Supplemental Information. Melanopsin-Encoded Response Properties. of Intrinsically Photosensitive. Retinal Ganglion Cells
|
|
|
- Leonard Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuron, Volume 90 Supplemental Information Melanopsin-Encoded Response Properties of Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells Ludovic S. Mure, Megumi Hatori, Quansheng Zhu, James Demas, Irene M. Kim, Surendra K. Nayak, and Satchidananda Panda
2 Supplementary Information Supplementary Table Table S1 (related to Fig. 3): Altered melanopsin C-terminus tail results in altered response properties that translate in vivo. Light responses from the retina of rd;opn4 -/- mice expressing WT (Opn4 WT, n=57) and altered melanopsins; truncated (Opn4 380, n=33; Opn4 397 n=45), phosphonull mutations (Opn4 2A, n=103; Opn4 4A, n=100; Opn4 9A, n=125) and phosphomimetic mutation (Opn4 2D, n=61,): MANOVA. p values Latency (fig3 F, G) Duration (fig3 H, I) Opn ns * Opn4 2D 0.73 ns ** Opn4 2A ** * Opn4 4A *** *** Opn4 9A *** ns
3 Supplementary Figures
4 Figure S1 (related to Fig. 2). FLIPER/Ca 2+ release assays. Melanopsin photoresponse in CHO cells transduced with different mutants. (A) Average (in sec, +s.e.m.) and relative time for the peak response to return to 30% and absolute (F/F 0, +s.e.m.) and relative peak amplitude (Raw values are the average of the pooled individual data (n=20) while relative values are the mean of the normalized data per plates (n=3)). (B) Progressive S to A mutation of the phosphorylable region of melanopsin C terminus tail results in additive effects on both photoresponse duration and peak. duration peak Opn4 WT p value p value Opn4 397Δ ** ** Opn4 9A397Δ *** *** Opn4 9A *** *** Opn4 8A *** *** Opn4 7A *** *** Opn4 6A *** *** Opn4 5A ** *** Opn4 4A ns ** Opn4 3A 0.53 ns *** Opn4 2A 0.22 ns 0.17 ns Opn4 1A 0.41 ns 0.44 ns Opn4 3Ai 0.04 * ** Opn4 3Ac 0.69 ns *** (C) Melanopsin photoresponse in CHO cells transduced with different non-phosphorylable mutants. The same residues are affected but in different cluster combinations. Average (in sec, +s.e.m.) and relative time for the peak response to return to 30% and absolute (F/F 0, +s.e.m.) and relative peak amplitude (Raw values are the average of the pooled individual data (n=20) while relative values are the mean of the normalized data per plates (n=3)).
5
6 Figure S2 (related to Fig. 3). Functional expression of melanopsin in mrgcs imparts sustained photosensitivity. (A) Restoration of circadian photoentrainment in rd;opn4 -/- mice upon AAV Opn4 WT administration in the retina (arrow). Daily wheel running activity over several days are shown. (a 1 ) Within few days of virus administration the daily activity pattern entrains to light:dark cycle and this entrainment is (a 2 ) stable over several weeks. (a 3 )As is known in WT mice under constant light, these mice also exhibit lengthening of circadian activity rhythm. (a 4 ) The AAV expression does not affect the intrinsic short period (<24 h) periodcity of the activity rhythm under constant darkness and the newly imparted photoentrainment property is intact even after several months of virus administration. (B) Lack of circadian photoentrainment in rd;opn4 Cre/Cre ;idtr mice with ablated iprgcs (red arrow representing DT administration), upon AAV Opn4 WT expression in the retina (blue arrow).. (C) Lack of circadian photoentrainment in rd;opn4 -/- mice upon AAV GFP expression in the retina. Expression of (D) AAV Opn4 4A or (E) AAV Opn4 2D restored circadian photoentrainment in rd;opn4 -/- mice upon viral mediated expression.
7
8 Figure S3 (related to Fig. 3). (A) Diagram summarizing the different parameters of iprgcs electrophysiological response as recorded extracellularly with MEA. Comparaison of responses from Opn4 WT and Opn4 9A to 10ms stimulations recorded in cells responding to 100ms stimulations. (B) in rd;opn4 -/- mice injected with Opn4 WT and Opn4 9A (n=6 and 14) and (C) in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice injected with floxed Opn4 WT and Opn4 9A (n=16 and 18). Representative single units responses to 1s, 10s and 60s stimulations recorded from rd;opn4 -/- mice retinas transduced with Opn4 WT, Opn4 380, Opn4 397, Opn4 2A, Opn4 4A, Opn4 9A and Opn4 2D (D) or in rd mice compared to rd;opn4 cre/cre mice conditionally transduced with Opn4 WT, Opn4 397, Opn4 9A and Opn4 9A397 (E). (F, G) Light responses from the retina of rd;opn4 -/- mice expressing WT (Opn4 WT, n=57) and altered melanopsins; truncated (Opn4 380, n=33; Opn4 397 n=45), phosphonull mutations (Opn4 2A, n=103; Opn4 4A, n=100; Opn4 9A, n=125) and phosphomimetic mutation (Opn4 2D, n=61,): number of spikes. MANOVA: p value Opn4 397Δ ** Opn4 2A * Opn4 4A * Opn4 9A ns Opn4 2D 0.54 ns
9 Figure S4 (related to Fig. 3 and 4): Altered melanopsin C-terminus tail results in altered response properties. Light responses of rd;opn4 -/- mice injected with WT (Opn4 WT, n=58 ) or truncated melanopsin; (Opn4 380, n=33). Average traces (A), response latency (B) and duration (C). Light responses of rd;opn4 cre/cre mice injected with floxed WT (Opn4 WT, n=54 ) or mutated/truncated melanopsin; (Opn4 9A397, n=29). average traces (D), response latency (E) and duration (F).
10
11 Figure S5 (related to Fig. 4). Melanopsin immunostaining in the retina of rd;opn4 cre-/cre mice intravitreally transduced with AAV-DIO-Opn4 constructs. Retina of rd;opn4 -/- mice intravitreally injected with the indicated viruses were collected at least 4 weeks after virus injection, fixed, flat mounted and immunostained with polyclonal rabbit anti-opn4 antibodies raised against the N-terminus region of the protein, and imaged using a Zeiss LSM 780 scanning confocal microscope with a 20X objective following standard protocols (Brown et al., 2010; Lin et al., 2008). Maximum intensity projection images are shown.(b-e) Restoration of circadian photoentrainment in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice upon viral mediated expression of different floxed melanopsin mutants with altered phosphorylation sites or truncations (Opn4 WT, Opn4 397, Opn4 9A, Opn4 9A397 ). Electrophysiological responses measured from rd mice retinas or rd;opn4 cre/cre mice conditionally expressing Opn4 WT are virtually identical.: Responses latency (F, ANOVA p=0.1732, ns) and duration (G, ANOVA p=0.2447, ns) to increasing stimulations lengths or increasing irradiance (H, sum of squares F test, p=0.8252, ns). 480nm, photons/cm 2 /s, 100ms, 1, 10 and 60s in and 480nm, 60s, photons/cm 2 /s to photons/cm 2 /s), average values +/-SEM. (n=91 and 54 respectively for rd and rd;opn4 cre/cre injected with Opn4 WT mice and DRC n=35 and 19 respectively for rd and rd;opn4 cre/cre injected with Opn4 WT mice).
12
13 Figure S6 (related to Fig. 4 and 5): While conditional expression of WT (Opn4 WT, n=54 ) and mutant melanopsins (Opn4 397, n=38; Opn4 9A, n=36; Opn4 9A397, n=29) restores photosensitivity in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice, the different groups display distinct response latencies (A) and durations (B) to 100ms, 1s, 10s and 60s stimulations. p values latency duration Opn ns *** Opn4 9A ns *** Opn4 9A ns ns (C) Dose response curve plotted for the discharge rate in responses to 1min stimulations of increasing irradiances in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice conditionally infected with melanopsins (Opn4 WT, n=35; Opn4 397, n=47; Opn4 9A, n=42).(manova, Opn4 9A vs Opn4 WT p=0.03, Opn4 397 vs Opn4 WT p=0.75). (D) Average pupil constriction recorded in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice conditionally infected with WT (Opn4 WT, n=4) and altered melanopsins; (Opn4 397 n=5, Opn4 9A, n=2 and Opn4 9A397 n=6) during the 60s light stimulation or during the 2min immediately following light OFF (persistence). 480nm, photons/cm 2 /s, average values +/-SEM. (E) Average pupil constriction recorded in response to successive 1s stimulation in rd;opn4 cre/cre mice conditionally infected with WT (Opn4 WT, n=4) and altered melanopsins; (Opn4 397 n=5, Opn4 9A, n=2). 480nm, photons/cm 2 /s, average values +/-SEM.
14 Figure S7 (related to Fig. 6). Deactivation speed of the mrgcs responding to increasing irradiance stimulations (at least 5/6) from retina transduced with either Opn4 WT (A, n=5) or Opn4 397 (B, n=10). (C and D) Deactivation of photoresponse from mrgcs expressing Opn4 WT or Opn4 397 following a 60sec light pulse. The 55sec-120sec portion of Fig 4A and 4B are shown. Last 5sec of 60sec illumination is shaded in cyan blue.
Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria toxin (adta) into the melanopsin locus. a,
 doi: 1.138/nature6829 a DTA HSV- TK PGK-Neo Targeting construct b kb.85.65 L WT adta/+ adta/ adta Melanopsin (Opn 4) Genomic Locus 1 kb.4 Supplementary Figure 1: Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria
doi: 1.138/nature6829 a DTA HSV- TK PGK-Neo Targeting construct b kb.85.65 L WT adta/+ adta/ adta Melanopsin (Opn 4) Genomic Locus 1 kb.4 Supplementary Figure 1: Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters. motor- and cue- dependent behaviors
 Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of the inducible tper2 is proportional to Dox/Tet concentration in Rosa-DTG/Per2 Per2-luc/wt MEFs.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of the inducible tper2 is proportional to Dox/Tet concentration in Rosa-DTG/Per2 Per2-luc/wt MEFs. (a) Dose-responsive expression of tper2 by Dox. Note that there are
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of the inducible tper2 is proportional to Dox/Tet concentration in Rosa-DTG/Per2 Per2-luc/wt MEFs. (a) Dose-responsive expression of tper2 by Dox. Note that there are
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Physiologic Diversity and Development of Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells
 Neuron, Vol. 48, 987 999, December 22, 2005, Copyright ª2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.031 Physiologic Diversity and Development of Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells
Neuron, Vol. 48, 987 999, December 22, 2005, Copyright ª2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.031 Physiologic Diversity and Development of Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Deng et al. 0.073/pnas.09038206 SI Text Animals and Subretinal Injections. Tr / mice were a gift from Dr. Janis Lem. GNAT2 cpfl3, rd7 and wildtype ALR/LtJ mice were purchased from
Supporting Information Deng et al. 0.073/pnas.09038206 SI Text Animals and Subretinal Injections. Tr / mice were a gift from Dr. Janis Lem. GNAT2 cpfl3, rd7 and wildtype ALR/LtJ mice were purchased from
Inducible Ablation of Melanopsin-Expressing Retinal Ganglion Cells Reveals Their Central Role in Non-Image Forming Visual Responses
 Inducible Ablation of Melanopsin-Expressing Retinal Ganglion Cells Reveals Their Central Role in Non-Image Forming Visual Responses Megumi Hatori 1, Hiep Le 1, Christopher Vollmers 1, Sheena Racheal Keding
Inducible Ablation of Melanopsin-Expressing Retinal Ganglion Cells Reveals Their Central Role in Non-Image Forming Visual Responses Megumi Hatori 1, Hiep Le 1, Christopher Vollmers 1, Sheena Racheal Keding
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
2. METHODS. 2.1 Apparatus
 Pupillary light reflex associated with melanopsin and cone photorecetors Sei-ichi Tsujimura, 1 Katsunori Okajima, 2 1 Faculty of Sciences and Engineering, Kagoshima University, Japan 2 Faculty of Environment
Pupillary light reflex associated with melanopsin and cone photorecetors Sei-ichi Tsujimura, 1 Katsunori Okajima, 2 1 Faculty of Sciences and Engineering, Kagoshima University, Japan 2 Faculty of Environment
CP116. Mixed-Color LED Lighting with Circadian Benefits
 Mixed-Color LED Lighting with Circadian Benefits Y. J. Tam, V. Kalavally, J. Parkkinen Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering, School of Engineering, Monash University, Jalan Lagoon
Mixed-Color LED Lighting with Circadian Benefits Y. J. Tam, V. Kalavally, J. Parkkinen Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering, School of Engineering, Monash University, Jalan Lagoon
Seeing Ultraviolet. Keeping Time with Neuropsin
 Seeing Ultraviolet Keeping Time with Neuropsin Ian Ashdown, P. Eng., FIES Chief Scientist, Lighting Analysts Inc. Wordpress Blog (www.agi32.com/blog) 2015/10/26 What does it mean to see? The word is ubiquitous
Seeing Ultraviolet Keeping Time with Neuropsin Ian Ashdown, P. Eng., FIES Chief Scientist, Lighting Analysts Inc. Wordpress Blog (www.agi32.com/blog) 2015/10/26 What does it mean to see? The word is ubiquitous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Small molecule antagonists of melanopsin-mediated phototransduction
 Small molecule antagonists of melanopsin-mediated phototransduction Kenneth A. Jones 1,*, Megumi Hatori 2,*, Ludovic S. Mure 2,*, Jayne R. Bramley 3, Roman Artymyshyn 1, Sang-Phyo Hong 1, Mohammad Marzabadi
Small molecule antagonists of melanopsin-mediated phototransduction Kenneth A. Jones 1,*, Megumi Hatori 2,*, Ludovic S. Mure 2,*, Jayne R. Bramley 3, Roman Artymyshyn 1, Sang-Phyo Hong 1, Mohammad Marzabadi
Utility of colored-light pupil response in patients with age-related macular degeneration
 Original Contribution Kitasato Med J 2014; 44: 195-200 Utility of colored-light pupil response in patients with age-related macular degeneration Ken Asakawa, 1 Hitoshi Ishikawa, 1 Yoshiaki Ichibe, 2 Kimiya
Original Contribution Kitasato Med J 2014; 44: 195-200 Utility of colored-light pupil response in patients with age-related macular degeneration Ken Asakawa, 1 Hitoshi Ishikawa, 1 Yoshiaki Ichibe, 2 Kimiya
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Design of isolated protein and RNC constructs, and homogeneity of purified RNCs. (a) Schematic depicting the design and nomenclature used for all the isolated proteins and RNCs used
Supplementary Figure 1 Design of isolated protein and RNC constructs, and homogeneity of purified RNCs. (a) Schematic depicting the design and nomenclature used for all the isolated proteins and RNCs used
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists
 Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists of: (i) the YPet domain (an enhanced YFP); (ii) the
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists of: (i) the YPet domain (an enhanced YFP); (ii) the
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Clicker Question. The Need to Decompose. Mechanism and Reduction: Decomposing Circadian Clocks
 Mechanism and Reduction: Decomposing Circadian Clocks Clicker Question On the Deductive-Nomological (DN) model of reduction, which of the following does not figure in providing the explanation (i.e., is
Mechanism and Reduction: Decomposing Circadian Clocks Clicker Question On the Deductive-Nomological (DN) model of reduction, which of the following does not figure in providing the explanation (i.e., is
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Mice Deficient of Glutamatergic Signaling from Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells Exhibit Abnormal Circadian Photoentrainment
 Mice Deficient of Glutamatergic Signaling from Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells Exhibit Abnormal Circadian Photoentrainment Nicole Purrier, William C. Engeland, Paulo Kofuji* Department
Mice Deficient of Glutamatergic Signaling from Intrinsically Photosensitive Retinal Ganglion Cells Exhibit Abnormal Circadian Photoentrainment Nicole Purrier, William C. Engeland, Paulo Kofuji* Department
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Small molecule antagonists of melanopsinmediated
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Veterinary and Biomedical Science Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, Department of 10-2013 Small molecule antagonists
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Veterinary and Biomedical Science Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, Department of 10-2013 Small molecule antagonists
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
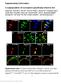 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Biological Clocks. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Why Does Melatonin Now Outsell Vitamin C??
 Biological Clocks Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Why Does Melatonin Now Outsell Vitamin C?? Wake / sleep complaints are extremely prevalent. Much melatonin is consumed in an attempt to overcome the
Biological Clocks Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Why Does Melatonin Now Outsell Vitamin C?? Wake / sleep complaints are extremely prevalent. Much melatonin is consumed in an attempt to overcome the
Biological Clocks. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. What is biological clock?
 Biological Clocks Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 What is biological clock? All eukaryotes and some prokaryotes display changes in gene activity, biochemistry, physiology, and behavior that wax and wane
Biological Clocks Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 What is biological clock? All eukaryotes and some prokaryotes display changes in gene activity, biochemistry, physiology, and behavior that wax and wane
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
A Role for Melanopsin in Alpha Retinal Ganglion Cells and Contrast Detection
 Report A Role for Melanopsin in Alpha Retinal Ganglion Cells and Contrast Detection Tiffany M. Schmidt, 1, * Nazia M. Alam, 2 Shan Chen, 3 Paulo Kofuji, 4 Wei Li, 3 Glen T. Prusky, 2 and Samer Hattar 1,5
Report A Role for Melanopsin in Alpha Retinal Ganglion Cells and Contrast Detection Tiffany M. Schmidt, 1, * Nazia M. Alam, 2 Shan Chen, 3 Paulo Kofuji, 4 Wei Li, 3 Glen T. Prusky, 2 and Samer Hattar 1,5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Type I intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells of early post-natal development correspond to the M4 subtype
 Sexton et al. Neural Development (15) 1:17 DOI 1.1186/s1364-15-42-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Type I intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells of early post-natal development correspond to the M4 subtype
Sexton et al. Neural Development (15) 1:17 DOI 1.1186/s1364-15-42-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Type I intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells of early post-natal development correspond to the M4 subtype
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources)
 Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
This Accepted Manuscript has not been copyedited and formatted. The final version may differ from this version.
 This Accepted Manuscript has not been copyedited and formatted. The final version may differ from this version. Research Article: New Research Integrative Systems Circadian Behavioral Responses to Light
This Accepted Manuscript has not been copyedited and formatted. The final version may differ from this version. Research Article: New Research Integrative Systems Circadian Behavioral Responses to Light
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina
 Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
A Distinct Contribution of Short-Wavelength-Sensitive Cones to Light-Evoked Activity in the Mouse Pretectal Olivary Nucleus
 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 16, 2011 31(46):16833 16843 16833 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive A Distinct Contribution of Short-Wavelength-Sensitive Cones to Light-Evoked Activity in the Mouse Pretectal
The Journal of Neuroscience, November 16, 2011 31(46):16833 16843 16833 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive A Distinct Contribution of Short-Wavelength-Sensitive Cones to Light-Evoked Activity in the Mouse Pretectal
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Intrinsic Photosensitivity Enhances Motility of T Lymphocytes by Phan X. Thieu, Barbara Jaruga, Sandeep C. Pingle, Bidhan C. Bandyopadhyay, & Gerard P. Ahern Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Information Intrinsic Photosensitivity Enhances Motility of T Lymphocytes by Phan X. Thieu, Barbara Jaruga, Sandeep C. Pingle, Bidhan C. Bandyopadhyay, & Gerard P. Ahern Supplementary Figure
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2 # )
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2 #13709-01) CIRCADIAN SIGNALING NETWORKS RG. Clerc May 19. 2010 www.fmi.ch/training/teaching Circadian rythms : most physiological processes
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes (Cycle G2 #13709-01) CIRCADIAN SIGNALING NETWORKS RG. Clerc May 19. 2010 www.fmi.ch/training/teaching Circadian rythms : most physiological processes
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Supplementary Figure 1. Transduction of adipocytes after intra-ewat administration of AAV vectors. A: Immunostaining against GFP (green) in sections of ewat two weeks after the intra-ewat administration
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms. Reading: BCP Chapter 19
 Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Movie Caption
 Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
Supplementary Movie Caption 1. Movie S1. Ultrasound-induced blood focusing in vitro (Fig.2b). 2. Movie S2. Acoustic canalization of blood flow in the gap between two capillaries (Fig. 2d). 3. Movie S3.
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
CIRCADIAN SIGNALING NETWORKS
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Cycle G2 (lecture 13709) FS 2014 P. Matthias and RG Clerc Roger G. Clerc 07.05.2014 CIRCADIAN SIGNALING NETWORKS Master pacemaker SCN «Slave clocks»
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Cycle G2 (lecture 13709) FS 2014 P. Matthias and RG Clerc Roger G. Clerc 07.05.2014 CIRCADIAN SIGNALING NETWORKS Master pacemaker SCN «Slave clocks»
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplemental Information. Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent. but Voltage-Dependent Secretion. in Mammalian Sensory Neurons
 Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent but Voltage-Dependent Secretion in Mammalian Sensory Neurons Zuying Chai, Changhe Wang, Rong Huang, Yuan Wang, Xiaoyu Zhang,
Neuron, Volume 96 Supplemental Information Ca V 2.2 Gates Calcium-Independent but Voltage-Dependent Secretion in Mammalian Sensory Neurons Zuying Chai, Changhe Wang, Rong Huang, Yuan Wang, Xiaoyu Zhang,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
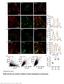 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
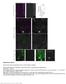 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects.
 Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
Supplemental Information. Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila. Supplemental Inventory
 1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Octopamine Neurons Mediate Flight-Induced Modulation of Visual Processing in Drosophila Marie P. Suver, Akira Mamiya, and Michael H. Dickinson Supplemental
Technology s Impact on Healthy Sleep
 Technology s Impact on Healthy Sleep JEFFREY S. DURMER, MD, PHD Adjunct Professor, Georgia State Univ. Chief Medical Officer, FusionHealth, Atlanta, GA Agenda How Technology Detracts from Your Sleep How
Technology s Impact on Healthy Sleep JEFFREY S. DURMER, MD, PHD Adjunct Professor, Georgia State Univ. Chief Medical Officer, FusionHealth, Atlanta, GA Agenda How Technology Detracts from Your Sleep How
Altered Entrainment to the Day/Night Cycle Attenuates the Daily Rise in Circulating Corticosterone in the Mouse
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Veterinary and Biomedical Science Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, Department of 2014 Altered Entrainment to
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Veterinary and Biomedical Science Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, Department of 2014 Altered Entrainment to
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Na V 1.1 channels are critical for intercellular communication in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and for normal circadian rhythms
 Na V 1.1 channels are critical for intercellular communication in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and for normal circadian rhythms Sung Han a, Frank H. Yu b,1, Michael D. Schwartz c,2, Jonathan D. Linton a,d,
Na V 1.1 channels are critical for intercellular communication in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and for normal circadian rhythms Sung Han a, Frank H. Yu b,1, Michael D. Schwartz c,2, Jonathan D. Linton a,d,
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM.
 J. exp. Biol. (1981), 94. 345~349 345 With 3 figures ferina nted in Great Britain LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM. BY JON W. JACKLET AND DAVID P.
J. exp. Biol. (1981), 94. 345~349 345 With 3 figures ferina nted in Great Britain LIGHT AND HIGH POTASSIUM CAUSE SIMILAR PHASE SHIFTS OF THE APLYSIA EYE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM. BY JON W. JACKLET AND DAVID P.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible. T H 17 cells
 Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
