Intrinsic innervation in the intestine of the lizard Podarcis hispanica
|
|
|
- Silvester Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Intrinsic innervation in the intestine of the lizard Podarcis hispanica C. Martinez-Ciriano, C. Junquera, T. Castiella, E. Gomez-Barrena, J. Aisa and J. Blasco Department of Morphological Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Zaragoza, Spain Summary. The aim of this study was the description of the morphology and distribution of nerve structure elements in the intestine of the lizard Podarcis hispanica using different histochemical methods; namely acetylcholinesterase (AChE), formol-induced fluorescence for catecholamines (FIF), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase (NADPH-d), and immunohistochemistry for vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), as well as substance P (SP) and electron microscopy. The AChE method showed fibres in the myenteric and submucosal plexus, with a higher fibre density in the large intestine. The highest number of related neurons was located in the myenteric plexus ganglia. Noradrenergic innervation was distributed through the myenteric and submucosal plexus, and also around blood vessels, with the highest fibre density in the large intestine. VIP immunohistochemistry showed a wide distribution of positive fibres throughout the intestine, although the highest density was again detected in the large intestine. Small positive cells for VIP were located at internodal segments in the plexus. SP labeling, although subtle, was present all along the intestine. It showed delicate varicose nets and few fibres innervating blood vessels. Small positive cells for SP were located in the large intestine. The indirect method to detect nitric oxide (NO)-producing system showed neural cells in the myenteric plexus ganglia of the large intestine. Electron microscopy showed ganglion neurons with scattered chromatin condensations, glial cells with higher electron density, and axons with varicosities occupied by different vesicles. We also identified certain cells as interstitial cells of Cajal due to their ultrastructural features. They were mostly located in the region of the myenteric plexus. Key words: Histochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, Ultrastructure, Enteric nervous system, Reptilia Offprint requests to: Dra. C. Martinez-Ciriano, Departamento de Ciencias Morfolbgicas, Facultad de Medicina, C1 Domingo Miral sln Zaragoza, Spain. Fax: carmar@ Introduction The enteric nervous system (ENS) can be defined as a tertiary division in the autonomic nervous system, because of its anatomic and functional independence from the central nervous system. The crucial role of the ENS in the regulation of digestive functions has been frequently stressed (Gershon, 1990; Gershon and Wade, 1993). Unfortunately, ENS-regulated behavior is highly complex, and its microcircuits have not been elicited (Costa and Brookes, 1994; Gershon and Wade, 1994). Considering that phylogenetic studies may help us understand it and following our ENS studies in amphibians (Junquera et al., 1986, 1987a,b, 1988), we focused on the reptilian ENS. References to intestinal extrinsic innervation in reptiles are scarce. The vagus nerve innervates the anterior region of the digestive system, but we do not even know if it spreads further than the stomach. In Trachydosaurus rugosus (Lacertidae), splachnic nerve stimulation reached the intestine to originate a contraction that was not inhibited by adrenergic and cholinergic antagonists. This supported a nonadrenergic, non-cholinergic (NANC) innervation (Burnstock, 1972; Sneddon et al., 1973; Berger and Burnstock, 1979). Studies on the intestinal ENS in reptilian species are incomplete. There was no detailed morphological description of the reptilian intestinal plexus until This was performed in a chelonian species using antiserum raised against neuron-specific enolase (NSE) (Timmermans et a1.,1991). Intestinal adrenergic innervation was previously studied in the reptile Trachydosaurus rugosus by Read and Burnstock (1968). Yung et al. (1965) studied peristalsis in the turtle intestine, and concluded that this reflex would be mostly myogenic, as distension alone would not be a sufficient stimulus to initiate peristalsis. When considering peptidergic innervation, available data are partial or even contradictory. Reinecke et al. (1981) described VIP immunoreactivity in enteric nerves and endocrine cells of Lacerta viridis. Buchan et al. (1983) described fourteen neuropeptides in the digestive system of
2 Intrinsic innervation of a reptilian intestine i I l l Alligator mississipiensis, within endocrine cells, neural bodies, and neural fibres. Bottcher et al. (1985) found PYY-like peptides in the central and peripheral nervous system of the turtle. Masini (1986) located the neuropeptide VIP only in the small intestine in vipers, within nerve terminals and body cells. Holmgren et al. (1989) found bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the crocodile ileum and colon, within neural fibres and cell bodies. Ohtani et al. (1989) showed positive immunoreactivity for calcitonin gene-related-peptide (CGRP) in the reptilian small intestine In the midgut of the turtle (Pseudemys scripta elegans), Gabriel et al. (1990) described the presence of neuropeptide Y (NPY), mostly in the myenteric plexus. The same species has been investigated for the occurrence of immunoreactivity to nine neuropeptides of the gastrointestinal tract (Scheuermann et al., 1991). Lamanna et al. (1999b) showed the distribution of galanin immunoreactive neurons (GALIIR) in the gastrointestinal tract of the lizard Podarcis S. siculu. Few references focus on neuronal NO studies in non-mammal vertebrates, such as fishes (Li and Furness, 1993; Green and Campbell, 1994; Olsson and Karila, 1995; Bruning et al., 1996), amphibian (Li et al., 1992, 1993; Murphy et al., 1994; Williams and Pearson, 1997), reptiles (Bruning and Wehrenfenning, 1997; Lamanna et al., 1999a; Olsson and Gibbins, 1999), and birds (Boros et al., 1994; Li et al., 1994; Balaskas et al., 1995). Finally, there is a surprising absence of detailed electron microscopy descriptions of the intestine ENS in reptiles. The aim of this study was to ascertain the neurochemical and ultrastructural pattern of gastrointestinal innervation in Class Reptilia, specifically in the lizard Podarcis hispanica. This might further our understanding of ENS evolution in the phylogenetic scale. In this study, we describe the intrinsic innervation of small and large intestines. Materials and methods We used twenty adult lizards Podarcis hispanica (Reptilia). The animals (12 males and 8 females) were collected in spring, summer, and autumn. They were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, under ether anesthesia. We studied the basic histology of the small and large intestine wall, in sections stained with haematoxylineosin or semi-thin sections with methylene blue. Acetylcholinesterase method (AChE) We adapted the method of El-Badawi and Schenk (1967), and Qayyum and Fatani (1985). Intestine samples of about 5 mm in length were longitudinally dissected, pinned on cork sheets and immersed in a 2% glyoxylic acid (ph 7) solution, for 5 to 30 minutes at room temperature. The tissue was then delaminated, to expose both the myenteric and the submucosal plexus, and postfixed in a 10% solution of formaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at ph 7, for 30 minutes. After washing in distilled water, samples were incubated in AchE-specific medium. Optimal cholinesterase activity was obtained after incubating periods of 1-2 hours. Tissue samples were then dehydrated through a graded ethanol series, cleared in xylene, and mounted with DPX. Formol-induced fluorescence (FIF) for catecholamines We applied the method of Furness and Costa (1975), adapted for wholemount preparations. Tissue samples were prepared as described above. Once the intestine (large or small) wall was delaminated, both tissue sheets were stretched on a slide and exposed to paraformaldehyde vapors (1-3 hours at 80 'K). Samples were visualized through a Leitz-Orthoplan Fluorescence microscope, and checked for apple green (noradrenaline) or yellow (histamine and serotonine) fluorescence. lmmunohistochemistry for vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and substance P (SP) We followed the method of Costa et al. (1980) with minor modifications, to visualize the plexus threedimensionally within "in toto" samples. Specimens were stretched and pinned on fine cork sheets. Fixation was made by immersion for 18 hours in a 15% picric acidsaturated solution with 2% formaldehyde in 0.1M PBS (ph 7.3), at 4 T. After 30 minutes washing in 80% ethanol, samples were dehydrated with graded ethanol, and cleared in xylene. Samples were then rehydrated back to PBS and delaminated. We applied rabbit antiserum to both exposed surfaces, and incubated the tissue in a humid chamber for 16 hours at room temperature. After 3 washes in PBS, samples were incubated for 1 hour with a secondary antibody: goat anti-rabbit IgO conjugated to fluorescein-isothiocyanate (GAR-FITC) (Sigma), then washed in PBS for 15 minutes, mounted in glycerine at a 3:l dilution in PBS, and kept under pressure overnight. Rabbit antiserum (INCSTAR, Stillwater, MN, USA) dilutions in PBS (ph ) were 1:200 (VIP), and 1:800 (SP). Controls were performed by absorbing the anti-vip and anti-sp antibodies with an excess of the respective antigens with PBS in the specific step. Controls were negative. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase (NADPH-d) histochemistry We applied a method adapted from Scherer-Singler et al. (1983). Portions of both small and large intestine were obtained and incised longitudinally. Tissue samples were stretched and pinned on fine cork sheets, prior to fixation. Immersion fixation was performed for 1 hour in a solution of 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1M PBS, ph 7.4, at 4 "C. At this stage, delamination was performed. We removed the mucosa, submucosa and inner muscular layer, exposing contact surfaces between circular and longitudinal muscle coating. We then treated specimens
3 Intrinsic innervation of a reptilian intestine for NADPH-diaphorase histochemistry for 30 minutes, using 0.25 mgr/ml Nitroblue tetrazolium (Sigma), 1 mgrlml B-NADPH (Sigma), and 0.5% Triton X-100 in 0.1M Tris buffer (ph 7.6), at 37 The reaction was stopped by rinsing the tissue in 0.1M PBS. The tissue was dehydrated and then mounted with DPX. In control experiments, the substrate B-NADPH was omitted from the reaction mixture and no positive staining was observed. The reaction product of NADPH-diaphorase appeared as a bluelviolet staining of different intensities. Electron microscopy (EM) We applied standard electron microscopy methods, including fixation in 2.5% glutaradehyde in Milloning buffer (ph 7.3), postfixation in 2% osmium tetroxide, staining with 7% uranyl acetate, dehydration and araldite embedding. Ultrathin sections were contrast-stained following conventional methods. Results AChE reaction We found a wide distribution of AchE-positive elements throughout the intestine. The large intestine showed the highest density of labelled fibres. The myenteric plexus was arranged in regular networks of elongated, polygonal shape. The long axis of these polygons followed the craniocaudal direction of the intestine. Ganglia of pyramidal or trapezoidal shape were located in the nodes of this network (Fig. la,b). In the largest ganglia, the number of neurons ranged from 6 to 12. Scattered neurons were frequently seen within interconnection tracts. These neurons were pyramidal and of variable size. The nucleus was oval. It was prominent and centrally located, within a moderate or even scarce cytoplasm. Networks forming the submucosal plexus were parallel to the vascular tree, and were particularly dense along the ileum (Fig. lc). AchE-positive fibre bundles were thinner than those in the myenteric plexus. Small ganglia containing 3 to 4 AchE-positive neurons (Fig. Id) were located at fibre intersections. Isolated neurons were also frequent, with similar morphology to that described above for myenteric plexus neurons. A second type of AchE-positive cells was observed in the submucosal plexus. These were bipolar, elongated cells, with a narrow, oval nucleus. These morphological features identified them as interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) (Fig. le). FIF reaction The myenteric plexus showed a wide catecholaminepositive reaction, especially in the large intestine. Polygonal networks of intensely fluorescing varicose nerve fibres were found in the circular muscle layer (Fig 2a). Ganglia in the myenteric plexus were surrounded by multiple fluorescent fibres. We did not observe any positive cell bodies in these myenteric ganglia. Innervation around blood vessels was profuse, arranged in their own plexus. Although close, this was separate from the above-mentioned myenteric primary plexus (Fig. 2b). A rich perivascular catecholaminergic innervation was present in the submucosa and mucosa. This was particularly remarkable in the basal zone of the mucosa, where the vascular network was highly innervated (Fig. 2c). Networks in the submucosal plexus included thin varicose fibres that progressed across the submucosa to innervate glandular bases within the mucosa.. VIP lmmunoreactivity We were able to observe a wide VIP-positive reaction in every intestinal segment of Podarcis hispanica. The large intestine again showed a higher density of VIP-ergic fibres. The primary myenteric plexus was formed by wide networks of varicose fibres (Fig. 3a). We observed VIP-positive immunoreactivity in the ganglia located at the primary plexus junctions. Nerve fascicles that contained immunoreactive fibres, originated at those ganglia. Small VIP-positive cells could be seen at internodal segments of the plexus network. Thin parallel fibrils followed the direction of muscle fibres in the inner muscle layer, and formed a delicate tertiary plexus (Fig. 3b). These fibres emerged perpendicular to the primary plexus, in a different focus plane. We did not observe VIP-ergic innervation surrounding blood vessels. SP lmmunoreactivity SP immunoreactivity was quantitatively less than VIP immunoreactivity. However, positive reaction was present in every intestinal segment. Positive fibres were arranged in slender varicose networks. These formed the main plexus, shaped in elongated polygonal networkss (Fig. 4a). Ganglia showing scarce immunoreactivity were found at the vertex of network polygons (Fig. 4b). We only observed SP-positive neurons in the large intestine, where small neurons with scarce cytoplasm were located among the myenteric plexus. Thin varicose fibres, that originated in this plexus were in the circular muscle layer. Some positive fibres innervated blood vessels. NADPH-d reaction We were able to observe a wide array of NADPH-dpositive structures, including epithelia1 cells, neural elements, and blood vessels. Isolated positive neuronal bodies were frequent at the myenteric plexus of the small intestine. However, in the large intestine, positive neurons were located in ganglia (8-10 cells). Positive neurons were also present along the plexus interconnection tracts (Fig. 5a).
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Organization of the innervation of the oesophagus and stomach in chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger, Molina)
 FOLIA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOBIOLOGICA Vol. 51, No. 2, 2013 pp. 115 120 original study Organization of the innervation of the oesophagus and stomach in chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger, Molina) Elzbieta Nowak
FOLIA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOBIOLOGICA Vol. 51, No. 2, 2013 pp. 115 120 original study Organization of the innervation of the oesophagus and stomach in chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger, Molina) Elzbieta Nowak
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Invited Revie W. Hirschsprung's disease - immunohistochemical findings. Histology and H istopathology
 Histol Histopath (1 994) 9: 615-629 Histology and H istopathology Invited Revie W Hirschsprung's disease - immunohistochemical findings L.T. Larsson Department of Pediatric Surgery, University of Lund,
Histol Histopath (1 994) 9: 615-629 Histology and H istopathology Invited Revie W Hirschsprung's disease - immunohistochemical findings L.T. Larsson Department of Pediatric Surgery, University of Lund,
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
The autonomic innervation of the liver and gallbladder of Rana ridibunda
 Histol Histopath (1 989) 4: 405-41 0 Histology and. Histopathology The autonomic innervation of the liver and gallbladder of Rana ridibunda M.J. Azanzal, J. Aisal, C. Junqueral and T. Castiella2 'Catedra
Histol Histopath (1 989) 4: 405-41 0 Histology and. Histopathology The autonomic innervation of the liver and gallbladder of Rana ridibunda M.J. Azanzal, J. Aisal, C. Junqueral and T. Castiella2 'Catedra
Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine
 Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System
 2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
Eliades, Erlandson, Ruiz UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVII (2014)
 Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER
 ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Overview of digestion
 Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall
 Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D.
 Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Gastrointestinal Motility 2: Intestinal and Colonic Motility Jack Grider, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Contrast the types of motility in the small intestine. 2. Describe the neural circuits that mediate peristalsis.
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach
 J. Vet. Sci. (2006),G7(4), 315 319 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach Heungshik
J. Vet. Sci. (2006),G7(4), 315 319 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach Heungshik
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 4, 254 259 DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL Summary I. S. STEFANOV
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 4, 254 259 DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL Summary I. S. STEFANOV
T he enteric nervous system controls the function of the
 70 INTESTINAL MOTILITY Cholinergic and nitrergic inter in the myenteric plexus of the human colon A J Porter, D A Wattchow, SJHBrookes, M Costa... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
70 INTESTINAL MOTILITY Cholinergic and nitrergic inter in the myenteric plexus of the human colon A J Porter, D A Wattchow, SJHBrookes, M Costa... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Autonomic Regulation of The Cardiovascular system. Cardiac
 Autonomic Regulation of The Cardiovascular system. Cardiac 1. Components of Regulation. 2. Autonomic Component. 3. Receptors. 4. Cardiac, Vascular (Systemic Pulm). 5. Comparative (anatomy). 6. Assessment.
Autonomic Regulation of The Cardiovascular system. Cardiac 1. Components of Regulation. 2. Autonomic Component. 3. Receptors. 4. Cardiac, Vascular (Systemic Pulm). 5. Comparative (anatomy). 6. Assessment.
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion
 Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion Implications for health and disease Billy & Bree Paper 1: Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion : Implications for health and disease By Team BBB
Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion Implications for health and disease Billy & Bree Paper 1: Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion : Implications for health and disease By Team BBB
MAST-CELLS are present in the digestive tract of all classes of vertebrates
 The Distribution of Mast-Cells in the Digestive Tract of Laboratory Animals: Its Bearings on the Problem of the Location of Histamine in Tissues By I. MOTA, A. G. FERRI, AND S. YONEDA 251 (From the Laboratory
The Distribution of Mast-Cells in the Digestive Tract of Laboratory Animals: Its Bearings on the Problem of the Location of Histamine in Tissues By I. MOTA, A. G. FERRI, AND S. YONEDA 251 (From the Laboratory
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
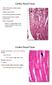 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Nitrinergic and peptidergic innervation of the
 1 690 Gut 1994; 35: 1690-1696 PAPERS Division of Gastroenterology, William S Middleton VA Hospital, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Wisconsin, USA C Singaram M A Sweet Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology
1 690 Gut 1994; 35: 1690-1696 PAPERS Division of Gastroenterology, William S Middleton VA Hospital, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Wisconsin, USA C Singaram M A Sweet Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology
H irschsprung s disease (HD) is a congenital disorder
 712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS
 Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
Three-Dimensional Morphology of c-kit Positive Cellular Network and Nitrergic Innervation in the Human Gut
 Three-Dimensional Morphology of c-kit Positive Cellular Network and Nitrergic Innervation in the Human Gut Laszlo Nemeth, MD; Prem Puri, MS, FRCS, FRCS(Ed) Context. c-kit positive interstitial cells of
Three-Dimensional Morphology of c-kit Positive Cellular Network and Nitrergic Innervation in the Human Gut Laszlo Nemeth, MD; Prem Puri, MS, FRCS, FRCS(Ed) Context. c-kit positive interstitial cells of
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
General principles of gastrointestinal motility
 General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
General principles of gastrointestinal motility OBJECTIVES Physiological anatomy General Principles Circulation of blood through the GIT organs Control of all GIT functions by local, nervous, and hormonal
Purinergic Neuron-to-Glia Signaling in the Enteric Nervous System Dr. Brian D. Gulbransen
 1 Assistant Professor Neuroscience Program and Department of Physiology Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan USA The requirement to nourish and sustain an organism, as well as to defend it
1 Assistant Professor Neuroscience Program and Department of Physiology Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan USA The requirement to nourish and sustain an organism, as well as to defend it
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon
 The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon ARTHUR G. WEINBERG, M.D. The Children's Hospital of Akron and Case-Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Akron, Ohio
The Anorectal Myenteric Plexus: Its Relation to Hypoganglionosis of the Colon ARTHUR G. WEINBERG, M.D. The Children's Hospital of Akron and Case-Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Akron, Ohio
Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Insulin and the brain. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Insulin and the brain Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD 1921 Banting & Macleod Nobel Prize 1923 White, M. F. (2003) Science Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L. and Stryer, L. (2007) Biochemistry
Insulin and the brain Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD 1921 Banting & Macleod Nobel Prize 1923 White, M. F. (2003) Science Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L. and Stryer, L. (2007) Biochemistry
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Nitrergic Hyperinnervation in Appendicitis and in Appendices Histologically Classified as Normal
 Nitrergic Hyperinnervation in Appendicitis and in Appendices Histologically Classified as Normal Laszlo Nemeth, MD; Udo Rolle, MD; Denis J. Reen, MSc, PhD; Prem Puri, MS, FRCS Context. The pathogenesis
Nitrergic Hyperinnervation in Appendicitis and in Appendices Histologically Classified as Normal Laszlo Nemeth, MD; Udo Rolle, MD; Denis J. Reen, MSc, PhD; Prem Puri, MS, FRCS Context. The pathogenesis
AN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE INTERSTITIAL CELLS OF CAJAL (ICCS) IN THE DOG INTESTINAL TRACT
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 11(2) 2865-2871 (2011) ISSN: 0974-0910 (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article AN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE INTERSTITIAL CELLS OF CAJAL
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 11(2) 2865-2871 (2011) ISSN: 0974-0910 (Available online at www.tcrjournals.com) Original Article AN IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE INTERSTITIAL CELLS OF CAJAL
Junctional Tissues of Human Heart
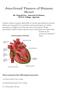 1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom
 Journal of Neurocytology z, 465-469 (I973) Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom R. C. HAMILTON 1 and P. M. ROBINSON~ 1Commonwealth
Journal of Neurocytology z, 465-469 (I973) Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom R. C. HAMILTON 1 and P. M. ROBINSON~ 1Commonwealth
HRP cytochemistry. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, Heidelberg, Germany
 HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
HRP cytochemistry WOLF D. KUHLMANN, M.D. Division of Radiooncology, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany A range of substrates is available for the cytochemical staining of peroxidase
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D
 Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the general organization of the gut. 2. Identify the levels of neural control and describe the interaction
Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the general organization of the gut. 2. Identify the levels of neural control and describe the interaction
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
The B-cell leukemia/lymphoma-2 (bcl-2) gene is a protooncogene
 Expression of in Enteric Neurons in Normal Human Bowel and Hirschsprung Disease Tomas Wester, MD, PhD; Yngve Olsson, MD, PhD; Leif Olsen, MD, PhD Objective. The protein has the functional role of blocking
Expression of in Enteric Neurons in Normal Human Bowel and Hirschsprung Disease Tomas Wester, MD, PhD; Yngve Olsson, MD, PhD; Leif Olsen, MD, PhD Objective. The protein has the functional role of blocking
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Intussuception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor with neural differentiation in a patient with. Von Recklinghausen Neurofibromatosis,
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol 31/ No.4 /2001 Intussuception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor with neural differentiation in a patient with Von Recklinghausen Neurofibromatosis (NF-1): A case report
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol 31/ No.4 /2001 Intussuception due to gastrointestinal stromal tumor with neural differentiation in a patient with Von Recklinghausen Neurofibromatosis (NF-1): A case report
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Reciprocal activity of longitudinal and circular. muscle during intestinal peristaltic reflex. Am J
 Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284: G768 G775, 2003; 10.1152/ajpgi.00384.1998. Reciprocal activity of longitudinal and circular muscle during intestinal peristaltic reflex J. R. Grider Departments
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284: G768 G775, 2003; 10.1152/ajpgi.00384.1998. Reciprocal activity of longitudinal and circular muscle during intestinal peristaltic reflex J. R. Grider Departments
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Development of Nitric Oxide Synthase-Immunoreactive Nerves in the Cerebral Arteries of the Rat
 FULL PAPER Anatomy Development of Nitric Oxide Synthase-Immunoreactive Nerves in the Cerebral Arteries of the Rat Koichi ANDO 1), Yoshikazu MISHIMA 1) and Mamoru SAKAI 1) 1) Biological Laboratory, Department
FULL PAPER Anatomy Development of Nitric Oxide Synthase-Immunoreactive Nerves in the Cerebral Arteries of the Rat Koichi ANDO 1), Yoshikazu MISHIMA 1) and Mamoru SAKAI 1) 1) Biological Laboratory, Department
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2008; 12(Suppl 1): 3-19 Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility M. COSTA, S.H. BROOKES Department of Physiology
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2008; 12(Suppl 1): 3-19 Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility M. COSTA, S.H. BROOKES Department of Physiology
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
What part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is composed of striated muscle and smooth muscle?
 CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
CASE 29 A 34-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with the complaint of increased difficulty swallowing both solid and liquid foods. He notices that he sometimes has more difficulty when
,. 1\)... ubj«pcl: Doclo1: M. Khatatbeh Handout # 1 8/4/ Gastreintestinal System. Lecture#: 1. Gastrointestinal Physiology
 Lecture#: 1 Mc:di
Lecture#: 1 Mc:di
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
8.2. Types of Neurons
 Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor
 An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor Geoffrey Rolls Leica Microsystems, iosystems Division, Melbourne,
An Evaluation of Xylene-free Processing of Tissues From the Central Nervous System Using the PelorisTM Dual Retort Rapid Tissue Processor Geoffrey Rolls Leica Microsystems, iosystems Division, Melbourne,
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module. 1) Connective tissue
 D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
 1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
1. GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY FOOD INGESTION Ingested foodstuff contributes to an increase in the overall weight of the animal, but does not become an integral part of the structure or metabolic activities
Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach
 Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach Narbada Saini and Madhur Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh 160012 India Corresponding author:
Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach Narbada Saini and Madhur Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh 160012 India Corresponding author:
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology
 The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
The Autonomic Nervous System Outline of class lecture for Physiology 1 After studying the endocrine system you should be able to: 1. Describe the organization of the nervous system. 2. Compare and contrast
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation of CNS blood flow
 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Dr. Randy Gollub HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation
HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology Dr. Randy Gollub HST-583 Cerebrovascular anatomy and neural regulation
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS):
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): ANS is the major involuntary, unconscious, automatic portion of the nervous system. involuntary voluntary The motor (efferent)portion of the ANS is the major pathway for
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
Morphometry and acetylcholinesterase activity of the myenteric plexus of the wild mouse Calomys callosus
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) : 627-632 Myenteric plexus in the wild mouse ISSN -879X 627 Morphometry and acetylcholinesterase activity of the myenteric plexus of the wild
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) : 627-632 Myenteric plexus in the wild mouse ISSN -879X 627 Morphometry and acetylcholinesterase activity of the myenteric plexus of the wild
