EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN RADIATION- INDUCED GENOME INSTABILITY AND CARCINOGENESIS: POWER, PROMISE AND OPPORTUNITIES
|
|
|
- Mae Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN RADIATION- INDUCED GENOME INSTABILITY AND CARCINOGENESIS: POWER, PROMISE AND OPPORTUNITIES Olga Kovalchuk, MD/PhD University of Lethbridge, AB, Canada
2 Sources of radiation exposure: Environmental and occupational exposure Diagnostic and therapeutic exposure One third of people are likely to get cancer More than half will receive radiotherapy
3 RADIATION EFFECTS Direct or targeted Effects in the directly exposed cells Indirect or non-targeted effects Effects in the neighboring unexposed cells Persisting effects in the progeny of exposed cells
4 Indirect/Non-targeted Effects of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Effects in unexposed cells and their progeny - in cells not directly hit. Genomic instability Bystander Effects Transgenerational effects
5 Genome instability molecular mechanisms "Genetic" - a heritable change in the DNA sequence GENETIC EPIGENETIC Epigenetic - information contained in chromatin and mediated via short RNAs, other than the actual DNA sequence. Epigenetic information defines a heritable specific gene expression pattern
6
7 EPIGENETIC CHANGES Epigenetic alterations changes induced in cells that alter expression of the information on transcriptional, translational, or post-translational levels without change in DNA sequence Methylation of DNA Modifications of histones RNA-mediated modifications DNMT1 DNMT3a DNMT3b Me P U sirna, mirna, pirna Control Treated SAM SAH A A - acetylation Me - methylation P - phosphorylation U - ubiquitination
8
9 SMALL INTERFERING RNAS Small non-coding RNAs refers nt regulatory RNAs acting as a major epigenetic regulators of cellular processes. A few classes of small RNAs that differ with respect to their size, nucleotide composition, biogenesis and mode of action were discovered in mammals. 1. microrna: nt, down-regulate protein translation, transcript cleavage; 2. pirna: nt, transposon silencing, establishment of epigenetic patterns in the germ line of developing embryo; 3. sirna (21-22 nt): regulation of transposable elements, pseudogenes and endogenous genes. Other classes of small regulatory RNAs with unknown function may be derived from active trna, rrna and snorna. Non-coding RNAs dominate transcriptional output in mammals, they are developmentally and stress regulated. Large number of mirnas are involved in cancer as either tumor-suppressors or oncogenes.
10 micrornas (mirs) play an integral role in gene regulation - 21nt, single stranded, RNA molecules result from the processing of primary, double-stranded transcripts Drosha Pre-miR Dicer Pasha Pri-miR NUCLEUS AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAA RISC Translational Repression CYTOPLASM
11 pirnas - a distinct class of 24- to 30-nucleotidelong RNAs are generated by Dicer-independent mechanism. pirnas associate with Piwi-class Argonaute proteins. Function: germline development, silencing of selfish DNA elements, and in maintaining germline DNA integrity. Klattenhoff & Theurkauf, Development, 2006
12 LOW DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN AN ANIMAL MODEL EPIGENETICS OF RADIATION-INDUCED IN VIVO BYSTANDER EFFECT EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE TRANSGENERTIONAL GENOME INSTABILITY THERAPEUTIC AND DIAGNOSTIC EXPOSURE CHALLENGES
13 LOW DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN AN ANIMAL MODEL EPIGENETICS OF RADIATION-INDUCED IN VIVO BYSTANDER EFFECT EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE TRANSGENERTIONAL GENOME INSTABILITY THERAPEUTIC AND DIAGNOSTIC EXPOSURE CHALLENGES
14 Low dose radiation-induced epigenetic changes in an animal model : Objective: to dissect the epigenetic basis of induction of the low dose radiationinduced genome instability and adaptive response and the specific fundamental roles of epigenetic changes (i.e. DNA methylation, histone modifications and mirnas) in their generation. Approach: we utilize an in vivo murine model to study epigenetic alterations in the radiation-target organs thymus and spleen in context of low dose radiation effects and adaptive responses. We also archive and analyze other tissues gonades, brain and liver. Results: Exposure Time points Organs Endpoints 0 Gy (sham) 0.01 Gy 0.1 Gy 1 Gy 10 x 0.01 Gy 0.01Gy prime followed by 1 Gy challenge 6 hours 96 hours 4 weeks thymus spleen Global and locus-specific DNA methylation analysis Global histone modification analysis Analysis of micrornaome DNA damage analysis by H2AX foci Genome stability analysis Gene expression analysis In this study, we for the first time found that low dose radiation (LDR) exposure causes profound and tissue-specific epigenetic changes in the exposed tissues We established that LDR exposure affects methylation of repetitive elements in the genome, causes changes in histone methylation, acethylation and phosphorylation Importantly, LDR causes profound and persistent effects on small RNAs profiles. MicroRNAs are excellent biomarkers of LDR exposure. LDR exposure causes tissue-specific changes in gene expression. We identified several novel biomarkers of LDR exposure.
15
16
17
18 LOW DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN AN ANIMAL MODEL EPIGENETICS OF RADIATION-INDUCED IN VIVO BYSTANDER EFFECT EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE TRANSGENERTIONAL GENOME INSTABILITY THERAPEUTIC AND DIAGNOSTIC EXPOSURE CHALLENGES
19 Radiation-induced bystander effects in spleen CT control animal CT control animal 0 Gy 0 Gy B - completely exposed animal B - completely exposed animal 1 Gy 1 Gy H - head exposed animal H - head exposed animal lead shielding 1 Gy lead shielding 1 Gy BALBc C57BL/6
20 The main findings are: Cranial irradiation leads to: elevated levels of DNA damage increased p53 expression altered levels of cellular proliferation and apoptosis altered DNA methylation levels The observed bystander changes were not caused by radiation scattering, and were observed in two different mouse strains, C57BL/6 and BALB/c, although certain strain specificity was noticed.
21 Whole body and cranial radiation exposure induces the significant and sex-specific loss of DNA methylation in the murine spleen BS IR CT male * * * * 96 H 6 H BS female IR CT * * 96 H 6 H % of unmethylated CCGG sites in genome as compared to control CT control animals; IR body-exposed animals; BS bystander/head-exposed animals
22 The other sex-specific responses to whole-body and cranial exposure in the spleen tissue included: Changes in apoptosis Proliferation changes MicroRNAome alterations Changes in the gene expression Sex hormones are involved in the sex-specificity of the radiation responses
23
24 Sequencing: Illumina GAIIx; Single-End; multiplexed; 36 cycles; 6 samples per lane, each sample was run in duplicate across two lanes. Reference: Rat, rn4 UCSC, downloaded from Illumina igenome site. Amongst various changes, we identified a predicted gene, which was strikingly upregulated in all of the male brain regions studied, but completely unaffected in females. Sequence within these coordinates did not contain any long open reading frames (ORFs), so the gene is most probably non-coding. There were no CpG islands found in the vicinity (2000 bp up- and downstream) of the gene. High confidence transcription binding sites as predicted by TFSEARCH software include CdxA, GATA-1, SRY, HFH-2, p300 and a couple of others. Interestingly, SRY is the sex determination factor which is expressed only in males, that may explain why this gene is upregulated in sex-specific manner. On the other hand, p300 is the histone acetyltransferase, which points at why this gene can stay activated long time after exposure?
25 LOW DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN AN ANIMAL MODEL EPIGENETICS OF RADIATION-INDUCED IN VIVO BYSTANDER EFFECT EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE TRANSGENERTIONAL GENOME INSTABILITY THERAPEUTIC AND DIAGNOSTIC EXPOSURE CHALLENGES
26 Epigenetic mechanisms involved in the transgenertional genome instability?????
27 Paternal radiation exposure affects DNA methylaton of LINE 1 and SINE B2 retrotransposable elements in the thymus tissue of the progeny Relative qpcr amplification LINE1 * SINE B2 4 * 2 0 CT EX CT EX
28 Change from control, % Paternal radiation exposure decreases LSH protein levels in the thymus of progeny in vivo LSH1 levels CT * EX LSH1 loading
29 Paternal radiation exposure results in micrornaome deregulation in the thymic tissue of the unexposed progeny DICER positive cells per field of view progeny of control progeny of exposed 3 DICER levels 2 p progeny of control progeny of exposed
30 Radiation exposure alters micrornaome of mouse testes
31 Relative qpcr amplification Change from control, % Radiation exposure alters mirna expression and methylation of LINE 1 and SINE B2 retrotransposons in male germline A B mirna Fold induction Target protein mir-29a 2.33 DNMT3a, DNMT3b mir-29b 1.23 DNMT3a, DNMT3b DNMT3a actin DNMT3a levels CT * EX C CT LINE1 SINE B2 * EX CT 1 2 EX
32 ANALYSIS OF RASIRNA (PIRNA) MOLECULES BY DEEP SEQUENCING all LTR LINE SINE low complexity DNA simple repeat CT EX
33 Parental germline Progeny DNA damage? Aberrant setting of methylation marks Altered DNA methylation Altered mirnaome Loss of pirnaome/ rasirnaome? Aberrant gene (including small RNAs) gene expression?? Downstream snowball effects?
34 LOW DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED EPIGENETIC CHANGES IN AN ANIMAL MODEL EPIGENETICS OF RADIATION-INDUCED IN VIVO BYSTANDER EFFECT EPIGENETIC MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN THE TRANSGENERTIONAL GENOME INSTABILITY THERAPEUTIC AND DIAGNOSTIC EXPOSURE CHALLENGES
35 Analysis of DNA methylation, gene expression and apoptosis in brain cancer cells lines reveals a potential anti-tumor effect of low dose radiation in neuroblastoma and an opposite tumor-promoting effect in malignant glioma
36 Gene-specific DNA methylation and gene expression changes induced by low dose radiation in human neuroblastoma (A-172 and IMR-32) and glioma cells (SK-N-BE) DNA methylation A-172 IMR-32 SK-B-NE 24 hours hours Gene expression A-172 IMR-32 SK-B-NE 24 hours hours Correlation between the levels of gene expression, methylation and apoptosis in the studied neuroblastoma and glioma cells DNA methylation A-172 IMR-32 SK-B-NE 24 hours hours Gene expression A-172 IMR-32 SK-B-NE 24 hours hours Apoptosis A-172 IMR-32 SK-B-NE 24 hours hours
37 Epigenetics a new frontier in radiation research
38
39 Advances are made by answering questions. Discoveries are made by questioning answers. Bernard Haisch
40 Kovalchuk group Slava Ilnytsky Jody Filkowski Matt Merrifield Bo Wang Dongping Li Rocio Rodriguez-Juarez Anna Kovalchuk Lidia Luzhna Corinne Sidler Alumni Jason Novak Jan Tamminga Kristy Kutanzi Igor Koturbash Mike Lowings Jonathan Loree James Meservy Natasha Singh Joel Stimson Munima Alam Paul Walz Acknowledgements Collaborators: Bryan Kolb, CCBN Eugene Berezikov, Hubrecht Institute Igor Pogribny, NCTR William Bonner, NCI/NIH Olga Martin, PeterMaccallum Cancer Center, Ausralia Funding: CIHR Institute of Gender, Sex and Health Chair Program
41 When used right, technology becomes an accelerator of momentum, not a creator of it. Contacts: Dr. Igor Kovalchuk igor.kovalchuk@uleth.ca
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology
 Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology Bhaskar Gollapudi, Ph.D The Dow Chemical Company Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches
Session 2: Biomarkers of epigenetic changes and their applicability to genetic toxicology Bhaskar Gollapudi, Ph.D The Dow Chemical Company Workshop: Genetic Toxicology: Opportunities to Integrate New Approaches
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS
 R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
R. Piazza (MD, PhD), Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca EPIGENETICS EPIGENETICS THE STUDY OF CHANGES IN GENE EXPRESSION THAT ARE POTENTIALLY HERITABLE AND THAT DO NOT ENTAIL A
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
MicroRNAs: a new source of biomarkers in radiation response. Simone Moertl, Helmholtz Centre Munich
 MicroRNAs: a new source of biomarkers in radiation response Simone Moertl, Helmholtz Centre Munich The RNA World mrna rrna coding snorna trna scarna RNA snrna noncoding lincrna rasirna RNAi anti-sense
MicroRNAs: a new source of biomarkers in radiation response Simone Moertl, Helmholtz Centre Munich The RNA World mrna rrna coding snorna trna scarna RNA snrna noncoding lincrna rasirna RNAi anti-sense
Role of epigenetic effectors in maintenance of the long-term persistent bystander effect in spleen in vivo
 Carcinogenesis vol.28 no.8 pp.1831 1838, 2007 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm053 Advance Access publication March 7, 2007 Role of epigenetic effectors in maintenance of the long-term persistent bystander effect
Carcinogenesis vol.28 no.8 pp.1831 1838, 2007 doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm053 Advance Access publication March 7, 2007 Role of epigenetic effectors in maintenance of the long-term persistent bystander effect
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3
 Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, JMIT, Radaur, Haryana, India 2 KITM, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India 3 NIDDK, National Institute of Health,
Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, JMIT, Radaur, Haryana, India 2 KITM, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India 3 NIDDK, National Institute of Health,
Stem Cell Epigenetics
 Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer. Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
 MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
RADIATION-INDUCED DEREGULATION OF PiRNA PATHWAY PROTEINS: A POSSIBLE MOLECULAR MECHANISM UNDERLYING TRANSGENERATIONAL EPIGENOMIC INSTABILITY
 RADIATION-INDUCED DEREGULATION OF PiRNA PATHWAY PROTEINS: A POSSIBLE MOLECULAR MECHANISM UNDERLYING TRANSGENERATIONAL EPIGENOMIC INSTABILITY Matthew Merrifield Bachelor of Science, University of Lethbridge,
RADIATION-INDUCED DEREGULATION OF PiRNA PATHWAY PROTEINS: A POSSIBLE MOLECULAR MECHANISM UNDERLYING TRANSGENERATIONAL EPIGENOMIC INSTABILITY Matthew Merrifield Bachelor of Science, University of Lethbridge,
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Cancer Problems in Indonesia
 mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN
 Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
Epigenetic Principles and Mechanisms Underlying Nervous System Function in Health and Disease Mark F. Mehler MD, FAAN Institute for Brain Disorders and Neural Regeneration F.M. Kirby Program in Neural
DNA methylation & demethylation
 DNA methylation & demethylation Lars Schomacher (Group Christof Niehrs) What is Epigenetics? Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression (active versus inactive genes) that do not
DNA methylation & demethylation Lars Schomacher (Group Christof Niehrs) What is Epigenetics? Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression (active versus inactive genes) that do not
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Epigenetics DNA methylation. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13. DNA Methylation
 Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease
 Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease Cambridge Masterclass Workshop on Epigenetics in GI Health and Disease 3 rd September 2013 Matt Zilbauer Overview Basic principals of Epigenetics
Epigenetics: Basic Principals and role in health and disease Cambridge Masterclass Workshop on Epigenetics in GI Health and Disease 3 rd September 2013 Matt Zilbauer Overview Basic principals of Epigenetics
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS IN VIVO IGOR KOTURBASH. B.Med., Medical University of Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine, 2001
 MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS IN VIVO IGOR KOTURBASH B.Med., Medical University of Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine, 2001 A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies of the
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF RADIATION-INDUCED BYSTANDER EFFECTS IN VIVO IGOR KOTURBASH B.Med., Medical University of Ivano-Frankivsk, Ukraine, 2001 A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies of the
Institute of Radiation Biology. Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014
 Institute of Radiation Biology Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014 Hippocrates: Cause is systemic excess of black humor. Paracelsus challenges the humor theory. Suggests external
Institute of Radiation Biology Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes DoReMi Course 2014 Hippocrates: Cause is systemic excess of black humor. Paracelsus challenges the humor theory. Suggests external
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module-9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 6 Epigenetics
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module-9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 6 Epigenetics
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The RNA revolution: rewriting the fundamentals of genetics
 RCH Grand Rounds - June 4 The RNA revolution: rewriting the fundamentals of genetics Ken Pang Overview 1. Genetics 101 2. Recent lessons from genomics 3. The expanding world of noncoding RNAs 4. Long noncoding
RCH Grand Rounds - June 4 The RNA revolution: rewriting the fundamentals of genetics Ken Pang Overview 1. Genetics 101 2. Recent lessons from genomics 3. The expanding world of noncoding RNAs 4. Long noncoding
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
RNA interference (RNAi)
 RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics
 The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression.George J. Quellhorst, Jr., PhD.Associate Director, R&D.Biological Content Development Topics to be Discussed Importance of Chromatin-Based Regulation Mechanism
Chromatin-Based Regulation of Gene Expression.George J. Quellhorst, Jr., PhD.Associate Director, R&D.Biological Content Development Topics to be Discussed Importance of Chromatin-Based Regulation Mechanism
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to the detection and repair of DNA damage DSBs induce a local decrease
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs
 What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
What are micrornas? V16: involvement of micrornas in GRNs How can one identify micrornas? What is the function of micrornas? Elisa Izaurralde, MPI Tübingen Huntzinger, Izaurralde, Nat. Rev. Genet. 12,
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience. Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1
 Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification
 Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
Eukaryotic small RNA Small RNAseq data analysis for mirna identification P. Bardou, C. Gaspin, S. Maman, J. Mariette, O. Rué, M. Zytnicki INRA Sigenae Toulouse INRA MIA Toulouse GenoToul Bioinfo INRA MaIAGE
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
 p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure
 Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global regulator during meiosis
 RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
Histones modifications and variants
 Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Gene Regulation Part 2
 Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
DNA methylation: a potential clinical biomarker for the detection of human cancers
 DNA methylation: a potential clinical biomarker for the detection of human cancers Name: Tong Samuel Supervisor: Zigui CHEN Date: 1 st December 2016 Department: Microbiology Source: cited from Jakubowski,
DNA methylation: a potential clinical biomarker for the detection of human cancers Name: Tong Samuel Supervisor: Zigui CHEN Date: 1 st December 2016 Department: Microbiology Source: cited from Jakubowski,
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2018 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Jan 3 rd Wed Mapping disease genes I: inheritance patterns and linkage analysis
A Transgenerational Process Defines pirna Biogenesis in Drosophila virilis
 Report A Transgenerational Process Defines pirna Biogenesis in Drosophila virilis Graphical Abstract Authors Adrien Le Thomas, Georgi K. Marinov, Alexei A. Aravin Correspondence aaa@caltech.edu In Brief
Report A Transgenerational Process Defines pirna Biogenesis in Drosophila virilis Graphical Abstract Authors Adrien Le Thomas, Georgi K. Marinov, Alexei A. Aravin Correspondence aaa@caltech.edu In Brief
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
Campbell Biology 10. A Global Approach. Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression
 Lecture on General Biology 2 Campbell Biology 10 A Global Approach th edition Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular
Lecture on General Biology 2 Campbell Biology 10 A Global Approach th edition Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular
Epigenetic Inheritance
 (2) The role of Epigenetic Inheritance Lamarck Revisited Lamarck was incorrect in thinking that the inheritance of acquired characters is the main mechanism of evolution (Natural Selection more common)
(2) The role of Epigenetic Inheritance Lamarck Revisited Lamarck was incorrect in thinking that the inheritance of acquired characters is the main mechanism of evolution (Natural Selection more common)
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus
 Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
Human Genetics 542 Winter 2017 Syllabus Monday, Wednesday, and Friday 9 10 a.m. 5915 Buhl Course Director: Tony Antonellis Module I: Mapping and characterizing simple genetic diseases Jan 4 th Wed Mapping
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, WA 98109
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0711 TITLE: Transgenerational Radiation Epigenetics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher J. Kemp, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-10-1-0711 TITLE: Transgenerational Radiation Epigenetics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Christopher J. Kemp, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle,
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics. DNA methylation in prostate cancer
 Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Dominic J Smiraglia, PhD Department of Cancer Genetics DNA methylation in prostate cancer Overarching theme Epigenetic regulation allows the genome to be responsive to the environment Sets the tone for
Are you the way you are because of the
 EPIGENETICS Are you the way you are because of the It s my fault!! Nurture Genes you inherited from your parents? Nature Experiences during your life? Similar DNA Asthma, Autism, TWINS Bipolar Disorders
EPIGENETICS Are you the way you are because of the It s my fault!! Nurture Genes you inherited from your parents? Nature Experiences during your life? Similar DNA Asthma, Autism, TWINS Bipolar Disorders
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
Epigenetics and Toxicology
 Epigenetics and Toxicology Aline.deconti@fda.hhs.gov Division of Biochemical Toxicology National Center for Toxicology Research U.S.-Food and Drug Administration The views expressed in this presentation
Epigenetics and Toxicology Aline.deconti@fda.hhs.gov Division of Biochemical Toxicology National Center for Toxicology Research U.S.-Food and Drug Administration The views expressed in this presentation
Epigenetics. Lyle Armstrong. UJ Taylor & Francis Group. f'ci Garland Science NEW YORK AND LONDON
 ... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
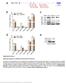 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Epigenetics and Environmental Health A Step-by-Step Tutorial
 Powerful ideas for a healthier world Epigenetics and Environmental Health A Step-by-Step Tutorial Andrea Baccarelli, MD, PhD, MPH Laboratory of Environmental Epigenetics Objective of my presentation To
Powerful ideas for a healthier world Epigenetics and Environmental Health A Step-by-Step Tutorial Andrea Baccarelli, MD, PhD, MPH Laboratory of Environmental Epigenetics Objective of my presentation To
Lecture 27. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development
 Lecture 27 Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development Development of a multicellular organism is not only determined by the DNA sequence but also epigenetically through DNA methylation
Lecture 27 Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development Development of a multicellular organism is not only determined by the DNA sequence but also epigenetically through DNA methylation
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
September 20, Submitted electronically to: Cc: To Whom It May Concern:
 History Study (NOT-HL-12-147), p. 1 September 20, 2012 Re: Request for Information (RFI): Building a National Resource to Study Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) The MDS Cohort Natural History Study (NOT-HL-12-147).
History Study (NOT-HL-12-147), p. 1 September 20, 2012 Re: Request for Information (RFI): Building a National Resource to Study Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) The MDS Cohort Natural History Study (NOT-HL-12-147).
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes,
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes,
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control
 Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control Chapter 10 - Post-transcriptional Gene Control 10.1 Processing of Eukaryotic Pre-mRNA 10.2 Regulation of Pre-mRNA Processing 10.3 Transport of mrna Across
Upcoming Webinars. Profiling genes by pathways and diseases. Sample & Assay Technologies -1-
 Upcoming Webinars -1- Keep up to date: Follow Pathway focused biology on Facebook www.facebook.com/pathwaycentral Latest information on, pathway focused research and demos. -2- Understanding Gene Expression
Upcoming Webinars -1- Keep up to date: Follow Pathway focused biology on Facebook www.facebook.com/pathwaycentral Latest information on, pathway focused research and demos. -2- Understanding Gene Expression
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation
 Epigenesis: Gene Regulation Epigenesis : Gene Regulation I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation (X chromosome inactivation or Lyonization) III) Regulation during
Epigenesis: Gene Regulation Epigenesis : Gene Regulation I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation (X chromosome inactivation or Lyonization) III) Regulation during
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription. 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra
 Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Where Splicing Joins Chromatin And Transcription 9/11/2012 Dario Balestra Splicing process overview Splicing process overview Sequence context RNA secondary structure Tissue-specific Proteins Development
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research
 MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing. Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven
 Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-1029 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mu-Shui Dai, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Oregon Health Science niversity, Portland, Oregon 97239 REPORT DATE: October 2013 TYPE
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32781 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benard, Anne Title: Epigenetic prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32781 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Benard, Anne Title: Epigenetic prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer Issue
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A
 MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A Heba Alkhatabi, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Medical Laboratory Collage of Applied Medical science King Abdul Aziz
MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A Heba Alkhatabi, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Medical Laboratory Collage of Applied Medical science King Abdul Aziz
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Meiosis and retrotransposon silencing during germ cell development in mice Citation for published version: Oellinger, R, Reichmann, J & Adams, IR 2010, 'Meiosis and retrotransposon
Edinburgh Research Explorer Meiosis and retrotransposon silencing during germ cell development in mice Citation for published version: Oellinger, R, Reichmann, J & Adams, IR 2010, 'Meiosis and retrotransposon
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
Gene Regulation. Bacteria. Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
