Evaluation of a dedicated brain metastases treatment planning optimization for radiosurgery: a new treatment paradigm?
|
|
|
- Melvin Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 DOI /s y RESEARCH Open Access Evaluation of a dedicated brain metastases treatment planning optimization for radiosurgery: a new treatment paradigm? Thierry Gevaert 1*, Femke Steenbeke 1, Luca Pellegri 2, Benedikt Engels 1, Nicolas Christian 2, Marie-Thérèse Hoornaert 2, Dirk Verellen 1, Carine Mitine 2 and Mark De Ridder 1 Abstract Purpose: To investigate the feasibility of a novel dedicated treatment planning solution, to automatically target multiple brain metastases with a single isocenter and multiple inversely-optimized dynamic conformal arcs (DCA), and to benchmark it against the well-established multiple isocenter DCA (MIDCA) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) approaches. Material and Methods: Ten previously treated patients were randomly selected, each representing a variable number of lesions ranging between 1 to 8. The original MIDCA treatments were replanned with both VMAT and the novel brain metastases tool. The plans were compared by means of Paddick conformity (CI) and gradient index (GI), and the volumes receiving 10 Gy (V10) and 12 Gy (V12). Results: The brain metastases software tool generated plans with similar CI (0.65 ± 0.08) as both established treatment techniques while improving the gradient (mean GI = 3.9 ± 1.4). The normal tissue exposure in terms of V10 (48.5 ± 35.9 cc) and V12 (36.3 ± 27.1 cc) compared similarly to the MIDCA technique and surpassed VMAT plans. Conclusions: The automated brain metastases planning algorithm software is an optimization of DCA radiosurgery by increasing delivery efficiency to the level of VMAT approaches. Improving dose gradients and normal tissue sparing over VMAT, revives DCA as the paradigm for linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery of multiple brain Keywords: Stereotactic radiosurgery, Brain metastases, Automated planning optimization, Single isocenter dynamic conformal arc Introduction Radiation therapy has become a popular treatment option in the management of patients with brain The role and effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) alone and in combination with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) for the treatment of brain metastases has been evaluated in two randomized clinical trials [1, 2]. One decade later, debate continues on to the role of SRS as the first line of care treatment modality for brain metastases patients, yet the controversy has shifted from overall survival to quality of life and * Correspondence: thierry.gevaert@uzbrussel.be 1 Department of Radiotherapy, Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium Full list of author information is available at the end of the article how this relates to neurocognitive decline, which is a more appropriate endpoint in times of personalized medicine. In the absence of level-1 evidence, best practice guidelines recommend a close monitoring of patients treated solely with SRS for an early detection of distant recurrences. The guidelines of the American Society of Radiation Oncology only support SRS without concurrent WBRT for patients with up to four brain metastases [3]. The reported successful radiosurgical outcome for two patients with ten or more metastases suggested at the absence of an essential number of metastases that can be treated with radiosurgery [4, 5]. Recently, Yamamoto et al. performed a multi-institutional prospective observational trial (JLGK0901) and concluded that SRS without WBRT as the initial treatment for 2016 Gevaert et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 2 of 7 patients with five to ten brain metastases is non-inferior to SRS alone in those with two to four brain metastases, in terms of overall survival [6]. Although a randomized trial should confirm these results, evidence grows that SRS alone is an important treatment option for brain metastases patients, irrespective of the number of Different radiosurgery technologies are available and accomplish the high ablative dose with a sharp dose fall-off in their respective ways. The dose distribution generated with a gantry-mounted linear accelerator (LINAC)-based SRS system is accomplished using multiple intersecting non-coplanar dynamic conformal arcs (DCA), multiple intensity-modulated beams or volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT). A previous study in our department showed that for linacbased SRS, DCA is still favorable to sculpt the dose around the lesion with respect to SRS treatment aims (i.e., high conformity and sharp gradient) [7]. Therefore, our standard of care for SRS treatments of multiple brain metastases is a multi isocentric set-up, aligning the micro multi-leaf collimator (MLC) around every individual lesion using DCA. This complex time consuming treatment planning translates in extended treatment delivery times, as it requires patient repositioning for every individual Recently, a new dedicated brain metastases treatment planning solution has been developed, intended to carefully balance normal tissue protection, target coverage and treatment efficiency. The automated brain metastases treatment planning software, named Elements, generates radiosurgery-grade treatment plans to treat up to ten metastases simultaneously with a single isocenter. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the feasibility of this novel treatment planning software for single isocenter SRS treatment in patients with multiple brain metastases and to compare the dosimetry and efficiency against the well-established multiple isocenter dynamic conformal arc (MIDCA) approach and the single isocenter VMAT approach. Material and methods Patient population Ten patients were randomly selected from the pool of previously treated brain metastases patients with the Novalis at the UZ Brussel hospital. They represent a variable number of lesions, range of target sizes and shapes most frequently observed in the practice of SRS for brain The number of lesions varied from 1(n =1),2(n =2),3(n =3),4(n =1),7(n =2)to8(n =1). The gross target volume (GTV) was defined as the area of contrast enhancement on MRI and was expanded with 2 mm based on our experienced and previous published data on intrafraction motion [8]. After delineation of targets and critical structures on MRI data sets, the CT data with their related DICOM Radiotherapy Structure Sets were transferred to several dedicated treatment planning systems: iplan dose v.4.5 (Brainlab AG, Feldkirchen, Germany) for MIDCA treatment planning, Eclipse RapidArc v10 (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA) for VMAT treatment planning, and to the automated brain metastases treatment planning software (Brainlab Elements, Brainlab AG, Feldkirchen, Germany) for single isocenter dynamic conformal arc (SIDCA) treatment planning. The treatment dose of 20 Gy was prescribed to the 80 % isodose line covering 99.5 % of the target volume. The dose to the surrounding healthy brain and critical structures (brainstem, cochlea, optical nerve, eyes and lens) were optimized to minimize complications for all the plans generated. A Novalis Tx (Brainlab AG, Feldkirchen, Germany) radiosurgery linac with 6 MV photon energy equipped with an integrated high definition multi-leaf collimator (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA), consisting of 120 leaves, including 64 central leaves with a width of 2.5 mm and 56 peripheral leaves with a width of 5 mm [9], was modelled for all treatment planning purposes. Dedicated automated brain metastases treatment planning This novel automated software solution is designed to simulate treatments for multiple individual metastases simultaneously. The contours are automatically imported for a correct comparison. The isocenter position is determined as the average position of the centers of mass of each individual target. The dose prescription is defined as the dose applied to 99.5 % of the target volume and this coverage is guaranteed by the optimization algorithm. The software uses a pre-configured set of non-coplanar DCA to treat the targets. The algorithm starts by considering a maximum of five couch positions and two independent arcs per couch position. By default, the couch positions are defined so that the arcs are equally distributed and opposing arcs are avoided. Depending on which hemisphere of the head the isocenter is located in, the arcs are mirrored about the sagittal plane. The start and stop angles of the arc are first set to default values and automatically modified during optimization. The MLC leaf positions are shaped conform to the targets, with an additional margin of up to 1 mm in addition to any margin that may have been defined in the template, for all fields of each arc. To prevent irradiation of normal tissue, all targets must be assigned to specific arcs and not necessarily treated by all arcs at the same time. In the latter scenario, it might occur that multiple targets line up along the direction of motion of a leaf pair, which would imply the pair to open widely and also expose the healthy tissue in between the targets. Therefore, each leaf pair is only allowed to expose one target at any time. This decision of assigning lesions to a specific arc is automatically performed by the algorithm itself.
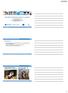
3 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 3 of 7 For the sake of efficiency, the algorithm bases this choice on the principle that as many targets as possible should be treated by each arc. The choices are made so that minimal number of arcs is used based on the amount of parallel lesions that can be treated by one arc. Additionally, a large range of collimator rotations is explored to smear out the overdosage caused by the radiation leakage between MLC leaves. Although this rotation is limited because all targets treated by an arc still have to fit into the effective MLC field, its contribution to the protection of healthy tissue is still deemed to be significant. After assigning individual targets to arcs, the weights of the arcs are optimized in terms of conformity and expressed by the conformity index (CI), one for each target. In addition to optimizing the arc weights, the algorithm evaluates several other approaches to improve the conformity further, like adding or subtracting small margins around the targets with suboptimal CI and varying start and stop angles of each arc. Figure 1a shows an example of the number of arcs, arrangement used for the treatment of a patient with 7 brain Established radiosurgery treatment strategies The DCA modality [10], which is used routinely at our department for the SRS treatments, is a rotational arc delivery technique in which the leaves move during the rotation of the gantry to dynamically adapt the shape of the treatment beam to the projection of the target. In this study, one isocenter for each target with 4 5 arcs equally distributed over was used to treat the target. The couch angles of the arcs were manually selected to minimize dose spread in normal brain as well as avoiding multiple targets to line up along the direction of an arc. Forward planning is applied to shape the prescription isodose (80 %) conform to the lesions. The isocenter of each group was at the center of mass of the associated target. The VMAT plans were developed according to the technique described by Clark et al. [11]. Constraints to targets and OAR were applied in order to achieve the planning objectives. Concentric ring-structures were utilized during optimization to achieve the steepest dose fall-off possible. Huang et al. [12] suggested VMAT plans with 4 arcs in order to achieve the steepest dose fall-off. The 4-arc plans consisted of one 358 axial arc and three 171 arcs at couch angles of 45, 90, and 315. During optimization, priorities were adjusted during optimization to achieve the best results for each patient. VMAT Rapidarc (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA) consists of optimizing a dose distribution from dose volume objectives. The optimizer is enabled to continuously vary the dose rate, MLC leaf positions and gantry rotation speed. The optimization itself is based on the Progressive Resolution Optimization algorithm. This optimization Fig. 1 Arc arrangement for the three different treatment modalities: (a) Single isocenter dynamic conformal arc (SIDCA), (b) Multi isocenter dynamic conformal arc (MIDCA) and (c) Volumetric Modulated Arc technique (VMAT) loop is based on a multi-resolution level and is ruled by means of a gradient back projection algorithm to minimize differences between current and desired doses in the cost function built on dose volume objectives defined by the planner. Variations of MLC shapes, dose rate or gantry speed settings are performed in the search of the optimal solution. An intrinsic stochastic component will avoid traps in local minima during this search. Figure 1b and c, respectively for MIDCA and VMAT, shows the arc arrangement, length and number used in order to optimize a plan for a patient with 7 brain Plan comparison In the radiosurgery community, the Paddick CI and gradient index (GI) are two well-known indices to analyze
4 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 4 of 7 how conformal the prescription dose sculpts the target volume and how steep the dose fall-off is in the brain. The Paddick CI, providing simultaneously information about the irradiation of the target volume and healthy tissues, was used for analysis [13]. To reflect the dose fall-off outside the target, the Paddick GI was used [14]. Blonigen et al. [15] found a higher risk for symptomatic radionecrosis for plans showing a large isodose volume receiving a dose of 12 Gy and 10 Gy. The positive correlation between the volume of the low dose outside the target and radiosurgical complications confirms the importance of the intermediate doses (10 and 12 Gy) for the prediction of complications. That is why we also evaluated the volume of brain receiving a dose of 10 Gy (V10) and 12 Gy (V12), respectively. The volume receiving a low isodose (5 Gy) was also analyzed. Statistical analysis A student t-test (Microsoft Office Excel; Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) was performed to obtain p-values to evaluate the differences between the different indices of the systems. Results Ten patients with in total 40 lesions were planned with the novel SIDCA treatment planning element, MIDCA and VMAT. The mean lesion size was 3.15 cc (range cc). The mean total treated volume per patient was cc (range cc). All plans were judged clinically acceptable regarding target coverage and organs at risk sparing, although differences in dosimetrical parameters were observed. Table 1 summarizes the different indices. Figure 2 gives an example of dose distribution achieved for a patient with 7 brain metastases with the three different planning systems. The mean conformity of the automated single-isocenter planning tool (SIDCA plans) compared similarly to the established MIDCA and VMAT treatment techniques (CI SIDCA = 0.65 ± 0.08, CI MIDCA = 0.66 ± 0.07 and CI VMAT = 0.67 ± 0.16). Comparable mean dose fall off was observed between SIDCA and MIDCA (GI SIDCA =3.9 ± 1.4 and GI MIDCA =4.5±1.6). On the other hand, compared to another single isocenter treatment, the GI and low dose of the VMAT plans (GI VMAT = 7.1 ± 3.1) were significantly higher compared to the automated single isocenter planning tool (SIDCA). The V10 and V12 were significantly higher for VMAT plans (V10 VMAT = 67.9 ± 55.9 cc, V12 VMAT = 46.3 ± 35.9 cc) (p < 0.05) compared to MIDCA (V10 MIDCA = 49.0 ± 38.1 cc, V12 MIDCA = 35.6 ± 26.4 cc) and SIDCA (V10 = 48.5 ± 35.9 cc, V12 = 36.3 ± 27.1 cc). Low dose spread, expressed as the volume receiving 5 Gy (V5), was significantly higher for VMAT plans (V5 VMAT = ± cc) compared to the MIDCA (V5 MIDCA = ± cc) and SIDCA (V5 = ± cc). If we stratify the total patient population into two groups, one comprising patients with up to 3 lesions and one comprising patients with more than 3 lesions, we found comparable conformity across both groups regardless of the delivery technique. For the gradient and low dose spread, the differences between the SIDCA and MIDCA versus VMAT were even more pronounced for patients with more than three lesions (Table 1). Discussion Increasing evidence demonstrates that SRS provides highly effective and predictable local tumor control for single and multiple brain Avoidance of WBRT can have a positive impact on the patient s cognitive status and health-related quality of life. Nowadays, there is clinical evidence to treat multiple brain metastases up to 10 upfront with a single radiosurgery session and apply repeat SRS when new lesions are detected [1 6]. Different dedicated radiosurgery systems (i.e., Gamma Knife, Cyberknife and linac-based systems) are available to perform these very precise single Table 1 Different dosimetrical paramters (i.e., conformity index (CI), gradient index (GI) and volume receiving 12Gy (V12), 10Gy (V10) and 5Gy (V5) for the different treatment techniques: multiple isocenter dynamic conformal arc (MIDCA), single isocenter DCA and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) CI GI V12 (cc) V10 (cc) V5 (cc) 1 3 lesions (n = 14) MIDCA 0.67 ± ± ± ± ± SIDCA 0.67 ± ± ± ± ± 85.1 VMAT 0.69 ± ± ± ± ± >3 lesions (n = 26) MIDCA 0.66 ± ± ± ± ± SIDCA 0.63 ± ± ± ± ± VMAT 0.65 ± ± ± ± ± All lesions (n = 40) MIDCA 0.66 ± ± ± 26, ± ± SIDCA 0.65 ± ± ± ± ± VMAT 0.67 ± ± ± ± ± 216.7
5 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 5 of 7 Fig. 2 Dose distribution for a patient with 7 brain metastases for the different treatment modalities: (a) Single isocenter dynamic conformal arc (SIDCA), (b) Multi isocenter dynamic conformal arc (MIDCA) and (c) Volumetric Modulated Arc technique (VMAT) fraction SRS treatments. We previously compared these different devices for vestibular schwannomas and arteriovenous malformations and found that although all systems achieve SRS requirements, multiple focal entries (i.e., Gamma Knife and Cyberknife) achieve better conformity while modulated beams (Cyberknife and IMRT beams) will spread more low dose into the brain [7]. The DCA technique, which is routinely applied in our department, achieved good conformity with a reduction in low dose spread compared to the modulated beams. These results also apply to single brain metastases radiosurgery. However, for multiple brain metastases, careful selection of arc orientation is needed in order to avoid possible overlap of arcs, which will result in decreased conformity, and higher volume of low doses into the brain leading to undesirable side effects. Valéry et al. [16] determined that the risk of radionecrosis after radiosurgery is related to the presence of normal tissue included in the prescription volume and found that the conformity of a treatment plan was the only parameter influencing the risk of radionecrosis. Furthermore, dose fall-off outside the target is of equal importance as conformity. Analysis of risk factors for brain necrosis showed that V10 and V12 were the most important independent predictors of both symptomatic and asymptomatic radionecrosis indicating that volume is more important than the number of lesions treated [17]. Furthermore, Xue et al. [18] found that mean normal brain dose correlated with the total volume of the lesions rather than with the treated number of lesions. Multiple isocenter DCA radiosurgery is less efficient in treating multiple lesions as treatment planning involves different isocenters, each with an arc arrangement. In order to reduce low dose spread, arc length and direction must be optimized. Patients also need to be repositioned for every lesion separately, which is more time consuming. Single isocenter treatments are more efficient for multiple brain Mayo et al. [19] showed the possibility to use VMAT to treat multiple metastatic lesions using a single isocenter with multiple arcs and anticipated that the ability to treat multiple lesions simultaneously will have a significant impact on care patterns for this patient population. Although this technique looks interesting, Huang et al. [20] found an increased low-dose spread that may be of concern. This technique is designed for speed, as there is no difference in treatment time whether you treat one or multiple However, this approach comes at the cost of more radiation exposure to normal tissue, which goes against the core principles of SRS. Furthermore, based on the dose interplay
6 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 6 of 7 effect analysis, Ma et al. [21] observed that multiple isocenter delivery (i.e., Gamma Knife and DCA) achieves better normal brain tissue sparing as compared to single isocentric or non-isocentric (i.e., CyberKnife) approaches. These conclusions are in according with our previous publication where modulated beams were found to smear the dose out over the normal tissue. In this manuscript we propose an automated algorithm to treat single or multiple brain metastases using a single isocenter with a pre-configured set of non-coplanar DCA. All established techniques mentioned above rely on user-defined empirical values for gantry angles, collimator and couch rotations, virtual objects and their corresponding constraints. The large number of parameters and many degrees of freedom involved with traditional radiosurgery plan optimization challenges the task at hand and may result in a suboptimal treatment plan and variable plan quality depending on the experience of the user. Despite all the parametric freedom routinely available, the planner is faced with the often conflicting ambitions of shaping the radiation dose as conformal as possible, while simultaneously optimizing the dose gradient. In this scenario, as an analogy, the jockey becomes more important than the horse. That is why it would be beneficial to have a treatment planning system automatically balancing the large number of parameters and degrees of freedom available and presenting a solution with minimal user interaction. The planning efforts for a forward planning technique such as MIDCA, scale with the number of lesions. That is why VMAT radiosurgery was likely to replace MIDCA for multiple lesions in terms of efficiency, at the cost of increased low dose spread. The automated Elements software is also an inverse planning optimization technique that uses a single isocenter and several non-coplanar DCA, which makes for an interesting tool in terms of planning and treatment efficiency. This novel software tool generated plans with similar conformity compared to the MIDCA and VMAT. For the low dose spread, comparable results were found as for MIDCA but with a significant decrease of low dose spread compared to the VMAT plans, improving stereotactic treatment planning in terms of gradient index and low dose spread while maintaining conformity. An important remark is that when multiple targets are separated far from each other, some of the lesions may be covered by the 5 mm MLC instead of the 2.5 mm. That is why for these lesions, if conformity seems not acceptable, a second group for that particular lesion must be created in order to achieve the planning constraints. Furhter investigations must now be performed in order to ensure that planning reproducibility can be performed once the patient will be treated. A small angular setup uncertainty can lead to significant dosimetric degradation especially for lesions located distant from the treatment isocenter. That is why stereoscopic x-ray images and 6 of freedom positioning will be used in order to cope with those uncertainties. Previously work in our department has showed that a threshold of 1 mm and 0.5 is sufficient to assure good dose deposition [8]. In order to maintain the setup accuracy during table rotations, we suggest to perform snapshot verifications and reposition if necessary at that particular table angle [22]. Conclusions The automated brain metastases treatment planning element, based on an inversely-optimized SIDCA approach, revealed comparable results to the general accepted and clinical used MIDCA approach. By reducing the time on planning, patient setup and repositioning of the treatment couch, this software tool significantly improves the treatment planning and delivery efficiency while preserving the plan quality of the MIDCA technique and lowering the low dose spread of the single isocenter VMAT approach, suggesting that this novel software offers the best of both worlds (i.e., efficient single-isocenter DCA delivery). Competing interest The authors are involved in an on-going collaboration with Brainlab AG. Authors contribution Concept and design: TG, FS, NC, MDR. Treatment planning: TG, FS, LP, MTH. Analysis and interpretation of data: TG, FS, BE, NC, DV, CM, MDR. Drafting of the manuscript: TG, FS, LP, NC, MDR. Reading and approval of final manuscript: all authors. Acknowledgement The authors would like to acknowledge Brainlab to give the opportunity to test the Elements software, for planning support, suggestions and review. Author details 1 Department of Radiotherapy, Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium. 2 Department of Radiotherapy, Centre Hospitalier Jolimont, Jolimont, Belgium. Received: 3 November 2015 Accepted: 20 January 2016 References 1. Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomized trial. Lancet. 2004;363: Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295: Tsao MN, Rades D, Wirth A, Lo SS, Danielson BL, Gaspar LE, et al. Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis(es): an American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2012;2:
7 Gevaert et al. Radiation Oncology (2016) 11:13 Page 7 of 7 4. Yamamoto M, Ide M, Jimbo M, Aiba M, Ito M, Hirai T, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery with numerous target points for intracranially disseminated metastases: early experience in 3 patients and experimental analysis of whole brain irradiation doses. In: Kondziolka D, editor. Radiosurgery, vol. 2. Basel: Karger; p Knisely JP, Yamamoto M, Gross CP, Castrucci WA, Jokura H, Chiang VL. Radiosurgery alone for 5 or more brain metastases: expert opinion survey. J Neurosurg. 2010;113(suppl): Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(4): Gevaert T, Levivier M, Lacornerie M, Verellen D, Engels B, Reynaert N, et al. Dosimetric comparison of different available treatment modalities for stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol. 2013;106(2): Gevaert T, Verellen D, Engels B, Depuydt T, Heuninckx K, Tournel K, et al. Clinical evaluation of a robotic 6-degree of freedom treatment couch for frameless radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83(1): Chang Z, Wang Z, Wu J, Yan H, Bowsher J, Zhang J, et al. Dosimetric characteristics of Novalis Tx system with high definition multileaf collimator. Med Phys. 2008;35(10): Nedzi LA, Kooy HM, Alexander E, Svensson GK, Loeffler JS. Dynamic field shaping for stereotactic radiosurgery: A modeling study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993;25: Clark GM, Popple RA, Prendergast BM, Spencer SA, Thomas EM, Stewart JG, et al. Plan quality and treatment planning technique for single isocenter cranial radiosurgery with volumetric modulated arc therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2012;2: Huang Y, Chin K, Robbins J, Kim J, Li H, Amro H, et al. Radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases with single-isocenter dynamic conformal arcs (SIDCA). Radiother Oncol. 2014;112(1): Paddick I. A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(3): Paddick I, Lippitz B. A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J Neurosurg. 2006;105: Blonigen B, Steinmetz R, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC. Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radio necrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(4): Valéry CA, Cornu P, Noel G, Duyme M, Boisserie G, Sakka LJ, et al. Predictive factors of radiation necrosis after radiosurgery for cerebral metises. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2003;81(1 4): Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, Osti MF, Trasimeni G, Bozzao A, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6: Xue J, Kubicek GJ, Grimm J, LaCouture T, Chen Y, Goldman HW, et al. Biological implications of whole-brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery of multiple brain J Neurosurg. 2014;121 Suppl 2: Mayo C, Ding L, Addesa A, Kadish S, Fitzgerald TJ, Moser R. Initial experience with volumetric IMRT (RapidArc) for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78(5): Huang C, Ren L, Kirkpatrick J, Wang Z. Treatment of multiple brain metastases using stereotactic radiosurgery with single-isocenter volumetric modulated arc therapy: comparison with conventional dynamic conformal arc and static beam stereotactic radiosurgery. Med Phys. 2012;39: Ma L, Nichol A, Hossain S, Wang B, Petti P, Vellani R, et al. Variable dose interplay effects across radiosurgical apparatus in treating multiple brain Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2014;9(6): Gevaert T, Boussaer M, Engels B, Litré CF, Prieur A, Wdowczyk D, et al. Evaluation of the clinical usefulness for using verification images during frameless radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108(1): Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
WHOLE-BRAIN RADIOTHERAPY WITH SIMULTANEOUS INTEGRATED BOOST TO MULTIPLE BRAIN METASTASES USING VOLUMETRIC MODULATED ARC THERAPY
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.03.029 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 253 259, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.03.029 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 75, No. 1, pp. 253 259, 2009 Copyright Ó 2009 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/09/$ see front
Feasibility of using the Vero SBRT system for intracranial SRS
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 1, 2014 Feasibility of using the Vero SBRT system for intracranial SRS Manuela Burghelea, 1,2a Dirk Verellen, 1 Thierry Gevaert, 1 Tom Depuydt,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 15, NUMBER 1, 2014 Feasibility of using the Vero SBRT system for intracranial SRS Manuela Burghelea, 1,2a Dirk Verellen, 1 Thierry Gevaert, 1 Tom Depuydt,
Overview of MLC-based Linac Radiosurgery
 SRT I: Comparison of SRT Techniques 1 Overview of MLC-based Linac Radiosurgery Grace Gwe-Ya Kim, Ph.D. DABR 2 MLC based Linac SRS Better conformity for irregular target Improved dose homogeneity inside
SRT I: Comparison of SRT Techniques 1 Overview of MLC-based Linac Radiosurgery Grace Gwe-Ya Kim, Ph.D. DABR 2 MLC based Linac SRS Better conformity for irregular target Improved dose homogeneity inside
Abstract ID 352 Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: A dose-volume study Tanya Kairn 123, Somayeh Zolfaghari 1, Daniel Papworth
 Abstract ID 352 Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: A dose-volume study Tanya Kairn 123, Somayeh Zolfaghari 1, Daniel Papworth 2, Mark West 2, David Schlect 2, Scott Crowe 13 1 Queensland
Abstract ID 352 Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: A dose-volume study Tanya Kairn 123, Somayeh Zolfaghari 1, Daniel Papworth 2, Mark West 2, David Schlect 2, Scott Crowe 13 1 Queensland
Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases
 Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases CASE STUDY Institution: Odette Cancer Centre Location: Sunnybrook
Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases CASE STUDY Institution: Odette Cancer Centre Location: Sunnybrook
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI)
 Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR
 Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FASTRO Department of Radiation Oncology Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN, USA Indra J. Das,
Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FASTRO Department of Radiation Oncology Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN, USA Indra J. Das,
Comparison of volumetric-modulated arc therapy and dynamic conformal arc treatment planning for cranial stereotactic radiosurgery
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 1, 2016 Comparison of volumetric-modulated arc therapy and dynamic conformal arc treatment planning for cranial stereotactic radiosurgery
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 1, 2016 Comparison of volumetric-modulated arc therapy and dynamic conformal arc treatment planning for cranial stereotactic radiosurgery
We have previously reported good clinical results
 J Neurosurg 113:48 52, 2010 Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional
J Neurosurg 113:48 52, 2010 Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional
Technique For Plan Quality and Efficiency Using VMAT Radiosurgery For Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases
 Technique For Plan Quality and Efficiency Using VMAT Radiosurgery For Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases Kimberly Dempsey, BS, CMD, RT(T) Heather Smith, MS, CMD, RT(R)(T) The University of Alabama
Technique For Plan Quality and Efficiency Using VMAT Radiosurgery For Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases Kimberly Dempsey, BS, CMD, RT(T) Heather Smith, MS, CMD, RT(R)(T) The University of Alabama
IMRT Planning Basics AAMD Student Webinar
 IMRT Planning Basics AAMD Student Webinar March 12, 2014 Karen Chin Snyder, MS Senior Associate Physicist Department of Radiation Oncology Disclosures The presenter has received speaker honoraria from
IMRT Planning Basics AAMD Student Webinar March 12, 2014 Karen Chin Snyder, MS Senior Associate Physicist Department of Radiation Oncology Disclosures The presenter has received speaker honoraria from
Original Article. Teyyiba Kanwal, Muhammad Khalid, Syed Ijaz Hussain Shah, Khawar Nadeem
 Original Article Treatment Planning Evaluation of Sliding Window and Multiple Static Segments Technique in Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy for Different Beam Directions Teyyiba Kanwal, Muhammad Khalid,
Original Article Treatment Planning Evaluation of Sliding Window and Multiple Static Segments Technique in Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy for Different Beam Directions Teyyiba Kanwal, Muhammad Khalid,
Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Implementation of radiosurgery and SBRT requires a fundamentally sound approach Errors don t blur out
Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Implementation of radiosurgery and SBRT requires a fundamentally sound approach Errors don t blur out
Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife
 Conflicts of Interest Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife David Schlesinger, Ph.D. Research support: Elekta Instruments, AB Lars Leksell Gamma Knife Center University
Conflicts of Interest Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife David Schlesinger, Ph.D. Research support: Elekta Instruments, AB Lars Leksell Gamma Knife Center University
Fractionated SRT using VMAT and Gamma Knife for brain metastases and gliomas a planning study
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 6, 2015 Fractionated SRT using VMAT and Gamma Knife for brain metastases and gliomas a planning study Marie Huss, 1a Pierre Barsoum, 2 Ernest
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 6, 2015 Fractionated SRT using VMAT and Gamma Knife for brain metastases and gliomas a planning study Marie Huss, 1a Pierre Barsoum, 2 Ernest
SRS Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency: VMAT vs Dynamic Conformal ARCs
 SRS Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency: VMAT vs Dynamic Conformal ARCs Ahpa Plypoo, MS, CMD, DABR Clinical Medical Physicist, Department of Radiation Oncology Loyola University Health System, Maywood,
SRS Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency: VMAT vs Dynamic Conformal ARCs Ahpa Plypoo, MS, CMD, DABR Clinical Medical Physicist, Department of Radiation Oncology Loyola University Health System, Maywood,
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties
 SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
Radiosurgery. Most Important! 8/2/2012. Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery
 Therapy SAM Symposium: WE-A-BRCD-1 Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery Kamil M. Yenice, PhD Associate Professor Chief of Clinical Physics
Therapy SAM Symposium: WE-A-BRCD-1 Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery Kamil M. Yenice, PhD Associate Professor Chief of Clinical Physics
IS SMALLER BETTER? COMPARISON OF 3-MM AND 5-MM LEAF SIZE FOR STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY: A DOSIMETRIC STUDY
 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 66, No. 4, Supplement, pp. S76 S81, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/06/$ see front matter doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.04.061
Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 66, No. 4, Supplement, pp. S76 S81, 2006 Copyright 2006 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/06/$ see front matter doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.04.061
Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Linear accelerators. Basic technique. Indications of SRS
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
A Comparison of IMRT and VMAT Technique for the Treatment of Rectal Cancer
 A Comparison of IMRT and VMAT Technique for the Treatment of Rectal Cancer Tony Kin Ming Lam Radiation Planner Dr Patricia Lindsay, Radiation Physicist Dr John Kim, Radiation Oncologist Dr Kim Ann Ung,
A Comparison of IMRT and VMAT Technique for the Treatment of Rectal Cancer Tony Kin Ming Lam Radiation Planner Dr Patricia Lindsay, Radiation Physicist Dr John Kim, Radiation Oncologist Dr Kim Ann Ung,
Work partially supported by VisionRT
 Work partially supported by VisionRT Background of frameless intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery UCSD SRS/SRT procedure Clinical Results Summary Total prescribed doses : order of 10 50 Gy Planning targets
Work partially supported by VisionRT Background of frameless intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery UCSD SRS/SRT procedure Clinical Results Summary Total prescribed doses : order of 10 50 Gy Planning targets
Can we hit the target? Can we put the dose where we want it? Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy
 Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
Chapters from Clinical Oncology
 Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
A treatment planning study comparing Elekta VMAT and fixed field IMRT using the varian treatment planning system eclipse
 Peters et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:153 RESEARCH Open Access A treatment planning study comparing Elekta VMAT and fixed field IMRT using the varian treatment planning system eclipse Samuel Peters
Peters et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:153 RESEARCH Open Access A treatment planning study comparing Elekta VMAT and fixed field IMRT using the varian treatment planning system eclipse Samuel Peters
Treatment Planning for Lung. Kristi Hendrickson, PhD, DABR University of Washington Dept. of Radiation Oncology
 Treatment Planning for Lung Kristi Hendrickson, PhD, DABR University of Washington Dept. of Radiation Oncology Outline of Presentation Dosimetric planning strategies for SBRT lung Delivery techniques Examples
Treatment Planning for Lung Kristi Hendrickson, PhD, DABR University of Washington Dept. of Radiation Oncology Outline of Presentation Dosimetric planning strategies for SBRT lung Delivery techniques Examples
A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 394 400, 2014 A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM * D. ADAM 1,2,
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 394 400, 2014 A TREATMENT PLANNING STUDY COMPARING VMAT WITH 3D CONFORMAL RADIOTHERAPY FOR PROSTATE CANCER USING PINNACLE PLANNING SYSTEM * D. ADAM 1,2,
Trajectory Modulated Arc Therapy: Application to Partial Breast Irradiation. Research and development to advance radiotherapy
 Trajectory Modulated Arc Therapy: Application to Partial Breast Irradiation Dimitre Hristov Radiation Oncology Stanford University Research and development to advance radiotherapy New imaging platforms:
Trajectory Modulated Arc Therapy: Application to Partial Breast Irradiation Dimitre Hristov Radiation Oncology Stanford University Research and development to advance radiotherapy New imaging platforms:
I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy
 I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy 5 linear accelerators (LINACs): Varian TrueBeam 6, 10 & 18 MV photons, 6-18 MeV electrons, image-guided (IGRT) and intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT),
I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy 5 linear accelerators (LINACs): Varian TrueBeam 6, 10 & 18 MV photons, 6-18 MeV electrons, image-guided (IGRT) and intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT),
Treatment accuracy without rotational setup corrections in intracranial SRT
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 4, 2016 Treatment accuracy without rotational setup corrections in intracranial SRT Eeva Boman, 1,2a Mika Kapanen, 1,2 Marko Laaksomaa, 1
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 4, 2016 Treatment accuracy without rotational setup corrections in intracranial SRT Eeva Boman, 1,2a Mika Kapanen, 1,2 Marko Laaksomaa, 1
Efficient SIB-IMRT planning of head & neck patients with Pinnacle 3 -DMPO
 Investigations and research Efficient SIB-IMRT planning of head & neck patients with Pinnacle 3 -DMPO M. Kunze-Busch P. van Kollenburg Department of Radiation Oncology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
Investigations and research Efficient SIB-IMRT planning of head & neck patients with Pinnacle 3 -DMPO M. Kunze-Busch P. van Kollenburg Department of Radiation Oncology, Radboud University Nijmegen Medical
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy. Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017
 CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
Is dosimetry of multiple mets radiosurgery vendor platform dependent? Y. Zhang
 Is dosimetry of multiple mets radiosurgery vendor platform dependent? Y. Zhang Linac Based -TrueBeam -Trilogy CyberKnife GammaKnife 2 Objectives To provide an overview of the physics of GammaKnife, CyberKnife
Is dosimetry of multiple mets radiosurgery vendor platform dependent? Y. Zhang Linac Based -TrueBeam -Trilogy CyberKnife GammaKnife 2 Objectives To provide an overview of the physics of GammaKnife, CyberKnife
Case Study. Institution Farrer Park Hospital
 Case Study Single isocenter high definition dynamic radiosurgery (HDRS) for multiple brain metastases HDRS with Monaco, Versa HD and HexaPOD allows multiple brain metastases treatment within standard 15-minute
Case Study Single isocenter high definition dynamic radiosurgery (HDRS) for multiple brain metastases HDRS with Monaco, Versa HD and HexaPOD allows multiple brain metastases treatment within standard 15-minute
FROM ICARO1 TO ICARO2: THE MEDICAL PHYSICS PERSPECTIVE. Geoffrey S. Ibbott, Ph.D. June 20, 2017
 FROM ICARO1 TO ICARO2: THE MEDICAL PHYSICS PERSPECTIVE Geoffrey S. Ibbott, Ph.D. June 20, 2017 1 DISCLOSURES My institution holds Strategic Partnership Research Agreements with Varian, Elekta, and Philips
FROM ICARO1 TO ICARO2: THE MEDICAL PHYSICS PERSPECTIVE Geoffrey S. Ibbott, Ph.D. June 20, 2017 1 DISCLOSURES My institution holds Strategic Partnership Research Agreements with Varian, Elekta, and Philips
Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency for Radiosurgery to Multiple Brain Metastases: Non- Coplanar RapidArc vs. Gamma Knife.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiation Oncology Faculty Papers Department of Radiation Oncology 2-11-2016 Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency for Radiosurgery to
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiation Oncology Faculty Papers Department of Radiation Oncology 2-11-2016 Plan Quality and Treatment Efficiency for Radiosurgery to
Original Date: April 2016 Page 1 of 7 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY: STEREO RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: Please refer to pages 5-6 LCD
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY: STEREO RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: Please refer to pages 5-6 LCD
Feasibility of the partial-single arc technique in RapidArc planning for prostate cancer treatment
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Feasibility of the partial-single arc technique in RapidArc planning for prostate cancer treatment Suresh Rana 1 and ChihYao Cheng 2 Abstract The volumetric modulated
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Feasibility of the partial-single arc technique in RapidArc planning for prostate cancer treatment Suresh Rana 1 and ChihYao Cheng 2 Abstract The volumetric modulated
Dosimetric Analysis of Respiratory-Gated RapidArc with Varying Gating Window Times
 Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS Vol. 26, No. 2, June, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.87 Dosimetric Analysis of Respiratory-Gated RapidArc with Varying Gating Window Times Mee
Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS Vol. 26, No. 2, June, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.87 Dosimetric Analysis of Respiratory-Gated RapidArc with Varying Gating Window Times Mee
Treating Multiple. Brain Metastases (BM)
 ESTRO 36 5-9 May 2017, Vienna Austria, Accuray Symposium Treating Multiple Brain Metastases (BM) with CyberKnife System Frederic Dhermain MD PhD, Radiation Oncologist Gustave Roussy University Hospital,
ESTRO 36 5-9 May 2017, Vienna Austria, Accuray Symposium Treating Multiple Brain Metastases (BM) with CyberKnife System Frederic Dhermain MD PhD, Radiation Oncologist Gustave Roussy University Hospital,
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung
 Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
8/2/2018. Disclosure. Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation
 Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation Deshan Yang, PhD, Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine Washington University in Saint Louis 1 Disclosure Received research
Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation Deshan Yang, PhD, Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine Washington University in Saint Louis 1 Disclosure Received research
Guidelines for the use of inversely planned treatment techniques in Clinical Trials: IMRT, VMAT, TomoTherapy
 Guidelines for the use of inversely planned treatment techniques in Clinical Trials: IMRT, VMAT, TomoTherapy VERSION 2.1 April 2015 Table of Contents Abbreviations & Glossary... 3 Executive Summary...
Guidelines for the use of inversely planned treatment techniques in Clinical Trials: IMRT, VMAT, TomoTherapy VERSION 2.1 April 2015 Table of Contents Abbreviations & Glossary... 3 Executive Summary...
Implementation of advanced RT Techniques
 Implementation of advanced RT Techniques Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Budapest, Hungary 2. Kongres radiološke tehnologije, Vukovar, 23-25. September 2016. Current RT equipments at NIO,
Implementation of advanced RT Techniques Tibor Major, PhD National Institute of Oncology Budapest, Hungary 2. Kongres radiološke tehnologije, Vukovar, 23-25. September 2016. Current RT equipments at NIO,
Improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain with hippocampus sparing: a comparison to the RTOG 0933 trial
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2017 Improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2017 Improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain
Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon. Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology
 Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology Outline Advances in radiotherapy technique Oligo - disease Advancements
Radiotherapy What are our options and what is on the horizon Dr Kevin So Specialist Radiation Oncologist Epworth Radiation Oncology Outline Advances in radiotherapy technique Oligo - disease Advancements
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon. Treatment information
 Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
A method to improve dose gradient for robotic radiosurgery
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 6, 2015 A method to improve dose gradient for robotic radiosurgery Tianfang Li, a Cihat Ozhasoglu, Steven Burton, John Flickinger, Dwight
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 6, 2015 A method to improve dose gradient for robotic radiosurgery Tianfang Li, a Cihat Ozhasoglu, Steven Burton, John Flickinger, Dwight
A Dosimetric Comparison of Whole-Lung Treatment Techniques. in the Pediatric Population
 A Dosimetric Comparison of Whole-Lung Treatment Techniques in the Pediatric Population Corresponding Author: Christina L. Bosarge, B.S., R.T. (R) (T) Indiana University School of Medicine Department of
A Dosimetric Comparison of Whole-Lung Treatment Techniques in the Pediatric Population Corresponding Author: Christina L. Bosarge, B.S., R.T. (R) (T) Indiana University School of Medicine Department of
NIA MAGELLAN HEALTH RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD. Dosimetry Planning
 NIA MAGELLAN HEALTH RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed
NIA MAGELLAN HEALTH RADIATION ONCOLOGY CODING STANDARD Dosimetry Planning CPT Codes: 77295, 77300, 77301, 77306, 77307, 77321, 77316, 77317, 77318, 77331, 77399 Original Date: April, 2011 Last Reviewed
Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in Eclipse and iplan RT Dose
 Petrovic B Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for stereotaxy Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in and RT Dose Borislava Petrovic 1, Aleksandra Grządziel
Petrovic B Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for stereotaxy Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in and RT Dose Borislava Petrovic 1, Aleksandra Grządziel
THE GOLD STANDARD IN INTRACRANIAL RADIOSURGERY
 THE GOLD STANDARD IN INTRACRANIAL RADIOSURGERY LEKSELL GAMMA KNIFE ICON GIVING SOUTH AFRICANS LOCAL ACCESS TO THE GOLD STANDARD FOR THE TREATMENT OF BRAIN CONDITIONS Exclusively for the brain: Gamma Knife
THE GOLD STANDARD IN INTRACRANIAL RADIOSURGERY LEKSELL GAMMA KNIFE ICON GIVING SOUTH AFRICANS LOCAL ACCESS TO THE GOLD STANDARD FOR THE TREATMENT OF BRAIN CONDITIONS Exclusively for the brain: Gamma Knife
Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015
 Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015 Most common brain tumor, affecting 8.5-15% of cancer patients. Treatment options: Whole brain radiation
Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015 Most common brain tumor, affecting 8.5-15% of cancer patients. Treatment options: Whole brain radiation
Evaluation of Three-dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy and Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques in High-Grade Gliomas
 1 Carol Boyd Comprehensive Case Study July 11, 2013 Evaluation of Three-dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy and Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques in High-Grade Gliomas Abstract: Introduction:
1 Carol Boyd Comprehensive Case Study July 11, 2013 Evaluation of Three-dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy and Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Techniques in High-Grade Gliomas Abstract: Introduction:
Cyberknife Stereotactic Treatment
 Cyberknife Stereotactic Treatment Eugene Lief, Ph.D. Christ Hospital Jersey City, New Jersey USA DISCLAIMER: I am not affiliated with any vendor and did not receive any financial support from any vendor.
Cyberknife Stereotactic Treatment Eugene Lief, Ph.D. Christ Hospital Jersey City, New Jersey USA DISCLAIMER: I am not affiliated with any vendor and did not receive any financial support from any vendor.
Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET
 University of Michigan Department of Radiation Oncology Division of Radiation Physics Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET Resident: Rotation staff mentor/ advisor: _Scott Hadley,
University of Michigan Department of Radiation Oncology Division of Radiation Physics Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET Resident: Rotation staff mentor/ advisor: _Scott Hadley,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Shanmugam Thirumalai Swamy 1,2 *, Chandrasekaran Anu Radha 2, Gandhi Arun 1, Murugesan Kathirvel 1, Sai Subramanian 1.
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.12.5019 Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Schwannoma RESEARCH ARTICLE Planning and Dosimetric Study of Volumetric Modulated Arc Based Hypofractionated
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.12.5019 Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Schwannoma RESEARCH ARTICLE Planning and Dosimetric Study of Volumetric Modulated Arc Based Hypofractionated
Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife. Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague
 Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague Radiosurgery - Definition Professor Lars Leksell The tools used by the surgeon must be adapted to the task and where the human
Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague Radiosurgery - Definition Professor Lars Leksell The tools used by the surgeon must be adapted to the task and where the human
Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using orthogonal MV and MV-CBCT
 Received: 28 September 2017 Revised: 17 November 2017 Accepted: 28 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12276 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using
Received: 28 September 2017 Revised: 17 November 2017 Accepted: 28 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12276 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using
A VMAT PLANNING SOLUTION FOR NECK CANCER PATIENTS USING THE PINNACLE 3 PLANNING SYSTEM *
 Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 401 410, 2014 A VMAT PLANNING SOLUTION FOR NECK CANCER PATIENTS USING THE PINNACLE 3 PLANNING SYSTEM * M. D. SUDITU 1,2, D. ADAM 1,2, R. POPA 1,2, V. CIOCALTEI
Romanian Reports in Physics, Vol. 66, No. 2, P. 401 410, 2014 A VMAT PLANNING SOLUTION FOR NECK CANCER PATIENTS USING THE PINNACLE 3 PLANNING SYSTEM * M. D. SUDITU 1,2, D. ADAM 1,2, R. POPA 1,2, V. CIOCALTEI
Helical Tomotherapy Experience. TomoTherapy Whole Brain Head & Neck Prostate Lung Summary. HI-ART TomoTherapy System. HI-ART TomoTherapy System
 The Challenges Associated with Differential Dose Delivery using IMRT Chester Ramsey, Ph.D. Director of Medical Physics Thompson Cancer Center Knoxville, Tennessee, U.S.A Collaborators Chester Ramsey, Ph.D.
The Challenges Associated with Differential Dose Delivery using IMRT Chester Ramsey, Ph.D. Director of Medical Physics Thompson Cancer Center Knoxville, Tennessee, U.S.A Collaborators Chester Ramsey, Ph.D.
Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas Thomas Samuel Ram, a Paul B. Ravindran,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas Thomas Samuel Ram, a Paul B. Ravindran,
Varian Treatment. Streamlined Treatment Delivery Management Application. Specifications
 Varian Treatment Streamlined Treatment Delivery Management Application Specifications Specifications Varian Treatment 1 Introduction Streamlined Treatment Delivery Management Varian Treatment verifies
Varian Treatment Streamlined Treatment Delivery Management Application Specifications Specifications Varian Treatment 1 Introduction Streamlined Treatment Delivery Management Varian Treatment verifies
THE TRANSITION FROM 2D TO 3D AND TO IMRT - RATIONALE AND CRITICAL ELEMENTS
 THE TRANSITION FROM 2D TO 3D AND TO IMRT - RATIONALE AND CRITICAL ELEMENTS ICTP SCHOOL ON MEDICAL PHYSICS FOR RADIATION THERAPY DOSIMETRY AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR BASIC AND ADVANCED APPLICATIONS March
THE TRANSITION FROM 2D TO 3D AND TO IMRT - RATIONALE AND CRITICAL ELEMENTS ICTP SCHOOL ON MEDICAL PHYSICS FOR RADIATION THERAPY DOSIMETRY AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR BASIC AND ADVANCED APPLICATIONS March
Elekta Synergy Digital accelerator for advanced IGRT
 Elekta Synergy Digital accelerator for advanced IGRT Setting the standard for confident care The Field of Radiation Therapy is Constantly Changing Being able to take full advantage of the latest clinical
Elekta Synergy Digital accelerator for advanced IGRT Setting the standard for confident care The Field of Radiation Therapy is Constantly Changing Being able to take full advantage of the latest clinical
Overview of Advanced Techniques in Radiation Therapy
 Overview of Advanced Techniques in Radiation Therapy Jacob (Jake) Van Dyk Manager, Physics & Engineering, LRCP Professor, UWO University of Western Ontario Acknowledgements Glenn Bauman Jerry Battista
Overview of Advanced Techniques in Radiation Therapy Jacob (Jake) Van Dyk Manager, Physics & Engineering, LRCP Professor, UWO University of Western Ontario Acknowledgements Glenn Bauman Jerry Battista
Additional radiation boost to whole brain radiation therapy may improve the survival of patients with brain metastases in small cell lung cancer
 Sun et al. Radiation Oncology (2018) 13:250 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1198-4 RESEARCH Open Access Additional radiation boost to whole brain radiation therapy may improve the survival of patients
Sun et al. Radiation Oncology (2018) 13:250 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1198-4 RESEARCH Open Access Additional radiation boost to whole brain radiation therapy may improve the survival of patients
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 27 th ICRO-AROI 2017 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Dr Sajal Kakkar MD, FUICC (USA), FAROI (Fr) Consultant Radiation Oncologist Max Super Speciality Hospital, Mohali SRS Introduction Stereotactic techniques
27 th ICRO-AROI 2017 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Dr Sajal Kakkar MD, FUICC (USA), FAROI (Fr) Consultant Radiation Oncologist Max Super Speciality Hospital, Mohali SRS Introduction Stereotactic techniques
Lung Spine Phantom. Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014
 Lung Spine Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 week. During this
Lung Spine Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 week. During this
CURRICULUM OUTLINE FOR TRANSITIONING FROM 2-D RT TO 3-D CRT AND IMRT
 CURRICULUM OUTLINE FOR TRANSITIONING FROM 2-D RT TO 3-D CRT AND IMRT Purpose The purpose of this curriculum outline is to provide a framework for multidisciplinary training for radiation oncologists, medical
CURRICULUM OUTLINE FOR TRANSITIONING FROM 2-D RT TO 3-D CRT AND IMRT Purpose The purpose of this curriculum outline is to provide a framework for multidisciplinary training for radiation oncologists, medical
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview. Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS
 Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Proton Stereotactic Radiotherapy: Clinical Overview Brian Winey, Ph.D. Physicist, MGH Assistant Professor, HMS Acknowledgements Radiation Oncologists and Physicists at various institutions (MGH, MDACC,
Historically, the appearance of multiple brain
 J Neurosurg (Suppl 2) 121:51 59, 2014 AANS, 2014 Comparison of radiation dose spillage from the Gamma Knife Perfexion with that from volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery during treatment of multiple brain
J Neurosurg (Suppl 2) 121:51 59, 2014 AANS, 2014 Comparison of radiation dose spillage from the Gamma Knife Perfexion with that from volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery during treatment of multiple brain
A dosimetric comparison between volumetric-modulated arc therapy and dynamic conformal arc therapy in SBRT
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 838-843 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A dosimetric comparison between volumetric-modulated arc therapy and
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 838-843 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A dosimetric comparison between volumetric-modulated arc therapy and
Image-guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cranial Lesions: Large Margins Compensate for Reduced Image Guidance Frequency
 Image-guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cranial Lesions: Large Margins Compensate for Reduced Image Guidance Frequency HARUN BADAKHSHI 1, DAVID KAUL 1, PETER WUST 1, EDZARD WIENER 2, VOLKER BUADCH 1
Image-guided Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cranial Lesions: Large Margins Compensate for Reduced Image Guidance Frequency HARUN BADAKHSHI 1, DAVID KAUL 1, PETER WUST 1, EDZARD WIENER 2, VOLKER BUADCH 1
Quality assurance of volumetric modulated arc therapy using Elekta Synergy
 Acta Oncologica, 2009; 48: 11931197 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality assurance of volumetric modulated arc therapy using Elekta Synergy AKIHIRO HAGA 1, KEIICHI NAKAGAWA 1, KENSHIRO SHIRAISHI 1, SAORI ITOH 1, ATSURO
Acta Oncologica, 2009; 48: 11931197 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality assurance of volumetric modulated arc therapy using Elekta Synergy AKIHIRO HAGA 1, KEIICHI NAKAGAWA 1, KENSHIRO SHIRAISHI 1, SAORI ITOH 1, ATSURO
Radiotherapy and Brain Metastases. Dr. K Van Beek Radiation-Oncologist BSMO annual Meeting Diegem
 Radiotherapy and Brain Metastases Dr. K Van Beek Radiation-Oncologist BSMO annual Meeting Diegem 24-02-2017 Possible strategies Watchful waiting Surgery Postop RT to resection cavity or WBRT postop SRS
Radiotherapy and Brain Metastases Dr. K Van Beek Radiation-Oncologist BSMO annual Meeting Diegem 24-02-2017 Possible strategies Watchful waiting Surgery Postop RT to resection cavity or WBRT postop SRS
Outline. Chapter 12 Treatment Planning Combination of Beams. Opposing pairs of beams. Combination of beams. Opposing pairs of beams
 Chapter 12 Treatment Planning Combination of Beams Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther Outline Combination
Chapter 12 Treatment Planning Combination of Beams Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther Outline Combination
Dosimetric effects of positioning shifts using 6D-frameless stereotactic Brainlab system in hypofractionated intracranial radiotherapy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 1, 2016 Dosimetric effects of positioning shifts using 6D-frameless stereotactic Brainlab system in hypofractionated intracranial radiotherapy
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 1, 2016 Dosimetric effects of positioning shifts using 6D-frameless stereotactic Brainlab system in hypofractionated intracranial radiotherapy
Unrivaled, End-to-End
 PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
Dosimetry Comparison of Gamma Knife and External Beam Radiation Therapy on Brain Tumors. Research Thesis
 Dosimetry Comparison of Gamma Knife and External Beam Radiation Therapy on Brain Tumors Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with research distinction in
Dosimetry Comparison of Gamma Knife and External Beam Radiation Therapy on Brain Tumors Research Thesis Presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with research distinction in
Disclosures. Overview 8/3/2016. SRS: Cranial and Spine
 SRS: Cranial and Spine Brian Winey, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures Travel and research funds from Elekta Travel funds from IBA
SRS: Cranial and Spine Brian Winey, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures Travel and research funds from Elekta Travel funds from IBA
SBRT fundamentals. Outline 8/2/2012. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session
 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session J Perks PhD, UC Davis Medical Center, Sacramento CA SBRT fundamentals Extra-cranial treatments Single or small number (2-5) of
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session J Perks PhD, UC Davis Medical Center, Sacramento CA SBRT fundamentals Extra-cranial treatments Single or small number (2-5) of
Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in Gamma Knife radiosurgery
 Received: 7 November 2016 Revised: 9 August 2017 Accepted: 21 August 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12193 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in
Received: 7 November 2016 Revised: 9 August 2017 Accepted: 21 August 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12193 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in
Clinical Impact of Couch Top and Rails on IMRT and Arc Therapy
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2011 Clinical Impact of Couch Top and Rails on IMRT and Arc Therapy
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2011 Clinical Impact of Couch Top and Rails on IMRT and Arc Therapy
IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience. Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor
 IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor Disclosures I have no research support or financial interest to disclose. Learning Objectives 1. Review
IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor Disclosures I have no research support or financial interest to disclose. Learning Objectives 1. Review
Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer
 1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
Technical Study. Institution University of Texas Health San Antonio. Location San Antonio, Texas. Medical Staff. Daniel Saenz. Niko Papanikolaou.
 Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
Stereotaxy. Outlines. Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry. SBRT - Simulation. Body Localizer. Sim. Sim. Sim. Stereotaxy?
 Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry Lu Wang, Ph.D. Radiation Oncology Department Fox Chase Cancer Center Outlines Illustrate the difference between SBRT vs. CRT Introduce the major procedures
Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry Lu Wang, Ph.D. Radiation Oncology Department Fox Chase Cancer Center Outlines Illustrate the difference between SBRT vs. CRT Introduce the major procedures
Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy. Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. A guidance document on behalf of:
 Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A guidance document on behalf of: Canadian Association of Radiation Oncology Canadian Organization
Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A guidance document on behalf of: Canadian Association of Radiation Oncology Canadian Organization
brain SPINE 2 SRS Matures into breast lung spine LUNG Dr. Robert Timmerman Discusses SBRT for Inoperable Lung Cancer BRAIN
 NEWS AND ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF SERIOUS DISEASE brain SPINE 2 SRS Matures into Mainstream Extracranial Technique lung spine breast LUNG Dr. Robert Timmerman Discusses SBRT for Inoperable
NEWS AND ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT OF SERIOUS DISEASE brain SPINE 2 SRS Matures into Mainstream Extracranial Technique lung spine breast LUNG Dr. Robert Timmerman Discusses SBRT for Inoperable
4 Essentials of CK Physics 8/2/2012. SRS using the CyberKnife. Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest
 SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
3D Pre-treatment Dose Verification for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Patients
 3D Pre-treatment Dose Verification for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Patients G Asuni *1, T vanbeek 1, E VanUtyven 1, P McCowan 1,2, and B.M.C. McCurdy 1,2,3 1 Medical Physics Department, CancerCare
3D Pre-treatment Dose Verification for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Patients G Asuni *1, T vanbeek 1, E VanUtyven 1, P McCowan 1,2, and B.M.C. McCurdy 1,2,3 1 Medical Physics Department, CancerCare
The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases
 The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases Icro Meattini, MD Radiotherapy-Oncology Unit AOU Careggi Hospital Florence University, Italy Liver Metastases - Background The
The role of Radiation Oncologist: Hi-tech treatments for liver metastases Icro Meattini, MD Radiotherapy-Oncology Unit AOU Careggi Hospital Florence University, Italy Liver Metastases - Background The
SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES
 SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES MELISSA C. MARTIN, M.S., FACR, FAAPM PRESIDENT AAPM - 2017 PRESIDENT - THERAPY PHYSICS INC., GARDENA, CA MELISSA@THERAPYPHYSICS.COM AAPM Spring
SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES MELISSA C. MARTIN, M.S., FACR, FAAPM PRESIDENT AAPM - 2017 PRESIDENT - THERAPY PHYSICS INC., GARDENA, CA MELISSA@THERAPYPHYSICS.COM AAPM Spring
RTTs role in lung SABR
 RTTs role in lung SABR Bart van Baaren Lineke van der Weide VU Medical Centre SBRT symposium VUMC 16 December 2017 Flow chart lung SABR Pre-treatment imaging Treatment planning On-line imaging Treatment
RTTs role in lung SABR Bart van Baaren Lineke van der Weide VU Medical Centre SBRT symposium VUMC 16 December 2017 Flow chart lung SABR Pre-treatment imaging Treatment planning On-line imaging Treatment
Jefferson Digital Commons. Thomas Jefferson University. Haisong Lui Thomas Jefferson University,
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiation Oncology Faculty Papers Department of Radiation Oncology 9-8-2016 Dosimetric validation for an automatic brain metastases planning
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Radiation Oncology Faculty Papers Department of Radiation Oncology 9-8-2016 Dosimetric validation for an automatic brain metastases planning
Translational Radiation Oncology, Physics & Supportive Care (TROP) Mark De Ridder, Wim Distelmans & Dirk Verellen
 Translational Radiation Oncology, Physics & Supportive Care (TROP) Mark De Ridder, Wim Distelmans & Dirk Verellen Tumor hypoxia: perfusion and diffusion limited oxygenation Hypoxia acute chronic 100 100
Translational Radiation Oncology, Physics & Supportive Care (TROP) Mark De Ridder, Wim Distelmans & Dirk Verellen Tumor hypoxia: perfusion and diffusion limited oxygenation Hypoxia acute chronic 100 100
A preplanning method for stereotactic radiosurgery to improve treatment workflow
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 3, 2016 A preplanning method for stereotactic radiosurgery to improve treatment workflow Kang-Hyun Ahn, 1,2 Naim Ozturk, 1,2 Brett Smith,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 17, NUMBER 3, 2016 A preplanning method for stereotactic radiosurgery to improve treatment workflow Kang-Hyun Ahn, 1,2 Naim Ozturk, 1,2 Brett Smith,
