Nucleolar organizer regions in various human brain tumors
|
|
|
- Ashley Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Neurosurg 74: , 1991 Nucleolar organizer regions in various human brain tumors TETSUYA SHIRAISHI, M.D., KAZUO TABUCHI, M.D., TOSHIHIRO MINETA, M.D., NOBUAKI MOMOZAKI, M.D., AND MASASHI TAKAGI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Saga Medical School, Saga, Japan t,- Nucleolar organizer regions (NOR's) are loops of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which transcribe to ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA) by RNA polymerase I. They possess vital significance in the ultimate synthesis of cellular proteins. A silver colloid staining technique for demonstration of NOR-associated proteins (Ag-NOR's) was applied to paraffin-embedded sections from 128 varied brain tumors and to chromosomal preparations from cultured brain-tumor cells. There was a statistically significant difference in the mean number of Ag-NOR's per nucleus between low-grade tumors (l.98/nucleus) and high-grade tumors (2.95/ nucleus). It is suggested that the mean number of Ag-NOR's may represent the proliferative potential of brain tumors. Furthermore, high-grade tumors usually showed relatively large Ag-NOR's in a scattered distribution. In chromosomal preparations, the cultured cells displayed five to 12 Ag-NOR's on acrocentric chromosomes. Five of eight cell lines examined demonstrated ectopic Ag-NOR's. This simple staining technique can be easily applied to routinely processed paraffin-embedded sections and will become a useful tool for quick estimation of the proliferative potential of human brain tumors. KEy WORDS 9 nucleolar organizer region 9 silver colloid staining 9 brain tumor 9 proliferative potential 9 chromosome A VARIETY of histological procedures have been applied to biopsy specimens of brain tumors in an effort to evaluate their proliferative activity. Recently, immunohistochemical assessment of proliferating cells has been attempted using antibodies to bromodeoxyuridine (BUdR) ~8 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA/cyclin), 2s and Ki-67 antigen. 2~ The BUdR method requires preoperative injection of BUdR, which may be toxic to the patient. Since PCNA/ cyclin and Ki-67 antigen easily lose their antigenic activities in conventional fixation procedures, 26 immunohistochemical staining with these antibodies is not suitable for retrospective studies on stored formalinfixed paraffin-embedded tissue specimens. Nucleolar organizer regions (NOR's) have been shown to be loops of ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid (rdna) which transcribe to ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rrna) ~ and are associated with several proteins. Since NOR-associated proteins (Ag-NOR's) are argyrophilic, silver staining methods have been used for demonstration of Ag-NOR's in chromosomal preparation. In 1980, Howell and Black ~9 developed a simple one-step silver colloid staining method which can clearly identify NOR's as black dots on paraffin sections under a pho- tomicroscope, It has been suggested that the number and size of Ag-NOR's correlate with cellular activity in general and may be an indicator of the degree of proliferative potential or malignancy of human neoplasms?,5.9-~ 1,14 We have examined the number and size of Ag-NOR's and have correlated their distribution pattern in paraffin-embedded tissue samples of various human brain tumors with their histological grades of malignancy according to the World Health Organization grading system. 3~ Nucleolar organizer regions are located on the five acrocentric chromosome pairs; 2 however, they have been reported in abnormal locations (ectopic NOR's) in human testicular tumors. 7 We also examined the expression of NOR's in the chromosomes of cultured cells from human brain tumors. Materials and Methods Staining of Ag-NOR's The tumor specimens examined were obtained from 128 varied brain tumors during surgical operations. Specimens were routinely fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and processed with paraffin wax. Sections of J. Neurosurg. / Volume 74/June,
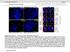
2 T. Shiraishi, et al. F](~. 1. L~{~:Photomicrograph of a high-grade astrocytoma demonstrating a mean number of nucleolar organizer region-associatedproteins (Ag-NOR's)of 2.6 per nucleus. Two or three distinct black dols are present within each nuclei. Ag-NORstain, x 285. Right: Photomicrographof a medul[oblastomashowing increased number of small Ag-NOR's.Ag-NOR slain, x ~m were cut and dewaxed in xylene, and then hydrated through decreasing grades of ethanol to deionized distilled water. The Ag-NOR staining was carried out by the one-step method of Howell and Black.~9 Briefly, a colloidal developer solution (freshly made each time), consisting of one volume of 2% gelatin in 1% aqueous formic acid and two volumes of 50% aqueous silver nitrate solution, was reacted on the surface of the sections for 60 minutes under safelight conditions at room temperature. The sections were washed with deionized water and dehydrated in ascending ethanol concentrations. The sections were placed in xylene and mounted in a synthetic medium. No counterstain was applied. Cell Culture The biopsy specimens were minced into pieces approximately 1 mm in diameter. The fragments were then layered on the bottom of Falcon plastic flasks with 5 ml of medium. To initiate the culture, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (MEM), supplemented with % inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) containing penicillin G (0 IU/ml), was used. All cultures were incubated at 37"C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. When the primary culture reached confluence, the cells were transferred by treatment with 0.05% trypsin and 0.02% ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid, and maintained in the same medium but containing 10% FBS. Established cultured glioma cell lines were maintained using the same procedure. Evaluation of Ag-NOR "s In each case, about 0 nuclei were examined under a x 100 oil-immersion objective lens. Multiple regions from each section were examined. The silver-stained dots were counted and the mean number of Ag-NOR's was determined for each nucleus. Careful focusing was used to visualize all Ag-NOR's in a nucleus. The areas 980 of the nucleoli and the Ag-NOR's of each cell were also measured by means of a microcomputer-assisted image analysis system, and the percentage of mean Ag-NOR area to mean nucleolus area was calculated (%A/N). The differences between the groups were analyzed by the use of Student's t-test. Chromosome Analysis To obtain cells in metaphase from established glioma cell lines and primary cultured tumor cells, cells were incubated in MEM containing 0.5 #g/ml of Colcemid for 6 hours. After hypotonic treatment (0.56% KCI) and triple fixation (3:1 methanol:acetic acid), slides were made and flame-dried. The Ag-NOR's were stained on the slides, and the slides were then rinsed several times in distilled water and counterstained with Giemsa solution for 2 to 3 minutes. Results Biopsy Specimens In all specimens, a variable number of silver dots (Ag-NOR's) were clearly stained black in yellow-stained nuclei. In seven cases of low-grade astrocytomas (grade 1 or 2), the mean number of Ag-NOR's per nucleus was 1.98 _ (_+ standard error of the mean). The mean nucleolus area, Ag-NOR area, and %A/N for these cells were.1 sq urn, 1.3 sq urn, and 6.5%, respectively. The Ag-NOR's were similar in size and location near the periphery, of the nuclei. Twenty-seven cases of high-grade astrocytomas (grade 3 or 4) showed a higher mean number of Ag-NOR's (2.41 _+0.39) than that of low-grade astrocytomas. The mean of %A/N was increased as well, to 11.1%. These tumors also displayed moderate pleomorphism of Ag-NOR's (Fig. I left). The highest mean number (3.57 _+ 0.88) of AgNOR's per nucleus among the brain tumors were found in two cases of medulloblastomas; however, the Ag- J. Neurosurg. / Volume 74/June. 1991
3 Nucleolar organizer regions in brain tumors HG. 2. Photomicrograph of a pituilary adenoma showing large nucleolar organizer region-associated protein (Ag-NOR) dots located in the central portion and smaller Ag-NOR dots in the periphery of the nuclei. Ag-NOR stain, x 280. FJ(~. 3. Photomicrograph of a malignant lymphoma demonstrating a mean number of nudeolar organizer regionassociated proteins (Ag-NOR's) of 3.8 per nucleus. Ag-NOR stain, x 285. NOR's were generally small (%A/N 5.6%) and were scattered throughout the nucleus (Fig. 1 righo. Among 53 cases of meningiomas there were a few large Ag-NOR's (mean 1.97 _+ 0.38), which were in a clustered distribution. Four cases of malignant meningiomas possessed a significantly high mean number of Ag-NOR's (3.22 _+ 0.68). The mean %A/N of meningiomas and malignant meningiomas was 8.0% and 10.8%, respectively. The mean Ag-NOR was 1.89 _ 0.28 (%A/N 7.4%) for 11 cases of neurinoma and 2.06 _ for seven cases of pituitary adenoma. There was a tendency for larger Ag-NOR's to be found in the central area and smaller ones at the periphery (Fig. 2). Macroadenomas had a higher mean number of Ag- NOR's ( , three cases) than did microadenomas (1.72 _+ 0.39, four cases). Three cases of craniopharyngiomas had a relatively high mean number of Ag-NOR's (2.36 _+ 0.28) and %A/N (12.9%) compared to other benign tumors. This might reflect that craniopharyngiomas tend to have increased activity of secretion compared to other benign tumors. Four cases of malignant lymphomas revealed many Ag-NOR's (mean number ) with a large area (%A/N 15.5%) and with a highly irregular shape (Fig. 3). These results are expressed as a scattergram in Fig. 4. There was a statistically significant difference in the mean number of Ag-NOR's in the nucleus between the 81 benign tumors (Grades I and 2: 1.98/nucleus) and the 47 malignant tumors (Grades 3 and 4: 2.95/nucleus; p < 0.01). Morphometric findings demonstrated a generally increasing trend in the areas of the Ag-NOR's with increasing tumor malignancy. However, it is noteworthy that medulloblastomas have small Ag-NOR's in spite of being malignant tumors and craniopharyngiomas have large Ag-NOR's in spite of being benign tumors. FIG. 4. Scattergram showing nucleolar organizer regionassociated protein (Ag-NOR) numbers per nucleus for various brain tumors. ~77romosome Analysis In chromosomal preparations, all cultured cells except T-98G expressed between five and eight Ag-NOR's on acrocentric chromosomes. The T-98G glioma cells expressed 12 Ag-NOR's and three constant ectopic Ag- Z ~k, urosurg. / Volume 74/June,
4 T. Shiraishi, et al. FIG. 5. Si ver stainedhumanmetaphasechr m s mesfr mthet-98gg i mace ine.nuc e ar rganizer region-associated proteins (Ag-NOR's) appear as black dots above the satellite stalks o f short arms of the acrocentric chromosomes. Arrows indicate ectopic Ag-NOR's. Ag-NOR and Giemsa stain, 830. a fibrillar center, a dense fibrillar component, and a granular component.~ Among these three components, the fibrillar centers are the so-called "nucleolar organizer regions" which consists of loops of DNA transcribing to 18S and 28S rrna subunits. ~'~2Although activated NOR's are found in the nucleolus, inactive NOR's may be detected in the extranucleolar nucleoplasm. 29 Several proteins, including RNA polymerase I, 24 C2s protein (nucleolin), 22 B23 protein, 2j 100-kDa proteinff and 80-kDa protein, 3 are known to be associated with NOR's. They include carboxyl- and sulfur-containing proteins that are of essential importance in the Ag- NOR's. These ectopic sites were located near the centromere of A, B, and C group-sized chromosomes. Abstracts of karyotypes are shown in Fig. 5 and the number of Ag-NOR's on chromosomes in certain cultured brain cells is shown in Table 1. Discussion Nucleolar OrganizerRegions The nucleolus is known to be a subce]lular organelle producing rrna and to be composed of the three components discernible under an electron microscope: TABLE 1 Ag-NOR "s on chromosomes of cultured brain tumor cells* Cell Line Origin of Cells No. of Cells Counted Modal No. of Chromosomes A 172 T-98G U251 ME-1 ME-2 ME-3 ME-4 GM-l glioblastoma glioblastoma mixed glioma glioblastoma, primary culture Modal No. of D+G Group Modal No. of Ag-NOR's Ectopic Ag-NOR's yes (B,E), often yes (A,B,C), constant no no no yes (B), often yes (B), often yes (A), often * A g - N O R ' s = nucleolar organizer region-associated proteins; A. B, C, E = A, B, C, E group-sized chromosomes. 982 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 74/June, 1991
5 Nucleolar organizer regions in brain tumors NOR reaction? 7 They are thought to act as regulators of DNA at NOR transcription ~ or to maintain the extended configuration of DNA at NOR's. t7 Corre]alion Belweetl &g-nor's and Mal(~,namT The exact significance of changes in the number and distribution of Ag-NOR's is not fully understood. However, since NOR's are transcribed to rrna and thus ultimately to ribosomes and finally to protein, it has been speculated that an increased number of Ag-NOR's might reflect an increased rdna transcriptional activity or potential ~ and might indicate increased nucleolar and cellular activities) ~3 Therefore, Ag-NOR's have been used as an index for the proliferative activity of cells. There have been several reports that higher numbers of Ag-NOR's correlate well with high-grade malignancy in intestinal tumorsfl neuroblastomas, ~~ malignant melanocytic lesions," and non-hodgkin's lymphomas? Hall, el al., ~4 reported that the proliferative activity of tumors, as determined by immunostaining with the monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (a marker of cell proliferation), correlated well with the mean number of Ag-NOR's in the tumor cells. Correlation was also reported between the mean number of Ag- NOR's and the S-phase cell populations determined by BUdR immunohistochemistry 2~' or DNA flow cytometry. 4 These data suggest that the mean number of Ag- NOR's may reflect the cellular proliferative activity. The authors studied a total of 128 human brain tumors in relation to the number and size of Ag-NOR's as well as their distribution pattern. A statistically significant difference was observed in the mean number of Ag-NOR's in the nuclei between low-grade tumors and high-grade tumors. There was also a tendency that the size of Ag-NOR's in high-grade tumors was increased compared to that in low-grade tumors. Cells of low-grade tumors tend to have a regular nucleolus with tightly clustered Ag-NOR's, while high-grade tumor cells often show dispersed Ag-NOR's throughout the nucleus assvnj asmultiple nucleoli containing clustered Ag-NOR's. Ag-NOR '6 on Chromosomes Nucleolar organizer regions are located on the satellite stalks of short arms of the five acrocentric chromosome pairs (Nos. 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22) in human diploid cells. ~L5 The number of Ag-NOR's on chromosomes in human diploid cells varies from five to 10, with a mean of seven to eight in phytohemagglutininstimulated lymphocytes. -'s Cytogenic studies have shown ectopic Ag-NOR's or unusual Ag-NOR patterns in certain malignancies. 7-'~ Our findings revealed that cultured brain-tumor cells except T-98G expressed five to eight Ag-NOR's on acrocentric chromosomes; the T- 98G glioma cells possessed an increased number of Ag- NOR's on chromosomes. Except for T-98G cells, the number of Ag-NOR's was similar to that reported in normal cells in spite of their increased modal chromo- some number and increased number of acrocentric chromosomes. Five of eight cell lines demonstrated inconstant ectopic Ag-NOR's. The T-98G glioma cells have three constant ectopic Ag-NOR's on their chromosomes and their increased Ag-NOR's may be ascribed to these ectopic Ag-NOR's. The active ectopic NOR's may be due to the participation of short-arm acrocentric chromosomes in translations or derepression of previously existing but inactive NOR sites on nonacrocentric chromosomes] It will be worthwhile to investigate the biological role of ectopic NOR's in brain tumors. Conclusions Silver colloid staining seems to be a useful method for evaluation of proliferative activity of brain tumors. It has an advantage over immunohistochemical methods because it can be easily applied to conventionally fixed and processed paraffin sections and enables the retrospective study of brain-tumor specimens for their proliferative potential. Acknowledgment We wish to thank Miss Yumiko Saho for technical assistance. References 1. Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, et al: The cell nucleus, in Alberts B. Bray D, Lewis J, et al (eds): Molecular Biology of the Cell, ed 2. New York: Garland Publishing, 1989, pp Cheung SW, Sun L, Featherstone T: Visualization of NORs in relation to the precise chromosomal localization of ribosomal RNA genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 50: 93-97, Courvalin JC, Maunoury R, Hernandez-Verdun D, et al: Une proteine de 80kD esl associee a l'organisateur nucleolaire (NOR) des cellules humaines. Biol Cell 49:10a, 1983 (Abstract) 4. Crocker J, Macartney JC, Smith P J: Correlation between DNA flow cytometric and nucleolar organizer region data in non-hodgkin's lymphomas. J Pathol 154: , Crocker J, Nat P: Nucleolar organizer regions in lymphomas. J Pathol 151: , Das BC, Rant R, Mitra AB, et al: The number of silverstaining NORs (rdna) in lymphocytes of newborns and its relationship to human development. Mech Ageing Dev 36: , DeLozier-Blanchet CD, Walt H, Engel E: Eetopic nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in human testieular tumors. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41: , Derenzini M, Farabegoli F, Pession A, et al: Spatial redistribution of ribosomal chromatin in the fibrillar centres of human circulating lymphocytes after stimulation of transcription. Exp Cell Res 170:31-4l, Derenzini M, Romagnoli T, Mingazzini P, et al: Interphasic nucleolar organizer region distribution as a diagnostic parameter to differentiate benign from malignant epithelial tumors of human intestine. Virch Arch (B) 54: , Egan M, Raafat F, Crocker J, eta[: Comparative study of" J. Neurosurg. / Volume 74/June, 199I 983
6 T. Shiraishi, et al. the degree of differentiation of neuroblastoma and mean numbers of nucleolar organiser regions. J Clin Pathol 41: , Egan M J, Crocker J: Nucleolar organizer regions in cutaneous tumours. J Pathol 154: , Fakan S, Hernandez-Verdun D: The nucleolus and the nucleolar organizer regions. Biol Cell 56:189-6, Field DH, Fitzgerald PH, Sin FYT: Nucleolar silverstaining patterns related to cell cycle phase and cell generation of PHA-stimulated human lymphocytes. Cytohios 41:23-33, Hall PA, Crocker J, Watts A, et al: A comparison of nucleolar organizer region staining and Ki-67 immunostaining in non-hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology 12: , Henderson AA, Warburton D, Atwood KC: Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69: , Hernandez-Verdun D: The nucleolar organizer regions. Biol Cell 49:191-2, Hernandez-Verdun D, Derenzini M, Bouteille M: Relationship between AgNOR proteins and ribosomal chromatin in situ during induced RNA synthesis inhibition. J Ultrastruct Res 88:55-65, Hoshino T, Nagashima T, Murovic JA, el al: In situ cell kinetics studies on human neuroectodermal tumors with bromodeoxyuridine labeling. J Neurosurg 64: , Howell WM, Black DA: Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a l-step method. Experientia 36: , Hubbell HR, Hsu TC: Identification of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in normal and neoplastic human cells by the silver-staining technique. Cytogenet Cell Genet 19: , Lischwe MA, Smetana K, Olson MOJ, et al: Proteins C23 and B23 are the major nucleolar silver staining proteins. Life Sci 25: , Ochs RL, Busch H: Further evidence that phosphoprotein C23 (110 kd/pi 5.1) is the nucleolar silver staining protein. Exp Cell Res 152: , Olson MOJ, Thompson BA: Distribution of proteins among chromatin components of nucleoli. Biochemistry 22: , Scheer U, Rose KM: Localization of RNA polymerase 1 in interphase cells and mitotic chromosomes by light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: , Schwarzacher HG, Wachtler F: Nucleolus organizer regions and nucleoli. Hum Genet 63:89-99, Shiraishi T: Cell kinetic analysis of brain tumors using the monoclonal antibody Ki-67: in vitro and in situ study. Acta Med Okayama 43:187-1, Smith PJ, Skilbeck N, Harrison A, et al: The effect of a series of fixatives on the AgNOR technique. J Patho1155: , Tabuchi K, Honda C, Nakane PK: Demonstration of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA/cyclin) in glioma cells. Neurol Med Chir 27:1-5, Tanaka T, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa A, et al: Nucleolar organizer regions in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N- 2-Fluorenylacetamide in rats: comparison with bromodeoxyuridine immunohistochemistry, dpn J Cancer Res 80: , , Ztilch KJ: Histological typing of tumors of the central nervous system, in: International Histological Classification of Tumours, No. 21. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1979 Manuscript received March 15, Accepted in final form October 25, Address reprint requests to." Tetsuya Shiraishi, M.D., Department of Neurosurgery., Saga Medical School, Nabeshima, Saga 849, Japan. 984 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 74~June, I991
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Significance of AgNORs Ratio as a P Author(s) Hatano, Kazuhiko Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39 Issue Date 1994-10-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15998
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Significance of AgNORs Ratio as a P Author(s) Hatano, Kazuhiko Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1994, 39 Issue Date 1994-10-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15998
Value of Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer regions in Benign, Premalignant, and Malignant Lesions of Cervix Uteri
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/97 Value of Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer regions in Benign, Premalignant, and Malignant Lesions of Cervix Uteri
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/97 Value of Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer regions in Benign, Premalignant, and Malignant Lesions of Cervix Uteri
Nucleolar organiser regions in adenocarcinoma in situ of
 J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1276-1280 Nucleolar organiser regions in adenocarcinoma in situ of the endocervix J E CULLIMORE, T P ROLLASON,* T MARSHALLt From the Birmingham and Midland Hospitalfor Women, and
J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1276-1280 Nucleolar organiser regions in adenocarcinoma in situ of the endocervix J E CULLIMORE, T P ROLLASON,* T MARSHALLt From the Birmingham and Midland Hospitalfor Women, and
DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF SILVER-STAINED NUCLEOLAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN OSTEOSARCOMA, FIBROUS DYSPLASIA AND OSSIFYING FIBROMA OF THE JAWS
 DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF SILVER-STAINED NUCLEOLAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN OSTEOSARCOMA, FIBROUS DYSPLASIA AND OSSIFYING FIBROMA OF THE JAWS M. Eslami 1, F. Baghaee 1 and M. Alaeddini 2* 1) Department of Oral Pathology,
DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF SILVER-STAINED NUCLEOLAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN OSTEOSARCOMA, FIBROUS DYSPLASIA AND OSSIFYING FIBROMA OF THE JAWS M. Eslami 1, F. Baghaee 1 and M. Alaeddini 2* 1) Department of Oral Pathology,
Satellite Nucleoli in the Megakaryocytic Lineage of Rats
 Physiol. Res. 50: 113-117, 2001 Satellite Nucleoli in the Megakaryocytic Lineage of Rats J. JANOUTOVÁ 1, Z. LIKOVSKÝ 2, K. SMETANA 3 1 Institute of Histology and Embryology, Third Faculty of Medicine,
Physiol. Res. 50: 113-117, 2001 Satellite Nucleoli in the Megakaryocytic Lineage of Rats J. JANOUTOVÁ 1, Z. LIKOVSKÝ 2, K. SMETANA 3 1 Institute of Histology and Embryology, Third Faculty of Medicine,
ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF NUCLEOLAR MATERIAL BY A SIMPLE SILVER STAINING TECHNIQUE DEVISED FOR PLANT CELLS
 J. Cell Sd. 79, 259-269 (1985) 259 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF NUCLEOLAR MATERIAL BY A SIMPLE SILVER STAINING TECHNIQUE DEVISED FOR PLANT
J. Cell Sd. 79, 259-269 (1985) 259 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF NUCLEOLAR MATERIAL BY A SIMPLE SILVER STAINING TECHNIQUE DEVISED FOR PLANT
Diagnostic Significance of Agnor Counting in Bovine Tumors
 Journal of Animal Husbandry and Dairy Science Volume 2, Issue 4, 2018, PP 19-23 ISSN 2637-5354 Diagnostic Significance of Agnor Counting in Bovine Tumors P.J.Shruthi, K.Sujatha *, Ch. Srilatha and Chengalvarayulu
Journal of Animal Husbandry and Dairy Science Volume 2, Issue 4, 2018, PP 19-23 ISSN 2637-5354 Diagnostic Significance of Agnor Counting in Bovine Tumors P.J.Shruthi, K.Sujatha *, Ch. Srilatha and Chengalvarayulu
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1993, 38
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (AgNORs), and Mitotic Indeces in Na Senba, Masachika; Zhong, Xue-Yun; I Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1993, 38
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (AgNORs), and Mitotic Indeces in Na Senba, Masachika; Zhong, Xue-Yun; I Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1993, 38
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Title Author(s) Citation Kobe University Repository : Kernel Issue date 1997-01-24 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions (AgNOR) in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Title Author(s) Citation Kobe University Repository : Kernel Issue date 1997-01-24 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions (AgNOR) in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Nuclealar Organizer Regians in Meningeal
 Turkish Neurosurgery 3: 63-67. 1993 Sav: AgNOR in MeningeaI Tumors Nuclealar Organizer Regians in Meningeal Tumars AYDIN SAV. FIGEN SÖYLEMEZOGLU. GÜLSÜN EKICIoGLU. M. MEMET ÖZEK Marmara University. Medical
Turkish Neurosurgery 3: 63-67. 1993 Sav: AgNOR in MeningeaI Tumors Nuclealar Organizer Regians in Meningeal Tumars AYDIN SAV. FIGEN SÖYLEMEZOGLU. GÜLSÜN EKICIoGLU. M. MEMET ÖZEK Marmara University. Medical
THE TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY OF INDIVIDUAL RIBOSOMAL DNA GENE CLUSTERS IS MODULATED BY SERUM CONCENTRATION*
 J. Cell Sci. 74, 21-35 (1985) 21 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Lmtited 1985 THE TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY OF INDIVIDUAL RIBOSOMAL DNA GENE CLUSTERS IS MODULATED BY SERUM CONCENTRATION*
J. Cell Sci. 74, 21-35 (1985) 21 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Lmtited 1985 THE TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY OF INDIVIDUAL RIBOSOMAL DNA GENE CLUSTERS IS MODULATED BY SERUM CONCENTRATION*
Nucleolus organizer regions, types of association and identification
 Original article Nucleolus organizer regions, types of association and identification of carrier chromosomes in domestic sheep M Moreno-Millán A Rodero-Franganillo Universidad de C6rdoba, Facultad de Veterinaria,
Original article Nucleolus organizer regions, types of association and identification of carrier chromosomes in domestic sheep M Moreno-Millán A Rodero-Franganillo Universidad de C6rdoba, Facultad de Veterinaria,
AgNOR and breast cancer. A study by image analysis
 Histol Histopath (1 994) 9: 309-31 3 Histology and Histopat hology AgNOR and breast cancer. A study by image analysis A. Ronco, J. Larran, A. Lopez and J. Vilches Department of Pathology and Cell Biology,
Histol Histopath (1 994) 9: 309-31 3 Histology and Histopat hology AgNOR and breast cancer. A study by image analysis A. Ronco, J. Larran, A. Lopez and J. Vilches Department of Pathology and Cell Biology,
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL)
 Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Original Research Article Nuclear morphometric study of Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) Sridhar Reddy Erugula 1, P. Sujatha 2, Ayesha Sameera 3, B. Suresh Reddy 4, Jesudass Govada 5, G. Sudhakar 6, Kandukuri
Comparison of bromodeoxyuridine labeling indices obtained from tissue sections and flow cytometry of brain tumors
 J Neurosurg 68:388-392, 1988 Comparison of bromodeoxyuridine labeling indices obtained from tissue sections and flow cytometry of brain tumors TADASHI NAGASHIMA, M.D., TAKAO HOSHINO, M.D., KYUNG G. CHO,
J Neurosurg 68:388-392, 1988 Comparison of bromodeoxyuridine labeling indices obtained from tissue sections and flow cytometry of brain tumors TADASHI NAGASHIMA, M.D., TAKAO HOSHINO, M.D., KYUNG G. CHO,
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D.
 Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Understanding the Human Karyotype Colleen Jackson Cook, Ph.D. SUPPLEMENTAL READING Nussbaum, RL, McInnes, RR, and Willard HF (2007) Thompson and Thompson Genetics in Medicine, 7th edition. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Detection of proliferating S-phase brain tumor cells by in situ DNA replication
 J Neurosurg 95:833 838, 2001 Detection of proliferating S-phase brain tumor cells by in situ DNA replication ROBERT J. WEIL, M.D., STEVEN A. TOMS, M.D., MAHLON D. JOHNSON, M.D., PH.D., AND AMANDA MEALER,
J Neurosurg 95:833 838, 2001 Detection of proliferating S-phase brain tumor cells by in situ DNA replication ROBERT J. WEIL, M.D., STEVEN A. TOMS, M.D., MAHLON D. JOHNSON, M.D., PH.D., AND AMANDA MEALER,
Quantitative estimation of AgNORs in normal, dysplastic and malignant oral mucosa
 Quantitative estimation of AgNORs in normal, dysplastic and malignant oral mucosa Aman Chowdhry a, Revati Shailesh Deshmukh b, Deepika Shukla a, Deepika Bablani a, Shashwat Mishra c Aims. Silver stainable
Quantitative estimation of AgNORs in normal, dysplastic and malignant oral mucosa Aman Chowdhry a, Revati Shailesh Deshmukh b, Deepika Shukla a, Deepika Bablani a, Shashwat Mishra c Aims. Silver stainable
SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS Dimple H Darad 1, Aditi D Dholakia 2, Savitri Chauhan 1 1 Associate professor;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SIGNIFICANCE OF SILVER STAINING OF NULCEAR ORGANIZER REGIONS IN FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SMEARS OF BREAST LESIONS Dimple H Darad 1, Aditi D Dholakia 2, Savitri Chauhan 1 1 Associate professor;
Neurocytoma a Rare Intraventricular Tumor
 Neurocytoma a Rare Intraventricular Tumor J. A. Mallick,S. A. Ali ( Department of Oncology, Liaquat National Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi. ) Introduction Central neurocytoma was first recognized
Neurocytoma a Rare Intraventricular Tumor J. A. Mallick,S. A. Ali ( Department of Oncology, Liaquat National Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi. ) Introduction Central neurocytoma was first recognized
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
AgNOR Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0300-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix Goyal Ritu Mohi Kaur Manjit Bal Singh Manjit Received: 15 December 2009 / Accepted: 7 August
DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0300-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Count and its Correlation with Colposcopy in Suspicious Cervix Goyal Ritu Mohi Kaur Manjit Bal Singh Manjit Received: 15 December 2009 / Accepted: 7 August
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Quantitative Evaluation of Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions in Different Histopathological
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Quantitative Evaluation of Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions in Different Histopathological
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Proportionally constant quantitative
 M264 MJClin Pathol: Mol Pathol 1995;48:M264-M268 Proportionally constant quantitative transmission of nucleolin and protein B23 in cycling cancer cells V Sirri, A Pession, D Trere, L Montanaro, M Derenzini
M264 MJClin Pathol: Mol Pathol 1995;48:M264-M268 Proportionally constant quantitative transmission of nucleolin and protein B23 in cycling cancer cells V Sirri, A Pession, D Trere, L Montanaro, M Derenzini
9/3/2009 DNA i DNA n euk euk yotes Organizatio Organ izatio n of o f gen ge e n tic Locati t on: In n ucleu e s material mater in e ial
 DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Karyology. Preparation and study of karyotypes is part of Cytogenetics.
 Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Chromosomal Karyotyping Karyology Karyotyping - process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual's chromosomes. Karyotypes describe
Chromatin position in HepG2 cells: Although being non-random, significantly changed in daughter cells
 Chromatin position in HepG2 cells: Although being non-random, significantly changed in daughter cells Ivan Raška mother cell nucleus Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine, and Institute
Chromatin position in HepG2 cells: Although being non-random, significantly changed in daughter cells Ivan Raška mother cell nucleus Charles University in Prague, First Faculty of Medicine, and Institute
 Table of Contents: TABLE OF CONTENTS:... 1 LIST OF TABLES:... 2 LIST OF FIGURES:... 3 LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS:... 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... 5 DEDICATION:... 6 CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION & REVIEW OF LITERATURES...
Table of Contents: TABLE OF CONTENTS:... 1 LIST OF TABLES:... 2 LIST OF FIGURES:... 3 LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS:... 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... 5 DEDICATION:... 6 CHAPTER ONE: INTRODUCTION & REVIEW OF LITERATURES...
The Structure of the Nucleolus Organizing Regions in Root Tip Meristems of Allium Cepa
 Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 The Structure of the Nucleolus
Caryologia International Journal of Cytology, Cytosystematics and Cytogenetics ISSN: 0008-7114 (Print) 2165-5391 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tcar20 The Structure of the Nucleolus
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes
 Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors
 Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Histopathological Study and Categorisation of Brain Tumors Ruchira Wadhwa 1*, Purvi Patel 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 Third Year Resident, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor and Head, Department of Pathology,
Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs
 151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 19/May 12, 2014 Page 5307
 PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
Supplemental Information. 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion. of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 64 Supplemental Information 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin Daniel G. Booth, Alison J. Beckett, Oscar Molina, Itaru Samejima, Hiroshi
Molecular Cell, Volume 64 Supplemental Information 3D-CLEM Reveals that a Major Portion of Mitotic Chromosomes Is Not Chromatin Daniel G. Booth, Alison J. Beckett, Oscar Molina, Itaru Samejima, Hiroshi
Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d
 هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
هللامسب Dr/ Sherein Saeid AbdElgayed, ph.d Professor of Veterinary Pathology, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt. Chairman of the Editorial Board of Arab Journal of Science & Research Publishing (AJSRP) http://www.ajsrp.com
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas
 Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Short Communication Nucleolar Localization of Upstream Binding Factor in HeLa Cells Depends on rrna Synthesis Activities
 Short Communication Nucleolar Localization of Upstream Binding Factor in HeLa Cells Depends on rrna Synthesis Activities (HeLa cells / nucleolus / transcription factor UBF / nascent rrna / immunogold labelling
Short Communication Nucleolar Localization of Upstream Binding Factor in HeLa Cells Depends on rrna Synthesis Activities (HeLa cells / nucleolus / transcription factor UBF / nascent rrna / immunogold labelling
Interpretation guide. Abnormal cytology can t hide anymore
 Interpretation guide Abnormal cytology can t hide anymore Unique dual-biomarker technology makes you certain about the presence of transforming HPV infection. The science that creates certainty. Table
Interpretation guide Abnormal cytology can t hide anymore Unique dual-biomarker technology makes you certain about the presence of transforming HPV infection. The science that creates certainty. Table
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nuclear morphometry and texture analysis on cytological smears of thyroid neoplasms: a study of 50 cases
 Malaysian J Pathol 2017; 39(1) : 33 37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nuclear morphometry and texture analysis on cytological smears of thyroid neoplasms: a study of 50 cases Lopamudra DEKA MD, Shilpa GUPTA MD, Ruchika
Malaysian J Pathol 2017; 39(1) : 33 37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nuclear morphometry and texture analysis on cytological smears of thyroid neoplasms: a study of 50 cases Lopamudra DEKA MD, Shilpa GUPTA MD, Ruchika
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
USE OF AgNOR INDEX IN GRADING AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF ASTROCYTIC LESIONS OF BRAIN
 Original Article USE OF AgNOR INDEX IN GRADING AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF ASTROCYTIC LESIONS OF BRAIN Mulazim Hussain Bukhari, 1 Shahida Niazi, 2 Ihsanullah Hashmi, 3 Samina Naeem, 4 Abdul Khalik Abro,
Original Article USE OF AgNOR INDEX IN GRADING AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF ASTROCYTIC LESIONS OF BRAIN Mulazim Hussain Bukhari, 1 Shahida Niazi, 2 Ihsanullah Hashmi, 3 Samina Naeem, 4 Abdul Khalik Abro,
AgNOR quantity in needle biopsy specimens of prostatic adenocarcinomas: correlation with proliferation state, Gleason score, clinical stage,
 J7 Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 1 996;49:M29-M2 13 Albert Einstein Medical Center, 551 Old York Road, Philadelphia, PA 19141-398, USA A Zilbering D Dittus P Kim P C Ginsberg I Daskal Dipartimento di Patologia
J7 Clin Pathol: Mol Pathol 1 996;49:M29-M2 13 Albert Einstein Medical Center, 551 Old York Road, Philadelphia, PA 19141-398, USA A Zilbering D Dittus P Kim P C Ginsberg I Daskal Dipartimento di Patologia
THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA
 J. Cell Sci. 18, 19-25(1975) 29 Printed in Great Britain THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA G.E.MARKS John Innes Institute, Colney Lane, Norwich, NR4 7 UH, England SUMMARY The centromere
J. Cell Sci. 18, 19-25(1975) 29 Printed in Great Britain THE GIEMSA-STAINING CENTROMERES OF NIGELLA DAMASCENA G.E.MARKS John Innes Institute, Colney Lane, Norwich, NR4 7 UH, England SUMMARY The centromere
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
CHAPTER-VII : SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS 199 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS t The rapid development of human genetics during the past couple of decades and the discovery of numerous cytogenetic abnormalities have
NORs in Rhoeo (Commelinaceae) revisited
 CARYOLOGIA Vol. 56, no. 1: 31-35, 2003 NORs in Rhoeo (Commelinaceae) revisited HIERONIM GOLCZYK* and ANDRZEJ JOACHIMIAK Department of Plant Cytology and Embryology, Jagiellonian University, ul. Grodzka
CARYOLOGIA Vol. 56, no. 1: 31-35, 2003 NORs in Rhoeo (Commelinaceae) revisited HIERONIM GOLCZYK* and ANDRZEJ JOACHIMIAK Department of Plant Cytology and Embryology, Jagiellonian University, ul. Grodzka
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
A preliminary note on banded karyotypes of the short-tailed shrew Blarina brevicauda (Mammalia, Insectivora)
 CARYOLOGIA Vol. 56, no. 4: 447-451, 2003 A preliminary note on banded karyotypes of the short-tailed shrew Blarina brevicauda (Mammalia, Insectivora) TATSUO OSHIDA 1, *, SATOSHI D. OHDACHI 2 and RYUICHI
CARYOLOGIA Vol. 56, no. 4: 447-451, 2003 A preliminary note on banded karyotypes of the short-tailed shrew Blarina brevicauda (Mammalia, Insectivora) TATSUO OSHIDA 1, *, SATOSHI D. OHDACHI 2 and RYUICHI
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
Comparative analysis of cell proliferation ratio in oral lichen planus, epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.14.e563 Comparative analysis of cell proliferation ratio in oral lichen planus, epithelial dysplasia and oral
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.14.e563 Comparative analysis of cell proliferation ratio in oral lichen planus, epithelial dysplasia and oral
Internationally indexed journal
 www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber
 Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man
 Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Identification of the spermatogenic stages in living seminiferous tubules of man V. Nikkanen, K.-O. S\l=o"\derstr\l=o"\m and M. Parvinen Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Turku University Central
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years
 Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
Contributions to Anatomic Pathology, over the years Anatomic Pathology, part 1 G.B. Morgagni Xavier Bichat Rudolf Wirchow Anatomic Pathology, part 1 Anatomic pathology materials: morphological samples
Detection of nucleoproteins in squamous cell carcinoma, and dysplastic and normal mucosa in the oral cavity by methyl green-pyronin staining
 239 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 2, 239-243, 2010 Original Detection of nucleoproteins in squamous cell carcinoma, and dysplastic and normal mucosa in the oral cavity by methyl green-pyronin staining
239 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 2, 239-243, 2010 Original Detection of nucleoproteins in squamous cell carcinoma, and dysplastic and normal mucosa in the oral cavity by methyl green-pyronin staining
, , 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
European Federation of Cytology Societies 4tu Annual Tutorial in Cytopathology Trieste, June 6-10, 2011 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA Classification The World Health Organization Classification of Lymphomas (2001)
Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes. Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome. Telophase Keywords Mitosis
 Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Cell Division Cell plate Carcinogen Oncogenes Haploid cell Diploid cell Chromosome Gene Interphase Anaphase Metaphase Telophase Keywords Mitosis Meiosis Centromere Cleavage furrow Middle lamella What is
Cytology for the Endocrinologist. Nicole Massoll M.D
 Cytology for the Endocrinologist Nicole Massoll M.D Objectives Discuss slide preperation Definitions of adequacy ROSE (Rapid On-Site Evaluation) Thyroid Cytology Adequacy Nicole Massoll M.D. University
Cytology for the Endocrinologist Nicole Massoll M.D Objectives Discuss slide preperation Definitions of adequacy ROSE (Rapid On-Site Evaluation) Thyroid Cytology Adequacy Nicole Massoll M.D. University
Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4. Introduction. This kit contains the following materials:
 CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellserv.org Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4 Introduction Each somatic cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. During the interphase stage of the
CellServ@FAES/NIH www.cellserv.org Preparation of Human Chromosome Spreads - Kit 4 Introduction Each somatic cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. During the interphase stage of the
STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Article STUDY OFPAEDIATRIC CNS TUMORS IN TERTIARY CARE CENTER Grishma P. Jobanputra Tutor, Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College,
The diagnostic and prognostic value of genetic aberrations in resectable distal bile duct cancer Rijken, A.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The diagnostic and prognostic value of genetic aberrations in resectable distal bile duct cancer Rijken, A.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The diagnostic and prognostic value of genetic aberrations in resectable distal bile duct cancer Rijken, A.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles Sexual reproduction mitosis
 meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
meiosis asexual reproduction CHAPTER 9 & 10 The Cell Cycle, Meiosis & Sexual Sexual reproduction Life Cycles mitosis Chromosomes Consists of a long DNA molecule (represents thousands of genes) Also consists
CHROMOSOME. Chromosomes are act as factors which distinguished one species from another.
 CHROMOSOMES The chromosome comes from Greek Chroma = color CHROMOSOME Soma= body (the colored body) Chromosomes are act as factors which distinguished one species from another. Chromosomes are formed of
CHROMOSOMES The chromosome comes from Greek Chroma = color CHROMOSOME Soma= body (the colored body) Chromosomes are act as factors which distinguished one species from another. Chromosomes are formed of
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Title malignancy. Issue Date Right 209, 12, (2013)
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A case of intracystic apocrine papi malignancy Hayashi, Hiroko; Ohtani, Hiroshi; Y Citation Pathology - Research and Practice, Issue Date 2013-12 URL Right
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A case of intracystic apocrine papi malignancy Hayashi, Hiroko; Ohtani, Hiroshi; Y Citation Pathology - Research and Practice, Issue Date 2013-12 URL Right
A morphometric analysis of nucleoli in cultured carcinoma cells of the human thyroid
 Analytical Cellular Pathology 16 (1998) 131 140 131 IOS Press A morphometric analysis of nucleoli in cultured carcinoma cells of the human thyroid Lars Andersen a,, Lars Kayser a, Niels Keiding b and Jens
Analytical Cellular Pathology 16 (1998) 131 140 131 IOS Press A morphometric analysis of nucleoli in cultured carcinoma cells of the human thyroid Lars Andersen a,, Lars Kayser a, Niels Keiding b and Jens
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1
 Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Continuous Cell Culture From a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. I. Propagation and Presence of Philadelphia Chromosome 1 LINDA S. LUCAS,2 JACQUELINE J. K..WHANG,3 J. H. TJIO,4 ROBERT A. MANAKER,2
Overview of the CELL CYCLE
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
A. Incorrect! All the cells have the same set of genes. (D)Because different types of cells have different types of transcriptional factors.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP. Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest
 USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
USCAP 2012: Companion Meeting of the AAOOP Vancouver BC, Canada, March 17, 2012 Update on lacrimal gland neoplasms: Molecular pathology of interest Valerie A. White MD, MHSc, FRCPC Department of Pathology
Yara shwabkeh. Osama Alkhader. Heba Kalbouneh
 2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
2 Yara shwabkeh Osama Alkhader Heba Kalbouneh CELL OVERVIEW -Note ; the important thing is to know how the organelles appear under the microscope - the stains we usually use in Histology are composed of
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad
 Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Anaplastic Pilocytic Astrocytoma: The fusion of good and bad Alexandrina Nikova 1, Charalampos-Chrysovalantis Chytoudis-Peroudis 2, Penelope Korkolopoulou 3 and Dimitrios Kanakis 4 Abstract 5 Pilocytic
Recent studies demonstrated that nucleoli are
 2006_02.qxd 7-07-2008 12:15 Pagina 119 ORIGINAL PAPER On the nucleolar size and density in human early granulocytic progenitors, myeloblasts K. Smetana, H. Klamová, D. Mikulenková, M. Pluskalová, Z. Hrkal
2006_02.qxd 7-07-2008 12:15 Pagina 119 ORIGINAL PAPER On the nucleolar size and density in human early granulocytic progenitors, myeloblasts K. Smetana, H. Klamová, D. Mikulenková, M. Pluskalová, Z. Hrkal
Chapter 8. The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance. Lecture by Mary C. Colavito
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
05. NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGIONS
 CHAPTER 05 05. NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGIONS 5.1 Introduction The nucleolar organizers are the chromosomal sites, where the genes for ribosomal RNA (rrna) are located. Organization of genes for ribosomal
CHAPTER 05 05. NUCLEOLUS ORGANIZER REGIONS 5.1 Introduction The nucleolar organizers are the chromosomal sites, where the genes for ribosomal RNA (rrna) are located. Organization of genes for ribosomal
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas
 The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas Stefan Prokop, MD Neuropathology Fellow Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Background
The New WHO Classification and the Role of Integrated Molecular Profiling in the Diagnosis of Malignant Gliomas Stefan Prokop, MD Neuropathology Fellow Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Background
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Utility of Modified Cell Block Technique in Cases of Pleural Effusion Suspected of Malignancy
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Utility of Modified Cell Block Technique in Cases of Pleural Effusion Suspected of Malignancy
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
J.K. Das and A.R. Khuda-Bukhsh 284
 J.K. Das and A.R. Khuda-Bukhsh 284 Preponderance of GC-rich sites in silver-stained nucleolus organizing regions of Rita rita (Hamilton) and Mystus gulio (Hamilton) (Bagridae, Pisces), as revealed by chromomycin
J.K. Das and A.R. Khuda-Bukhsh 284 Preponderance of GC-rich sites in silver-stained nucleolus organizing regions of Rita rita (Hamilton) and Mystus gulio (Hamilton) (Bagridae, Pisces), as revealed by chromomycin
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Assessment of the distribution of AMG positive material in the brain of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2009 Assessment of the distribution
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange University of Tennessee Honors Thesis Projects University of Tennessee Honors Program 5-2009 Assessment of the distribution
