Anaplastic A term used to describe cancer cells that divide rapidly and have little or no resemblance to normal cells.
|
|
|
- Esmond Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oncology Terminology A Adenocarcinoma A cancerous tumor that arises in or resembles glandular tissue. Adjunct agent In cancer therapy, a drug or substance used in addition to the primary therapy. Adjuvant chemotherapy A term used to describe the role of chemotherapy relative to other cancer treatments. It is typically given alone or with radiation after surgical resection. Adjuvant radiation therapy The use of radiation after treatment in order to prevent a cancer from recurring. Anaplastic A term used to describe cancer cells that divide rapidly and have little or no resemblance to normal cells. Anastomosis The joining together of two ends of healthy bowel after diseased bowel has been cut out (resected) by the surgeon. This may be contrasted to a colostomy, when the bowel ends may be permanently diverted, or anastamosed at a later surgery. Antigen A substance that is recognized by the body as being foreign and, as such, can trigger an immune response. Archived Tumor Sample A tumor sample that has been routinely preserved and stored. Tumor tissue is commonly preserved for storage by being treated with a preservative called formalin and then embedded in paraffin (wax). Aromatase Inhibitor A medication that reduces the amount of estrogen in the body. Aromatase inhibitors may be used to treat women with estrogenreceptor-positive breast cancer. B Barium enema A barium enema is a series of x-rays of the lower gastrointestinal tract. The barium enema procedure consists of the insertion of barium (a radiolucent solution) to coat the lower gastrointestinal tract. The barium coats the lower gastrointestinal tract and x-rays are taken. On X-ray, areas in which the barium lights up may indicate abnormal cell proliferation. This procedure is also called a lower GI series. Biopsy A procedure where tumor tissue is removed from the body for laboratory examination to determine whether or not cancer is present. A biopsy can be performed using a needle to extract a small piece of tissue or as a surgical procedure to remove a larger piece of tissue. BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes that normally help control cell growth. A person who inherits an altered version of the BRCA1 and/or BRCA2 gene(s) has a higher risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer. C Cancer A condition in which abnormal cells divide without control or fail to die as part of a normal cell's lifecycle. Cancer cells can also invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body. Cancer staging The process of assigning a descriptor (usually numbers I to IV) of how much a cancer has spread in the body. Criteria for staging include: size of tumor, amount of tissue penetration, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many lymph Carcinoma Any malignant cancer that comes from epithelial cells. Carcinomas will invade surrounding tissue, and have the propensity to metastasize to the lymph nodes and beyond. Carcinoma in situ Epithelial tumor cells confined to the tissue of origin, without invasion through the basement membrane. Chemotherapy Treatment with cytotoxic drugs that destroy cancer cells (fast-growing cells). Chemotherapy may be used in addition to surgery, and is sometimes used in combination with other therapies such as radiation therapy or hormonal therapy.
2 Chromosome A microscopically visible carrier of genetic information. Clinical Laboratory Services The biological, microbiological, serological, chemical, immuno-hematological, hematological, biophysical, cytological, pathological or other examination of materials derived from the human body for the purpose of providing information for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of any disease or impairment of or the assessment of the health of human beings. Clinical Trial A research study to test drugs, procedures or testing technologies to determine whether these are effective and/or safe. Clinically Validated Determination that a test is accurate in determining the presence of, or predicting the risk for, a health condition or phenotype, including determination of sensitivity, specificity and positive and negative predictive values. Colectomy Surgical resection of all or part of the colon (also called the large intestine). Colitis inflammation of the colon. Colitis has many forms including ulcerative, Crohn s, infectious, pseudomembranous, and spastic. Colon polyp A fleshy growth on the inside (the lining) of the colon. Colonoscopy Inspection through a fiber-optic scope of the inside of the colon. Colorectal Related to the colon and/or rectum. Core Biopsy A procedure which uses a needle to remove a small, intact sample of tissue from an identified breast mass in order to examine it and obtain a preliminary diagnosis. D Diagnosis Identification of a condition, such as breast cancer, by its signs and symptoms and the results of laboratory tests or other examinations. Distant Recurrence The spread of cancer to parts of the body other than the place where the cancer first occurred. In breast cancer, the cancer can spread to the lungs, liver, brain or bones. Dukes staging system A system of staging rectal cancers developed by Cuthbert Duke in The original system had 3 stages but has been modified over time to include four stages with variations on two of the four stages. Dysplasia A term that refers to abnormal cells that have the potential to progress to cancer. E Early-Stage Breast Cancer A term that can be used to describe stage I and II, lymph-node-negative breast cancer. Endoscope A long slender medical instrument for examining the interior of a bodily organ or performing minor surgery. Endoscopy Visual examination of a bodily orifice, canal or organ using an endoscope. ER (Estrogen Receptor) A feature (protein) that may be present on certain cells to which estrogen molecules can attach. The term "ER positive" refers to tumor cells that contain the estrogen-receptor protein. These cells are generally sensitive to hormone therapy. G Gastroenterologist a physician who specializes in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
3 Gastroenterology The branch of medicine that focuses on the digestive system and its disorders. Gene The functional and physical units of inheritance that are passed from parents to their offspring. The genes found in normal breast tissue can change their expression (see below), which can give rise to breast cancer. Gene Expression The level of activity of a gene or group of genes. Gene Expression Profile A picture of the activity or expression of multiple genes from a single specimen. Genetics The study of genes and heredity. Heredity is the passing of genetic information and traits, such as eye color or an increased chance of getting a certain disease, from parents to offspring. Genome The complete genetic material of a living thing. Genomic Test A test that looks at groups of genes and how active they are. This activity can influence how a cancer is likely to grow and respond to treatment. Genomics The study of complex sets of genes, how they are expressed in cells (what their level of activity is), and the role they play in biology. H Hand Foot Syndrome (Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysesthesia) Also called hand-foot syndrome or hand-to-foot syndrome, Palmar-Plantar Erythrodysesthesia is a side effect, which can occur with several types of chemotherapy or biologic therapy drugs used to treat cancer. Leakage of the drug through the capillaries of the skin of the hands and feet can cause redness, tenderness, and peeling of the skin of the palms and soles. Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC) An inherited cancer syndrome. Individuals with HNPCC have an increased risk of developing colon and rectal cancer, as well as other types of cancer. Hormonal Treatment (Hormone Therapy) Medications used to reduce the effect of hormones in the body. In many cases of breast cancer, hormones can fuel the growth of breast cancer. Common hormonal therapies include tamoxifen and a newer class of drugs called aromatase inhibitors. Hormonal therapies are used to treat women with estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Hormone Receptor A protein on the surface of a tumor cell that binds to a certain hormone, activating tumor growth. Human Genome Project An international research and technology-development effort aimed at mapping and sequencing the entire genome of human beings. I In Situ Non-invasive cancer in which abnormal cells are isolated within the lobes or milk ducts of the breast and have not spread to nearby tissue. Invasive Breast Cancer Cancer that has spread from where it started in the breast into surrounding, healthy tissue. Most invasive breast cancers start in the ducts (tubes that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple). Invasive breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. Invasive breast cancer is also called infiltrating breast cancer. L Local Recurrence The reappearance of cancer in the part of the body where it first occurred. Lumpectomy A surgical procedure that removes a localized mass of tissue, including the breast cancer tumor and a small amount of normal, noncancerous tissue surrounding the tumor.
4 M Malignant Tending to be severe and become progressively worse; a malignant tumor is one that has the ability to invade and destroy nearby tissue and/or spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Mastectomy A surgical procedure to remove all or a large part of the breast. Metastasize A term that is used to refer to cancer spreading from its site of origin to other sites in the body. Metastatic Breast Cancer Breast cancer that has spread beyond the breast and local lymph nodes to other parts of the body such as the lungs, liver, brain or bones or other tissues. Molecular Diagnostics The measurement of DNA, RNA, proteins or metabolites to detect genotypes, mutations or biochemical changes. N Newly Diagnosed A term used to describe breast cancer that has recently been identified. Node-Negative Breast Cancer Breast cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes. Node-Positive Breast Cancer Breast cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes (most commonly the axillary lymph nodes under the arms). O Oncotype DX Test The Oncotype DX breast, colon, and prostate cancer assays are unique diagnostic tests that help patients and their physicians make informed, individualized treatment decisions. To learn more about the Oncotype DX tests for DCIS, breast, colon and prostate cancer please visit the Oncotype DX product website or call Tel: +1 (888) ONCOTYPE Oncologist A physician who specializes in the study and treatment of tumors. Oncology The study and treatment of cancer. P Pathologist Physician who identifies diseases by studying cells and tissues under a microscope. Pathology Report A report ordered by authorized healthcare professionals that describes what was found in tissue removed from the patient s body. The report is generated after the tumor and surrounding tissue are checked by a pathologist. It usually includes information on the tumor s grade and stage. Polyethylene glycol An electrolyte-based laxative solution used to clean the bowel before a gastrointestinal exam. Polyp A usually nonmalignant growth or tumor protruding from the mucous lining of an organ, such as the colon. Colon polyps are fleshy growths that occur on the inside (the lining) of the large intestine. PR (Progesterone Receptor) A feature (protein) that may be present on certain cells to which progesterone molecules can attach. The term PR positive refers to tumor cells that contain the progesterone receptor protein. These cells are generally sensitive to hormone therapy. Predispose To make more likely or render susceptible. PSA (Prostate-specific antigen) A protein exclusively produced by the prostate. Increased levels of PSA may be found in the blood of men who have prostate cancer or other prostate diseases such as BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or inflammation of the prostate.
5 R Radiation Therapy The use of radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery, and is sometimes used in combination with chemotherapy. Radiation is used for local control of the cancer at the site of the tumor. Recurrence The return of cancer after treatment. This can be either local (at the site of the original tumor), or distant (beyond the original site). Resection Surgery to remove a cancer and some surrounding tissue. S Sarcoma A malignant tumor growing from connective tissues, such as cartilage, fat, muscle, or bone. Screening (for breast cancer) Looking for masses or suspicious areas in breast tissue on a periodic basis. Screening (for colon cancer) Looking for masses or suspicious areas in colon tissue on a periodic basis. Sigmoidoscopy Inspection through a fiber-optic scope of the inside of the sigmoid colon, which is part of the large intestine that empties into the rectum. The test is useful for diagnosing the cause of diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain, and for identifying cancerous tissue. Stage I Breast Cancer The tumor is up to 2 centimeters in diameter and has not spread beyond the breast. Stage IIA Breast Cancer The tumor is up to 2 centimeters and has spread to the axillary lymph nodes under the arm, or the tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters and has not spread to the lymph nodes. Stage IIB Breast Cancer The tumor is between 2 and 5 centimeters and has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm, or the tumor is larger than 5 centimeters in diameter and has not spread to the lymph nodes. Stage IIIA Breast Cancer The tumor is larger than 5 centimeters in diameter and has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm, or the tumor is any size and has spread more extensively in the lymph nodes. Stage IIIB Breast Cancer The tumor is any size and has extended to other tissues near the breast; the tumor may or may not have spread to the lymph nodes. Stage IV Breast Cancer Cancer that has spread (metastasized) to other locations in the body, such as the lungs, liver, bones or brain. Staging A classification system for breast cancer based on the size of the tumor, whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and whether the cancer has spread to other sites in the body (metastasis). Surveillance/Follow-Up An ongoing assessment by a patient s medical team, once treatment has been completed, to assess the cancer s remission and to look for any evidence of a cancer s return. Synchronous cancer Multiple primary cancers occurring simultaneously. Syndrome A set of signs and symptoms that tend to occur together and which reflect the presence of a particular disease or an increased chance of developing a particular disease. T TAILORx Although the Oncotype DX test has already been approved for use, research involving the test is ongoing. The Oncotype DX test plays a key role in a current clinical trial, the Trial Assigning IndividuaLized Options for Treatment (Rx), known as TAILORx. Participants will be divided into different treatment groups depending on their Recurrence Score results. Patients with Recurrence Score results of less than 11, who are at low risk for recurrence and for whom chemotherapy is expected to provide little benefit, will
6 receive hormone therapy alone. Patients with Recurrence Score results greater than 25, who are at higher risk for recurrence and for whom chemotherapy is expected to provide substantial benefit, will receive hormonal therapy and chemotherapy. Patients with Recurrence Score results between 11 and 25, whose risk for recurrence is moderate and for whom the benefit of chemotherapy is unclear, will be randomized to treatment with hormonal therapy plus chemotherapy versus hormonal therapy alone. The primary objective of the trial is to determine whether hormonal therapy alone offers no less benefit than chemotherapy plus hormonal therapy in women whose Recurrence Score results range from 11 to 25. For more information, click here. Tamoxifen A medication that interferes with the activity of the hormone estrogen to prevent it from fueling the growth of breast cancer. Tamoxifen is used to treat women with estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors (TNM) A cancer staging system that describes the extent of cancer in a patient s body. TNM literally describes Tumor/Nodes/Metastasis. T describes the size of the tumor and whether it has invaded nearby tissue, N describes the number of regional lymph nodes that are involved, and M describes the presence of other metastases. This system is jointly maintained by the International Union Against Cancer (UICC), and the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Treatment Monitoring An ongoing and frequent assessment by the medical team, during the time of treatment, to monitor how the patient is tolerating the treatment and how the cancer is responding. Tumor Tissue growth where the cells that make up the tissue have multiplied uncontrollably. A tumor can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Tumor Grade The characterization of a tumor based on how similar in appearance the cancer cells are to normal cells, and on how many of those tumor cells are dividing. Tumor grade is one of many factors that, when used in combination, can indicate how aggressive a patient s cancer is. Tumor Stage This is a number that refers to the size of the tumor and whether the cancer has spread. Tumor stage, expressed as the tumor T score, is one of many factors that, when used in combination, can indicate how aggressive a patient s cancer is. U Ulcerative colitis A disease where sores, or ulcers, form in the top layers of the lining of the large intestine. Inflammation usually occurs in the lower part of the colon and rectum. W Wire Localization Biopsy A type of biopsy performed when an abnormality can be seen on a mammogram but cannot be felt. A wire localization biopsy utilizes a mammogram to locate and identify the breast abnormality, after which a biopsy is performed
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
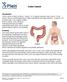 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater
 Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Breast Cancer Task Force of the Greater Miami Valley A collaborative effort of health care professionals and breast cancer survivors in the Greater Dayton Area Last Updated Fall 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time.
 Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
Cancer Glossary Acute: Symptoms that start and worsen quickly but do not last over a long period of time. Adjuvant therapy: Treatment given after the main treatment. It usually refers to chemotherapy,
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment
 Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This is your booklet. It is designed to help you through this challenging time. Use it as a guide during
Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment An educational guide prepared by Genomic Health This is your booklet. It is designed to help you through this challenging time. Use it as a guide during
Understanding Your Pathology Report
 Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Understanding Your Pathology Report Because every person s breast cancer is unique, it s important to understand the underlying biology of your tumor to personalize your treatment plan. Your physicians
Introduction to Basic Oncology
 Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Introduction to Basic Oncology Cancer Cell AHS 102 Med Term Dr. Susie Turner 1/3/13 General Oncology Study of Tumors Neoplasms/Tumors Abnormal growth of new tissue Are either; Benign or Malignant Onc/o
Colorectal Cancer Care
 Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. ROUND2.3_CRCa_20pages_5.5x8.5_FINAL.indd
Colorectal Cancer Care A Cancer Care Map for Patients Understanding the process of care that a patient goes through in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer in BC. ROUND2.3_CRCa_20pages_5.5x8.5_FINAL.indd
Colorectal cancer starts in the colon or rectum.
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated December 7, 2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated December 7, 2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq
Quiz. b. 4 High grade c. 9 Unknown
 Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
Quiz 1. 10/11/12 CT scan abdomen/pelvis: Metastatic liver disease with probable primary colon malignancy. 10/17/12 Colonoscopy with polypectomy: Adenocarcinoma of sigmoid colon measuring at least 6 mm
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology. Report. Key Questions. Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help:
 Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report Key Questions Here are important questions to be sure you understand, with your doctor s help: Your Guide to the Breast Cancer Pathology Report 1. Is this
[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
![[A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE] [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]](/thumbs/88/117127924.jpg) 2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
2013 COLORECTAL SURGERY GROUP Dr. Carl J. Brown Dr. Ahmer A. Karimuddin Dr. P. Terry Phang Dr. Manoj J. Raval Authored by Jennifer Lee A cartoon about colonoscopies. 1 [A RESEARCH COORDINATOR S GUIDE]
Case Scenario 1. 2/15/2011 The patient received IMRT 45 Gy at 1.8 Gy per fraction for 25 fractions.
 Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Case Scenario 1 1/3/11 A 57 year old white female presents for her annual mammogram and is found to have a suspicious area of calcification, spread out over at least 4 centimeters. She is scheduled to
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information
 Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Screening What is colorectal cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to identify disease in individuals who lack any signs or symptoms. The
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Screening What is colorectal cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to identify disease in individuals who lack any signs or symptoms. The
Breast Cancer. Excess Estrogen Exposure. Alcohol use + Pytoestrogens? Abortion. Infertility treatment?
 Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen Exposure Nulliparity or late pregnancy + Early menarche + Late menopause + Cystic ovarian disease + External estrogens exposure + Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen
Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen Exposure Nulliparity or late pregnancy + Early menarche + Late menopause + Cystic ovarian disease + External estrogens exposure + Breast Cancer Excess Estrogen
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine
 What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
AllinaHealthSystems 1
 Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Breast Health. Knowledge and self-awareness are powerful tools. Understanding and utilizing these tools starts with
 k Breast Health Knowledge and self-awareness are powerful tools. Understanding and utilizing these tools starts with Lake Charles Memorial s Breast Health Program. Developing a sense of what the everyday
k Breast Health Knowledge and self-awareness are powerful tools. Understanding and utilizing these tools starts with Lake Charles Memorial s Breast Health Program. Developing a sense of what the everyday
Health Bites Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer. Normal breast
 Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Health Bites Breast Cancer Breast Cancer Normal breast The normal breast tissue varies in size and shape. The breasts rest in front of the rib cage. The breasts are made up of fatty tissue, milk ducts
Cancer Endorsement Maintenance 2011-Maintenance Measures
 Measure Number Title Description Measure Steward 0210 Proportion receiving chemotherapy in the last 14 days of life 0211 Proportion with more than one emergency room visit in the last days of life 0212
Measure Number Title Description Measure Steward 0210 Proportion receiving chemotherapy in the last 14 days of life 0211 Proportion with more than one emergency room visit in the last days of life 0212
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Different Types of Cancer
 Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Different Types of Cancer Cancer can originate almost anywhere in the body. Sarcomas (connective tissue) Ø arise from cells found in the supporting tissues of the body such as bone, cartilage, fat, connective
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide
 Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Pathology Report Patient Companion Guide Breast Cancer - Understanding Your Pathology Report Pathology Reports can be overwhelming. They contain scientific terms that are unfamiliar and might be a bit
Colorectal Cancer Glossary. Colorectal Cancer Glossary
 1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
1 A Abdomen: (AB-do-men) The part of the body between the chest and the pelvis that contains organs including the pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), liver and gallbladder. Adjuvant
COPE Library Sample
 Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Breast Anatomy LOBULE LOBE ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) NIPPLE AREOLA COMPLEX ENLARGEMENT OF DUCT AND LOBE LOBULE SUPRACLAVICULAR NODES INFRACLAVICULAR NODES DUCT DUCT ACINI (MILK PRODUCING UNITS) 8420
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels.
 Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Listed below are some of the words that you might come across concerning diseases and conditions of the bowels. Abscess A localised collection of pus in a cavity that is formed by the decay of diseased
Educator Navigation Guide
 Decoding Breast Cancer Virtual Lab Educator Navigation Guide Decoding Cancer Nav Guide 2 Introduction In this virtual lab, students test tissue samples from different patients with breast cancer in order
Decoding Breast Cancer Virtual Lab Educator Navigation Guide Decoding Cancer Nav Guide 2 Introduction In this virtual lab, students test tissue samples from different patients with breast cancer in order
Cell Death and Cancer. SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou
 Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
HAVE YOU BEEN recently DIAGNOSED with stage II or stage III colon cancer?
 To learn more about the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer Test, please visit www. oncotypedx.com and talk to your health care team. For insurance, financial aid or other questions about the Oncotype DX test, please
To learn more about the Oncotype DX Colon Cancer Test, please visit www. oncotypedx.com and talk to your health care team. For insurance, financial aid or other questions about the Oncotype DX test, please
A superficial radiotherapy B single pass curettage C excision with 2 mm margins D excision with 5 mm margins E Mohs micrographic surgery.
 1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
GENERAL COLORECTAL CANCER INFORMATION. What is colorectal cancer?
 GENERAL COLORECTAL CANCER INFORMATION What is colorectal cancer? Colorectal cancer is cancer that develops in the colon or the rectum. The colon and rectum are parts of the digestive system, which is also
GENERAL COLORECTAL CANCER INFORMATION What is colorectal cancer? Colorectal cancer is cancer that develops in the colon or the rectum. The colon and rectum are parts of the digestive system, which is also
Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan?
 Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan? This guide is designed to educate newly diagnosed women with early-stage
Have you been newly diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer? Have you discussed whether chemotherapy will be part of your treatment plan? This guide is designed to educate newly diagnosed women with early-stage
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases that are characterized by uncontrolled cellular growth,
Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment. Mercy Cancer Services. baggotstreet.mercy.net/benefits. Your life is our life s work.
 Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment Your life is our life s work. baggotstreet.mercy.net/benefits Mercy Cancer Services Introduction An estimated one out of eight women will develop breast
Patient Guide to Breast Cancer Surgery and Treatment Your life is our life s work. baggotstreet.mercy.net/benefits Mercy Cancer Services Introduction An estimated one out of eight women will develop breast
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
What is the Oncotype DX test?
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 What is the Oncotype DX test? www.nscancercare.ca What is the Oncotype DX test? Information for women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer What is the Oncotype DX test?
Patient & Family Guide 2018 What is the Oncotype DX test? www.nscancercare.ca What is the Oncotype DX test? Information for women diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer What is the Oncotype DX test?
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Ulcerative Colitis. ulcerative colitis usually only affects the colon.
 Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Ulcerative Colitis Introduction Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease. It is one of the 2 most common inflammatory bowel diseases. The other one is Crohn s disease. Ulcerative colitis and
Breast Cancer. Saima Saeed MD
 Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
Breast Cancer Saima Saeed MD Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Incidence/mortality rates have declined Breast
3/9/2017. Chapter 56. Care of the Patient with Cancer. Cancer Rates in the US. Carcinogenesis
 Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
Chapter 56 Care of the Patient with Cancer All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Cancer Rates in the US 1 in 2 men and 1 in 3 women
Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer
 Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Patient Information English Glossary of Terms Primary Urethral Cancer Advanced cancer A tumour that grows into deeper layers of tissue, adjacent organs, or surrounding muscles. Anaesthesia (general, spinal,
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Cancer statistics (US)
 Disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Vickie Matthias Hagen, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line
Disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Vickie Matthias Hagen, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line
LET S TALK ABOUT CANCER
 LET S TALK ABOUT CANCER COLORECTAL CANCER AND CROHN S DISEASE & ULCERATIVE COLITIS crohnsandcolitis.ca BACKGROUND Colorectal cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in this country. In 2013,
LET S TALK ABOUT CANCER COLORECTAL CANCER AND CROHN S DISEASE & ULCERATIVE COLITIS crohnsandcolitis.ca BACKGROUND Colorectal cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death in this country. In 2013,
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Breast Cancer in Women
 The Crawford Clinic 1900 Leighton Avenue Suite 101 Anniston, Alabama 36207 Phone: 256-240-7272 Fax: 256-240-7242 Breast Cancer in Women What is breast cancer? When abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, they
The Crawford Clinic 1900 Leighton Avenue Suite 101 Anniston, Alabama 36207 Phone: 256-240-7272 Fax: 256-240-7242 Breast Cancer in Women What is breast cancer? When abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, they
Learning Objectives. ! At the end of the presentation,students will be able to:
 Learning Objectives! At the end of the presentation,students will be able to: Define Breast Cancer Identify the controllable and uncontrollable risk factors of breast cancer Recognize the 4 stages of breast
Learning Objectives! At the end of the presentation,students will be able to: Define Breast Cancer Identify the controllable and uncontrollable risk factors of breast cancer Recognize the 4 stages of breast
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION
 BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
BLADDER CANCER: PATIENT INFORMATION The bladder is the balloon like organ located in the pelvis that stores and empties urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys, is conducted to the bladder by the ureters,
Bowel Cancer Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
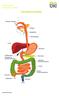 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM This factsheet is about bowel cancer Throughout our lives, the lining of the bowel constantly renews itself. This lining contains many millions of tiny cells, which grow, serve their
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Sheri Saluga A/P 2 May 1, Breast Cancer
 Sheri Saluga A/P 2 May 1, 2010 Breast Cancer Cancer, one word common to the word and one word no one wants to hear. There are many forms of cancer but of particular interest is stomach cancer. So what
Sheri Saluga A/P 2 May 1, 2010 Breast Cancer Cancer, one word common to the word and one word no one wants to hear. There are many forms of cancer but of particular interest is stomach cancer. So what
Presented by: Lillian Erdahl, MD
 Presented by: Lillian Erdahl, MD Learning Objectives What is Breast Cancer Types of Breast Cancer Risk Factors Warning Signs Diagnosis Treatment Options Prognosis What is Breast Cancer? A disease that
Presented by: Lillian Erdahl, MD Learning Objectives What is Breast Cancer Types of Breast Cancer Risk Factors Warning Signs Diagnosis Treatment Options Prognosis What is Breast Cancer? A disease that
Cancer arises from the mutation of a normal gene. A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen.
 Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
Cancer Single cells divide by mitosis to form many cells. This cells undergo physical and chemical changes in order to perform specific functions. (we say the cells have Differentiated) in this way we
A916: rectum: adenocarcinoma
 General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
General facts of colorectal cancer The colon has cecum, ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon sections. Cancer can start in any of the r sections or in the rectum. The wall of each of these
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER
 The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
The Alvin & Lois Lapidus Cancer Institute BREAST CANCER What is breast cancer? Breast cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. The breast is made up of lobes and ducts.
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Barriers to Understanding
 Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Behind the Scenes: The Critical Importance of Cancer Cell Pathology and the Pathologist Sherry T. Emery, M.D., Chief of Pathology Northeast Health System Barriers to Understanding Questions for 2010 What
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer.
 Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Retrospective analysis to determine the use of tissue genomic analysis to predict the risk of recurrence in early stage invasive breast cancer. Goal of the study: 1.To assess whether patients at Truman
Cell Biology and Cancer
 Name: Cell Biology and Cancer Date: Questions 1. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are what types of genes? 2. List two ways that cancerous and healthy cells differ. 3. Which organelle makes proteins? 4. At what phase of
Name: Cell Biology and Cancer Date: Questions 1. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are what types of genes? 2. List two ways that cancerous and healthy cells differ. 3. Which organelle makes proteins? 4. At what phase of
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated. FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia.
 DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Navigators Lead the Way
 RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes
 Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
11/21/13 CEA: 1.7 WNL
 Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Case Scenario 1 A 70 year-old white male presented to his primary care physician with a recent history of rectal bleeding. He was referred for imaging and a colonoscopy and was found to have adenocarcinoma.
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer
 Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Diseases of the breast (2 of 2) Breast cancer Epidemiology & etiology The most common type of cancer & the 2 nd most common cause of cancer death in women 1 of 8 women in USA Affects 7% of women Peak at
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine
 Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
Maram Abdaljaleel, MD Dermatopathologist and Neuropathologist University of Jordan, School of Medicine The most common non-skin malignancy of women 2 nd most common cause of cancer deaths in women, following
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Breast Cancer and You A guide for women living with Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer and You A guide for women living with Breast Cancer Amgen Canada Inc., 6755 Mississauga Road, Suite 400 Mississauga, Ontario L5N 7Y2 CA245860E Introduction A diagnosis of breast cancer can
Breast Cancer and You A guide for women living with Breast Cancer Amgen Canada Inc., 6755 Mississauga Road, Suite 400 Mississauga, Ontario L5N 7Y2 CA245860E Introduction A diagnosis of breast cancer can
Caring for a Patient with Colorectal Cancer. Objectives. Poll question. UNC Cancer Network Presented on 10/15/18. For Educational Use Only 1
 Caring for a Patient with Colorectal Cancer Tammy Triglianos RN, APRN-BC, AOCNP Nurse Practitioner, GI Oncology 10/15/2018 Objectives Describe common signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer Understand
Caring for a Patient with Colorectal Cancer Tammy Triglianos RN, APRN-BC, AOCNP Nurse Practitioner, GI Oncology 10/15/2018 Objectives Describe common signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer Understand
Cancer. Chapter 31 Lesson 2
 Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Cancer Chapter 31 Lesson 2 Tumors All cancers are tumors- masses of tissue. Not all tumors are cancers. Some tumors are benign- noncancerous. These tumors are surrounded by membranes that prevent them
Chapter 3. Neoplasms. Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Chapter 3 Neoplasms Terminology Related to Neoplasms and Tumors Neoplasm New growth Tumor Swelling or neoplasm Leukemia Malignant disease of bone marrow Hematoma Bruise or contusion Classification of Neoplasms
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
2012 update. Bowel Cancer. Information for people at increased risk of bowel cancer. Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group
 2012 update Bowel Cancer Information for people at increased risk of bowel cancer Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group i Contents Introduction 1 The bowel 1 Bowel cancer 3 What are the symptoms
2012 update Bowel Cancer Information for people at increased risk of bowel cancer Published by the New Zealand Guidelines Group i Contents Introduction 1 The bowel 1 Bowel cancer 3 What are the symptoms
COLORECTAL CANCER 44
 COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
COLORECTAL CANCER 44 Colorectal Cancer Highlights from the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Edited by Stuart M. Lichtman, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Commack,
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
is time consuming and expensive. An intra-operative assessment is not going to be helpful if there is no more tissue that can be taken to improve the
 My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus).
 THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
THE COLON This is the portion of the intestine which lies between the small intestine and the outlet (Anus). 3 4 5 This part is responsible for formation of stool. The large intestine (colon- coloured
NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM
 Cancer Endorsement Maintenance Table of Submitted Measures Phase I 0210 1 Proportion receiving chemotherapy in the last 14 days of life Percentage of patients who died from cancer receiving chemotherapy
Cancer Endorsement Maintenance Table of Submitted Measures Phase I 0210 1 Proportion receiving chemotherapy in the last 14 days of life Percentage of patients who died from cancer receiving chemotherapy
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Types of Breast Cancer
 IOWA RADIOLOGY 1 Types of Breast Cancer 515-226-9810 Ankeny Clive Downtown Des Moines IOWA RADIOLOGY 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Ductal Carcinoma... 2 Paget s Disease of the Nipple... 8 Lobular
IOWA RADIOLOGY 1 Types of Breast Cancer 515-226-9810 Ankeny Clive Downtown Des Moines IOWA RADIOLOGY 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Ductal Carcinoma... 2 Paget s Disease of the Nipple... 8 Lobular
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
STAGE CATEGORY DEFINITIONS
 CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery TX Tis Tis (DCIS) Tis (LCIS) Tis (Paget s) T1 T1mi T1a T1b T1c a b c
CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery TX Tis Tis (DCIS) Tis (LCIS) Tis (Paget s) T1 T1mi T1a T1b T1c a b c
Mammography and Other Screening Tests. for Breast Problems
 301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM Mammography and Other Screening Tests What is a screening test? for Breast Problems A screening test is used to find diseases, such as cancer, in people who do not have signs
301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM Mammography and Other Screening Tests What is a screening test? for Breast Problems A screening test is used to find diseases, such as cancer, in people who do not have signs
BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY
 BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY FACT SHEET Version 4, Aug 2013 This fact sheet was produced by Breast Cancer Network Australia with input from The Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia I m a nurse and know
BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY FACT SHEET Version 4, Aug 2013 This fact sheet was produced by Breast Cancer Network Australia with input from The Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia I m a nurse and know
