P. C Campbell *, O. O Oladeyi **. * (Department of Community Health and Primary Care, College of Medicine, Lagos University Teaching
|
|
|
- Tracy Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. III. (May. 2014), PP Compliance To and Knowledge of Anti-Hypertensive Therapy amongst Hypertensive Patients Attending Lagos University Teaching Hospital (Luth), Idi-Araba, Lagos, Nigeria. P. C Campbell *, O. O Oladeyi **. * (Department of Community Health and Primary Care, College of Medicine, Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Lagos, Nigeria). ** (Ultimate Health Management Services Limited, Wema Bank Building, Central Business District, Abuja, Nigeria). Abstarct: Good knowledge and compliant to antihypertensive therapy can have a positive effect on high blood pressure control. The objective of this study is to assess compliance to and knowledge of antihypertensive therapy amongst outpatient s attending the hypertensive clinic of the Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Idi- Araba, Lagos. This descriptive cross-sectional study on out-patients attending the hypertension clinic of LUTH, was conducted from the16 th June to 20 th July, Multistage sampling technique was utilized to select the calculated minimum sample size of 282 (133 males and 149 females). A validated questionnaire by Morisky Green was modified to suite the study, pretested and self administered by two (2) trained medical personnel (nurses). Collected data was entered, cleaned and analyzed using Epi-Info version 2007 statistical software. Up to 252(96.18%) of the hypertensive patients showed good knowledge of anti-hypertensive therapy while only 10(3.82%) had poor knowledge. Majority 196 (74.81%) of the respondents were not compliant to antihypertensive treatment while only 66(25.19%) complied. Poor compliance was found to be mainly due to forgetfulness 188(71.76%) and non-availability of drugs in respondent s place of domicile 136(51.91%). There was relationship between sex, religion, education and knowledge of respondents to hypertensive therapy. Significant association was found between knowledge of hypertensive therapy and forgetfulness. There was a significant association between forgetfulness and poor compliance 14.8( ). Good knowledge of antihypertensive therapy has not significantly improved compliance to antihypertensive therapy thereby leading to low healthcare outcome. Keyword: Antihypertensive therapy, Compliant, Hypertension, Knowledge. I. Introduction Hypertension is the single most common and most important risk factor for cardiovascular disease in the world [1]. The prevalence of hypertension varies around the world with the lowest prevalence in rural India (3.4% in men and 6.8% in women) and the highest prevalence in Poland (68.9% in men and 72.5% in women) [2]. Global prevalence of hypertension is increasing. About 54% of stroke and 47% of ischemic heart disease worldwide were attributable to high blood pressure [3]. The analysis of world wide data gives a projection of 1.54 billion affected individual and a prevalence rate of 29.2% by year 2025[2]. At present, the prevalence of hypertension (blood pressure > 160/95mmHg) among adults > 25 years of age in West Africa is estimated to be around 8% in the rural areas and between 15-20% in the urban areas [4]. A community based study on rural and semi-urban population in Enugu, Nigeria put a prevalence of hypertension in Nigeria at 32.8% [5], and this was later estimated in a hospital setting to be 17-20% [6]. Hypertension is an important public health problem that is difficult to control for several reasons, among them is non-compliant to treatment [7]. Compliance is defined as the degree to which the patient conforms to medical advice about lifestyle and dietary changes as well to keep appointments for follow-up and taking treatment as prescribed [8]. WHO report 2003, defines compliance to medication as the extent to which patients take medications as prescribed by their health care providers [9]. Understanding the reasons for patient s non-compliance with antihypertensive medication is essential if blood pressure is to be more effectively managed [10]. Non-compliance to antihypertensive medication has been associated with misunderstanding of the condition, perceived improvement in health, worsening in health, general disapproval of medications and concern over side effects. This is one possible reason why success in clinical trials has not been translated into everyday practice [7]. The aim of this study therefore is to assess the knowledge of and compliance to antihypertensive therapy amongst hypertensive patients attending the outpatient hypertensive clinic of the Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Idi-Araba, Lagos, Nigeria. 108 Page
2 II. Methodology. 1.1 Study Setting Lagos University Teaching Hospital, (LUTH) Idi-Araba, is Federal Government owned tertiary hospital in Nigeria. LUTH is located in Mushin Local Government with a population size of 1,321,517 [11]. LUTH has high patients' attendance among the south-western tertiary hospitals in Nigeria, comprising of over forty departments that provides tertiary health services and with staff strength of 1,715. Medical, surgical, obstetric, laboratory, radiology and physiotherapy services are offered in the different departments of the hospital [12]. In the Faculty of Clinical Sciences, the Department of Medicine runs an out-patient hypertension clinic by the Cardiology Unit twice weekly. As at March 2012 there were 762 (359 males and 403 females) registered hypertensive patients with the Medical Records Department, and an average of 100 patients seen per clinic day. 1.2 Methods A descriptive cross-sectional study design was conducted on out-patients attending the hypertension clinic in LUTH. Participants eligible for the study were between the ages 18 and 80 years, who had been diagnosed as stage 1 and 2 hypertension. Also included in the study were follow up patients who had been attending the clinic for at least six months and had been placed on anti hypertensive therapy by a physician. All pregnant women and individuals who had psychiatric, renal, physical, or sensory alterations were excluded. All ethical protocols were strictly adhered to and ethical clearance obtained from the LUTH Research and Ethics Committee. The minimum sample size of 282 patients was calculated using the Cochrane formular [13]. Using a multistage sampling technique, a proportionate sample size of 133 males and 149 females were calculated for stratification; a sample frame was attained from the list of patients on each clinic day; a total number of 50 patients were selected using systematic random sampling technique for a period of five weeks until the desired sample sizes were attained. A validated questionnaire by Morisky Green [14] was modified to suite the study, pretested and self administered by two (2) trained medical personnel (nurses) over a period of three days, for an hour per day. The 51 items instrument consisted of four sections: A, B, C and D; which sought to answer questions on sociodemographic characteristics and personal data (13); knowledge on antihypertensive therapy (10); compliance to antihypertensive therapy (9); and reasons for non-compliance to anti hypertensive therapy (19) respectively. Concerning knowledge of hypertensive therapy, a score of 1 was allotted to each correctly answered question and 0 for wrong answers. Scores were then converted to percentage and scores below 50% were considered poor and 50 as good. The protocol for Morisky-Green test on compliance to hypertension therapy was used to ascertain respondents compliance to hypertension therapy [13], with the answering options of Yes and No. Respondents were considered compliant to the treatment when they obtained the maximum score of 4 points, and patients were considered non-compliant when they obtained 3 points or less [15,16]. Collected data was entered, cleaned and analyzed using Epi-Info version 2007 statistical software. Categorical variables were presented in tables and charts, associations were made using chi square test and test of significance was set at p 0.05 while T-test was used to analyzed continuous variables. Similarly, quantitative variables was described using measures of central tendency (mean, median) and measures of dispersion (range, standard deviation) as appropriate. 1.3 Limitation This study was limited by being a purely hospital based study on a population of referred hypertensive cases only. III. Results Table 1: Demographic Characteristics of Respondents. Variable Frequency N (%) N=262 Socio-demographic Variables: Age Group (Years) (3.81) (10.68) (22.13) (31.29) (23.66) (8.39) Age (Means ± SD) Year 54.5± 11.6 Level of Education Primary 23(8.77) 109 Page
3 Secondary 83 (31.67) Tertiary 152 (58.01) None 2(1.53) Others 2(1.53) Marital Status Divorced 14(5.34) Married 221(84.35) Single 15(5.72) Widowed 12(4.58) Ethnicity Hausa 6(2.29) Igbo 74(28.24) Yoruba 176(67.18) Others 6(2.29) Religion Christian 188(71.56) Islam 74(28.24) Employed Yes 201(76.71) No 61(23.28) Occupation (n=201) Skilled 64(31.84) Semi Skilled 124(61.69) Unskilled 13(6.46) BMI (Means ± SD) Kg/m ± 3.94 BMI Range Below Normal ( ) 5(1.92) Normal ( ) 55(20.99) > Normal (25 30) 105(40.07) Obese (> 30) 97(37.02) Blood Pressure Normal 70(26.72) Abnormal 192(73.28) Table 2: Knowledge of the Respondents Preventive Measures Yes N (%) No N (%) N=260 Weight loss 239(91.92) 21(8.08) Reduce salt intake 239(91.92) 21(8.08) Low fat diet 222(84.73) 40(15.27) Reduce calcium and potassium Intake 122(47.66) 134(52.34) Lifestyle Changes Stop tobacco use 241(92.69) 19(7.31) Reduce alcohol Intake 253(97.31) 7(2.69) Reduce sleeping hours 240(92.31) 20(7.69) Regular exercise 235(90.38) 25(9.62) Diet modification Adequate fruit and vegetable 252(96.92) 8(3.08) Remove skin of chicken 240(92.31) 20(7.69) Eat Fast food 216(83.40) 43(16.60) Reduce fat intake 240(92.31) 20(7.69) Table 3: Rating of Respondents Knowledge. Knowledge Frequency Percent (%) Poor 10 (3.82) Good 252 (96.18) Total 262 (100) 110 Page
4 Table 4: Compliance to Anti-hypertensive therapy and reasons for non compliance Level of Compliant Yes No Frequency (%) (N =258) Morisky-Green Test. Forgotten to take medication (N=258) 178(68.99) 80(31.01) Neglectful to medication (N=258) 70(27.13) 188(72.87) Skip medication when feeling good. (N=258) 104(40.47) 153(59.53) Skip medication when feeling badly. (N=258) 57(22.09) 201(77.91) Compliant (N =262) 66(25.19) 196(74.8) Appointment days Keep appointment days (N=262) 245(93.51) 17(6.49) Regularity for clinic days Regular 205(83.67) 40(16.32) Prescribed dose. Failed to use 118(45.03) 144(54.96) Days with no medication since last visit to clinic (N=244) 0-1 days 158(64.75) 2 3 days 75(30.74) 4 5 days 11(4.51) Reasons for Non Compliance. Insufficient funds to purchase drugs. 90(34.3) Absence of symptoms. 81(30.9) Avoiding side effects. 97(37.0) Ran out of prescribed drugs. 136(51.9) Forgetfulness. 188 (71.7) Busy schedule. 40(15.2) Drug change by another doctor. 57(21.7) Misunderstood instructions. 12(4.5) Frustrated of the illness. 8(3.05) Multiple Responses. Table 5: Odd Ratios (95% CI) for Logistic Regression of Effect of Some Reasons on Poor Compliance to Hypertension Therapy. Reasons OR(95%CI) P-value Insufficient funds to purchase drug 1.2( ) Absence of symptoms 3.3( )* Avoid side effect 3.0( )* Non availability of drugs/drugs disappeared from the 1.1( ) market Ran out of prescribed drugs 1.3( )* Too many drugs to swallow 0.2( ) Have a normal blood pressure 3.6( ) Forgetfulness 14.8( )* Busy schedule 1.2( ) Misunderstood instructions 4.7( ) Frustrated of the illness 0.7( ) Preference for alternative medicine 2.0( ) Irrational fears 0.4( ) Inability to pay for transport on clinic days 0.6( ) Inability to swallow drugs 1.0( ) Drug change by another doctor 0.5( ) Contrary advice by pharmacist 4.8( ) *significant at 5%; OR=odd ratio and CI=confidence interval 111 Page
5 Table 6: Relationship between Socio- Demograhic Variables, Knowledge and Compliance of the Respondents. Socio-Demographic Non - Compliant N (%) Compliant N (%) P-value X 2 Sex Female 108(78.83) 29(21.17) Male 88(70.40) 37(29.60) TOTAL 196(74.81) 66(25.19) Marital Status Divorced 13(92.86) 1(7.14) Married 160(72.40) 61(27.60) Single 11(73.33) 4(26.67) Widowed 12(100) 0(0.00) Total 196(74.81) 66(25.19) Level of Education None 1(50.00) 1(50.00) Others 2(100.00) 0(0.00) Primary 15(65.22) 8(34.78) Secondary 60(71.43) 24(28.57) Tertiary 118(78.15) 33(21.85) Total 196(74.81) 66(25.19) Knowledge Knowledge Compliant No Yes P-value Fisher Exact df X 2 Yes N (%) 4(40.0) 6(60.0) No N (%) 192(76.2) 60(23.8) TOTAL 196(74.18) 66(25.19) A total of 282 hypertensive patients attending the Lagos University Teaching Hospital, Idi-Araba, Lagos were surveyed with a response rate of 89% and 11% non-response. The study participants consisted of 124 (47.32%) males and 138 (52.67%) females. Their ages ranged from years with a mean age of 54.5 ± 11.6 years. Majority of the respondents (34.35%) were between years of age. The Yoruba ethnic group constituted the majority (67.18%) of the respondents, followed by Igbo (27.86%), and Hausa (2.67%). The predominantly Christians 187 (71.37%) and Muslims 75(28.63%) respondents were made up of 221(84.35%) married men and women, 15(5.73%) single, while the rest were widowed, divorced or separated. A total of 151(57.63%) of study sample had university/ higher education and 23 (8.78%) primary education. Up to 64(31.84%) of the respondents were skilled, 126(61.69%) were semi skilled and 13(6.46%) were unskilled Table1 Most 239 (91.92%) knows that losing weight and reducing high salt intake reduces high blood pressure (HBP), 220 (84.73%) believed that reducing fat consumption reduces high blood pressure and 134 (52.34%) did not know that reducing the consumption of fat could reduce HBP Table 2. The level of knowledge on antihypertensive therapy was good 252 (96.18%) and 10(3.82%) had poor knowledge Table 3. In rating compliance using the Morisky- Green test [14], 178(69.0%) of the respondents would forget to take their medication; 57(22.1%) would skip medication when they felt good. Compliance rate was low 25.19% (66). The main reason for non compliance was forgetfulness 188(71.76%); other prominent ones were ran out of prescribed drugs 136(51.9%) avoiding side effects 97(37.0%), insufficient funds 90(34.3%) amongst others Table 4. Forgetfulness was the most significant reason influencing poor compliance. The odd of a person having poor compliance was 14.8 times higher for someone who forgot to take drug than for person who did not forget. Also significant association was forgetfulness and poor compliance 14.8( ). Other reasons such as absence of symptoms 3.3( ), avoid side effect 3.0 ( ) and ran out of prescribed drugs 1.3( ) significantly contributed to poor compliance to antihypertensive therapy. An individual who misunderstood instructions was 4.7 times more likely to have poor compliant however the association was not significant Page
6 ( ). Frustration of the illness was protective. The more an individual got frustrated, the less likely he/she reported poor compliant to hypertensive drugs 0.7( ) Table5. There was a statistical significant association between religion (X 2 =5.0068, df=1, P-value=0.025), knowledge (X 2 =6.6848, df = 1, P-value= , F-exact Test= ) and compliance to antihypertensive therapy. However, the association between sex (X 2 =2.4661, df=1, P-value= ), marital status (X 2 = df=3, P-value=0.8248), level of education (X 2 = Df=4, P-value=0.1296), and respondents compliance to anti-hypertensive therapy were not significant Table 6. IV. Discussion Hypertension is a serious public health problem due to its high prevalence and good control of the disease has always been considered to be essential for reducing its morbidity and mortality [15]. This study however, shows that nine out of ten respondents 252(96.18%) had good knowledge of anti-hypertensive therapy. This showed a significant association between good knowledge of hypertensive therapy and level of education (P<0.02). This finding on the other hand contrasts with very low knowledge rates from other parts of Nigeria and other countries [8, 17-19]. However, this finding is not unexpected as the patients level of education is generally known to have positive influence on their understanding of specific health education programmes and relevant behavior change techniques [20, 21]. It is important to note that many patients still have a lopsided understanding of their treatment. A qualitative contact time between patient and the physician to sort out these areas is encouraged so the patient can be involved in his/her own care. This obviously has ready consequences in poor compliance and poor control of high blood pressure especially among males with increased risk of morbidity and mortality [20, 21]. Previous studies that used Morisky-Green Test to measure compliance of anti-hypertensive therapy actually discovered a compliant rate of (54.2%) [17]. However, previous researches [18,22,23] conducted in some parts of the world and Nigeria on patient s compliance were classified by using the regular attendance of patients at follow-up clinics, obtaining and taking all drugs as prescribed. The method used in these studies were however subjective and had shown that more than half of patients that were regular for clinics days often forgot to follow their treatment pattern as prescribed by their physician. A similar study conducted in Nigeria discovered a compliant rate of (65.8%) and non- compliant rate of (34.2%) [24]. The Morsiky-Green Test used in this study, a more objective instrument classifying compliance and the variation in instrument for data analysis gave a more objective and higher non-compliance rate of 74.8% expectedly. However, studies conducted in other parts of the world such as Saudi-Arabia had a non-compliant rate of (65.8%) [25], in Sudan (40.4%) [26] and (37%) [27] In Hongkong. Non-compliance with anti-hypertensive therapy is an inherent problem in the treatment of chronic asymptomatic conditions and is one major reason why hypertension may not be treated effectively with drugs. In order to improve non-compliance, high attention needs to be given to reasons for poor compliance and appropriate measures to improve the compliant rate need to be taken. This study also showed that commonest causes of poor compliance was forgetfulness in contrast to exhaustion of drugs, ignorance and lack of funds [19], too many drugs to swallow and low level of education status [28] in other Nigerian studies. It was noted that patients just often forget to use their medication even though they were on once daily regimen. Majority 84( 68.9%) of the patients that forgets to use their medications were business professionals who will leave home very early hours of the morning and return late hours of the night due to their work schedule and long distance from home resulting in tiredness. In developed countries, electronic monitoring devices have been developed to remind patient of their pills and treatment therapy [17]. Other reasons cited by respondents in this study were exhaustion of drugs, lack of finances for replacement resulting in skipping appointments/failure to get a refill of prescription. The survey from University of Ibadan Teaching Hospital also identified economic constraint, use of alternative treatment, frustrations with daily drug ingestion and feeling of well being as constraint to compliance [19]. The observed association between poor compliance and lack of funds for the purchase of drugs was also observed in other previous research [8] whereas; in Iran anti-hypertensive drugs are given free to hypertensive patients at no extra-cost [17]. This helps to curtail lack of finance being a reason for non compliance. As high as twenty four patients (9.16%) stopped taking their drugs because they believed that their blood pressure was normal as a result of the short time treatment of initially prescribed drugs. This implies that either instructions were not properly grasped or the patients knowledge base regarding the disease was weak. The need for healthcare physicians to continually educate the patient and re-enforce the importance of continuous surveillance by the doctor and that treatment is long term and for life. The survey from University of Ibadan Teaching Hospital also identified economic constraint, use of alternative treatment, frustrations with daily drug ingestion and feeling of well being as constraint to compliance [24]. 113 Page
7 Identifying factors that determines non- compliance of hypertensive patients to treatment is, therefore, of vital importance in applying therapeutic strategy and in obtaining satisfactory results [28, 29]. V. Conclusion In this study, knowledge of antihypertensive therapy was good however, compliance is relatively poor and forgetfulness was the major reason for non-compliance. However, good knowledge did not translate to compliance. The major reasons for non-compliance where forgetfulness, insufficient funds, absence of symptoms, avoiding side effects, have a normal blood pressure and busy schedule. However, forgetfulness 14.8( ) was the most significant reason influencing poor compliance. The odd of a person having poor compliance was 14.8 times higher for someone who forgot to take his or her drugs for person who did not forgets. Other reasons such as absence of symptoms 3.3( ), avoid side effect 3.0( ) and ran out of prescribed drugs 1.3( ) significantly contributed to the poor compliance to hypertensive therapy. In conclusion, good knowledge of hypertension and its treatment regimen does not necessarily translate to better compliance to hypertension. Hypertension itself can be best controlled when patients comply with their treatment regimen, do some sort of physical activity regularly and in this way, prevent themselves from the hypertensive complications. VI. Recommendation It is therefore recommended that: 1. Hypertensive patients in LUTH should be counseled every time whenever they visit physician in order to improve their compliance to anti hypertensive therapy, thereby having a better control of hypertension. 2. Health practitioners should be involved in developing models that will always remind patients to take their medications regularly without forgetting it. 3. Patient-Physician communication should be strengthened and appropriate educational and behavioural strategies should be implemented. 4. An electronic monitoring device should be provided for patients to reduce patient s forgetfulness and enhance compliant to hypertensive treatment. 5. Healthcare providers should educate their patients concerning long term treatment of the disease. References [1] P.M Kearney, M Whelton, K Reynolds, P.K Whelton and J. He. Worldwide prevalence of hypertension: a systematic Review; Journal of Hypertension, 22(1), 2004 PP [2] P.M Kearney, M Whelton, K Reynolds, P.K Whelton and J. He. Global Burden of hypertension; analysis of worldwide data. Lancet 365 (9455), 2005 PP [3] M.M Carlene, S.V Hoorn, A. Rodgers. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, Lancet 2008; 371, [4] R. Cooper, C. Rotimi, S. Ataman, D. McGee, B. Osotimehin, S. Kadiri, et al. The prevalence of hypertension in seven populations of West African origin. American Journal of Public Healt h, 87(2), 1997, [5] I.I Ulasi, C.K. Ijoma, and O.D Oriodago. A community-based study of hypertension and cardio-metabolic syndrome in semi-urban and rural communities in Nigeria, BMC Health Services Research, Vol.10 (71), [6] S. Kadiri, O. Walker, B.L Salako, O.O Akinkugbe. Blood Pressure, Hypertension and Correlates in Urbanized Workers in Ibadan, Nigeria a revisit. J Hum Hypertens, 13, 1999, [7] The US. Department of Health and Human Services. The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. NIH Publication No. 03-5,933; [8] M. Kabira, Z. Iliyasu a, I. S. Abubakara and M. Jibrilb. Compliance to medication among hypertensive patients in Murtala Mohammed Specialist Hospital, Kano, Nigeria. Journal of Community Medicine & Primary Health Care. 16(1), 2004, [9] World Health Organization Report Adherence to Long term therapies. Evidence for Action, (iii) 2003, P 27. [10] I. Meissner, J.P Whisnant, S.G Seps, et al. Detection and control of high blood pressure in the community ; do we need a wakeup call? Hypertension 1999; 34: [11] Lagos State Government. Lagos overview; history of Lagos State. Available from.http\\: (Accessed 15 th June 2012). [12] Lagos University Teaching Hospital (LUTH). History of Lagos University Teaching Hospital. Available from. http\\: (Accessed 15 th June 2012). [13] W.G Cochran. Sampling techniques (3rd ed.), New York: John Wiley & Sons, [14] D.E Morisky, L.W Green, D.M Levine. Concurrent and predictive validity of a self-reported measure of medication adherence. Med Care. 1986; 24: [15] M.A Strelec, A.M Mion Jr. The influence of patient's consciousness regarding high blood pressure and patient's attitude in face of disease controlling medicine intake. Arq Bras Cardiol, 81(4) 2003, [16] O.A Busari, T.O Olanrewaju, O.O Desalu, et al. Impact of patients knowledge, attitude and practices on hypertension on compliance with antihypertensive drugs in a resource-poor setting. TAF Preventive Medicine Bulletin, 9(2) 2010, [17] A. Samim. Al-Dabbagh, S.M Aswad. Compliance of hypertensive patients to management in Duhok Governorate using Morisky- Green Test. Duhok Med J, 4(1) 2010, [18] P. Bovet, M. Burnier, G. Mandeleine, B Waeber, and F. Paccaud, Monitoring one year compliance to antihypertensive medication in the Seychelles. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 80(1), Page
8 [19] J.O Olubodun, A.O Falase and T.O Cole. Drug compliance in hypertensive Nigerians with and without heart failure. International Joournal of Cardiology, 27(2), 1990, [20] J. Proschaska, C.C DiClemente, J.C Norcross. In Search of How People Change: Application to Addictive Behaviours. Am Psychol. 47, 1992, [21] J. Proschaska, C.C DiClemente. Towards a comprehensive model of change. In: Miller W, Heather N, eds. Treating Addictive Behaviours: Processes of Change. New York, NY. Plenum Press, 1986, p [22] R. Muesch, K. Schroeder, T. Dieterle, B. Martina and E. Battegay. Relationship between insufficient response to antihypertensive treatment and poor compliance with treatment; a prospective case control study. BMJ 2001; (32): [23] A.S Isezuo, T.C Opera. Hypertension awareness among Nigerians in a Nigerian tertiary health institution. Sahel Medical Journal 3(2), 2000, P [24] C.O Amira, N.U Okubadejo. Factors influencing non-compliance with anti-hypertensive drug therapy in Nigerians. Niger Postgrad Med J. 14(4), 2007, [25] L.S Al-Sowielem, A.G Elzubier. Compliance and knowledge of hypertensive patients attending PHC centres in Al-khobar, Saudi- Arabia. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, 4(2), [26] A.G Elzubier, A.A Husain, I.A Suleiman, Z.A Hamid. Drug Compliance among hypertensive patients in kassala eastern Sudan. Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 6(1), 2000, [27] J.A Cramer, A. Benedict, N. Muszbek, A. Keskinaslan, and Z.M Khan. The significance of compliance and persistence in the treatment of diabetics, hypertension and dyslipidaemia; a review. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 62(1). 2008, [28] Akpa MR, Agomuoh DI, Odia OJ. Drug compliance among hypertensive patients in Port Harcourt Nigeria. Niger J Med, 14(1), [29] Andrade J.P, Fabio V, Chagas H and Andrade M. Epidemiological aspect of adherence to the treatment of hypertension. Arq Bras Cardiol 79(4), 2002, Page
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul Sep - 2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.4 Issue 3 Jul Sep - 2015 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
Compliance and Knowledge of Hypertensive Patients Attending Shorsh Hospital in Kirkuk Governorate
 THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Compliance and Knowledge of Hypertensive Patients Attending Shorsh Hospital in Kirkuk Governorate Haitham Issa Al Banna*, Layla Hassan Mohmed** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Compliance and Knowledge of Hypertensive Patients Attending Shorsh Hospital in Kirkuk Governorate Haitham Issa Al Banna*, Layla Hassan Mohmed** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
 (2007) 21, 579 584 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
(2007) 21, 579 584 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validity of four indirect methods to measure adherence in primary care hypertensives
EFFECT OF PLANT SOURCE DIETARY INTAKE ON BLOOD PRESSURE OF ADULTS IN BAYELSA STATE
 EFFECT OF PLANT SOURCE DIETARY INTAKE ON BLOOD PRESSURE OF ADULTS IN BAYELSA STATE 1 Dr. Olusegun, A. Kuforiji & 2 John Samuel 1 Department of Agricultural Technology, Federal Polytechnic, Ekowe, Bayelsa
EFFECT OF PLANT SOURCE DIETARY INTAKE ON BLOOD PRESSURE OF ADULTS IN BAYELSA STATE 1 Dr. Olusegun, A. Kuforiji & 2 John Samuel 1 Department of Agricultural Technology, Federal Polytechnic, Ekowe, Bayelsa
Knowledge of Diabetic Foot Care among Nursing Practitioners in Rivers State, Nigeria
 Knowledge of Diabetic Foot Care among Nursing Practitioners in Rivers State, Nigeria Article by Lilly-West B. R 1, Mildred E. John 2, Clement I 3 1,3 Department of Nursing Sciences, Texila American University,
Knowledge of Diabetic Foot Care among Nursing Practitioners in Rivers State, Nigeria Article by Lilly-West B. R 1, Mildred E. John 2, Clement I 3 1,3 Department of Nursing Sciences, Texila American University,
TITLE: STI AND HIV KNOWLEDGE, PREVALENCE AND RELATED BEHAVIOR AMONG YOUNG FEMALE TRADERS IN AN URBAN SLUM IN LAGOS NIGERIA Authors: Sekoni A.
 TITLE: STI AND HIV KNOWLEDGE, PREVALENCE AND RELATED BEHAVIOR AMONG YOUNG FEMALE TRADERS IN AN URBAN SLUM IN LAGOS NIGERIA Authors: Sekoni A.O, Oyedele D.K Department of Community Health and Primary Care
TITLE: STI AND HIV KNOWLEDGE, PREVALENCE AND RELATED BEHAVIOR AMONG YOUNG FEMALE TRADERS IN AN URBAN SLUM IN LAGOS NIGERIA Authors: Sekoni A.O, Oyedele D.K Department of Community Health and Primary Care
AWARENESS LEVEL OF KIDNEY DISEASES AMONG NON-MEDICAL STUDENTS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences June 2012, Vol. 11 No.1 pp 29-34 AWARENESS LEVEL OF KIDNEY DISEASES AMONG NON-MEDICAL STUDENTS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA *OKAKA EI and OJOGWU LI ABSTRACT
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences June 2012, Vol. 11 No.1 pp 29-34 AWARENESS LEVEL OF KIDNEY DISEASES AMONG NON-MEDICAL STUDENTS IN BENIN CITY, NIGERIA *OKAKA EI and OJOGWU LI ABSTRACT
Immunization Status of Under-5 Children in A Rural Community in Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. II (January. 2017), PP 126-130 www.iosrjournals.org Immunization Status of Under-5 Children
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. II (January. 2017), PP 126-130 www.iosrjournals.org Immunization Status of Under-5 Children
IDSP-NCD Risk Factor Survey
 Sumary: Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factor Survey, 2007-08, Phase-I states of India IDSP-NCD Risk Factor Survey Fact Sheet - India Phase - I States State AP MP MH MZ KE TN UTK Population Household surveyed
Sumary: Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factor Survey, 2007-08, Phase-I states of India IDSP-NCD Risk Factor Survey Fact Sheet - India Phase - I States State AP MP MH MZ KE TN UTK Population Household surveyed
Shiftwork and cardiometabolic outcomes. Dr Anil Adisesh
 Shiftwork and cardiometabolic outcomes Dr Anil Adisesh 1 FACULTY/PRESENTER DISCLOSURE Faculty: Dr Anil Adisesh Relationships with commercial interests: - None 2 Aims 1) Participants will be able to describe
Shiftwork and cardiometabolic outcomes Dr Anil Adisesh 1 FACULTY/PRESENTER DISCLOSURE Faculty: Dr Anil Adisesh Relationships with commercial interests: - None 2 Aims 1) Participants will be able to describe
Abstract. Non-Compliance to Antihypertensive Treatment among Patients Attending Prince Zaid Military Hospital
 Non-Compliance to Antihypertensive Treatment among Patients Attending Prince Zaid Military Hospital Lana Sati Goussous (1) Nashat Ayoub Halasah (1) Manhal Halasa (2) (1) Royal medical Services, Jordan
Non-Compliance to Antihypertensive Treatment among Patients Attending Prince Zaid Military Hospital Lana Sati Goussous (1) Nashat Ayoub Halasah (1) Manhal Halasa (2) (1) Royal medical Services, Jordan
Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population
 STUDY REPORT SUMMARY Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population Descriptive study on the management of asthma in an asthmatic Middle East Africa adult population Background/Rationale:
STUDY REPORT SUMMARY Evaluation of Asthma Management in Middle EAst North Africa Adult population Descriptive study on the management of asthma in an asthmatic Middle East Africa adult population Background/Rationale:
A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic Variables Associated with Non-Communicable Diseases Among Bangladeshi Adults
 American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2018; 4(3): 24-29 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajbse ISSN: 2381-103X (Print); ISSN: 2381-1048 (Online) A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic
American Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2018; 4(3): 24-29 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajbse ISSN: 2381-103X (Print); ISSN: 2381-1048 (Online) A Study on Identification of Socioeconomic
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: Vol.8, No.8, pp , 2015
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.8, No.8, pp 131-135, 2015 Assessment of Hypertension ledge Among Pharmacists in Medan City, North Sumatera Khairunnisa*,
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.8, No.8, pp 131-135, 2015 Assessment of Hypertension ledge Among Pharmacists in Medan City, North Sumatera Khairunnisa*,
Knowledge and lifestyle practices of hypertensive patients attending a primary health care clinic in Botswana
 Knowledge and lifestyle practices of hypertensive patients attending a primary health care clinic in Botswana Zungu LI 1 Professor, Department of Health Studies, University of South Africa, Pretoria Department
Knowledge and lifestyle practices of hypertensive patients attending a primary health care clinic in Botswana Zungu LI 1 Professor, Department of Health Studies, University of South Africa, Pretoria Department
A study on nutritional status of lactating mothers attending the immunization clinic of a Medical College Hospital of Kolkata, West Bengal
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. IX (July. 2017), PP 30-34 www.iosrjournals.org A study on nutritional status of lactating
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. IX (July. 2017), PP 30-34 www.iosrjournals.org A study on nutritional status of lactating
Choice of place for childbirth: prevalence and correlates of utilization of health facilities in Chongwe district, Zambia
 Choice of place for childbirth: prevalence and correlates of utilization of health facilities in Chongwe district, Zambia * Hazemba AN, Siziya S Department of Community Medicine, School of Medicine, University
Choice of place for childbirth: prevalence and correlates of utilization of health facilities in Chongwe district, Zambia * Hazemba AN, Siziya S Department of Community Medicine, School of Medicine, University
Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak, F Puepet
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endocrinology Volume 6 Number 1 Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endocrinology Volume 6 Number 1 Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak,
Looking Toward State Health Assessment.
 CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH Policy, Planning and Analysis. Looking Toward 2000 - State Health Assessment. Table of Contents Glossary Maps Appendices Publications Public Health Code PP&A Main
CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH Policy, Planning and Analysis. Looking Toward 2000 - State Health Assessment. Table of Contents Glossary Maps Appendices Publications Public Health Code PP&A Main
THE RISK OF HIV/AIDS AMONG THE POOR RURAL FAMILIES IN RURAL COMMUNITIES IN SOUTH WESTERN-NIGERIA 1, 2
 THE RISK OF HIV/AIDS AMONG THE POOR RURAL FAMILIES IN RURAL COMMUNITIES IN SOUTH WESTERN-NIGERIA 1, 2 Bisiriyu, L.A. 1 and Adewuyi A.A. 1. 1. Demography and Social Statistics Department, Obafemi Awolowo
THE RISK OF HIV/AIDS AMONG THE POOR RURAL FAMILIES IN RURAL COMMUNITIES IN SOUTH WESTERN-NIGERIA 1, 2 Bisiriyu, L.A. 1 and Adewuyi A.A. 1. 1. Demography and Social Statistics Department, Obafemi Awolowo
The Burden of Geriatric Depression on the Family Caregiver
 Clinical Neurology and Neuroscience 2017; 1(2): 41-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cnn doi: 10.11648/j.cnn.20170102.14 The Burden of Geriatric Depression on the Family Caregiver Onya Obianma
Clinical Neurology and Neuroscience 2017; 1(2): 41-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/cnn doi: 10.11648/j.cnn.20170102.14 The Burden of Geriatric Depression on the Family Caregiver Onya Obianma
A pre experimental study to assess the effect of administration of pomegranate juice among prehypertensive men and women aged between 25-45
 2015; 1(11): 597-601 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(11): 597-601 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-08-2015 Accepted: 06-09-2015 Anoop Masih Sandhu Assistant
2015; 1(11): 597-601 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(11): 597-601 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-08-2015 Accepted: 06-09-2015 Anoop Masih Sandhu Assistant
Awareness of Hypertension, Risk Factors and Complications among Attendants of a Primary Health Care Center In Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 6, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 16-21 www.iosrjournals.org Awareness of Hypertension, Risk
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 6, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. - Feb. 2017), PP 16-21 www.iosrjournals.org Awareness of Hypertension, Risk
Subathra Vengatesan, Kishore S. Gudegowda*, Ranganath T. Sobagiah, Anil K. Krishnappa
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Vengatesan S et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2016 Nov;3(11):3086-3091 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Vengatesan S et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2016 Nov;3(11):3086-3091 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original
CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA
 Original Article CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA Financial Support: None declared
Original Article CORRELATES OF DELAYED INITIATION OF TREATMENT AFTER CONFIRMED DIAGNOSIS UNDER RNTCP: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY IN AHMEDABAD MUNICIPAL CORPORATION, INDIA Financial Support: None declared
Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka
 Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka DM Gomez, C Gunarathna, S Gunarathna, K Gnanapragasam, R Hanwella Abstract Background Mental
Help-seeking behaviour and its impact on patients attending a psychiatry clinic at National Hospital of Sri Lanka DM Gomez, C Gunarathna, S Gunarathna, K Gnanapragasam, R Hanwella Abstract Background Mental
Diabetes Education and Diabetes Prevention Education Needs Assessment, Las Vegas, Nevada
 Diabetes Education and Diabetes Prevention Education Needs Assessment, Las Vegas, Nevada Julie Plasencia, MS, RD University of Nevada Cooperative Extension 2009 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Objective...
Diabetes Education and Diabetes Prevention Education Needs Assessment, Las Vegas, Nevada Julie Plasencia, MS, RD University of Nevada Cooperative Extension 2009 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Objective...
AWARENESS OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS RISK FACTORS IN MAIDUGURI, NORTH EASTERN NIGERIA
 AWARENESS OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS RISK FACTORS IN MAIDUGURI, NORTH EASTERN NIGERIA Ibrahim Ummate, Ibrahim M. Kida, Abdullahi Talle, Bukar Bakki, Baba Waru Goni Department of Medicine, University of Maiduguri,
AWARENESS OF HYPERTENSION AND ITS RISK FACTORS IN MAIDUGURI, NORTH EASTERN NIGERIA Ibrahim Ummate, Ibrahim M. Kida, Abdullahi Talle, Bukar Bakki, Baba Waru Goni Department of Medicine, University of Maiduguri,
A Comparison of Nutritional Status of Women Suffering from Mental Illness in Urban and Rural Areas of Bangladesh
 International Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences 2017; 6(2): 65-70 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijnfs doi: 10.11648/j.ijnfs.20170602.12 ISSN: 2327-2694 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2716 (Online)
International Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences 2017; 6(2): 65-70 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijnfs doi: 10.11648/j.ijnfs.20170602.12 ISSN: 2327-2694 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2716 (Online)
programme. The DE-PLAN follow up.
 What are the long term results and determinants of outcomes in primary health care diabetes prevention programme. The DE-PLAN follow up. Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Noël C Barengo, Jaana Lindström, Ewa
What are the long term results and determinants of outcomes in primary health care diabetes prevention programme. The DE-PLAN follow up. Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Noël C Barengo, Jaana Lindström, Ewa
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Assessment of Susceptibility to Diabetes Mellitus among Rural Population using Indian Diabetic
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Assessment of Susceptibility to Diabetes Mellitus among Rural Population using Indian Diabetic
THE PREVALENCE OF, AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH, OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY IN BOTSWANA
 J. Biosoc. Sci., (2011) 43, 75 84, Cambridge University Press, 2010 doi:10.1017/s0021932010000519 First published online 17 Sep 2010 THE PREVALENCE OF, AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH, OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY
J. Biosoc. Sci., (2011) 43, 75 84, Cambridge University Press, 2010 doi:10.1017/s0021932010000519 First published online 17 Sep 2010 THE PREVALENCE OF, AND FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH, OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY
Impact of Counseling on Patient Caretaker s Knowledge and Medication Adherence to Paediatric Antiepileptic Drug Therapy
 International Journal of Science and Healthcare Research Vol.3; Issue: 4; Oct.-Dec. 2018 Website: www.ijshr.com Original Research Article ISSN: 2455-7587 Impact of Counseling on Patient Caretaker s Knowledge
International Journal of Science and Healthcare Research Vol.3; Issue: 4; Oct.-Dec. 2018 Website: www.ijshr.com Original Research Article ISSN: 2455-7587 Impact of Counseling on Patient Caretaker s Knowledge
Rivu Basu 1, Abhishek Paul 2, Suresh Chandra Malick 2, Somdipta Bhattacharya
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2015), PP 37-42 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of Tobacco Use and Its Different
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2015), PP 37-42 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of Tobacco Use and Its Different
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge and Attitude Regarding Early Detection
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Structured Teaching Programme on Knowledge and Attitude Regarding Early Detection
Awareness, Knowledge and Practice of Breast-Self Examination amongst Female Health Workers in A igerian Community. Omolase Charles Oluwole 1
 Awareness, Knowledge and Practice of Breast-Self Examination amongst Female Health Workers in A igerian Community. Omolase Charles Oluwole 1 ABSTRACT AIM : This study was designed to assess the awareness,
Awareness, Knowledge and Practice of Breast-Self Examination amongst Female Health Workers in A igerian Community. Omolase Charles Oluwole 1 ABSTRACT AIM : This study was designed to assess the awareness,
Adherence to antiretroviral drugs among AIDS patients in Sagamu, Nigeria
 International Journal of Biomedical and Health Sciences 094-44/200 $12.00 + 0.00 Vol. 4, No. 2, June 0, 200 200 African Studies on Population and Health Printed in Nigeria http://www.asopah.org IJBHS 20009/4201
International Journal of Biomedical and Health Sciences 094-44/200 $12.00 + 0.00 Vol. 4, No. 2, June 0, 200 200 African Studies on Population and Health Printed in Nigeria http://www.asopah.org IJBHS 20009/4201
Drug use pattern with standard indicators in Jos University Teaching Hospital Nigeria. Henry C. Ndukwe, Ikoni J. Ogaji and Comfort N.
 West African Journal of Pharmacy (201) 24 (1) 88-9 Drug use pattern with standard indicators in Jos University Teaching Hospital Nigeria 1 2 1 Henry C. Ndukwe, Ikoni J. Ogaji and Comfort N. Sariem 1 Department
West African Journal of Pharmacy (201) 24 (1) 88-9 Drug use pattern with standard indicators in Jos University Teaching Hospital Nigeria 1 2 1 Henry C. Ndukwe, Ikoni J. Ogaji and Comfort N. Sariem 1 Department
Situation of Obesity in Different Ages in Albania
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Sports & Exercise Science, 2018, 6 (1): 5-10 (http://www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com) Situation of Obesity in Different Ages in Albania
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Sports & Exercise Science, 2018, 6 (1): 5-10 (http://www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com) Situation of Obesity in Different Ages in Albania
An Assessment of the Knowledge and Attitude of Academic Staff of Aminu Saleh College of Education, Azare toward Hypertension
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e- ISSN: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. I (May-June.2018), PP 67-72 www.iosrjournals.org An Assessment of the Knowledge and Attitude
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e- ISSN: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. I (May-June.2018), PP 67-72 www.iosrjournals.org An Assessment of the Knowledge and Attitude
Correspondence should be addressed to S. Pirasath;
 Hindawi International Hypertension Volume 2017, Article ID 9656450, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9656450 Research Article A Study on Knowledge, Awareness, and Medication Adherence in Patients with
Hindawi International Hypertension Volume 2017, Article ID 9656450, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9656450 Research Article A Study on Knowledge, Awareness, and Medication Adherence in Patients with
Case study: Individual with inadequate glycaemic control due to poor adherence to medication
 Case study: Individual with inadequate glycaemic control due to poor adherence to medication Authored by Linong Ji and Clifford Bailey on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Case study: Individual with inadequate glycaemic control due to poor adherence to medication Authored by Linong Ji and Clifford Bailey on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Hypertension: Global Burden & Barriers
 Hypertension: Global Burden & Barriers A/Prof Clara Chow The George Institute, University of Sydney Dept. of Cardiology, Westmead Hospital Affiliated with the University of Sydney Dr Chow is supported
Hypertension: Global Burden & Barriers A/Prof Clara Chow The George Institute, University of Sydney Dept. of Cardiology, Westmead Hospital Affiliated with the University of Sydney Dr Chow is supported
Nutrition knowledge on diet related chronic non communicable diseases among the graduates from South Eastern University of Sri Lanka
 A.H.M.Mufas (1), A.H.M.Rifas (2), A.H.L. Fareeza (3) and O.D.A.N.Perera (1) Nutrition knowledge on diet related chronic non communicable diseases among the graduates from South Eastern University of Sri
A.H.M.Mufas (1), A.H.M.Rifas (2), A.H.L. Fareeza (3) and O.D.A.N.Perera (1) Nutrition knowledge on diet related chronic non communicable diseases among the graduates from South Eastern University of Sri
Expectations Of Patients Using Mental Health Services
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2017), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Expectations Of Patients Using Mental Health
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. I (Aug. 2017), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Expectations Of Patients Using Mental Health
CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY
 74 CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY This study was designed to determine the effectiveness of nurse-led cardiac rehabilitation on adherence and quality of life among patients with heart failure. 3.1. RESEARCH
74 CHAPTER - III METHODOLOGY This study was designed to determine the effectiveness of nurse-led cardiac rehabilitation on adherence and quality of life among patients with heart failure. 3.1. RESEARCH
Diabetes self-care: A community based cross sectional study from Kollam district, Kerala
 Original article Diabetes self-care: A community based cross sectional study from Kollam district, Kerala 1Vincy Nelson MD, 2 Prabhakumari C MD, 3 Chinmayi P, 3 Deepak Raj, 3 Diana Juliet, 4Sony Simon,
Original article Diabetes self-care: A community based cross sectional study from Kollam district, Kerala 1Vincy Nelson MD, 2 Prabhakumari C MD, 3 Chinmayi P, 3 Deepak Raj, 3 Diana Juliet, 4Sony Simon,
Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose (Smbg) Among Diabetic Patients Belongs to Waghodia Taluka
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 06-11 www.iosrjournals.org Knowledge And Attitude on Self Monitoring
BURNOUT SYNDROME AND DEPRESSION AMONG HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS IN MAIDUGURI TERTIARY HOSPITALS
 BURNOUT SYNDROME AND DEPRESSION AMONG HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS IN MAIDUGURI TERTIARY HOSPITALS Pindar S.K, Wakil MA, Jidda MS, Morakinyo A O, Coker MA Federal Neuropsychiatric Hospital Maiduguri, Borno
BURNOUT SYNDROME AND DEPRESSION AMONG HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS IN MAIDUGURI TERTIARY HOSPITALS Pindar S.K, Wakil MA, Jidda MS, Morakinyo A O, Coker MA Federal Neuropsychiatric Hospital Maiduguri, Borno
Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.3, September 015, ISSN 49-7110 Quality of life of people with non communicable diseases 1 3 Anju Rose, Shashidhara Y.N. & Manjula 1 3 MSc Nursing Student, Associate Professor
Impact of social factors on health practices of the elderly: an analytical study in rural Surendranagar
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20130516 Impact of social factors on health practices
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20130516 Impact of social factors on health practices
Determinants of Infertility and Treatment Seeking Behaviour among Currently Married Women in India. Ramesh Chellan India
 Determinants of Infertility and Treatment Seeking Behaviour among Currently Married Women in India Ramesh Chellan India Background Infertility is a worldwide problem affecting about 50 80 million couples
Determinants of Infertility and Treatment Seeking Behaviour among Currently Married Women in India Ramesh Chellan India Background Infertility is a worldwide problem affecting about 50 80 million couples
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. DOI: /sjams Narayana Institute of Medical Sciences, Puducherry, India
 DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.39 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8C):2924-2928 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.39 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8C):2924-2928 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
Determinants of Hypertension Complications Among Adult Hypertensive Patients in Medical Wards at Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi
 American Journal of Nursing Science 2016; 5(5): 213-221 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 110.11648/j.ajns.20160505.16 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) Determinants of
American Journal of Nursing Science 2016; 5(5): 213-221 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajns doi: 110.11648/j.ajns.20160505.16 ISSN: 2328-5745 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5753 (Online) Determinants of
Clinical Students Perception towards the Care of HIV Positive Patients in Tertiary Hospitals, Bayelsa State, Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSRJNHS) eissn: 2320 959.p ISSN: 2320 940 Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. IV (v.dec. 204), PP 072 Clinical Students Perception towards the Care of HIV Positive Patients
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSRJNHS) eissn: 2320 959.p ISSN: 2320 940 Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. IV (v.dec. 204), PP 072 Clinical Students Perception towards the Care of HIV Positive Patients
Dr. Charles Tobin-West Department of Preventive and Social Medicine College of Health Sciences University of Port Harcourt
 Dr. Charles Tobin-West Department of Preventive and Social Medicine College of Health Sciences University of Port Harcourt Sexual risk behaviors are among the key drivers of the HIV epidemic in Nigeria,
Dr. Charles Tobin-West Department of Preventive and Social Medicine College of Health Sciences University of Port Harcourt Sexual risk behaviors are among the key drivers of the HIV epidemic in Nigeria,
Lack of documentation on overweight & obese status in patients admitted to the coronary care unit: Results from the CCU study
 Lack of documentation on overweight & obese status in patients admitted to the coronary care unit: Results from the CCU study Meriam F. Caboral,, RN, MSN, NP-C Clinical Coordinator Heart Failure Components
Lack of documentation on overweight & obese status in patients admitted to the coronary care unit: Results from the CCU study Meriam F. Caboral,, RN, MSN, NP-C Clinical Coordinator Heart Failure Components
Medications adherence level and its associated factors among hypertensive patients at a major referral hospital, in Riyadh, KSA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Medications adherence level and its associated factors among hypertensive patients at a major referral hospital, in Riyadh, KSA Shaffi Ahamed Shaik 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Medications adherence level and its associated factors among hypertensive patients at a major referral hospital, in Riyadh, KSA Shaffi Ahamed Shaik 1,
Status of oral polio vaccination program for international travellers and its determinants: an experience from a designated centre of West Bengal
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Sarkar M et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Apr;4(4):1223-1229 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Sarkar M et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Apr;4(4):1223-1229 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
IMPACT OF PATIENT COUNSELING BY CLINICAL PHARMACIST ON QUALITY OF LIFE IN CANCER PATIENTS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Chowdary et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 4, 1093-1099 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 IMPACT OF PATIENT COUNSELING BY CLINICAL PHARMACIST
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Chowdary et al. SJIF Impact Factor 6.647 Volume 6, Issue 4, 1093-1099 Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 IMPACT OF PATIENT COUNSELING BY CLINICAL PHARMACIST
Early Detection of Breast Cancer: Awareness and Practice of Self Breast Examination among Female Traders and Shoppers In Sagamu.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2015), PP 01-09 www.iosrjournals.org Early Detection of Breast Cancer: Awareness
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. III (Dec. 2015), PP 01-09 www.iosrjournals.org Early Detection of Breast Cancer: Awareness
KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICE OF SELF-BREAST EXAMINATION AMONG FEMALE UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS IN A NORTHERN NIGERIA UNIVERSITY.
 JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 203, Vol. 2 No.2 pp 62-68 KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICE OF SELF-BREAST EXAMINATION AMONG FEMALE UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS IN A NORTHERN NIGERIA UNIVERSITY.
JMBR: A Peer-review Journal of Biomedical Sciences December 203, Vol. 2 No.2 pp 62-68 KNOWLEDGE AND PRACTICE OF SELF-BREAST EXAMINATION AMONG FEMALE UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS IN A NORTHERN NIGERIA UNIVERSITY.
Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia: The Role of Knowledge and Self-Management - A Cross-Sectional Study
 Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 9, No. 12; 2017 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia: The Role
Global Journal of Health Science; Vol. 9, No. 12; 2017 ISSN 1916-9736 E-ISSN 1916-9744 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia: The Role
Judy Kruger, PhD, MS, Deborah A. Galuska, PhD, MPH, Mary K. Serdula, MD, MPH, Deborah A. Jones, PhD
 Attempting to Lose Weight Specific Practices Among U.S. Adults Judy Kruger, PhD, MS, Deborah A. Galuska, PhD, MPH, Mary K. Serdula, MD, MPH, Deborah A. Jones, PhD Background: Methods: Results: Conclusions:
Attempting to Lose Weight Specific Practices Among U.S. Adults Judy Kruger, PhD, MS, Deborah A. Galuska, PhD, MPH, Mary K. Serdula, MD, MPH, Deborah A. Jones, PhD Background: Methods: Results: Conclusions:
Study setting. Background and objectives. Associations between sleep parameters,
 Associations between sleep parameters, Health and Aging in Africa: A Longitudinal Study of an INDEPTH Community - HAALSI (2014 2015) non-communicable diseases, HIV status and ART in older, rural South
Associations between sleep parameters, Health and Aging in Africa: A Longitudinal Study of an INDEPTH Community - HAALSI (2014 2015) non-communicable diseases, HIV status and ART in older, rural South
Abstract. Introduction. Journal of Social Sciences Sri Lanka. AHM Mufas, AHM Rifas, AHL Fareeza and ODAN Perera
 1 Nutrition knowledge, food habits and healthy attitude of graduates on diet related chronic non-communicable disease: a cross sectional study in the Southern Eastern University of Sri Lanka AHM Mufas,
1 Nutrition knowledge, food habits and healthy attitude of graduates on diet related chronic non-communicable disease: a cross sectional study in the Southern Eastern University of Sri Lanka AHM Mufas,
LAURETTE P. N. MADU, Ph.D
 KNOWLEDGE OF MILITATING FACTORS AGAINST BREAST CANCER EARLY DETECTION PRACTICES AMONG NUNS IN ANAMBRA STATE, NIGERIA LAURETTE P. N. MADU, Ph.D OMICS 4th International Conference on Nursing & Healthcare
KNOWLEDGE OF MILITATING FACTORS AGAINST BREAST CANCER EARLY DETECTION PRACTICES AMONG NUNS IN ANAMBRA STATE, NIGERIA LAURETTE P. N. MADU, Ph.D OMICS 4th International Conference on Nursing & Healthcare
Health Promoting Practices - Patient follow up survey (Dental)
 Health Promoting Practices - Patient follow up survey (Dental) * 1. I recall completing the Health Promoting Practices Health Self-Assessment questionnaire at my dental practice Yes No * 2. Eating at least
Health Promoting Practices - Patient follow up survey (Dental) * 1. I recall completing the Health Promoting Practices Health Self-Assessment questionnaire at my dental practice Yes No * 2. Eating at least
University Journal of Medicine and Medical Specialities
 ISSN 2455-2852 2019, Vol. 5(1) A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AND FACTORS INFLUENCING OBESITY AMONG SCHOOL GOING ADOLESCENTS IN CHENNAI, 2016 Author :KARTHICK B Department of PUBLIC HEALTH,MADRAS
ISSN 2455-2852 2019, Vol. 5(1) A STUDY ON PREVALENCE OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY AND FACTORS INFLUENCING OBESITY AMONG SCHOOL GOING ADOLESCENTS IN CHENNAI, 2016 Author :KARTHICK B Department of PUBLIC HEALTH,MADRAS
Hae Won KIM. KIM Reproductive Health (2015) 12:91 DOI /s x
 KIM Reproductive Health (2015) 12:91 DOI 10.1186/s12978-015-0076-x RESEARCH Open Access Sex differences in the awareness of emergency contraceptive pills associated with unmarried Korean university students
KIM Reproductive Health (2015) 12:91 DOI 10.1186/s12978-015-0076-x RESEARCH Open Access Sex differences in the awareness of emergency contraceptive pills associated with unmarried Korean university students
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 1, Issue: 3, April 2013, Pages
 Prevalence of hypertension in an urban and rural area of Jaipur District *KAMLESH KUMAR, * R.P. KOTHARI, *KUNAL KOTHARI, *SUMEET GARG, *MANOJ KUMAR KHANDELWAL, **RESHU GUPTA DEPTT.OF MEDICINE* & PHYSIOLOGY**
Prevalence of hypertension in an urban and rural area of Jaipur District *KAMLESH KUMAR, * R.P. KOTHARI, *KUNAL KOTHARI, *SUMEET GARG, *MANOJ KUMAR KHANDELWAL, **RESHU GUPTA DEPTT.OF MEDICINE* & PHYSIOLOGY**
Improving Medication Adherence through Collaboration between Colleges of Pharmacy and Community Pharmacies
 Improving Medication Adherence through Collaboration between Colleges of Pharmacy and Community Pharmacies Megan Willson, PharmD, BCPS; Catrina Schwartz, PharmD, BS; Jennifer Robinson, PharmD Spokane,
Improving Medication Adherence through Collaboration between Colleges of Pharmacy and Community Pharmacies Megan Willson, PharmD, BCPS; Catrina Schwartz, PharmD, BS; Jennifer Robinson, PharmD Spokane,
Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension, among adults residing in an urban area of North India
 Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 338-344 (2015) Research Article Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension,
Available online at www.ijpab.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE & APPLIED BIOSCIENCE ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (2): 338-344 (2015) Research Article Prevalence and risk factors of hypertension,
Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1
 Research Article JMCJMS Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1 Department of Public Health, Nobel
Research Article JMCJMS Health Related Quality of Life, Anxiety and Depression among Tuberculosis Patients in Kathmandu, Nepal Devkota J* 1,3, Devkota N 2, Lohani SP 1 Department of Public Health, Nobel
Assessment of Risk Factors Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Central Zone of Tigray, North Ethiopia
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences Fundamentals, Vol. 07, Issue 01, October 2014 WWW..COM ISSN: 2278-3997 Assessment of Risk Factors Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Sciences Fundamentals, Vol. 07, Issue 01, October 2014 WWW..COM ISSN: 2278-3997 Assessment of Risk Factors Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health Services
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861Volume 17, Issue 12 Ver 2 (December 2018), PP 16-23 wwwiosrjournalsorg Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861Volume 17, Issue 12 Ver 2 (December 2018), PP 16-23 wwwiosrjournalsorg Stigma in Patients Using Mental Health
Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control
 O r i g i n a l P a p e r Prevalence of Self-Reported High Blood Pressure Awareness, Advice Received From Health Professionals, and Actions Taken to Reduce High Blood Pressure Among US Adults Healthstyles
O r i g i n a l P a p e r Prevalence of Self-Reported High Blood Pressure Awareness, Advice Received From Health Professionals, and Actions Taken to Reduce High Blood Pressure Among US Adults Healthstyles
Correlation between Education and Effect on Increase Knowledge High Blood Pressure Patients Referral to Hospital
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 60-64 www.ijcrar.com Correlation between Education and Effect on Increase Knowledge High Blood Pressure Patients Referral to Hospital Hassan Reza Anbarlo
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 1 (January-2015) pp. 60-64 www.ijcrar.com Correlation between Education and Effect on Increase Knowledge High Blood Pressure Patients Referral to Hospital Hassan Reza Anbarlo
Prevalence of mental morbidities among the slum dwellers of Kolkata, West Bengal
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-0853, p-issn: 79-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 16), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of mental morbidities among the
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-0853, p-issn: 79-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (Jan. 16), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of mental morbidities among the
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 10, No. 6,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 10, No. 6, 2004 789 Invited paper Overweight and obesity in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: can we control it? A.O. Musaiger 1 SUMMARY Obesity has become an
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 10, No. 6, 2004 789 Invited paper Overweight and obesity in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: can we control it? A.O. Musaiger 1 SUMMARY Obesity has become an
Knowledge and practice regarding prevention of myocardial infarction among visitors of Sahid Gangalal national heart center, Kathmandu, Nepal
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diabetes Management Knowledge and practice regarding prevention of myocardial infarction among visitors of Sahid Gangalal national heart center, Kathmandu, Nepal Punam Dahal* & Rekha Karki
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diabetes Management Knowledge and practice regarding prevention of myocardial infarction among visitors of Sahid Gangalal national heart center, Kathmandu, Nepal Punam Dahal* & Rekha Karki
CHAPTER 5. Summary, main findings, conclusions, limitations and recommendations 5.1 INTRODUCTION
 80 CHAPTER 5 Summary, main findings, conclusions, limitations and recommendations 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter summarises the study and its main findings, outlines the limitations and makes recommendations
80 CHAPTER 5 Summary, main findings, conclusions, limitations and recommendations 5.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter summarises the study and its main findings, outlines the limitations and makes recommendations
Hypertension in the South-East Asia Region: an overview
 Hypertension in the South-East Asia Region: an overview Anand Krishnan i, Renu Garg ii and Athula Kahandaliyanage iii Abstract Raised blood pressure or hypertension is the single most important risk factor
Hypertension in the South-East Asia Region: an overview Anand Krishnan i, Renu Garg ii and Athula Kahandaliyanage iii Abstract Raised blood pressure or hypertension is the single most important risk factor
Effectiveness of planned teaching programme on knowledge regarding ill effects of alcohol consumption.
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep.-Oct. 2014), PP 16-21 Effectiveness of planned teaching programme on knowledge
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. II (Sep.-Oct. 2014), PP 16-21 Effectiveness of planned teaching programme on knowledge
CHAPTER 3: METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3: METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This study is a secondary data analysis of the 1998 South African Demographic and Health Survey (SADHS) data set of women and households. According to the SADHS
CHAPTER 3: METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This study is a secondary data analysis of the 1998 South African Demographic and Health Survey (SADHS) data set of women and households. According to the SADHS
Perceived quality of antenatal care service by pregnant women in public and private health facilities in Northern Ethiopia
 American Journal of Health Research 204; 2(4): 46-5 Published online August 20, 204 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajhr) doi: 0.648/j.ajhr.2040204.7 ISSN: 2330-8788 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8796 (Online)
American Journal of Health Research 204; 2(4): 46-5 Published online August 20, 204 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajhr) doi: 0.648/j.ajhr.2040204.7 ISSN: 2330-8788 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8796 (Online)
Keywords: Awareness, Vasectomy, Intention, Barriers
 Men s awareness of, Barriers to, and Intention to adopt Vasectomy among Married Men in Ibadan, Nigeria Names, initials and Addresses of Authors: Desmennu AT* and Ajuwon AJ, Department of Health Promotion
Men s awareness of, Barriers to, and Intention to adopt Vasectomy among Married Men in Ibadan, Nigeria Names, initials and Addresses of Authors: Desmennu AT* and Ajuwon AJ, Department of Health Promotion
Participation - Demographics. Age Ranges*
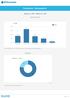 Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
An Epidemiological Study of Hypertension and Its Risk Factors in Rural Population of Bangalore Rural District
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (3 ):2 6 4-2 7 0 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE An Epidemiological Study of Hypertension
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (2 012 )5 (3 ):2 6 4-2 7 0 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE An Epidemiological Study of Hypertension
Study Objectives. To understand the influence of socio-economic factors, from a physician viewpoint, regarding the patients :
 1 Impact of Socio-Economic Factors on Patients Knowledge of their Condition, Involvement in Treatment Decisions and Subsequent Compliance with their Treatment Regimen ISPOR, Dublin Oct 20-23 2007 M Palm,
1 Impact of Socio-Economic Factors on Patients Knowledge of their Condition, Involvement in Treatment Decisions and Subsequent Compliance with their Treatment Regimen ISPOR, Dublin Oct 20-23 2007 M Palm,
Anxiety and Depression among Nursing Staff at King Fahad Medical City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
 Anxiety and Depression among Nursing Staff at King Fahad Medical City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Mostafa A F. Abbas 1, 2 ; Lamiaa Z. Abu Zaid 1, 2 ; Mona Hussaein 3 ; Khaled H. Bakheet 1 and Nasser A. AlHamdan
Anxiety and Depression among Nursing Staff at King Fahad Medical City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Mostafa A F. Abbas 1, 2 ; Lamiaa Z. Abu Zaid 1, 2 ; Mona Hussaein 3 ; Khaled H. Bakheet 1 and Nasser A. AlHamdan
DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION
 DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION Mr. Sharad V. Dighe Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Mr. Eknath M. Gawade Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Abstract Statement: A study to assess the depression among
DEPRESSION AMONG RURAL ELDERLY POPULATION Mr. Sharad V. Dighe Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Mr. Eknath M. Gawade Lecturer, PIMS (DU), CON, Loni Abstract Statement: A study to assess the depression among
Maternal Malnutrition in Urban India: A Study of Indian Cities (Mega, Large and Small)
 International Research Journal of Social Sciences ISSN 2319 3565 Maternal Malnutrition in Urban India: A Study of Indian Cities (Mega, Large and Small) Abstract Yogendra Musahar * Centre for the Study
International Research Journal of Social Sciences ISSN 2319 3565 Maternal Malnutrition in Urban India: A Study of Indian Cities (Mega, Large and Small) Abstract Yogendra Musahar * Centre for the Study
Prevalence of Obesity among High School Children in Chennai Using Discriminant Analysis
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 50-56 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of Obesity among High School Children
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. III (Jul. Aug. 2017), PP 50-56 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence of Obesity among High School Children
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary Health Care in Bahrain
 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 45(2), July - August 2017; Article No. 18, Pages:
 Research Article Nutrition and Healthy Lifestyle: Knowledge, Attitude and Practice in Medical Students of Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. A Questionnaire Based Study. Dr. Sadaf Ali 1*, Dr. Greeshma
Research Article Nutrition and Healthy Lifestyle: Knowledge, Attitude and Practice in Medical Students of Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. A Questionnaire Based Study. Dr. Sadaf Ali 1*, Dr. Greeshma
Knowledge and Attitude towards Prevention and Management of Hypertension in Jatinangor Sub-district
 222 AMJ June 2016 Knowledge and Attitude towards Prevention and Management of Hypertension in Jatinangor Sub-district Kartika Malahayati, 1 Rudi Supriyadi, 2 Herri S. Sastramihardja 3 1 Faculty of Medicine,
222 AMJ June 2016 Knowledge and Attitude towards Prevention and Management of Hypertension in Jatinangor Sub-district Kartika Malahayati, 1 Rudi Supriyadi, 2 Herri S. Sastramihardja 3 1 Faculty of Medicine,
FACTORS INFLUENCING ADHERENCE TO ANTIHYPERTENSIVE USE: A FAITH- BASED PERSPECTIVE
 FACTORS INFLUENCING ADHERENCE TO ANTIHYPERTENSIVE USE: A FAITH- BASED PERSPECTIVE By DR SOBOWALE TIWALADE O. B.SC, M.B.Ch.B, MPH(Babcock) Department of internal medicine,olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching
FACTORS INFLUENCING ADHERENCE TO ANTIHYPERTENSIVE USE: A FAITH- BASED PERSPECTIVE By DR SOBOWALE TIWALADE O. B.SC, M.B.Ch.B, MPH(Babcock) Department of internal medicine,olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching
Self-Care Behaviors among women with Hypertension in Saudi Arabia
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Self-Care Behaviors among women
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 5, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. - Jun. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Self-Care Behaviors among women
AWARENESS AND KNOWLEDGE OF AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS AMONG MOTHERS IN UKWUANI LOCAL GOVERNMENT AREA, DELTA STATE
 .2 March, 12-13 2015-University of Ilorin, 1000 Capacity Lecture Theatre Hall, Ilorin, Kwara State - Nigeria AWARENESS AND KNOWLEDGE OF AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS AMONG MOTHERS IN UKWUANI LOCAL GOVERNMENT
.2 March, 12-13 2015-University of Ilorin, 1000 Capacity Lecture Theatre Hall, Ilorin, Kwara State - Nigeria AWARENESS AND KNOWLEDGE OF AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS AMONG MOTHERS IN UKWUANI LOCAL GOVERNMENT
