Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
|
|
|
- Norma Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods Table S1. Primers used for PTEN amplification and sequencing Exon Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1 AGTCGCTGCAACCATCCA TCTAAGAGAGTGACAGAAAGGTA 2 TGACCACCTTTTATTACTCCA TAGTATCTTTTTCTGTGGCTTA 3 ATAGAAGGGGTATTTGTTGGA TCCTCACTCTAACAAGCAGATA 4 TTCAGGCAATGTTTGTTA TTCGATAATCTGGATGACTCA 5 ACCTGTTAAGTTTGTATGCAAC TCCAGGAAGAGGAAAGGAAA 6 CATAGCAATTTAGTGAAATAACT GATATGGTTAAGAAAACTGTTC 7 TGACAGTTTGACAGTTAAAGG GGATATTTCTCCCAATGAAAG 8 CTCAGATTGCCTTATAATAGTC TCATGTTACTGCTACGTAAAC 9 AAGGCCTCTTAAAAGATCATG TTTTCATGGTGTTTTATCCCTC Forward and reverse primers used for PCR amplification and sequencing of each indicated PTEN exon. One additional primer for sequence analysis of the reverse strand of exon 8 was also synthesized: AACTTGTCAAGCAAGTTCTTC.
2 Figure S1. Akt levels are similar in primary T-ALL samples with or without activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and in normal thymocytes. (A) Primary T-ALL cells and thymocytes were analyzed for Akt expression by immunoblot. Patient samples indicated in red (T-ALL#07 and T-ALL#08) display low levels of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation, comparable to those of normal thymocytes (Figure 5E and Table 1), whereas samples in black (T-ALL#01 and T-ALL#04) show PI3K/Akt pathway hyperactivation (Figure 1A). Figure S2. Hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt pathway in T-ALL cell lines. Cell lysates of normal human thymocytes or PTEN-positive (TAIL7, HPB-ALL) and PTENnegative (MOLT4, Jurkat) T-ALL cell lines were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
3 Figure S3. Isolated normal T-cell precursor subpopulations display lower levels of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation than their malignant immunophenotypical equivalents. (A) Simplified scheme of normal T-cell development in humans and total number and percentage of primary T-ALL cases analyzed with corresponding immunophenotype. The most common T-ALL phenotypes are indicated in bold (TP and SP8). (B) Normal thymocytes were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8, and CD3+CD4+CD8+ (TP), and CD3+CD4-CD8+ (SP8) subpopulations were isolated by FACS (TP: >83%; SP8: >96% purity) and immediately lysed for immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated Akt and GSK3!. Primary T-ALL samples with equivalent immunophenotype were subjected to the same procedure.
4 Figure S4. Major normal T-cell precursor subpopulations exhibit similar PIP3 levels that are lower than those of primary T-ALL cells. (A) Normal thymocytes were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8 and subsequently assessed for PIP3 levels using an anti-pip3-specific antibody by flow cytometry analysis within the gated subpopulations: TN, CD3-CD4-CD8-; ISP, CD3-CD4+CD8-; DP, CD3-CD4+CD8+; TP, CD3+CD4+CD8+; SP4, CD3+CD4+CD8-; SP8, CD3+CD4-CD8+. One representative thymus out of six analyzed is shown. Values indicate PIP3 mean intensity of fluorescence for each subpopulation. (B) Four primary T-ALL samples were subjected to the same procedure and analyzed at the same time. T-ALL were ISP (n=2), TP (n=1) and SP8 (n=1). Columns indicate average PIP3 MIF ± sem for each thymic subpopulation (n=5) and T-ALL cells (n=4). One-way ANOVA statistical analysis with Bonferroni s correction showed that none of the thymic subpopulations differed from each other (P>0.05 for all comparisons), but each and every normal thymic subset was significantly different from the T-ALL group (P<0.001 for DN, ISP or SP8 vs T-ALL; P<0.01 for DP, TP or SP4 vs T-ALL).
5 Figure S5. Normal T-cell precursor subpopulations express similar PTEN protein levels. (A,B) Flow cytometry analysis of PTEN expression was initially calibrated using two T-ALL cell lines whose PTEN expression levels were already known: Jurkat (A) are PTEN-null, whereas TAIL7 (B) display PTEN levels similar to most primary T-
6 ALL cells (panel E in this figure, Figure 2A, and data not shown). Values indicate PTEN mean intensity of fluorescence (MIF). (C) Normal thymocytes were stained for CD4 and CD8 and the four major thymic T-cell precursor subpopulations evaluated for PTEN protein expression by flow cytometry analysis. PTEN expression within gated CD4-CD8- (DN), CD4+CD8+ (DP), CD4+CD8- (SP4) and CD4-CD8+ (SP8) subpopulations is indicated by different histogram colors. Corresponding negative controls (secondary antibody only) are denoted by the same colors (lighter histograms). Values indicate PTEN MIF within each subpopulation. One representative thymus (THY#24) is shown out of three analyzed. (D) PTEN expression within each subpopulation was analyzed in three different thymic samples. Differences are not statistically significant (P=0.57; One-way ANOVA). TAIL7 and Jurkat PTEN levels are represented as references. (E) To ensure that TAIL7 cells are representative of PTENpositive primary T-ALL samples, PTEN expression was evaluated by densitometry analysis after immunoblotting in T-ALL primary cells and cell lines, including TAIL7. Black columns: PTEN-negative T-ALL cells; Red columns: PTEN-positive T-ALL cells. (F) A second thymic sample (THY#26) is depicted to further illustrate that each thymic subpopulation has higher PTEN levels than PTEN-null Jurkat T-ALL cells and lower levels than PTEN-positive TAIL7 T-ALL cells. Values indicate PTEN MIF in each thymocyte subpopulation. Jurkat and TAIL7 histograms are the same as in panels A and B, respectively, and are overlaid with each thymocyte subpopulation to simplify visual comparison. (G) Immunoblot analysis of PTEN expression in CD3+CD4+CD8+ TP and CD3+CD4-CD8+ SP8 T-ALL cells and sorted thymocytes. Actin was used as a loading control.
7 Figure S6. T-ALL cells displaying high levels of phosphorylated PTEN have increased phospho-pten / total PTEN ratio as compared to normal thymocytes. Levels of phosphorylated PTEN (S380) and total PTEN were assessed by immunoblot and quantified by densitometry analysis in normal thymocytes (n=8), T-ALL primary cells displaying high phospho-pten (P-PTEN+, n=10) and T-ALL primary cells displaying normal levels of phospho-pten (P-PTEN-, n=2). Columns and error bars indicate the mean ± sem ratio of phosphorylated PTEN over total PTEN (P-PTEN / PTEN). One-way ANOVA statistical analysis with Bonferroni s correction showed that P-PTEN+ T-ALL cells presented P-PTEN/PTEN ratios that were significantly higher than those of normal thymocytes (P<0.001) or P-PTEN- T-ALL cells (P<0.05). In contrast, P-PTEN/PTEN ratios did not differ significantly in normal thymocytes versus P-PTEN- T-ALL cells (P>0.05).
8 Figure S7. Isolated normal T-cell precursor subpopulations express lower CK2 protein levels than their malignant immunophenotypical equivalents. Normal thymocytes were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8, and CD3+CD4+CD8+ (TP), and CD3+CD4-CD8+ (SP8) subpopulations were isolated by FACS (TP: 83%; SP8: 97% purity) and immediately lysed for immunoblot analysis of CK2". Primary T-ALL samples with equivalent immunophenotype were subjected to the same procedure. Figure S8. Downregulation of Akt phosphorylation upon CK2 inhibition using TBB is largely dependent on PTEN expression. PTEN-negative T-ALL Jurkat cells stably transfected with either PTEN or the empty vector containing a tetracycline response element were cultured with or without doxycycline for 24h and subsequently incubated for 2h30 in the presence or absence of 25#M TBB. Cells were then lysed and assessed for phospho-akt, phospho-pten and PTEN by immunoblot.
9 Figure S9. PTEN phosphorylation correlates with CK2 expression in PTENpositive primary T-ALL cells. (A) Expression of CK2" and phosphorylated PTEN (S380) was analyzed by immunoblot in two T-ALL cases with high phospho-pten levels (T-ALL#12 and #26) and one with phospho-pten levels similar to normal thymocytes (T-ALL#05). The two primary T-ALL cases with high phospho-pten levels overexpressed CK2, whereas T-ALL#05 displayed CK2 levels that are similar to normal controls. Blots concerning T-ALL#26 are from the same analysis presented in Figure S7. (B) Immunoblot analysis of CK2" and phospho-pten (S380) in T-ALL was quantified by densitometry, normalized to actin loading control and expressed as foldincrease in expression as compared to normal control thymocytes. T-ALLs# 04, 10, 12, 19 and 26 presented fold increases ranging from 1.79 to 3.09 (CK2") and from 2.92 to 6.06 (P-PTEN); whereas T-ALL#05 showed similar levels to normal thymocytes (<1.5 fold increase): 1.28 (CK2") and from 1.38 (P-PTEN).
10 Figure S10. Normal T-cell precursor subpopulations exhibit lower ROS levels than primary T-ALL cells with equivalent immunophenotype. Normal thymocytes were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8 and subsequently assessed for ROS levels with DCF- DA by flow cytometry analysis within gated (A) CD3+CD4+CD8+ (TP), (B) CD3+CD4-CD8+ (SP8), (C) CD3-negative, or (D) CD3-positive subpopulations. Primary T-ALL cells with the equivalent immunophenotypes were subjected to the same procedure and analyzed at the same time. Columns indicate average DCF-DA MIF ± sem for each thymic subpopulation and corresponding T-ALL cells.
11 Figure S11. Analysis of modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling by ROS manipulation in additional primary T-ALL samples. PTEN-positive primary T-ALL cells were treated for 2h with 0.5 mm!-me (A) or 30 min. with 1 mm H 2 O 2 (B) and levels of phospho- Akt were determined by immunoblot. Figure S12. Combination of low doses of the CK2 inhibitor TBB and the antioxidant NAC cooperate in inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway activation. TAIL7 cells were treated for 2h30min with 12.5#M TBB, 4mM NAC, or a combination of the two (T+N), and analyzed by immunoblotting. Figure S13. ROS scavenging using!-me does not significantly affect CK2 levels in T-ALL cells. T-ALL cell lines TAIL7 and HPB-ALL were treated with 1mM b-me for 24h. Expression of CK2" and CK2! was evaluated by immunoblot.
12 Figure S14. Isolated normal T-cell precursor subpopulations are not sensitive to PI3K pharmacological inhibition, in contrast to their malignant immunophenotypical equivalents. Normal thymocytes were stained for CD3, CD4 and CD8, and (A,B) CD3+CD4+CD8+ (TP), (C,D) CD3+CD4-CD8+ (SP8) subpopulations were isolated by FACS (TP: >83%; SP8: >90% purity) and cultured for
13 24h in medium alone or with 25#M LY (LY). Primary T-ALL samples with the corresponding immunophenotype were cultured under the same conditions. (A,C) Mean (± sem) viability index to control untreated cells. (B,D) Representative AnnexinV / PI dot plots. Values indicate percent live cells. Similar results were obtained after 48h of culture and also using 10#M LY (not shown). (E,F) Normal CD3- and CD3+ thymocytes were isolated by FACS (both populations: >98% purity) and cultured for 24h in medium alone or with 25#M LY Primary CD3-negative and CD3- positive T-ALL samples (immature and mature T-ALL specimens, respectively, according to the classification by Uckun et al. see Table 1) were cultured under the same conditions. Mean (± sem) viability index of CD3-negative (E) and CD3-positive (F) LY-treated to control untreated cells is indicated.
14 Figure S15. Inhibition of PI3K induces cell death of both PTEN-negative and PTEN-positive T-ALL cell lines. T-ALL cell lines were cultured for 48h (TAIL7; PTEN-positive) or 24h (MOLT4, CEM; PTEN-negative) in the presence or absence of LY (50#M) and percent viability was determined by flow cytometry analysis. Columns and error bars indicate mean ± sem of triplicates. Figure S16. Effect of CK2 inhibition or ROS scavenging on viability of T-ALL cells is largely dependent on PTEN expression. PTEN-negative T-ALL Jurkat cells stably transfected with a vector containing a tetracycline response element driving the expression of PTEN were cultured with (PTEN +) or without (PTEN -) doxycycline for 24h and subsequently cultured in medium or with 40#M TBB, 25#M DRB or 0.1mM!- ME for 48h. Empty vector Tet-on T-ALL Jurkat cells responded to TBB, DRB and ROS similarly to PTEN cells and independently of being treated with or without doxycycline (not shown).
15 Figure S17. Cooperative effects of combinatorial treatment of HPB-ALL cells with pharmacological antagonists of PI3K, CK2 and ROS. (A,B) Inhibition of CK2 and ROS scavenging cooperate in inducing T-ALL cell death. HPB-ALL cells were cultured with the indicated concentrations of TBB and!-me (A), TBB and NAC (B) or their combination and viability was assessed at 24h. (C-F) Inhibition of PI3K signaling cooperates with inhibition of CK2 and ROS scavenging in inducing T-ALL cell death. HPB-ALL cells were cultured with the indicated concentrations of LY (LY) and TBB (C), LY and DRB (D), LY and!-me (E), LY and NAC (F) or their combination and viability was assessed at 24h. Percent viability relative to untreated control (vehicle alone) is indicated for each condition (average ± sem of duplicates).
16 Figure S18. Cooperative effects of combinatorial treatment of primary T-ALL cells with pharmacological antagonists of PI3K, CK2 and ROS. (A,B) Inhibition of CK2 and ROS scavenging cooperate in inducing T-ALL cell death. Primary leukemia cells were cultured with the indicated concentrations of TBB and!-me (A), TBB and NAC (B) or their combination and viability was assessed at 48h. (C-F) Inhibition of PI3K signaling cooperates with inhibition of CK2 and ROS scavenging in inducing T-ALL cell death. Primary leukemia cells were cultured with the indicated concentrations of LY (LY) and TBB (C), LY and NAC (D) or their combination and viability was assessed at 48h. Percent viability relative to untreated control (vehicle alone) is indicated for each condition. Representative results out of six patients analyzed are shown. (E) Summary of results from all patients evaluated. Frequency refers to the percentage of primary samples for which cooperative effects were observed. Median and Range refer to the 'fold increase' in inhibitory effect of combination in relation the most effective single agent.
17 Figure S19. PI3K inhibition does not affect ROS levels in T-ALL cells. T-ALL cell lines TAIL7 (A) and HPB-ALL (B), and three different primary T-ALL patient samples (C) were treated with 25#M LY (LY) for the indicated time points and intracellular H 2 O 2 levels were analyzed by flow cytometry using the ROS-sensitive dye DCF-DA. (D) A proportion of HPB-ALL cells from the same experimental setting were lysed and phosphorylation of Akt (P-Akt) was determined by immunoblot to confirm that LY was effectively inhibiting PI3K. Cells lines were also treated with 50#M LY with similar results (not shown).
18 Figure S20. Percentage of PTEN-expressing PI3K/Akt pathway- hyperactivated primary T-ALL cases concomitantly overexpressing CK2/P-PTEN and/or ROS. (A) Percentage of T-ALL specimens with PI3K/Akt pathway hyperactivation was calculated from a total of 24 cases. Percentage of PTEN-positive T-ALL cases was calculated within those that were classified as displaying PI3K/Akt pathway hyperactivation (n=21). In turn, percentage of cases with overexpression of CK2/P- PTEN and/or ROS was calculated within those that expressed PTEN (n=16). (B) Detailed distribution of overexpression of CK2/P-PTEN and/or ROS within PTENexpressing PI3K/Akt pathway- hyperactivated primary T-ALL cases. + denotes high levels; - denotes normal levels; n.d. not determined. Approximate percentages are indicated.
19 Figure S21. Summary of conclusions. (A) A minority of primary T-ALL cells lack PTEN protein expression as a consequence of PTEN gene alterations, whereas most specimens actually show increased PTEN expression that associates with PTEN phosphorylation and inactivation. Oxidation further promotes functional downregulation of PTEN activity. PTEN inactivation in leukemia cells contributes to constitutive hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. (B) In contrast to their normal counterparts, T-ALL cells are clearly sensitive to inhibition of PI3K, upstream regulators and downstream effectors. Hence, specific small molecule inhibitors of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway may be valuable therapeutic tools for T-cell leukemia.
20 Supplemental Materials and Methods Fluorescence-activated cell Sorting of thymic subpopulations. Normal thymocytes (10 8 cells) were surface stained with anti-cd3 APC-Alexa Fluor 750 (Ebioscience), anti-cd4 PE (Pharmingen), and anti-cd8 FITC (Pharmingen) conjugated antibodies at a 1:50 dilution. Cells were washed in PBS and CD8 + CD3 + (SP8), CD8 + CD4 + CD3 + (TP), CD3 + and CD3 - thymocyte subpopulations were isolated using a FACSAria cell sorter (Becton-Dickinson). Sorted populations with purities ranging from 83% to 99% were immediately lysed or used for culture experiments. PTEN intracellular staining. Cells were fixed in 1% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized in 0.05% saponin and incubated 30 minutes at 4 C with a mouse anti-pten monoclonal antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnolgy) at 1:100 dilution. Primary antibody was detected with Alexa488-conjugated donkey anti-mouse antibody (Molecular Probes). Thymocyte samples were surface stained with anti-cd4pe and anti-cd8 APC (Ebioscience) conjugated antibodies. Samples were analyzed by flow cytometry to quantify mean fluorescence intensity using FACSCanto flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson) and FlowJo (Tree Star) software. PIP3 levels in surface-stained cells. Cells were washed in PBS and fixed in 1% paraformaldehyde, blocked with 10% normal goat serum in PBS, and incubated overnight at 4 C with mouse anti-pip3 monoclonal antibody (Echelon) at 1:10 dilution. Primary antibody was detected with Alexa488-conjugated donkey anti-mouse antibody (Molecular Probes). Samples were washed and surface stained with anti-cd3 APC- Alexa Fluor 750, anti-cd4pe and anti-cd8 APC antibodies. Samples were acquired on a FACSCanto flow cytometer and analyzed with FlowJo software. Intracellular ROS levels in surface-stained cells. Cells were stained with DCF-DA as described previously, washed and surface stained with anti-cd3 APC-Alexa Fluor 750, anti-cd4 PE-Cy7 (Ebioscience), and anti-cd8 APC antibodies. Samples were acquired on a FACSCanto flow cytometer and analyzed with FlowJo software.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis
 Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
Muse Assays for Cell Analysis Multiple Assay Outputs for Cell Analysis Cell Health Cell Signalling Immunology Muse Count & Viability Kit Muse Cell Cycle Kit Muse Annexin V & Dead Cell Kit Muse Caspase
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell. Tumor type
 Fig S1 A B Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell Tumor type -/- (n = 46) Q/- (n = 76) Q/Q (n = 31) Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
Fig S1 A B Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 All T-lymph B-lymph Sarcomas Carcinomas Germ cell Tumor type -/- (n = 46) Q/- (n = 76) Q/Q (n = 31) Tumors per mouse 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Escaper p38a-expressing cancer cells repopulate the tumors (A) Scheme of the mt/mg reporter that expresses a
 Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Targeting p38a Increases DNA Damage, Chromosome Instability, and the Anti-tumoral Response to Taxanes in Breast Cancer Cells Begoña Cánovas, Ana Igea, Alessandro
Cancer Cell, Volume 33 Supplemental Information Targeting p38a Increases DNA Damage, Chromosome Instability, and the Anti-tumoral Response to Taxanes in Breast Cancer Cells Begoña Cánovas, Ana Igea, Alessandro
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice
 Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
x Lymphocyte count /µl CD8+ count/µl 800 Calculated
 % Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
% Lymphocyte in CBC A. 50 40 30 20 10 Lymphocyte count /µl B. x10 3 2.5 1.5 C. 50 D. 1000 % CD3+CD8+ Cells 40 30 20 Calculated CD8+ count/µl 800 600 400 200 10 0 #61 #63 #64 #65 #68 #71 #72 #75 Figure
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma
 Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
Supplementary information for: Pharmacologic inhibition of histone demethylation as a therapy for pediatric brainstem glioma Rintaro Hashizume 1, Noemi Andor 2, Yuichiro Ihara 2, Robin Lerner 2, Haiyun
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry Detection of Cytokines, Transcription Factors, and Phosphoprotein by Flow Cytometry Presented by Erika O Donnell, PhD, BD Biosciences 23-14876-00 Outline Basic principles
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
BD Flow Cytometry Reagents Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-20 Cell Analyzer
 Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-2 Cell Analyzer Proper multicolor panel design takes into account fluorochrome brightness, antigen density, co-expression, and
Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-2 Cell Analyzer Proper multicolor panel design takes into account fluorochrome brightness, antigen density, co-expression, and
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible. T H 17 cells
 Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
Akt and mtor pathways differentially regulate the development of natural and inducible T H 17 cells Jiyeon S Kim, Tammarah Sklarz, Lauren Banks, Mercy Gohil, Adam T Waickman, Nicolas Skuli, Bryan L Krock,
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/114/ra23/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Zap70 Expression During Thymocyte Development Enables Temporal Separation of CD4 and CD8 Repertoire Selection
Supplementary Fig. 1 No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells.
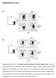 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Supplemental information
 Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: (A) (B)
 SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12
 1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
Activity of the clinical-stage CK2-specific inhibitor CX against chronic lymphocytic leukemia
 Activity of the clinical-stage CK2-specific inhibitor CX-4945 against chronic lymphocytic leukemia Leila R. Martins, Paulo Lúcio, Alice Melão, Inês Antunes, Bruno A. Cardoso, Ryan Stansfield, Maria Teresa
Activity of the clinical-stage CK2-specific inhibitor CX-4945 against chronic lymphocytic leukemia Leila R. Martins, Paulo Lúcio, Alice Melão, Inês Antunes, Bruno A. Cardoso, Ryan Stansfield, Maria Teresa
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Exposure of CRT occurs independently from the apoptosisassociated loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). (A) HeLa cells treated with MTX
Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous
 Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
Cancer Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Effective Targeting of Quiescent Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Combination with Imatinib Mesylate Bin Zhang,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.2109
 HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel
 Analyze A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Alexa Fluor is a registered trademark of Life Technologies
Analyze A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Alexa Fluor is a registered trademark of Life Technologies
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
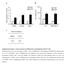 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a. Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease
 Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or
 Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase attenuates T cell signaling to maintain tolerance in mice
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase attenuates T cell signaling to maintain tolerance in mice Florian Wiede 1, Benjamin J. Shields 1, Sock Hui Chew 1, Konstantinos Kyparissoudis 2,
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase attenuates T cell signaling to maintain tolerance in mice Florian Wiede 1, Benjamin J. Shields 1, Sock Hui Chew 1, Konstantinos Kyparissoudis 2,
a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper
 a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper An 8-color DuraClone IM panel for detection of Human blood dendritic cells by flow cytometry Nathalie Dupas 1, Snehita Sattiraju 2, Neha Girish 2, Murthy Pendyala
a Beckman Coulter Life Sciences: White Paper An 8-color DuraClone IM panel for detection of Human blood dendritic cells by flow cytometry Nathalie Dupas 1, Snehita Sattiraju 2, Neha Girish 2, Murthy Pendyala
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Supplementary Figure 1
 d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1:
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
<10. IL-1β IL-6 TNF + _ TGF-β + IL-23
 3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS
 SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS Mice MT/ret RetCD3ε KO α-cd25 treated MT/ret Age 1 month 3 mnths 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 2/87 Survival 87/87 incidence of 17/87 1 ary tumor
SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS Mice MT/ret RetCD3ε KO α-cd25 treated MT/ret Age 1 month 3 mnths 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 1 month 3 months 6 months 2/87 Survival 87/87 incidence of 17/87 1 ary tumor
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
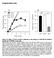 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
ILC1 and ILC3 isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the ILC1, ILC2 and
 Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
Supplementary Methods and isolation and culture Following cell sorting, we confirmed that the recovered cells belonged to the, ILC2 and subsets. For this purpose we performed intracellular flow cytometry
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
genome edited transient transfection, CMV promoter
 Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGEND Supplementary Figure 1. Enhanced detection of CTLA-4 on the surface of HIV-specific CD4 + T cells correlates with intracellular CTLA-4 levels. (a) Comparative CTLA-4 levels
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
pro-b large pre-b small pre-b CCCP (µm) Rag1 -/- ;33.C9HCki
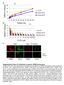 a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
a TMRM FI (Median) b TMRM FI (Median) c 20 15 10 5 0 8 6 4 2 0 pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 TMRM (nm) pro-b large pre-b small pre-b 0 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 CCCP (mm)
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Supplementary Figures. T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ
 Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. Supplemental Figure 2.
 Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. To evaluate the antigen sensitivity of mutant CARs transduced Jurkat T cells were stimulated with varying concentrations
Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. To evaluate the antigen sensitivity of mutant CARs transduced Jurkat T cells were stimulated with varying concentrations
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
ProteoScan Cancer Lysate Arrays. QC and Validation Data
 ProteoScan Cancer Lysate Arrays QC and Validation Data 4.5 mm Barcode Cancer Lysate Array Layout PA02 60 mm B1 C2 K3 Ly1 O2 P3 Mel1 Lv2 St3 B2 C3 L1 Ly2 O3 Pr1 Mel2 Lv3 B3 K1 L2 Ly3 P1 Pr2 Mel3 St1 C1
ProteoScan Cancer Lysate Arrays QC and Validation Data 4.5 mm Barcode Cancer Lysate Array Layout PA02 60 mm B1 C2 K3 Ly1 O2 P3 Mel1 Lv2 St3 B2 C3 L1 Ly2 O3 Pr1 Mel2 Lv3 B3 K1 L2 Ly3 P1 Pr2 Mel3 St1 C1
