Airway Vista 2013 Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases Symposium Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea When Should Macrolide Antibiotics be Prescribed to Prevent COPD Exacerbations in Usual Clinical Practice?
Airway Vista 2013 Chronic Obstructive Airway Diseases Symposium Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea When Should Macrolide Antibiotics be Prescribed to Prevent COPD Exacerbations in Usual Clinical Practice?
Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable: Secondary Outcome/Efficacy Variable(s): Statistical Methods:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population
 STUDY REPORT SUMMARY Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population Descriptive study on the management of asthma in an asthmatic Middle East Africa adult population Background/Rationale:
STUDY REPORT SUMMARY Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population Descriptive study on the management of asthma in an asthmatic Middle East Africa adult population Background/Rationale:
Inhaled Corticosteroid vs. Add-On Long-Acting Beta-Agonist for Step-Up Therapy in Asthma
 Online Data Supplement Inhaled Corticosteroid vs. Add-On Long-Acting Beta-Agonist for Step-Up Therapy in Asthma Elliot Israel, Nicolas Roche, Richard J. Martin, Gene Colice, Paul M. Dorinsky, Dirkje S.
Online Data Supplement Inhaled Corticosteroid vs. Add-On Long-Acting Beta-Agonist for Step-Up Therapy in Asthma Elliot Israel, Nicolas Roche, Richard J. Martin, Gene Colice, Paul M. Dorinsky, Dirkje S.
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary
 Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) October 26 th, 2018 Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Zahava.Picado@va.gov
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) October 26 th, 2018 Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Zahava.Picado@va.gov
OPTIMIZING MANAGEMENT OF COPD IN THE PRACTICE SETTING 10/16/2018 DISCLOSURES I have no financial or other disclosures
 OPTIMIZING MANAGEMENT OF COPD IN THE PRACTICE SETTING J. Michael Fuller, MD, MEd, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine University of South Carolina Greenville DISCLOSURES I have no financial or other
OPTIMIZING MANAGEMENT OF COPD IN THE PRACTICE SETTING J. Michael Fuller, MD, MEd, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor of Medicine University of South Carolina Greenville DISCLOSURES I have no financial or other
THIS TALK STATINS REDUCE: Immortal time bias Immeasurable time bias Time-window bias TIME-RELATED BIASES IN PHARMACOEPIDEMIOLOGY
 TIME-RELATED BIASES IN PHARMACOEPIDEMIOLOGY Samy Suissa McGill University and Jewish General Hospital Montreal, Canada ISPE mid-year meeting, Miami April 22, 2012 STATINS REDUCE: JAMA 2000: Fracture rate
TIME-RELATED BIASES IN PHARMACOEPIDEMIOLOGY Samy Suissa McGill University and Jewish General Hospital Montreal, Canada ISPE mid-year meeting, Miami April 22, 2012 STATINS REDUCE: JAMA 2000: Fracture rate
National COPD Audit Programme
 National COPD Audit Programme Planning for every breath National Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Audit Programme: Primary care audit () 2015 17 Data analysis and methodology Section 4: Providing
National COPD Audit Programme Planning for every breath National Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Audit Programme: Primary care audit () 2015 17 Data analysis and methodology Section 4: Providing
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university
 What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial. Online Data Supplement
 Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial Nicolas Roche, Kenneth R. Chapman, Claus F. Vogelmeier, Felix JF Herth, Chau Thach, Robert Fogel, Petter Olsson,
Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial Nicolas Roche, Kenneth R. Chapman, Claus F. Vogelmeier, Felix JF Herth, Chau Thach, Robert Fogel, Petter Olsson,
COPD: Treatment Update Property of Presenter. Not for Reproduction. Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health
 COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
COPD/Asthma. Prudence Twigg, AGNP
 COPD/Asthma Prudence Twigg, AGNP COPD/Asthma Qualifying Diagnosis Known diagnosis of COPD/asthma or CXR showing COPD with hyperinflated lungs and no infiltrates + two or more: Wheezing, SOB, increased
COPD/Asthma Prudence Twigg, AGNP COPD/Asthma Qualifying Diagnosis Known diagnosis of COPD/asthma or CXR showing COPD with hyperinflated lungs and no infiltrates + two or more: Wheezing, SOB, increased
COPD: Preventable and Treatable. Lecture Outline. Diagnosis of COPD. COPD: Defining Terms
 COPD: Preventable and Treatable Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis and
COPD: Preventable and Treatable Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis and
Australian Asthma Handbook. Key table and figures Version 1.2
 Australian Asthma Handbook Key table and figures Version 1.2 DIAGNOSIS OF ASTHMA Figure. Steps in the diagnosis of asthma in adults Table. Findings that increase or decrease the probability of asthma in
Australian Asthma Handbook Key table and figures Version 1.2 DIAGNOSIS OF ASTHMA Figure. Steps in the diagnosis of asthma in adults Table. Findings that increase or decrease the probability of asthma in
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline. MedStar Health
 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Disclosure and Conflict of Interest 8/15/2017. Pharmacist Objectives. At the conclusion of this program, the pharmacist will be able to:
 Digging for GOLD Rebecca Young, PharmD, BCACP, Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Practice Site Advocate Medical Group-Nesset Pavilion Disclosure and Conflict
Digging for GOLD Rebecca Young, PharmD, BCACP, Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Practice Site Advocate Medical Group-Nesset Pavilion Disclosure and Conflict
umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline
 umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline 07 November 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
umeclidinium, 55 micrograms, powder for inhalation (Incruse ) SMC No. (1004/14) GlaxoSmithKline 07 November 2014 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Estimated date of first patient enrolled Q III/IV Estimated date of last patient completed Q3 2015
 PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS A 26 week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active controlled, multicenter, multinational safety study evaluating the risk of serious asthma-related events during treatment with
PROTOCOL SYNOPSIS A 26 week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active controlled, multicenter, multinational safety study evaluating the risk of serious asthma-related events during treatment with
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice. Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital
 Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
Michael S. Blaiss, MD
 Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
PART VI: SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 PART VI: SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.1 Summary of risk management plan for RELVAR ELLIPTA (fluticasone furoate/vilanterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for RELVAR ELLIPTA.
PART VI: SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.1 Summary of risk management plan for RELVAR ELLIPTA (fluticasone furoate/vilanterol) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for RELVAR ELLIPTA.
THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable
 THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable This activity is supported by an educational grant from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. COPD in the United States Third leading cause
THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable This activity is supported by an educational grant from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. COPD in the United States Third leading cause
THE USE OF LONG-ACTING β 2 -AGONISTS AS MONOTHERAPY IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS
 THE USE OF LONG-ACTING β 2 -AGONISTS AS MONOTHERAPY IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS Pat G Camp 1,2, Tingting Zhang 3, M Anne Smith 3, Bruce C Carleton 3 1 UBC James Hogg Research Centre and the Institute for Heart
THE USE OF LONG-ACTING β 2 -AGONISTS AS MONOTHERAPY IN CHILDREN AND ADULTS Pat G Camp 1,2, Tingting Zhang 3, M Anne Smith 3, Bruce C Carleton 3 1 UBC James Hogg Research Centre and the Institute for Heart
COPD Update. Muhammad Talha Khan MD. COPD Exacerbations. COPD Clinical Importance. COPD Pathophysiology. Overview/Objectives
 Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
Drug prescriptions (Pharm) Exposure (36/48 months)
 ANNEX SECTION PART A - Study design: Figure 1 overview of the study design Drug prescriptions (Pharm) 2006-2010 Exposure (36/48 months) flexible time windows (e.g. 90 days) time index date (hospital discharge)
ANNEX SECTION PART A - Study design: Figure 1 overview of the study design Drug prescriptions (Pharm) 2006-2010 Exposure (36/48 months) flexible time windows (e.g. 90 days) time index date (hospital discharge)
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
COPD: Current Medical Therapy
 COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
What s New in the Pulmonary Medicine Literature. 24 March 2017 Boca Raton Florida
 What s New in the Pulmonary Medicine Literature MARGARET M JOHNSON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CHAIR, DIVISION OF PULMONARY MEDICINE JOHNSON.MARGARE T2@MAY O.E DU 24 March 2017 Boca Raton Florida
What s New in the Pulmonary Medicine Literature MARGARET M JOHNSON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE CHAIR, DIVISION OF PULMONARY MEDICINE JOHNSON.MARGARE T2@MAY O.E DU 24 March 2017 Boca Raton Florida
REACH II: Stage 2. Final Report
 Study protocol: R02813 REACH II stage 2 31 st August 2017 Final Report REACH II: Stage 2 Examining real-life outcomes for UK patients with COPD after initiating Fostair pmdi according to its licensed indication
Study protocol: R02813 REACH II stage 2 31 st August 2017 Final Report REACH II: Stage 2 Examining real-life outcomes for UK patients with COPD after initiating Fostair pmdi according to its licensed indication
Treatment Responses. Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma. Respiratory department
 Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma Respiratory department Content Overview Research References Overview Asthma is a chronic breathing condition that affects more than 300
Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma Respiratory department Content Overview Research References Overview Asthma is a chronic breathing condition that affects more than 300
Disclosure Statement. Epidemiological Data
 EVALUATION OF THE MEDICATION UTILIZATION OF COPD PATIENTS AT THE MIAMI VA HEALTHCARE SYSTEM Simone Edgerton, PharmD. PGY 1 Pharmacy Resident Miami VA Healthcare System Miami, Florida Simone.edgerton2@va.gov
EVALUATION OF THE MEDICATION UTILIZATION OF COPD PATIENTS AT THE MIAMI VA HEALTHCARE SYSTEM Simone Edgerton, PharmD. PGY 1 Pharmacy Resident Miami VA Healthcare System Miami, Florida Simone.edgerton2@va.gov
GSK Medicine: Study No.: Title: Rationale: Objectives: Indication: Study Investigators/Centers: Research Methods:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines Where appropriate the following should be offered before commencing inhaled treatment: Offer treatment and support to stop smoking. Smoking
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Treatment Guidelines Where appropriate the following should be offered before commencing inhaled treatment: Offer treatment and support to stop smoking. Smoking
Asthma Population Management: Identifying Persistent Asthma, Defining High Risk Asthma, and Measuring Quality of Asthma Care
 Asthma Population Management: Identifying Persistent Asthma, Defining High Risk Asthma, and Measuring Quality of Asthma Care Michael Schatz, MD, MS Allergy Department Kaiser Permanente, San Diego, CA Constructs
Asthma Population Management: Identifying Persistent Asthma, Defining High Risk Asthma, and Measuring Quality of Asthma Care Michael Schatz, MD, MS Allergy Department Kaiser Permanente, San Diego, CA Constructs
2012 Chronic Respiratory. Program Evaluation. Our mission is to improve the health and quality of life of our members
 2012 Chronic Respiratory Program Evaluation Our mission is to improve the health and quality of life of our members 2012 Chronic Respiratory Program Evaluation Program Title: Chronic Respiratory Program
2012 Chronic Respiratory Program Evaluation Our mission is to improve the health and quality of life of our members 2012 Chronic Respiratory Program Evaluation Program Title: Chronic Respiratory Program
Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care
 Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care Establish diagnosis of COPD in patients 35 years with appropriate symptoms with history, examination and spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio < 70%) Establish
Prescribing guidelines: Management of COPD in Primary Care Establish diagnosis of COPD in patients 35 years with appropriate symptoms with history, examination and spirometry (FEV1/FVC ratio < 70%) Establish
Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans. Introduction to Scientific Research. Submitted: 12/4/08
 Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans Introduction to Scientific Research Submitted: 12/4/08 Introduction: Obstructive airways can be characterized as inflammation or structural changes
Pharmacological Management of Obstructive Airways in Humans Introduction to Scientific Research Submitted: 12/4/08 Introduction: Obstructive airways can be characterized as inflammation or structural changes
Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1
 791 Journal Club: Rehospitalization Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
791 Journal Club: Rehospitalization Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD
 Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory disorder largely caused by smoking. It is characterized by progressive, partially
Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of COPD Introduction Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a respiratory disorder largely caused by smoking. It is characterized by progressive, partially
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN. Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department
 TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
Secondary Outcome/Efficacy Variable(s):
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Combination Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers
 Combination Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Last Review: 7/2017 Origination: 6/2014 Next Review: 7/2018 LoB: ACA Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Combination Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Last Review: 7/2017 Origination: 6/2014 Next Review: 7/2018 LoB: ACA Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
The beneficial effects of ICS in COPD
 BIOLOGY AND HEALTH Journal website: www.biologyandhealth.com Narrative review The beneficial effects of ICS in COPD Stacha Reumers Stacha Reumers I6111431 Maastricht University Faculty of Health, Medicine
BIOLOGY AND HEALTH Journal website: www.biologyandhealth.com Narrative review The beneficial effects of ICS in COPD Stacha Reumers Stacha Reumers I6111431 Maastricht University Faculty of Health, Medicine
Adherence to asthma controller medication regimens
 Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 1263 1267 Adherence to asthma controller medication regimens D.A. Stempel a,, S.W. Stoloff b, J.R. Carranza Rosenzweig c, R.H. Stanford c, K.L. Ryskina d, A.P. Legorreta
Respiratory Medicine (2005) 99, 1263 1267 Adherence to asthma controller medication regimens D.A. Stempel a,, S.W. Stoloff b, J.R. Carranza Rosenzweig c, R.H. Stanford c, K.L. Ryskina d, A.P. Legorreta
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
LAMA Products for the Treatment of COPD
 FINAL REPORT LAMA Products for the Treatment of COPD Pharmacoepidemiology Unit: Censored Final Report Tara Gomes, Andrea Gershon, Matthew Stanbrook, Ximena Camacho, Diana Martins, Samantha Singh, Zhan
FINAL REPORT LAMA Products for the Treatment of COPD Pharmacoepidemiology Unit: Censored Final Report Tara Gomes, Andrea Gershon, Matthew Stanbrook, Ximena Camacho, Diana Martins, Samantha Singh, Zhan
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 4 March 2015
 Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 4 March 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Respiratory Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 4 March 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Respiratory Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo,
 Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
Combination Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: Last Review: Origination: Next Review: Policy When Policy Topic is covered:
 Combina ation Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2014 Next Review: 07/2015 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for the combination beta2-agonist/corticosteroid
Combina ation Beta2-Agonist/Corticosteroid Inhalers Policy Number: 5.01.572 Origination: 06/2014 Last Review: 07/2014 Next Review: 07/2015 Policy BCBSKC will provide coverage for the combination beta2-agonist/corticosteroid
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A.
 aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
Algorithm for the use of inhaled therapies in COPD
 Berkshire West Integrated Care System Representing Berkshire West Clinical Commisioning Group Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire West Primary Care
Berkshire West Integrated Care System Representing Berkshire West Clinical Commisioning Group Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire West Primary Care
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management. Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018
 Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
Update on bronchiectasis guidelines. James Chalmers MD, PhD, FRCPE, FERS University of Dundee, UK
 Update on bronchiectasis guidelines James Chalmers MD, PhD, FRCPE, FERS University of Dundee, UK University of Dundee Bronchiectasis guidelines 2017 2010 2006 2008 2015 2015 Currently valid guidelines
Update on bronchiectasis guidelines James Chalmers MD, PhD, FRCPE, FERS University of Dundee, UK University of Dundee Bronchiectasis guidelines 2017 2010 2006 2008 2015 2015 Currently valid guidelines
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
 A F O C A l p O I N T l E A r N I N g p r O g r A m m E CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE S E C O N D E D I T I O N BOOK 1 September 2013 FP120/1 CENTRE FOR PHARMACY POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION About CPPE
A F O C A l p O I N T l E A r N I N g p r O g r A m m E CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE S E C O N D E D I T I O N BOOK 1 September 2013 FP120/1 CENTRE FOR PHARMACY POSTGRADUATE EDUCATION About CPPE
Pulmonary Year in Review
 Pulmonary Year in Review Rachel Givelber, MD University of Pittsburgh SOM Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Rachel Givelber, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine PACCM, UPSOM Disclosures
Pulmonary Year in Review Rachel Givelber, MD University of Pittsburgh SOM Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Rachel Givelber, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine PACCM, UPSOM Disclosures
