Impact of the availability of active cytotoxic agents on the survival of patients with advanced gastric cancer
|
|
|
- Dylan Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: , 2015 Impact of the availability of active cytotoxic agents on the survival of patients with advanced gastric cancer BYUNG HA CHO 1, HYE SOOK HAN 1, JIHYUN KWON 1, JOUNG HO HAN 1, SOON MAN YOON 1, DAE HOON KIM 2, HYO YUNG YUN 2, KI HYEONG LEE 1, SEI JIN YOUN 1 and SEUNG TAIK KIM 1 Departments of 1 Internal Medicine and 2 Surgery, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, North Chungcheong , Republic of Korea Received August 1, 2014; Accepted April 29, 2015 DOI: /ol Abstract. Several cytotoxic agents, including fluoropyrimidines, platinums, taxanes and irinotecan, are effective in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer (AGC). However, the effect of the availability of cytotoxic agents on survival has not yet been evaluated. Therefore, the present study assessed the impact of the availability of active cytotoxic agents on the survival of patients with AGC. The records of 216 patients with newly diagnosed AGC that were treated with palliative chemotherapy between March 2002 and November 2012 at Chungbuk National University Hospital were reviewed. For the present study, the patients were divided according to the availability of active cytotoxic agents over the course of treatment: Group 1 received fluoropyrimidine and platinum; group 2 received fluoropyrimidine, platinum and taxane or irinotecan; and group 3 received fluoropyrimidine, platinum, taxane and irinotecan. The median overall survival times for groups 1, 2 and 3 were 6.3, 9.9 and 14.3 months, respectively (P<0.0001). Multivariate analysis revealed that the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status and the availability of active cytotoxic agents were independent prognostic factors, as the hazard ratios for mortality were 3.25 for patients with an ECOG performance status of 2 3 [95% confidence interval (CI), ; P<0.0001], 0.58 for patients in group 2 (95% CI, ; P=0.0009), and 0.40 for patients in group 3 (95% CI, ; P<0.0001). The present study reveals that the availability of active cytotoxic agents is associated with an improved survival time in patients with AGC. Introduction Gastric cancer is the fourth most frequent malignancy and the second most common cause of cancer associated mortality Correspondence to: Dr Hye Sook Han, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, 52 Naesudong ro, Seowon-gu, Cheongju, North Chungcheong , Republic of Korea E mail: sook3529@hanmail.net Key words: availability, cytotoxic agent, gastric cancer, survival worldwide (1). This cancer is also the second most frequent malignancy in Korea (2). Although patients with early gastric cancer may be successfully treated by surgical resection, the majority of patients experience a relapse subsequent to the first surgical resection (3) or are initially diagnosed with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic disease (4). For these patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, the objective of treatment is to relieve symptoms, prevent tumor progression and prolong the survival time. Therefore, palliative chemotherapy may play an extremely important role in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer (AGC). It has been reported that chemotherapy improves the survival of AGC patients in comparison to best supportive care, and it has also been reported that combination chemotherapy is superior to monotherapy in terms of survival, response rate and symptom control (5). In general, fluoropyrimidine, such as 5 fluorouracil (5 FU) or its oral prodrugs, and platinum, such as cisplatin or oxaliplatin, combination regimens are widely accepted as the standard first line chemotherapy, with a response rate of 25 54% and a median overall survival time of 8 13 months (5 6). However, more than one half of the patients with AGC that receive first line chemotherapy do not demonstrate a response, and even in responders the duration of response may be as short as a few months (6). In addition, the number of patients that maintain a good general condition following the failure of first line chemotherapy has increased due to the improvements in supportive care. As a result, the number of patients that are good candidates for subsequent salvage chemotherapy has increased. In previous years, novel drugs, including docetaxel, paclitaxel and irinotecan, have been tested in salvage chemotherapy for pre treated AGC (7,8). With the availability of these active cytotoxic agents, numerous patients with refractory or relapsed gastric cancer subsequent to first line chemotherapy have received salvage chemotherapy in routine clinical practice, particularly in Asia (8). Although salvage chemotherapy following first line treatment may be considered a confirmed option for the treatment of AGC, the impact of the availability of several active cytotoxic agents has not yet been assessed in AGC. Therefore, the present study assessed the impact of the availability of fluoropyrimidines, platinums, taxanes and irinotecan over the course of treatment on the survival of patients with AGC.
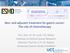
2 2482 CHO et al: AVAILABILITY OF CYTOTOXIC AGENTS IN GASTRIC CANCER Materials and methods Study population. A retrospective chart review was performed on all patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer that were treated with standard palliative chemotherapy between March 2002 and November 2012 at the Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital (Cheongju, North Chungcheong, Republic of Korea). All patients were consecutive non selected cases from the Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital and all patients were treated outside of clinical trials. Patients were included in the present study if they possessed a histologically confirmed diagnosis of adenocarcinoma, newly diagnosed locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer, and medical records containing details of palliative chemotherapy administered. Patients were excluded if they had not received palliative chemotherapy, had received only fluoropyrimidine monotherapy or molecular targeted agents during the course of treatment, had succumbed to AGC during the first hospitalization, or possessed a history of another malignancy. The present study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chungbuk National University Hospital. Data collection. The baseline clinical and pathological characteristics at the time of the diagnosis of locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer were reviewed, including the age, gender, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, location of the primary tumor, histological grading according to the World Health Organization (WHO) system, timing of metastatic disease, location of metastasis, number of metastases, baseline hemoglobin and baseline albumin of the patients. Data from medical records on the palliative chemotherapeutic agents administered was also collected, and the patients were divided according to the availability of active cytotoxic agents over the course of treatment, regardless of dose or schedule, as follows: Group 1 received two cytotoxic agents, fluoropyrimidine (5 FU, capecitabine or S 1) and platinum (cisplatin or oxaliplatin); group 2 received three cytotoxic agents, fluoropyrimidine, platinum and taxane (docetaxel or paclitaxel) or irinotecan; and group 3 received four cytotoxic agents, fluoropyrimidine, platinum, taxane and irinotecan. Statistical analysis. Overall survival was measured from the date of the first administration of first line chemotherapy to the date of mortality, from any cause, or last follow up visit. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan Meier method and the survival curves of patients were compared using the log rank test. A prognostic model for overall survival was constructed using an assessment of variables by univariate analysis followed by multivariate analysis, which was performed using a stepwise Cox proportional hazard regression model. The following variables were included in the univariate analysis: Age, <65 years vs. 65 years; gender, male vs. female; pre treatment ECOG performance status, 0 1 vs. 2 3; histological grading according to the WHO system, good (well or moderately differentiated) vs. poor (poorly differentiated or signet ring cell carcinoma) vs. no data; timing of metastatic disease, synchronous vs. metachronous; presence of peritoneal metastases or malignant ascites, present vs. absent; number of metastases, 1 vs. 2 vs. 3; hemoglobin level, <10 g/dl vs. 10 g/dl; and Figure 1. Overall survival according to the availability of active cytotoxic agents. Enrolled patients were divided according to the availability of active cytotoxic agents during the course of treatment, as follows: Group 1 received fluoropyrimidine and platinum; group 2 received fluoropyrimidine, platinum, taxane or irinotecan; and group 3 received fluoropyrimidine, platinum, taxane, and irinotecan. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval. albumin level, <3.5 g/dl vs. 3.5 g/dl. Hazard ratios (HRs) of the studied outcomes were calculated for each parameter estimate, in addition to the 95% confidence interval (CI). P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software for Windows, version 15.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Results Baseline patient characteristics. Of the 262 patients with newly diagnosed locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer that received palliative chemotherapy between March 2002 and November 2012 at the Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital, 216 patients were included in the final analysis. The baseline clinicopathological characteristics of the patients are reported in Table I. The median age was 57 years (range, years), and 161 patients (74.5%) were male. In total, 196 patients (90.7%) demonstrated good performance status (ECOG status, 0 1). The majority of the patients (97.7%) possessed metastatic disease, and only five patients (2.3%) possessed locally advanced disease. The most common metastatic sites were the peritoneum (56.9%), liver (35.6%) and distant lymph nodes (31.0%). Treatment regimens. The characteristics of the cytotoxic agents used are listed in Table II. The most commonly used cytotoxic agents were 5 FU in 171 patients (79.2%), cisplatin in 140 patients (64.8%) and oxaliplatin in 117 patients (54.2%). Of the patients enrolled, 92 patients (42.6%) were treated with fluoropyrimidine and platinum, classed as group 1, 75 patients (34.7%) were treated with fluoropyrimidine, platinum and taxane or irinotecan, classed as group 2, and 49 patients (22.7%) were treated with fluoropyrimidine, platinum, taxane and irinotecan, classed as group 3, over the course of palliative treatment. Univariate and multivariate analysis. The median overall survival time for all patients was 9.3 months (95% CI, months). The results of the univariate and multivariate analyses for
3 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: , Table I. Patient characteristics (n=216). Characteristics Value, n (%) Age Median, years (range) 57.0 (18 79) <65 years 126 (58.3) 65 years 90 (41.7) Gender Male 161 (74.5) Female 55 (25.5) ECOG performance status (90.7) (9.3) Location of primary tumor EGJ and cardia 25 (11.6) Fundus and body 87 (40.3) Antrum 104 (48.1) Histological grade Good 72 (33.3) Poor 122 (56.5) No data 22 (10.2) Timing of locally advanced or metastatic disease Synchronous 139 (64.4) Metachronous 77 (35.6) Extent of disease Locally advanced 5 (2.3) Metastatic 211 (97.7) Liver 77 (35.6) Peritoneum 123 (56.9) Distant lymph nodes 67 (31.0) Bone 22 (10.2) Lung 13 (6.0) Number of metastases 1 98 (45.4) 2 89 (41.2) 3 29 (13.4) Baseline hemoglobin Median, g/dl (range) 11.9 ( ) <10.0 g/dl 59 (27.3) 10.0 g/dl 157 (72.7) Baseline albumin Median, g/dl (range) 3.9 ( ) <3.5 g/dl 42 (19.4) 3.5 g/dl 174 (80.6) ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; EGJ, esophago gastric junction. overall survival are summarized in Table III. Univariate analysis revealed that the ECOG performance status (0 1 vs. 2 3) and the availability of the active cytotoxic agents (group 1 vs. group 2 vs. group 3) had prognostic significance. The median overall Table II. Characteristics of palliative chemotherapy (n=216). Characteristics Value, n (%) Cytotoxic agents Fluoropyrimidines 5 FU 171 (79.2) Capecitabine 70 (32.4) S 1 51 (23.6) Platinum Cisplatin 140 (64.8) Oxaliplatin 117 (54.2) Taxanes Docetaxel 55 (25.5) Paclitaxel 45 (20.8) Irinotecan 74 (34.3) Availability of active cytotoxic agents Group 1 92 (42.6) Group 2 75 (34.7) Group 3 49 (22.7) 5 FU, 5 Fluorouracil. survival time was significantly longer in patients with an ECOG performance status of 0-1 compared with in patients with an ECOG performance status of 2-3 (9.9 vs. 4.7 months, respectively; HR for mortality, 3.52; 95% CI, ; P<0.0001). The median overall survival times were 6.3 months in group 1, 9.9 months in group 2, and 14.3 months in group 3; these differences were statistically significant (P<0.0001). The estimated HRs for mortality were 0.56 for group 2 (95% CI, ) and 0.41 for group 3 (95% CI, ; Fig. 1). A multivariate Cox proportional hazard model revealed that the ECOG performance status and the availability of active cytotoxic agents were independent prognostic factors for AGC outcome (Table III). The estimated HRs for mortality in patients with an ECOG performance status of 2 3 compared to patients with an ECOG performance status of 0 1 was 3.25 (95% CI, ; P<0.0001). The estimated HRs for mortality in groups 2 and 3 compared to group 1 were 0.58 (95% CI, ; P=0.0009) and 0.40 (95% CI, ; P<0.0001), respectively. Discussion The present study retrospectively analyzed data obtained from 216 patients with AGC that had undergone palliative chemotherapy with active cytotoxic agents, such as fluoropyrimidines and platinums or taxanes or irinotecan. The present analysis demonstrated that the availability of these active cytotoxic agents in the course of treatment had a positive impact on the survival of patients with AGC. In the present study, 92 patients (42.6%) were treated with fluoropyrimidine and platinum only, while 75 patients (34.7%) received one more cytotoxic agent, irinotecan or a taxane,
4 2484 CHO et al: AVAILABILITY OF CYTOTOXIC AGENTS IN GASTRIC CANCER Table III. Univariate and multivariate analyses of overall survival. Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis Median OS, Characteristics Total, n months (95% CI) HR 95% CI P value HR 95% CI P value Age <65 years ( ) years ( ) Gender Male ( ) Female ( ) ECOG performance status ( ) < ( ) < Histological grade Good ( ) Poor ( ) No data ( ) Timing of locally advanced or metastatic disease Synchronous ( ) Metachronous ( ) Peritoneal metastases Yes ( ) No ( ) Number of metastases ( ) ( ) ( ) Baseline hemoglobin <10.0 g/dl ( ) g/dl ( ) Baseline albumin <3.5 g/dl ( ) g/dl ( ) Availability of active cytotoxic agents Group ( ) <0.001 Group ( ) Group ( ) < OS, overall survival; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; 5 FU, 5 Fluorouracil. and 49 patients (22.7%) received all four active cytotoxic agents. Multivariate analysis revealed that the availability of more active cytotoxic drugs was an independent prognostic factor for survival compared with fluoropyrimidine and platinum only. This finding suggests that it is important to use all cytotoxic agents that have well demonstrated clinical activity in AGC to guarantee the maximal benefit of systemic therapy for overall survival in patients with AGC. Although the median survival time of patients with AGC remained below one year, numerous cytotoxic agents have been investigated over the previous decades, including fluoropyrimidines, which are administered orally or intravenously, anthracyclines, cisplatin, oxaliplatin, taxanes and irinotecan (5 7). Currently, various targeted agents are being tested in clinical trials and promising data have been recently published for trastuzumab containing therapy, with median survival time exceeding
5 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 10: , one year (9). Novel oral fluoropyrimidines, including capecitabine and S 1, are not clinically inferior to 5 FU in terms of survival, and additional advantages of novel oral fluoropyrimidines include the convenience of oral chemotherapy, which avoids the potential morbidity associated with central venous access, and the opportunity to make simple dose adjustments to the oral agent during the treatment cycle to manage toxicity (10 13). Cisplatin has been an integral component of AGC reference regimens (6). However, oxaliplatin has been extensively studied in AGC due to the specific side effects of cisplatin, including nephrotoxicity, emetogenicity and ototoxicity. Due to the non inferior efficacy, oxaliplatin may be substituted for cisplatin in the treatment of AGC, and elderly patients may derive a particular benefit from treatment with oxaliplatin instead of cisplatin (10,14). Taxanes, such as docetaxel or paclitaxel, which bind and stabilize microtubules and therefore lead to cell cycle arrest, have also been used as a first line therapy for AGC (15,16). In addition, irinotecan has been reported to demonstrate activity in gastrointestinal cancers, and irinotecan based combination regimens have been studied as a first line alternative to platinum based chemotherapy (17,18). The availability of these active cytotoxic agents opened the option of sequential salvage chemotherapy in AGC patients. Second line chemotherapy is currently considered to be a standard therapy option for patients that demonstrate disease progression during or subsequent to first line chemotherapy. Docetaxel and irinotecan have been evaluated extensively for second line therapy in patients for whom fluoropyrimidine and platinum have failed (19). Three randomized controlled trials have revealed the increased survival of patients administered with either docetaxel or irinotecan monotherapy compared with those receiving best supportive care (20 22). As the majority of patients with AGC are initially treated with fluoropyrimidine and platinum, it appears more prudent to avoid these drugs in second line regimens for these patients. No statistically significant differences were observed between the overall survival, progression free survival and response rates for patients receiving taxanes and those receiving irinotecan (19,23). Thus, either taxanes or irinotecan may be recommended as a treatment option for second line chemotherapy in patients with AGC. Although evidence is limited with regard to the efficacy of third line chemotherapy in AGC, this therapy may have contributed to the prolonged overall survival time. Several studies have demonstrated that third line chemotherapy performs better compared with best supportive care in patients with AGC in terms of overall survival and quality of life (24 26). The sequence of second and third line regimens, including taxanes and irinotecan, did not present any significant difference in overall survival or time to progression subsequent to the failure of fluoropyrimidine and platinum chemotherapy (24). The differences in toxicity profiles, previous chemotherapy agents, and treatment schedules between the two treatments may aid in choosing between taxanes or irinotecan. The current results suggest that the use of all active cytotoxic agents improves the overall survival in patients with AGC. However, if sequential treatment with all active cytotoxic agents cannot be guaranteed for 100% of the patients, the use of a triplet combination protocol may be considered as first line therapy. The safety and efficacy of this approach has been assessed in previous clinical trials (15,16). Triplet combination chemotherapy comprising an anthracycline or a taxane in addition to fluoropyrimidine and platinum compounds has resulted in higher response rates and a modest improvement in overall survival compared with doublet combinations (6). In the majority of European countries, the epirubicin, cisplatin and fluorouracil (ECF) regimen is more commonly used, based on a phase 3 randomized trial that compared the administration of the ECF regimen with the administration of fluorouracil, doxorubicin and methotrexate (27). The docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil (DCF) regimen has previously been tested in the V325 phase 3 trial. In this trial, it was found that the DCF regimen not only significantly improved the clinical benefit of chemotherapy, but also improved the quality of life, time to progression and overall survival compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil without docetaxel (15). However, the high rate of treatment associated toxicity limits the applicability of this regimen to all patients, particularly those that are elderly or have a poor performance status. Therefore, several modifications to the schedule of triplet combination chemotherapy or growth factor support have been investigated in an attempt to minimize the toxicity that occurs with this regimen (28,29). Although the benefit of sequential salvage chemotherapy is evident, the disease control rate is 30 40%. This indicates that more than one half of patients do not benefit from salvage chemotherapy and suffer from toxicities. Therefore, it is important to predict whether patients may benefit from sequential salvage chemotherapy. Previous studies have indicated that several factors should be considered in order to assess the response to sequential salvage chemotherapy, such as the performance status of the patient, extent of disease (locally advanced or metastatic), cumulative toxicity, lack of cross resistance of the tumor cells to previously used drugs and progression free survival of the patient following previous chemotherapy (26,30). Therefore, predictive factors for the potential survival benefit of salvage chemotherapy with active cytotoxic agents require additional investigation to avoid the development of toxic effects in patients that are unlikely to benefit from the therapy. The present study demonstrates several limitations. Firstly, it is a retrospective analysis. However, all patients were consecutive non selected cases that received chemotherapy treatment outside clinical trials and were followed by the Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University Hospital under the supervision of the same oncology team, which also addresses real life situations. Secondly, a shorter overall survival time was demonstrated in the present study compared with previous studies. This is due to the population in the present study possessing a poor prognosis, with 97.7% of the patients experiencing metastatic cancer, 56.1% possessing peritoneal carcinomatosis and 9.3% demonstrating an ECOG performance status of 2 3. In conclusion, the present study suggests that the availability of active cytotoxic agents in the course of treatment is associated with improved survival in patients with AGC. Additional prospective studies of effective administration schedules for patients receiving all active cytotoxic agents, in addition to studies investigating the factors that predict the survival benefit from salvage chemotherapy should continue in patients with AGC.
6 2486 CHO et al: AVAILABILITY OF CYTOTOXIC AGENTS IN GASTRIC CANCER Acknowledgements This study was supported by a Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (grant no., ). References 1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61: 69 90, Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG and Lee JS: Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in Cancer Res Treat 45: 1 14, D'Angelica M, Gonen M, Brennan MF, et al: Patterns of initial recurrence in completely resected gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg 240: , Macdonald JS: Gastric cancer new therapeutic options. N Engl J Med 355: 76 77, Wagner AD, Grothe W, Haerting J, et al: Chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta analysis based on aggregate data. J Clin Oncol 24: , Wagner AD, Unverzagt S, Grothe W, et al: Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD004064, Wesolowski R, Lee C and Kim R: Is there a role for second line chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer? Lancet Oncol 10: , Baek SK, Kim SY, Jeong JH, Cho KS and Yoon HJ: Second line chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer in Korea. Gastric Cancer 15: , Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al; ToGA Trial Investigators: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2 positive advanced gastric or gastro oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3, open label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376: , Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, Middleton G, Daniel F, Oates J and Norman AR; Upper Gastrointestinal Clinical Studies Group of the National Cancer Research Institute of the United Kingdom. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med 358: 36 46, Kang YK, Kang WK, Shin DB, Chen J, Xiong J, Wang J, Lichinitser M, Guan Z, Khasanov R, Zheng L, Philco Salas M, et al: Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5 fluorouracil/cisplatin as first line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: A randomised phase III noninferiority trial. Ann Oncol 20: , Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, Takagane A, Akiya T, Takagi M, Miyashita K, Nishizaki T, Kobayashi O, Takiyama W, Toh Y, et al: S 1 plus cisplatin versus S 1 alone for first line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): A phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 9: , Boku N, Yamamoto S, Fukuda H, Shirao K, Doi T, Sawaki A, Koizumi W, Saito H, Yamaguchi K, Takiuchi H, Nasu J and Ohtsu A; Gastrointestinal Oncology Study Group of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group. Fluorouracil versus combination of irinotecan plus cisplatin versus S 1 in metastatic gastric cancer: A randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 10: , Al Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, Rethwisch V, Seipelt G, Homann N, Wilhelm G, Schuch G, et al; Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: A study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol 26: , Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi E, Risse ML and Ajani JA; V325 study group. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A report of the V325 study group. J Clin Oncol 24: , Chen XL, Chen XZ, Yang C, Liao YB, Li H, Wang L, Yang K, Li K, Hu JK, Zhang B, Chen ZX, et al: Docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil (DCF) regimen compared with non taxane containing palliative chemotherapy for gastric carcinoma: A systematic review and meta analysis. PLoS One 8: e60320, Dank M, Zaluski J, Barone C, Valvere V, Yalcin S, Peschel C, Wenczl M, Goker E, Cisar L, Wang K and Bugat R: Randomized phase III study comparing irinotecan combined with 5 fluorouracil and folinic acid to cisplatin combined with 5 fluorouracil in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Ann Oncol 19: , Moehler M, Kanzler S, Geissler M, Raedle J, Ebert MP, Daum S, Flieger D, Seufferlein T, Galle PR and Hoehler T; Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie, Germany. A randomized multicenter phase II study comparing capecitabine with irinotecan or cisplatin in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Ann Oncol 21: 71 77, Kim HS, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim TY, Lee KW, Baek SK, Kim TY, Ryu MH, Nam BH and Zang DY: Second line chemotherapy versus supportive cancer treatment in advanced gastric cancer: A meta analysis. Ann Oncol 24: , Thuss Patience PC, Kretzschmar A, Bichev D, Deist T, Hinke A, Breithaupt K, Dogan Y, Gebauer B, Schumacher G and Reichardt P: Survival advantage for irinotecan versus best supportive care as second line chemotherapy in gastric cancer a randomised phase III study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie (AIO). Eur J Cancer 47: , Kang JH, Lee SI, Lim do H, Park KW, Oh SY, Kwon HC, Hwang IG, Lee SC, Nam E, Shin DB, Lee J, et al: Salvage chemotherapy for pretreated gastric cancer: A randomized phase III trial comparing chemotherapy plus best supportive care with best supportive care alone. J Clin Oncol 30: , Ford HE, Marshall A, Bridgewater JA, Janowitz T, Coxon FY, Wadsley J, Mansoor W, Fyfe D, Madhusudan S, Middleton GW, Swinson D, et al; COUGAR 02 Investigators: Docetaxel versus active symptom control for refractory oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (COUGAR 02): An open label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 15: 78 86, Hironaka S, Ueda S, Yasui H, et al: Randomized, open label, phase III study comparing irinotecan with paclitaxel in patients with advanced gastric cancer without severe peritoneal metastasis after failure of prior combination chemotherapy using fluoropyrimidine plus platinum: WJOG 4007 trial. J Clin Oncol 31: , Park JS, Lim JY, Park SK, Kim MK, Ko HS, Yoon SO, Kim JW, Choi SH and Cho JY: Prognostic factors of second and third line chemotherapy using 5 fu with platinum, irinotecan and taxane for advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat 43: , Shim HJ, Yun JY, Hwang JE, Bae WK, Cho SH and Chung IJ: Prognostic factor analysis of third line chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 14: , Lee MJ, Hwang IG, Jang JS, Choi JH, Park BB, Chang MH, Kim ST, Park SH, Kang MH and Kang JH: Outcomes of third line docetaxel based chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer who failed previous oxaliplatin based and irinotecan based chemotherapies. Cancer Res Treat 44: , Webb A, Cunningham D, Scarffe JH, Harper P, Norman A, Joffe JK, Hughes M, Mansi J, Findlay M, Hill A, Oates J, et al: Randomized trial comparing epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil versus fluorouracil, doxorubicin and methotrexate in advanced esophagogastric cancer. J Clin Oncol 15: , Overman MJ, Kazmi SM, Jhamb J, Lin E, Yao JC, Abbruzzese JL, Ho L, Ajani J and Phan A: Weekly docetaxel, cisplatin and 5 fluorouracil as initial therapy for patients with advanced gastric and esophageal cancer. Cancer 116: , Polyzos A, Felekouras E, Karatzas T, Griniatsos J, Dimitroulis D, Polyzos K, Kontzoglou K, Mantas D, Karavokyros J, Nikiteas N, Tsavaris N, et al: Modified docetaxel cisplatin in combination with capecitabine as first line treatment in metastatic gastric cancer. A phase II study. Anticancer Res 32: , Kanagavel D, Pokataev IA, Fedyanin MY, Tryakin AA, Bazin IS, Narimanov MN, Yakovleva ES, Garin AM and Tjulandin SA: A prognostic model in patients treated for metastatic gastric cancer with second line chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 21: , 2010.
Trastuzumab for the treatment of HER2 positive advanced gastric cancer Appraisal Consultation Document (ACD)
 Trastuzumab for the treatment of HER2 positive advanced gastric cancer Appraisal Consultation Document (ACD) Comments submitted by Dr Patrick Cadigan, RCP registrar on behalf of: NCRI/RCP/RCR/ACP/JCCO
Trastuzumab for the treatment of HER2 positive advanced gastric cancer Appraisal Consultation Document (ACD) Comments submitted by Dr Patrick Cadigan, RCP registrar on behalf of: NCRI/RCP/RCR/ACP/JCCO
Prognostic factor analysis of third-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer
 Gastric Cancer (2011) 14:249 256 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0032-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic factor analysis of third-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer Hyun Jeong Shim Ju Young Yun
Gastric Cancer (2011) 14:249 256 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0032-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic factor analysis of third-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer Hyun Jeong Shim Ju Young Yun
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 2: , 2011
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 2: 241-245, 2011 Irinotecan monotherapy offers advantage over combination therapy with irinotecan plus cisplatin in second-line setting for treatment of advanced gastric cancer following
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 2: 241-245, 2011 Irinotecan monotherapy offers advantage over combination therapy with irinotecan plus cisplatin in second-line setting for treatment of advanced gastric cancer following
Analysis of esophagogastric cancer patients enrolled in the National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program sponsored phase 1 trials
 Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:481 488 DOI 10.1007/s10120-016-0629-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of esophagogastric cancer patients enrolled in the National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program sponsored
Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:481 488 DOI 10.1007/s10120-016-0629-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of esophagogastric cancer patients enrolled in the National Cancer Institute Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program sponsored
Dong Hoe Koo Min-Hee Ryu Baek-Yeol Ryoo Jinjoo Seo Mi-Yeon Lee Heung-Moon Chang Jae-Lyun Lee Sung-Sook Lee Tae Won Kim Yoon-Koo Kang
 Gastric Cancer (15) 18:346 353 DOI 1.17/s11-14-385-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving trends in survival of patients who receive chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer: 12 years of experience
Gastric Cancer (15) 18:346 353 DOI 1.17/s11-14-385-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving trends in survival of patients who receive chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer: 12 years of experience
CHEMOTHERAPY FOR METASTATIC GASTRIC CANCER
 CHEMOTHERAPY FOR METASTATIC GASTRIC CANCER Dr Elizabeth Smyth Royal Marsden, UK ESMO Gastric Cancer Preceptorship Valencia 2017 IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS WHEN TREATING ADVANCED GASTRIC CANCER Short OS Pain
CHEMOTHERAPY FOR METASTATIC GASTRIC CANCER Dr Elizabeth Smyth Royal Marsden, UK ESMO Gastric Cancer Preceptorship Valencia 2017 IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS WHEN TREATING ADVANCED GASTRIC CANCER Short OS Pain
Published Ahead of Print on August 20, 2018 as /theoncologist
 Clinical Trial Results A Phase III Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of Paclitaxel Versus Irinotecan in Patients with Metastatic or Recurrent Gastric Cancer Who Failed in First-line Therapy (KCSG
Clinical Trial Results A Phase III Study to Compare the Efficacy and Safety of Paclitaxel Versus Irinotecan in Patients with Metastatic or Recurrent Gastric Cancer Who Failed in First-line Therapy (KCSG
Prognostic Factors of Second and Third Line Chemotherapy Using 5-FU with Platinum, Irinotecan, and Taxane for Advanced Gastric Cancer
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2011;43(4):236-243 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4143/crt.2011.43.4.236 Open Access Prognostic Factors of Second and Third Line Chemotherapy Using
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2011;43(4):236-243 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4143/crt.2011.43.4.236 Open Access Prognostic Factors of Second and Third Line Chemotherapy Using
First-line single-agent chemotherapy for patients with recurrent or metastatic gastric cancer with poor performance status
 562 First-line single-agent chemotherapy for patients with recurrent or metastatic gastric cancer with poor performance status JUN-EUL HWANG 1, HA-NA KIM 1, DAE-EUN KIM 1, HYUN-JEONG SHIM 1, WOO-KYUN BAE
562 First-line single-agent chemotherapy for patients with recurrent or metastatic gastric cancer with poor performance status JUN-EUL HWANG 1, HA-NA KIM 1, DAE-EUN KIM 1, HYUN-JEONG SHIM 1, WOO-KYUN BAE
Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer
 Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine DISCLOSURE OF INTEREST Employment: None Consultant or Advisory Role: Merck Serono, Roche, Beigene, Bayer, Servier, Lilly,
Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine DISCLOSURE OF INTEREST Employment: None Consultant or Advisory Role: Merck Serono, Roche, Beigene, Bayer, Servier, Lilly,
Fluoropyrimidine plus cisplatin for patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis
 Gastric Cancer (2013) 16:48 55 DOI 10.1007/s10120-012-0143-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fluoropyrimidine plus cisplatin for patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis Kohei Shitara
Gastric Cancer (2013) 16:48 55 DOI 10.1007/s10120-012-0143-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fluoropyrimidine plus cisplatin for patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis Kohei Shitara
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 33: (2013)
 Non-randomized Comparison Between Irinotecan plus Mitomycin C and Irinotecan Alone in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer Refractory to Fluoropyrimidine and Platinum AKIRA UEDA 1, AYUMU HOSOKAWA 1, KOHEI
Non-randomized Comparison Between Irinotecan plus Mitomycin C and Irinotecan Alone in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer Refractory to Fluoropyrimidine and Platinum AKIRA UEDA 1, AYUMU HOSOKAWA 1, KOHEI
Irinotecan monotherapy as third-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer refractory to fluoropyrimidines, platinum, and taxanes
 Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:655 662 DOI 10.1007/s10120-016-0670-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Irinotecan monotherapy as third-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer refractory to fluoropyrimidines, platinum, and
Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:655 662 DOI 10.1007/s10120-016-0670-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Irinotecan monotherapy as third-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer refractory to fluoropyrimidines, platinum, and
Modified EOX (Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine) as Palliative First-line Chemotherapy for Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma
 Modified EOX (Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine) as Palliative First-line Chemotherapy for Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma URSULA PLUSCHNIG 1, SEBASTIAN F. SCHOPPMANN 2,5, MATTHIAS PREUSSER 1,5,
Modified EOX (Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine) as Palliative First-line Chemotherapy for Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma URSULA PLUSCHNIG 1, SEBASTIAN F. SCHOPPMANN 2,5, MATTHIAS PREUSSER 1,5,
ESMO 2017, Madrid, Spain Dr. Loredana Vecchione Charite Comprehensive Cancer Center, Berlin HIGHLIGHTS ON CANCERS OF THE UPPER GI TRACT
 ESMO 2017, Madrid, Spain Dr. Loredana Vecchione Charite Comprehensive Cancer Center, Berlin HIGHLIGHTS ON CANCERS OF THE UPPER GI TRACT DOCETAXEL, OXALIPLATIN AND FLUOROURACIL/LEUCOVORIN (FLOT) FOR RESECTABLE
ESMO 2017, Madrid, Spain Dr. Loredana Vecchione Charite Comprehensive Cancer Center, Berlin HIGHLIGHTS ON CANCERS OF THE UPPER GI TRACT DOCETAXEL, OXALIPLATIN AND FLUOROURACIL/LEUCOVORIN (FLOT) FOR RESECTABLE
Real-World Treatment Patterns among Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer in South Korea
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2017;49(3):578-587 Original Article https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.001 Open Access Real-World Treatment Patterns among Patients with Advanced Gastric
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 2005-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 2017;49(3):578-587 Original Article https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.001 Open Access Real-World Treatment Patterns among Patients with Advanced Gastric
Van Cutsem E et al. Proc ASCO 2009;Abstract LBA4509.
 Efficacy Results from the ToGA Trial: A Phase III Study of Trastuzumab Added to Standard Chemotherapy in First-Line HER2- Positive Advanced Gastric Cancer Van Cutsem E et al. Proc ASCO 2009;Abstract LBA4509.
Efficacy Results from the ToGA Trial: A Phase III Study of Trastuzumab Added to Standard Chemotherapy in First-Line HER2- Positive Advanced Gastric Cancer Van Cutsem E et al. Proc ASCO 2009;Abstract LBA4509.
Key words: advanced gastric cancer, elderly, prognosis, survival, taxane
 JBUON 2018; 23(2): 416-421 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Adding taxane to platin-5-fluorouracil combination does not improve
JBUON 2018; 23(2): 416-421 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Adding taxane to platin-5-fluorouracil combination does not improve
Continuation of trastuzumab beyond disease progression in HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer: the MD Anderson experience
 Original Article Continuation of trastuzumab beyond disease progression in HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer: the MD Anderson experience Humaid O. Al-Shamsi 1, Yazan Fahmawi 1, Ibrahim Dahbour 1,
Original Article Continuation of trastuzumab beyond disease progression in HER2-positive metastatic gastric cancer: the MD Anderson experience Humaid O. Al-Shamsi 1, Yazan Fahmawi 1, Ibrahim Dahbour 1,
Introduction. pissn , eissn https://doi.org/ /crt Open Access. Original Article
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 217;49(3):76-716 Original Article https://doi.org/1.4143/crt.216.216 Open Access A Multicenter Randomized Phase II Study of Docetaxel vs. Docetaxel Plus
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 217;49(3):76-716 Original Article https://doi.org/1.4143/crt.216.216 Open Access A Multicenter Randomized Phase II Study of Docetaxel vs. Docetaxel Plus
Updated Apr 2017 by Dr. Ko (Medical Oncologist, Abbotsford Cancer Centre)
 Metastatic Esophagogastric Cancer Summary Updated Apr 2017 by Dr. Ko (Medical Oncologist, Abbotsford Cancer Centre) Reviewed by Dr. Yoo-Joung Ko (Medical Oncologist, Sunnybrook Odette Cancer Centre, University
Metastatic Esophagogastric Cancer Summary Updated Apr 2017 by Dr. Ko (Medical Oncologist, Abbotsford Cancer Centre) Reviewed by Dr. Yoo-Joung Ko (Medical Oncologist, Sunnybrook Odette Cancer Centre, University
Evaluation of pharmacological therapies used in Costa Rica in patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a retrospective study
 Original Article Evaluation of pharmacological therapies used in Costa Rica in patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a retrospective study Eugenia Cordero-García 1,2, Allan Ramos-Esquivel 3,4, Warner
Original Article Evaluation of pharmacological therapies used in Costa Rica in patients with metastatic gastric cancer: a retrospective study Eugenia Cordero-García 1,2, Allan Ramos-Esquivel 3,4, Warner
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Bo He 1, Hui-Qing Zhang 1 *, Shu-Ping Xiong 2, Shan Lu 1, Yi-Ye Wan 1, Rong-Feng Song 1. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.8.3111 Changes of CEA and CA199 Levels in Advanced Gastric Adenocarcinoma RESEARCH ARTICLE Changing patterns of Serum CEA and CA199 for Evaluating the Response
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.8.3111 Changes of CEA and CA199 Levels in Advanced Gastric Adenocarcinoma RESEARCH ARTICLE Changing patterns of Serum CEA and CA199 for Evaluating the Response
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Gokmen Umut Erdem*, Yakup Bozkaya, Nuriye Yildirim Ozdemir, Nebi Serkan Demirci, Ozan Yazici, Nurullah Zengin
 BOSNIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ARTICLE WWW.BJBMS.ORG 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) as a third-line chemotherapy treatment in metastatic gastric cancer, after
BOSNIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES RESEARCH ARTICLE WWW.BJBMS.ORG 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) as a third-line chemotherapy treatment in metastatic gastric cancer, after
Decline of serum CA724 as a probable predictive factor for tumor response during chemotherapy of advanced gastric carcinoma
 Original Article Decline of serum CA724 as a probable predictive factor for tumor response during chemotherapy of advanced gastric carcinoma Li Zou 1 *, Jun Qian 2 * 1 Department of Oncology, 2 Department
Original Article Decline of serum CA724 as a probable predictive factor for tumor response during chemotherapy of advanced gastric carcinoma Li Zou 1 *, Jun Qian 2 * 1 Department of Oncology, 2 Department
Medicinae Doctoris. One university. Many futures.
 Medicinae Doctoris The Before and The After: Can chemotherapy revise the trajectory of gastric and esophageal cancers? Dr. David Dawe MD, FRCPC Medical Oncologist Assistant Professor Disclosures None All
Medicinae Doctoris The Before and The After: Can chemotherapy revise the trajectory of gastric and esophageal cancers? Dr. David Dawe MD, FRCPC Medical Oncologist Assistant Professor Disclosures None All
Docetaxel Oxaliplatin Gastric cancer. Keywords. Introduction
 Gastric Cancer (2014) 17:341 347 DOI 10.1007/s10120-013-0266-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biweekly docetaxel, fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin (TEF) as first-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer and adenocarcinoma
Gastric Cancer (2014) 17:341 347 DOI 10.1007/s10120-013-0266-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biweekly docetaxel, fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin (TEF) as first-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer and adenocarcinoma
Materials and Methods
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Oxaliplatin Plus 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin (Modified FOLFOX6) with Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients having a Good or Poor Performance
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Oxaliplatin Plus 5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin (Modified FOLFOX6) with Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients having a Good or Poor Performance
Survival benefit of anti-angiogenic agents in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 57), pp: 97565-97570 Survival benefit of anti-angiogenic agents in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis Jung Han
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 57), pp: 97565-97570 Survival benefit of anti-angiogenic agents in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis Jung Han
GASTRIC CANCER TREATMENT REGIMENS (Part 1 of 6)
 GASTRIC CANCER TREATMENT S (Part 1 of 6) Clinical Trials: The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment. Cancer
GASTRIC CANCER TREATMENT S (Part 1 of 6) Clinical Trials: The National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment. Cancer
Gastric cancer is the fourth
 Section Editors: Christopher J. Campen and Beth Eaby-Sandy Ramucirumab: A New Therapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer ANDREA LANDGRAF OHOLENDT, PharmD, BCOP, and JENNIFER L. ZADLO, PharmD, BCOP From The University
Section Editors: Christopher J. Campen and Beth Eaby-Sandy Ramucirumab: A New Therapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer ANDREA LANDGRAF OHOLENDT, PharmD, BCOP, and JENNIFER L. ZADLO, PharmD, BCOP From The University
Sun Young Kim 1,5 Min Joo Yoon 2 Young Iee Park 3 Mi Jung Kim 3 Byung Ho Nam 2,4,6 Sook Ryun Park 3,5
 Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:453 463 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-017-0756-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nomograms predicting survival of patients with unresectable or metastatic gastric cancer who receive combination
Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:453 463 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-017-0756-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nomograms predicting survival of patients with unresectable or metastatic gastric cancer who receive combination
pissn , eissn Open Access Original Article
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 216;48(2):553-56 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.4143/crt.215.155 Open Access A Retrospective Analysis for Patients with HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 216;48(2):553-56 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.4143/crt.215.155 Open Access A Retrospective Analysis for Patients with HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer
Phase II study of weekly paclitaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil for advanced gastric cancer
 Gastric Cancer (2011) 14:332 338 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0043-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phase II study of weekly paclitaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil for advanced gastric cancer Takuo Hara Kazuhiro Nishikawa
Gastric Cancer (2011) 14:332 338 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0043-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phase II study of weekly paclitaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil for advanced gastric cancer Takuo Hara Kazuhiro Nishikawa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Gastric Cancer (2012) 15: DOI /s
 Gastric Cancer (2012) 15:313 322 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0118-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of trastuzumab in Japanese patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a subgroup
Gastric Cancer (2012) 15:313 322 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0118-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of trastuzumab in Japanese patients with HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a subgroup
: Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME Hyun Woo Lee, M.D. EDUCATION 1991.3.-2001.2 : Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Doctor of Medicine 2004.3-2006.2 Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate School,
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME Hyun Woo Lee, M.D. EDUCATION 1991.3.-2001.2 : Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Doctor of Medicine 2004.3-2006.2 Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate School,
Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda
 Xeloda A blockbuster in the making Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda Xeloda unique tumor-activated mechanism Delivering more cancer-killing agent straight into cancer Highly effective comparable efficacy
Xeloda A blockbuster in the making Jonathan Dickinson, LCL Xeloda Xeloda unique tumor-activated mechanism Delivering more cancer-killing agent straight into cancer Highly effective comparable efficacy
Chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic gastric cancer; a single Turkish cancer center experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic gastric cancer; a single Turkish cancer center experience Cemil Bilir¹, Hüseyin Engin¹, Bekir Hakan Bakkal², Sevil Uygun İlikhan³, Dilek
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic gastric cancer; a single Turkish cancer center experience Cemil Bilir¹, Hüseyin Engin¹, Bekir Hakan Bakkal², Sevil Uygun İlikhan³, Dilek
A Case Report of Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Producing Advanced Gastric Cancer
 Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 5, No. 2; 2016 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Case Report of Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Producing Advanced Gastric
Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 5, No. 2; 2016 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education A Case Report of Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Producing Advanced Gastric
Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients
 Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010
 Original Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:530-535 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.4.530 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010 Yun Mi
Original Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:530-535 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.4.530 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Standardized Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Korea between 1985 and 2010 Yun Mi
A retrospective study of the safety and efficacy of paclitaxel plus ramucirumab in patients with advanced or recurrent gastric cancer with ascites
 Matsumoto et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:120 DOI 10.1186/s12885-018-4057-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A retrospective study of the safety and efficacy of paclitaxel plus ramucirumab in patients with advanced
Matsumoto et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:120 DOI 10.1186/s12885-018-4057-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A retrospective study of the safety and efficacy of paclitaxel plus ramucirumab in patients with advanced
Prognostic Factors for Node-Negative Advanced Gastric Cancer after Curative Gastrectomy
 pissn : 293-582X, eissn : 293-564 J Gastric Cancer 26;6(3):6-66 http://dx.doi.org/.523/jgc.26.6.3.6 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Node-Negative Advanced Gastric Cancer after Curative Gastrectomy
pissn : 293-582X, eissn : 293-564 J Gastric Cancer 26;6(3):6-66 http://dx.doi.org/.523/jgc.26.6.3.6 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Node-Negative Advanced Gastric Cancer after Curative Gastrectomy
Successful treatment of liver metastases arising from early gastric cancer achieved clinical complete response by nivolumab
 Namikawa et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0479-3 CASE REPORT Successful treatment of liver metastases arising from early gastric cancer achieved clinical complete
Namikawa et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0479-3 CASE REPORT Successful treatment of liver metastases arising from early gastric cancer achieved clinical complete
London Cancer New Drugs Group APC/DTC Briefing
 London Cancer New Drugs Group Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced gastric and oesophageal (oesophago-gastric) cancer APC/DTC Briefing Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced gastric and oesophageal
London Cancer New Drugs Group Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced gastric and oesophageal (oesophago-gastric) cancer APC/DTC Briefing Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced gastric and oesophageal
Key words: gastric cancer, tumor location, pathology, outcome
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 650-655 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Addition of taxanes to combination chemotherapy in distal intestinal
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 650-655 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Addition of taxanes to combination chemotherapy in distal intestinal
University Hospital Gasthuisberg, Leuven, Belgium
 The Oncologist The Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: New Findings on the Activity of the Taxanes ERIC VAN CUTSEM University Hospital Gasthuisberg, Leuven, Belgium Key Words. Taxanes Docetaxel Paclitaxel
The Oncologist The Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: New Findings on the Activity of the Taxanes ERIC VAN CUTSEM University Hospital Gasthuisberg, Leuven, Belgium Key Words. Taxanes Docetaxel Paclitaxel
Phase 2 study of adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, capecitabine, and cisplatin in patients with curatively resected stage IIIB IV gastric cancer
 Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:182 189 DOI 10.1007/s10120-015-0580-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phase 2 study of adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, capecitabine, and cisplatin in patients with curatively resected stage
Gastric Cancer (2017) 20:182 189 DOI 10.1007/s10120-015-0580-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Phase 2 study of adjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, capecitabine, and cisplatin in patients with curatively resected stage
stage III gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of capecitabine and oxaliplatin with S-1 as adjuvant chemotherapy in stage III gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy Jang Ho Cho, Jae Yun Lim, Jae Yong Cho* Division of Medical
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparison of capecitabine and oxaliplatin with S-1 as adjuvant chemotherapy in stage III gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy Jang Ho Cho, Jae Yun Lim, Jae Yong Cho* Division of Medical
Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 January 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta378
 Ramucirumab for treating advanced gastric cancer or gastro oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma previously treated with chemotherapy Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 January 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta378
Ramucirumab for treating advanced gastric cancer or gastro oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma previously treated with chemotherapy Technology appraisal guidance Published: 27 January 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ta378
A meta-analysis of clinical trials over regimens with or without cetuximab for advanced gastric cancer patients
 JBUON 2017; 22(4): 900-904 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A meta-analysis of clinical trials over regimens with or without cetuximab
JBUON 2017; 22(4): 900-904 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A meta-analysis of clinical trials over regimens with or without cetuximab
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Summary of the study protocol of the FLOT3-Study
 Summary of the study protocol of the FLOT3-Study EudraCT no. 2007-005143-17 Protocol Code: S396 Title A Prospective Multicenter Study With 5-FU, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin and Docetaxel (FLOT) in Patients
Summary of the study protocol of the FLOT3-Study EudraCT no. 2007-005143-17 Protocol Code: S396 Title A Prospective Multicenter Study With 5-FU, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin and Docetaxel (FLOT) in Patients
Reference No: Author(s) Approval date: 12/05/16. Committee. June Operational Date: Review:
 Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Biliary Tract Cancer (BTC) Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Biliary Tract Cancer (BTC) Dr Colin Purcell, Consultant Medical Oncologist on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group, Cancer
Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy
 Anna Dorothea Wagner, PD & MER Department of Oncology University of Lausanne Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy Structure 1. Background and overview 2. Adjuvant chemotherapy:
Anna Dorothea Wagner, PD & MER Department of Oncology University of Lausanne Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy Structure 1. Background and overview 2. Adjuvant chemotherapy:
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)?
 Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY. Bo Zhu, Jun-Rong Wu, and Xiao-Ping Zhou. INTRODUCTION Patients with gastric cancer are often diagnosed in an
 Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY A Retrospective Comparison of Trastuzumab Plus Cisplatin and Trastuzumab Plus Capecitabine in Elderly HER2-Positive Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients Bo Zhu, Jun-Rong Wu, and
Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY A Retrospective Comparison of Trastuzumab Plus Cisplatin and Trastuzumab Plus Capecitabine in Elderly HER2-Positive Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients Bo Zhu, Jun-Rong Wu, and
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Resectable locally advanced oesophagogastric cancer
 Resectable locally advanced oesophagogastric cancer Clinical Case Discussion Florian Lordick University Cancer Center Leipzig University Clinic Leipzig Leipzig, Germany esmo.org DISCLOSURES Honoraria for
Resectable locally advanced oesophagogastric cancer Clinical Case Discussion Florian Lordick University Cancer Center Leipzig University Clinic Leipzig Leipzig, Germany esmo.org DISCLOSURES Honoraria for
Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers in the Elderly. Choo Su Pin Senior Consultant Medical Oncology National Cancer Centre Singapore
 Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers in the Elderly Choo Su Pin Senior Consultant Medical Oncology National Cancer Centre Singapore Gastric Cancer --High Global Burden Global Cancer Deaths % of all cancer (2008)
Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers in the Elderly Choo Su Pin Senior Consultant Medical Oncology National Cancer Centre Singapore Gastric Cancer --High Global Burden Global Cancer Deaths % of all cancer (2008)
Original article. E. Mitry 1 *, J.-Y. Douillard 2, E. Van Cutsem 3, D. Cunningham 4, E. Magherini 5, D. Mery-Mignard 5, L. Awad 5 & P.
 Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 1013 1017, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh267 Predictive factors of survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an individual data analysis of 602 patients
Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 1013 1017, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh267 Predictive factors of survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: an individual data analysis of 602 patients
Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer: Review and Update of Current Practices
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 4, July 2013, pp. 385-393 Review Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer: Review and Update of Current Practices Sung Chul Park* and Hoon Jai Chun *Division of Gastroenterology
Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 4, July 2013, pp. 385-393 Review Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer: Review and Update of Current Practices Sung Chul Park* and Hoon Jai Chun *Division of Gastroenterology
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Kuanoon Boupaijit, Prapaporn Suprasert* Abstract. Introduction. Materials and Methods
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Survival Outcomes of Advanced and Recurrent Cervical Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy: Experience of Northern Tertiary Care Hospital in Thailand Kuanoon Boupaijit, Prapaporn Suprasert*
RESEARCH ARTICLE Survival Outcomes of Advanced and Recurrent Cervical Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy: Experience of Northern Tertiary Care Hospital in Thailand Kuanoon Boupaijit, Prapaporn Suprasert*
Perioperative chemotherapy: individualized therapy or same treatment for all? Prof. Dr. med. Salah-Eddin Al-Batran
 Perioperative chemotherapy: individualized therapy or same treatment for all? Prof. Dr. med. Salah-Eddin Al-Batran Institute of Clinical Cancer Research Krankenhaus Nordwest UCT - University Cancer Center
Perioperative chemotherapy: individualized therapy or same treatment for all? Prof. Dr. med. Salah-Eddin Al-Batran Institute of Clinical Cancer Research Krankenhaus Nordwest UCT - University Cancer Center
Original article. Introduction
 Gastric Cancer (2009) 12: 153 157 DOI 10.1007/s10120-009-0517-8 Original article 2009 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Efficacy of sequential methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (MTX/5FU)
Gastric Cancer (2009) 12: 153 157 DOI 10.1007/s10120-009-0517-8 Original article 2009 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Efficacy of sequential methotrexate and 5-fluorouracil (MTX/5FU)
Establishment and validation of prognostic nomograms in firstline metastatic gastric cancer patients
 Original Article Establishment and validation of prognostic nomograms in firstline metastatic gastric cancer patients Yukiya Narita 1 *, Shigenori Kadowaki 1 *, Isao Oze 2 *, Yosuke Kito 3, Takeshi Kawakami
Original Article Establishment and validation of prognostic nomograms in firstline metastatic gastric cancer patients Yukiya Narita 1 *, Shigenori Kadowaki 1 *, Isao Oze 2 *, Yosuke Kito 3, Takeshi Kawakami
Ivyspring International Publisher. Introduction. Journal of Cancer 2017, Vol. 8. Abstract
 1371 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2017; 8(8): 1371-1377. doi: 10.7150/jca.17102 Antiemetic Effectiveness and Cost-Saving of Aprepitant plus Granisetron Is Superior
1371 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2017; 8(8): 1371-1377. doi: 10.7150/jca.17102 Antiemetic Effectiveness and Cost-Saving of Aprepitant plus Granisetron Is Superior
Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer
 Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ramucirumab (Cyramza) for Gastric Cancer October 29, 2015
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ramucirumab (Cyramza) for Gastric Cancer October 29, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily intended
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ramucirumab (Cyramza) for Gastric Cancer October 29, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily intended
Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy
 Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy Priv. Doz. Dr. Dr. med. T.O. Götze Institute of Clinical Cancer Research Director: Prof. Dr. S.-E. Al- Batran University Cancer
Neo- and adjuvant treatment for gastric cancer: The role of chemotherapy Priv. Doz. Dr. Dr. med. T.O. Götze Institute of Clinical Cancer Research Director: Prof. Dr. S.-E. Al- Batran University Cancer
Three-year outcomes of a phase II study of adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 plus docetaxel for stage III gastric cancer after curative D2 gastrectomy
 Gastric Cancer (2014) 17:348 353 DOI 10.1007/s10120-013-0273-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-year outcomes of a phase II study of adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 plus docetaxel for stage III gastric cancer after
Gastric Cancer (2014) 17:348 353 DOI 10.1007/s10120-013-0273-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Three-year outcomes of a phase II study of adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 plus docetaxel for stage III gastric cancer after
ESOPHAGEAL AND ESOPHAGOGASTRIC JUNCTION CANCER TREATMENT REGIMENS (Part 1 of 7)
 CANCER TREATMENT S (Part 1 of 7) Clinical Trials: The NCCN recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment. Cancer therapy selection, dosing, administration,
CANCER TREATMENT S (Part 1 of 7) Clinical Trials: The NCCN recommends cancer patient participation in clinical trials as the gold standard for treatment. Cancer therapy selection, dosing, administration,
Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer(review) WagnerAD,SynNLX,MoehlerM,GrotheW,YongWP,TaiBC,HoJ,UnverzagtS WagnerAD,SynNLX,MoehlerM,GrotheW,YongWP,TaiBC,HoJ,UnverzagtS.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer(review) WagnerAD,SynNLX,MoehlerM,GrotheW,YongWP,TaiBC,HoJ,UnverzagtS WagnerAD,SynNLX,MoehlerM,GrotheW,YongWP,TaiBC,HoJ,UnverzagtS.
Systemic treatment in early and advanced gastric cancer
 Systemic treatment in early and advanced gastric cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer n Surgical resection n Pathology assessment and estimation
Systemic treatment in early and advanced gastric cancer Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer n Surgical resection n Pathology assessment and estimation
Third-line docetaxel chemotherapy for recurrent and metastatic gastric cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:314-321 Third-line docetaxel chemotherapy for recurrent and metastatic gastric cancer Ji Hyun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim, Sung Yong Oh, Suee Lee, Hojin Lee, Hye Jung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:314-321 Third-line docetaxel chemotherapy for recurrent and metastatic gastric cancer Ji Hyun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim, Sung Yong Oh, Suee Lee, Hojin Lee, Hye Jung
Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China Yu-Tao Liu, Xue-Zhi Hao, Jun-Ling Li, Xing-Sheng
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Survival of patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma before and after approved use of gefitinib in China Yu-Tao Liu, Xue-Zhi Hao, Jun-Ling Li, Xing-Sheng
NCCP Chemotherapy Regimen. FLOT Therapy-14 day
 INDICATIONS FOR USE: FLOT Therapy-14 Regimen Code 00344a *Reimbursement Indicator INDICATION ICD10 Treatment of locally advanced ( T2) and/or nodal positive (N+) C16 resectable gastric adenocarcinoma Treatment
INDICATIONS FOR USE: FLOT Therapy-14 Regimen Code 00344a *Reimbursement Indicator INDICATION ICD10 Treatment of locally advanced ( T2) and/or nodal positive (N+) C16 resectable gastric adenocarcinoma Treatment
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Advanced duodenal carcinoma: Chemotherapy efficacy and analysis of prognostic factors
 Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-015-0094-8 February 2016, Vol. 2, No. 1, P16 P20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advanced duodenal carcinoma: Chemotherapy efficacy and analysis of prognostic factors
Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-015-0094-8 February 2016, Vol. 2, No. 1, P16 P20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advanced duodenal carcinoma: Chemotherapy efficacy and analysis of prognostic factors
Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: Where Do We Stand?
 Review 1281 Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Amit Mahipal, MD, MPH a ; Minsig Choi, MD b ; and Richard Kim, MD a Abstract Gastric cancer is a leading cause of cancer
Review 1281 Second-Line Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Amit Mahipal, MD, MPH a ; Minsig Choi, MD b ; and Richard Kim, MD a Abstract Gastric cancer is a leading cause of cancer
Fatih Teker*, Bahiddin Yilmaz, Yasemin Kemal, Engin Kut, Idris Yucel
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6727 Efficacy of DCF and ECF Regimens as First Line Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Docetaxel or Epirubicin,
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.16.6727 Efficacy of DCF and ECF Regimens as First Line Chemotherapy for Advanced Gastric Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Efficacy and Safety of Docetaxel or Epirubicin,
STUDY FINDINGS PRESENTED ON TAXOTERE REGIMENS IN HEAD AND NECK, LUNG AND BREAST CANCER
 Contact: Anne Bancillon + 33 (0)6 70 93 75 28 STUDY FINDINGS PRESENTED ON TAXOTERE REGIMENS IN HEAD AND NECK, LUNG AND BREAST CANCER Key results of 42 nd annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical
Contact: Anne Bancillon + 33 (0)6 70 93 75 28 STUDY FINDINGS PRESENTED ON TAXOTERE REGIMENS IN HEAD AND NECK, LUNG AND BREAST CANCER Key results of 42 nd annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical
Second-line systemic treatment for advanced cholangiocarcinoma
 Original Article Second-line systemic treatment for advanced cholangiocarcinoma Jane E. Rogers 1, Lindsey Law 2, Van D. Nguyen 1, Wei Qiao 3, Milind M. Javle 2, Ahmed Kaseb 2, Rachna T. Shroff 2 1 Pharmacy
Original Article Second-line systemic treatment for advanced cholangiocarcinoma Jane E. Rogers 1, Lindsey Law 2, Van D. Nguyen 1, Wei Qiao 3, Milind M. Javle 2, Ahmed Kaseb 2, Rachna T. Shroff 2 1 Pharmacy
Advances in gastric cancer: How to approach localised disease?
 Advances in gastric cancer: How to approach localised disease? Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer Surgical resection Pathology assessment and estimation
Advances in gastric cancer: How to approach localised disease? Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer Surgical resection Pathology assessment and estimation
Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis
 Mikami et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:8 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-1091-2 RESEARCH Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis Open Access
Mikami et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:8 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-1091-2 RESEARCH Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis Open Access
Treatment options in patients with metastatic gastric cancer: Current status and future perspectives
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ bpgoffice@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3905 World J Gastroenterol 2014 April 14; 20(14): 3905-3915 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2014
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ bpgoffice@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3905 World J Gastroenterol 2014 April 14; 20(14): 3905-3915 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2014
MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients
 Yonago Acta Medica 2017;60:174 178 Original Article Gross Appearance and Curability Are Predictive Factors of a Better Prognosis After Gastrectomy in Gastric Cancer Patients with Metastasis to the Adjacent
Yonago Acta Medica 2017;60:174 178 Original Article Gross Appearance and Curability Are Predictive Factors of a Better Prognosis After Gastrectomy in Gastric Cancer Patients with Metastasis to the Adjacent
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Analysis of the outcome of young age tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil (known as S1) for first-line palliative treatment of advanced gastric cancer
 LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil (known as S1) for first-line palliative treatment of advanced gastric cancer Tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil (known as S1) in
LONDON CANCER NEW DRUGS GROUP RAPID REVIEW Tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil (known as S1) for first-line palliative treatment of advanced gastric cancer Tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil (known as S1) in
clinical practice guidelines
 Annals of Oncology 21 (Supplement 5): v50 v54, 2010 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq164 Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up A. Okines 1, M. Verheij 2, W. Allum
Annals of Oncology 21 (Supplement 5): v50 v54, 2010 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq164 Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up A. Okines 1, M. Verheij 2, W. Allum
Randomized controlled trial of S-1 maintenance therapy in metastatic esophagogastric cancer the multinational MATEO study
 Haag et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:509 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3497-9 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Randomized controlled trial of S-1 maintenance therapy in metastatic esophagogastric cancer the multinational
Haag et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:509 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3497-9 STUDY PROTOCOL Open Access Randomized controlled trial of S-1 maintenance therapy in metastatic esophagogastric cancer the multinational
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer
 Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Current Standard of Care of Gastric Cancer:
 Current Standard of Care of Gastric Cancer: Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer Surgical resection Pathology assessment and estimation of risk Treatment
Current Standard of Care of Gastric Cancer: Andrés Cervantes Professor of Medicine Classical approach to localised gastric cancer Surgical resection Pathology assessment and estimation of risk Treatment
Cyramza (ramucirumab)
 Cyramza (ramucirumab) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 10/01/2015 Current Effective Date: 03/01/2017TBD03/01/2018 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications
Cyramza (ramucirumab) Line(s) of Business: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration Akamai Advantage Original Effective Date: 10/01/2015 Current Effective Date: 03/01/2017TBD03/01/2018 POLICY A. INDICATIONS The indications
Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease
 GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
 Seite 1 von 5 A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Now Available: Final Rule for FDAAA 801 and NIH Policy on Clinical Trial Reporting Trial record 1 of 1 for: BO18255 Previous Study Return
Seite 1 von 5 A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Now Available: Final Rule for FDAAA 801 and NIH Policy on Clinical Trial Reporting Trial record 1 of 1 for: BO18255 Previous Study Return
