Role of Shunt Surgery in Pediatric Tubercular Meningitis with Hydrocephalus. Deepak Agrawal, Aditya Gupta and V. S. Mehta
|
|
|
- Branden Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Reports Role of Shunt Surgery in Pediatric Tubercular Meningitis with Hydrocephalus Deepak Agrawal, Aditya Gupta and V. S. Mehta From the Department of Neurosurgery, Neurosciences Center, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi , India Correspondence to Prof. V.S. Mehta, Head, Department of Neurosurgery and Gamma Knife Surgery, Neurosciences Center, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi , India. Manuscript received: December 2, 2003, Initial review completed: December 23, 2003; Revision accepted: July 28, This study was designed to evaluate the indications for ventriculoperitoneal shunting in cases of children with tubercular meningitis, presenting with hydrocephalus. Thirty seven children (less than 18 years of age) of tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus (TBMH) who underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunting over a three year period (1999 to 2001) were included in the study. Sixteen (43%) children were Palur stage II, 15 (40%) stage III, and 6 (16%) stage IV. Fifteen (40%) children had received antitubercular therapy for less than 4 months and 17 (46%) received therapy for more than 4 months prior to presentation. Five (14%) children had not previously received antitubercular therapy. Shunt related complications occurred in 11 (30%) children and 3 children had undergone revision of the shunt multiple times. Good outcome was seen in 16 (43%) children. Thirteen (35%) had moderate disability and 6 (16%) had severe disability at 3 months of follow up. 62% (n =10) children in grade II had a good outcome compared to 40% (n = 6) in grade III. All six children in grade IV had a poor outcome. 2 children, both having multiple infarcts, died and the remaining 4 were left with severe disability. We recommend shunt placement in all children of grade II and III TBMH as this policy has yielded the best results. For grade IV children external ventricular drainage, followed by shunting if improvement occurs remains the most cost-effective procedure. Key words: Hydrocephalus, Tubercular meningitis, Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. THE indications and timing of surgical intervention for tubercular meningitis associated hydrocephalus (TBMH) remain controversial, and only few studies have tried to address this issue previously(1-9). Although previous studies have shown age to be an independent prognostic factor in TBMH, there are very few studies dedicated to the pediatric population(1,2). The general tendency is to avoid shunting in this age group, due to its attendant complications, besides the risk of making the child shunt dependent. Shunt malfunction is also very common in children and is related partly to the CSF protein content, which may be very high in the majority of the cases. In this study we retrospectively analyzed the outcome in 37 children with Palur grade II to grade IV TBMH managed with ventriculoperitoneal shunting. Subjects and Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on children (less then 18 years of age) with INDIAN PEDIATRICS 245 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
2 TBMH who underwent placement of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt in the Department of Neurosurgery at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, between January 1999 and December The diagnosis of TBM was made on the basis of typical clinical, radiological and CSF features, as well as positive sputum or CSF culture wherever possible. Children were graded according to the grading system devised by Palur, et al.(9) (Table I), and only grade II to grade IV children were considered for this study. All children received standard four drug antitubercular therapy (consisting of rifampicin, ethambutol, isoniazid and pyrazinamide) according to body weight. Steroids were given only if CT showed thick basal exudates and / or there was evidence of infarct(s). Children presenting in Palur Grade II and III (having a neurological deficit or altered sensorium) underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement, as soon as the diagnosis of TBMH was established. Postoperatively, active chamber pressing was initiated, which was continued till patient s clinical condition stabilized. An external ventricular drain TABLE I Grading system (Palur, et al.) (9) Grade Description I. 1. Headache, vomiting, fever, and/or neck stiffness 2. No neurological deficit. 3. Normal sensorium. II. 1. Normal sensorium. 2. Neurological deficit present. III.1. In altered sensorium but easily arousable. 2. Dense neurological deficit may or may not be present. IV.1. Deeply comatose. 2. Decerebrate or decorticate posturing (EVD) was placed in grade IV children for 48 hours and only those children who showed neurological improvement during this period were taken up for shunt surgery. Children were followed up on OPD basis regularly and evaluated regarding their scholastic performance and ability to perform daily activities. Based on these parameters the children s outcome was graded into five outcome groups using the Glasgow outcome scale (GOS)(10). Results Thirty-seven children underwent ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement for TBMH during the study period. Their age ranged from one year to 18 years with a mean of years. There were 25 males and 12 females. Sixteen (43%) cases were Palur stage II, 15 (40%) stage III, and 6 (16%) stage IV. Five (14%) children were diagnosed as TBM only after they presented with hydrocephalus and antitubercular therapy was started subsequently, as compared to 15 (40%) children who had received antitubercular therapy for less than four months prior to presentation, and 17 (46%) children who received therapy for more than four months. Fundus findings had been recorded in 19 (51%) children. Amongst them papilloedema was present in 10 (27%), primary optic atrophy in 1 (3%) and secondary optic atrophy in 3 (8%). The fundus was found to be normal in 5 (14%) children. CSF protein content was less then 50 mg% in 12 (32%) children, between 50 mg% and 200 mg% in 13 (36%) children and was greater than 200 mg% in 12 (32%) children. All children had a contrast enhanced CT (CECT) scan of the head which showed marked ventriculomegaly with periventricular ooze in 14 children, mild to moderate hydrocephalus with periventricular ooze in 16 INDIAN PEDIATRICS 246 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
3 children and without periventricular ooze in 7 children. Thick basal exudates were present in 11 children and exudates were absent or minimally present in the remaining 26 children. Interestingly five out of the six grade IV children had thick exudates on CT compared to only six out of the 21 children in grade II or III. Though none of the grade II or III children had infarcts, two children, both in grade IV had multiple infarcts on CT. Shunt related complications occurred in 11 (30%) children and consisted of shunt malfunction (mechanical failure) in 6 (16%) and shunt infection in 5 (14%) children. Three children underwent revision of the shunt more than once (one child had two revisions and two children had three revisions each). The average follow up was nine months with a range of six months to 24 months. Good outcome was seen in 16(43%). Thirteen (35%) had moderate disability and 6 (16%) had severe disability at 3 months of follow up. There was no child in vegetative state. As expected, children in grade II had the best results, with 10 out of 16 children (62%) having a good outcome compared to 40% (n = 6) in grade III. All six children in grade IV had a poor outcome. Two children, both having multiple infarcts, died and the remaining 4 were left with severe disability. Discussion Cairns for the first time made bilateral burr holes for estimation of ventricular size as well as CSF sampling in TBMH in 1951(11). Bhagwati in 1971 described ventriculoatrial shunting in TBMH in 7 patients(6). However, due to fear of miliary spread of the disease, ventriculoatrial shunting has since been replaced by ventriculoperitoneal shunting universally. Lamprecht, et al.(1) recommended shunting in patients only if they failed maximal medical therapy, deteriorated neurologically, or developed obstructive hydrocephalus to reduce shunt related complications. We use Indian shunts (like the Chhabra shunt ) costing Rs (US$ 30) for all shunt procedures and they have proven to be very cost effective in the setting of TBMH. The chamber of the these shunt are also suited for manual pressing invivo, which is important in TBMH as the CSF protein content may be very high in these children, resulting in shunt malfunction. Czosnyka, et al.(12) simulated chamber pressing in a Chhabra medium pressure shunts by the addition of a pulsating waveform of variable amplitude to the proximal pressure (frequency varied from 90 revolutions/min to 5/min) and showed that the lower end of the pressure-flow performance curve consistently shifted to the left (towards lower pressures). Thus chamber pressing results in increased drainage of CSF and may also help in flushing the system off proteinaceous debris, decreasing shunt malfunction rates. Our shunt malfunction rate of 16% is much less than that of other recent studies on TBMH(1,5). This view is however, not shared by all and some feel that the negative pressure applied to the chambers sucks in ventricular fimbria and blocks the shunt(13). The shunt infection rate in our study was 14%, which is similar to other studies(1,5) in TBMH. All the shunts were done on an emergency basis, and this factor could have had a bearing on the increased shunt infection rates. Recently, antibiotic impregnated shunts and ventricular drainage systems have been introduced, which reportedly have a much lower rate of colonization(14,15), but are relatively expensive. We, however, do not have any experience in using such devices. Another likely cause of the high incidence of shunt infection could be the depressed immunity, in such children. Other infective shunt complications such as peritonitis and INDIAN PEDIATRICS 247 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
4 Key Messages Shunt placement is advisable in all children in Palur grade II and III TBMH. For Palur grade IV children external ventricular drainage for 48 hours, followed by shunting if improvement occurs, remains the most cost-effective procedure. pseudocyst formation, mentioned in the literature(13), were not seen in our series. Using multivariate analysis Misra, et al. (16) have shown that hydrocephalus, besides stage of TBM, age and cranial nerve palsies have significant prognostic value in TBM. Other studies have also shown the presence of hydrocephalus to be associated with persistent disability and poor prognosis(5,7). Although communicating hydrocephalus is seen in up to 82% of the cases of TBMH(3), it is the obstructive variety that carries a poorer prognosis. This differentiation is however superfluous if there is a policy (like ours) of shunt placement in all cases of hydrocephalus, irrespective of the fact whether it is obstructive or communicating in nature. Demarcation of hydrocephalus into obstructive and communicative varieties may, in fact, prove counterproductive, as it instills a sense of complacency in treating the communicating variety, as seen in the study by Lamprecht(1). The role of CT scan in evaluating the intracranial pressure is also controversial and periventricular lucencies may be indicative of inflammatory process rather then an increase in intraventricular pressure(5). The reverse is also true and children can have a high intracranial pressure without priventricular lucencies. We have also seen the CSF to be under high pressure on inserting the ventricular end of the shunt, in a number of children who did not have periventricular lucencies on CT scans. Palur, et al.(9), for the first time laid down guidelines for shunt surgery in TBMH. They recommended that grade 1 and grade 2 patients with TBMH are ideal candidates for shunt surgery and poor grade patients (Grade III and IV) should initially undergo external ventricular drainage via a ventriculostomy, and only if clinical improvement occurs in the neurological status within 48 hours, they could be taken up for shunt placement. Although being a seminal study on TBMH, the recommendation of shunt placement in Grade I patients is controversial in view of the fact that only 5 out of their 114 patients with TBMH were in grade 1. We excluded grade I children from our study as their number was small (n = 3) and all had shown improvement on medical therapy (antitubercular therapy with the addition of acetazolamide and furosemide). Also the fact that only three children in palur grade I presented with hydrocephalus is a pointer towards the extremely good prognosis this group. Bullock, et al.(5), did not shunt all patients in grade I and II TBMH, and reserved the procedure for those cases which showed progressive increase in ventricular size on CT in spite of full medical treatment. We, however, shunt all children of grade II and III TBMH, and in grade IV initially an external ventricular drain was put for 48 hours, proceeding to shunting only if there is improvement in neurological status. We keep the EVD for 48 hours as a previous study at our center has shown that the rate of CSF colonization and infection increases dramatically after this period(17). This policy has yielded good results with 62% INDIAN PEDIATRICS 248 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
5 children in grade II and 40% in grade III having good outcome in our series. Role of steroids remains controversial in the treatment of TBM. One Meta analysis involving 595 patients has shown beneficial effects of steroids in TBM(18). Steroids were associated with fewer deaths and a reduced incidence of death and severe residual disability. We therefore add steroids if CT shows thick basal exudates and / or there is evidence of infarct(s). As these findings were seen mainly in grade IV patients, steroids were prescribed in this group. We however could not document any beneficial effect of addition of steroids, as all grade IV children had a poor prognosis. In conclusion we recommend shunt placement in all children of grade II and III TBMH as this policy has yielded the best results. For grade IV children external ventricular drainage, followed by shunting if improvement occurs remains the most costeffective procedure in this group of children. Contributors: DA participated in collection and interpretation of data and drafted the manuscript. AG helped in analysis and final draft of the manuscript. VSM conceptualized and designed the study and shall act as the guarantor. Funding: None. Competing interests: None. REFERENCES 1. Lamrecht D, Schoeman J, Donald P, Hartzenberg H. Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in childhood tubercular meningitis. Br J Neurosurg 2001; 15: Kemaloglu S, Ozkan U, Bukte Y, Ceviz A, Ozates M. Timing of shunt surgery in childhood tuberculous meningitis with hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 2002; 37: Schoeman JF, Laubscher JA, Donald PR. Serial lumbar CSF pressure measurements and cranial computed tomographic findings in childhood tubercular meningitis. Childs Nerv Syst 2000; 16: Bhargava S, Gupta AK, Tandon PN. Tuberculous meningitis-a CT scan study. Br J Radiol 1982; 55: Bullock MRR, Van Dellen JR. The role of cerebrospinal fluid shunting in tubercular meningiis. Surg Neurol 1982; 18: Bhagwati SN. Ventriculoatrial shunt in tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 1971; 35: Schoeman JF, Van Zyl LE, Laubscher JA, Donald PR. Effect of corticosteroids on intracranial pressure, CT findings and clinical outcome in young children with tubercular meningitis. Pediatrics 1997; 99: Gelabert M, Castro-Gago M. Hydrocephalus and tubercular meningitis in children. Child s Nerv Syst 1988; 4: Palur R, Rajshekhar V, Chandy MJ, Joseph T, Abraham J. Shunt surgery for hydrocephalous in tubercular meningitis: A long-term follow up study. J Neurosurg 1991; 74: Jennett B, Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. A practical scale. Lancet 1975; 1: Cairns H. Neurosurgical methods in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Arch Dis Child 1951; 26: Czosnyka Z, Czosnyka M, Richards HK, Pickard JD. Chhabra hydrocephalus shunt: lessons for gravitational valves. Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998; 65: Sarin YK, Saffar M, Sharma AK, Cerebrospinal pseudocyst complicating VP shunt done for hydrocephalus associated with tuberculosis meningitis. Indian J Tuber 1994; 4: Lundberg F, Schliamser S, Ljungh A. Vitronectin may mediate staphylococcal adhesion to polymers exposed to perfusing human cerebrospinal fluid. J Med Microbiol 1997; 46: Hampl J, Schierholz J, Jansen B, Aschoff A. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of a Rifampin-loaded INDIAN PEDIATRICS 249 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
6 silicone catheter for prevention of CSF shunt infections. Acta neurochir (Wien) 1995; 133: Misra UK, Kalita J, Srivastava M, Mandal SK. Prognosis of tubercular meningitis: A multivariate analysis. J Neurol Sci 1996; 137: Gupta A, Mehta VS, Singh VP, Mahapatra AK. Percutaneous ventriculostomy infections: Experience at AIIMS and a review. Neurosciences Today 2001; 5: Prasad K, Volmink J, Menon GR. Steroids for treating tuberculous meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000; 3: CD Correlation of Serum Parathormone Level with Biochemical Parameters in Chronic Renal Failure M.H. Rahman, M.M. Hossain, S. Sultana, C.Y. Jamal and M.A. Karim From the Department of Pediatrics, Pediatric Nephrology Unit, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Shahbagh, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh. Correspondence to: Dr. Md. Habibpur Rahman, Associate Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Pediatric Nephrology Unit, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University, Shahbagh, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh. mhrahman@bdcom.com Manuscript received: December 2, 2003, Initial review completed: December 23, 2003; Revision accepted: July 28, A prospective study was carried out to assay the level of serum intact parathormone and its correlation with biochemical parameters in patients with chronic renal failure (CRF). The study included 64 children (44 with CRF, and 20 age and sex matched controls). Serum intact parathormone (ipth), serum creatinine, urea, calcium, inorganic phosphate and alkaline phosphatase were estimated. Creatinine clearance (Ccr) was estimated by Schwartz formula. Patients with CRF were divided into four groups based on their Ccr (mild CRF with mean Ccr ± 1:18.53 ml/min/1.73 m2 (n = 6) moderate CRF with mean Ccr ± 7.75 ml/min/ m2 (n = 7); severe CRF with mean Ccr ± 5.40 ml/min/1.73 m2 (n =15); and end-stage renal disease with mean Ccr 6.46 ± 1.71 ml/min/1.73 m2 (n = 16). Mean serum ipth levels were ± pg/ml in CRF and ± 9.35 pg/ml in controls. Groupwise mean serum (ipth) levels were ± 4.76, ± 7.91, ± 9.67 and ± pg/ml in mild, moderate, severe CRF and end-stage renal failure respectively. Mean serum ipth level of CRF (93.00 ± pg/ ml) negatively correlated with mean Ccr (22.02 ± ml/min/l.73 m2) (P <0.001) and mean serum calcium (7.30 ± 1.02 mg/dl) (P<0.001) and positively correlated with mean inorganic phosphate (5.76 ± 1.1 mg/dl) (P<0.05) and mean alkaline phosphatase ( ± UL) (P <0.001). We conclue that increased ipth level occur even early in the course of CRF and progressive hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia are the initiating factors for the development of hyperparathyroidism. Keywords: Chronic renal failure, Hyperparathyroidism, Parathormone CHRONIC renal failure (CRF) produces a number of abnormalities of calcium and phosphorus metabolism. Secondary hyperparathyroidism develops early in the course of chronic renal insufficiency(1), even at the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of ml/ min/1.73 m 2 (2). It is generally thought to result from hypocalcemia as a result of INDIAN PEDIATRICS 250 VOLUME 42 MARCH 17, 2005
Tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus with HIV co-infection: role of cerebrospinal fluid diversion procedures
 clinical article J Neurosurg 122:1087 1095, 2015 Tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus with HIV co-infection: role of cerebrospinal fluid diversion procedures Raman Mohan Sharma, MBBS, MCh, Nupur Pruthi,
clinical article J Neurosurg 122:1087 1095, 2015 Tubercular meningitis with hydrocephalus with HIV co-infection: role of cerebrospinal fluid diversion procedures Raman Mohan Sharma, MBBS, MCh, Nupur Pruthi,
Infusion studies in clinical practice. Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London
 Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
VALUE OF CT SCAN IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MENINGITIS. Rashmi Kumar, N. Kohli, H. Thavnani, A. Kumar and B. Sharma
 Original Articles M VALUE OF CT SCAN IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MENINGITIS Rashmi Kumar, N. Kohli, H. Thavnani, A. Kumar and B. Sharma From the Departments of Pediatrics and Radiodiagnosis, King George's Medical
Original Articles M VALUE OF CT SCAN IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MENINGITIS Rashmi Kumar, N. Kohli, H. Thavnani, A. Kumar and B. Sharma From the Departments of Pediatrics and Radiodiagnosis, King George's Medical
Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt
 Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
Cryptococcal Meningitis
 Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature
 Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature Mohamad Bakhaidar Division of Neurological Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz
Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature Mohamad Bakhaidar Division of Neurological Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz
Researcher 2018;10(3)
 Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Comparative study between frontal and posterior parietal ventriculo-peritoneal shunts in management of hydrocephalus Prof. Dr. Abdelhalim Moasa, Dr. Mohamed Hasan and Mohamed Abdelrazek Department of Neurosurgery,
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Predictors of long-term neurological sequelae of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis
 European Journal of Neurology 2007, 14: 33 37 doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01534.x Predictors of long-term neurological sequelae of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis J. Kalita, U. K. Misra
European Journal of Neurology 2007, 14: 33 37 doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01534.x Predictors of long-term neurological sequelae of tuberculous meningitis: a multivariate analysis J. Kalita, U. K. Misra
Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey. Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center
 Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center Past, present and future Past, present and future Cerebral Blood Flow Past, present and future
Stroke & Neurovascular Center of New Jersey Jawad F. Kirmani, MD Director, Stroke and Neurovascular Center Past, present and future Past, present and future Cerebral Blood Flow Past, present and future
Nature and Science 2017;15(7) Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus
 Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor
 Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor Raed M Aljubour, MD *, Ahmed K Alomari, MD*, Awni F Musharbash, MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To investigate the Predictors
Risk factors for Ventriculoperitoneal shunting in children with posterior fossa tumor Raed M Aljubour, MD *, Ahmed K Alomari, MD*, Awni F Musharbash, MD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To investigate the Predictors
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN-CLINICAL PROFILE, MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY OF BACTERIOLOGICALLY CONFIRMED CASES
 TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN-CLINICAL PROFILE, MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY OF BACTERIOLOGICALLY CONFIRMED CASES N. Thilothammal P.V. Krishnamurthy K. Banu S.R. Ratnam ABSTRACT One hundred and seven cases
TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN-CLINICAL PROFILE, MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY OF BACTERIOLOGICALLY CONFIRMED CASES N. Thilothammal P.V. Krishnamurthy K. Banu S.R. Ratnam ABSTRACT One hundred and seven cases
The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t.
 The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t. Davson et al 1970, The mechanism of drainage of CSF. Brain 93:665-8 1989, Copenhagen, Alfred Benzon Foundation CSf outflow is
The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t. Davson et al 1970, The mechanism of drainage of CSF. Brain 93:665-8 1989, Copenhagen, Alfred Benzon Foundation CSf outflow is
Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD)
 Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Perioperative Management Of Extra-Ventricular Drains (EVD) Dr. Vijay Tarnal MBBS, FRCA Clinical Assistant Professor Division of Neuroanesthesiology Division of Head & Neck Anesthesiology Michigan Medicine
Tuberculous Meningitis and HIV
 Original Article Tuberculous Meningitis and HIV Sunil Karande, Vishal Gupta, Madhuri Kulkarni, Anagha Joshi 1 and Mhisti Rele 2 Division of Pediatric Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, and Departments
Original Article Tuberculous Meningitis and HIV Sunil Karande, Vishal Gupta, Madhuri Kulkarni, Anagha Joshi 1 and Mhisti Rele 2 Division of Pediatric Neurology, Department of Pediatrics, and Departments
NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*±
 NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*± *no pediatricians were harmed in the making of this presentation ±nonetheless, please do not try this at home
NEUROSURGEON VS. HOSPITALIST Pediatric Hospital Medicine meeting Nashville, TN July 21, 2017*± *no pediatricians were harmed in the making of this presentation ±nonetheless, please do not try this at home
Outcome Evaluation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Using Glasgow Outcome Score
 Outcome Evaluation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Using Glasgow Outcome Score Mehdi Abouzari, Marjan Asadollahi, Hamideh Aleali Amir-Alam Hospital, Medical Sciences/University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Introduction
Outcome Evaluation of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Using Glasgow Outcome Score Mehdi Abouzari, Marjan Asadollahi, Hamideh Aleali Amir-Alam Hospital, Medical Sciences/University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Introduction
Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip
 197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
 INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children
 J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature
 Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature Eriks A. Lusis Ananth K. Vellimana Wilson
Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature Eriks A. Lusis Ananth K. Vellimana Wilson
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts. Information for patients
 Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Do cytokines correlate with disease activity in tuberculous meningitis?
 Neurology Asia 215; 2(3) : 243 25 Do cytokines correlate with disease activity in tuberculous meningitis? Human P Sinha MD DM, Manish Modi MD DM, Sudesh Prabhakar MD DM, *Paramjit Singh MD Department of
Neurology Asia 215; 2(3) : 243 25 Do cytokines correlate with disease activity in tuberculous meningitis? Human P Sinha MD DM, Manish Modi MD DM, Sudesh Prabhakar MD DM, *Paramjit Singh MD Department of
ADENOSINE DEAMINASE LEVELS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AS A DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN
 ADENOSINE DEAMINASE LEVELS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AS A DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN Satya Vati Rana, Raj Kumar Singhal*, Kartar Singh & Lata Kumar* Department of *Paediatrics
ADENOSINE DEAMINASE LEVELS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AS A DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS IN CHILDREN Satya Vati Rana, Raj Kumar Singhal*, Kartar Singh & Lata Kumar* Department of *Paediatrics
S ome hydrocephalic patients with extracranial shunts
 PAPER Quantitative analysis of continuous intracranial pressure recordings in symptomatic patients with extracranial shunts P K Eide... Competing interests: none declared... Correspondence to: Dr Per Kristian
PAPER Quantitative analysis of continuous intracranial pressure recordings in symptomatic patients with extracranial shunts P K Eide... Competing interests: none declared... Correspondence to: Dr Per Kristian
Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after Brain Parenchymal Catheterization
 CLINICL RTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.118 Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after rain Parenchymal Catheterization
CLINICL RTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2016;12(2):118-122 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.2.118 Multiple Intracranial High Density Foci after rain Parenchymal Catheterization
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Spontaneous bowel perforation complicating ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a case report Theodosios Birbilis 1, Petros Zezos 2 *, Nikolaos Liratzopoulos 3, Anastasia Oikonomou 4, Michael
Open Access Case report Spontaneous bowel perforation complicating ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a case report Theodosios Birbilis 1, Petros Zezos 2 *, Nikolaos Liratzopoulos 3, Anastasia Oikonomou 4, Michael
Role of Invasive ICP Monitoring in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: An Experience of 98 Cases
 31 Original Article Indian Journal of Neurotrauma (IJNT) 2006, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 31-36 Role of Invasive ICP Monitoring in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: An Experience of 98 Cases Deepak Kumar Gupta
31 Original Article Indian Journal of Neurotrauma (IJNT) 2006, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 31-36 Role of Invasive ICP Monitoring in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: An Experience of 98 Cases Deepak Kumar Gupta
BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN
 Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Original The Diagnostic Parameters in Brain Tuberculosis Meningeal and Parenchymal Farooq Ahmad Ganie* 1, Manzoor Ahmad Lone 1, Altaf Umar
Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Original The Diagnostic Parameters in Brain Tuberculosis Meningeal and Parenchymal Farooq Ahmad Ganie* 1, Manzoor Ahmad Lone 1, Altaf Umar
Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases
 American Journal of Infectious Diseases 4 (3): 187-192, 2008 ISSN 1553-6203 2008 Science Publications Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases 1 P. Di Carlo, 2 D. Cabibi,
American Journal of Infectious Diseases 4 (3): 187-192, 2008 ISSN 1553-6203 2008 Science Publications Features in Tubercular Meningoencephalitis Diagnosis: 18 Childhood Cases 1 P. Di Carlo, 2 D. Cabibi,
Undernutrition as Risk Factor of Hydrocephalus Prevalence in Children with Tuberculous Meningitis
 143 Undernutrition as Risk Factor of Prevalence in Children with Tuberculous Meningitis John Patria Maruli Sinaga, 1 Nelly Amalia Risan, 2 Uni Gamayani 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran,
143 Undernutrition as Risk Factor of Prevalence in Children with Tuberculous Meningitis John Patria Maruli Sinaga, 1 Nelly Amalia Risan, 2 Uni Gamayani 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran,
Hydrocephalus is extremely common in the developing
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 13:140 144, 2014 AANS, 2014 Effectiveness of the Bactiseal Universal Shunt for reducing shunt infection in a sub-saharan African context: a retrospective cohort study in 160 Ugandan
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 13:140 144, 2014 AANS, 2014 Effectiveness of the Bactiseal Universal Shunt for reducing shunt infection in a sub-saharan African context: a retrospective cohort study in 160 Ugandan
Factors Influencing the Presentation and Outcome of Tuberculous Meningitis in Childhood
 Factors Influencing the Presentation and Outcome of Tuberculous Meningitis in Childhood F.S. FAELLA 1, P. PAGLIANO 1, V. ATTANASIO 1, M. ROSSI 1, C. RESCIGNO 1, F. SCARANO, M. CONTE 2 and U. FUSCO 1 1
Factors Influencing the Presentation and Outcome of Tuberculous Meningitis in Childhood F.S. FAELLA 1, P. PAGLIANO 1, V. ATTANASIO 1, M. ROSSI 1, C. RESCIGNO 1, F. SCARANO, M. CONTE 2 and U. FUSCO 1 1
Procedures commonly seen at Vanderbilt Medical Center PACU s: Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine surgeries. Goes to 6N
 Procedures commonly seen at Vanderbilt Medical Center PACU s: Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine surgeries Goes to 6N Burr holes and Craniotomies for hemorrhage, tumors, trauma, debulking Goes
Procedures commonly seen at Vanderbilt Medical Center PACU s: Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral spine surgeries Goes to 6N Burr holes and Craniotomies for hemorrhage, tumors, trauma, debulking Goes
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases-
 Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with
 Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report
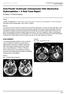 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 7 Number 1 Intra-Fourth Ventricular Schwannoma With Obstructive Hydrocephalus A Rare Case Report A Babbu, R Katheerayson Citation A Babbu, R Katheerayson..
Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir
 Original Paper Pediatr Neurosurg 2000;32:180 186 Received: January 27, 1999 Accepted: April 27, 2000 Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir S. Sood A.I. Canady Steven D. Ham Section
Original Paper Pediatr Neurosurg 2000;32:180 186 Received: January 27, 1999 Accepted: April 27, 2000 Evaluation of Shunt Malfunction Using Shunt Site Reservoir S. Sood A.I. Canady Steven D. Ham Section
A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection
 74 Original Article THIEME A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection T. P. Jeyaselvasenthilkumar 1 V. G. Ramesh 1 C. Sekar 1 S. Sundaram 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery,
74 Original Article THIEME A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection T. P. Jeyaselvasenthilkumar 1 V. G. Ramesh 1 C. Sekar 1 S. Sundaram 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery,
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach
 Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
Traumatic brain Injury- An open eye approach Dr. Sunit Dr Sunit, Apollo children's hospital Blah blah Lots of head injury Lot of ill children Various methods of injury Various mechanisms of brain damage
Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis in HIV-infected children in National Pediatric Hospital
 Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis in HIV-infected children in National Pediatric Hospital Olivier Marcy 1,2, Sam Sophan 2, Ung Vibol 2, Chan Bunthy 2, Pok Moroun 2, Chy Kam Hoy 2, Ban Thy 2, Chhour
Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis in HIV-infected children in National Pediatric Hospital Olivier Marcy 1,2, Sam Sophan 2, Ung Vibol 2, Chan Bunthy 2, Pok Moroun 2, Chy Kam Hoy 2, Ban Thy 2, Chhour
Appendix 1: search terms
 Appendix 1: search terms MEDLINE (PubMed) Abbreviated search strategy (full syntax available) 1. human 2. immunodeficiency 3. virus 4. 1 AND 2 AND 3 5. human immunodeficiency virus 6. HIV 7. acquired 8.
Appendix 1: search terms MEDLINE (PubMed) Abbreviated search strategy (full syntax available) 1. human 2. immunodeficiency 3. virus 4. 1 AND 2 AND 3 5. human immunodeficiency virus 6. HIV 7. acquired 8.
Treatment of Acute Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture
 19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study
 Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
Original Paper Med Principles Pract 2001;10:135 139 Received: October 8, 2000 Revised: July 4, 2001 Pattern of Intracranial Tuberculomas in Kuwait: A Computed Tomographic Study Salwa Ramadan Aduh Prosper
Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series
 ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group
 CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI, M.D., PH.D., TAKEO TANISHIMA, M.D., PH.D., Clinical Material and Methods
 J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
J Neurosurg 93:791 795, 2000 Relationship between drainage catheter location and postoperative recurrence of chronic subdural hematoma after burr-hole irrigation and closed-system drainage HIROSHI NAKAGUCHI,
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION
 IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION ASSESSMENT OF VISUAL FUNCTION AND PROGNOSIS FOR VISUAL OUTCOME Doctor of Philosophy thesis Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge Fiona J. Rowe Department of Orthoptics,
IDIOPATHIC INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION ASSESSMENT OF VISUAL FUNCTION AND PROGNOSIS FOR VISUAL OUTCOME Doctor of Philosophy thesis Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge Fiona J. Rowe Department of Orthoptics,
Hydrocephalus in children. Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno
 Hydrocephalus in children Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno Ventricle system Ventricle system, cerebral cisterns Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus in children Eva Brichtova, M.D., Ph.D., Department of Pediatric Sugery, Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University Hospital Brno Ventricle system Ventricle system, cerebral cisterns Hydrocephalus
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
 International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
The value of transcranial Doppler imaging in children with tuberculous meningitis
 Childs Nerv Syst (2014) 30:1711 1716 DOI 10.1007/s00381-014-2435-2 ORIGINAL PAPER The value of transcranial Doppler imaging in children with tuberculous meningitis Ronald van Toorn & H. Simon Schaaf &
Childs Nerv Syst (2014) 30:1711 1716 DOI 10.1007/s00381-014-2435-2 ORIGINAL PAPER The value of transcranial Doppler imaging in children with tuberculous meningitis Ronald van Toorn & H. Simon Schaaf &
Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London
 Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London HIV and Lumbar punctures in 2018 Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals I have no competing interests Summary of
Dr Paul Holmes Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London HIV and Lumbar punctures in 2018 Paul Holmes Consultant Neurologist Guy s and St Thomas Hospitals I have no competing interests Summary of
Brain and Spine Tumors
 Brain and Spine Tumors Andrew J. Fabiano, MD FAANS Associate Professor of Neurosurgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Brain Tumors Brain Tumor Basics Types of Tumors Cases
Brain and Spine Tumors Andrew J. Fabiano, MD FAANS Associate Professor of Neurosurgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Brain Tumors Brain Tumor Basics Types of Tumors Cases
Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement
 Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement Kelsey Bourm 1*, Cory Pfeifer 2, Adam Zarchan 3 1. Department of Radiology, Wesley Medical Center, Wichita, KS, USA
Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement Kelsey Bourm 1*, Cory Pfeifer 2, Adam Zarchan 3 1. Department of Radiology, Wesley Medical Center, Wichita, KS, USA
CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT. All Medicare information is current as of the time of printing.
 CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT All Medicare information is current as of the January 2014 Hydrocephalus ing Coding Options Commonly Billed Codes for Physicians, Hospitals, and Ambulatory Surgery
CODING SHEET HYDROCEPHALUS REIMBURSEMENT All Medicare information is current as of the January 2014 Hydrocephalus ing Coding Options Commonly Billed Codes for Physicians, Hospitals, and Ambulatory Surgery
Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari Malformation
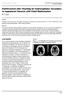 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A CASE REPORT Babu B. Hundekar 1
 TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
3.1. Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children. R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H.
 3.1 Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H. Visser P.R. Donald B.J. Marais J.F. Schoeman A.M. van Furth Clin
3.1 Uniform research case definition criteria differentiate tuberculous and bacterial meningitis in children R.S. Solomons M. Wessels D.H. Visser P.R. Donald B.J. Marais J.F. Schoeman A.M. van Furth Clin
THOMAS G. SAUL, M.D., THOMAS B. DUCKER, M.D., MICHAEL SALCMAN, M.D., AND ERIC CARRO, M.D.
 J Neurosurg 54:596-600, 1981 Steroids in severe head injury A prospective randomized clinical trial THOMAS G. SAUL, M.D., THOMAS B. DUCKER, M.D., MICHAEL SALCMAN, M.D., AND ERIC CARRO, M.D. Department
J Neurosurg 54:596-600, 1981 Steroids in severe head injury A prospective randomized clinical trial THOMAS G. SAUL, M.D., THOMAS B. DUCKER, M.D., MICHAEL SALCMAN, M.D., AND ERIC CARRO, M.D. Department
Stereotactic Burr Hole Aspiration Surgery for Spontaneous Hypertensive Cerebellar Hemorrhage
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN 2234-8565, EISSN 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.170 Original Article Stereotactic Burr Hole Aspiration Surgery for Spontaneous
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery ISSN 2234-8565, EISSN 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.170 Original Article Stereotactic Burr Hole Aspiration Surgery for Spontaneous
Rational Use of Dexamethasone in Tuberculous Meningitis
 Rational Use of Dexamethasone in Tuberculous Meningitis Sidra Khushnood 1, Toseef Fatima Noshahi 1, Khawaja Tahir Mehmood 2 1 Department of Pharmacy, Lahore College for Women University; 2 Drug Testing
Rational Use of Dexamethasone in Tuberculous Meningitis Sidra Khushnood 1, Toseef Fatima Noshahi 1, Khawaja Tahir Mehmood 2 1 Department of Pharmacy, Lahore College for Women University; 2 Drug Testing
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.01 Utility of Serial Transcranial
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.01 Utility of Serial Transcranial
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine
 Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Abstract Introduction Methods Results
 An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Jason Duong, DO 1, Dan Miulli DO 1, Fanglong Dong, PhD 2, Andrew Sumida MSIV 3, 1 Neurosurgery
An approach using the occipital parietal point for placement of ventriculoperitoneal catheters in adults. Jason Duong, DO 1, Dan Miulli DO 1, Fanglong Dong, PhD 2, Andrew Sumida MSIV 3, 1 Neurosurgery
Spontaneous intraventricular rupture of pyogenic brain abscess: A short series of three cases and review of literature
 SNI: Infection, a supplement to Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California,
SNI: Infection, a supplement to Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California,
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.165 Clinico Radiological Profile
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.165 Clinico Radiological Profile
Unfortunately, shunt malfunction is one of the
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:160 166, 2014 AANS, 2014 Utility of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of ventricular morphology in suspected cerebrospinal fluid shunt malfunction Clinical
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 14:160 166, 2014 AANS, 2014 Utility of computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of ventricular morphology in suspected cerebrospinal fluid shunt malfunction Clinical
Clinical characteristics and neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with tuberculous meningitis and hydrocephalus
 DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical characteristics and neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with tuberculous meningitis and hydrocephalus URSULA K ROHLWINK 1,2 KIRSTY
DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical characteristics and neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with tuberculous meningitis and hydrocephalus URSULA K ROHLWINK 1,2 KIRSTY
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of hydrocephalus
 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of hydrocephalus Artur Xhumari 1,2, Ermira Pajaj 2, Maren Ruka 2, Mithat Demneri 2, Mentor Petrela
BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS ALBANIAN MEDICAL JOURNAL The role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy in the treatment of hydrocephalus Artur Xhumari 1,2, Ermira Pajaj 2, Maren Ruka 2, Mithat Demneri 2, Mentor Petrela
MANAGEMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA TUMORS
 MANAGEMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA TUMORS S. M. Abdollahzadeh-Hosseini 1*, H. Rezaishiraz 2 and F. Allahdini 3 1) Department of Neurosurgery, Shariati Hospital, Tehran University of
MANAGEMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN POSTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA TUMORS S. M. Abdollahzadeh-Hosseini 1*, H. Rezaishiraz 2 and F. Allahdini 3 1) Department of Neurosurgery, Shariati Hospital, Tehran University of
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material
 143 Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material Edward C. Benzel 1 Mansour Mirfakhraee 2 Theresa A. Hadden 1 Functional positive-contrast shuntography includes
143 Evaluation of CSF Shunt Function: Value of Functional Examination with Contrast Material Edward C. Benzel 1 Mansour Mirfakhraee 2 Theresa A. Hadden 1 Functional positive-contrast shuntography includes
Shunt infection in a single institute: a retrospective study
 Qin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0115-x CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY RESEARCH Open Access Shunt infection in a single
Qin et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0115-x CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION CHINESE NEUROSURGICAL SOCIETY RESEARCH Open Access Shunt infection in a single
External Ventricular Drainage & Lumbar Drainage Procedure and Care. Amey R. Savardekar Assistant Professor Neurosurgery, NIMHANS.
 External Ventricular Drainage & Lumbar Drainage Procedure and Care. Amey R. Savardekar Assistant Professor Neurosurgery, NIMHANS. External Ventricular Drain Indications: Therapeutic (To relieve raised
External Ventricular Drainage & Lumbar Drainage Procedure and Care. Amey R. Savardekar Assistant Professor Neurosurgery, NIMHANS. External Ventricular Drain Indications: Therapeutic (To relieve raised
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM
 NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
Extent of subarachnoid hemorrhage and development of hydrocephalus
 Clinical Science Extent of subarachnoid hemorrhage and development of hydrocephalus Mirsad Hodžić, Mirza Moranjkić, Zlatko Ercegović, Harun Brkić Department of neurosurgery, University Clinical Center
Clinical Science Extent of subarachnoid hemorrhage and development of hydrocephalus Mirsad Hodžić, Mirza Moranjkić, Zlatko Ercegović, Harun Brkić Department of neurosurgery, University Clinical Center
Original Article Bilateral large chronic ossified epidural hematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a special case report and treatment management
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14515-14522 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026676 Original Article Bilateral large chronic ossified epidural hematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a special case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14515-14522 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0026676 Original Article Bilateral large chronic ossified epidural hematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a special case
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba. Department of Neurological Surgery
 Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
Moron General Hospital Ciego de Avila Cuba Department of Neurological Surgery Early decompressive craniectomy in severe head injury with intracranial hypertension Angel J. Lacerda MD PhD, Daisy Abreu MD,
Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis
 198 Original Article THIEME Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis Vamsi Krishna Yerramneni 1 Vamsi Krishna Kotha 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Nizam s Institute
198 Original Article THIEME Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis Vamsi Krishna Yerramneni 1 Vamsi Krishna Kotha 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Nizam s Institute
A Case of Difficult Management of Fluid-Electrolyte Imbalance in Choroid Plexus Papilloma
 Case Report doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr2012-0380 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) xx, xxx xxx, 20xx A Case of Difficult Management of Fluid-Electrolyte Imbalance in Choroid Plexus Papilloma Atsushi Saito, 1 Shinjitsu Nishimura,
Case Report doi: 10.2176/nmc.cr2012-0380 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) xx, xxx xxx, 20xx A Case of Difficult Management of Fluid-Electrolyte Imbalance in Choroid Plexus Papilloma Atsushi Saito, 1 Shinjitsu Nishimura,
External Ventricular Drainage Infections: Experience from a Tertiary Care Center in Nepal
 72 Original article External Ventricular Drainage Infections: Experience from a Tertiary Care Center in Nepal Pradhanang AB, Sharma MR 3, Sedain G 2, Shilpakar SK 3 MCh Resident, 2 Assistant Professor,
72 Original article External Ventricular Drainage Infections: Experience from a Tertiary Care Center in Nepal Pradhanang AB, Sharma MR 3, Sedain G 2, Shilpakar SK 3 MCh Resident, 2 Assistant Professor,
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know
 Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Tuberculous meningitis diagnosis and treatment in adults: A series of 189 suspected cases
 2770 Tuberculous meningitis diagnosis and treatment in adults: A series of 189 suspected cases MENGCHUAN LUO 1, WEIFEI WANG 2, QIUMING ZENG 1, YUEBEI LUO 1, HUAN YANG 1 and XIAOSU YANG 1 1 Department of
2770 Tuberculous meningitis diagnosis and treatment in adults: A series of 189 suspected cases MENGCHUAN LUO 1, WEIFEI WANG 2, QIUMING ZENG 1, YUEBEI LUO 1, HUAN YANG 1 and XIAOSU YANG 1 1 Department of
BMI Medical. Ventricular Catheter T
 Shunting System Ventricular Catheter 01101 01101T Barium-impregnated silicone catheter provides resistance to kinking and compression. Stainless steel stylet allows catheter to be directed during catheter
Shunting System Ventricular Catheter 01101 01101T Barium-impregnated silicone catheter provides resistance to kinking and compression. Stainless steel stylet allows catheter to be directed during catheter
Case Report Meningeal TB in a 39-Year-Old Male Presenting with Headache
 Hindawi Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2017, Article ID 4753670, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4753670 Case Report Meningeal TB in a 39-Year-Old Male Presenting with Headache Jason Selinger
Hindawi Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2017, Article ID 4753670, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4753670 Case Report Meningeal TB in a 39-Year-Old Male Presenting with Headache Jason Selinger
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
A rare association of tuberculous longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) with brain tuberculoma
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1232-z CASE STUDY A rare association of tuberculous longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) with brain tuberculoma Rajendra Singh Jain 1, Sunil Kumar 1* and Shankar Tejwani
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1232-z CASE STUDY A rare association of tuberculous longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) with brain tuberculoma Rajendra Singh Jain 1, Sunil Kumar 1* and Shankar Tejwani
Gram Negative Bacillary Brain Abscess: Clinical Features And Therapeutic Outcome
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Gram Negative Bacillary Brain Abscess: Clinical Features And Therapeutic Outcome F Huda, V Sharma, W Ali, M Rashid Citation F Huda, V Sharma,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 4 Number 2 Gram Negative Bacillary Brain Abscess: Clinical Features And Therapeutic Outcome F Huda, V Sharma, W Ali, M Rashid Citation F Huda, V Sharma,
Insertion of an external ventricular drain (EVD) is a
 Short Communication Intracerebral Hemorrhage With Severe Ventricular Involvement Lumbar Drainage for Communicating Hydrocephalus Hagen B. Huttner, MD; Simon Nagel, MD; Elena Tognoni; Martin Köhrmann, MD;
Short Communication Intracerebral Hemorrhage With Severe Ventricular Involvement Lumbar Drainage for Communicating Hydrocephalus Hagen B. Huttner, MD; Simon Nagel, MD; Elena Tognoni; Martin Köhrmann, MD;
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome
 Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
Management of pediatric brain tumors, strategies and long term outcome SAN The Sudanese association of neurosurgeons By Dr. Abubakr Darrag Salim Ahmed Dr. Mohammed Awad Elzain Khartoum Sudan Pediatric
Hydrocephalus. Patient and Family Education. What is hydrocephalus? What are the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus?
 Patient and Family Education Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus happens when too much fluid builds up in the cavities (ventricles) of your child s brain causing pressure. This handout includes information on
Patient and Family Education Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus happens when too much fluid builds up in the cavities (ventricles) of your child s brain causing pressure. This handout includes information on
Characteristics of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Tuberculous Meningitis Patients with Hydrocephalus
 Original Article Characteristics of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Tuberculous Meningitis Patients with Hydrocephalus Astrid Tamara Maajid Budiman, 1 Nida Suraya, 2 Ahmad Faried, 3 Ida Parwati 2 1 Faculty of Medicine,
Original Article Characteristics of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Tuberculous Meningitis Patients with Hydrocephalus Astrid Tamara Maajid Budiman, 1 Nida Suraya, 2 Ahmad Faried, 3 Ida Parwati 2 1 Faculty of Medicine,
External ventricular drainage (EVD) is one of the most. External Ventricular Drainage Infections: Experience From a Tertiary Care Center in Nepal
 Original Article Amit Pradhanang, MS Mohan R Sharma, MS Gopal Sedain, MS, MCh Sushil K Shilpakar, MS Address for Correspondence: Mohan R Sharma, MS Email: mohanrajsharma@gmail.com Received, 9 August, 2015
Original Article Amit Pradhanang, MS Mohan R Sharma, MS Gopal Sedain, MS, MCh Sushil K Shilpakar, MS Address for Correspondence: Mohan R Sharma, MS Email: mohanrajsharma@gmail.com Received, 9 August, 2015
