Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer (Tis) updated results and toxicity
|
|
|
- Shon Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer (Tis) updated results and toxicity Aditya Manjunath 1, Thomas Brenton 1, Sarah Wylie 1, Catherine M. Corbishley 2, Nick A. Watkin 1 1 Department of Urology, 2 Department of Cellular Pathology, St George s Hospital, London, UK Contributions: (I) Conception and design: NA Watkin; (II) Administrative support: None; (III) Provision of study material or patients: A Manjunath; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: None; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: None; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Mr. Aditya Manjunath. Department of Urology, St George s Hospital, London, UK. aditya.m@doctors.org.uk. Abstract: Penile cancer is a rare malignancy estimated to affect 26,000 men globally each year. The association with penile cancer, in particular non-invasive disease, and human papilloma virus (HPV) is well known. Ninety-five percent of cases of penile cancer are squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which are staged using the TNM staging system. Terminology describing the histological appearance of non-invasive penile cancer has changed with all cases grouped under the umbrella term of penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN); either undifferentiated or differentiated. This replaces previous terms such as carcinoma in situ (CIS) and eponymous names such as Bowen s disease. This change is recognised by the World Health Organisation (WHO). The topical treatments most commonly used for PeIN are 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and imiquimod (IQ). Other treatments such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) are used but to a lesser degree. The evidence for all of these treatments is heterogenous with no randomised data available. Overall up to 57% complete response has been reported with a low number of serious adverse events. In this article, we aim to review the available evidence for the topical treatment of non-invasive penile cancer specifically regarding its efficacy and toxicity. Keywords: Carcinoma in situ (CIS); penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN); 5-flurouracil (5-FU); imiquimod (IQ) Submitted Apr 18, Accepted for publication Jun 15, doi: /tau View this article at: Epidemiology of penile cancer Penile cancer is a rare malignancy. It has been estimated to affect 26,000 men globally every year. The incidence appears to be particularly higher in the developing countries; however regions with religious practices that exercise neonatal circumcision appear to experience lower incidence rates (1). Incidence rates of penile cancer in the UK was estimated at 0.1/100,000 (man-years), with approximately half of these cases attributed to human papilloma virus (HPV). The histology behind penile cancer is commonly squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) 95%, which is highly associated with HPV 16/18 (2). What is Non-invasive penile cancer? Penile cancer is staged via the current 7 th edition AJCC TNM staging system (Table 1) (3). To improve the accuracy of staging, a complete resection of the site insuring negative surgical margins is preferable to a biopsy. Several factors are taken into account with staging, determining whether the cancer is invasive, or non-invasive. Once it has been classified, the appropriate treatment options can be explored. A non-invasive cancer constitutes as a carcinoma in situ (CIS), which has not invaded the sub-epithelial connective tissue and has not spread to the lymphovascular system (4). Updated histopathological and clinical terminology In recent years there has been a change of terminology used in the histopathological classification of premalignant penile
2 804 Manjunath et al. Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer Table TNM clinical and pathological classification of penile cancer (3) Clinical classification T primary tumour TX primary tumour cannot be assessed T0 no evidence of primary tumour Tis carcinoma in situ Ta non-invasive carcinoma T1 tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue T1a tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue without lymphovascular invasion and is not poorly differentiated or undifferentiated (T1G1-2) T1b tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue with lymphovascular invasion or is poorly differentiated or undifferentiated (T1G3-4) T2 tumour invades corpus spongiosum and/or corpora cavernosa T3 tumour invades urethra T4 tumour invades other adjacent structures N regional lymph nodes NX regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed N0 no palpable or visibly enlarged inguinal lymph node N1 palpable mobile unilateral inguinal lymph node N2 palpable mobile multiple unilateral or bilateral inguinal lymph nodes N3 fixed inguinal nodal mass or pelvic lymphadenopathy, unilateral or bilateral M distant metastasis M0 no distant metastasis M1 distant metastasis Pathological classification (the pt categories correspond to the clinical T categories; the pn categories are based upon biopsy or surgical excision) pn regional lymph nodes pnx regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed pn0 no regional lymph node metastasis pn1 intranodal metastasis in a single inguinal lymph node pn2 metastasis in multiple or bilateral inguinal lymph nodes pn3 metastasis in pelvic lymph node(s), unilateral or bilateral or extranodal extension of any regional lymph node metastasis pm distant metastasis pm0 no distant metastasis pm1 distant metastasis G histopathological grading GX grade of differentiation cannot be assessed G1 well differentiated G2 moderately differentiated G3 4 poorly differentiated/undifferentiated
3 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 6, No 5 October Figure 1 Pathologic slide demonstrating undifferentiated PeIN (400 magnification). PeIN, penile intraepithelial neoplasia. as well as previously defined squamous CIS (Figure 1). Since the recognition of the role of HPV, undifferentiated PeIN can be further subdivided into basaloid and/or warty subtypes (5). These are frequently associated with HPV 16. The association between undifferentiated PeIN and invasive warty and basaloid type tumours encourages treatment undifferentiated PeIN as opposed to observation (6). Differentiated PeIN is defined histologically by atypical squamous cells which are confined to the lower layers of the penile squamous epithelium. It is usually associated with architectural atypia, elongated rete ridges and aberrant intraepithelial keratinisation (Figure 2). It is not usually associated with high risk HPV subtypes (5). Diagnosis of non-invasive penile cancer Figure 2 Pathologic slide demonstrating differentiated PeIN (400 magnification). PeIN, penile intraepithelial neoplasia. lesions. In order to better understand the management of these lesions it is essential to be clear about these changes. Previously a number of terms existed in the histopathological description of premalignant lesions. These include penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PeIN), squamous CIS, high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) and low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL) (5). In addition PeIN has been further subdivided into grade I to III (low to high grade). A simpler classification has been proposed and endorsed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) (6). This acknowledges the role of HPV in the pathophysiology of these lesions (7). The change in classification has resulted in removal of all of the above terms including the subgrouping of PeIN to leave two categories; undifferentiated PeIN or differentiated PeIN. Undifferentiated PeIN encompasses the clinically defined entities of Bowen s disease and erythroplasia of Queyrat, PeIN typically presents as a solitary lesion on the penis, and usually presents in men over the age of 35, with a peak incidence of years. According to the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) guidelines any suspicious persistent or atypical penile lesions should be managed with a full anogenital examination followed with a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and exclude invasive malignancy (8). When assessing the penis by clinical examination, we recommend using a swab soaked with 5% acetic acid on the genital skin. After a few minutes abnormal epithelium demonstrates an aceto-white reaction. Although not specific for premalignant changes, Wikström et al. identified 20% of men with aceto-positive reaction as having PeIN (9). Aim of review Currently European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines suggest non-invasive penile malignancy can be managed with topical treatments such as Imiquimod (IQ) or 5-FU. Although, other options have been suggested such as total or partial glans resurfacing which have shown up to 20% of patients had superficial invasive disease (3). The aim of this review will be to update readers on the topical treatment options specifically with regards to their efficacy and toxicity. Topical treatment of non-invasive penile cancer The two main topical treatments for non-invasive penile cancer are 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and IQ. The next section provides the up to data evidence of their efficacy as well as
4 806 Manjunath et al. Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer their toxicity. The EAU guidelines report that for CIS, up to 57% of patients reported a complete response with a low number of adverse events (3). 5-FU 5 Fluoro Uracil exerts its chemotherapeutic effects through inhibition of the enzyme thymidylate synthetase (10). The antimetabolite effects occur through increased uptake in rapidly dividing cancer cells. 5-FU was first recognised in the 1960s as a treatment for Actinic Keratosis. As this became a widely practiced way of topical and effective management it was trialed in other topical low grade cancers, in particular penile cancer (11). Penile tissue is suited to topical 5-FU treatment as recurrence from secondary progression of bowenoid areas from hair follicles is common (12). This is a significant step as tissue preservation in penile cancer is very important for psychological and sexual preserving reasons. 5-FU is a topical agent and it is well tolerated by patients. Close follow up is of particular importance in topical therapies for cancers. If the initial course of topical 5-FU fails, then this treatment is not usually repeated (3). One of the first studies assessing 5-FU in less aggressive superficial penile cancer showed in the group of patients treated with 5FU the post treatment biopsies were normal, with a 70-month follow up (13). Even though this study had a small treatment group (n=7), there was a significant treatment effect. These findings were also replicated in a small study (n=3), patients were recurrence free from a follow up time of between months (14). These findings have been shown in further studies on larger scales. In a retrospective study of 86 patients with penile CIS, followed over a 10-year period showed that topical 5-FU had a 50% complete response compared to 44% in IQ. Thirty-one percent of patients treated with 5-FU had a partial response, while IQ had 56% non-response (15). These are the two main stay topical therapies in superficial penile cancers. Although the numbers in the study are small, there is a notable difference between 5-FU and IQ. It is challenging to come to a firm conclusion as there is limited evidence available and moreover existing data has small numbers and are not randomised controlled trials. As there is a limited evidence base in topical treatment for superficial less aggressive penile cancer it is beneficial to see that topical therapies have a substantial effect. Moreover with close surveillance of the patients detrimental effects of the disease progression can be curtailed. IQ IQ is an immuno-modulating drug which acts on several levels of the adaptive immune system. It activates the cells of this aspect of the immune system through toll like receptor 7 (TLR-7) causing secretion of cytokines such as interferon alpha, interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor alpha. The treatment is usually given for 5 days a week for a period of 4 to 6 weeks. The evidence for the use of topical IQ in PeIN is very heterogenous with most data coming from small case series and case reports. There has been more extensive use of IQ in extra genital CIS. A recent review picked up a total of 29 articles (22 case reports and 7 small case series) where IQ was used in the treatment of PeIN. In total this amounts to 48 patients, this is the largest aggregated number of patients in a review of IQ treatment to date. The majority of patients present with the clinical entity erythroplasia of query at (n=32), the remaining present with Bowen s disease (n=8) or bowenoid papulosis (n=8). The small studies included in this review are quite heterogenous; the duration of treatment, frequency of application etc. is very variable. This makes drawing firm conclusions about the efficacy of topical IQ difficult. From the data we have, 30 out of 48 patients demonstrated a complete response (62.5%), 4 patients (8%) had a partial response and 14 patients (29%) no response. Treatment given less than 4 times weekly appears to give a longer duration of complete response (81% complete response), although, inevitably the treatment regime lasts longer (mean duration 113 days). This compares with a 68% complete response in those patients receiving treatment greater than 4 times weekly (mean duration 53 days) (16). Toxicity data for the use of topical IQ is reported in extra genital disease. The most common adverse effect is local skin irritation at the application site. Other adverse effects include headache, flu like symptoms and myalgia. In our experience of a small number of patients treated with topical IQ for PeIN it is well tolerated. There is no evidence to suggest that any patients have ceased treatment due to toxicity. Other treatment modalities for non-invasive penile cancer In our tertiary referral center those patients who relapse following topical chemotherapy for the treatment of their non invasive penile cancer are offered surgery. This is either in the form of partial or total glans resurfacing, this has
5 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 6, No 5 October been shown to identify 20% of patients with underlying invasion. Other treatments such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), laser ablation and Mohs micrographic surgery are also used. The disadvantage of PDT and laser ablation are the lack of histological tissue for analysis. Evidence for these treatments once again is rather heterogeneous with small study populations. Filonenko et al. treated 10 patients over a 2-year period with PDT and achieved complete response in 9 patients (17). The follow up period was short and this illustrates the difficulties in demonstrating durability of this treatment. PDT was used to treat 7 out of 10 patients successfully with a mean follow up of 35 months by Paoli s group in Sweden. Three patients recurred with PeIN but no patient developed invasive cancer (18). Reported toxicity was minor with all patients experiencing a degree of pain, although this was not quantified. In addition superficial erosions were common but reportedly healed in a matter of days (18). Comparative trials of the various treatments available for non invasive penile cancer have not been performed to date. Conclusions The management of this rare disease has only been assessed in relatively small trials and no randomized evidence exists to guide best practice. It is clear that in select cases topical chemotherapy can provide an excellent treatment response with minimal long term side effects. Future double blinded randomized trials comparing different these different topical treatment modalities for non invasive penile cancer are essential to provide a more definitive answer as to the anticipated long term outcomes with such therapeutic agents. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. References 1. Christodoulidou M, Sahdev V, Houssein S, et al. Epidemiology of penile cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 2015;39: Hartwig S, Syrjänen S, Dominiak-Felden G, et al. Estimation of the epidemiological burden of human papillomavirus-related cancers and non-malignant diseases in men in Europe: a review. BMC Cancer 2012;12: Hakenberg OW, Watkin N, Compérat E, et al. EAU Guidelines on Penile Cancer Available online: Penile-Cancer-2016-Pocket.pdf 4. Heyns CF, Mendoza-Valdés A, Pompeo AC. Diagnosis and staging of penile cancer. Urology 2010;76:S Kaul A, Corbishley CM, Watkin NA. Diagnosis and management of premalignant penile lesions. In: Culkin DJ. Editor. Management of Penile Cancer. New York: Springer Science + Business Media, 2014: Chaux A, Pfannl R, Lloveras B, et al. Distinctive association of p16ink4a overexpression with penile intraepithelial neoplasia depicting warty and/or basaloid features: a study of 141 cases evaluating a new nomenclature. Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34: Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, et al. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur Urol 2016;70: UK National Guideline on the Management of Balanoposthitis. Clinical Effectiveness Group. British Association for Sexual Health and HIV. Available online: 9. Wikström A, Hedblad MA, Johansson B, et al. The acetic acid test in evaluation of subclinical genital papillomavirus infection: a comparative study on penoscopy, histopathology, virology and scanning electron microscopy findings. Genitourin Med 1992;68: Eaglstein WH, Weinstein GD, Frost P. Fluorouracil: mechanism of action in human skin and actinic keratoses. I. Effect on DNA synthesis in vivo. Arch Dermatol 1970;101: Micali G, Lacarrubba F, Nasca MR, et al. Topical pharmacotherapy for skin cancer. J Am Academ Dermatol 2014;70: Schellhammer PF, Jordan GH, Robey EL, et al. Premalignant lesions and nonsquamous malignancy of the penis and carcinoma of the scrotum. Urol Clin North Am 1992;19: Goette DK, Carson TE. Erythroplasia of Queyrat: treatment with topical 5-fluorouracil. Cancer 1976;38: Goette DK, Elgart M, DeVillez, RL. Erythroplasia of Queyrat. Treatment with topically applied fluorouracil.
6 808 Manjunath et al. Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer JAMA 1975;232: Alnajjar HM, Lam W, Bolgeri M, et al. Treatment of Carcinoma in Situ of the Glans Penis with Topical Chemotherapy Agents. Eur Urol 2012;62: Deen K, Burdon-Jones D. Imiquimod in the treatment of penile intraepithelial neoplasia: An update. Australas J Dermatol 2017;58: Filonenko E, Kaprin A, Alekseev B, et al. Own experience in treatment of patients with penile cancer using photodynamic therapy. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015: Paoli J, Ternesten Bratel A, Löwhagen GB, et al. Penile intraepithelial neoplasia: results of photodynamic therapy. Acta Derm Venereol 2006;86: Cite this article as: Manjunath A, Brenton T, Wylie S, Corbishley CM, Watkin NA. Topical Therapy for non-invasive penile cancer (Tis) updated results and toxicity. Transl Androl Urol 2017;6(5): doi: /tau
EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2014) O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), N. Watkin, E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel Introduction and epidemiology The incidence of penile cancer increases
EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2014) O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), N. Watkin, E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel Introduction and epidemiology The incidence of penile cancer increases
EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2014) O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel, N. Watkin Guidelines Associate: R. Robinson Introduction and epidemiology
EAU GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2014) O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel, N. Watkin Guidelines Associate: R. Robinson Introduction and epidemiology
GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2010) G. Pizzocaro, F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, E. Solsona, S. Tana, H. Van Der Poel, N. Watkin 78 Penile Cancer Eur Urol 2010 Jun;57(6):1002-12 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text update April 2010) G. Pizzocaro, F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, E. Solsona, S. Tana, H. Van Der Poel, N. Watkin 78 Penile Cancer Eur Urol 2010 Jun;57(6):1002-12 Introduction
GUIDELINEs ON PENILE CANCER
 GUIDELINEs ON PENILE CANCER (update April 2010) G. Pizzocaro, F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, E. Solsona, S. Tana, H. Van Der Poel, N. Watkin Eur Urol 2010, doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.01.039 Introduction Over
GUIDELINEs ON PENILE CANCER (update April 2010) G. Pizzocaro, F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, E. Solsona, S. Tana, H. Van Der Poel, N. Watkin Eur Urol 2010, doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2010.01.039 Introduction Over
GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text updated March 2005) G. Pizzocaro (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, H. van der Poel, E. Solsona, S. Tana, N. Watkin 58 Penile Cancer Eur Urol 2004;46(1);1-8 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER (Text updated March 2005) G. Pizzocaro (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, H. van der Poel, E. Solsona, S. Tana, N. Watkin 58 Penile Cancer Eur Urol 2004;46(1);1-8 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON PENILE CANCER
 46 E. Solsona (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, G. Pizzocaro, T. Windahl Eur Urol 2002;42(3):199-203 Introduction Penile carcinoma is an uncommon malignant disease with an incidence ranging from 0.1
46 E. Solsona (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Horenblas, G. Pizzocaro, T. Windahl Eur Urol 2002;42(3):199-203 Introduction Penile carcinoma is an uncommon malignant disease with an incidence ranging from 0.1
ACCME/Disclosures. 52 year old man who consulted for a long-standing mass on the distal penis 4/13/2016
 ACCME/Disclosures United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology Seattle, WA 2016 Elsa F Velazquez, MD Director of Dermatopathology, V.P. Clinical Assistant Professor of Dermatology Tufts University,
ACCME/Disclosures United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology Seattle, WA 2016 Elsa F Velazquez, MD Director of Dermatopathology, V.P. Clinical Assistant Professor of Dermatology Tufts University,
ONCOGENIC BALANITIS. G. Tchernev 1, J. Ananiev 2, J. C. Cardoso 3, S. Philipov 4 and U. Wollina 5
 ONCOGENIC BALANITIS G. Tchernev 1, J. Ananiev 2, J. C. Cardoso 3, S. Philipov 4 and U. Wollina 5 1 Polyclinic for Dermatology and Venerology, University Hospital Lozenetz, Saint Kliment Ohridski University,
ONCOGENIC BALANITIS G. Tchernev 1, J. Ananiev 2, J. C. Cardoso 3, S. Philipov 4 and U. Wollina 5 1 Polyclinic for Dermatology and Venerology, University Hospital Lozenetz, Saint Kliment Ohridski University,
Penile cancer teams in UK. Common variants. Penile cancer teams. Basaloid squamous carcinoma. The Pathology of Penile Tumours
 The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Treatment of Carcinoma In Situ of the Glans Penis with Topical Chemotherapy Agents
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 923 928 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Penile Cancer Treatment of Carcinoma In Situ of the Glans Penis with Topical Chemotherapy
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 923 928 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Penile Cancer Treatment of Carcinoma In Situ of the Glans Penis with Topical Chemotherapy
EAU Guidelines on Penile Cancer
 EAU Guidelines on Penile Cancer O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel, N. Watkin Guidelines Associate: R. Robinson European Association of Urology 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS
EAU Guidelines on Penile Cancer O.W. Hakenberg (Chair), E. Compérat, S. Minhas, A. Necchi, C. Protzel, N. Watkin Guidelines Associate: R. Robinson European Association of Urology 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology
 Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical & Partial Cystectomy, Cystoprostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical & Partial Cystectomy, Cystoprostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva Malignant melanoma sho
 Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Carcinoma Vulva & Vagina Subdivisi Onkologi Ginekologi Bagian Obgin FK USU Vulvar Carcinoma. Definition: Cases should be classified as carsinoma of the vulva when the primary site growth is in the vulva
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology
 Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
Carcinoma of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter Histopathology Reporting Proforma (NEPHROURETERECTOMY AND URETERECTOMY) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family
MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Page 28 Oropharynx p16 positive Pathological Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3 N0,N1 M0 Stage II,T2 N2 M0 T3,T4 N0,N1 M0 Page 61 Oesophagus Adenocarcinoma Pathological
Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008
 Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008 There is a staging graph below Blood in the urine is the most common indication that something is wrong. Often one will experience pain or difficulty
Staging and Grading Last Updated Friday, 14 November 2008 There is a staging graph below Blood in the urine is the most common indication that something is wrong. Often one will experience pain or difficulty
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata
 UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
UICC TNM 8 th Edition Errata ions are in italics Head and Neck Tumours Pages 20, p27, p34, p38, p41, and p49 ly pn2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, less than 3cm in greatest dimension with
Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care?
 Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care? Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Professor and Director of Surgical Pathology The Methodist Hospital, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Houston,
Prognostic factors of genitourinary tumors: Do we have to care? Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD Professor and Director of Surgical Pathology The Methodist Hospital, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, Houston,
S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN G1.01 COMMENTS S2.01 SPECIMEN LABELLED AS G2.01 *SPECIMEN DIMENSIONS (PROSTATE) S2.03 *SEMINAL VESICLES
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions
 Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER VULVAR Last Revision Date July 2015 1 Site Group: Gynecologic Cancer Vulvar Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION
A RARE CASE OF VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN MIDDLE AGED MALE
 A RARE CASE OF VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN MIDDLE AGED MALE *Alagar Samy R. and Elankumar S. ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Penile verrucous
A RARE CASE OF VERRUCOUS CARCINOMA IN MIDDLE AGED MALE *Alagar Samy R. and Elankumar S. ESIC Medical College and Hospital, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Penile verrucous
Guidelines for Management of Penile Cancer
 Guidelines for Management of Penile Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Sections 3, 5, 6 and 16 updated. Page 1 of 10 1. Scope
Guidelines for Management of Penile Cancer Date Approved by Network Governance July 2012 Date for Review July 2015 Changes Between Versions 2 and 3 Sections 3, 5, 6 and 16 updated. Page 1 of 10 1. Scope
Uropathology January Jon Oxley
 Uropathology January 2012 Jon Oxley Background to seminar These slides were available to view via the web from scanned slides The junior pathologists answered questions on them via the web The answers
Uropathology January 2012 Jon Oxley Background to seminar These slides were available to view via the web from scanned slides The junior pathologists answered questions on them via the web The answers
Diagnosis and management of premalignant penile lesions
 Therapeutic Advances in Urology Review Diagnosis and management of premalignant penile lesions Majid Shabbir, Suks Minhas and Asif Muneer Ther Adv Urol (2011) 3(3) 151 158 DOI: 10.1177/ 1756287211412657!
Therapeutic Advances in Urology Review Diagnosis and management of premalignant penile lesions Majid Shabbir, Suks Minhas and Asif Muneer Ther Adv Urol (2011) 3(3) 151 158 DOI: 10.1177/ 1756287211412657!
Mohs surgery for the nail unit
 Mohs surgery for the nail unit olivier.cogrel@chu-bordeaux.fr Dermatologic surgery, Mohs surgery and lasers unit CHU Bordeaux, France Squamous cell carcinoma +++ Acral lentiginous melanoma Lichte et al.
Mohs surgery for the nail unit olivier.cogrel@chu-bordeaux.fr Dermatologic surgery, Mohs surgery and lasers unit CHU Bordeaux, France Squamous cell carcinoma +++ Acral lentiginous melanoma Lichte et al.
Proposal for a 2-stage RCT in high risk primary SCC: COMMISSAR Catherine Harwood Barts Health NHS Trust / QMUL
 Proposal for a 2-stage RCT in high risk primary SCC: COMMISSAR Catherine Harwood Barts Health NHS Trust / QMUL on behalf of Dr Louise Lansbury, Prof Fiona Bath-Hextall Nottingham Centre for Evidence Based
Proposal for a 2-stage RCT in high risk primary SCC: COMMISSAR Catherine Harwood Barts Health NHS Trust / QMUL on behalf of Dr Louise Lansbury, Prof Fiona Bath-Hextall Nottingham Centre for Evidence Based
PENILE CANCER. Date Developed: January, Date Revised: February, 2012
 PENILE CANCER Date Developed: January, 2011 Date Revised: February, 2012 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial Genitourinary Tumour Team synthesis of
PENILE CANCER Date Developed: January, 2011 Date Revised: February, 2012 The recommendations contained in this guideline are a consensus of the Alberta Provincial Genitourinary Tumour Team synthesis of
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
Skin Cancer. 5 Warning Signs. American Osteopathic College of Occupational and Preventive Medicine OMED 2012, San Diego, Monday, October 8, 2012 C-1
 Skin Cancer AMERICAN OSTEOPATHIC COLLEGE OF OCCUPATIONAL & PREVENTIVE MEDICINE OMED 2012 October 8, 2012 E. Robert Wanat II, D.O., M.P.H. Learning Objectives: Identify the 3 Basic Types of Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer AMERICAN OSTEOPATHIC COLLEGE OF OCCUPATIONAL & PREVENTIVE MEDICINE OMED 2012 October 8, 2012 E. Robert Wanat II, D.O., M.P.H. Learning Objectives: Identify the 3 Basic Types of Skin Cancer
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGICAL PATHOLOGISTS USCAP COMPANION MEETING PROGRAM WASHINGTON D.C. New Concepts and Entities in Penile Cancer Pathology
 INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGICAL PATHOLOGISTS USCAP COMPANION MEETING PROGRAM WASHINGTON D.C. New Concepts and Entities in Penile Cancer Pathology Elsa F. Velazquez, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGICAL PATHOLOGISTS USCAP COMPANION MEETING PROGRAM WASHINGTON D.C. New Concepts and Entities in Penile Cancer Pathology Elsa F. Velazquez, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital
HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area
 HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area Theo Panoskaltsis MD, FRCOG, CCST (UK) Epidemiology Anal cancer is increasing in both men and women Groups at risk: - HIV (+)
HPV-related papillomatous-condylomatous lesions in female anogenital area Theo Panoskaltsis MD, FRCOG, CCST (UK) Epidemiology Anal cancer is increasing in both men and women Groups at risk: - HIV (+)
Handling and Pathology Reporting of Circumcision and Penectomy Specimens $
 European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 434 439 Review Handling and Pathology Reporting of Circumcision and Penectomy Specimens $ Gregor Mikuz a,*, Alison M. Winstanley b, Claude C. Schulman c, Frans
European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 434 439 Review Handling and Pathology Reporting of Circumcision and Penectomy Specimens $ Gregor Mikuz a,*, Alison M. Winstanley b, Claude C. Schulman c, Frans
Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM
 Dilemmas and Challenges in Skin Cancer Therapies and Management Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM Roger I. Ceilley, M.D. Clinical Professor of Dermatology The University of Iowa
Dilemmas and Challenges in Skin Cancer Therapies and Management Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM Roger I. Ceilley, M.D. Clinical Professor of Dermatology The University of Iowa
A schematic of the rectal probe in contact with the prostate is show in this diagram.
 Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
The pathology of bladder cancer
 1 The pathology of bladder cancer Charles Jameson Introduction Carcinoma of the bladder is the seventh most common cancer worldwide [1]. It comprises 3.2% of all cancers, with an estimated 260 000 new
1 The pathology of bladder cancer Charles Jameson Introduction Carcinoma of the bladder is the seventh most common cancer worldwide [1]. It comprises 3.2% of all cancers, with an estimated 260 000 new
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy
 Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Greater Manchester & Cheshire Guidelines for Pathology Reporting for Oesophageal and Gastric Malignancy Authors: Dr Gordon Armstrong, Dr Sue Pritchard 1. General Comments 1.1 Cancer reporting: Biopsies
Testicular Malignancies /8/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
GUIDELINES ON PROSTATE CANCER
 10 G. Aus (chairman), C. Abbou, M. Bolla, A. Heidenreich, H-P. Schmid, H. van Poppel, J. Wolff, F. Zattoni Eur Urol 2001;40:97-101 Introduction Cancer of the prostate is now recognized as one of the principal
10 G. Aus (chairman), C. Abbou, M. Bolla, A. Heidenreich, H-P. Schmid, H. van Poppel, J. Wolff, F. Zattoni Eur Urol 2001;40:97-101 Introduction Cancer of the prostate is now recognized as one of the principal
25 TH ICRO DEHRADUN STAGING OF GENITOURINARY MALIGNANCIES
 25 TH ICRO DEHRADUN STAGING OF GENITOURINARY MALIGNANCIES SPEAKER DR DEEPAK ABROL CLINICAL ONCOLOGIST JAND K HEALTH SERVICES CONSULTANT ONCOLOGIST MAHARISHI DAYANAND HOSPITAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH CENTER
25 TH ICRO DEHRADUN STAGING OF GENITOURINARY MALIGNANCIES SPEAKER DR DEEPAK ABROL CLINICAL ONCOLOGIST JAND K HEALTH SERVICES CONSULTANT ONCOLOGIST MAHARISHI DAYANAND HOSPITAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH CENTER
CPC on Cervical Pathology
 CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
S1.04 Principal clinician. G1.01 Comments. G2.01 *Specimen dimensions (prostate) S2.02 *Seminal vesicles
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Diseases of the penis & testis
 Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two
 Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
Faculty Pap Smear Guidelines: Family Planning Update 2008 Part Two Seshu P. Sarma, MD, FAAP Emory University Regional Training Center Atlanta, Georgia Produced by the Alabama Department of Public Health
Carcinoma of the penis. Report of three cases and review of literature.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 20 Number 2 Carcinoma of the penis. Report of three cases and review of literature. V Yagnik Citation V Yagnik. Carcinoma of the penis. Report of three
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 20 Number 2 Carcinoma of the penis. Report of three cases and review of literature. V Yagnik Citation V Yagnik. Carcinoma of the penis. Report of three
CURRENT ISSUES IN TRANSPLANT DERMATOLOGY
 CURRENT ISSUES IN TRANSPLANT DERMATOLOGY NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST TO DISCLOSE SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION: 2015 As of April 10, 2015.. 123,319 patients waiting for an organ transplant 2,557 performed this
CURRENT ISSUES IN TRANSPLANT DERMATOLOGY NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST TO DISCLOSE SOLID ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION: 2015 As of April 10, 2015.. 123,319 patients waiting for an organ transplant 2,557 performed this
The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
 30 th Congress of the European Society of Pathology Tuesday, September 11, 2018 The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
30 th Congress of the European Society of Pathology Tuesday, September 11, 2018 The Depth of Tumor Invasion is Superior to 8 th AJCC/UICC Staging System to Predict Patients Outcome in Radical Cystectomy.
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour
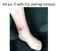 64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
A Retrospective Study of Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In situ. Övermark, Meri.
 https://helda.helsinki.fi A Retrospective Study of Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In situ Övermark, Meri 2016 Övermark, M, Koskenmies, S & Pitkanen, S 2016, ' A Retrospective Study of Treatment of
https://helda.helsinki.fi A Retrospective Study of Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma In situ Övermark, Meri 2016 Övermark, M, Koskenmies, S & Pitkanen, S 2016, ' A Retrospective Study of Treatment of
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee
 I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
Genital lichen sclerosus/balanitis xerotica obliterans in men with penile carcinoma: a critical analysis
 Genital lichen sclerosus/balanitis xerotica obliterans in men with penile carcinoma: a critical analysis Prodromos Philippou, Majid Shabbir, David J. Ralph, Peter Malone, Raj Nigam, Alex Freeman*, Asif
Genital lichen sclerosus/balanitis xerotica obliterans in men with penile carcinoma: a critical analysis Prodromos Philippou, Majid Shabbir, David J. Ralph, Peter Malone, Raj Nigam, Alex Freeman*, Asif
JAM ACAD DERMATOL VOLUME 76, NUMBER 2. Research Letters 351
 JAM ACAD DERMATOL Research Letters 351 Standard step sectioning of skin biopsy specimens diagnosed as superficial basal cell carcinoma frequently yields deeper and more aggressive subtypes To the Editor:
JAM ACAD DERMATOL Research Letters 351 Standard step sectioning of skin biopsy specimens diagnosed as superficial basal cell carcinoma frequently yields deeper and more aggressive subtypes To the Editor:
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging
 Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CARCINOMA B. Ljungberg (chairman), D.C. Hanbury, M.A. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, P.F.A. Mulders, J-J. Patard, I.C. Sinescu Introduction This EAU guideline was prepared to help urologists
Clinical Pathological Conference. Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva
 Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Clinical Pathological Conference Malignant Melanoma of the Vulva History F/48 Chinese Married Para 1 Presented in September 2004 Vulval mass for 2 months Associated with watery and blood stained discharge
Guideline for the Management of Vulval Cancer
 Version History Guideline for the Management of Vulval Cancer Version Date Brief Summary of Change Issued 2.0 20.02.08 Endorsed by the Governance Committee 2.1 19.11.10 Circulated at NSSG meeting 2.2 13.04.11
Version History Guideline for the Management of Vulval Cancer Version Date Brief Summary of Change Issued 2.0 20.02.08 Endorsed by the Governance Committee 2.1 19.11.10 Circulated at NSSG meeting 2.2 13.04.11
Clinical characteristics
 Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 742 747 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Penile Cancer Prognostic Factors for Occult Inguinal Lymph Node Involvement in Penile Carcinoma
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 742 747 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Penile Cancer Prognostic Factors for Occult Inguinal Lymph Node Involvement in Penile Carcinoma
Subject Index. Dry desquamation, see Skin reactions, radiotherapy
 Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Penis
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Penis Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual For accreditation
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Penis Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual For accreditation
Major Rule Changes. Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging
 AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Major Rule Changes Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving patient
AJCC 8 th Edition Staging Major Rule Changes Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Technical Editor, AJCC Cancer Staging Manual First Author, Chapter 1: Principles of Cancer Staging Validating science. Improving patient
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Diagnosis and classification
 Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But...
 european urology 50 (2006) 1129 1138 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial 50th Anniversary Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But... Urs E. Studer
european urology 50 (2006) 1129 1138 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial 50th Anniversary Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But... Urs E. Studer
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
This form may provide more data elements than required for collection by standard setters such as NCI SEER, CDC NPCR, and CoC NCDB.
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Case Report Warty Carcinoma Penis: An Uncommon Variant
 Hindawi Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2017, Article ID 2937592, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2937592 Case Report Warty Carcinoma Penis: An Uncommon Variant Sushma Thapa, 1 Arnab Ghosh, 1 Santosh
Hindawi Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2017, Article ID 2937592, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2937592 Case Report Warty Carcinoma Penis: An Uncommon Variant Sushma Thapa, 1 Arnab Ghosh, 1 Santosh
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD J M O R G A N
 VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
VIN/VAIN O C T O B E R 3 RD 2 0 1 8 J M O R G A N Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia VAIN I, II, III Incidence 0.1/100,000 women in US Mean age 50s (J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2009:18:1731) (J Obstet Gynaecol
BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BLADDER CANCER WHAT IS NEW AND CLINICALLY RELEVANT Canadian Geese - Geist Reservoir (my backyard), Indianapolis, USA BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY Urinary bladder 17,960 2% Urinary bladder 4,390 1.6% Siegel
BLADDER CANCER WHAT IS NEW AND CLINICALLY RELEVANT Canadian Geese - Geist Reservoir (my backyard), Indianapolis, USA BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY Urinary bladder 17,960 2% Urinary bladder 4,390 1.6% Siegel
Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer COPYRIGHT. Marissa Heller, M.D.
 Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer Marissa Heller, M.D. Associate Director of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center December 10, 2016 Skin Cancer Non-melanoma
Cutaneous Malignancies: A Primer Marissa Heller, M.D. Associate Director of Dermatologic Surgery Department of Dermatology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center December 10, 2016 Skin Cancer Non-melanoma
Urinary Bladder, Ureter, and Renal Pelvis
 Urinary Bladder, Ureter, and Renal Pelvis Protocol applies to all carcinomas of the urinary bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6th edition Procedures
Urinary Bladder, Ureter, and Renal Pelvis Protocol applies to all carcinomas of the urinary bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6th edition Procedures
Understanding Your Pathology Report
 Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma
 Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Vulva Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma Mandatory questions (i.e. protocol standards) are in bold (e.g. S1.01). S1.01 Identification Family name Given name(s) Ethnicity Unknown AboriginalTorres
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Pathology Reporting Proforma DD MM YYYY. *Tumour site. *Specimen laterality. *Specimen type
 Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Pathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY Sex Male Female
Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Pathology Reporting Proforma Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth DD MM YYYY Sex Male Female
Case Report Pannus Is the New Prepuce? Penile Cancer in a Buried Phallus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 403545, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/403545 Case Report Pannus Is the New Prepuce? Penile Cancer in a Buried Phallus Jared Manwaring, 1 Srinivas
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2015, Article ID 403545, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/403545 Case Report Pannus Is the New Prepuce? Penile Cancer in a Buried Phallus Jared Manwaring, 1 Srinivas
Squamous carcinoma of the penis: a case report
 Squamous carcinoma of the penis: a case report De Fiores A., Diosi D., Bella G., De Marco V. Introdution Penile cancer is a relatively rare neoplasm in the developed world and 95% of the cases histologically
Squamous carcinoma of the penis: a case report De Fiores A., Diosi D., Bella G., De Marco V. Introdution Penile cancer is a relatively rare neoplasm in the developed world and 95% of the cases histologically
Cervical cancer presentation
 Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Uterine Cervix. Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix.
 Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
This form may provide more data elements than required for collection by standard setters such as NCI SEER, CDC NPCR, and CoC NCDB.
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Thyroid INTRODUCTION ANATOMY SUMMARY OF CHANGES
 AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
CODING STAGE: TNM AND OTHER STAGING SYSTEMS. Liesbet Van Eycken Otto Visser
 CODING STAGE: TNM AND OTHER STAGING SYSTEMS Liesbet Van Eycken Otto Visser OVERVIEW PART I Introduction What is stage? Why stage? History and publications of TNM Classification Clinical and pathologic
CODING STAGE: TNM AND OTHER STAGING SYSTEMS Liesbet Van Eycken Otto Visser OVERVIEW PART I Introduction What is stage? Why stage? History and publications of TNM Classification Clinical and pathologic
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
 THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by A Kennedy/AG Macdonald/Others Approved by NOT APPROVED Issue date April
THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by A Kennedy/AG Macdonald/Others Approved by NOT APPROVED Issue date April
Periocular Malignancies
 Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Enrollment Form: Pancreas
 Tissue Source Site (TSS) Name: TSS Identifier: _ TSS Unique Patient #: Completed By: Completion Date (MM/DD/YYYY): Form Notes: An Enrollment Form should be completed for each TCGA qualified case upon qualification
Tissue Source Site (TSS) Name: TSS Identifier: _ TSS Unique Patient #: Completed By: Completion Date (MM/DD/YYYY): Form Notes: An Enrollment Form should be completed for each TCGA qualified case upon qualification
Case Scenario 1 Worksheet. Primary Site C44.4 Morphology 8743/3 Laterality 0 Stage/ Prognostic Factors
 CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
CASE SCENARIO 1 9/10/13 HISTORY: Patient is a 67-year-old white male and presents with lesion located 4-5cm above his right ear. The lesion has been present for years. No lymphadenopathy. 9/10/13 anterior
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Carcinoma of the Penis
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Carcinoma of the Penis Protocol applies to primary carcinoma of the penis. Primary urethral carcinomas and melanomas are not included. Version:
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens from Patients with Carcinoma of the Penis Protocol applies to primary carcinoma of the penis. Primary urethral carcinomas and melanomas are not included. Version:
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
