ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
|
|
|
- Gabriella King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp , October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION *3 Dr. Archana Jayakumar 1 Dr.M.Adaikkappan and 2 Dr.S.Sethurajan 1 Professor, Department of Radiology, RMMCH, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar 2 Lecturer, Department of Radiology, RMMCH, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar 3 PostGraduate, Department of Radiology, RMMCH, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar Article History: Received 15 th September,2015, Accepted 9 th October, 2015, Published 10 th October,2015 ABSTRACT AIM: To use x-ray mammogram for classifying palpable breast lumps into benign and malignant lesions, using various mammographic features and to correlate the findings with histopathological gold standard.methodology: Women referred for the evaluation of palpable breast lumps and nipple discharge were included in the study.result: In this study, mammography had a sensitivity of 94%, specificity of 97 %, positive predictive value of 89% and a negative predictive value of 98%. Sensitivity of x-ray mammogram in younger age group (<40 years) is 89% and in older age group (>40 years) is 96%.CONCLUSION: There is positive correlation between xray mammogram and histopathology. Mammography is a very sensitive and specific test for detection of breast malignancy. Mammographic features like microcalcification and spiculated margin are the most specific findings in malignancy. Mammography has a better sensitivity in older age group than in the younger age group. Keywords: Breast lump, X-ray mammogram, histopathology, sensitivity, specificity, microcalcification, spiculated margin. 1.INTRODUCTION Women present with a number of breast complaints like mastalgia, nipple discharge and a feeling of lump in the breast. Of these a lump in the breast is a matter of great concern for the patients as they equate it to cancer. The most important decision for the radiologist to make, is whether the lesion is benign or malignant. In spite of all the recent advances in breast imaging, mammography remains as the most exclusively used modality for breast cancer screening and early breast carcinoma detection. It is estimated that one in eight women will develop breast carcinoma in their lifetime, which further stresses the importance of early detection of cancer in a treatable stage. This study is an attempt to characterize the mammography features of breast masses and to evaluate the accuracy of each in diagnosing breast lesions and to correlate them with histopathological gold standard. *Corresponding author: Dr. Archana Jayakumar, Department of Radiology, Rajah Muthiah Medical College Hospital,Annamalai University, Chidambaram 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS A descriptive study was done, for a period of 2 years, from October 2013 to October 2015 on 152 patients who presented with palpable breast lumps, in the Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences of Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram. All the patients were referred from the Department of Surgery, Rajah Muthiah Medical College and Hospital, Chidambaram. As per inclusion criteria, all patients above 15 years of age with palpable breast lumps and patients with nipple discharge were included in the study. As per exclusion criteria Patients with advanced breast carcinoma (e.g. fungating lesions), known inflammatory lesions (e.g. breast abscess), post operative or previously treated cases, post biopsy cases, patients with known histopathological report and patients who refuse to give consent for imaging are excluded from the study. After detailed history and clinical examination, patients underwent mammography in our dedicated mammography unit Philips Mamodiagnost. The craniocaudal and mediolateral oblique views were employed in all cases. For the craniocaudal view, the cassette is placed at the level of the inframammary fold below the breast and then elevated so 807
2 [ Dr. Archana Jayakumar et al., 2015 that the breast is pulled forward and raised until the skin below the inframammary level is seen taut. Compression is given to the breast from above. X ray beam is also directed vertically from above. For mediolateral oblique view compression is given perpendicular to the long axis of the pectoralis major muscle. And the xray beam is directed perpendicular to the pectoralis major from superomedial to inferolateral direction. criteria used for lesions in mammography are low density, circumscribed margin and presence of macrocalcification. criteria in mammography are high density, spiculated margins and presence of fine pleomorphic/ fine linear/ fine linear branching microcalcifications. 3.RESULT In this study mammography had a sensitivity of 94%, specificity of 97 %, positive predictive value of 89% and a negative predictive value of 98%. Sensitivity of x-ray mammogram in younger age group (<40 years) is 89% and in older age group (>40 years) is 96% Table 1 Association of Age with reference to the type of lesion. Age (in Number Percenta Number Percentage years) ge Maximum number of patients who presented with breast lumps, irrespective of their benign or malignant nature belonged to the age group of years. The most common benign lesion observed in the study population is fibroadenoma, which was present in 77 patients (51% of study population). As per literature, fibroadenoma is commonly seen below 35 years of age. In this study 53 out of 77 patients having fibroadenoma, were below 35 years (68.8%). The youngest patient with malignancy was 27 years of age and the oldest patient with malignancy was 65 years old. In the study no malignancy (0%) was seen in the age group and the lowest percentage of malignancy (11%) was seen in age group. Highest percentage of malignancy (60%) was seen in years age group where 6 out of 10 cases are malignant. This is followed by the age group of years where 9 out of 21 cases i.e. 43% of cases were malignant. Therefore there is a higher chance of malignancy in patients older than 45 years of age. Table 2 Association of quadrant wise distribution with type of lesions Quadrant Upper outer Lower outer Lower Inner Upper Inner Retroareolar Total The most common site of location of both benign as well as malignant lesions is in the upper outer quadrant. This location had lesions in 47% of the study population. 45% of benign lesions are located in the upper outer quadrant. 51.5% of malignant cases had breast lump in the upper outer quadrant and 21.2% in the retroareolar region. As per literature also, more than 50% of carcinomas are located in the upper outer quadrant, probably due to more concentration of terminal ductal lobar units over the same. Table 3 Relationship of Family History with age of onset of disease Age Family History (in years) Absent Present Total p value is which is >0.001 Relationship of family history with the age of occurrence was not found to be statistically significant in the study probably due to the reduced sample size. Table 4 Association of xray mammogram density of lesion to type of lesion Density Type of Lesions of lesion Low High Table 5 Association of Xray mammogram Margin with benign and malignant lesions Margin Type of Lesions Circumscribed Lobulated Indistinct Spiculated Table 6 Association of nature of calcification with type of lesions Calcification Type of Lesions Nil Microcalcific ation Macrocalcifi cation Table 7 Distribution of Type of Lesions in Relation to BIRADS BIRADS Type of Lesions
3 Volume 3, Issue 10, pp , October, 2015 Table 8 Distribution according to mammographic diagnosis Mammographic Number Percentage diagnosis Total Xray mammogram showed 23% of malignant cases and 77 % benign cases. Criteria for benign lesions in Xray mammogram are low density, circumscribed margin and macrocalcification (presence of 2 or more criteria). In the study, 99% of cases with a well circumscribed margin, 92% of the cases with low density, 95% of cases with macrocalcification and 94% of cases with no evidence of any calcifications were found to be benign. All the 95% of cases with macrocalcification were histologically proven to be benign, most of them being calcified fibroadenomas. Of these features well circumscribed margin is found to be the most specific finding in benign lesions. On statistical analysis, all these findings were found to have a significant correlation with benign etiology. Criteria for benign lesions in x-ray mammogram (presence of 2 or more criteria), are high density, spiculated margins and presence of microcalcifications. 100% of cases having spiculated borders and 100% of cases having fine linear or pleomorphic microcalcifications were proven to be malignant. Hence these mammographic findings have a positive predictive value of 100% towards malignancy. 66% of cases presenting with a low density on mammogram showed malignancy. So all these findings are found to have a statistically significant correlation with malignant etiology. As per the criteria of malignancy in xray mammography, 4 cases which were diagnosed as malignant lesions turned out to be benign as per histopathology. 2 cases with high density and spiculated margins (satisfying 2 malignant criteria in xray mammogram) was proven to be granulomatous mastitis or abscess in histopathology. Mammographic appearance of breast abscess can mimic carcinoma. Clinical diagnosis of breast abscess should be employed in such cases. 2 cases had high density and spiculated margins thus satisfying 2 criteria in malignancy, but histopathologicaly it was proved to be a fibroadenoma. Generally fibroadenomas have a regular margin in xray mammography, but rarely the margins can show small lobulations which can be mistaken as a spiculated margin. Applying criteria for benign lesions in xray mammogram, 77% of cases were reported as benign. Of these, 2 cases which were reported as benign turned out to be malignant as per histopathology. These lesions were mammographically categorised as benign lesions as they had a low density with smooth circumscribed margins thus satisfying 2 benign criteria in mammography (satisfying 2 benign criteria in mammography) but on histopathology they were proven to be invasive ductal carcinoma. Circumscribed carcinoma is a well described entity and is difficult to differentiate in earlier stages with imaging. Table 9 Comparison of Xray mammography diagnosis with Histopathological Gold Standard Xray Histopathological type of Lesions Mammography diagnosis Table 10. Xray Mammogram diagnosis and Histopathology Cross tabulation Histopathology Total Mammogra Count m Diagnosis Histopathology 93.9% 3.4% 23.0% Count Histopathology 6.1% 96.6% 76.9% Total Count Histopathology 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% For xray mammography the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value are 93.9%, 96.6%, 88.6% and 98.3% respectively. In the published study conducted on 408 women having palpable breast lumps by Yang et al (11) in 1996 the results obtained for Xray mammography are: Sensitivity: 92%, Specificity: 94% Positive predictive value: 84%. The results obtained are comparable to the study quoted. Table 11. Xray Mammogram Diagnosis and Histopathology Cross tabulation in younger age group <40 years Histopathology Total Mammogra Count m Diagnosis Histopathology 88.8% 4.1% 13.4% Count Histopathology 11.1% 95.8% 86.5% Total Count Histopathology 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% Sensitivity in younger age group (less than 40 years): Xray Mammogram: 89% Table 12. Xray Mammogram Diagnosis and Histopathology Cross tabulation in older age group >40 years Mammogram in Diagnosis Histopathology Total Count Histopathology 95.8% 0% 32.8% Count Histopathology 4.1% 100% 67.1% Total Count Histopathology 100.0% 100.0% % Sensitivity in older age group (more than 40 years): Xray Mammogram: 96% 809
4 Volume 3, Issue 10, pp , October, 2015 ACR pattern breast compositions ACR composition a ACR composition b 810
5 Dr. Archana Jayakumar et al., 2015 A CR composition c ACR composition d Lipid cyst Breast cyst Fibroadenoma Phyllodes tumor Multiple fibroadenoma Coarse heterogenous Popcorn calcification Lucent centered calcification calcification 811
6 Volume 3, Issue 10, pp , October, 2015 Xray-Mammogram Diffuse calcification Regional calcification Grouped calcification Pleomorphic ca lcification Rod like/ Secretory calcification Vascular calcification 812
7 Dr. Archana Jayakumar et al., 2015 Xray-Mammogram Radial Scar BI-RADS 2 BI-RADS 3 BI-RADS 4 BI-RADS 5 BI-RADS 6 In the published study by Kolb et al (12) it is stated that in women with fatty breasts in older age group the sensitivity of mammography was 98%. In this study the results thus obtained, are comparable to the studies quoted. 4.DISCUSSION High resolution mammography is the best imaging tool for identification and characterization of breast calcifications. Development of dedicated mammography units has given a new dimension to breast imaging, by reduced radiation dose and improved resolution which has improved the diagnostic sensitivity of mammography. Various parameters used in xray mammogram are listed below. MASS DENSITY: A mass with a density, which is higher than the rest of the breast fibroglandular tissue is considered malignant while lesions with a density lesser than that of the breast 813
8 Volume 3, Issue 10, pp , October, 2015 parenchyma are more likely to be benign. However according to the study conducted by Jackson V.P et al., this is found to be unreliable. (1) MARGINS: masses usually have well defined circumscribed margins. However, circumscribed margins may also be seen in medullary / mucinous malignancy. Lobulated margin is seen both in benign and well as malignant conditions. Poorly defined / ill-defined / indistinct margins are also seen in both benign and malignant lesions. Spiculated margins have a very high probability for malignancy (> 95%). Only exception is seen in radial scar / post operative changes, which can also present with spiculated borders and mimic malignancy. Apart from this, even the presence of slight spiculation is suggestive of malignancy. (2) CALCIFICATION: Pattern of calcification is a very important mammographic parameter for characterizing breast lesions. Fibroadenomas usually show coarse calcification mainly at the periphery. Egg shell calcification located in the wall of the lesion are suggestive of benign lesions. (2) Popcorn pattern of coarse calcification is also seen in fibroadenoma. Branching pattern of microcalcification is suggestive of malignant pattern usually seen in ductal adenocarcinoma. SHAPE: Various shapes in mammography are described according to the nature of the lesion Oval lesions are usually seen in fibroadenoma. Round lesions are commonly benign. Exception to this is seen in lymphoma, sarcoma and mucinous carcinoma, which also presents as round lesions. Lobular mass having undulations or few microlobulations are seen in both benign and malignant conditions. Irregular shape is a common finding in malignancy. Inflammatory conditions like abscess can also have an irregular shape and mimics malignancy. SIZE STABILITY: Stability of the size of the lesions in the present and previously taken mammograms suggest a benign etiology. A mass which has increased in size, especially in a post menopausal woman suggests a malignant etiology. (3) FAT Presence of fat density in a hamartoma, fat necrosis, intramammary lymphnode or lipoma does not exclude the possibility of malignancy. MULTIPLICITY: Multiple lesions are usually seen in benign conditions such as multiple lymph nodes, multiple cysts and fibroadenomas. Sickles found in his study, a cancer incidence of 2% for solitary masses and 0.4% for multiple masses. (4) PERIFOCAL HAZINESS: It is common feature of malignant lesions and rarely seen in benign ones. ARCHITECTURAL DISTORSION: Sometimes in early stages of malignancy, an area of architectural distortion might be the only finding, with the absence of any other supportive features. TYPES OF CALCIFICATIONS IN BREAST MASSES: Breast calcifications are small deposits of calcium that develop in a woman s breast tissue. They are a very common mammographic finding and most of the cases are benign. In some cases, certain patterns of breast calcification are suggestive of development of early breast cancer. (5-8) On an x-ray mammogram, these calcifications will appear as macrocalcifications or microcalcifications. Macrocalcifications: They are almost always benign and do not require any biopsy or follow up. Typically benign calcifications are coarse or popcorn like calcification, egg shell or rim calcifications, lucent centered calcifications, skin or dermal calcifications, vascular calcifications, round and punctate calcifications, large rod like calcifications, milk of calcium calcifications, suture calcifications and dystrophic calcifications. (9,10) Microcalcifications: They can be non-cancerous but certain patterns of microcalcifications are pathognomic for cancer. They are seen as five, white specks of radiopacity in mammogram. Calcifications suggestive of malignancy are amorphous, coarse heterogenous, fine pleomorphic, fine linear and fine linear branching. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Patients with breast lumps were classified into both benign and malignant form of the disease, by using the above mentioned radiological parameters, specific to xray mammogram. The findings thus obtained were compared with the histopathological gold standard. The association of age, quadrant, shape, size, margin and calcification are studied with reference to benign and malignant involvement. The chi-square test of association is used to study this relationship. There is a significant association if the p value is less than The mammographic findings are compared with gold standard method by cross tabulation and through sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value. The statistical analysis is carried out using Statistical Package of Social Sciences (SPSS 21) and by manual method. Suitable tabular illustrations are also presented alongwith. 6. CONCLUSION 1.In this study, there is a statistically significant correlation between the x ray mammogram features of benign and malignant breast lesions on comparison with the histopathological gold standard. 2. In xray mammography, spiculated borders and fine linear or pleomorphic pattern of microcalcification, is found have a high positive predictive value for malignancy. 3. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value of xray mammography were 94%, 97%, 89%, 98% respectively which is comparable with international studies. 4. The sensitivity of mammogram is better in older patients (over 40 years) with a sensitivity of 96% when compared to younger age group (less than 40 years) where the sensitivity is 89%. ***** 814
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Leonard M. Glassman MD Analysis of Breast Calcifications
 Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
 MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
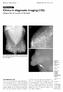 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER
 RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2009; 50(9) :
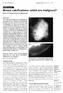 907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms
 342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California
 37 th Annual Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM TABLE OF CONTENTS Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM SAM Session - Breast Imaging Update 12:45 PM 1:30
37 th Annual Radiology Review Course Hotel del Coronado Coronado, California Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM TABLE OF CONTENTS Friday, April 21, 2017 - PM SAM Session - Breast Imaging Update 12:45 PM 1:30
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2016: Vol.-6, Issue- 1, P
 Original article: DIAGNOSTIC EFFICACY OF COMBINED MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS WITH PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION AND BIRADS ASSESSMENT Dr. G Harini*, Dr. S Shrinuvasan, Dr.
Original article: DIAGNOSTIC EFFICACY OF COMBINED MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS WITH PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION AND BIRADS ASSESSMENT Dr. G Harini*, Dr. S Shrinuvasan, Dr.
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
8/31/2016 HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS
 HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES DEBORAH THAMES R.T. (R)(M)(QM) ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS Definition is disruption of the natural flow of breast pattern towards the
HIDING IN PLAIN SITE, ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS AND BREAST ASYMMETRIES DEBORAH THAMES R.T. (R)(M)(QM) ARCHITECTURAL DISTORTIONS Definition is disruption of the natural flow of breast pattern towards the
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Breast Imaging Essentials
 Breast Imaging Essentials Module 5 Transcript 2016 ASRT. All rights reserved. Breast Imaging Essentials Module 5 Pathology 1. ASRT Animation 2. Welcome Welcome to Module 5 of Breast Imaging Essentials
Breast Imaging Essentials Module 5 Transcript 2016 ASRT. All rights reserved. Breast Imaging Essentials Module 5 Pathology 1. ASRT Animation 2. Welcome Welcome to Module 5 of Breast Imaging Essentials
OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE
 SCOPE TUTORIAL RADIOLOGY CT BRIAN BREASTS US MRCP Natrada Rawdhetubhai, M.D. Radiology Department, Lerdsin General Hospital CT OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE Intra-axial Extra-axial Intraventricular
SCOPE TUTORIAL RADIOLOGY CT BRIAN BREASTS US MRCP Natrada Rawdhetubhai, M.D. Radiology Department, Lerdsin General Hospital CT OF HEMATOMA INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE Intra-axial Extra-axial Intraventricular
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
IBCM 2, April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions
 Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
Segmental Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography
 Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
Progress in Public Health Breast Cancer Screening with Mammography JMAJ 44(7): 318 324, 2001 Tokiko ENDO Director, Department of Radiology, National Nagoya Hospital Abstract: Breast cancer has been increasing
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Index. C Calcifications fat necrosis 1, 61 fat necrosis 4, 69 nipple/peri-areolar involvement 1, 165
 A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns
 Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Breast Health. Learning Objectives. Breast Anatomy. Poll Question. Breast Anatomy
 Learning Objectives Describe breast anatomy to a patient Breast Health Answer questions about causes of breast pain and masses Explain breast cancer screening/diagnostic modalities Appropriately triage
Learning Objectives Describe breast anatomy to a patient Breast Health Answer questions about causes of breast pain and masses Explain breast cancer screening/diagnostic modalities Appropriately triage
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the breast: a rare entity, representation of two cases
 International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
International Surgery Journal Siripurapu Y et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Aug;4(8):2848-2853 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173434
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
 Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 62 (2011) 50e59 www.carjonline.org Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging / Imagerie cardiaque et imagerie thoracique Avoiding Pitfalls in Mammographic Interpretation
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019. AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division
 BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Breast imaging in general practice
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Correlation between Sonomammography and Mammography in the Evaluation of Breast Lesions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 13-20 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between Sonomammography
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 13-20 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between Sonomammography
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review
 Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Linear Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AB MR Interpretation Overview
 AB MR Interpretation Overview Goal of AB MR interpretation is to maintain high sensitivity and specificity In order to minimize false positives and short term follow ups, it is fundamental to focus only
AB MR Interpretation Overview Goal of AB MR interpretation is to maintain high sensitivity and specificity In order to minimize false positives and short term follow ups, it is fundamental to focus only
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Excerpts from: The Breast
 Excerpts from: The Breast Jonathan J. James, Robin M. Wilson and Andrew J Evans Grainger & Allison s Diagnostic Radiology Chapter 69 1664-1689.e2. Sheryl Jordan and Sheila Lee June 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS:
Excerpts from: The Breast Jonathan J. James, Robin M. Wilson and Andrew J Evans Grainger & Allison s Diagnostic Radiology Chapter 69 1664-1689.e2. Sheryl Jordan and Sheila Lee June 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS:
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Localization of Breast Lesion Using Mammographic-Basic Views
 Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Vol. 2 No. 1: 2 Localization of Breast Lesion Using Mammographic-Basic Views Nikki Mishra*, Meena Chakradhar, Ranjit Jha and Rauniyar RK Department of
Research Article imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Vol. 2 No. 1: 2 Localization of Breast Lesion Using Mammographic-Basic Views Nikki Mishra*, Meena Chakradhar, Ranjit Jha and Rauniyar RK Department of
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
FACT: FACT: Breast Cancer Staging. For cancer to occur, something must damage nucleus of the cell. Stage I. Stage II 10/9/2018
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Pathology Findings: Case Studies and Beyond For cancer to occur, something must damage nucleus of the cell. Advanced Health Education Center www.aheconline.com Copyright
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Pathology Findings: Case Studies and Beyond For cancer to occur, something must damage nucleus of the cell. Advanced Health Education Center www.aheconline.com Copyright
Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 42 year old with right breast mass Rina Kiyota Petek Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, OMS-III Kossivi Dantey, MD Bibianna Klepchick, MD Matthew Hartman,
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 42 year old with right breast mass Rina Kiyota Petek Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, OMS-III Kossivi Dantey, MD Bibianna Klepchick, MD Matthew Hartman,
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
 Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Linda M. Roberts, Charles E. Kahn, Jr., Peter Haddawy {roberts,kahn,haddawy}@cs.uwm.edu Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Development of a Bayesian Network for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Linda M. Roberts, Charles E. Kahn, Jr., Peter Haddawy {roberts,kahn,haddawy}@cs.uwm.edu Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases?
 BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
The Abnormal Mammogram Radiographic Findings, Diagnostic Options, Pathology, and Stage of Cancer Diagnosis
 244 The Abnormal Mammogram Radiographic Findings, Diagnostic Options, Pathology, and Stage of Cancer Diagnosis Robert 1. McKenna, Sr., M.D. An abnormal mammogram often will detect a mass, a cluster of
244 The Abnormal Mammogram Radiographic Findings, Diagnostic Options, Pathology, and Stage of Cancer Diagnosis Robert 1. McKenna, Sr., M.D. An abnormal mammogram often will detect a mass, a cluster of
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
DR AISHA A UMAR CHIEF CONSULTANT RADIOLOGIST NATIONAL HOSPITAL ABUJA.
 DR AISHA A UMAR CHIEF CONSULTANT RADIOLOGIST NATIONAL HOSPITAL ABUJA. OUTLINE WHY DO WE IMAGE WHOM TO IMAGE WHEN TO IMAGE HOW TO IMAGE WHAT TO IMAGE WITH PERSONAL EXPERIENCE CONCLUSION/RECOMMENDATIONS
DR AISHA A UMAR CHIEF CONSULTANT RADIOLOGIST NATIONAL HOSPITAL ABUJA. OUTLINE WHY DO WE IMAGE WHOM TO IMAGE WHEN TO IMAGE HOW TO IMAGE WHAT TO IMAGE WITH PERSONAL EXPERIENCE CONCLUSION/RECOMMENDATIONS
Reduction mammoplasty. What radiologists should know.
 Reduction mammoplasty. What radiologists should know. Poster No.: C-1558 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Plaza Loma 1, Y. Rodríguez de Diego 1, M. E. Villacastín Ruiz 1, R. Pintado
Reduction mammoplasty. What radiologists should know. Poster No.: C-1558 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Plaza Loma 1, Y. Rodríguez de Diego 1, M. E. Villacastín Ruiz 1, R. Pintado
Mimickers of breast malignancy
 Mimickers of breast malignancy Poster No.: C-0477 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: S. H. Park, H.-Y. Choi; Incheon/KR Keywords: mimickers, breast malignancy, ultrasound
Mimickers of breast malignancy Poster No.: C-0477 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: S. H. Park, H.-Y. Choi; Incheon/KR Keywords: mimickers, breast malignancy, ultrasound
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation
 Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
Evaluation of surgical margins by specimen in impalpable breast carcinoma: a radiopathological correlation Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, L. Koren,
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Hands-on Breast Screening and Diagnosis Course * Screening of 315 full field digital mammography cases. * Reading a mixture of normals and proven abnormals at high resolution viewing stations. * Immediate
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign
 Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center
 Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
