FDA-approved radiopharmaceuticals
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Copeland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FDA-approved radiopharmaceuticals Medication Management This is a current list of all FDA-approved radiopharmaceuticals. Nuclear medicine practitioners that receive radiopharmaceuticals that originate from sources other than the manufacturers listed in these tables may be using unapproved copies. Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 1 Carbon-11 choline Various Indicated for PET imaging of patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based upon elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following initial therapy and non-informative bone scintigraphy, computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help identify potential sites of prostate cancer recurrence for subsequent histologic confirmation 2 Carbon-14 urea Kimberly-Clark PYtest Detection of gastric urease as an aid in the diagnosis of H.pylori infection in the stomach 3 Fluorine-18 florbetaben Piramal Imaging Neuraceq Indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the brain to estimate β amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer s disease (AD) or other causes of cognitive decline 4 Fluorine-18 florbetapir Eli Lilly Amyvid 5 Fluorine-18 flucicovine 6 Fluorine-18 sodium fluoride Blue Earth Diagnostics Axumin A radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following prior treatment Various PET bone imaging agent to delineate areas of altered osteogenesis Package Inserts may be viewed at Radiopharmaceuticals that may potentially have unapproved copies of FDAapproved commercially available radiopharmaceuticals in the marketplace. Rev of 6
2 Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 7 Fluorine-18 fludeoxyglucose 8 Fluorine-18 flutemetamol Various As a PET imaging agent to: Assess abnormal glucose metabolism in oncology Assess myocardial hibernation Identify regions of abnormal glucose metabolism associated with foci of epileptic seizures GE Healthcare Vizamyl Indicated for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the brain to estimate β amyloid neuritic plaque density in adult patients with cognitive impairment who are being evaluated for Alzheimer s disease (AD) or other causes of cognitive decline 9 Gallium-67 citrate Curium Useful to demonstrate the presence/extent of: Lantheus Medical Imaging Hodgkin s disease Lymphoma Bronchogenic carcinoma Aid in detecting some acute inflammatory lesions 10 Gallium-68 dotatate Advanced Accelerator Applications 11 Indium-111 capromab pendetide Aytu Pharmaceuticals NETSPOT ProstaScint A radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) for localization of somatostatin receptor positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in adult and pediatric patients A diagnostic imaging agent in newly-diagnosed patients with biopsy-proven prostate cancer, thought to be clinically-localized after standard diagnostic evaluation (e.g. chest x-ray, bone scan, CT scan, or MRI), who are at high-risk for pelvic lymph node metastases A diagnostic imaging agent in post-prostatectomy patients with a rising PSA and a negative or equivocal standard metastatic evaluation in whom there is a high clinical suspicion of occult metastatic disease 12 Indium-111 chloride Curium Indicated for radiolabeling: ProstaScint used for in vivo diagnostic imaging procedures 13 Indium-111 pentetate GE Healthcare For use in radionuclide cisternography 14 Indium-111 oxyquinoline 15 Indium-111 pentetreotide 16 Iodine I-123 iobenguane GE Healthcare Indicated for radiolabeling autologous leukocytes which may be used as an adjunct in the detection of inflammatory processes to which leukocytes migrate, such as those associated with abscesses or other infection Curium Octreoscan An agent for the scintigraphic localization of primary and metastatic neuroendocrine tumors bearing somatostatin receptors GE Healthcare AdreView Indicated for use in the detection of primary or metastatic pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma as an adjunct to other diagnostic tests. Indicated for scintigraphic assessment of sympathetic innervation of the myocardium by measurement of the heart to mediastinum (H/M) ratio of radioactivity uptake in patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II or class III heart failure and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 35%. Among these patients, it may be used to help identify patients with lower one and two year mortality risks, as indicated by an H/M ratio 1.6. Limitations of Use: In patients with congestive heart failure, its utility has not been established for: selecting a therapeutic intervention or for monitoring the response to therapy; using the H/M ratio to identify a patient with a high risk for death. Package Inserts may be viewed at Radiopharmaceuticals that may potentially have unapproved copies of FDAapproved commercially available radiopharmaceuticals in the marketplace. Rev of 6
3 Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 17 Iodine I-123 ioflupane GE Healthcare DaTscan Indicated for striatal dopamine transporter visualization using SPECT brain imaging to assist in the evaluation of adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes (PS) in whom it may help differentiate essential tremor due to PS (idiopathic Parkinson s disease, multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy) 18 Iodine I-123 sodium iodide capsules 19 Iodine I-125 human serum albumin 20 Iodine I-125 iothalamate 21 Iodine I-131 human serum albumin 22 Iodine I-131 sodium iodide 23 Molybdenum Mo-99 generator Cardinal Health Indicated for use in the evaluation of thyroid: Curium Function Morphology IsoTex Diagnostics Jeanatope Indicated for use in the determination of: Total blood Plasma volume IsoTex Diagnostics Glofil-125 Indicated for evaluation of glomerular filtration IsoTex Diagnostics Megatope Indicated for use in determinations of: Total blood and plasma volumes Cardiac output Cardiac and pulmonary blood volumes and circulation times Protein turnover studies Heart and great vessel delineation Localization of the placenta Localization of cerebral neoplasms Curium Diagnostic: DRAXIMAGE HICON Performance of the radioactive iodide (RAI) uptake test to evaluate thyroid function Localizing metastases associated with thyroid malignancies Therapeutic: Treatment of hyperthyroidism Treatment of carcinoma of the thyroid Curium GE Healthcare Lantheus Medical Imaging Ultra- TechneKow V4 DRYTEC Technelite Generation of Tc-99m sodium pertechnetate for administration or radiopharmaceutical preparation 24 Nitrogen-13 ammonia Various Indicated for diagnostic Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate myocardial perfusion in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease 25 Radium-223 dichloride Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. Xofigo Indicated for the treatment of patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer, symptomatic bone metastases and no known visceral metastatic disease Package Inserts may be viewed at Radiopharmaceuticals that may potentially have unapproved copies of FDAapproved commercially available radiopharmaceuticals in the marketplace. Rev of 6
4 Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 26 Rubidium-82 chloride Bracco Diagnostics Cardiogen-82 PET myocardial perfusion agent that is useful in distinguishing normal from DRAXIMAGE Ruby-Fill abnormal myocardium in patients with suspected myocardial infarction 27 Samarium-153 lexidronam Lantheus Medical Imaging Quadramet Indicated for relief of pain in patients with confirmed osteoblastic metastatic bone lesions that enhance on radionuclide bone scan 28 Strontium-89 chloride GE Healthcare Metastron Indicated for the relief of bone pain in patients with painful skeletal metastases that have been confirmed prior to therapy 29 Technetium-99m bicisate 30 Technetium-99m disofenin 31 Technetium-99m exametazine 32 Technetium-99m macroaggregated albumin 33 Technetium-99m mebrofenin 34 Technetium-99m medronate 35 Technetium-99m mertiatide 36 Technetium-99m oxidronate 37 Technetium-99m pentetate Lantheus Medical Imaging Neurolite SPECT imaging as an adjunct to conventional CT or MRI imaging in the localization of stroke in patients in whom stroke has already been diagnosed Pharmalucence Hepatolite Diagnosis of acute cholecystitis as well as to rule out the occurrence of acute cholecystitis in suspected patients with right upper quadrant pain, fever, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness and mass or rebound tenderness, but not limited to these signs and symptoms DRAXIMAGE* As an adjunct in the detection of altered regional cerebral perfusion in stroke GE Healthcare Ceretec Leukocyte labeled scintigraphy as an adjunct in the localization of intra abdominal infection and inflammatory bowel disease* DRAXIMAGE An adjunct in the evaluation of pulmonary perfusion (adult and pediatric) Evaluation of peritoneo-venous (LaVeen) shunt patency Bracco Diagnostics Choletec As a hepatobiliary imaging agent Pharmalucence DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 As a bone imaging agent to delineate areas of altered osteogenesis GE Healthcare MDP Multidose Pharmalucence Curium Technescan In patients > 30 days of age as a renal imaging agent for use in the diagnosis of: MAG3 Congenital and acquired abnormalities Renal failure Urinary tract obstruction and calculi Diagnostic aid in providing: Renal function Split function Renal angiograms Renogram curves for whole kidney and renal cortex Curium Technescan HDP As a bone imaging agent to delineate areas of altered osteogenesis (adult and pediatric use) DRAXIMAGE Brain imaging Kidney imaging: - To assess renal perfusion - To estimate glomerular filtration rate Package Inserts may be viewed at Radiopharmaceuticals that may potentially have unapproved copies of FDAapproved commercially available radiopharmaceuticals in the marketplace. Rev of 6
5 Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 38 Technetium-99m pyrophosphate Curium Pharmalucence Technescan PYP As a bone imaging agent to delineate areas of altered osteogenesis As a cardiac imaging agent used as an adjunct in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction As a blood pool imaging agent useful for: - Gated blood pool imaging - Detection of sites of gastrointestinal bleeding 39 Technetium-99m red blood cells 40 Technetium-99m sestamibi 41 Technetium-99m sodium pertechnetate 42 Technetium-99m succimer 43 Technetium-99m sulfur colloid 44 Technetium-99m tetrofosmin Curium UltraTag Tc99m-labeled red blood cells are used for: Blood pool imaging including cardiac first pass and gated equilibrium imaging Detection of sites of gastrointestinal bleeding Cardinal Health Myocardial perfusion agent that is indicated for: Curium DRAXIMAGE Lantheus Medical Cardiolite Imaging Pharmalucence Detecting coronary artery disease by localizing myocardial ischemia (reversible defects) and infarction (non-reversible defects) Evaluating myocardial function Developing information for use in patient management decisions Planar breast imaging as a second line diagnostic drug after mammography to assist in the evaluation of breast lesions in patients with an abnormal mammogram or a palpable breast mass Curium Brain Imaging (including cerebral radionuclide angiography)* GE Healthcare Thyroid Imaging* Salivary Gland Imaging Lantheus Medical Placenta Localization Imaging Blood Pool Imaging (including radionuclide angiography)* Urinary Bladder Imaging (direct isotopic cystography) for the detection of vesico-ureteral reflux* Nasolacrimal Drainage System Imaging (*adult and pediatric use) GE Healthcare An aid in the scintigraphic evaluation of renal parenchymal disorders Pharmalucence Imaging areas of functioning retriculoendothelial cells in the liver, spleen and bone marrow* It is used orally for: - Esophageal transit studies* - Gastroesophageal reflux scintigraphy* - Detection of pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents* Aid in the evaluation of peritoneo-venous (LeVeen) shunt patency To assist in the localization of lymph nodes draining a primary tumor in patients with breast cancer or malignant melanoma when used with a hand-held gamma counter (*adult and pediatric use) GE Healthcare Myoview Myocardial perfusion agent that is indicated for: Detecting coronary artery disease by localizing myocardial ischemia (reversible defects) and infarction (non-reversible defects) The assessment of left ventricular function (left ventricular ejection fraction and wall motion) Package Inserts may be viewed at Radiopharmaceuticals that may potentially have unapproved copies of FDAapproved commercially available radiopharmaceuticals in the marketplace. Rev of 6
6 Radiopharmaceutical Manufacturer Trade Names Approved Indications in Adults (Pediatric use as noted) 45 Technetium-99m tilmanocept 46 Thallium-201 chloride Cardinal Health Lymphoseek Indicated with or without scintigraphic imaging for: Lymphatic mapping using a handheld gamma counter to locate lymph nodes draining a primary tumor site in patients with solid tumors for which this procedure is a component of intraoperative management. Guiding sentinel lymph node biopsy using a handheld gamma counter in patients with clinically node negative squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, breast cancer or melanoma. Curium Useful in myocardial perfusion imaging for the diagnosis and localization GE Healthcare of myocardial infarction As an adjunct in the diagnosis of ischemic heart disease (atherosclerotic Lantheus Medical coronary artery disease) Imaging Localization of sites of parathyroid hyperactivity in patients with elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone levels 47 Xenon-133 gas Curium The evaluation of pulmonary function and for imaging the lungs Lantheus Medical Assessment of cerebral flow Imaging 48 Yttrium-90 chloride 49 Yttrium-90 ibritumomab tiuxetan Eckert & Ziegler Nuclitec Spectrum Pharmaceuticals Indicated for radiolabeling: Zevalin used for radioimmunotherapy procedures Zevalin Indicated for the: Treatment of relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma (NHL) Treatment of previously untreated follicular NHL in patients who achieve a partial or complete response to first-line chemotherapy Package Inserts may be viewed at Any reader of this document is cautioned that Cardinal Health makes no representation, guarantee, or warranty, express or implied as to the accuracy and appropriateness of the information contained in this document, and will bear no responsibility or liability for the results or consequences of its use. The information provided on this document is non-promotional. It is intended for informational purposes only and is not intended to promote or recommend any individual product. Contact the applicable manufacturer if you have any questions regarding a product listed on this document. cardinalhealth.com Cardinal Health 7000 Cardinal Place 2017 Cardinal Health. All Rights Reserved. CARDINAL HEALTH, the Cardinal Health LOGO, and ESSENTIAL TO CARE are Dublin, Ohio trademarks of Cardinal Health and may be registered in the US and/or in other countries. All other marks are the property of their respective owners Lit. No. 1NPS (11/2017) Rev of 6
7 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection, USP Initial U.S. Approval: INDICATIONS AND USAGE Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: Oncology: For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist in the evaluation of malignancy in patients with known or suspected abnormalities found by other testing modalities, or in patients with an existing diagnosis of cancer. Cardiology: For the identification of left ventricular myocardium with residual glucose metabolism and reversible loss of systolic function in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction, when used together with myocardial perfusion imaging. Neurology: For the identification of regions of abnormal glucose metabolism associated with foci of epileptic seizures (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection emits radiation. Use procedures to minimize radiation exposure. Screen for blood glucose abnormalities. In the oncology and neurology settings, instruct patients to fast for 4 6 hours prior to the drug s injection. Consider medical therapy and laboratory testing to assure at least two days of normoglycemia prior to the drug s administration (5.2). In the cardiology setting, administration of glucose-containing food or liquids (e.g., grams) prior to the drug s injection facilitates localization of cardiac ischemia (2.3). Aseptically withdraw Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection from its container and administer by intravenous injection (2). The recommended dose: for adults is 5 10 mci ( MBq), in all indicated clinical settings (2.1). for pediatric patients is 2.6 mci in the neurology setting (2.2). Initiate imaging within 40 minutes following drug injection; acquire static emission images minutes from time of injection (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Multiple-dose glass vial containing GBq ( mci/ml) of Fludeoxyglucose F- 18 Injection and 4.5 mg of sodium chloride in citrate buffer (10 ml vial: approximately 5-10 ml volume; 30 ml vial: approximately ml volume) for intravenous administration (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Radiation risks: use smallest dose necessary for imaging (5.1). Blood glucose abnormalities: may cause suboptimal imaging (5.2) ADVERSE REACTIONS Hypersensitivity reactions have occurred; have emergency resuscitation equipment and personnel immediately available (6). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Cardinal Health at or FDA at FDA-1088 or USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Pregnancy Category C: No human or animal data. Consider alternative diagnostics; use only if clearly needed (8.1). Nursing mothers: Use alternatives to breast feeding (e.g., stored breast milk or infant formula) for at least 10 half-lives of radioactive decay, if Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is administered to a woman who is breast-feeding (8.3). Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established in the oncology and cardiology settings (8.4). See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Revised: 11/2015 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS* 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 1.1 Oncology 1.2 Cardiology 1.3 Neurology 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Recommended Dose for Adults 2.2 Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients 2.3 Patient Preparation 2.4 Radiation Dosimetry 2.5 Radiation Safety Drug Handling 2.6 Drug Preparation and Administration 2.7 Imaging Guidelines 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Radiation Risks 5.2 Blood Glucose Abnormalities 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy 8.3 Nursing Mothers 8.4 Pediatric Use 11 DESCRIPTION 11.1 Chemical Characteristics 11.2 Physical Characteristics 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action 12.2 Pharmacodynamics 12.3 Pharmacokinetics 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility 14 CLINICAL STUDIES 14.1 Oncology 14.2 Cardiology 14.3 Neurology 15 REFERENCES 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION *Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed. FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: 1.1 Oncology For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist in the evaluation of malignancy in patients with known or suspected abnormalities found by other testing modalities, or in patients with an existing diagnosis of cancer. 1.2 Cardiology For the identification of left ventricular myocardium with residual glucose metabolism and reversible loss of systolic function in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction, when used together with myocardial perfusion imaging. 1.3 Neurology For the identification of regions of abnormal glucose metabolism associated with foci of epileptic seizures. 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection emits radiation. Use procedures to minimize radiation exposure. Calculate the final dose from the end of synthesis (EOS) time using proper radioactive decay factors. Assay the final dose in a properly calibrated dose calibrator before administration to the patient [see Description (11.2)]. 2.1 Recommended Dose for Adults Within the oncology, cardiology and neurology settings, the recommended dose for adults is 5 10 mci ( MBq) as an intravenous injection. 2.2 Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients Within the neurology setting, the recommended dose for pediatric patients is 2.6 mci, as an intravenous injection. The optimal dose adjustment on the basis of body size or weight has not been determined [see Use in Special Populations (8.4)]. 2.3 Patient Preparation To minimize the radiation absorbed dose to the bladder, encourage adequate hydration. Encourage the patient to drink water or other fluids (as tolerated) in the 4 hours before their PET study. Encourage the patient to void as soon as the imaging study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour. Screen patients for clinically significant blood glucose abnormalities by obtaining a history and/or laboratory tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Prior to Fludeoxyglucose F-18 PET imaging in the oncology and neurology settings, instruct patient to fast for 4 6 hours prior to the drug s injection. In the cardiology setting, administration of glucose-containing food or liquids (e.g., grams) prior to Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection facilitates localization of cardiac ischemia. 2.4 Radiation Dosimetry The estimated human absorbed radiation doses (rem/mci) to a newborn (3.4 kg), 1-year old (9.8 kg), 5-year old (19 kg), 10-year old (32 kg), 15-year old (57 kg), and adult (70 kg) from intravenous administration of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection are shown in Table 1. These estimates were calculated based on human 2 data and using the data published by the International Commission on Radiological Protection 4 for Fludeoxyglucose 18 F. The dosimetry data show that there are slight variations in absorbed radiation dose for various organs in each of the age groups. These dissimilarities in absorbed radiation dose are due to developmental age variations (e.g., organ size, location, and overall metabolic rate for each age group). The identified critical organs (in descending order) across all age groups evaluated are the urinary bladder, heart, pancreas, spleen, and lungs.
8 Table 1. Estimated Absorbed Radiation Doses (rem/mci) After Intravenous Administration of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection a Newborn 1-year old 5-year old 10-year old 15-year old Adult Organ (3.4 kg) (9.8 kg) (19 kg) (32 kg) (57 kg) (70 kg) Bladder wall b Heart wall Pancreas Spleen Lungs Kidneys Ovaries Uterus LLI wall* Liver Gallbladder wall Small intestine ULI wall** Stomach wall Adrenals Testes Red marrow Thymus Thyroid Muscle Bone surface Breast Skin Brain Other tissues a MIRDOSE 2 software was used to calculate the radiation absorbed dose. Assumptions on the biodistribution based on data from Gallagher et al. 1 and Jones et al. 2 b The dynamic bladder model with a uniform voiding frequency of 1.5 hours was used. * LLI = lower large intestine; ** ULI = upper large intestine 2.5 Radiation Safety Drug Handling Use waterproof gloves, effective radiation shielding, and appropriate safety measures when handling Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient, occupational workers, clinical personnel and other persons. Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides. Calculate the final dose from the end of synthesis (EOS) time using proper radioactive decay factors. Assay the final dose in a properly calibrated dose calibrator before administration to the patient [see Description (11.2)]. The dose of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 used in a given patient should be minimized consistent with the objectives of the procedure, and the nature of the radiation detection devices employed. 2.6 Drug Preparation and Administration Calculate the necessary volume to administer based on calibration time and dose. Aseptically withdraw Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection from its container. Inspect Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer the drug if it contains particulate matter or discoloration; dispose of these unacceptable or unused preparations in a safe manner, in compliance with applicable regulations. Use Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection within 12 hours from the EOS. 2.7 Imaging Guidelines Initiate imaging within 40 minutes following Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection administration. Acquire static emission images minutes from the time of injection. 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Multiple-dose glass vial containing GBq ( mci/ml) of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection and 4.5 mg of sodium chloride in citrate buffer (10 ml vial: approximately 5-10 ml volume; 30 ml vial: approximately ml volume) for intravenous administration. 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS None 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Radiation Risks Radiation-emitting products, including Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection, may increase the risk for cancer, especially in pediatric patients. Use the smallest dose necessary for imaging and ensure safe handling to protect the patient and health care worker [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. 5.2 Blood Glucose Abnormalities In the oncology and neurology setting, suboptimal imaging may occur in patients with inadequately regulated blood glucose levels. In these patients, consider medical therapy and laboratory testing to assure at least two days of normoglycemia prior to Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection administration. 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS Hypersensitivity reactions with pruritus, edema and rash have been reported in the postmarketing setting. Have emergency resuscitation equipment and personnel immediately available. 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS The possibility of interactions of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection with other drugs taken by patients undergoing PET imaging has not been studied. 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection. It is also not known whether Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Consider alternative diagnostic tests in a pregnant woman; administer Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection only if clearly needed. 8.3 Nursing Mothers It is not known whether Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is excreted in human milk. Consider alternative diagnostic tests in women who are breast-feeding. Use alternatives to breast feeding (e.g., stored breast milk or infant formula) for at least 10 half-lives of radioactive decay, if Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is administered to a woman who is breast-feeding. 8.4 Pediatric Use The safety and effectiveness of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection in pediatric patients with epilepsy is established on the basis of studies in adult and pediatric patients. In pediatric patients with epilepsy, the recommended dose is 2.6 mci. The optimal dose adjustment on the basis of body size or weight has not been determined. In the oncology or cardiology settings, the safety and effectiveness of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection have not been established in pediatric patients. 11 DESCRIPTION 11.1 Chemical Characteristics Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is a positron emitting radiopharmaceutical that is used for diagnostic purposes in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. The active ingredient 2-deoxy-2-[ 18 F]fluoro-D-glucose has the molecular formula of C6H1118 FO5 with a molecular weight of , and has the following chemical structure: Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is provided as a ready to use sterile, pyrogen free, clear, colorless citrate buffered solution. Each ml contains between to 11.1GBq ( mci) of 2 deoxy-2-[ 18 F]fluoro-D-glucose at the EOS, 4.5 mg of sodium chloride in citrate buffer. The ph of the solution is between 4.5 and 7.5. The solution is packaged in a multiple-dose glass vial and does not contain any preservative Physical Characteristics Fluorine F-18 has a physical half-life of minutes and decays to Oxygen O-18 (stable) by positron decay. The principal photons useful for imaging are the dual 511 kev annihilation gamma photons that are produced and emitted simultaneously in opposite directions when the positron interacts with an electron (Table 2). Table 2. Principal Radiation Emission Data for Fluorine F-18 Radiation/Emission % Per Disintegration Mean Energy Positron(β+) kev Gamma(±)* kev * Produced by positron annihilation From: Kocher, D.C. Radioactive Decay Tables DOE/TIC-I 1026, 89 (1981) The specific gamma ray constant (point source air kerma coefficient) for fluorine F-18 is 5.7 R/hr/mCi (1.35 x 10-6 Gy/hr/kBq) at 1 cm. The half-value layer (HVL) for the 511 kev photons is 4 mm lead (Pb) or 2.9 mm tungsten (W) alloy. The range of attenuation coefficients for this radionuclide as a function of shield thickness is shown in Table 3. For example, the interposition of an 8 mm thickness of Pb or 5.8 mm thickness of (W) alloy, with a coefficient of attenuation of 0.25, will decrease the external radiation by 75%. Table 3. Radiation Attenuation of 511 kev Photons by Lead (Pb) and Tungsten (W) Alloy Shielding Shield Thickness (Pb) mm Shield Thickness (W) Alloy mm Coefficient of Attenuation For use in correcting for physical decay of this radionuclide, the fractions remaining at selected intervals after calibration are shown in Table 4. Table 4. Physical Decay Chart for Fluorine F-18 Minutes Fraction Remaining 0* * calibration time
9 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is a glucose analog that concentrates in cells that rely upon glucose as an energy source, or in cells whose dependence on glucose increases under pathophysiological conditions. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is transported through the cell membrane by facilitative glucose transporter proteins and is phosphorylated within the cell to [18F] FDG-6-phosphate by the enzyme hexokinase. Once phosphorylated it cannot exit until it is dephosphorylated by glucose-6-phosphatase. Therefore, within a given tissue or pathophysiological process, the retention and clearance of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 reflect a balance involving glucose transporter, hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase activities. When allowance is made for the kinetic differences between glucose and Fludeoxyglucose F-18 transport and phosphorylation (expressed as the ''lumped constant'' ratio), Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is used to assess glucose metabolism. In comparison to background activity of the specific organ or tissue type, regions of decreased or absent uptake of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 reflect the decrease or absence of glucose metabolism. Regions of increased uptake of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 reflect greater than normal rates of glucose metabolism Pharmacodynamics Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is rapidly distributed to all organs of the body after intravenous administration. After background clearance of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection, optimal PET imaging is generally achieved between 30 to 40 minutes after administration. In cancer, the cells are generally characterized by enhanced glucose metabolism partially due to (1) an increase in activity of glucose transporters, (2) an increased rate of phosphorylation activity, (3) a reduction of phosphatase activity, or (4) a dynamic alteration in the balance among all these processes. However, glucose metabolism of cancer as reflected by Fludeoxyglucose F-18 accumulation shows considerable variability. Depending on tumor type, stage, and location, Fludeoxyglucose F-18 accumulation may be increased, normal, or decreased. Also, inflammatory cells can have the same variability of uptake of Fludeoxyglucose F-18. In the heart, under normal aerobic conditions, the myocardium meets the bulk of its energy requirements by oxidizing free fatty acids. Most of the exogenous glucose taken up by the myocyte is converted into glycogen. However, under ischemic conditions, the oxidation of free fatty acids decreases, exogenous glucose becomes the preferred myocardial substrate, glycolysis is stimulated, and glucose taken up by the myocyte is metabolized immediately instead of being converted into glycogen. Under these conditions, phosphorylated Fludeoxyglucose F-18 accumulates in the myocyte and can be detected with PET imaging. In the brain, cells normally rely on aerobic metabolism. In epilepsy, the glucose metabolism varies. Generally, during a seizure, glucose metabolism increases. Interictally, the seizure focus tends to be hypometabolic Pharmacokinetics Distribution: In four healthy male volunteers, receiving an intravenous administration of 30 seconds in duration, the arterial blood level profile for Fludeoxyglucose F-18 decayed triexponentially. The effective half-life ranges of the three phases were minutes, minutes with a mean and standard deviation (STD) of 11.6 (±) 1.1 min, and minutes with a mean and STD of 88 (±) 4 min. Plasma protein binding of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 has not been studied. Metabolism: Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is transported into cells and phosphorylated to [18F]-FDG-6phosphate at a rate proportional to the rate of glucose utilization within that tissue. [F-18]-FDG6-phosphate presumably is metabolized to 2-deoxy-2-[F-18]fluoro-6-phospho-D-mannose([F18]FDM-6-phosphate). Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection may contain several impurities (e.g., 2-deoxy-2-chloro-Dglucose (ClDG)). Biodistribution and metabolism of ClDG are presumed to be similar to Fludeoxyglucose F-18 and would be expected to result in intracellular formation of 2-deoxy-2chloro-6-phospho-D-glucose (ClDG-6-phosphate) and 2-deoxy-2-chloro-6-phospho-D-mannose (ClDM-6-phosphate). The phosphorylated deoxyglucose compounds are dephosphorylated and the resulting compounds (FDG, FDM, ClDG, and ClDM) presumably leave cells by passive diffusion. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 and related compounds are cleared from non-cardiac tissues within 3 to 24 hours after administration. Clearance from the cardiac tissue may require more than 96 hours. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 that is not involved in glucose metabolism in any tissue is then excreted in the urine. Elimination: Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is cleared from most tissues within 24 hours and can be eliminated from the body unchanged in the urine. Three elimination phases have been identified in the reviewed literature. Within 33 minutes, a mean of 3.9% of the administrated radioactive dose was measured in the urine. The amount of radiation exposure of the urinary bladder at two hours post-administration suggests that 20.6% (mean) of the radioactive dose was present in the bladder. Special Populations: The pharmacokinetics of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection have not been studied in renallyimpaired, hepatically impaired or pediatric patients. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 is eliminated through the renal system. Avoid excessive radiation exposure to this organ system and adjacent tissues. The effects of fasting, varying blood sugar levels, conditions of glucose intolerance, and diabetes mellitus on Fludeoxyglucose F-18 distribution in humans have not been ascertained [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility. 14 CLINICAL STUDIES 14.1 Oncology The efficacy of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection in positron emission tomography cancer imaging was demonstrated in 16 independent studies. These studies prospectively evaluated the use of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 in patients with suspected or known malignancies, including nonsmall cell lung cancer, colo-rectal, pancreatic, breast, thyroid, melanoma, Hodgkin's and nonhodgkin's lymphoma, and various types of metastatic cancers to lung, liver, bone, and axillary nodes. All these studies had at least 50 patients and used pathology as a standard of truth. The Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection doses in the studies ranged from 200 MBq to 740 MBq with a median and mean dose of 370 MBq. In the studies, the diagnostic performance of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection varied with the type of cancer, size of cancer, and other clinical conditions. False negative and false positive scans were observed. Negative Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection PET scans do not exclude the diagnosis of cancer. Positive Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection PET scans cannot replace pathology to establish a diagnosis of cancer. Non-malignant conditions such as fungal infections, inflammatory processes and benign tumors have patterns of increased glucose metabolism that may give rise to false-positive scans. The efficacy of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection PET imaging in cancer screening was not studied Cardiology The efficacy of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection for cardiac use was demonstrated in ten independent, prospective studies of patients with coronary artery disease and chronic left ventricular systolic dysfunction who were scheduled to undergo coronary revascularization. Before revascularization, patients underwent PET imaging with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection ( MBq, 2 10 mci) and perfusion imaging with other diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals. Doses of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection ranged from MBq (2-10 mci). Segmental, left ventricular, wall-motion assessments of asynergic areas made before revascularization were compared in a blinded manner to assessments made after successful revascularization to identify myocardial segments with functional recovery. Left ventricular myocardial segments were predicted to have reversible loss of systolic function if they showed Fludeoxyglucose F-18 accumulation and reduced perfusion (i.e., flowmetabolism mismatch). Conversely, myocardial segments were predicted to have irreversible loss of systolic function if they showed reductions in both Fludeoxyglucose F-18 accumulation and perfusion (i.e., matched defects). Findings of flow-metabolism mismatch in a myocardial segment may suggest that successful revascularization will restore myocardial function in that segment. However, false-positive tests occur regularly, and the decision to have a patient undergo revascularization should not be based on PET findings alone. Similarly, findings of a matched defect in a myocardial segment may suggest that myocardial function will not recover in that segment, even if it is successfully revascularized. However, false-negative tests occur regularly, and the decision to recommend against coronary revascularization, or to recommend a cardiac transplant, should not be based on PET findings alone. The reversibility of segmental dysfunction as predicted with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 PET imaging depends on successful coronary revascularization. Therefore, in patients with a low likelihood of successful revascularization, the diagnostic usefulness of PET imaging with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is more limited Neurology In a prospective, open label trial, Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection was evaluated in 86 patients with epilepsy. Each patient received a dose of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection in the range of MBq (5-10 mci). The mean age was 16.4 years (range: 4 months - 58 years; of these, 42 patients were less than 12 years and 16 patients were less than 2 years old). Patients had a known diagnosis of complex partial epilepsy and were under evaluation for surgical treatment of their seizure disorder. Seizure foci had been previously identified on ictal EEGs and sphenoidal EEGs. Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection PET imaging confirmed previous diagnostic findings in 16% (14/87) of the patients; in 34% (30/87) of the patients, Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection PET images provided new findings. In 32% (27/87), imaging with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection was inconclusive. The impact of these imaging findings on clinical outcomes is not known. Several other studies comparing imaging with Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection results to subsphenoidal EEG, MRI and/or surgical findings supported the concept that the degree of hypometabolism corresponds to areas of confirmed epileptogenic foci. The safety and effectiveness of Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection to distinguish idiopathic epileptogenic foci from tumors or other brain lesions that may cause seizures have not been established. 15 REFERENCES 1. Gallagher B.M., Ansari A., Atkins H., Casella V., Christman D.R., Fowler J.S., Ido T., MacGregor R.R., Som P., Wan C.N., Wolf A.P., Kuhl D.E., and Reivich M. Radiopharmaceuticals XXVII. 18F-labeled 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose as a radiopharmaceutical for measuring regional myocardial glucose metabolism in vivo: tissue distribution and imaging studies in animals, J Nucl Med, 1977; 18, Jones S.C., Alavi, A., Christman D., Montanez, I., Wolf, A.P., and Reivich M. The radiation dosimetry of 2 [F-18] fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose in man, J Nucl Med, 1982; 23, Kocher, D.C. Radioactive Decay Tables: A handbook of decay data for application to radiation dosimetry and radiological assessments, 1981, DOE/TIC-I 1026, ICRP Publication 53, Volume 18, No. l-4,1987, pages HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection is supplied in a multi-dose, capped 10 ml or 30 ml glass vial containing between GBq/mL ( mci/ml), of no carrier added 2-deoxy-2-[F18] fluoro-d-glucose, at end of synthesis, in approximately 5-10 ml volume for the 10 ml vial and approximately ml volume for the 30 ml vial. The contents of each vial are sterile, pyrogen-free and preservative-free. NDC (10 ml) NDC (30 ml) Receipt, transfer, handling, possession, or use of this product is subject to the radioactive material regulations and licensing requirements for the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, Agreement States or Licensing States as appropriate. Store the Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection vial upright in a lead or tungsten alloy shielded container at 25 C (77 F); excursions permitted to C (59-86 F). The expiration date and time are provided on the container label. Use Fludeoxyglucose F-18 Injection within 12 hours from the EOS time. 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Instruct patients in procedures that increase renal clearance of radioactivity. Encourage patients to: drink water or other fluids (as tolerated) in the 4 hours before their PET study. void as soon as the imaging study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour. Manufactured by: Cardinal Health 414, LLC 7000 Cardinal Place Dublin, OH Distributed by: Cardinal Health 414, LLC 7000 Cardinal Place Dublin, OH NPS-PI-0003 ver 1.0
10
11
12 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP. Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: INDICATIONS AND USAGE Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP is a radioactive diagnostic agent for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) indicated for diagnostic PET imaging of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate myocardial perfusion in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Rest Imaging Study (2.1): Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP from its container and administer mci ( GBq) as a bolus through a catheter inserted into a large peripheral vein. Start imaging 3 minutes after the injection and acquire images for a total of minutes. Stress Imaging Study (2.2): If a rest imaging study is performed, begin the stress imaging study 40 minutes or more after the first Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP to allow sufficient isotope decay. Administer a pharmacologic stress-inducing drug in accordance with its labeling. Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP from its container and administer mci ( GBq) of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP as a bolus at 8 minutes after the administration of the pharmacologic stress-inducing drug. Start imaging 3 minutes after the Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP and acquire images for a total of minutes. Patient Preparation (2.3): To increase renal clearance of radioactivity and to minimize radiation dose to the bladder, hydrate the patient before the procedure and encourage voiding as soon as each image acquisition is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour. FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS* 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Rest Imaging Study 2.2 Stress Imaging Study 2.3 Patient Preparation 2.4 Radiation Dosimetry 2.5 Drug Handling 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Radiation Risks 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy 8.3 Nursing Mothers 8.4 Pediatric Use DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Glass vial containing GBq ( mci/ml) of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP in aqueous 0.9 % sodium chloride solution (approximately 8 ml to 10 ml volume) (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP may increase the risk of cancer. Use the smallest dose necessary for imaging and ensure safe handling to protect the patient and health care worker (5) ADVERSE REACTIONS No adverse reactions have been reported for Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP based on a review of the published literature, publicly available reference sources, and adverse drug reaction reporting system (6). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Cardinal Health at or FDA at FDA-1088 or USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Alternatives to breastfeeding (e.g. using stored breast milk or infant formula) should be used for 2 hours (>10 half-lives of radioactive decay for N-13 isotope) after administration of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP (8.3). The safety and effectiveness of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP has been established in pediatric patients (8.4). See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION 11 DESCRIPTION 11.1 Chemical Characteristics 11.2 Physical Characteristics 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action 12.2 Pharmacodynamics 12.3 Pharmacokinetics 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility 14 CLINICAL STUDIES 15 REFERENCES 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION 17.1 Pre-study Hydration 17.2 Post-study Voiding 17.3 Post-study Breastfeeding Avoidance *Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed Revised: 12/2015 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP is indicated for diagnostic Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate myocardial perfusion in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease. 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Rest Imaging Study Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP from its container and administer mci ( GBq) as a bolus through a catheter inserted into a large peripheral vein. Start imaging 3 minutes after the injection and acquire images for a total of minutes. 2.2 Stress Imaging Study If a rest imaging study is performed, begin the stress imaging study 40 minutes or more after the first Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP to allow sufficient isotope decay. Administer a pharmacologic stress-inducing drug in accordance with its labeling. Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP from its container and administer mci ( GBq) of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP as a bolus at 8 minutes after the administration of the pharmacologic stress-inducing drug. Start imaging 3 minutes after the Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP and acquire images for a total of minutes. 2.3 Patient Preparation To increase renal clearance of radioactivity and to minimize radiation dose to the bladder, ensure that the patient is well hydrated before the procedure and encourage voiding as soon as a study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour. 2.4 Radiation Dosimetry The converted radiation absorbed doses in rem/mci are shown in Table 1. These estimates are calculated from the Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiation Protection. 1 Table 1: N-13 Absorbed Radiation Dose Per Unit Activity (rem/mci) for Adults and Pediatric Groups Organ Adult 15-year old 10-year old 5-year old 1-year old Adrenals Bladder wall Bone surfaces Brain Breast Stomach wall Small intestine Table 1: N-13 Absorbed Radiation Dose Per Unit Activity (rem/mci) for Adults and Pediatric Groups Organ Adult 15-year old 10-year old 5-year old 1-year old *ULI **LLI Heart Kidneys Liver Lungs Ovaries Pancreas Red marrow Spleen Testes Thyroid Uterus Other tissues * Upper large intestine; ** Lower large intestine 2.5 Drug Handling Inspect Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP containing particulate matter or discoloration; dispose of these unacceptable or unused preparations in a safe manner, in compliance with applicable regulations. Wear waterproof gloves and effective shielding when handling Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP. Use aseptic technique to maintain sterility during all operations involved in the manipulation and administration of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP. The contents of each vial are sterile and non-pyrogenic. Use appropriate safety measures, including shielding, consistent with proper patient management to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient, occupational workers, clinical personnel, and other persons. Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides. Before administration of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP, assay the dose in a properly calibrated dose calibrator. 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Glass vial (10 ml) containing GBq ( mci/ml) of Ammonia N-13 Injection, USP in aqueous 0.9 % sodium chloride solution (approximately 8 ml to 10 ml volume) that is suitable for intravenous administration. 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS None
Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer
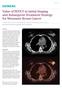 Case Study Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer By Dustin Osborne, PhD, and Yong Bradley, MD, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA Data
Case Study Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer By Dustin Osborne, PhD, and Yong Bradley, MD, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA Data
Contrast Agents and Radiopharmaceuticals 2017
 Contrast Agents and Radiopharmaceuticals 207 Covered: Code Code Description Allow with Code(s) Code Description Max Units A464 Radiopharmaceutical, diagnostic, not otherwise classified n/a Invoice Req'd
Contrast Agents and Radiopharmaceuticals 207 Covered: Code Code Description Allow with Code(s) Code Description Max Units A464 Radiopharmaceutical, diagnostic, not otherwise classified n/a Invoice Req'd
GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION
 511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
FP/1-61//- p-o37 A mb. Precision Nuclear, LLC. July 7, 2011
 211 JUL Ili A II 5b Precision Nuclear, LLC July 7, 211 Amendment to Citizen Petition docket no. FDA-211-P-337-1/CP filed on 5/6/211 I, Jon L. McReynolds, PharmD, representing Precision Nuclear, LLC submit
211 JUL Ili A II 5b Precision Nuclear, LLC July 7, 211 Amendment to Citizen Petition docket no. FDA-211-P-337-1/CP filed on 5/6/211 I, Jon L. McReynolds, PharmD, representing Precision Nuclear, LLC submit
Page 1 of CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AXUMIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AXUMIN. AXUMIN (fluciclovine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AXUMIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AXUMIN. AXUMIN (fluciclovine
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
GLUCEPTATE. Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION
 27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging
 Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging for Prostate Cancer Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* ( 18 F NaF) PET/CT Imaging of Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer About Prostate Cancer According to the
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging for Prostate Cancer Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* ( 18 F NaF) PET/CT Imaging of Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer About Prostate Cancer According to the
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
 1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
 BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS L/4739/0 1 CHOLETEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin For Diagnostic Use DESCRIPTION Each reaction vial contains a nonradioactive, sterile, nonpyrogenic mixture
To report suspected adverse reactions to Axumin, call AXUMIN1 ( ) or contact FDA at FDA-1088 or
 An Axumin scan can detect and localize recurrent prostate cancer Axumin is an FDA-approved diagnostic imaging agent, also known as a tracer, which may help your physician determine if and where your prostate
An Axumin scan can detect and localize recurrent prostate cancer Axumin is an FDA-approved diagnostic imaging agent, also known as a tracer, which may help your physician determine if and where your prostate
R: March, E D T P A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC. For Oral Use DESCRIPTION
 DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES, USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules, USP are color-coded capsules containing sodium iodide I 131 for diagnostic use by oral administration.
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC. For Oral Use DESCRIPTION
 DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution is an aqueous solution of sodium iodide I-131 for diagnostic use by oral administration. The
DRAXIMAGE SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION USP DIAGNOSTIC For Oral Use DESCRIPTION Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution is an aqueous solution of sodium iodide I-131 for diagnostic use by oral administration. The
TABLE 1 Principal Radiation Emission Data Radiation Mean % per Disintegration Mean Energy (kev) Gamma
 KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
KIT FOR THE PREPARATION OF TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEBROFENIN - mebrofenin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution ---------- Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Mebrofenin DESCRIPTION Each multidose
DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection. For Intravenous Use DIAGNOSTIC FOR SKELETAL IMAGING
 TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEDRONATE - medronic acid injection, powder, for solution Jubilant DraxImage Inc ---------- DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection For Intravenous
TECHNETIUM TC 99M MEDRONATE - medronic acid injection, powder, for solution Jubilant DraxImage Inc ---------- DRAXIMAGE MDP-25 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Medronate Injection For Intravenous
NUCLEAR MEDICINE APC TASK FORCE
 NUCLEAR MEDICINE APC TASK FORCE American College of Nuclear Physicians American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Council on Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals, Inc. Academy of Molecular Imaging Society
NUCLEAR MEDICINE APC TASK FORCE American College of Nuclear Physicians American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Council on Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals, Inc. Academy of Molecular Imaging Society
RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS AND DRUGS ELIGIBLE FOR CONTINUED SEPARATE MEDICARE PAYMENT ( 2 TO 3 Year Transitional Period )
 NUCLEAR MEDICINE APC TASK FORCE American College of Nuclear Physicians American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Council on Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals, Inc. Academy of Molecular Imaging Society
NUCLEAR MEDICINE APC TASK FORCE American College of Nuclear Physicians American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Council on Radionuclides and Radiopharmaceuticals, Inc. Academy of Molecular Imaging Society
SUGGESTED PRESCRIBED DOSAGE LIST
 approved and issued by a noted Authorized User on your Materials License. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Metabolism Brain Perfusion Cisternography Ventricular Shunt 18 F-FDG 10-20 mci (370 740 MBq) 99m Tc
approved and issued by a noted Authorized User on your Materials License. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Brain Metabolism Brain Perfusion Cisternography Ventricular Shunt 18 F-FDG 10-20 mci (370 740 MBq) 99m Tc
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography
 Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan SULFUR COLLOID Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan SULFUR COLLOID Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
1/13
 KIT FOR THE PREPARTION OF TECHNETIUM TC99M SULFUR COLLOID - technetium tc 99m sulfur colloid Pharmalucence Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
KIT FOR THE PREPARTION OF TECHNETIUM TC99M SULFUR COLLOID - technetium tc 99m sulfur colloid Pharmalucence Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005
 Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005 This FDG Core SPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature dated from more than 10 years. Then
Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005 This FDG Core SPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature dated from more than 10 years. Then
POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET)
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. for. BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation
 February 9, 2010 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS for BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT BRIDATEC 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION N-(3-bromo-2,4,6-trimethylphenylcarbamoyl
February 9, 2010 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS for BRIDATEC, kit for radiopharmaceutical preparation 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT BRIDATEC 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION N-(3-bromo-2,4,6-trimethylphenylcarbamoyl
OTHER NON-CARDIAC USES OF Tc-99m CARDIAC AGENTS Tc-99m Sestamibi for parathyroid imaging, breast tumor imaging, and imaging of other malignant tumors.
 DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
Official Listing of Radioactive Materials Approved for the Four Groups of Diagnostic Uses as Defined in 15A NCAC
 Division of Environmental Health Radiation Protection Section Radioactive Materials Branch PUBLICATION 97-01 Official Listing of Radioactive Materials Approved for the Four Groups of Diagnostic Uses as
Division of Environmental Health Radiation Protection Section Radioactive Materials Branch PUBLICATION 97-01 Official Listing of Radioactive Materials Approved for the Four Groups of Diagnostic Uses as
AdreView. Iobenguane I 123 Injection
 AdreView Iobenguane I 123 Injection HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AdreView safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
AdreView Iobenguane I 123 Injection HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AdreView safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
Ultra-TechneKow FM. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Ultra-TechneKow FM Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Ultra-TechneKow FM Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Table 1 Principal Radiation Emission Data * Disintegration. Gamma Ka 1 X-ray
 DESCRIPTIONGeneralGlofil-125 (Sodium Iothalamate I-125 Injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic aqueous injection containing approximately 1 mg sodium iothalamate per ml, and 0.9 percent benzyl alcohol as
DESCRIPTIONGeneralGlofil-125 (Sodium Iothalamate I-125 Injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic aqueous injection containing approximately 1 mg sodium iothalamate per ml, and 0.9 percent benzyl alcohol as
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes
 Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
M A A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March 1998 27248 0001E m TM M A A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain
R: March 1998 27248 0001E m TM M A A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Albumin Aggregated Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain
1. OVERVIEW 2. RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL UTILIZED
 1. OVERVIEW F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: a) Oncology: For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist
1. OVERVIEW F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: a) Oncology: For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate)
 Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Ultra-TechneKow DTE. Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Ultra-TechneKow DTE Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
Ultra-TechneKow DTE Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table of
NEURACEQ (florbetaben F 18 injection), for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEURACEQ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEURACEQ. NEURACEQ (florbetaben
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEURACEQ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEURACEQ. NEURACEQ (florbetaben
General Nuclear Medicine
 General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 PET Scanning: Oncologic Applications Page 1 of 88 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scanning: Oncologic Applications
PET Scanning: Oncologic Applications Page 1 of 88 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scanning: Oncologic Applications
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RADIOGENIX SYSTEM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RADIOGENIX TM SYSTEM.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RADIOGENIX SYSTEM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RADIOGENIX TM SYSTEM.
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PROSTATE CANCER STUDY (In-111-Capromab Pendetide [ProstaScint ])
![Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PROSTATE CANCER STUDY (In-111-Capromab Pendetide [ProstaScint ]) Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PROSTATE CANCER STUDY (In-111-Capromab Pendetide [ProstaScint ])](/thumbs/81/82771892.jpg) Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PROSTATE CANCER STUDY (In-111-Capromab Pendetide [ProstaScint ]) Overview Indications The Prostate Cancer Study with an indium-111 labeled murine
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PROSTATE CANCER STUDY (In-111-Capromab Pendetide [ProstaScint ]) Overview Indications The Prostate Cancer Study with an indium-111 labeled murine
Recent initiatives of the FANC. Michel Biernaux Health Protection Service Health and Environment Department
 Recent initiatives of the FANC Michel Biernaux Michel.biernaux@fanc.fgov.be Health Protection Service Health and Environment Department Reminder objectives of the national survey : 1.Review the average
Recent initiatives of the FANC Michel Biernaux Michel.biernaux@fanc.fgov.be Health Protection Service Health and Environment Department Reminder objectives of the national survey : 1.Review the average
Dose Calibration for DaTscan
 GE Healthcare Dose Calibration for DaTscan Please review the simple steps below to learn how to properly calibrate your dose of DaTscan. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reading DaTscan in the Dose Calibrator 1. Place
GE Healthcare Dose Calibration for DaTscan Please review the simple steps below to learn how to properly calibrate your dose of DaTscan. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reading DaTscan in the Dose Calibrator 1. Place
2017 St. Luke's-Roosevelt Nuclear Medicine Department Procedure Catalog. meds
 2017 St. Luke's-Roosevelt Nuclear Medicine Department Procedure Catalog Procedure Name Patient Preparation Cardiac Studies Stress Myocardial Perfusion Study Gated pool study (MUGA) Myocardial Cell Damage
2017 St. Luke's-Roosevelt Nuclear Medicine Department Procedure Catalog Procedure Name Patient Preparation Cardiac Studies Stress Myocardial Perfusion Study Gated pool study (MUGA) Myocardial Cell Damage
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH
 INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS, ACADEMY OF SCIENCE OF UZBEKISTAN STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH 42-006-2008 Description and Composition
INSTITUTE OF NUCLEAR PHYSICS, ACADEMY OF SCIENCE OF UZBEKISTAN STATE ENTERPRISE «RADIOPREPARAT» Generator of 99 Mo/ 99m Tc TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION AND INSTRUCTIONS ТSH 42-006-2008 Description and Composition
Summary of Product Characteristics
 Summary of Product Characteristics Sodium Phosphate ( 32 P) 18.5-185 MBq/ml Injection 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sodium Phosphate ( 32 P) 18.5-185 MBq/ml Injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE
Summary of Product Characteristics Sodium Phosphate ( 32 P) 18.5-185 MBq/ml Injection 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Sodium Phosphate ( 32 P) 18.5-185 MBq/ml Injection 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE
Gastrointestinal tract
 Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
Gastrointestinal tract Colloidal liver-spleen imaging Presented by: Jehad Felemban Introduction: To obtain better anatomic display of liver and spleen architecture, we use (CT Ultrasound). (Radionuclide
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION THERAPEUTIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM IODIDE I 131 SOLUTION THERAPEUTIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Sestamibi Injection safely and effectively. See full
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Sestamibi Injection safely and effectively. See full
Cardiovascular nuclear imaging employs non-invasive techniques to assess alterations in coronary artery flow, and ventricular function.
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIOVASCULAR NUCLEAR MEDICINE -MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING -MUGA Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 9 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4 Codes:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIOVASCULAR NUCLEAR MEDICINE -MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING -MUGA Original Date: October 2015 Page 1 of 9 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4 Codes:
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST
 HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
Description MRI, TMJ C T Head Without Contrast C T Head With Contrast C T Head Without & With Contrast
 s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F)
 Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) This fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) Core SmPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature
Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) This fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) Core SmPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Vial 1 (reaction vial with lyophilized powder) containing 40 mcg of dotatate (3)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NETSPOT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NETSPOT. NETSPOT (kit for the
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NETSPOT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NETSPOT. NETSPOT (kit for the
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS. MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use
 BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION Macrotec is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized preparation of albumin
BRACCO DIAGNOSTICS MAGROTEC Kit for the Preparation of Technetium To 99m Albumin Aggregated Diagnostic For Intravenous Use DESCRIPTION Macrotec is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, lyophilized preparation of albumin
Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc99m Sestamibi Injection
 Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc99m Sestamibi Injection FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Kit for the Preparation
Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc99m Sestamibi Injection FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Kit for the Preparation
PHYTACIS. Kit for the preparation of technetium [ 99m Tc] phytate injection USER PACKAGE LEAFLET
![PHYTACIS. Kit for the preparation of technetium [ 99m Tc] phytate injection USER PACKAGE LEAFLET PHYTACIS. Kit for the preparation of technetium [ 99m Tc] phytate injection USER PACKAGE LEAFLET](/thumbs/92/110393678.jpg) PHYTACIS Kit for the preparation of technetium [ 99m Tc] phytate injection USER PACKAGE LEAFLET CIS bio international, member of IBA Molecular group of companies T1800nH (T1800- T1817) 01/2017 IDENTIFICATION
PHYTACIS Kit for the preparation of technetium [ 99m Tc] phytate injection USER PACKAGE LEAFLET CIS bio international, member of IBA Molecular group of companies T1800nH (T1800- T1817) 01/2017 IDENTIFICATION
SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES THERAPEUTIC 01/ Page 1 of 11
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES THERAPEUTIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM IODIDE I 131 CAPSULES THERAPEUTIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
Nuclear Medicine in Oncology
 Radiopharmaceuticals Nuclear Medicine in Oncology Practice Pharmaceutical Radionuc lide Function Tumor type Diphosphonates Tc-99m Osteoblast Bone tumor & metast. Ga-citrate Ga-67 Fe-analogue Bronchogenous
Radiopharmaceuticals Nuclear Medicine in Oncology Practice Pharmaceutical Radionuc lide Function Tumor type Diphosphonates Tc-99m Osteoblast Bone tumor & metast. Ga-citrate Ga-67 Fe-analogue Bronchogenous
Department of Nuclear Medicine with Positron Emission Tomography
 (PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
(PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates
![Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates](/thumbs/87/95592963.jpg) Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Molecular Imaging Branch, NIMH Bldg. 1 Rm. B3-10 September 6 th, 2006 The
Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the β-amyloid radioligand [ 11 C]MeS-IMPY in non-human primates Molecular Imaging Branch, NIMH Bldg. 1 Rm. B3-10 September 6 th, 2006 The
https://rm2.scinet.fda.gov/druglabel/rs/spl/by-id/207036/ html 1/12
 NEURACEQ - florbetaben f-18 injection, solution Piramal Imaging, SA ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEURACEQ safely and
NEURACEQ - florbetaben f-18 injection, solution Piramal Imaging, SA ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEURACEQ safely and
Cardiovascular nuclear imaging employs non-invasive techniques to assess alterations in coronary artery flow, and ventricular function.
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIOVASCULAR NUCLEAR MEDICINE -MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING -MUGA CPT4 Codes: Refer to pages 6-9 LCD ID Number: L33960 J 15 = KY, OH Responsible
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CARDIOVASCULAR NUCLEAR MEDICINE -MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING -MUGA CPT4 Codes: Refer to pages 6-9 LCD ID Number: L33960 J 15 = KY, OH Responsible
Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer
 Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Legal Disclaimer These materials were prepared in good faith by MITA as a service to the profession and are believed to be reliable based on current scientific literature.
Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Legal Disclaimer These materials were prepared in good faith by MITA as a service to the profession and are believed to be reliable based on current scientific literature.
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
NUCLEAR MEDICINE IN VIVO
 PREAMBLE SPECIIC ELEMENTS or acility ee Component ( fee) A. Preparing the patient for the procedure. B. Performing the diagnostic procedure(s). C. Making arrangements for any appropriate follow-up care.
PREAMBLE SPECIIC ELEMENTS or acility ee Component ( fee) A. Preparing the patient for the procedure. B. Performing the diagnostic procedure(s). C. Making arrangements for any appropriate follow-up care.
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013
 Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Vizamyl Flutemetamol F 18 Injection
 Vizamyl Flutemetamol F 18 Injection HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIZAMYL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
Vizamyl Flutemetamol F 18 Injection HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIZAMYL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
PUBLIC ASSESSMENT REPORT Scientific Discussion
 Direction de l Evaluation des Médicaments et des Produits Biologiques PUBLIC ASSESSMENT REPORT Scientific Discussion STAMICIS Kit for preparation of Technetium ( 99m Tc), Sestamibi injection [Tetrakis(2-methoxy-2-methylpropyl-1
Direction de l Evaluation des Médicaments et des Produits Biologiques PUBLIC ASSESSMENT REPORT Scientific Discussion STAMICIS Kit for preparation of Technetium ( 99m Tc), Sestamibi injection [Tetrakis(2-methoxy-2-methylpropyl-1
Radiopharmacy. Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL. CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı
 Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
(angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion
 ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
HIP RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LISTS
 EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey
 Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey A. M. Bomben, C. A. Chiliutti Autoridad Regulatoria
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey A. M. Bomben, C. A. Chiliutti Autoridad Regulatoria
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Anatomy of the liver Liver scintigraphy The labelled colloid (200 MBq 99mTc-Fyton) is phagocyted by the Kuppfer-cells
Nuclear medicine studies of the digestiv system Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine Anatomy of the liver Liver scintigraphy The labelled colloid (200 MBq 99mTc-Fyton) is phagocyted by the Kuppfer-cells
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA)
 CMR Group of Companies info@isotope-cmr.com www.isotope-cmr.com SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PENTATECH lyophilized powder for injection (DTPA) 2. QUALITATIVE
CMR Group of Companies info@isotope-cmr.com www.isotope-cmr.com SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PENTATECH lyophilized powder for injection (DTPA) 2. QUALITATIVE
TECHNESCAN SESTAMIBI NAME OF THE MEDICINE DESCRIPTION. Kit for the preparation of Technetium [ 99m Tc] Sestamibi Injection
![TECHNESCAN SESTAMIBI NAME OF THE MEDICINE DESCRIPTION. Kit for the preparation of Technetium [ 99m Tc] Sestamibi Injection TECHNESCAN SESTAMIBI NAME OF THE MEDICINE DESCRIPTION. Kit for the preparation of Technetium [ 99m Tc] Sestamibi Injection](/thumbs/74/70410941.jpg) TECHNESCAN SESTAMIBI Kit for the preparation of Technetium [ 99m Tc] Sestamibi Injection NAME OF THE MEDICINE Tetrakis (2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile) copper (I) tetrafluoroborate. The abbreviated notation
TECHNESCAN SESTAMIBI Kit for the preparation of Technetium [ 99m Tc] Sestamibi Injection NAME OF THE MEDICINE Tetrakis (2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile) copper (I) tetrafluoroborate. The abbreviated notation
VIII. 9. FDG-PET for Diagnosis of an Advanced Jejunal Adenocarcinoma with Distant Metastases, Compared with Gallium Scintigraphy
 CYRIC Annual Report 2003 VIII. 9. FDG-PET for Diagnosis of an Advanced Jejunal Adenocarcinoma with Distant Metastases, Compared with Gallium Scintigraphy Yamaura G., Yoshioka T., Yamaguchi K. *, Fukuda
CYRIC Annual Report 2003 VIII. 9. FDG-PET for Diagnosis of an Advanced Jejunal Adenocarcinoma with Distant Metastases, Compared with Gallium Scintigraphy Yamaura G., Yoshioka T., Yamaguchi K. *, Fukuda
ELSPAR (asparaginase) For injection, intravenous or intramuscular Initial U.S. Approval: 1978
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Elspar safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Elspar. ELSPAR (asparaginase)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Elspar safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Elspar. ELSPAR (asparaginase)
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING
 RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
CanTrace PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. Parenteral Solution, up to 1.4 GBq/mL (38.2 mci/ml) Diagnostic Radiopharmaceutical
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH CanTrace 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18 F-FDG) Parenteral Solution, up to 1.4 GBq/mL (38.2 mci/ml) Diagnostic Radiopharmaceutical IPET Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Suite 880, 1090 West Georgia,
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH CanTrace 18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18 F-FDG) Parenteral Solution, up to 1.4 GBq/mL (38.2 mci/ml) Diagnostic Radiopharmaceutical IPET Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Suite 880, 1090 West Georgia,
Click here for Link to References: CMS Website HOPPS CY 2018 Final Rule. CMS Website HOPPS CY2018 Final Rule Updated November 2017.
 Final Compared to 3Q 2017 Rates Medicare Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System HOPPS () Nuclear Cardiology Procedures, Radiopharmaceuticals, and Drugs Click here for Link to References: CMS Website
Final Compared to 3Q 2017 Rates Medicare Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System HOPPS () Nuclear Cardiology Procedures, Radiopharmaceuticals, and Drugs Click here for Link to References: CMS Website
An investigation of the effect of ionising radiation on nurses and their patients during dialysis
 International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy
 APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected
APPROVED BY: Director of Radiology Page 1 of 6 Tc-99m Sestamibi/Tetrofosmin Stress-Rest Myocardial Primary Indications: Evaluation of myocardial perfusion and viability in patients with known or suspected
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses)
 weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
weighing risks against benefits ALARA principle appropriate activities (radiopharmaceutical doses) based on EANM references adequate appointment method (patient booking system) Appropriate activities (doses)
Amira K. Brown, Ph.D. Molecular Imaging Branch, NIMH Bldg. 1 Rm. B3-10
 Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mglur5) radioligand [ 18 F]SP203 in nonhuman primates Amira K. Brown, Ph.D. Molecular Imaging
Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry estimates for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mglur5) radioligand [ 18 F]SP203 in nonhuman primates Amira K. Brown, Ph.D. Molecular Imaging
Your guide to NETSPOT
 Your guide to NETSPOT A tool to help your doctors diagnose and plan the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) NETSPOT, after radiolabeling with Ga 68, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for
Your guide to NETSPOT A tool to help your doctors diagnose and plan the treatment of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) NETSPOT, after radiolabeling with Ga 68, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for
JUBILANT DRAXIMAGE IS LEADING THE WAY IN FUNCTIONAL LUNG IMAGING
 JUBILANT DRAXIMAGE IS LEADING THE WAY IN FUNCTIONAL LUNG IMAGING DRAXIMAGE DTPA & DRAXIMAGE MAA together provide you: Flexibility of Use For use with Planar, SPECT, and low-dose SPECT/CT imaging 1 For
JUBILANT DRAXIMAGE IS LEADING THE WAY IN FUNCTIONAL LUNG IMAGING DRAXIMAGE DTPA & DRAXIMAGE MAA together provide you: Flexibility of Use For use with Planar, SPECT, and low-dose SPECT/CT imaging 1 For
Deleted Effective Beginning of Calendar Year Not Paid under Outpatient PPS Not Paid Under OPPS or any other Medicare payment system
 FINAL 2010 Compared to FINAL 2011 Rates Medicare Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System HOPPS (APC) Nuclear Medicine Procedures, Radiopharmaceuticals, and Drugs CMS Website HOPPS CY2011 FINAL Rule
FINAL 2010 Compared to FINAL 2011 Rates Medicare Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System HOPPS (APC) Nuclear Medicine Procedures, Radiopharmaceuticals, and Drugs CMS Website HOPPS CY2011 FINAL Rule
Nuclear Medicine and PET. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Important Safety Information for Feraheme (ferumoxytol) Injection
 Dear Radiologist: (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is an IV iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients with chronic kidney disease
Dear Radiologist: (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is an IV iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients with chronic kidney disease
Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153
 APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Octreoscan Kit for preparation of 111 In-Pentetreotide 111 MBq/ ml 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Octreoscan is supplied
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Octreoscan Kit for preparation of 111 In-Pentetreotide 111 MBq/ ml 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Octreoscan is supplied
Components of Preparedness
 Components of Preparedness Domain I: Radiation Physics & Detection 7% Domain II: Radiation Safety & Regulations 13% Domain III: Pharmaceutical & Radiopharmaceutical Agents 25% Domain IV: Instrument Operations
Components of Preparedness Domain I: Radiation Physics & Detection 7% Domain II: Radiation Safety & Regulations 13% Domain III: Pharmaceutical & Radiopharmaceutical Agents 25% Domain IV: Instrument Operations
