Antineoplastic agents selective destruction of malignant tumor cells. Cytostatics. Antineoplastic Agents I. Factors leading to cancer
|
|
|
- Julianna Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Antineoplastic Agents I. Antineoplastic agents selective destruction of malignant tumor cells. Cytostatics Single condition or illness more than 100 different diseases (no wonder drugs). Biochemical and morpholigical differences between normal and neoplastic cells are slight, they do not arouse an immunological response. Causes: Faulty, unbalanced regulation leads to overexpression of growth factor receptors Failure of cells to undergo apoptosis, no response to DNA damages. (Normal cells: unreparable damage leads to apoptosis.) Invasiveness - tumors do not stay harmlessly in one place, spread to other parts metathesis Factors leading to cancer Viruses (e.g. human papilloma virus uterine cervix, HHV8 Kaposi s sarcoma, hepatitis B liver cancer) Chemical mutagens (e.g. aflatoxin, smoke components, asbestos) Radioactive agents Role and activation of oncogenes Elimination by apoptosis Unregulated multiplication A few carcinogens EGFR A few carcinogens 4 metabolic activation 5 7
2 Types of malignant tumors Solid tumors glandular tissue, epithelium carcinoma, adenoma, melanoma, etc. connective tissue sarcoma (myoma, fibroma) etc. nervous system glioma, neuroblastoma Hematological tumors lymphoma lymphoid leukemia myeloid leukemia Therapy Monotherapy (almost) never used antineoplastics of different mode of actions are combined to overcome resistance. drugs sorted out should have minimally overlapping toxicity. Surgical- and radiotherapy is usually combined with chemotherapy. Intermittent chemotherapy allow healthy cells to regenerate. General side effects (damage of rapidly proliferating tissues): alopecia, leukopenia and neutropenia (bone marrow repression), nausea and vomiting. Antineoplastic agents selective destruction of malignant tumor cells. ld classification: Cytostatics = antineoplastics = anticancer agents comprise the full arsenal of chemotherapeutics against cancer. Cytotoxic agents Recent classification: Cytostatic agents Classification of antineoplastic agents Cytotoxic agents Antimetabolites (inhibition of the DNA synthesis) Alkylating agents (disruption of the function of the DNA) Chelating, complex formating agents inhibition of microtubule assembly (inh. of proliferation) complex formation with DNA (inh. of DNA or topoisomerases) Hormones and antihormones Centrally acting agents (via endocryn system) Blocking of cellular receptors Cytostatic agents MAB and immunoconjugates Small molecule kinase etc. inhibitors Specific supportive, cytoprotective agents 11 Cytotoxic agents lack intrinsic tumor cell selectivity, selectivity relies on rate of proliferation, target basic cell proliferation processes. DNA disruptors (alkylating agents, chain cutters) DNA intercalating agents, topoisomerase inhibitors Nucleotid antimetabolites 12 Cytostatic agents target biochemical processes or specific proteins, which are unique to the tumor cells or are overexpressed compared to the normal cell tumorspecific less toxic side effects Targeted chemotherapy Monoclonal antibodies Tyrosine kinase inhibitors Angiogenesis inhibitors (Antisense and ribozyme therapeutics) 13
3 Antimetabolites Nucleosides Folic acid antagonists Antimetabolites prevent the biosynthesis of compounds necessary in other biochemical processes, in building DNA or they lead to false intermediers and terminate DNA synthesis. purine Folic acid and tetrahydrofolic acid have crucial role in the synthesis of nucleosides THF pyrimidine Folic acid antagonists Folic acid antagonists Purin antagonists Methotrexate Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Used against several type of tumors, lymphomas Permetrexed Non-small cell lung carcinoma. The only agant specially used to treat mesothelioma (e.g. asbestosis) Raltitrexed - inhibits thymidilate synthetase. Used to treat colorectal cancers Leucovorin (folinic acid): prevents the lethal effect of inhibition of DHF reductase on normal cells Prodrug of mercaptopurine, provides very long therapeutic concentration by slow hydrolysis. Used mainly for treating acute leukemia. 20 Immunsupressive effect
4 Pyrimidine antagonists Pyrimidine antagonists Basic structures X Fluoro-2 -deoxy-uridylic acid is a competitive inhibitor of thymidylate synthetase leading to the lack of available thymidylic acid. 5-FU is used for the treatment of breast, stomach, colon etc. carcinomas. 23 HN F N This tetrahydrofuranyl derivative is prodrug of 5FU: good oral absorption, coverted back to 5FU in the liver. 24 Contains D-arabinose instead of the usual D-ribose. Two modes of action: 1) After the first phosphorylation it inhibits the cytidylic acid 2 -deoxycytidylic acid converting reductase enzyme. 2) The triphosphate inhibits the DNA polymerase enzyme. Used mainly in the case of different leukemia diseases. Adverse effects: severe leukopenia, anemia. 25 The phosphorilated derivative inhibits the corresponding reductase enzyme, thus the cell is in short of 2 -deoxycytidine phosphate. Used in treatment of adenocarcinomas of the pancreas and non-small cell lung carcinoma, in combination with cisplatine against bladder carcinoma. 26
5 Alkylating agents Very rapid absorption Prodrog of 5-fluorouracil, activated via three enzyamtic steps. Used for the treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal carcinoma, which do not respond well for other agents. Activation of capecitabine Reagents capable to alkylate under physiological conditions nu-h + alkyl-y alkyl-nu + H + + Y - nu = -H, >NH, -NH 2, -SH etc. Y= -Cl, -Br, -S 2 CH 3, epoxydes, aziridinium, tiiranium Selectivity problem. nly DNA should be targeted. Irreversible crosslinking of DNA chains Alkylating agents Synthesis of cyclophophamide Mustards highly toxic compounds used in the 1st WW Gilman and Philips (1946) inhibition of cell proliferation by nitrogen mustard Nitrogen mustards are not active at acidic ph They are the most important antitumor agents, used in acute and chronic myeloid and lymphoid leukemia, lymphomas, and several carcinomas (breast, lung, head, pancreas, etc.), usually in combinations. Selectivity depends on R
6 Cyclophosphamide needs metabolic activation Cyclophosphamide The toxic acrolein (bladder bleeding) can be neutralized with the addition of Mesna (Uromitexan): Nitroso-urea derivatives Unstable compounds that serve very reactive CH 3 + or R-CH 2 + type carbenium ions during activation. Carcinogen compounds, therefore they must be converted to the active agent only at the desired site of action Activation of Carnustine Activation of triazenes Somewhat differently are activated the triazene derivatives Double action: carbamoylation and alkylation
7 Nitrosourea and triazene derivatives Mitomycin mode of action Nitrosourea and triazene derivatives readily absorb, are quite lipophylic and cross the BBB. Indications: different brain tumors (astrocytoma, gliablastoma), malignant melanomas and Hodgkin s disease. Mitomycin antibiotics, Wakiki et al., (1956) from Streptomyces caespitosus. Contains two active sites: carbamoyl and aziridine groups. Indications: adenocarcinomas of stomach, oesophagus, pancreas and bladder Hormones and antihormones Several cell types are dependent on hormonal control. Membrane embedded hormone receptors convert the extracellular signal to the intracellular signal processing system. Neoplastic cells usually retain their receptors and hormone dependency, sometimes hormon receptors are overexpressed. (Tissue sections of breast etc. tumors are always checked for ER and PR receptors by immunohistochemical methods at pathology) (Anti)Hormones do not kill tumor cells but proliferation is inhibited by complex mechanisms Beatson (1896) Estrogens and breast cancer Dr. George Beatson (1896): ovariectomy (removal of the ovaries) causes tumor remission in a subset of patients with MBC. Estrogen binds 1 of 2 estrogen receptors (ERα/ERβ) that function as transcriptional activators to regulate the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation. ver 70% of tumors in women with breast cancer are ER+ and appr. 60% are progesteron, PR+. Hormonal manipulations induce tumor regression in 50-60% of hormone receptor-positive tumors. Hormones Immunohistochemical staining
8 Antiandrogenes Antiandrogens Estrogens Strong antiandrogen activity with very high affinity to the androgen receptors competitive inhibition of the natural substrates testosteron or dihydrotestosteron. Effectively inhibit the proliferation of malignant prostata epithelial cells. riginally developed as nitrogen mustard-type alkylation agent, but it acts as estrogen. Indication: solely prostata carcinoma Antiestrogens Antiestrogens, Tamoxifen Estrogen receptors have two activation domains AF1 and AF2 Tamoxifen attaches to the AF2 domain of estrogen receptors of the tumor cells, which blocks estrogen's effect. AF2 activity is dominant in breast cancer. It is partially agonistic on AF1 elsewhere, such as the uterus or bone protective effect against osteoporosis because it even stimulates the estrogen receptor in bone. Adverse effects of long use: increases the risk of blood clot (thromboembolism) and endometrial cancer. Main indication: postmenopausal breast cancer. Side effects: Hot flushes, sweats, vaginal dryness vaginal discharge. Synthesis of tamoxifen
9 In spite of tamoxifen, fulvestrant destroys estrogen receptors and leads to downregulation. Used for treatment of (recurrent) hormone dependent breast cancer when tamoxifen is not effective. No protective effect against osteoporosis, no effect on Aromatase inhibitors Used for the treatment of postmenopausal hormone dependent breast cancer. Long term (5 years) treatment may promote osteoporosis. Adverse reactions: hot flashes etc. endometrium Aromatase inhibitors Me Me Me Me H NADPH H H NADPH H H H 2 H H 2 H H Androstendion (or testosteron) aromatase NADPH 2 Fe 3+ Me Me H H H H H H H H Estron (or estradiol) Complete block of the biosynthesis of estrogens, which are synthesized after the menopause outside the ovaries. 54 Gestagens Gestagens Gestagens do not bind to estrogen receptors; the activation of progesterone receptors decreases the quantity of ER. Feedback via the hypothalamus decreases the level of FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) and LH (Luteinizing Hormone) cut down of estrogens and androgens. Hypothalamus GnRH Pituitary LH and FSH Testosterone Testes Estrogens and progesterone varies Modified progesterone derivatives, used in gynecology and in e-pills. Medroxiprogesterone has very long half-life (60 hours) 57
10 Synthetic GnRH analogues Synthetic GnRH analogues Complex formating agents Inhibiton of microtubule assembly Several alkaloids belong to this group Synthetic nona-decapeptide analogues of the natural GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone) times stronger stimulate the release of FSH and LH than the natural GnRH. 58 Continuous stimulation transient early rise in gonadotropin release pituitary desensitisation, downregulation, leading to suppressed levels of gonadotropins and sex hormones. Indications: advanced prostatic cancer, breast cancer (postadjuvant treatment) endometriosis and precocious puberty. Alkaloid of Colchicum autumnale (meadow saffron) Quite toxic compound Treatment of acute gout myeloid leukemia not used today Depo formulation: 1 inj./month, Diphereline: 3 month Microtubule formation Vinca alkaloids Vinca alkaloids protofilament microtubule α-tubulin β-tubulin tubulin dimer stablize the monomer, inhibit association taxol stabilizes polymer vinca-alkaloids, colchicine centrosoma (MTC) chromosoma Microtubules are tube-like protein structures, serve as structural components within cells and are involved in many cellular processes including mitosis ( mitotic spindle), cytokinesis, and Alkaloids of Vinca rosea (Cataranthus rosea, periwinkle), isolated in Belong to the complicated bisindole family of alkaloids vesicular transport
11 Vinca alkaloids Taxanes Vincrystine is recommended for leukemia, neuroblastoma, Hodgin- and non-hodgkin lymphomas. It is neurotoxic. Vinblastine is recommended for tumors of the hemopoietic system, testicle tumors (in combination with bleomycin/cisplatin). It has myelotoxicity. The semisynthetic vinorelbine is used to treat lung carcinomes. Mode of action: causes depolymerization of microtubules. 64 Paclitaxel: isolated in small amounts from the bark of Taxus brevifolia (Pacific yew tree) (1971). Semisynthesis from deacetylbaccatin, obtained from the leaves of Taxus brevifolia (European yew tree). Nowadays: plant cell fermentation of a specific taxus cell line. 65 Taxol is approved for (metastatic) non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, usually in combination with citoxane and epidaunorubicin (TEC) Side effect: strong allergic reactions, hypersensitivity addition of steroids and antihystamines prior to infusion. 66 Microtubule and taxole DNA Complex formating agents Platinum complexes Accidental discovery when investigating the effect of electrical field on E. coli between Pt electrodes (Rosenberg, 1965). Active agent: platinum ammonium complex. Cisplatin: only the cis configuration is active. H3N Cl Pt H3N Cl H 3 N H 2 Pt H 3N Cl + H 3 N H 2 Pt H 3N H 2 2+ H 3 N DNS Pt H 3N DNS Taxol binds to the beta subunit of tubulin and stabilizes the complex. H 3 N Cl - Pt 2+ H 3 N Cl - H 3 N H 3 N Cl Pt Cl Cl H 3 N Pt NH 3 Cl
12 Platinum complexes Cisplatin forms coordinative bonds between N atoms within the range of Å. Crosslinking of DNA (usually within the same chain, GpG) makes impossible for rapidly dividing cells to duplicate their DNA and sets off DNA repair mechanism. Initial phase: Cl - ions exchange with H 2 charged complex interacts with DNA. 70 DNA - cisplatin Platinum complexes Cisplatin: ovarian, testicular and urogenital cancers usually in combination. Adverse effects: nephrotoxicity (hydration!), one of the most emetogenic chemotherapy agents; ototoxicity. Carboplatin: similar to cisplatin with much less adverse effects. Main indications: ovarian and smallcell lung cancer. xaliplatin: combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for the treatment of colorectal cancers. 73
Cancer Chemotherapy. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018
 Cancer Chemotherapy Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018 االدوية Polyfunctional Alkylating Agents االستخالبية متعددة الوظائف Not cell cycle-specific.
Cancer Chemotherapy Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018 االدوية Polyfunctional Alkylating Agents االستخالبية متعددة الوظائف Not cell cycle-specific.
2. Mitotic Spindle Inhibitors (modulators of tubulin polymerisation) 3. Antimetabolites (anti-folates, pyrimidine and purine analogues)
 CANCER DRUG CLASSES The classes of drugs currently used in the cancer clinic are 1. DNA Binding Agents (intercalating and alkylating agents) 2. Mitotic Spindle Inhibitors (modulators of tubulin polymerisation)
CANCER DRUG CLASSES The classes of drugs currently used in the cancer clinic are 1. DNA Binding Agents (intercalating and alkylating agents) 2. Mitotic Spindle Inhibitors (modulators of tubulin polymerisation)
through the cell cycle. However, how we administer drugs also depends on the combinations that we give and the doses that we give.
 Hello and welcome to this lecture. My name is Hillary Prescott. I am a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My colleague, Jeff Bryan and I have prepared this
Hello and welcome to this lecture. My name is Hillary Prescott. I am a Clinical Pharmacy Specialist at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. My colleague, Jeff Bryan and I have prepared this
Anti-cancer drugs. Introduction : Body : 1) Alkylating Agents
 Anti-cancer drugs Introduction : In this journal I will try to explain what is anti-cancer agents, how they work, how can they inhibit the growth of tumor and what is the advantages and disadvantages of
Anti-cancer drugs Introduction : In this journal I will try to explain what is anti-cancer agents, how they work, how can they inhibit the growth of tumor and what is the advantages and disadvantages of
Year III Pharm D. Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm D. Dr. V. Chitra 50.2 Rang Etiolopathology Cell Cycle = Growth, Division 18_01_cell_cycle.jpg Characteristics of Cancer Cells The problem: Cancer cells divide rapidly (cell cycle is accelerated)
Year III Pharm D. Dr. V. Chitra 50.2 Rang Etiolopathology Cell Cycle = Growth, Division 18_01_cell_cycle.jpg Characteristics of Cancer Cells The problem: Cancer cells divide rapidly (cell cycle is accelerated)
*Combination therapy: *Cancer drugs are divided into groups: I) DNA binding agents (Intercalating and Alkylating agents) 2 types: Doxorubicin
 *Combination therapy: - Cancer is heterogeneous, and resistant anticancer drugs are common, so combination of drugs together is needed in order to attack cancer. *Cancer drugs are divided into groups:
*Combination therapy: - Cancer is heterogeneous, and resistant anticancer drugs are common, so combination of drugs together is needed in order to attack cancer. *Cancer drugs are divided into groups:
Cancer Incidence and Mortality
 Cancer Incidence and Mortality Cancer is a common disease. One in three people in the Western World contract cancer and one in four die from it. The cure rate is 50% Cancer is strongly age-related, the
Cancer Incidence and Mortality Cancer is a common disease. One in three people in the Western World contract cancer and one in four die from it. The cure rate is 50% Cancer is strongly age-related, the
Part III: Anticancer Agents Antibiotics
 Part III: Anticancer Agents Antibiotics Classification of Antibiotics: Anthracycline Mitomycin C Bleomycin Actinomycin D Antibiotics Anthracyclines Anthracycline antibiotics are characterized by a planner
Part III: Anticancer Agents Antibiotics Classification of Antibiotics: Anthracycline Mitomycin C Bleomycin Actinomycin D Antibiotics Anthracyclines Anthracycline antibiotics are characterized by a planner
Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
 Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo
Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo
Cancer Incidence and Mortality
 Cancer Incidence and Mortality Cancer is a common disease. One in three people in the Western World contract cancer and one in four die from it. The cure rate is 50% Cancer is strongly age-related, the
Cancer Incidence and Mortality Cancer is a common disease. One in three people in the Western World contract cancer and one in four die from it. The cure rate is 50% Cancer is strongly age-related, the
Anticancer Drugs. Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents
 Anticancer Drugs Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents 1 Principles of Cancer Chemotherapy Cancer chemotherapy strives to cause a lethal cytotoxic event or apoptosis in the cancer cells that can arrest
Anticancer Drugs Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents 1 Principles of Cancer Chemotherapy Cancer chemotherapy strives to cause a lethal cytotoxic event or apoptosis in the cancer cells that can arrest
Principles of chemotherapy
 Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 09
 01) Proflavine is an intercalating agent which was used to treat wounded soldiers in the Far East during the second world war. Which of the following statements is false regarding proflavine? a. It a useful
01) Proflavine is an intercalating agent which was used to treat wounded soldiers in the Far East during the second world war. Which of the following statements is false regarding proflavine? a. It a useful
Anticancer Drugs. Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents
 Anticancer Drugs Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents 1 Principles of Cancer Chemotherapy Cancer chemotherapy strives to cause a lethal cytotoxic event or apoptosis in the cancer cells that can arrest
Anticancer Drugs Cytotoxic drugs Antineoplastic agents 1 Principles of Cancer Chemotherapy Cancer chemotherapy strives to cause a lethal cytotoxic event or apoptosis in the cancer cells that can arrest
Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
 Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment Dr. Pran Kishore Deb and Dr Balakumar Chandrasekaran Assistant Professor Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia
Common Herbal Product Used in Cancer Prevention and Treatment Dr. Pran Kishore Deb and Dr Balakumar Chandrasekaran Assistant Professor Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA. Chapter 37
 DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA Chapter 37 Keywords- You tell Me! Cancer dz characterized by abnormal, uncontrolled cell division Tumor swelling, abnormal enlargement or mass of tissue Carcinogen any substance or
DRUGS FOR NEOPLASIA Chapter 37 Keywords- You tell Me! Cancer dz characterized by abnormal, uncontrolled cell division Tumor swelling, abnormal enlargement or mass of tissue Carcinogen any substance or
Antineoplastic Drugs. Antineoplastic Drugs. Herbal Alert. Pharmacology Chapter 51. Green tea
 Antineoplastic Drugs Pharmacology Chapter 51 Carolyn Wright, RN, BSN Ford, S. & Roach, S. (2010). Roach's introductory clinical pharmacology (9 th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams
Antineoplastic Drugs Pharmacology Chapter 51 Carolyn Wright, RN, BSN Ford, S. & Roach, S. (2010). Roach's introductory clinical pharmacology (9 th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams
I. ANTIMETABOLITES. A- Antifolates (Methotrexate, Pemetrexed, and Pralatrexate)
 I. ANTIMETABOLITES Antimetabolites are structurally related to normal cellular components. They generally interfere with the availability of normal purine or pyrimidine nucleotide precursors by inhibiting
I. ANTIMETABOLITES Antimetabolites are structurally related to normal cellular components. They generally interfere with the availability of normal purine or pyrimidine nucleotide precursors by inhibiting
Answer ALL questions. For each question, there is ONE correct answer. Use the answer grid provided for ALL your answers.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CLINICAL THERAPEUTICS 8: ONCOLOGY PHA-MHCY Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For each question, there
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Pharmacy Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CLINICAL THERAPEUTICS 8: ONCOLOGY PHA-MHCY Time allowed: 2 hours Part ONE Answer ALL questions. For each question, there
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Medication Review. Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Medication Review Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Medication Review, Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program Medication
Medication Review Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC Medication Review, Cancer Chemotherapy Drugs PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Program Medication
Lecture 10: Hormonal agents
 Lecture 10: Hormonal agents The survival and proliferation (growth) of some cancer cells is dependent on the action of steroid hormones. Early stage breast cancer and early stage prostate cancer are the
Lecture 10: Hormonal agents The survival and proliferation (growth) of some cancer cells is dependent on the action of steroid hormones. Early stage breast cancer and early stage prostate cancer are the
Anti-cancer Therapy: Antimitotic Agents. Edy Suwarso
 Anti-cancer Therapy: Antimitotic Agents Edy Suwarso Discussion Points What is cancer? Mitosis and mitotic checkpoints How deregulation of the above contributes to cancer formation Antimitotic agents as
Anti-cancer Therapy: Antimitotic Agents Edy Suwarso Discussion Points What is cancer? Mitosis and mitotic checkpoints How deregulation of the above contributes to cancer formation Antimitotic agents as
Lecture 10: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids. Vincristine (Oncovin):
 Lecture 10: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids Vincristine (Oncovin): Uses: Acute leukemia, Hodgkin s lymphoma (part of the MOPP, COPP, BEACOPP regimens); non- Hodgkin
Lecture 10: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids Vincristine (Oncovin): Uses: Acute leukemia, Hodgkin s lymphoma (part of the MOPP, COPP, BEACOPP regimens); non- Hodgkin
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Tumour Structure and Nomenclature. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 Tumour Structure and Nomenclature Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Malignant Metastasis Core idea of cancer Normal Cell Slightly
Tumour Structure and Nomenclature Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Malignant Metastasis Core idea of cancer Normal Cell Slightly
4. Shown below is the structure of doxorubicin (Adriamycin). What is true about this agent?
 Midterm 2: 3 points each (except final question worth 1 point 1. A useful regimen for treating colorectal cancer is FOLFIRI. What is true about this regimen? A. The regimen includes folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil
Midterm 2: 3 points each (except final question worth 1 point 1. A useful regimen for treating colorectal cancer is FOLFIRI. What is true about this regimen? A. The regimen includes folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil
Signal Transduction. & Mechanisms of Drug Action
 Signal Transduction & Mechanisms of Drug Action Why do some drugs produce effects that persist for long after the drug is no longer present? Why do response to other drugs diminish rapidly with repeated
Signal Transduction & Mechanisms of Drug Action Why do some drugs produce effects that persist for long after the drug is no longer present? Why do response to other drugs diminish rapidly with repeated
"Pharmacology. Anticancer Drugs
 I "Pharmacology Anticancer Drugs Include: 1) Cytotoxic drugs. 2) Isotopes: which emit β-irradiation that destroy cancer cells, e.g. I 131, P 32, Au 193 3) Hormones: A- Steroids: prednisolone used in leukemia
I "Pharmacology Anticancer Drugs Include: 1) Cytotoxic drugs. 2) Isotopes: which emit β-irradiation that destroy cancer cells, e.g. I 131, P 32, Au 193 3) Hormones: A- Steroids: prednisolone used in leukemia
Estrogens & Antiestrogens
 Estrogens & Antiestrogens Menstrual cycle... Changes and hormonal events Natural estrogens: Estadiol >> Estrone > Estriol Ineffective orally Synthesis: From cholesterol ; role of aromatase enzyme in converting
Estrogens & Antiestrogens Menstrual cycle... Changes and hormonal events Natural estrogens: Estadiol >> Estrone > Estriol Ineffective orally Synthesis: From cholesterol ; role of aromatase enzyme in converting
Intro to Cancer Therapeutics
 An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
An Intro to Cancer Therapeutics Christopher R. Chitambar, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Hematology & Oncology Froedtert and Medical College of Wisconsin Clinical Cancer Center cchitamb@mcw.edu Intro
Microtubule Targeting Anti-mitotic Agents as Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Review
 Microtubule Targeting Anti-mitotic Agents as Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Review Dr. Taradas Sarkar Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose College, Kolkata-700020, West Bengal,
Microtubule Targeting Anti-mitotic Agents as Anti-Cancer Drugs: A Review Dr. Taradas Sarkar Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose College, Kolkata-700020, West Bengal,
Lecture 11: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids (we will discuss 3) Vincristine (Oncovin):
 Lecture 11: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids (we will discuss 3) Vincristine (Oncovin): Uses: Acute leukemia, Hodgkin s lymphoma (part of the MOPP, COPP, BEACOPP
Lecture 11: Antimitotic agents cell cycle specific (M phase mainly) 1. Vinca alkaloids (we will discuss 3) Vincristine (Oncovin): Uses: Acute leukemia, Hodgkin s lymphoma (part of the MOPP, COPP, BEACOPP
ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS CHEMOTHERAPY PRODUCTS (PART I) DISCLAIMER
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, September 2006 Doc. Ref.: EMEA/384641/2006 ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS CHEMOTHERAPY PRODUCTS (PART I) DISCLAIMER The Paediatric
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, September 2006 Doc. Ref.: EMEA/384641/2006 ASSESSMENT OF THE PAEDIATRIC NEEDS CHEMOTHERAPY PRODUCTS (PART I) DISCLAIMER The Paediatric
TUMOR M ARKERS MARKERS
 TUMOR MARKERS M.Shekarabi IUMS Definition Many cancers are associated with the abnormal production of some molecules l which h can be measured in plasma. These molecules are known as tumor markers. A good
TUMOR MARKERS M.Shekarabi IUMS Definition Many cancers are associated with the abnormal production of some molecules l which h can be measured in plasma. These molecules are known as tumor markers. A good
Chapter 9. Cells Grow and Reproduce
 Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 37. Media Directory. Tumor (neoplasm) Cancer (carcinoma) Causes of Cancer. Drugs for Neoplasia
 Chapter 37 Media Directory Drugs for Neoplasia Slide 39 Slide 41 Cyclophosphamide Animation Methotrexate Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cancer (carcinoma) Tumor (neoplasm)
Chapter 37 Media Directory Drugs for Neoplasia Slide 39 Slide 41 Cyclophosphamide Animation Methotrexate Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cancer (carcinoma) Tumor (neoplasm)
Lipoplatin monotherapy for oncologists
 Lipoplatin monotherapy for oncologists Dr. George Stathopoulos demonstrated that Lipoplatin monotherapy against adenocarcinomas of the lung can have very high efficacy (38% partial response, 43% stable
Lipoplatin monotherapy for oncologists Dr. George Stathopoulos demonstrated that Lipoplatin monotherapy against adenocarcinomas of the lung can have very high efficacy (38% partial response, 43% stable
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Oral Chemotherapy Nathan Brashear, PharmD Candidate 2017 University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy
 Oral Chemotherapy Nathan Brashear, PharmD Candidate 2017 University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy 1 Objectives Identify the more commonly dispensed oral chemotherapy drugs and their indications/dosage
Oral Chemotherapy Nathan Brashear, PharmD Candidate 2017 University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy 1 Objectives Identify the more commonly dispensed oral chemotherapy drugs and their indications/dosage
5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation
 168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
168 IARC MONOGRAPHS VOLUME 91 5. Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation 5.1 Exposure data The first oral hormonal contraceptives that were found to inhibit both ovulation and implantation were developed
H&HD ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUG CARD ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
 H&HD ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUG CARD ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Each of you should have 37 new cards: 7 orange cards for antimetabolites 11 white cards for miscellaneous drugs (2 DNA synthesis inhibitors, 1 enzyme,
H&HD ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUG CARD ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Each of you should have 37 new cards: 7 orange cards for antimetabolites 11 white cards for miscellaneous drugs (2 DNA synthesis inhibitors, 1 enzyme,
Lecture 16: Therapeutics to Treat Cancer
 Lecture 16: Therapeutics to Treat Cancer Therapeutic Objectives Primary prevention stop the risk of cancer before it occurs o Smoking cessation o Coxibs COX2 selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor PGE2 facilitates
Lecture 16: Therapeutics to Treat Cancer Therapeutic Objectives Primary prevention stop the risk of cancer before it occurs o Smoking cessation o Coxibs COX2 selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor PGE2 facilitates
It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue
 59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
59 Breast cancer 1 It is a malignancy originating from breast tissue including both early stages which are potentially curable, and metastatic breast cancer (MBC) which is usually incurable. Most breast
Lecture 3: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) 1. Folate analogs
 Lecture 3: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) All the antimetabolites mimic endogenous molecules. They trick enzymes involved in the synthesis of DNA, and instead of metabolizing the proper
Lecture 3: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) All the antimetabolites mimic endogenous molecules. They trick enzymes involved in the synthesis of DNA, and instead of metabolizing the proper
Reproductive physiology
 Reproductive physiology Sex hormones: Androgens Estrogens Gestagens Learning objectives 86 (also 90) Sex Genetic sex Gonadal sex Phenotypic sex XY - XX chromosomes testes - ovaries external features Tha
Reproductive physiology Sex hormones: Androgens Estrogens Gestagens Learning objectives 86 (also 90) Sex Genetic sex Gonadal sex Phenotypic sex XY - XX chromosomes testes - ovaries external features Tha
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
CHEMOTHERAPY/ ANTICANCER DRUGS/ NEOPLASTIC AGENTS
 CHEMOTHERAPY/ 1 Oncology, Misc, Vaccines ANTICANCER DRUGS/ NEOPLASTIC AGENTS Important Terms: Cancer: A group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other
CHEMOTHERAPY/ 1 Oncology, Misc, Vaccines ANTICANCER DRUGS/ NEOPLASTIC AGENTS Important Terms: Cancer: A group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other
Estrogens and progestogens
 Estrogens and progestogens Estradiol and Progesterone hormones produced by the gonads are necessary for: conception embryonic maturation development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Estrogens and progestogens Estradiol and Progesterone hormones produced by the gonads are necessary for: conception embryonic maturation development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Results of implication of aromatase inhibitors in therapy of genital endometriosis Yarmolinskaya M. (Speaker), Bezhenar V., Molotkov A.
 Results of implication of aromatase inhibitors in therapy of genital endometriosis Yarmolinskaya M. (Speaker), Bezhenar V., Molotkov A. Ott's Research Institute of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductology,
Results of implication of aromatase inhibitors in therapy of genital endometriosis Yarmolinskaya M. (Speaker), Bezhenar V., Molotkov A. Ott's Research Institute of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductology,
Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis. Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc
 Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with
Combined drug and ionizing radiation: biological basis Prof. Vincent GREGOIRE Université Catholique de Louvain, Cliniques Universitaires St-Luc Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
ANTI CANCER DRUGS. Dr. Datten Bangun MSc,SpFK. Dept. Farmakologi dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas HKBP Nomensen
 ANTI CANCER DRUGS Dr. Datten Bangun MSc,SpFK Dept. Farmakologi dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas HKBP Nomensen SITOSTATIKA CYTOSTATICS INTRODUCTION : Cyto : Cells Static : statis Synonim
ANTI CANCER DRUGS Dr. Datten Bangun MSc,SpFK Dept. Farmakologi dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas HKBP Nomensen SITOSTATIKA CYTOSTATICS INTRODUCTION : Cyto : Cells Static : statis Synonim
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
 Mdi Medical Management of Breast Cancer Morbidity and Mortality Aug 13, 2009 Irina Kovatch, PGY3 Introduction Metastatic disease is the principal cause of death from breast cancer Metastatic events often
Mdi Medical Management of Breast Cancer Morbidity and Mortality Aug 13, 2009 Irina Kovatch, PGY3 Introduction Metastatic disease is the principal cause of death from breast cancer Metastatic events often
Systemic Treatment of Cancer
 Systemic Treatment of Cancer Irwin H. Krakoff, MD It was demonstrated in the early 1940s that changing the hormonal milieu of certain cancers could result in their regression and that administration of
Systemic Treatment of Cancer Irwin H. Krakoff, MD It was demonstrated in the early 1940s that changing the hormonal milieu of certain cancers could result in their regression and that administration of
 Exhibit B United States Patent Application 20020012663 Kind Code A1 Waksal, Harlan W. January 31, 2002 Treatment of refractory human tumors with epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists Abstract A
Exhibit B United States Patent Application 20020012663 Kind Code A1 Waksal, Harlan W. January 31, 2002 Treatment of refractory human tumors with epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists Abstract A
Cytostatics Definition, Terminology
 Dept. of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University in Brno Cytostatics Notes for Pharmacology II Practicals This study material is exclusively for students of general medicine and dentistry
Dept. of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University in Brno Cytostatics Notes for Pharmacology II Practicals This study material is exclusively for students of general medicine and dentistry
Cancer Chemotherapy. Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018
 Cancer Chemotherapy Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018 Modalities of Cancer Chemotherapy Curative: Only in 10-15% of cases. In certain disseminated
Cancer Chemotherapy Munir Gharaibeh MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan December 2018 Modalities of Cancer Chemotherapy Curative: Only in 10-15% of cases. In certain disseminated
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository:
 This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/103187/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
This is an Open Access document downloaded from ORCA, Cardiff University's institutional repository: http://orca.cf.ac.uk/103187/ This is the author s version of a work that was submitted to / accepted
Chemotherapy and the development of novel therapeutics
 SCPA607-Pathobiology and mechanisms of cancer Chemotherapy and the development of novel therapeutics Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science Mahidol University E-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th
SCPA607-Pathobiology and mechanisms of cancer Chemotherapy and the development of novel therapeutics Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science Mahidol University E-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th
Horizon Scanning Centre November Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887
 Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a
Horizon Scanning Centre November 2012 Vinflunine (Javlor) monotherapy for advanced breast cancer SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 7887 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
DRUGS YOU NEED TO KNOW
 jfitzake@d.umn.edu Page 1 of 7 DRUGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ALKYLATING AGENTS (blue cards) BUSULFAN CARMUSTINE (BCNU) CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE DACARBAZINE LOMUSTINE (CCNU) MECHLORETHAMINE MELPHALAN THIOTEPA NATURAL
jfitzake@d.umn.edu Page 1 of 7 DRUGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ALKYLATING AGENTS (blue cards) BUSULFAN CARMUSTINE (BCNU) CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE DACARBAZINE LOMUSTINE (CCNU) MECHLORETHAMINE MELPHALAN THIOTEPA NATURAL
Lecture 5: Drug targets (continued)
 Lecture 5: Drug targets (continued) IIa. Enzymes as drug targets (HMG-CoA example) Many drugs are inhibitors of enzymes that catalyze biologically important reactions. The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic
Lecture 5: Drug targets (continued) IIa. Enzymes as drug targets (HMG-CoA example) Many drugs are inhibitors of enzymes that catalyze biologically important reactions. The conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY Michael Lea
 CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY 2010 Michael Lea Cancer Chemotherapy - Lecture Outline 1. Targets for cancer chemotherapy 2. Classification of anticancer drugs 3. Cell cycle specificity 4. Drug resistance 5. New approaches
CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY 2010 Michael Lea Cancer Chemotherapy - Lecture Outline 1. Targets for cancer chemotherapy 2. Classification of anticancer drugs 3. Cell cycle specificity 4. Drug resistance 5. New approaches
Microtubule-based Cancer Therapeutics BIOS-010 September 12, 2018
 Microtubule-based Cancer Therapeutics 1 BIOS-010 September 12, 2018 Jessica C. Leung PhD Candidate Cassimeris Lab What are microtubules? Why target them in cancer therapy? How do microtubule-based cancer
Microtubule-based Cancer Therapeutics 1 BIOS-010 September 12, 2018 Jessica C. Leung PhD Candidate Cassimeris Lab What are microtubules? Why target them in cancer therapy? How do microtubule-based cancer
Targeted Therapy Vijay Narang
 25 Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2013, Online: Targeted Therapy Vijay Narang ABSTRACT This is a review on targeted therapy that blocks the growth and spread of cancer by interfering with specific molecules
25 Volume 1, Issue 1, January 2013, Online: Targeted Therapy Vijay Narang ABSTRACT This is a review on targeted therapy that blocks the growth and spread of cancer by interfering with specific molecules
Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
Nucleotide Metabolism. Pyrimidine Met. Purine Met.
 Nucleotide Metabolism Pyrimidine Met. Purine Met. Learning Objectives 1. How Are Purines Synthesized? 2. How Are Purines Catabolized? 3. How Are Pyrimidines Synthesized and Catabolized? 4. How Are Ribonucleotides
Nucleotide Metabolism Pyrimidine Met. Purine Met. Learning Objectives 1. How Are Purines Synthesized? 2. How Are Purines Catabolized? 3. How Are Pyrimidines Synthesized and Catabolized? 4. How Are Ribonucleotides
Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014
 Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014 G Protein Coupled Receptors Actually 4% of the human genome GPCR dysfunction contributes to some of the most prevalent human diseases GPCRs represent 60% of
Targeting GPCRs for Cancer Therapy 03/11/2014 G Protein Coupled Receptors Actually 4% of the human genome GPCR dysfunction contributes to some of the most prevalent human diseases GPCRs represent 60% of
Cancer. October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa
 Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa In Ontario, someone is diagnosed with cancer every eight minutes
Cancer Causes Preventions Treatments Presentation By Dr. Bhavani Nair. MBBS;DGO;FRCP(C) Retired Radiation Oncologist University of Ottawa In Ontario, someone is diagnosed with cancer every eight minutes
This brings me to my point. Disease starts when there is a surplus or deficiency of certain nutritive or non-nutritive substances in the human body.
 WHAT IS DISEASE? A pathological condition of a part of an organ, or system of an organism resulting from various causes, such as infection, genetic defect, or environmental stress, and characterized by
WHAT IS DISEASE? A pathological condition of a part of an organ, or system of an organism resulting from various causes, such as infection, genetic defect, or environmental stress, and characterized by
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
1 Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #3 April 27, 2007 Name: Med. Chem. #
 1 Medicinal hemistry 410 Exam #3 April 27, 2007 ame: Med. hem. # Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. 1. The
1 Medicinal hemistry 410 Exam #3 April 27, 2007 ame: Med. hem. # Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. 1. The
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health. Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital
 Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Cancer. Chapter 31 Lesson 2
 Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Docetaxel. Class: Antineoplastic agent, Antimicrotubular, Taxane derivative.
 Docetaxel Class: Antineoplastic agent, Antimicrotubular, Taxane derivative. Indications: -Breast cancer: -Non small cell lung cancer -Prostate cancer -Gastric adenocarcinoma _Head and neck cancer Unlabeled
Docetaxel Class: Antineoplastic agent, Antimicrotubular, Taxane derivative. Indications: -Breast cancer: -Non small cell lung cancer -Prostate cancer -Gastric adenocarcinoma _Head and neck cancer Unlabeled
Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment
 Cancer treatments Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment What are the main treatments? Hormone therapy Surgery Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Targeted anti-cancer therapy (immunotherapy)
Cancer treatments Animal chemotherapy Film radiotherapy Music cancer treatment What are the main treatments? Hormone therapy Surgery Chemotherapy Radiotherapy Targeted anti-cancer therapy (immunotherapy)
Lecture 4: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) 1. Folate analogs
 Lecture 4: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) All the antimetabolites mimic endogenous molecules. They trick enzymes involved in the synthesis of DA, and instead of metabolizing the proper endogenous
Lecture 4: Antimetabolites cell cycle specific (S-phase) All the antimetabolites mimic endogenous molecules. They trick enzymes involved in the synthesis of DA, and instead of metabolizing the proper endogenous
SPRMs, androgens and breast cancer
 SPRMs, androgens and breast cancer Dr Joëlle Desreux BMS 04/06/2016 WHI : the nuclear explosion Looking for the perfect menopause treatment Hot flushes relieve Osteoporosis prevention Cardio-vascular health
SPRMs, androgens and breast cancer Dr Joëlle Desreux BMS 04/06/2016 WHI : the nuclear explosion Looking for the perfect menopause treatment Hot flushes relieve Osteoporosis prevention Cardio-vascular health
Cancer Fundamentals. Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource
 Cancer Fundamentals Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource Cancer Overview Leading cause of death in US 1.2 million diagnosed each year More common after age
Cancer Fundamentals Julie Randolph-Habecker, Ph.D. Director, Experimental Histopathology Shared Resource Cancer Overview Leading cause of death in US 1.2 million diagnosed each year More common after age
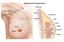 Radiation therapy Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer
Radiation therapy Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer
Choice of Cancer Chemotherapy u Is it a science, art or voodoo medicine?
 PRINCIPLES OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Dr.Erdem Göker Ege Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi TÜLAY AKTAŞ ONKOLOJİ HASTANESİ Choice of Cancer Chemotherapy u Is it a science, art or voodoo medicine? BEST Tx OF CANCER
PRINCIPLES OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Dr.Erdem Göker Ege Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi TÜLAY AKTAŞ ONKOLOJİ HASTANESİ Choice of Cancer Chemotherapy u Is it a science, art or voodoo medicine? BEST Tx OF CANCER
6/22/2017 TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017 TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017
 TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017 Primary Care Focus Symposium July 1, 2017 Grace Wang MD I do not have any relevant financial relationships to disclose at this time TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017 What are
TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017 Primary Care Focus Symposium July 1, 2017 Grace Wang MD I do not have any relevant financial relationships to disclose at this time TARGETING THE TARGETS IN 2017 What are
Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents. Intervention Educational Materials Audio Script (version 1)
 Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents Intervention Educational Materials... 1 Audio Script (version 1)... 1 Text (version 1)... 5 Slides (version 1)... 17 Audio Script (version
Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents Intervention Educational Materials... 1 Audio Script (version 1)... 1 Text (version 1)... 5 Slides (version 1)... 17 Audio Script (version
Lecture 1: Carcinogenesis
 Lecture 1: Carcinogenesis Anti-cancer (oncology agents): These are perhaps the most dangerous of drugs, other than the narcotic analgesics. This is due to their toxicities. Killing or inhibiting cancer
Lecture 1: Carcinogenesis Anti-cancer (oncology agents): These are perhaps the most dangerous of drugs, other than the narcotic analgesics. This is due to their toxicities. Killing or inhibiting cancer
Featured Topic: Breast Cancer (6 slides)
 Featured Topic: Breast Cancer (6 slides) Breast Cancer Rates are Going Up Breast cancer rates have increased 20% in the last five years As the baby boomer generation ages, the total number of women with
Featured Topic: Breast Cancer (6 slides) Breast Cancer Rates are Going Up Breast cancer rates have increased 20% in the last five years As the baby boomer generation ages, the total number of women with
AllinaHealthSystems 1
 Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Essentials. Oncology Practise Essentials. Oncology Basics. Tutorial 2. Cancer Chemotherapy
 Practise Practise This tutorial introduces you to the history, goals of therapy, classification, and clinical uses of chemotherapy. It also reviews some of the barriers to successful therapy. Goals and
Practise Practise This tutorial introduces you to the history, goals of therapy, classification, and clinical uses of chemotherapy. It also reviews some of the barriers to successful therapy. Goals and
