Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors. Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation?
|
|
|
- Sheila Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation?
2 Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line Condition Media from the Moloney MuSV transformed 3T3 cell line Normal NRK Cells Tumor NRK cells Todaro and De Larco PNAS 1978
3 Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line SGF: sarcoma growth factor Todaro and De Larco PNAS 1978
4 Transforming Activities is Due to TGF-beta Moloney MuSV transformed 3T3 Cell Pellet Acid-ethanol extraction Gel filtration HPLC TGF-α EGF TGF-β + + EGF NO colony formation Stimulate colony formation Anzano, M. et al. (1982) Cancer Res. 42:4776
5 Paradoxical Activity of TGF-β Effects of TGF-ß on the anchorage-independent growth of Myc-1 cells. In the presence of PDGF, TGF-ß stimulates growth (A) and in the presence of EGF, TGF-ß inhibits growth (B). Roberts, A. et al. (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:119.
6 Purification of Bone Inducing Factors
7 Purification of Bone Inducing Factors CIF-A = TGF-beta 1 CIF-B = TGF-beta 2
8 Purification of Bone Inducing Factors SCIENCES VOL. 242
9 SCIENCES VOL. 242 Purification of BMPs
10 TGF-β Structure and Function furin cystine knot motif White balls cystine residues and disulfide bonds Daopin, Science 257:
11 TGF-β Maturation Khalil Microbes Infect. 1999
12 Massague Ann Rev Biochem 1998
13 Massague Ann Rev Biochem 1998
14 TGF-beta Binds to Cell Surface Receptors TGF-beta was labeled with radioactive I 125 Type III Type II Type I
15 TGF-beta Inhibits Normal Cell Proliferation 0pM 1pM 5pM 10pM 25pM 50pM
16 Isolation of TGF-beta Resistance Mutant Cells Mink lung epithelial Cells 25 pm TGF-beta 7 1.6X10 cells treated with EMS (ethyl methansulfonate) for 24 hr 40% killing rate TGF-beta Resistance Clonies
17 Cell Proliferation Assay in the Presence of TGF-β Laiho M, 1990 JBC
18 Some of the Mutant Cell Lines Show Abnormal TGF-b Receptor Expression Laiho M, 1990 JBC
19 Genetic Screening of the Cell lines Lacking of TGF-beta Receptors Three types of cell clones: -R cells: Loss of Type I receptor binding -DR Cells: loss of both Type I and Type II binding -S Cells: Receptor binding normal but no signaling Why there are no mutant cell clones in which the type I receptors are normal but lacking the type II receptors? Laiho M, 1990 JBC
20 TGF-beta Receptor Signaling Mechanism Laiho M, 1990 JBC
21 Expression Cloning of TGF-beta Receptors Transient transfection of COS cells Ligand binding Isolating positive cells Recovering plasmid DNA encoding gene of interest Lin and Lodish 1991 Cell
22 Cloning of TGF-beta I Receptor Franze et al. Cell 75,
23 TGF-beta Receptor Signaling Modeling
24 Type I and II TGF-beta receptor families Massague Ann Rev Biochem 1998
25 Functional Reconstitution of TGF-beta Signaling Wrana and Massague 1992 Cell
26 Reporter Gene Assay for Studying TGF-beta Signaling Wrana and Massague 1992 Cell
27 TβTRI Kinase Complexed with Inhibitor FKBP12
28 Decapentaplegic (dpp) Wild type Class I Class II Class III
29 Identification and Cloning of dpp Downstream Targets Wild Type dpp/maddpp dpp/mad+ Loss of function mutations of Mad are dominant maternal effect enhancers of dpp during early embryogenesis and dominant zygotic enhancers of dpp in imaginal discs Newfeld et al., 1995
30 Phosphorylation of Smad3 by TGF-beta RI at the C-terminus SSXS Motif Liu et al. PNAS 1997
31 TGF-β-dependent &Independent Smad2 Phosphorylation Mv1Lu wt R1B (TβRI Defective) TGFβ Nocodazole TGFβ Nocodazole Mps1
32 Phosphorylation of R-Smads by TGF-beta Receptor Kinase Smad1 Smad5 Smad8 Smad2 Smad3 Smad4 Smad6 Smad7 BMP Signaling TGF-β and Activin Signaling TGF-β/Activin/BMP Signaling TGF-β/Activin/BMP? R-Smads Co-Smad Inhibitory-Smad
33 Smads Are DNA Binding Proteins
34 Reporter Gene Assays for Studying TGF-beta Signaling SBE: Smad Binding Element 5 -GTCTAGAC-3
35 TβRI TβRII Cytoplasmic retention factor Smad2/3 P Phosphorylation Smad2/3? Smad2/3 P Smad4 Smad4 Smad2/3 Nuclear retention factor Smad2/3 P Smad4 Smad4 Smad2/3 P TFs Smad4 Transcription Smad2/3 Dephosphorylation
36 Transcription Activation and Repression by TGF-beta Derynck and Zhang Nature 2002
37 33% ovarian cancer TβRI TβRII 10-15% colon cancer Smad2 Smad2 P <2% colon cancer 50% pancreatic cancer 20-30% colon cancer Smad4 Smad3 Smad3 P Smad2 P Smad3 P Smad4 TFs Smad2 P Smad3 P Smad4 Transcription Massague et al. Cell 2000
38 Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of Smads 2, 3, and 4 Permits Sensing of TGF- Receptor Activity Gareth J. Inman, Francisco J. Nicola s and Caroline S. Hill
39 What is p-smad2? How to detect it? Why is cycloheximide used?
40 What was the inhibitor added at different time points?
41 TGF-beta receptors remain active for at least 3 4 hr in HaCaT cells
42
43 What does this experiment tell us about Smad2 and Smad4 in relationship to receptor activity?
44 What happened to P-Smad2 upon treatment with SB ?
45 Why there is less Smad4 in Smad2 IP samples treated with SB ?
46 What accounts for low nuclear staining of Smad2/3 in the presence of SB ?
47
48 What is LMB? What does it do? What does this experiment tell us?
49
50
51 Domain Organization of Smad
52 Phosphorylation of Smad1
53 Protease Digestion of Labeled Smad1
54 Protease Digestion of Labeled Smad1
55 Phosphorylation of Smad1 Why the predicted digestion pattern of Smad1 allowed us to identify the phosphorylated region as part of the linker region of Smad1?
56 Chymotrypsin cleaves peptides at the carboxyl side of tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine
57 EGF induced Smad1 Phosphorylation
58 EGF induced Smad1 Phosphorylation at the Linker Region
59 HGF induced Smad1 Phosphorylation
60 In vitro Phosphorylation of Smad1 by Erk2 and BMPR1
61 Smad1 linker has potential MAPK sites Serines were mutated to alanine to prevent MAPK-induced phosphorylation
62 EGF-induced phosphorylation of the Smad1 linker region does not prevent Smad1/Smad4 complex formation RTK block in BMP signaling is downstream of Smad1/Smad4 complex formation
63 Phosphorylation of Linker Region Represses Smad1
64 BMP induces nuclear accumulation of Smad1 No treatment BMP BMP + EGF BMP/EGF + U0126 U0126 Smad-linker mutant EGF-induced phosphorylation of Smad inhibits nuclear accumulation induced by BMP
65 Phosphorylation of Linker Region Represses Smad1
66 MAPK phosphorylation of Smad1 prevents translocation of Smad1/Smad4 complexes BMP target gene expression is blocked due to a block in Smad1-Smad4 nuclear translocation
67 BMP signaling is regulated at multiple steps in the pathway Extracellular Intracellular
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
 Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/305/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Controlling Long-Term Signaling: Receptor Dynamics Determine Attenuation and Refractory Behavior of the TGF-β Pathway
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/305/ra106/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Controlling Long-Term Signaling: Receptor Dynamics Determine Attenuation and Refractory Behavior of the TGF-β Pathway
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008
 MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Hormones. Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6
 Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Cell Signaling II: A circuitous pursuit
 Cell Signaling II: A circuitous pursuit Joe W. Ramos, Ph.D. joeramos@hawaii.edu www2.hawaii.edu/~joeramos From Genes and the Biology of Cancer, Varmus and Weinberg, 1993 1 Epinephrine binds β adrenergic
Cell Signaling II: A circuitous pursuit Joe W. Ramos, Ph.D. joeramos@hawaii.edu www2.hawaii.edu/~joeramos From Genes and the Biology of Cancer, Varmus and Weinberg, 1993 1 Epinephrine binds β adrenergic
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
The development of all organisms requires execution of
 14 high SIGNALING ATHWAYS THAT CNTRL GENE ACTIVITY low Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) detects time and location of activation of Ras protein in live cells triggered by epidermal growth factor.
14 high SIGNALING ATHWAYS THAT CNTRL GENE ACTIVITY low Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) detects time and location of activation of Ras protein in live cells triggered by epidermal growth factor.
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors
 Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
ABSTRACT. plays an important role in male spermatogenesis. The hormone is secreted by pituitary
 ABSTRACT SAFWAT, NEDAL WAFIK. Activin Induction of Follicle Stimulating Hormone is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Activated Kinase-1 (TAK-1) in Pituitary Gonadotropes (Under the direction
ABSTRACT SAFWAT, NEDAL WAFIK. Activin Induction of Follicle Stimulating Hormone is Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor Beta Activated Kinase-1 (TAK-1) in Pituitary Gonadotropes (Under the direction
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA
 MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA Joan Seoane ICREA Research Professor Vall d Hebron Institute of Oncology Vall d Hebron University Hospital Barcelona jseoane@vhio.net Glioma Stupp et al. New
MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA Joan Seoane ICREA Research Professor Vall d Hebron Institute of Oncology Vall d Hebron University Hospital Barcelona jseoane@vhio.net Glioma Stupp et al. New
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes
 1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript FEBS Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 November 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: FEBS Lett. 2012 July 4; 586(14): 1871 1884. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.010. Post-translational regulation of TGF-β receptor and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: FEBS Lett. 2012 July 4; 586(14): 1871 1884. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.010. Post-translational regulation of TGF-β receptor and
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health and Science University Portland, Oregon
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-05-1-0152 TITLE: A Novel Mechanism of Androgen Receptor Action PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Charles T. Roberts, Jr., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health and Science University
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-05-1-0152 TITLE: A Novel Mechanism of Androgen Receptor Action PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Charles T. Roberts, Jr., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health and Science University
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
Review of relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor family & receptors and tumor angiogenesis
 16 1 2004 2 hinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 1 Feb., 2004 1004-0374 (2004) 01-0019-05 1 201203 2 200025 (vascular endothelial growth factor, ) (vascular permeability factor, VPF), -A -B -
16 1 2004 2 hinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 1 Feb., 2004 1004-0374 (2004) 01-0019-05 1 201203 2 200025 (vascular endothelial growth factor, ) (vascular permeability factor, VPF), -A -B -
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) phosphorylates themselves
 Enzyme-coupled receptors Transmembrane proteins Ligand-binding domain on the outer surface Cytoplasmic domain acts as an enzyme itself or forms a complex with enzyme 1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases
Enzyme-coupled receptors Transmembrane proteins Ligand-binding domain on the outer surface Cytoplasmic domain acts as an enzyme itself or forms a complex with enzyme 1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases
Andrea W. Tu. University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0357 TITLE: Smad Acetylation: a New Level of Regulation in TGF-Beta Signaling PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrea W. Tu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, Berkeley
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0357 TITLE: Smad Acetylation: a New Level of Regulation in TGF-Beta Signaling PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrea W. Tu CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, Berkeley
TGF-β. transforming. growth factor. growth factor-β TGF-β. Transforming growth factor-β TGF-β. Smad. DNA Smad Smad cofactor. transcription factor Smad
 24 3 65 73 2009 TGF-β Smad cofactors 2 Transforming growth factor-β TGF-β TGF-β Smad Smad DNA Smad Smad cofactor TGF-β Maid Maid Smad cofactor Smad cofactor TGF-β -β signal transduction transcription factor
24 3 65 73 2009 TGF-β Smad cofactors 2 Transforming growth factor-β TGF-β TGF-β Smad Smad DNA Smad Smad cofactor TGF-β Maid Maid Smad cofactor Smad cofactor TGF-β -β signal transduction transcription factor
MAPK Pathway
 MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling
 4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
Cellular Signaling Pathways. Signaling Overview
 Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Phospholipase C γ Prof. Graham Carpenter
 Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Transforming growth factor β superfamily signaling and its role in B-cell lymphoma
 Transforming growth factor β superfamily signaling and its role in B-cell lymphoma by Maren Bakkebø Department of Immunology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University
Transforming growth factor β superfamily signaling and its role in B-cell lymphoma by Maren Bakkebø Department of Immunology Institute for Cancer Research The Norwegian Radium Hospital Oslo University
THE SMAD3 LINKER REGION: TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY AND PHOSPHORYLATION-MEDIATED REGULATION GUANNAN WANG. A dissertation submitted to the
 THE SMAD3 LINKER REGION: TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY AND PHOSPHORYLATION-MEDIATED REGULATION by GUANNAN WANG A dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of
THE SMAD3 LINKER REGION: TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY AND PHOSPHORYLATION-MEDIATED REGULATION by GUANNAN WANG A dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of
Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis
 Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural. Neural Development
 Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp 477-506 (sorta) 4 th ed, pp 545-575 (sorta) References : Fainsod, A., Steinbeisser, H., & De Robertis, E. M. (1994).
Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp 477-506 (sorta) 4 th ed, pp 545-575 (sorta) References : Fainsod, A., Steinbeisser, H., & De Robertis, E. M. (1994).
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes.
 What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
Biol220 Cellular Signalling. Non-receptor tyrosine kinases
 Biol220 Cellular Signalling Non-receptor tyrosine kinases The 7TM receptors initiate signal transducton pathways through changes in tertiary structure that are induced by ligand binding. A fundamentally
Biol220 Cellular Signalling Non-receptor tyrosine kinases The 7TM receptors initiate signal transducton pathways through changes in tertiary structure that are induced by ligand binding. A fundamentally
C. elegans Embryonic Development
 Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3218
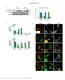 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Familial PAH. Genetics and pulmonary arterial hypertension. PAH and mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor (BMPR-II)
 athology of vascular lesions in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension Genetics and pulmonary arterial hypertension Concentric intimal lesion Nick Morrell British Heart Foundation rofessor of Cardiopulmonary
athology of vascular lesions in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension Genetics and pulmonary arterial hypertension Concentric intimal lesion Nick Morrell British Heart Foundation rofessor of Cardiopulmonary
TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β AND SMAD4 REGULATION OF INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BEHAVIOR IN CANCER CELLS. Sheng-Ru Shiou.
 TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β AND SMAD4 REGULATION OF INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BEHAVIOR IN CANCER CELLS By Sheng-Ru Shiou Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β AND SMAD4 REGULATION OF INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BEHAVIOR IN CANCER CELLS By Sheng-Ru Shiou Dissertation Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Vanderbilt University
Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi. Bayan Abusheikha. Faisal
 24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Nuclear Retention of the Tumor Suppressor cpml by the Homeodomain Protein TGIF Restricts TGF-b Signaling
 Molecular Cell 23, 547 559, August 18, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.018 Nuclear Retention of the Tumor Suppressor cpml by the Homeodomain Protein TGIF Restricts TGF-b Signaling
Molecular Cell 23, 547 559, August 18, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.018 Nuclear Retention of the Tumor Suppressor cpml by the Homeodomain Protein TGIF Restricts TGF-b Signaling
HAL author manuscript
 HAL author manuscript Methods in molecular medicine 2005; 117 69-80 Transforming growth factor-β: the Smad pathway and its implications in fibrosis Alain Mauviel INSERM U532, Institut de Recherche sur
HAL author manuscript Methods in molecular medicine 2005; 117 69-80 Transforming growth factor-β: the Smad pathway and its implications in fibrosis Alain Mauviel INSERM U532, Institut de Recherche sur
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
THE ROLES OF A LIM DOMAIN PROTEIN, HIC-5/ARA55, IN TGF-β SIGNALING IN PROSTATE CANCER CELLS HUI WANG
 THE ROLES OF A LIM DOMAIN PROTEIN, HIC-5/ARA55, IN TGF-β SIGNALING IN PROSTATE CANCER CELLS by HUI WANG Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation
THE ROLES OF A LIM DOMAIN PROTEIN, HIC-5/ARA55, IN TGF-β SIGNALING IN PROSTATE CANCER CELLS by HUI WANG Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 Award Number: W81XWH 15 1 0650 TITLE: ALK and TGF-Beta Resistance in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xin-Hua Feng CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of Medicine Houston, TX 77030 REPORT DATE:
Award Number: W81XWH 15 1 0650 TITLE: ALK and TGF-Beta Resistance in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xin-Hua Feng CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of Medicine Houston, TX 77030 REPORT DATE:
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test
 Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy
 (Courtesy of Magda Stumpfova. Used with permission.) Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy M.D. Gomes, S.H. Lecker, R.T. Jagoe, A. Navon, and A.L. Goldberg PNAS,
(Courtesy of Magda Stumpfova. Used with permission.) Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy M.D. Gomes, S.H. Lecker, R.T. Jagoe, A. Navon, and A.L. Goldberg PNAS,
Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways. Other Pathways. Cancer Pathways
 Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways Limited number of pathways control proliferation and differentiation Transmit signals from growth factors, hormones, cell-to-cell communications/interactions Pathways turn into
Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways Limited number of pathways control proliferation and differentiation Transmit signals from growth factors, hormones, cell-to-cell communications/interactions Pathways turn into
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
 Cellular Signalling Cells must be ready to respond to essential signals in their environment. These are often chemicals in the extracellular fluid (ECF) from distant locations in a multicellular organism
Cellular Signalling Cells must be ready to respond to essential signals in their environment. These are often chemicals in the extracellular fluid (ECF) from distant locations in a multicellular organism
Role of the Type III TGF-beta Receptor Cytoplasmic Domain in Breast Cancer. Progression. Jason Dole Lee
 Role of the Type III TGF-beta Receptor Cytoplasmic Domain in Breast Cancer Progression by Jason Dole Lee Department of Pharmacology and Cancer Biology Duke University Date: Approved: Gerard Blobe, Supervisor
Role of the Type III TGF-beta Receptor Cytoplasmic Domain in Breast Cancer Progression by Jason Dole Lee Department of Pharmacology and Cancer Biology Duke University Date: Approved: Gerard Blobe, Supervisor
Previous Class. Today. Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism. Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties
 Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
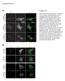 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch
 EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
EGFR: fundamenteel en klinisch Guido Lammering MAASTRO Clinic Maastricht, NL What is EGFR?? The EGFR some facts 1186 amino acids 170 kda Expressed by all cells of epithelial origin Increased activation
