Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
|
|
|
- Monica Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
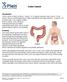
2 Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are diseases in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissue covering the ovary or lining the fallopian tube or peritoneum. The ovaries are a pair of organs in the female reproductive system. They are in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where a baby grows). Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. The ovaries make eggs and female hormones (chemicals that control the way certain cells or organs work). The fallopian tubes are a pair of long, slender tubes, one on each side of the uterus. Eggs pass from the ovaries, through the fallopian tubes, to the uterus. Cancer sometimes begins at the end of the fallopian tube near the ovary and spreads to the ovary. Fallopian tube Image Copyright 2018 The StayWell Company, LLC 2
3 The peritoneum is the tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers organs in the abdomen. Primary peritoneal cancer is cancer that forms in the peritoneum and has not spread there from another part of the body. Cancer sometimes begins in the peritoneum and spreads to the ovary. Ovarian germ cell tumor is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the germ (egg) cells of the ovary. Ovarian germ cell tumor describes several different types of cancer. The most common ovarian germ cell tumor is called dysgerminoma. You can learn more about ovarian germ cell tumors on page 16. Risk Factors Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors does not mean that you will not get cancer. Women who have one first-degree relative (mother, daughter, or sister) with a history of ovarian cancer have an increased risk of ovarian cancer. This risk is higher in women who have one first-degree relative and one second-degree relative (grandmother or aunt) with a history of ovarian cancer. This risk is even higher in women who have two or more firstdegree relatives with a history of ovarian cancer. The genes in cells carry the hereditary information received from a person s parents. Some ovarian, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancers 3
4 are caused by inherited gene mutations (changes). Hereditary ovarian cancer makes up about 1 out of 5 of all cases of ovarian cancer. There are 3 hereditary patterns: ovarian cancer alone, ovarian and breast cancers, and ovarian and colon cancers. There are tests that can detect gene mutations. Genetic testing can help determine treatment and help family members know of their own risk for the future. All patients with ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer should be referred for genetic risk evaluation. Signs and Symptoms Signs and symptoms of ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer include pain or swelling in the abdomen. Signs and symptoms may include the following: Bloating (swelling or feeling of fullness of the abdomen) Pain in the pelvis or abdomen Having a hard time eating or feeling of fullness Problems with frequent need to pass urine or need to go suddenly Ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer may not cause early signs or symptoms. When signs or symptoms do appear, the cancer is often advanced. 4
5 Tests for diagnosis and monitoring Not every person needs every test or procedure. Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of your health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken. Pelvic exam: An exam of the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and rectum. A speculum is inserted into the vagina and the provider looks at the vagina and cervix for signs of disease. A Pap test of the cervix may be done. The provider also inserts 1 or 2 lubricated, gloved fingers of 1 hand into the vagina and places the other hand over the lower abdomen to feel the size, shape, and position of the uterus and ovaries. The provider also inserts a lubricated, gloved finger into the rectum to feel for lumps or abnormal areas. CA 125 assay: A test that measures the level of CA 125 in the blood. CA 125 is a substance released by cells into the bloodstream. An increased CA 125 level can be a sign of cancer or another condition such as endometriosis. Ultrasound exam: An imaging test in which highenergy sound waves (ultrasound) are bounced off internal tissues or organs in the abdomen, and make echoes. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram. A transvaginal ultrasound uses a special probe that is put into the vagina. 5
6 CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography. PET scan (positron emission tomography scan): A procedure to find malignant tumor cells in the body. A very small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI). Chest x-ray: An x-ray of the organs and bones inside the chest. An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body. Biopsy: The removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. 6
7 Certain factors affect treatment options and prognosis (chance of recovery). The prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options depend on the following: The type of ovarian cancer and how much cancer there is The stage and grade of the cancer Whether you have extra fluid in the abdomen that causes swelling Whether all of the tumor can be removed by surgery Whether there are changes in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes Your age and general health Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred (come back) 7
8 How cancer spreads Cancer spreads three ways in the body. Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood: Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas. Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body. Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body. Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body. When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood. Staging The following stages are used for ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, primary peritoneal, and germ cell cancer: Stage I Stage II Stage III Stage IV The process used to find out whether cancer has spread within the organ or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. 8
9 It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnose cancer are often also used to stage the disease. The following stages are used for ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancer: Stage I In stage I, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes. Stage I is divided into stage IA, stage IB, and stage IC. Stage IA: Cancer is found inside a single ovary or fallopian tube. Stage IB: Cancer is found inside both ovaries or fallopian tubes. Stage IC: Cancer is found inside one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and one of the following is true: o Cancer is also found on the outside surface of one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes; or o The capsule (outer covering) of the ovary ruptured (broke open) before or during surgery; or o Cancer cells are found in the fluid of the peritoneal cavity (the body cavity that contains most of the organs in the abdomen) or in washings of the peritoneum (tissue lining the peritoneal cavity). Stage II (2) In stage II, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread into other areas of the pelvis, or primary peritoneal cancer is found within 9
10 the pelvis. Stage II ovarian epithelial and fallopian tube cancers are divided into stage IIA and stage IIB. Stage IIA: Cancer has spread from where it first formed to the uterus and/or the fallopian tubes and/ or the ovaries. Stage IIB: Cancer has spread from the ovary or fallopian tube to organs in the peritoneal cavity (the space that contains the abdominal organs). Stage III (3) In stage III, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes, or is primary peritoneal cancer, and has spread outside the pelvis to other parts of the abdomen and/or to nearby lymph nodes. Stage III is divided into stage IIIA, stage IIIB, and stage IIIC. In stage IIIA, one of the following is true: o Cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the area outside or behind the peritoneum only; or o Cancer cells that can be seen only with a microscope have spread to the surface of the peritoneum outside the pelvis. Cancer may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Stage IIIB: Cancer has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis and the cancer in the peritoneum is 2 centimeters or smaller. Cancer may have spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum. Stage IIIC: Cancer has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis and the cancer in the peritoneum is larger than 2 centimeters. Cancer may have spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum or to the surface of the liver or spleen. 10
11 Stage IV (4) In stage IV, cancer has spread beyond the abdomen to other parts of the body. Stage IV is divided into stage IVA and stage IVB. Stage IVA: Cancer cells are found in extra fluid that builds up around the lungs. Stage IVB: Cancer has spread to organs and tissues outside the abdomen, including lymph nodes in the groin. Ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancers are grouped for treatment as early or advanced cancer. Stage I ovarian epithelial and fallopian tube cancers are treated as early cancers. Stages II, III, and IV ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancers are treated as advanced cancers. 11
12 Treatment Option Overview Key points to learn in this section There are different types of treatment depending on the type of cancer. These could include surgery, drug treatment, or radiation therapy. Clinical trials: You can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting your cancer treatment. Surgery Most patients have surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Different types of surgery may include: Hysterectomy: Surgery to remove the uterus and, sometimes, the cervix. When only the uterus is removed, it is called a partial hysterectomy. When both the uterus and the cervix are removed, it is called a total hysterectomy. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through the vagina, the operation is called a vaginal hysterectomy. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a large incision (cut) in the abdomen, the operation is called a total abdominal hysterectomy. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a small incision (cut) in the abdomen using a laparoscope, the operation is called a total laparoscopic hysterectomy. 12
13 Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: A surgical procedure to remove one ovary and one fallopian tube. Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: A surgical procedure to remove both ovaries and both fallopian tubes. Omentectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the omentum (tissue in the peritoneum that contains blood vessels, nerves, lymph vessels, and lymph nodes). Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Tumor debulking: A surgical procedure in which as much of the tumor as possible is removed. Some tumors cannot be completely removed. 13
14 Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Systemic chemotherapy: When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body. Regional chemotherapy: When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas. A type of regional chemotherapy used to treat ovarian cancer is intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy. In IP chemotherapy, the anticancer drugs are carried directly into the peritoneal cavity (the space that contains the abdominal organs) through a thin tube. Combination chemotherapy: Treatment with more than one anticancer drug. Targeted therapy A type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. Monoclonal antibody therapy: A type of targeted therapy that uses antibodies made in the laboratory, from a single type of immune system cell. These antibodies can identify substances on cancer cells or normal substances that may help cancer cells grow. The antibodies attach to the substances and kill the cancer cells, block their growth, or keep them from 14
15 spreading. Monoclonal antibodies are given by infusion. They may be used alone or to carry drugs, toxins, or radioactive material directly to cancer cells. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the patient s immune system to fight cancer. Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body s natural defenses against cancer. This type of cancer treatment is also called biotherapy. Radiation therapy Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. The use of radiation in ovarian cancer is limited based on the patient s disease. 15
16 Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Ovarian germ cell tumor is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the germ (egg) cells of the ovary. Ovarian germ cell tumor is a general name that is used to describe several different types of cancer. The most common ovarian germ cell tumor is called dysgerminoma Signs of ovarian germ cell tumor are swelling of the abdomen or vaginal bleeding after menopause. Ovarian germ cell tumors can be hard to diagnose (find) early. Often there are no symptoms in the early stages, but tumors may be found during regular gynecologic exams (checkups). The following signs may be present: Swollen abdomen without weight gain in other parts of the body. Bleeding from the vagina after menopause (when you are no longer having menstrual periods for 1 year). The following stages are used for ovarian germ cell tumors: Stage I In stage I, cancer is found in one or both ovaries. Stage I is divided into stage IA, stage IB, and stage IC. Stage IA: Cancer is found inside a single ovary. Stage IB: Cancer is found inside both ovaries. 16
17 Stage IC: Cancer is found inside one or both ovaries and one of the following is true: o Cancer is also found on the outside surface of one or both ovaries; or o The capsule (outer covering) of the ovary has ruptured (broken open); or o Cancer cells are found in the fluid of the peritoneal cavity (the body cavity that contains most of the organs in the abdomen) or in washings of the peritoneum (tissue lining the peritoneal cavity). Stage II (2) In stage II, cancer is found in one or both ovaries and has spread into other areas of the pelvis. Stage II is divided into stage IIA, stage IIB, and stage IIC. Stage IIA: Cancer has spread to the uterus and/or fallopian tubes (the long slender tubes through which eggs pass from the ovaries to the uterus). Stage IIB: Cancer has spread to other tissue within the pelvis. Stage IIC: Cancer is found inside one or both ovaries and has spread to the uterus and/or fallopian tubes, or to other tissue within the pelvis. Also, one of the following is true: o Cancer is found on the outside surface of one or both ovaries; or o The capsule (outer covering) of the ovary has ruptured (broken open); or 17
18 o Cancer cells are found in the fluid of the peritoneal cavity (the body cavity that contains most of the organs in the abdomen) or in washings of the peritoneum (tissue lining the peritoneal cavity). Stage III (3) In stage III, cancer is found in one or both ovaries and has spread outside the pelvis to other parts of the abdomen and/or nearby lymph nodes. Stage III is divided into stage IIIA, stage IIIB, and stage IIIC. Stage IIIA: The tumor is found in the pelvis only, but cancer cells that can be seen only with a microscope have spread to the surface of the peritoneum (tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in the abdomen), the small intestines, or the tissue that connects the small intestines to the wall of the abdomen. Stage IIIB: Cancer has spread to the peritoneum and the cancer in the peritoneum is 2 centimeters or smaller. Stage IIIC: Cancer has spread to the peritoneum and the cancer in the peritoneum is larger than 2 centimeters and/or cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the abdomen. Cancer that has spread to the surface of the liver is also considered stage III ovarian cancer. 18
19 Stage IV (4) In stage IV, cancer has spread beyond the abdomen to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or tissue inside the liver. Cancer cells in the fluid around the lungs is also considered stage IV ovarian cancer. Recurrent Cancer Recurrent cancer is cancer that has recurred (come back) after it has been treated. Persistent cancer is cancer that does not go away with treatment. There are different types of treatment for patients with ovarian germ cell tumors Surgery Surgery is the most common treatment of ovarian germ cell tumor. A doctor may take out the cancer using one of the following types of surgery. Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: A surgical procedure to remove one ovary and one fallopian tube. Total hysterectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the uterus, including the cervix. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through the vagina, the operation is called a vaginal hysterectomy. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a large incision (cut) in the abdomen, the operation is called a total abdominal hysterectomy. If the uterus and cervix are taken out through a small incision (cut) in the abdomen using a laparoscope, 19
20 the operation is called a total laparoscopic hysterectomy. Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: A surgical procedure to remove both ovaries and both fallopian tubes. Tumor debulking: A surgical procedure in which as much of the tumor as possible is removed. Some tumors cannot be completely removed. Adjuvant therapy: Even if the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the operation, some patients may be offered chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called adjuvant therapy. Second-look laparotomy: After chemotherapy for an ovarian germ cell tumor, a second-look laparotomy may be done. This is similar to the laparotomy that is done to find out the stage of the cancer. Secondlook laparotomy is a surgical procedure to find out if tumor cells are left after primary treatment. During this procedure, the doctor will take samples of lymph nodes and other tissues in the abdomen to see if any cancer is left. This procedure is not done for dysgerminomas. Observation Observation is closely watching a patient s condition without giving any treatment unless signs or symptoms appear or change. 20
21 Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Systemic chemotherapy: When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body. Regional chemotherapy: When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas. Combination chemotherapy: When more than one anticancer drug is used. The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. Radiation therapy Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. The use of radiation in ovarian cancer is limited based on the patient s disease. 21
22 Clinical trials Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment. People who take part in a clinical trial may receive: The standard drugs alone or The standard drugs plus the new treatment being studied Many of today s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Ask if there is a clinical trial right for you. Taking part in a clinical trial helps improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward. Some clinical trials only include people who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for those whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from coming back or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment. As treatment progresses Some tests may be repeated to see how well your treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests. A plan for your long term care will be discussed with your treatment team and shared with your primary care provider. 22
23 To learn more about American Cancer Society National Cancer Institute National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines for Patients index.html MedlinePlus 23
24 Common Questions What does my pathology report tell me? What is the stage of my cancer? What are my goals for treatment? What are my treatment choices? What kind of support services are available for me about finances, emotions, spiritual questions, etc.? 24
25 My Health Care Team Contact Information Navigator: Medical Oncologist: Pharmacy: Radiation Oncologist: Nutritionist/Dietitian: Surgeon: Primary Care Doctor: Counselor/Therapist: Other: Other: 25
26 NOTES 26
27 NOTES 27
28 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer(PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated February 20, /18
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Colorectal cancer starts in the colon or rectum.
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated December 7, 2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated December 7, 2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect
 Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
Vulvar cancer: Know what to expect For women with vulvar cancer What is the vulva? The vulva is the external (outside) part of the female genitals. The vulva includes the outer and inner lip, the clitoris,
What is Thyroid Cancer?
 Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
What is Cervical Cancer?
 What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical cancer starts in a woman's cervix, the lower narrow part of the uterus. The uterus holds the growing fetus during pregnancy. The cervix connects the lower part of the
What is Cervical Cancer? Cervical cancer starts in a woman's cervix, the lower narrow part of the uterus. The uterus holds the growing fetus during pregnancy. The cervix connects the lower part of the
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer
 What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
General information about skin cancer
 Skin Cancer General information about skin cancer Key points Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. There are different types of cancer that start in
Skin Cancer General information about skin cancer Key points Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. There are different types of cancer that start in
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
What is ovarian cancer?
 What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Vaginal Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Screening tests. When you need them and when you don t
 Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
ENDOMETRIAL CANCER: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS
 ENDOMETRIAL CANCER: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS PATIENT INFORMATION BASED ON ESMO CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES This guide for patients has been prepared by Reliable Cancer Therapies (RCT) as a service to patients,
ENDOMETRIAL CANCER: A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS PATIENT INFORMATION BASED ON ESMO CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES This guide for patients has been prepared by Reliable Cancer Therapies (RCT) as a service to patients,
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Cancer of the Ovary
 North of Scotland Cancer Network Cancer of the Ovary Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by NOSCAN Gynaecology Cancer
North of Scotland Cancer Network Cancer of the Ovary Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by NOSCAN Gynaecology Cancer
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Cervical Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Childhood Craniopharyngioma Treatment (PDQ )
 1 di 12 27/06/2016 09.45 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 12 27/06/2016 09.45 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
Childhood Central Nervous System Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Treatment (PDQ )
 1 di 10 27/06/2016 08.16 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 10 27/06/2016 08.16 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
What is Esophageal Cancer?
 What is Esophageal Cancer? The esophagus is a hollow, muscular tube, about 10 inches long which connects the throat to the stomach. When a person swallows, the walls of the esophagus contract to push food
What is Esophageal Cancer? The esophagus is a hollow, muscular tube, about 10 inches long which connects the throat to the stomach. When a person swallows, the walls of the esophagus contract to push food
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Symptoms. Types
 Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate
 Search Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate 19-5-2017 If you've been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, it's natural to wonder about your prognosis. Learn about survival rates, outlook, and more. Take the
Search Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate 19-5-2017 If you've been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, it's natural to wonder about your prognosis. Learn about survival rates, outlook, and more. Take the
Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate
 Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate Gogamz Menu The latest ovarian cancer survival statistics for the UK for Health Professionals. See data for age, trends over time, stage at diagnosis and more. 5-8-2014
Stage 3 ovarian cancer survival rate Gogamz Menu The latest ovarian cancer survival statistics for the UK for Health Professionals. See data for age, trends over time, stage at diagnosis and more. 5-8-2014
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
4:00 into mp3 file Huang_342831_5_v1.mp3
 Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors
 Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors An adult central nervous system (CNS) tumor is a disease in which abnormal cells form in the tissues of the brain and or the spinal cord. Major Parts of the Brain Anatomy
Adult Brain and Spinal Cord Tumors An adult central nervous system (CNS) tumor is a disease in which abnormal cells form in the tissues of the brain and or the spinal cord. Major Parts of the Brain Anatomy
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER
 The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
Cancer in Women. Lung cancer. Breast cancer
 Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
Cancer in Women You can get cancer at any age, but it is more likely as you get older. The types of cancer people get and the risk of dying from cancer are not the same for all ethnic groups. Here are
See the latest estimates for new cases of ovarian cancer and deaths in the US and what research is currently being done.
 About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
What is Thyroid Cancer? Here are four types of thyroid cancer:
 What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
Ovarian Cancer. What you should know. making cancer less frightening by enlightening
 Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER
 INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
INFORMATION GUIDE FOR GYNAECOLOGICAL CANCER 1 The Australia New Zealand Gynaecological Oncology Group is Australia s peak national research organisation. It raises awareness and funds for gynaecological
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
Acute Salpingitis. Fallopian Tubes. Uterus
 Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Acute Salpingitis Introduction Acute salpingitis is a type of infection that affects the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Acute salpingitis is one of the
Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Gynecologic Cancer. Cleveland Clinic Offers State-of-the-Art Cancer Care
 Gynecologic Cancer Cleveland Clinic experts tailor treatment to their patients needs, taking into account the type of cancer, the age of the individual, the degree to which the cancer has spread and the
Gynecologic Cancer Cleveland Clinic experts tailor treatment to their patients needs, taking into account the type of cancer, the age of the individual, the degree to which the cancer has spread and the
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured!
 Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured! Throughout history, doctors and scientists have extensively studied Their researchers have not only yielded a wealth of information on the disease,
Philippine Cancer Society Forum: Cancer can be cured! Throughout history, doctors and scientists have extensively studied Their researchers have not only yielded a wealth of information on the disease,
Different Types of Cancer
 Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Mammography. The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Women s health promotion series
 The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series Mammography When breast cancer is diagnosed at an early stage it could be treated and the patient would have a high chance
The Lebanese Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology Women s health promotion series Mammography When breast cancer is diagnosed at an early stage it could be treated and the patient would have a high chance
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) Mammography
 Mammography WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Mammography is an X-ray technique used to study the breasts. It can help doctors find breast cancer at an early stage (when treatment
Mammography WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Mammography is an X-ray technique used to study the breasts. It can help doctors find breast cancer at an early stage (when treatment
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
COMENIUS-Project: SM&CLIL Radiation & Medicine
 Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Breast Cancer in Women
 The Crawford Clinic 1900 Leighton Avenue Suite 101 Anniston, Alabama 36207 Phone: 256-240-7272 Fax: 256-240-7242 Breast Cancer in Women What is breast cancer? When abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, they
The Crawford Clinic 1900 Leighton Avenue Suite 101 Anniston, Alabama 36207 Phone: 256-240-7272 Fax: 256-240-7242 Breast Cancer in Women What is breast cancer? When abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, they
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater
 Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Ovarian Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
patient education Fact Sheet
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Improving Methods for Breast Cancer Detection and Diagnosis. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) is funding numerous research projects to improve
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Improving Methods for
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Improving Methods for
Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Magnitude of Cancer Problem in the Philippines
 Cancer in Women Magnitude of Cancer Problem in the Philippines INCIDENCE 3rd in incidence after communicable & cardiovascular diseases 1 out of 1,000 Filipinos has cancer 114:103 Females to Males, Filipino
Cancer in Women Magnitude of Cancer Problem in the Philippines INCIDENCE 3rd in incidence after communicable & cardiovascular diseases 1 out of 1,000 Filipinos has cancer 114:103 Females to Males, Filipino
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors
 Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging of Ewing Tumors Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Case Scenario 1. Pathology report Specimen from mediastinoscopy Final Diagnosis : Metastatic small cell carcinoma with residual lymphatic tissue
 Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Case Scenario 1 Oncology Consult: Patient is a 51-year-old male with history of T4N3 squamous cell carcinoma of tonsil status post concurrent chemoradiation finished in October two years ago. He was hospitalized
Adult Central Nervous System Tumors Treatment (PDQ )
 1 di 20 28/06/2016 11.18 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
1 di 20 28/06/2016 11.18 NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute
What Causes Cervical Cancer? Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
 Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Cervical Health Awareness Month is a chance to raise awareness about how women can protect themselves from HPV (human papillomavirus) and cervical cancer. HPV is a very common infection that spreads through
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General
 Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer - General Introduction Breast cancer is a common condition that affects one out of every 11 women. Your doctor has recommended chemotherapy for your breast cancer. Chemotherapy
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Colorectal Cancer Glossary. Colorectal Cancer Glossary
 1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Case Scenario 1. History
 History Case Scenario 1 A 53 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with post-menopausal vaginal bleeding. The patient is not a smoker and does not use alcohol. She has no family
History Case Scenario 1 A 53 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with post-menopausal vaginal bleeding. The patient is not a smoker and does not use alcohol. She has no family
Welcome! Here s our agenda for today:
 Welcome! Here s our agenda for today: What is ovarian cancer? What causes it? When does genetic testing come in? When are families at risk for ovarian cancer? What are the treatments? 3 things to remember
Welcome! Here s our agenda for today: What is ovarian cancer? What causes it? When does genetic testing come in? When are families at risk for ovarian cancer? What are the treatments? 3 things to remember
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know
 Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
 To the Patient and Family This booklet has been written for people who have received a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or who are being tested for this illness. If you have questions that are not answered
To the Patient and Family This booklet has been written for people who have received a diagnosis of thyroid cancer or who are being tested for this illness. If you have questions that are not answered
Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Lymphoma of the Skin Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Arteriogram An X-ray of an artery after the injection of dye.
 A Abscess A localized collection of pus in any part of the body, usually surrounded by inflamed tissue. Anesthetic An agent that causes loss of sensation with or without the loss of consciousness. Angiography,
A Abscess A localized collection of pus in any part of the body, usually surrounded by inflamed tissue. Anesthetic An agent that causes loss of sensation with or without the loss of consciousness. Angiography,
Cancer Facts for People Over 50
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Cancer Facts for People Over 50 Cancer strikes people of all ages, but you are more likely to get cancer as you get older, even if no one in your family has ever had
National Institute on Aging AgePage Cancer Facts for People Over 50 Cancer strikes people of all ages, but you are more likely to get cancer as you get older, even if no one in your family has ever had
Uterine sarcoma. Information for patients Gynaecology
 Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Uterine sarcoma Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 12 This leaflet is intended to offer you support and information at a very difficult and stressful time in your life. To be told that you
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Cervical Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer is the term used to describe malignant tumors that start in the lining of the cervix the lower part of the uterus
Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer is the term used to describe malignant tumors that start in the lining of the cervix the lower part of the uterus
Anemia: A condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
 Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
Veterinary Teaching Hospital Oncology Service Virginia-Maryland Regional College of Veterinary Medicine 245 Duck Pond Drive Blacksburg, VA 24061 Phone: 540-231-4621 Definitions This fact sheet is based
New Cancer Cases By Site Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3%
 Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program. Patient information for. Last revised: November
 Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
