The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
|
|
|
- Philomena Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi The Center for bioinformatics East China Normal University Aug. 30, 2018 Hayama Compus, Japan
2 Why Do We Focus on DNA Methylation? DNAm changes in the non-islands regions, such as shores and gene bodies also play important roles in gene expression regulation. Aberrant methylation could be used as biomarker for clinical decisions, such as cancer diagnosis and prognosis. DNA methylation markers can also be used to predict the origin of tumors with metastases. The Cancer Genome Atlas Project (TCGA) now provides unprecedented cancer genomic and methylation data resources for various cancer researches.
3 Progressive Change in DNA Methylation from Normal Tissue to Breast Cancer Tissue DNA methylation field defects in cancer tissue Progression of field defects in breast cancer. (c) Example of a DNAm profile of a hypervariable and hypermethylated DVMC, showing the progressive change in DNA methylation. N represents normal tissue from cancer-free women, NADJ for age-matched normal samples adjacent to breast cancers.
4 DNA Methylation Markers Distinguish Prostate Cancers from Benign Adjacent Tissue BMC Cancer, 17(1): 273, 2017
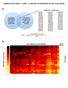
5 Methylation Markers can be Used for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Common Cancers Fig. Methylation signatures can differentiate different cancer types from corresponding normal tissues. (A) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering and heat map presentation associated with the methylation profile (according to the color scale shown) in different cancer types. (B) ROC curve showing the high sensitivity and specificity in predicting different cancer types. (C) Zoom-in view of the block diagram in B. PNAS, 114: , 2017
6 ctdna Methylation Markers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma ROC of the diagnostic prediction model with methylation markers in the training (c) and validation data sets (d). Nature materials, 16:1155, 2017 All of the studies confirmed that there are distinguished DNA methylation patterns between cancer tissues and their related normal tissues.
7 Data Resources and Methods Datasets (TCGA) Gene expression data: Level 3 expression data from TCGA, log2(x+1) transformed. DNA methylation data: (i) The probes mapped to sex chromosomes were removed; (ii) The samples with missing data (i.e. NAs) in more than 30% of the probes were excluded; (iii) The probes with missing data in more than 30% of the samples were discarded; (iv) The rest of the probes with NAs were imputed using the EMimpute algorithm; (v) BMIQ was employed to correct for the type II probe bias. Validation dataset GEO: GSE69914, GSE76938, GSE48684, GSE73549, GSE65820, GSE66836, GSE89852, GSE58999 and GSE38240
8 Feature Selection & Function Analysis Definition of differentially methylated probes between tumor and normal samples β-difference > 0.2 and a false discovery rate (FDR) corrected P-value (Benjamini/Hochberg) < 0.05 Definition of differentially methylated probes between different cancer types β-difference > 0.3 and FDR < 0.01 Feature selection & Tumor specific multiclass classifier Recursive feature elimination & logistic regression, OneVsRest Classifier Statistical analysis All statistical analyses and visualization were performed with Python3.5.2 on anaconda Gene ontology enrichment analysis and pathway enrichment analysis DAVID
9 Data Resources and Methods for Survival Analysis Cox regression analysis (1) Standard deviation (SD) across all tumor samples of 26 cancers should be > 0.2. (2) FDR (Benjamini/Hochberg method) for every probe was calculated via univariate cox regression in each cancer, the probes with FDR < 0.05 were retained for further filtration. (3) Log-rank test P-value for survival time among tumor samples should be < (4) Multivariate cox regression was performed for the left probes, and stepwise regression was conducted, the probes of multivariate cox regression p-value < 0.05 were removed from the feature set in each iteration. (5) The remaining probes were used to fit the prognostic classifier. Python package lifelines and cox s proportional hazard model was implemented in cox regression analysis.
10 Methylation Profiles of Different Cancers Vary Tremendously Countplot or differential methylated probes in different cancer types. The number of hypermethylated and hypomethylated CpG sites vary greatly in 18 different cancer types. 1. Esophageal carcinoma (ESCA) has the largest count of hypermethylated CpG sites, whereas pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma (PCPG) has the least. 2. Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma (CESC) has the least count of hypomethylated CpG sites, while liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) shows the highest number of hypomethylated CpG sites
11 Methylation Profiles of Different Cancers Vary Tremendously The distribution of differential methylated probes based on Relation to Island vary significantly in different groups. 1. Differential methylated CpG sites (DMCs) located at gene body are far more than that of other regions, and OpenSea holds a large proportion DMCs among all different Relation To Island (OpenSea, S_Shelf, S_Shore, Island, N_Shore and N_Shelf). 2. The number of differential methylated CpG sites located in the gene body regions is the highest among different genomic regions (TSS1500, TSS200, 5'UTR, 1stExon, Body and 3'UTR).
12 Methylation Profiles of Different Cancers Vary Tremendously Spearman s correlation analysis between the methylation level of CpG sites and the expression of their corresponding genes for each cancer. Indicating that aberrant DNAms in different tumors may have different functions. Boxplot of Spearman s correlation among different cancer types. The hypermethylated CpG sites tends to negatively correlate with the expression of their corresponding genes in almost all different tumor types. The methylation level of most hypomethylated CpG sites are positively correlated with the expression of their corresponding genes in cancers, but some of them are negatively correlated with the expression of their relevant genes in other cancers
13 Seven Probes Classifier has Good Performance in Distinguishing Tumor and Normal a, ROC curve of training (12 cancer types and 1216 samples) showing the high sensitivity and specificity in predicting different cancer types from corresponding normal tissues. b Learning curve of 5-fold cross validation in training (ROC = 0.979).
14 Seven Probes Classifier has Good Performance in Distinguishing Tumor and Normal BRCA PRAD COAD c, d, e ROC curve for the validation data set of GSE69914(Breast Cancer), GSE48684(Colorectal Cancer) and GSE76938 (Prostate Cancer). f ROC curve for the independent validation data set of the remaining 9 TCGA cancers not included in the training set. T and N indicate numbers of tumor and normal samples
15 Seven Probes Classify Those Samples of 12 Cancer Types into Two Distinguished Groups Unsupervised hierarchical clustering and heatmap associated with the methylation profile of the seven probes across all 1216 samples of 12 cancers. Those samples were classified into two distinct classes by the 7 CpG sites Right color bars mark the tissue type and cancer type.
16 GO Biological Process and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis Results Enrichment analyses for those genes that their expression levels were significantly correlated with 4 probes, highly associated with tumor biogenesis.
17 Tumor-Specific Classifier with 12 Probes Effectively Distinguishes Different Cancers Unsupervised hierarchical clustering and heatmap showing the methylation profile of the selected 12 probes across 7605 tumor samples of 26 cancer types reals that those 12 probes complement with each other to distinguish different cancer types.
18 Tumor-Specific Classifier Effectively Distinguishes Different Cancers The micro-average AUC of OneVsRestClassifier based on those 12 selected CpG sites reaches to 0.98 for those 26 different cancers. The results indicate the high sensitivity and specificity of our multiclass tumor specific classifier in predicting different cancers.
19 Tumor-Specific Classifier Effectively Distinguishes Different Cancers Validation based on GEO datasets of breast cancer (BRCA), colorectal cancer (COAD), prostate cancer (PRAD), ovarian cancer (OV), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and hepatocellular carcinomas (LIHC). micro-average AUC > 0.89 ROC curve in six independent validation dataset of different cancers. T indicates the numbers of tumor samples used in each dataset.
20 a Tumor-Specific Classifier Effectively Predict the Origin of Tumors with Metastases GSE58999: Breast cancer with metastases to lymph node. GSE73549 and GSE38240: Prostate cancer with metastases to bone or lymph node (26 metastatic samples in total). ROC curve of multiclass tumor specific classifier in metastatic breast cancer and metastatic prostate cancer. T indicates the numbers of tumor samples with metastasis used in each dataset.
21 These 12 Probes can Effectively Distinguish Metastatic Tumors From Normal Tissues Unsupervised clustering of the DNA methylation levels of the 12 CpGs between normal prostate samples, prostate tumor and prostate tumor with metastases from GSE73549 and GSE Annotations of the column of the heatmap indicate disease states of patients.
22 Construction of the Probe-based Prognostic Classifier on 28 cancer types Methylation profile of the probes used by the prognostic classifier in patients Z-score distribution of the prognostic classifier and patient survival status
23 The Performance of Probe-based Prognostic Classifier Construction of the probe-based prognostic classifier. a The pipeline of feature selection for prognostic classifier. b-h The result of Prognostic classifier for 7 cancer types Upper panel: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for the patients in each of the 7 cancers Middle panel: heatmap showing methylation of the CpGs used by the prognostic classifier in patients.. Lower panel: Z-score distribution of the prognostic classifier and patient survival status. The patients were divided into low-risk and high-risk groups using the median value of the partial hazard as cutoff. p-value were calculated by the log-rank test.
24 Conclusions 1. Methylation profiles of different cancers vary tremendously, which can be used to distinguish the cancer from normal as well as different cancer types. 2. Results with independent validation datasets of various cancers demonstrate the performance and robustness of our DNAm site-based tumor-normal classifier. 3. Tumor-specific classifier can effectively distinguish different cancers. The DNAm markers for tumor-specific classifier can also be used to predict the origin of tumor with metastases or with unknown primary origin. 4. Prognostic classifier with DNAm pattern successfully divides patients into high-risk or low-risk group in different cancer types. 5. We identified potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers based on the methylation changes of DNAm patterns in diverse TCGA cancers, which have the potential application in clinical practices.
25 Thank You for Your Attention Questions?
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
User s Manual Version 1.0
 User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers
 Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity
 Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
Expanded View Figures
 Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt, Weizhou Zhang 1-4
 SOFTWARE TOOL ARTICLE TRGAted: A web tool for survival analysis using protein data in the Cancer Genome Atlas. [version 1; referees: 1 approved] Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt,
SOFTWARE TOOL ARTICLE TRGAted: A web tool for survival analysis using protein data in the Cancer Genome Atlas. [version 1; referees: 1 approved] Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt,
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser
 Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic and predictive value
 Lehmann et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:179 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1102-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic
Lehmann et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:179 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1102-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of public cancer datasets and signatures identifies TP53 mutant signatures with robust prognostic
Computational Investigation of Homologous Recombination DNA Repair Deficiency in Sporadic Breast Cancer
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 11-16-2017 Computational Investigation of Homologous Recombination DNA Repair
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 11-16-2017 Computational Investigation of Homologous Recombination DNA Repair
Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer
 Varn et al. BMC Medical Genomics (2015) 8:11 DOI 10.1186/s12920-015-0086-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer Frederick S Varn 1, Matthew
Varn et al. BMC Medical Genomics (2015) 8:11 DOI 10.1186/s12920-015-0086-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Integrative analysis of survival-associated gene sets in breast cancer Frederick S Varn 1, Matthew
DiffVar: a new method for detecting differential variability with application to methylation in cancer and aging
 Genome Biology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. DiffVar: a new method for detecting
Genome Biology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. DiffVar: a new method for detecting
Research Article Breast Cancer Prognosis Risk Estimation Using Integrated Gene Expression and Clinical Data
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 459203, 15 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/459203 Research Article Breast Cancer Prognosis Risk Estimation Using Integrated Gene Expression and Clinical Data
BioMed Research International, Article ID 459203, 15 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/459203 Research Article Breast Cancer Prognosis Risk Estimation Using Integrated Gene Expression and Clinical Data
LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer
 Original Article LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer patients Xiaoshun Shi 1 *, Yusong Chen 2,3 *, Allen M.
Original Article LncRNA TUSC7 affects malignant tumor prognosis by regulating protein ubiquitination: a genome-wide analysis from 10,237 pancancer patients Xiaoshun Shi 1 *, Yusong Chen 2,3 *, Allen M.
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals hepatocellular carcinoma-specific diagnostic biomarkers
 Cheng et al. Genome Medicine (218) 1:42 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1373-18-548-z RESEARCH Open Access Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals hepatocellular carcinoma-specific
Cheng et al. Genome Medicine (218) 1:42 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1373-18-548-z RESEARCH Open Access Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals hepatocellular carcinoma-specific
Integrative DNA methylome analysis of pan-cancer biomarkers in cancer discordant monozygotic twin-pairs
 Roos et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2016) 8:7 DOI 10.1186/s13148-016-0172-y RESEARCH Integrative DNA methylome analysis of pan-cancer biomarkers in cancer discordant monozygotic twin-pairs Open Access Leonie
Roos et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2016) 8:7 DOI 10.1186/s13148-016-0172-y RESEARCH Integrative DNA methylome analysis of pan-cancer biomarkers in cancer discordant monozygotic twin-pairs Open Access Leonie
Phenotype prediction based on genome-wide DNA methylation data
 Wilhelm BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15:193 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Phenotype prediction based on genome-wide DNA methylation data Thomas Wilhelm Abstract Background: DNA methylation (DNAm) has important
Wilhelm BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15:193 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Phenotype prediction based on genome-wide DNA methylation data Thomas Wilhelm Abstract Background: DNA methylation (DNAm) has important
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Elevated RNA Editing Activity Is a Major Contributor to Transcriptomic Diversity in Tumors
 Cell Reports Supplemental Information Elevated RNA Editing Activity Is a Major Contributor to Transcriptomic Diversity in s Nurit Paz-Yaacov, Lily Bazak, Ilana Buchumenski, Hagit T. Porath, Miri Danan-Gotthold,
Cell Reports Supplemental Information Elevated RNA Editing Activity Is a Major Contributor to Transcriptomic Diversity in s Nurit Paz-Yaacov, Lily Bazak, Ilana Buchumenski, Hagit T. Porath, Miri Danan-Gotthold,
The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley
 The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley Department of Genetics Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill What is TCGA? The Cancer Genome
The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley Department of Genetics Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill What is TCGA? The Cancer Genome
NEpiC: a network-assisted algorithm for epigenetic studies using mean and variance combined signals
 Published online 14 June 2016 Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, Vol. 44, No. 16 e134 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw546 NEpiC: a network-assisted algorithm for epigenetic studies using mean and variance combined signals
Published online 14 June 2016 Nucleic Acids Research, 2016, Vol. 44, No. 16 e134 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw546 NEpiC: a network-assisted algorithm for epigenetic studies using mean and variance combined signals
OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients. Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA
 OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA cfna Blood Assays Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients.
OverView Circulating Nucleic Acids (CFNA) in Cancer Patients Dave S.B. Hoon John Wayne Cancer Institute Santa Monica, CA, USA cfna Blood Assays Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients.
Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer. Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and
 Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data. Paired-end short-read RNA-seq data were mapped to human reference genome hg19, and unmapped reads in the TCR regions were extracted
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow of CDR3 sequence assembly from RNA-seq data. Paired-end short-read RNA-seq data were mapped to human reference genome hg19, and unmapped reads in the TCR regions were extracted
Contents. 1.5 GOPredict is robust to changes in study sets... 5
 Supplementary documentation for Data integration to prioritize drugs using genomics and curated data Riku Louhimo, Marko Laakso, Denis Belitskin, Juha Klefström, Rainer Lehtonen and Sampsa Hautaniemi Faculty
Supplementary documentation for Data integration to prioritize drugs using genomics and curated data Riku Louhimo, Marko Laakso, Denis Belitskin, Juha Klefström, Rainer Lehtonen and Sampsa Hautaniemi Faculty
Significance Analysis of Prognostic Signatures
 Andrew H. Beck 1 *, Nicholas W. Knoblauch 1, Marco M. Hefti 1, Jennifer Kaplan 1, Stuart J. Schnitt 1, Aedin C. Culhane 2,3, Markus S. Schroeder 2,3, Thomas Risch 2,3, John Quackenbush 2,3,4, Benjamin
Andrew H. Beck 1 *, Nicholas W. Knoblauch 1, Marco M. Hefti 1, Jennifer Kaplan 1, Stuart J. Schnitt 1, Aedin C. Culhane 2,3, Markus S. Schroeder 2,3, Thomas Risch 2,3, John Quackenbush 2,3,4, Benjamin
Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2
 APPLIED PROBLEMS Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2 A. N. Polovinkin a, I. B. Krylov a, P. N. Druzhkov a, M. V. Ivanchenko a, I. B. Meyerov
APPLIED PROBLEMS Solving Problems of Clustering and Classification of Cancer Diseases Based on DNA Methylation Data 1,2 A. N. Polovinkin a, I. B. Krylov a, P. N. Druzhkov a, M. V. Ivanchenko a, I. B. Meyerov
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
LinkedOmics. A Web-based platform for analyzing cancer-associated multi-dimensional data. Manual. First edition 4 April 2017 Updated on July 3, 2017
 LinkedOmics A Web-based platform for analyzing cancer-associated multi-dimensional data Manual First edition 4 April 2017 Updated on July 3, 2017 LinkedOmics is a publicly available portal (http://linkedomics.org/)
LinkedOmics A Web-based platform for analyzing cancer-associated multi-dimensional data Manual First edition 4 April 2017 Updated on July 3, 2017 LinkedOmics is a publicly available portal (http://linkedomics.org/)
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer
 Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
Gene-microRNA network module analysis for ovarian cancer Shuqin Zhang School of Mathematical Sciences Fudan University Oct. 4, 2016 Outline Introduction Materials and Methods Results Conclusions Introduction
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes
 Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing. Whole-exome sequencing of six plasmacytoid-variant bladder
Supplementary Figure 1 CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing. Whole-exome sequencing of six plasmacytoid-variant bladder
Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion overview can be found in Supp Data 9. Training set (103)
 Roepman P, et al. An immune response enriched 72-gene prognostic profile for early stage Non-Small- Supplementary Data 1. Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion
Roepman P, et al. An immune response enriched 72-gene prognostic profile for early stage Non-Small- Supplementary Data 1. Patient characteristics of training and validation set. Patient selection and inclusion
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplemental Information. Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune. Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade
 Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade Glioma from the HERBY Phase II Randomized Trial Alan Mackay,
Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Molecular, Pathological, Radiological, and Immune Profiling of Non-brainstem Pediatric High-Grade Glioma from the HERBY Phase II Randomized Trial Alan Mackay,
Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific
 /, Advance Publications 2015 Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific Andrew Woolston 1, Nardnisa Sintupisut 1, Tzu-Pin Lu 2, Liang-Chuan Lai 3, Mong-Hsun
/, Advance Publications 2015 Putative effectors for prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma are ethnic and gender specific Andrew Woolston 1, Nardnisa Sintupisut 1, Tzu-Pin Lu 2, Liang-Chuan Lai 3, Mong-Hsun
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer
 Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Distinct cellular functional profiles in pan-cancer expression analysis of cancers with alterations in oncogenes c-myc and n-myc
 Honors Theses Biology Spring 2018 Distinct cellular functional profiles in pan-cancer expression analysis of cancers with alterations in oncogenes c-myc and n-myc Anne B. Richardson Whitman College Penrose
Honors Theses Biology Spring 2018 Distinct cellular functional profiles in pan-cancer expression analysis of cancers with alterations in oncogenes c-myc and n-myc Anne B. Richardson Whitman College Penrose
Impact of Prognostic Factors
 Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
DNA methylation profiling in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study defines cancer subclasses differing in clinicopathologic characteristics and survival
 Conway et al. Breast Cancer Research 2014, 16:450 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access DNA methylation profiling in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study defines cancer subclasses differing in clinicopathologic characteristics
Conway et al. Breast Cancer Research 2014, 16:450 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access DNA methylation profiling in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study defines cancer subclasses differing in clinicopathologic characteristics
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer
 Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD
 Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
Case Studies on High Throughput Gene Expression Data Kun Huang, PhD Raghu Machiraju, PhD Department of Biomedical Informatics Department of Computer Science and Engineering The Ohio State University Review
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD
 RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 28
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 28
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Table S1. Donor and sample information for blood samples used in the microarray and gene expression studies. Sample ID Age (Years) Diagnosis Smoking Classification DNA Methylation
Supplementary Information Table S1. Donor and sample information for blood samples used in the microarray and gene expression studies. Sample ID Age (Years) Diagnosis Smoking Classification DNA Methylation
Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles
 Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a. fixed feature subset
 SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a fixed feature subset Youxi Luo,3,*, Qinghan Meng,2,*, Ruiquan Ge,2, Guoqin Mai, Jikui Liu, Fengfeng Zhou,#. Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced
SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a fixed feature subset Youxi Luo,3,*, Qinghan Meng,2,*, Ruiquan Ge,2, Guoqin Mai, Jikui Liu, Fengfeng Zhou,#. Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced
Cancer Informatics Lecture
 Cancer Informatics Lecture Mayo-UIUC Computational Genomics Course June 22, 2018 Krishna Rani Kalari Ph.D. Associate Professor 2017 MFMER 3702274-1 Outline The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Genomic Data Commons
Cancer Informatics Lecture Mayo-UIUC Computational Genomics Course June 22, 2018 Krishna Rani Kalari Ph.D. Associate Professor 2017 MFMER 3702274-1 Outline The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Genomic Data Commons
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas
 Paul et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2017) 9:32 DOI 10.1186/s13148-017-0331-9 RESEARCH Open Access DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas Yashna Paul, Baisakhi
Paul et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2017) 9:32 DOI 10.1186/s13148-017-0331-9 RESEARCH Open Access DNA methylation signatures for 2016 WHO classification subtypes of diffuse gliomas Yashna Paul, Baisakhi
Promoter methylation of DNA damage repair (DDR) genes in human tumor entities: RBBP8/CtIP is almost exclusively methylated in bladder cancer
 Mijnes et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2018) 10:15 DOI 10.1186/s13148-018-0447-6 RESEARCH Promoter methylation of DNA damage repair (DDR) genes in human tumor entities: RBBP8/CtIP is almost exclusively methylated
Mijnes et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2018) 10:15 DOI 10.1186/s13148-018-0447-6 RESEARCH Promoter methylation of DNA damage repair (DDR) genes in human tumor entities: RBBP8/CtIP is almost exclusively methylated
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant
 Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Geisinger Clinic Annual Progress Report: 2011 Nonformula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Nonformula Grant Overview The Geisinger Clinic received $1,000,000 in nonformula funds for the
Integrated Cox s model for predicting survival time of glioblastoma multiforme
 694574TUB0010.1177/1010428317694574Tumor BiologyAi et al. research-article2017 Original Article Integrated Cox s model for predicting survival time of glioblastoma multiforme Tumor Biology April 2017:
694574TUB0010.1177/1010428317694574Tumor BiologyAi et al. research-article2017 Original Article Integrated Cox s model for predicting survival time of glioblastoma multiforme Tumor Biology April 2017:
Applying Tissue Phenomics to Colorectal Clinical Questions
 Applying Tissue Phenomics to Colorectal Clinical Questions International Symposium for Tissue Phenomics San Francisco October 2014 Peter Caie Senior Research Fellow University of St Andrews Systems Pathology
Applying Tissue Phenomics to Colorectal Clinical Questions International Symposium for Tissue Phenomics San Francisco October 2014 Peter Caie Senior Research Fellow University of St Andrews Systems Pathology
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer
 Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Identification of mir-187 and mir-182 as biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis in prostate cancer patients treated with radical prostatectomy Irene Casanova-Salas 1, José
Supplementary Material Identification of mir-187 and mir-182 as biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis in prostate cancer patients treated with radical prostatectomy Irene Casanova-Salas 1, José
Tissue-specific DNA methylation loss during ageing and carcinogenesis is linked to chromosome structure, replication timing and cell division rates
 7022 7039 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 14 Published online 9 June 2018 doi: 10.1093/nar/gky498 Tissue-specific DNA methylation loss during ageing and carcinogenesis is linked to chromosome
7022 7039 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 14 Published online 9 June 2018 doi: 10.1093/nar/gky498 Tissue-specific DNA methylation loss during ageing and carcinogenesis is linked to chromosome
Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction
 Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Associate Professor Dept. Computer Science & Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Dept. CSE, UT Arlington Scalable
Big Image-Omics Data Analytics for Clinical Outcome Prediction Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Associate Professor Dept. Computer Science & Engineering University of Texas at Arlington Dept. CSE, UT Arlington Scalable
TCGA. The Cancer Genome Atlas
 TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
Layered-IHC (L-IHC): A novel and robust approach to multiplexed immunohistochemistry So many markers and so little tissue
 Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables. File Name: Peer Review File Description:
 File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables File Name: Peer Review File Description: Primer Name Sequence (5'-3') AT ( C) RT-PCR USP21 F 5'-TTCCCATGGCTCCTTCCACATGAT-3'
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes
 MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes Olivier Gevaert May 3, 2016 Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Department of Medicine 1265 Welch Road Stanford CA, 94305-5479
MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes Olivier Gevaert May 3, 2016 Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Department of Medicine 1265 Welch Road Stanford CA, 94305-5479
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data
 Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data Christopher Sauer, Rishi Bedi, Duc Nguyen, Benedikt Bünz Abstract Cancers are on par with heart disease as the leading cause for mortality in the United
Predicting Kidney Cancer Survival from Genomic Data Christopher Sauer, Rishi Bedi, Duc Nguyen, Benedikt Bünz Abstract Cancers are on par with heart disease as the leading cause for mortality in the United
The Cancer Genome Atlas
 The Cancer Genome Atlas July 14, 2011 Kenna M. Shaw, Ph.D. Deputy Director The Cancer Genome Atlas Program TCGA: Core Objectives Launched in 2006 as a pilot and expanded in 2009, the goals of TCGA are
The Cancer Genome Atlas July 14, 2011 Kenna M. Shaw, Ph.D. Deputy Director The Cancer Genome Atlas Program TCGA: Core Objectives Launched in 2006 as a pilot and expanded in 2009, the goals of TCGA are
Transcriptional Profiles from Paired Normal Samples Offer Complementary Information on Cancer Patient Survival -- Evidence from TCGA Pan-Cancer Data
 Transcriptional Profiles from Paired Normal Samples Offer Complementary Information on Cancer Patient Survival -- Evidence from TCGA Pan-Cancer Data Supplementary Materials Xiu Huang, David Stern, and
Transcriptional Profiles from Paired Normal Samples Offer Complementary Information on Cancer Patient Survival -- Evidence from TCGA Pan-Cancer Data Supplementary Materials Xiu Huang, David Stern, and
CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets
 Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Planey and Gevaert Genome Medicine (2016) 8:27 DOI 10.1186/s13073-016-0281-4 METHOD CoINcIDE: A framework for discovery of patient subtypes across multiple datasets Catherine R. Planey and Olivier Gevaert
Supplementary Figure 1 Overall study design
 Supplementary Figure 1 Overall study design We obtained 19 tumour specimens from 14 men with prostate cancer who harboured pathogenic germline BRCA2-mutations. Germline DNA was available for five patients
Supplementary Figure 1 Overall study design We obtained 19 tumour specimens from 14 men with prostate cancer who harboured pathogenic germline BRCA2-mutations. Germline DNA was available for five patients
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification. Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland
 Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland Oncoscape.sttrcancer.org Paul Lisa Ken Jenny Desert Eric The challenge Given - patient clinical
Expert-guided Visual Exploration (EVE) for patient stratification Hamid Bolouri, Lue-Ping Zhao, Eric C. Holland Oncoscape.sttrcancer.org Paul Lisa Ken Jenny Desert Eric The challenge Given - patient clinical
S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A. b Normal Generalized Fraction 0.075
 Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
An annotated list of bivalent chromatin regions in human ES cells: a new tool for cancer epigenetic research
 An annotated list of bivalent chromatin regions in human ES cells: a new tool for cancer epigenetic research Franck Court, Philippe Arnaud To cite this version: Franck Court, Philippe Arnaud. An annotated
An annotated list of bivalent chromatin regions in human ES cells: a new tool for cancer epigenetic research Franck Court, Philippe Arnaud To cite this version: Franck Court, Philippe Arnaud. An annotated
LncMAP: Pan-cancer atlas of long noncoding RNA-mediated transcriptional network perturbations
 Published online 9 January 2018 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 3 1113 1123 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1311 LncMAP: Pan-cancer atlas of long noncoding RNA-mediated transcriptional network perturbations
Published online 9 January 2018 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 3 1113 1123 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1311 LncMAP: Pan-cancer atlas of long noncoding RNA-mediated transcriptional network perturbations
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target?
 Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
Androgen Receptor Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A New Actionable Target? New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology Juan Chipollini, MD Clinical Fellow Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks
 Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Expression and methylation patterns partition luminal-a breast tumors into distinct prognostic subgroups
 Netanely et al. Breast Cancer Research (2016) 18:74 DOI 10.1186/s13058-016-0724-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Expression and methylation patterns partition luminal-a breast tumors into distinct prognostic
Netanely et al. Breast Cancer Research (2016) 18:74 DOI 10.1186/s13058-016-0724-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Expression and methylation patterns partition luminal-a breast tumors into distinct prognostic
ncounter Assay Automated Process Immobilize and align reporter for image collecting and barcode counting ncounter Prep Station
 ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine. Bei Li, Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club
 Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER
 EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy
 Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
An integrative pan-cancer-wide analysis of epigenetic enzymes reveals universal patterns of epigenomic deregulation in cancer
 Yang et al. Genome Biology (2015) 16:140 DOI 10.1186/s13059-015-0699-9 RESEARCH Open Access An integrative pan-cancer-wide analysis of epigenetic enzymes reveals universal patterns of epigenomic deregulation
Yang et al. Genome Biology (2015) 16:140 DOI 10.1186/s13059-015-0699-9 RESEARCH Open Access An integrative pan-cancer-wide analysis of epigenetic enzymes reveals universal patterns of epigenomic deregulation
