Case Report. Case Report
|
|
|
- Christal Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
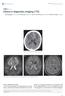
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26: , February 2005 Case Report Differential Chemosensitivity of Tumor Components in a Malignant Oligodendroglioma: Assessment with Diffusion-Weighted, Perfusion- Weighted, and Serial Volumetric MR Imaging Hans Rolf Jäger, Adam D Waldman, Christopher Benton, Nicholas Fox, and Jeremy Rees Summary: We report the case of malignant oligodendroglioma in a 36-year-old man who underwent diffusionweighted, perfusion-weighted, and volumetric MR imaging before and after PCV (procarbazine, CCNU, vincristine) chemotherapy. The tumor regions exhibiting a low apparent diffusion coefficient and increased relative cerebral blood volume showed a marked response to chemotherapy and dramatic decrease in volume, whereas the remaining tumor regions showed little change. Diffusion-weighted and perfusion-weighted MR imaging may be helpful in predicting chemosensitivity of glial tumors. The realization that certain primary brain tumors are chemosensitive has changed our therapeutic approach, particularly with respect to anaplastic or aggressive oligodendrogliomas. Although uncommon comprising only 5 10% of adult CNS gliomas they have a number of clinical and biological features that make them particularly worthy of study. Accurate diagnosis of oligodendrogliomas is now an important issue in clinical neuro-oncology, because overall survival rate and response to treatment may be substantially better than those of other gliomas. Recently, allelic loss of chromosomes 1p and 19q has been identified as an important molecular marker of chemostensitivity (1). Advanced MR imaging methods such as MR diffusion and MR perfusion provide information about physiological parameters of brain tumors not available with conventional MR images. This additional information can be used to increase the sensitivity of MR imaging in predicting the histologic tumor grade (2, 3). Received February 12, 2004; accepted after revision June 14. From the Institute of Neurology (H.R.J., A.D.W., C.B., N.F., J.R.); Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery (H.R.J.); and Department of Imaging, Charing Cross Hospital (A.D.W.), London, United Kingdom. Address correspondence to Hans Rolf Jäger, Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology, National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Queen Square, London, United Kingdom WC1N 3BG. American Society of Neuroradiology Case Report A 36-year-old man presented with a nocturnal generalized seizure. MR imaging showed a T2-hyperintense mass lesion in the right cerebral hemisphere involving the frontal and temporal lobes and insula. Surgical biopsy revealed a low-grade oligodendroglioma. The biopsy was complicated by hemorrhage, from which the patient recovered. Because the histologic findings revealed a low tumor grade and the patient was clinically well and seizure-free, a policy of observation was instituted. Serial MR imaging studies over the next 5 years showed no change in size of the tumor. Subsequently, a small area of subtle, pathologic contrast enhancement appeared in the insular region on an MR image; on this occasion, however, a double dose of gadolinium (2 mmol/kg meglumine gadoterate) had been given, whereas previous studies had used a single dose. Because the patient was clinically well and the tumor had not changed in size, it was decided to await events rather than treat. Follow-up MR imaging study 6 months later (Fig 1), which included diffusion- and perfusion-weighted and volumetric MR images, showed that the tumor had grown considerably, with the development of mass effect resulting in medial displacement of the basal ganglia, compression of the right lateral ventricle, and midline shift. The posterior and superior portions of the tumor, which involved mostly the right insula, contained areas of cystic degeneration and pathologic contrast enhancement. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps showed restricted diffusion with a mean ADC of mm 2 /s in the solid tumor portion surrounding the complex cyst in the insula. The temporal tumor portion had a mean ADC of mm 2 /s. The mean ADC measurements of the insular and temporal tumor portions, respectively, corresponded to 93% and 178% of the contralateral normal white matter ADC. MR perfusion imaging showed a large area of increased relative cerebral blood volume (rcbv) in the insular tumor component, with a mean rcbv of 5.49 (ratio to rcbv of contralateral white matter). In contrast, the rcbv of the temporal tumor component was close to that of normal white matter. The areas with decreased ADC and with increased rcbv were both larger than the area of pathologic enhancement on the postcontrast T1-weighted images. At the time of this MR imaging study, the patient had developed a left hemiparesis. He declined a further biopsy and was treated with four cycles of PCV (procarbazine, CCNU, vincristine) chemotherapy. He noticed an improvement within a 274
2 AJNR: 26, February 2005 MALIGNANT OLIGODENDROGLIOMA 275 FIG 1. MR imaging study of a 37-yearold patient with a grade 3 oligodendroglioma before treatment. A, Axial T2-weighted image (6000/ 105.5/2 [TR/TE/NEX]) at the level of the lateral ventricles shows a large heterogeneous tumor mass centered on the insular region and containing a complex cyst. B and C, rcbv maps of a perfusionweighted MR image obtained by using a dynamic susceptibility-weighted single shot echo planar sequence (1200/40/1) and 1 mmol/kg meglumine gadoterate bolus injected at a rate of 5 ml/s. B, Areas of increased rcbv (shown in red) are seen in the insular tumor portion. Measurements of the rcbv in that area ranged from 4.74 to 6.82 (mean, 5.49), by using the contralateral white matter as reference. C, There is no increased of rcbv in the temporal tumor portion, situated posterior to the right middle cerebral artery, which is a structure of a high blood volume and therefore shows up as red. The mean rcbv of the temporal tumor was D and E, ADC maps of a diffusion-weighted image (10,000/93.3 [TR/TE]; b 1,000 s/mm 2 ). D, Axial section at the level of the lateral ventricles shows that the tumor surrounding the complex cyst in right insular region appears hypointense relative to normal white matter. Regions of interest placed in this area had ADC measurements from 0.70 to mm 2 /s (mean, 0.76) E, Axial section through the temporal lobes shows that the tumor in the right temporal lobe appears hyperintense relative to normal white matter, with ADC measurements ranging from 1.39 to mm 2 /s (mean 1.44). few days of the first cycle and completely recovered function down the left side by the end of the second cycle. A further MR imaging study, including perfusion- and diffusion-weighted and volumetric sequences, was performed after the fourth chemotherapy cycle (Fig 2). This showed a dramatic reduction of the posterior and superior tumor components that had exhibited low ADC and high rcbv measurements on the initial image. There was near-complete resolution of the complex cyst and normalization of the rcbv. The mean ADC of the small residual insular tumor was now mm 2 /s. There remained, however, a small area of enhancement. In contrast, the temporal tumor component showed no significant change in volume, signal intensity characteristics, ADC, or rcbv. We obtained an objective confirmation of the regional differences in tumor volume change following chemotherapy with difference images of the coregistered T1-weighted volumetric images, on which areas of tumor shrinkage are shown in green and areas of CSF expansion in red (Fig 3). Discussion Advanced MR imaging techniques are increasingly used as an adjunct to conventional MR imaging in the investigation of cerebral mass lesions, including gliomas. Visual inspection of diffusion-weighted trace images provides little additional information and is hampered by T2-dependent effects; however, measurement of the ADC, which is independent of T2 effects, is a potentially useful method to distinguish between high- and low-grade gliomas (3 6). Water diffusion appears to be more restricted in high-grade gliomas than in low-grade gliomas, resulting in significantly lower ADC values in high-grade tumors. Ranges of ADC measurements in high-grade gliomas reported in different series (expressed as 10 3
3 276 JÄGER AJNR: 26, February 2005 FIG 2. MR imaging study following four cycles of chemotherapy with PCV. A, Axial T2-weighted image (6000/105.5/2 [TR/TE/NEX]) at the level of the lateral ventricles shows a marked reduction of the insular tumor component with almost complete resolution of the complex cyst. B, rcbv map of an axial dynamic susceptibility-weighted single shot echo planar sequence (1200/40/1 [TR/TE/NEX]) no longer show any areas of increased rcbv in the residual insular tumor. C, ADC map of an axial diffusion-weighted image (10,000/93.3 [TR/TE]; b 1000 s/mm 2 ) at the level of the lateral ventricles shows that the small residual tumor in the insula is no longer hypointense but hyperintense compared with contralateral white matter, with ADC measurements ranging from 1.21 to mm 2 /s (mean, 1.30). FIG 3. Difference image of volumetric pre- and post-treatment studies. Red-green difference image of pre- and post-treatment coregistered nonenhanced T1-weighted volumetric images (14.4/ 6.4/1[TR/TE/NEX]) with a section thickness of 1 mm. Green indicates a shift from lower to higher signal intensity between the first and second study; red, the reverse. Reduction in size of the superior (mostly insular) tumor component is shown in green, which indicates replacement of T1-hypointense tumor by tissue of higher signal intensity. Re-expansion of the hypointense CSF spaces because of a decrease in mass effect is indicated in red (this includes a track leading down to the right lateral ventricle, which is related to a previous biopsy). Note the absence of boundary shifts of the temporal tumor component between the pre- and post-treatment studies. mm 2 /s) were , mean (3); , mean (4); , mean (5); and , mean (6). Sugahara et al (4) demonstrated a statistically significant inverse relationship between the histologic cell count of gliomas and their ADC measurement, but not with T2 measurements. They postulated that the decreased ADC measurements of high-grade gliomas are primarily due to the increased density of cell nuclei in these tumors, leading to restricted diffusion of water molecules. A recent study (6) showed, however, that the composition of the extracellular tumor matrix, which forms a substantial part of the tumor volume, also influences the ADC measurement. Lowgrade tumors contain a greater proportion of hydrophylic components such as hyaluran in their extracellular matrix, which also contributes to an increase in ADC. Malignant oligodendrogliomas frequently appear as inhomogeneous tumors. In the case reported here, we demonstrated marked differences of regional variation in ADC measurements within the tumor before chemotherapy. The solid portion surrounding the cystic necrotic area in the insular region had markedly lower ADC measurements (range, mm 2 /s) than the temporal portion. On the basis of the above-cited study results, it appears likely that the areas with reduced ADC are indicative of regions that have undergone malignant transformation. These were the areas that happened to respond well to chemotherapy, which led not only to a dramatic regional tumor shrinkage, but also to a significant increase of regional ADC. Following four cycles of chemotherapy, the lowest measured tumor ADC was mm 2 /s compared with mm 2 /s before chemotherapy. This corresponds to previously described changes following gene therapy in animal experiments. Stegman et al (7) observed a 31% increase in ADC of gliomas in rats within 8 days of cytosine deaminase gene therapy, preceding changes in tumor growth kinetics and tumor regression. As far as we are aware, there are no previous
4 AJNR: 26, February 2005 MALIGNANT OLIGODENDROGLIOMA 277 reports of measuring ADC changes as an indicator of therapeutic response in humans. In the reported case, we found markedly increased rcbv measurements (up to 6.82) in the insular tumor portion but not in the temporal region. The area of increased rcbv overlapped with the region of decreased ADC and both were more extensive than the region of pathologic enhancement. Formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) represents an important aspect of tumor progression and growth. Microvascular density in glial tumors correlates with histologic tumor grade, and MR perfusion imaging is a noninvasive method of assessing the tumor microvasculature. Sugahara et al (8) were able to show that rcbv measurements correlate closely with angiographic and histologic measures of tumor vascularity. The rcbv measurements of tumors are usually expressed as a ratio with the rcbv of the normal contralateral white matter, because absolute quantification of perfusion parameters with MR imaging is still unreliable. Several studies have shown statistically significant differences of the maximum rcbv (regional rcbv over the most vascular portion of the tumor) in high- and low-grade gliomas. Sugahara et al (8) found mean maximum rcbv values of 7.32, 5.84, and 1.26 for glioblastomas, anaplastic astrocytomas and low-grade gliomas, respectively, which correlate closely with the findings of Yang et al (5), who found mean maximum rcbv values of 6.10 for high-grade gliomas and 1.74 for low-grade gliomas. Law et al (9) recently reported a large study examining the sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion-weighted MR imaging in predicting the histologic grade of 160 primary cerebral gliomas. They found that rcbv measurements significantly increased the sensitivity and positive predictive value (PPV) of conventional MR imaging. By using rcbv thresholds of 1.75, MR perfusion imaging had a sensitivity of 95% and PPV of 87%. In the reported case, the findings at MR perfusion imaging changed significantly after four cycles of chemotherapy. There was no longer any pathologic increase of rcbv within the tumor, whereas a small area of pathologic enhancement persisted on the T1- weighted images, which indicates disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Regression of rcbv at MR perfusion imaging has previously been described following antiangiogenic therapy of high-grade gliomas, but not after PCV chemotherapy of oligodendrogliomas. Cha et al (10) described 18 patients with recurrent malignant gliomas receiving a combination of thalidomide as an antiangiogenic drug and carboplatin. They found a decline of the rcbv from an average of 6.55 at baseline to 3.40 at 2 months after antiangiogenic therapy. A control group receiving carboplatin alone showed no significant change in rcbv in their study, which included mostly patients with glioblastoma multiforme and a single patient with an oligoastrocytoma in each group. They also found that rcbv measurements correlated better with the clinical status than those of conventional MR imaging. We acquired volumetric T1-weighted MR images before and after treatment and co-registered these images by using MIDAS image analysis software (11), which permits objective measurement of cerebral volume changes of approximately 0.2% of whole brain volume. There is extensive experience with this technique in the assessment of regional brain volume changes in patients with Alzheimer disease (11), but to our knowledge, this is the first time it has been applied to monitor the therapeutic response of a brain tumor. The dramatic tumor reduction in the insular region is obvious on visual inspection but more objectively shown on the red-green difference images of the coregistered volumetric studies, which confirm also that there has been no subtle volume change in the temporal region. In addition, this technique has revealed changes in the contralateral hemisphere because of reduction of mass effect resulting in opening up of the central sulci. This is the first report correlating regional differences in chemosensitivity of a malignant oligodendroglioma with diffusion and perfusion MR imaging. Tumor heterogeneity within glial tumors is well documented. It represents a potential source of sampling error during surgical biopsy, which may result in erroneous tumor grading. It has been suggested that MR perfusion imaging might be useful in guiding surgical tumor biopsy (2), because it has the potential to pinpoint areas of malignant transformation with a greater accuracy than conventional MR imaging. We have been able to demonstrate that perfusionand diffusion-weighted MR imaging may also be useful for predicting which components of the tumor are likely to respond to chemotherapy and how much tumor shrinkage can be expected. This case report demonstrates that regions showing diffusion and perfusion characteristics of high-grade tumors appear to be more chemosensitive than tumor components exhibiting imaging characteristics of low-grade tumors. As neoadjuvant chemotherapy of malignant oligodendrogliomas is now discussed as an alternative firstline treatment to radiation therapy (1), these advanced MR imaging methods could be potentially useful in predicting treatment response. The initial findings reported here will need to be corroborated in a larger prospective study. Such a study could also address the question of whether oligodendrogliomas with allelic losses of chromosome 1p and 19q, which are known to be highly chemosensitive, show differences in microvasculature and water diffusion. References 1. Behin A, Hoang-Xuan K, Carpetier AF, Delattre JY. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 2003;361: Cha S, Knopp EA, Johnson G, et al. Intracranial mass lesions: dynamic contrast- enhanced susceptibility-weighted echo- planar perfusion MR imaging. Radiology 2002;223:11 29
5 278 JÄGER AJNR: 26, February Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K, et al. The role of diffusionweighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22: Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, et al. Usefullness of diffusionweighted MRI with echo- planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 1999;9: Yang D, Korogi T, Sugahara T, et al. Cerebral gliomas: prospective comparison of multivoxel 2D chemical-shift imaging proton MR spectroscopy, echoplanar perfusion and diffusion- weighted MRI. Neuroradiol 2002;44: Sadeghi N, Camby I, Goldman S, et al. Effect of hydrophilic components of the extracellular matrix on quantifiable diffusionweighted imaging of human gliomas: preliminary results of correlating apparent diffusion coefficient values and hyaluronan expression level. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;181: Stegman LD, Rehemtulla A, Hamstra DA, et al. Diffusion MRI detects early events in the response of a glioma model to the yeast cytosine deaminase gene therapy strategy. Gene Ther 2000;7: Sugahara T, Koroghi Y, Kochi M, et al. Correlation of MR imaging-determined cerebral blood maps with histologic and angiographic determination of vascularity of gliomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;171: Law M, Yang S, Wang H, et al. Glioma grading: sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of perfusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopic imaging compared with conventional MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003;24: Cha S, Knopp EA, Johnson G, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced T2-weighted MR imaging of recurrent malignant gliomas treated with thalidomide and carboplatin. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21: Freeborough P, Woods R, Fox N. Accurate registration of serial 3D MR brain images and its application to visualizing change in neurodegenerative disorders. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1996;20:
Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade
 Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade Sun Joo Lee, MD 1 Jae Hyoung Kim, MD 1,4 Young Mee Kim, MD 1 Gyung Kyu Lee, MD 1 Eun Ja Lee, MD 1 In Sung Park, MD 2,4 Jin-Myung
Perfusion MR Imaging in Gliomas: Comparison with Histologic Tumor Grade Sun Joo Lee, MD 1 Jae Hyoung Kim, MD 1,4 Young Mee Kim, MD 1 Gyung Kyu Lee, MD 1 Eun Ja Lee, MD 1 In Sung Park, MD 2,4 Jin-Myung
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
LOW GRADE ASTROCYTOMAS
 LOW GRADE ASTROCYTOMAS This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Associate Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at University of Virginia, Charlottesville. We appreciate his generous
LOW GRADE ASTROCYTOMAS This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Associate Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at University of Virginia, Charlottesville. We appreciate his generous
General Identification. Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27
 General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
General Identification Name: 江 X X Age: 29 y/o Gender: Male Height:172cm, Weight: 65kg Date of admission:95/09/27 Chief Complaint Sudden onset of seizure for several minutes Present illness This 29-year
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Diffusion Restriction Precedes Contrast Enhancement in Glioblastoma Multiforme Adil Bata 1, Jai Shankar 2 1 Faculty of Medicine, Class of 2017 2 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Division of Neuroradiology,
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls.
 Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
Role of functional MRI in evaluating intraaxial brain tumors Advances and pitfalls. Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. R. Udare, A. Mahajan, S. Juvekar, P. Shetty,
ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas: Does Lower ADC Predict a Worse Prognosis Independent of Grade of Tumor?
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Zulfiqar et al. ADC Values and Prognosis of Malignant Astrocytomas Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Maria Zulfiqar 1 David M.
Oligodendrogliomas & Oligoastrocytomas
 Oligodendrogliomas & Oligoastrocytomas ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization dedicated solely
Oligodendrogliomas & Oligoastrocytomas ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the first national nonprofit organization dedicated solely
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1738 1742, October 2001 Restricted Diffusion within Ring Enhancement Is Not Pathognomonic for Brain Abscess Marius Hartmann, Olav Jansen, Sabine Heiland, Clemens Sommer, Kristin
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors.
 Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: A Novel MR Method for High-grade Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1732 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Ida, M. Ishizuka, T. Suzuki, Y. Kubo, K. Hino, S.
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1455 1460, June/July 2005 Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Radiation- Induced Brain Injury for Differentiation from Tumor Recurrence Chiaki Asao, Yukunori Korogi, Mika Kitajima, Toshinori
Diagnostic Value of Peritumoral Minimum Apparent Diffusion Coefficient for Differentiation of Glioblastoma Multiforme From Solitary Metastatic Lesions
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI to Diagnose Glioblastoma Multiforme Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Eun Ja Lee 1,2 Karel terbrugge
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Glioma Grading by Using Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements at Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast Enhanced Perfusion MR Imaging
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, December 681-686, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Glioma Grading by Using Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements at Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, December 681-686, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Glioma Grading by Using Cerebral Blood Volume Measurements at Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
The estimated annual incidence of central nervous system
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Hayashida T. Hirai S. Morishita M. Kitajima R. Murakami Y. Korogi K. Makino H. Nakamura I. Ikushima M. Yamura M. Kochi J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Metastatic
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Perfusion MR Imaging: Clinical Utility for the Differential Diagnosis of Various Brain Tumors
 Perfusion MR Imaging: Clinical Utility for the Differential Diagnosis of Various Brain Tumors Sung Ki Cho, MD 1 Dong Gyu Na, MD 1 Jae Wook Ryoo, MD 1 Hong Gee Roh, MD 1 Chan Hong Moon, PhD 1 Hong Sik Byun,
Perfusion MR Imaging: Clinical Utility for the Differential Diagnosis of Various Brain Tumors Sung Ki Cho, MD 1 Dong Gyu Na, MD 1 Jae Wook Ryoo, MD 1 Hong Gee Roh, MD 1 Chan Hong Moon, PhD 1 Hong Sik Byun,
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a sensitive technique
 Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Published December 7, 2007 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0842 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.S. Seo K.-H. Chang D.G. Na B.J. Kwon D.H. Lee High b-value Diffusion (b 3000 s/mm 2 )MR Imaging in Cerebral Gliomas at 3T: Visual and
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
DISTINCTION BETWEEN RECURRENT GLIOMA AND RADIATION INJURY USING MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY IN COMBINATION WITH DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 1, pp. 151 158, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION. Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma
 AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Oligodendroglioma and Oligoastrocytoma ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ABOUT THE AMERICAN BRAIN TUMOR ASSOCIATION Founded in 1973, the American Brain Tumor Association (ABTA) was the
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM ANAPLASTIC GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Anaplastic Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM ANAPLASTIC GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Anaplastic Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
Supratentorial brain tumors in the first year of life are challenging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PEDIATRICS Diffusion Imaging for Tumor Grading of Supratentorial Brain Tumors in the First Year of Life S.F. Kralik, A. Taha, A.P. Kamer, J.S. Cardinal, T.A. Seltman, and C.Y. Ho ABSTRACT
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours. Colin Kennedy March 2015
 Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Lara A. Brandão, MD a,b, *, Mark S. Shiroishi, MD c, Meng Law, MD c. mri.theclinics.com KEYWORDS KEY POINTS
 Brain Tumors A Multimodality Approach with Diffusion- Weighted Imaging, Diffusion Tensor Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic
Brain Tumors A Multimodality Approach with Diffusion- Weighted Imaging, Diffusion Tensor Imaging, Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic
Dong Gyu Na, Vincent N. Thijs, Gregory W. Albers, Michael E. Moseley, and Michael P. Marks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: , September 2004
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1331 1336, September 2004 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Acute Ischemia: Value of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Signal Intensity Thresholds in Predicting Tissue at Risk
Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1084 1089, June/July 2000 Effects of Contrast Material on Single-volume Proton MR Spectroscopy J. Keith Smith, Lester Kwock, and Mauricio Castillo BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Administration
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the
 Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Whole-tumor apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in nephroblastoma: Can it identify blastemal predominance? Abstract Purpose To explore the potential relation between whole-tumor apparent diffusion
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
High-grade astrocytomas (WHO class III or IV) are the
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai R. Murakami H. Nakamura M. Kitajima H. Fukuoka A. Sasao M. Akter Y. Hayashida R. Toya N. Oya K. Awai K. Iyama J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Prognostic Value of Perfusion MR Imaging
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai R. Murakami H. Nakamura M. Kitajima H. Fukuoka A. Sasao M. Akter Y. Hayashida R. Toya N. Oya K. Awai K. Iyama J.-i. Kuratsu Y. Yamashita Prognostic Value of Perfusion MR Imaging
SSRG International Journal of Medical Science (SSRG-IJMS) volume 2 Issue 2 Feb 2015
 Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Study of Brain Mass Lesions by MRI- On Special Sequences Ravi Ningappa 1, Bagath Singh K 2 1. Associate Professor, 2. Resident, Dept. of Radio diagnosis BMC&RI, Bangalore, India Author s address: Department
Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage
 Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage Di Ieva (2007) 120 Fractal dimension as a quantitator the microvasculat ure normal and adenomatous tissue. Clinical experience characterizing vascular surface fractal
Table 9: Vascularity and Hemorrhage Di Ieva (2007) 120 Fractal dimension as a quantitator the microvasculat ure normal and adenomatous tissue. Clinical experience characterizing vascular surface fractal
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Brain Tumors: Radiologic Perspective
 Brain Tumors: Radiologic Perspective Alberto Bizzi, M.D. Neuroradiology Humanitas Research Hospital Milan, Italy The job of the neuroradiologist in the work-up of brain tumors has quite changed in the
Brain Tumors: Radiologic Perspective Alberto Bizzi, M.D. Neuroradiology Humanitas Research Hospital Milan, Italy The job of the neuroradiologist in the work-up of brain tumors has quite changed in the
Susceptibility Imaging in Glial Tumor Grading; Using 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance (MR) System and 32 Channel Head Coil
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 179-187 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.900374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.07.02 Accepted: 2016.07.31 Published: 2017.04.01 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 179-187 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.900374 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.07.02 Accepted: 2016.07.31 Published: 2017.04.01 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :969 976, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Intracerebral Masses: Comparison with Conventional MR Imaging and Histologic Findings Tadeusz W. Stadnik, Cristo Chaskis, Alex Michotte,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy, Intracavitary Balloon Catheter for Brain Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_intracavitary_balloon_catheter_for_brain_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Brachytherapy, Intracavitary Balloon Catheter for Brain Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: brachytherapy_intracavitary_balloon_catheter_for_brain_cancer
Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:231-236 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.4.231 Tumor-like Presentation of Tubercular Brain Abscess: Case Report Dan B. Karki 1, Ghanashyam Gurung 2,
Dynamic 1H-MRS assessment of brain tumors: A novel approach for differential diagnosis of glioma
 Dynamic 1H-MRS assessment of brain tumors: A novel approach for differential diagnosis of glioma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Dynamic 1H-MRS assessment of brain tumors: A novel approach for differential diagnosis of glioma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES
 MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES DISCLOSURE No conflicts of interest to disclose Patricia Bruns APRN, CNS Givens Brain Tumor Center Abbott Northwestern Hospital October 12, 2018 OBJECTIVES THEN
MALIGNANT GLIOMAS: TREATMENT AND CHALLENGES DISCLOSURE No conflicts of interest to disclose Patricia Bruns APRN, CNS Givens Brain Tumor Center Abbott Northwestern Hospital October 12, 2018 OBJECTIVES THEN
Goals for this Lecture. Case 1. Key Points MRI TECHNIQUES FOR DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF RECURRENT BRAIN LESIONS
 MRI TECHNIQUES FOR DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF RECURRENT BRAIN LESIONS Goals for this Lecture 1. Review common appearances for recurrent tumor and treatment effects on conventional MRI 2. Discuss current
MRI TECHNIQUES FOR DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF RECURRENT BRAIN LESIONS Goals for this Lecture 1. Review common appearances for recurrent tumor and treatment effects on conventional MRI 2. Discuss current
Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors.
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 73 (2), Page 6090-6096 Role of Diffusion Mri In Differentiation Between The Common Pediatric Posterior Fossa Brain Tumors. HanaaAbdelkader Ahmed
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care
 Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Pediatric Brain Tumors: Updates in Treatment and Care Writer Classroom Rishi R. Lulla, MD MS Objectives Introduce the common pediatric brain tumors Discuss current treatment strategies for pediatric brain
Preoperative prediction of the malignancy or benignancy of
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:761 765, May 2004 Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Imaging of Intracranial Metastases Nil Ercan, Serap Gultekin, Halil Celik, Turgut
MRI perfusion of brain tumors: any differences between supratentorial and infratentorial?
 MRI perfusion of brain tumors: any differences between supratentorial and infratentorial? Poster No.: C-2034 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Martucci, S. Gaudino, C. Schiarelli, R.
MRI perfusion of brain tumors: any differences between supratentorial and infratentorial? Poster No.: C-2034 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Martucci, S. Gaudino, C. Schiarelli, R.
Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1645 1649, October 2000 Correlation of Myo-inositol Levels and Grading of Cerebral Astrocytomas Mauricio Castillo, J. Keith Smith, and Lester Kwock BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In a
Masayuki Maeda, Tatsuya Yamamoto, Shouichiro Daimon, Hajime Sakuma, and Kan Takeda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :6 66, April 001 Arterial Hyperintensity on Fast Fluid-attenuated Inversion Recovery Images: A Subtle Finding for Hyperacute Stroke Undetected by Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Masayuki
Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR Imaging of Brain Tumors.
 Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR Imaging of Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. E. F. De Belder, L. van den Hauwe, J. Van Goethem,
Dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR Imaging of Brain Tumors. Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. E. F. De Belder, L. van den Hauwe, J. Van Goethem,
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms
 New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
New Imaging Concepts in Central Nervous System Neoplasms Maarten Lequin Department of Pediatric Radiology Wilhelmina Children s Hospital/University Medical Center Utrecht New Imaging Concepts in Central
MR image guided gamma knife radiosurgery is often
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.F. Barajas J.S. Chang P.K. Sneed M.R. Segal M.W. McDermott S. Cha Distinguishing Recurrent Intra-Axial Metastatic Tumor from Radiation Necrosis Following Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Using
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.F. Barajas J.S. Chang P.K. Sneed M.R. Segal M.W. McDermott S. Cha Distinguishing Recurrent Intra-Axial Metastatic Tumor from Radiation Necrosis Following Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Using
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Grading of Intracranial Neoplasms with MR Perfusion and MR Spectroscopy Niharika
International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Grading of Intracranial Neoplasms with MR Perfusion and MR Spectroscopy Niharika
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors. Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006
 Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006 MRI Difference maps «Longitudinal study of brain morphometrics using quantitative MRI and difference analysis», Liu,Lemieux,
Review of Longitudinal MRI Analysis for Brain Tumors Elsa Angelini 17 Nov. 2006 MRI Difference maps «Longitudinal study of brain morphometrics using quantitative MRI and difference analysis», Liu,Lemieux,
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Perfusion MR imaging with the DSC method is widely used
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai M. Kitajima H. Nakamura T. Okuda A. Sasao Y. Shigematsu D. Utsunomiya S. Oda H. Uetani M. Morioka Y. Yamashita Quantitative Blood Flow Measurements in Gliomas Using Arterial
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Hirai M. Kitajima H. Nakamura T. Okuda A. Sasao Y. Shigematsu D. Utsunomiya S. Oda H. Uetani M. Morioka Y. Yamashita Quantitative Blood Flow Measurements in Gliomas Using Arterial
Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:633 637, April 2003 Differentiation of Toxoplasmosis and Lymphoma in AIDS Patients by Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficients Daniel L. A. Camacho, J. Keith Smith, and Mauricio Castillo
An estimated 69,720 new cases of primary central nervous system. Perfusion Measurement in Brain Gliomas with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Perfusion Measurement in Brain Gliomas with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI C. Federau, R. Meuli, K. O Brien, P. Maeder, and P. Hagmann ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Intravoxel
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Perfusion Measurement in Brain Gliomas with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI C. Federau, R. Meuli, K. O Brien, P. Maeder, and P. Hagmann ABSTRACT BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Intravoxel
Modern magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques facilitate
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:3 12 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dynamic contrast-enhanced susceptibilityweighted perfusion imaging of intracranial tumors: a study using
Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:3 12 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dynamic contrast-enhanced susceptibilityweighted perfusion imaging of intracranial tumors: a study using
MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis
 MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis CGS Administrators, LLC Jump to Section... Please Note: This is a Proposed LCD. Proposed LCDs are works in progress and not necessarily a reflection of the current
MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis CGS Administrators, LLC Jump to Section... Please Note: This is a Proposed LCD. Proposed LCDs are works in progress and not necessarily a reflection of the current
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Evaluation of Perfusion CT in Grading and Prognostication of High-Grade Gliomas at Diagnosis: A Pilot Study
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shankar et al. Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jai Jai Shiva Shankar John Woulfe 2 Vasco Da Silva 2 Thanh B. Nguyen 3 Shankar
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shankar et al. Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Jai Jai Shiva Shankar John Woulfe 2 Vasco Da Silva 2 Thanh B. Nguyen 3 Shankar
PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES
 PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES by Kenny K Israni Mar 28, 2006 PERFUSION - MRI Dynamic Susceptibility contrast Dynamic Relaxivity contrast STEADY-STATE STATE TECHNIQUES Steady-state Susceptibility
PERFUSION MRI CONTRAST BASED TECHNIQUES by Kenny K Israni Mar 28, 2006 PERFUSION - MRI Dynamic Susceptibility contrast Dynamic Relaxivity contrast STEADY-STATE STATE TECHNIQUES Steady-state Susceptibility
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor
 107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
107 Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Proton MR Spectroscopy in Distinguishing between Pyogenic Brain Abscess and Necrotic Brain Tumor Ping-Hong Lai 1,4, Shu-Shong Hsu 2,4, Yuk-Keung Lo 3,4, and Shang-Wu
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Gliomas of the adult cerebral hemispheres are typically classified into one of the following three World
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:214 221, February 2004 Glial Tumor Grading and Outcome Prediction Using Dynamic Spin-Echo MR Susceptibility Mapping Compared with Conventional Contrast-Enhanced MR: Confounding
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:214 221, February 2004 Glial Tumor Grading and Outcome Prediction Using Dynamic Spin-Echo MR Susceptibility Mapping Compared with Conventional Contrast-Enhanced MR: Confounding
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Original Research. Robert Young, MD, 1 James Babb, PhD, 1 Meng Law, MD, 1,2 * Erica Pollack, BA, 1 and Glyn Johnson, PhD 1
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 26:1053 1063 (2007) Original Research Comparison of Region-of-Interest Analysis With Three Different Histogram Analysis Methods in the Determination of Perfusion Metrics
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 26:1053 1063 (2007) Original Research Comparison of Region-of-Interest Analysis With Three Different Histogram Analysis Methods in the Determination of Perfusion Metrics
Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy of Perfusion MR Imaging in Primary and Metastatic Solitary Malignant Brain Tumors
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2187 2199, October 2005 Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy of Perfusion MR Imaging in Primary and Metastatic Solitary Malignant Brain Tumors Nail Bulakbasi, Murat Kocaoglu, Anar
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2187 2199, October 2005 Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy of Perfusion MR Imaging in Primary and Metastatic Solitary Malignant Brain Tumors Nail Bulakbasi, Murat Kocaoglu, Anar
Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours. Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH
 Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH General Most common tumours are metastatic 10x more common than primary Incidence of primary neoplasms is 20 per 100000 per year
Neurosurgical Management of Brain Tumours Nicholas Little Neurosurgeon RNSH General Most common tumours are metastatic 10x more common than primary Incidence of primary neoplasms is 20 per 100000 per year
Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics. Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky
 Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky plan of attack what IS a pathologist, anyway? what s so special
Understanding general brain tumor pathology, Part I: The basics Craig Horbinski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology University of Kentucky plan of attack what IS a pathologist, anyway? what s so special
FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS
 Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Anvita Bieza FUNCTIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN FOLLOW-UP OF CEREBRAL GLIAL TUMORS Summary of Doctoral Thesis to obtain PhD degree in medicine Specialty Diagnostic Radiology Riga, 2013 Doctoral thesis
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis (DL36483)
 moldx: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis (DL36483) Page 1 of 8 PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis (DL36483) Close Section Navigation
moldx: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis (DL36483) Page 1 of 8 PROPOSED/DRAFT Local Coverage Determination (LCD): MolDX: Chromosome 1p/19q deletion analysis (DL36483) Close Section Navigation
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
CNS SESSION 3/8/ th Multidisciplinary Management of Cancers: A Case based Approach
 CNS SESSION Chair: Ruben Fragoso, MD/PhD UC Davis Fellow: Michael Cardenas, MD UC Davis Panel: Gordon Li, MD Stanford Seema Nagpal, MD Stanford Jennie Taylor, MD UCSF HPI: 46 yo right handed woman who
CNS SESSION Chair: Ruben Fragoso, MD/PhD UC Davis Fellow: Michael Cardenas, MD UC Davis Panel: Gordon Li, MD Stanford Seema Nagpal, MD Stanford Jennie Taylor, MD UCSF HPI: 46 yo right handed woman who
Published January 15, 2015 as /ajnr.A4218
 Published January 15, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4218 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Diffusion and Perfusion MRI to Differentiate Treatment- Related Changes Including Pseudoprogression from Recurrent Tumors in High-Grade
Published January 15, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4218 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Diffusion and Perfusion MRI to Differentiate Treatment- Related Changes Including Pseudoprogression from Recurrent Tumors in High-Grade
Imaging for suspected glioma
 Imaging for suspected glioma 1.1.1 Offer standard structural MRI (defined as T2 weighted, FLAIR, DWI series and T1 pre- and post-contrast volume) as the initial diagnostic test for suspected glioma, unless
Imaging for suspected glioma 1.1.1 Offer standard structural MRI (defined as T2 weighted, FLAIR, DWI series and T1 pre- and post-contrast volume) as the initial diagnostic test for suspected glioma, unless
Meningiomas are the second most common primary intracranial
 Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Published April 16, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4309 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Chordoid Meningioma: Differentiating a Rare World Health Organization Grade II Tumor from Other Meningioma Histologic Subtypes
Enormous effort has been invested in clinical trials for malignant
 Published February 13, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0963 REVIEW ARTICLE J.W. Henson S. Ulmer G.J. Harris Brain Tumor Imaging in Clinical Trials SUMMARY: There are substantial challenges in the radiologic evaluation
Published February 13, 2008 as 10.3174/ajnr.A0963 REVIEW ARTICLE J.W. Henson S. Ulmer G.J. Harris Brain Tumor Imaging in Clinical Trials SUMMARY: There are substantial challenges in the radiologic evaluation
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM LOW GRADE GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Low Grade Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM LOW GRADE GLIOMAS CNS Site Group Low Grade Gliomas Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING
MR imaging is the technique of choice to characterize
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K.E. Emblem D. Scheie P. Due-Tonnessen B. Nedregaard T. Nome J.K. Hald K. Beiske T.R. Meling A. Bjornerud Histogram Analysis of MR Imaging Derived Cerebral Blood Volume Maps: Combined
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K.E. Emblem D. Scheie P. Due-Tonnessen B. Nedregaard T. Nome J.K. Hald K. Beiske T.R. Meling A. Bjornerud Histogram Analysis of MR Imaging Derived Cerebral Blood Volume Maps: Combined
The Significance of Lactate and Lipid Peaks for Predicting Primary Neuroepithelial Tumor Grade with Proton MR Spectroscopy
 Magn Reson Med Sci 207; XX; XXX XXX doi:0.2463/mrms.mp.207-0042 Published Online: August 6, 207 MAJOR PAPER The Significance of Lactate and Lipid Peaks for Predicting Primary Neuroepithelial Tumor Grade
Magn Reson Med Sci 207; XX; XXX XXX doi:0.2463/mrms.mp.207-0042 Published Online: August 6, 207 MAJOR PAPER The Significance of Lactate and Lipid Peaks for Predicting Primary Neuroepithelial Tumor Grade
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
VOLUME: 1 ARTICLE NUMBER: 0027 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Rapid intraoperative histology of unprocessed surgical specimens via fibre-laser-based stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors John R. Hesselink, M.D. MRS & Perfusion of Brain Tumors Tumor histology Degree of malignancy Delineate tumor
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MRS and Perfusion of Brain Tumors John R. Hesselink, M.D. MRS & Perfusion of Brain Tumors Tumor histology Degree of malignancy Delineate tumor
