(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
|
|
|
- April Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface (e) function in signal transduction Visit site-
2 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface (e) function in signal transduction ANSWER-D Visit site-
3 According to the fluid mosaic model, membranes consist of (a) a lipid-protein sandwich (b) mainly phospholipids with scattered nucleic acids (c) a fluid phospholipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded (d) a fluid phospholipid bilayer in which carbohydrates are embedded (e) a protein bilayer that behaves as a liquid crystal
4 According to the fluid mosaic model, membranes consist of (a) a lipid-protein sandwich (b) mainly phospholipids with scattered nucleic acids (c) a fluid phospholipid bilayer in which proteins are embedded (d) a fluid phospholipid bilayer in which carbohydrates are embedded (e) a protein bilayer that behaves as a liquid crystal ANSWER-C Visit site-
5 Transmembrane proteins (a) are peripheral proteins (b) are receptor proteins (c) extend completely through the membrane (d) extend along the surface of the membrane (e) are secreted from the cell
6 Transmembrane proteins (a) are peripheral proteins (b) are receptor proteins (c) extend completely through the membrane (d) extend along the surface of the membrane (e) are secreted from the cell ANSWER-C
7 Which of the following statements is NOT part of the cell theory? a. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. b. Cells come from other cells by division. c. Cells are the smallest living things. d. Eukaryotic cells have evolved from prokaryotic cells.
8 Which of the following statements is NOT part of the cell theory? a. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. b. Cells come from other cells by division. c. Cells are the smallest living things. d. Eukaryotic cells have evolved from prokaryotic cells. ANSWER-D Visit site-
9 All cells have all of the following except a. plasma membrane. c. cytoplasm. b. genetic material. d. cell wall.
10 All cells have all of the following except a. plasma membrane. c. cytoplasm. b. genetic material. d. cell wall. ANSWER-D Visit site-
11 Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. Which of the following are found only in a eukaryotic cell? a. Cell wall b. Plasma membrane c. Endoplasmic reticulum d. Ribosomes
12 Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. Which of the following are found only in a eukaryotic cell? a. Cell wall b. Plasma membrane c. Endoplasmic reticulum d. Ribosomes ANSWER-C
13 The most important factor that limits the size of a cell is the a. quantity of proteins and organelles a cell can make. b. rate of diffusion of small molecules. c. surface area-to-volume ratio of the cell. d. amount of DNA in the cell.
14 The most important factor that limits the size of a cell is the a. quantity of proteins and organelles a cell can make. b. rate of diffusion of small molecules. c. surface area-to-volume ratio of the cell. d. amount of DNA in the cell. ANSWER-C
15 All eukaryotic cells possess each of the following except A. mitochondria. c. cytoskeleton. b. cell wall. d. nucleus. Visit site-
16 All eukaryotic cells possess each of the following except a. mitochondria. c. cytoskeleton. b. cell wall. d. nucleus. ANSWER-B Visit site-
17 Which of these organelles is NOT associated with the production or sorting of proteins in a cell? a. Ribosomes b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) c. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) d. Golgi apparatus
18 Visit site-
19 Different motor proteins like kinesin and myosin are similar in that they can A.interact with microtubules. b. use energy from ATP to produce movement. c. interact with actin. d. do both a and b. Visit site-
20 Different motor proteins like kinesin and myosin are similar in that they can a. interact with microtubules. b. use energy from ATP to produce movement. c. interact with actin. d. do both a and b. ANSWER-B
21 The protein sorting pathway involves the following organelles/ compartments in order: a. SER, RER, transport vesicle, Golgi. b. RER, lysosome, Golgi. c. RER, transport vesicle, Golgi, final destination. d. Golgi, transport vesicle, RER, final destination.
22 The protein sorting pathway involves the following organelles/ compartments in order: a. SER, RER, transport vesicle, Golgi. b. RER, lysosome, Golgi. c. RER, transport vesicle, Golgi, final destination. d. Golgi, transport vesicle, RER, final destination. ANSWER-C
23 Chloroplasts and mitochondria have many common features because both a. are present in plant cells. b. arose by endosymbiosis. c. function to oxidize glucose. d. function to produce glucose.
24 Chloroplasts and mitochondria have many common features because both a. are present in plant cells. b. arose by endosymbiosis. c. function to oxidize glucose. d. function to produce glucose. ANSWER-B Visit site-
25 Eukaryotic cells are composed of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. How are these three filaments similar? a. They contribute to the shape of the cell. b. They are all made of the same type of protein. c. They are all the same size and shape. d. They are all equally dynamic and flexible.
26 Eukaryotic cells are composed of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. How are these three filaments similar? a. They contribute to the shape of the cell. b. They are all made of the same type of protein. c. They are all the same size and shape. d. They are all equally dynamic and flexible. ANSWER-A
27 Plasmodesmata in plants and gap junctions in animals are functionally similar in that a. each is used to anchor layers of cells. b. they form channels between cells that allow diffusion of small molecules. c. they form tight junctions between cells. d. they are anchored to the extracellular matrix.
28 Plasmodesmata in plants and gap junctions in animals are functionally similar in that a. each is used to anchor layers of cells. b. they form channels between cells that allow diffusion of small molecules. c. they form tight junctions between cells. d. they are anchored to the extracellular matrix. ANSWER-B Visit site-
29 The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a. involved in protein synthesis. b. a site of protein glycosylation. c. used to store a variety of ions. d. the site of lipid and membrane synthesis.
30 The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is a. involved in protein synthesis. b. a site of protein glycosylation. c. used to store a variety of ions. d. the site of lipid and membrane synthesis. ANSWER-D Visit site-
31 The cytoskeleton includes a. microtubules made of actin filaments. b. microfilaments made of tubulin. c. intermediate filaments made of twisted fibers of vimentin and keratin. d. smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
32 The cytoskeleton includes a. microtubules made of actin filaments. b. microfilaments made of tubulin. c. intermediate filaments made of twisted fibers of vimentin and keratin. d. smooth endoplasmic reticulum. ANSWER-C
33 Which of the following are differences between bacteria and archaea? a. The molecular architecture of their cell walls b. The type of ribosomes found in each c. Archaea have an internal membrane system that bacteria lack. d. Both a and b
34 Which of the following are differences between bacteria and archaea? a. The molecular architecture of their cell walls b. The type of ribosomes found in each c. Archaea have an internal membrane system that bacteria lack. d. Both a and b ANSWER-A Visit site-
35 Junctions that help form the blood brain barrier are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata
36 Junctions that help form the blood brain barrier are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata ANSWER-A
37 Junctions that permit the transfer of water, ions, and molecules between adjacent plant cells are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata
38 Junctions that permit the transfer of water, ions, and molecules between adjacent plant cells are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata ANSWER-E
39 Anchoring junctions that hold cells together at one point like a spot weld are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata
40 Anchoring junctions that hold cells together at one point like a spot weld are (a) tight junctions (b) adhering junctions (c) desmosomes (d) gap junctions (e) plasmodesmata ANSWER-C
41 When a ligand binds with a receptor (a) tight junctions develop (b) a third messenger is activated (c) cell signaling is stopped (d) it activates the receptor (e) a G protein is destroyed
42 When a ligand binds with a receptor (a) tight junctions develop (b) a third messenger is activated (c) cell signaling is stopped (d) it activates the receptor (e) a G protein is destroyed ANSWER-D Visit site-
43 G proteins (a) relay a message from the activated receptor to an enzyme that activates a second messenger (b) are GTP molecules (c) stop cell signaling (d) directly activate protein kinases (e) Are hormones that function as first messengers
44 G proteins a. relay a message from the activated receptor to an enzyme that activates a second messenger (b) are GTP molecules (c) stop cell signaling (d) directly activate protein kinases (e) are hormones that function as first messengers ANSWER-A
45 A cell takes in dissolved materials by forming tiny vesicles around fluid droplets trapped by folds of the plasma membrane. This process is (a) carrier-mediated active transport (b) pinocytosis (c) receptormediated endocytosis (d) exocytosis (e) facilitated diffusion
46 A cell takes in dissolved materials by forming tiny vesicles around fluid droplets trapped by folds of the plasma membrane. This process is (a) carrier-mediated active transport (b) pinocytosis (c) receptormediated endocytosis (d) exocytosis (e) facilitated diffusion ANSWER-B
47 When plant cells are in a hypotonic medium, they (a) Undergo plasmolysis (b) build up turgor pressure (c) wilt (d) decrease pinocytosis (e) lose water to the environment
48 When plant cells are in a hypotonic medium, they (a) undergo plasmolysis (b) build up turgor pressure (c) wilt (d) decrease pinocytosis (e) lose water to the environment ANSWER-B Visit site-
49 After a ligand binds to receptors in coated pit (a) the ligand binds to receptors in coated vesicle (b) a coated vesicle forms by endocytosis (c) a vesicle enters the cytosol by facilitated diffusion (d) lysosomes destroy protein coating of the pit (e) G proteins signal phagocytosis
50 After a ligand binds to receptors in coated pit (a) the ligand binds to receptors in coated vesicle (b) a coated vesicle forms by endocytosis (c) a vesicle enters the cytosol by facilitated diffusion (d) lysosomes destroy protein coating of the pit (e) G proteins signal phagocytosis ANSWER-B
51 In signal transduction (a) an extracellular signal is converted to an intracellular signal (b) a signal is relayed through a series of molecules in the membrane (c) signal molecules are destroyed before target cells can respond to the signal (d) answers a, b, and c are correct (e) only answers a and b are correct
52 In signal transduction (a) an extracellular signal is converted to an intracellular signal (b) a signal is relayed through a series of molecules in the membrane (c) signal molecules are destroyed before target cells can respond to the signal (d) answers a, b, and c are correct (e) only answers a and b are correct ANSWER-E Visit site-
53 Visit site-
54 The patch clamp technique (a) cannot be applied to plant cells (b) is mainly used to study exocytosis (c) allows researchers to study single ion channels (d) helped researchers understand signal transduction involving G proteins (e) was developed by Singer and Nicolson
55 The patch clamp technique (a) cannot be applied to plant cells (b) is mainly used to study exocytosis (c) allows researchers to study single ion channels (d) helped researchers understand signal transduction involving G proteins (e) was developed by Singer and Nicolson ANSWER-C Visit site-
56 The action of sodium-potassium pumps is an example of (a) carrier-mediated active transport (b) pinocytosis (c) aquaporin transport (d) exocytosis (e) facilitated diffusion
57 The action of sodium-potassium pumps is an example of (a) carrier-mediated active transport (b) pinocytosis (c) aquaporin transport (d) exocytosis (e) facilitated diffusion ANSWER-A
58 Which of the following is an example of carrier-mediated transport? (a) simple diffusion (b) facilitated diffusion (c) movement of water through aquaporins (d) osmosis (e) osmosis when a cell is in a hypertonic solution
59 Which of the following is an example of carrier-mediated transport? (a) simple diffusion (b) facilitated diffusion (c) movement of water through aquaporins (d) osmosis (e) osmosis when a cell is in a hypertonic solution ANSWER-B Visit site-
60 Which of the following processes requires the cell to expend metabolic energy directly (for example, from ATP)? (a) active transport (b) facilitated diffusion (c) all forms of carrier-mediated transport (d) osmosis (e) simple diffusion
61 Which of the following processes requires the cell to expend metabolic energy directly (for example, from ATP)? (a) active transport (b) facilitated diffusion (c) all forms of carrier-mediated transport (d) osmosis (e) simple diffusion ANSWER-C
62 Which of the following is not a function of the plasma membrane? (a) transports materials (b) helps to structurally link cells together (c) manufactures proteins (d) anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix (e) has receptors that relay signals
63 Which of the following is not a function of the plasma membrane? (a) transports materials (b) helps to structurally link cells together (c) manufactures proteins (d) anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix (e) has receptors that relay signals ANSWER-C
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell
 Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
Chapter 4 Organization of the Cell Cell basic unit of life o Small o Self-sufficient o Self-replicating Cell Theory organisms are composed of cells and all cells come from the division of other cells Cells
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS
 CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Lesson 3 Cell and Cell Membrane Structure and Function Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 The Cell Theory Three principles comprise the cell theory 1) Every living organism is made up of one or
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated!
 3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated! 4. Vacuoles ii. Large Central Vacuole (Plants)! Fills up most of plant cell! Membrane bound (tonoplast)! Helps cell s water balance! Dump site for hazardous
3. Endomembrane System: It s all integrated! 4. Vacuoles ii. Large Central Vacuole (Plants)! Fills up most of plant cell! Membrane bound (tonoplast)! Helps cell s water balance! Dump site for hazardous
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Cytology I Study of Cells
 Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
Cytology I Study of Cells Biology 20 Which cell type has organelles such as mitochondria, nuclues, Golgi bodies, etc? A) prokaryotic B) eukaryotic C) bacterial D) viral E) none of these Cellular Basis
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and function
 Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Cell Structure and Cell Structure and function Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Cells Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
Outline. Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport
 Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Name: Class: Date: Unit 1 Test: Cells. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: _ Date: _ Unit 1 Test: Cells Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins? A) They
Class: _ Date: _ Unit 1 Test: Cells Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins? A) They
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life
 AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell
 Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Chapter 7: Membranes
 Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Chapter 7: Membranes Roles of Biological Membranes The Lipid Bilayer and the Fluid Mosaic Model Transport and Transfer Across Cell Membranes Specialized contacts (junctions) between cells What are the
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Cell Structure & Interactions
 Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
Cells Structures & Interactions Overview 1830s-Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory All living things are composed of one
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Diffusion across cell membrane
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power?
 AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Chapter Seven. A View of the Cell
 Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
Chapter Seven A View of the Cell Cellular Organization Cell Tissue group of cells functioning together. Organ group of tissues functioning together. Organ System group of organs functioning together. Organism
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function. Key Terms:
 Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function The Discovery of the Cell - microscopes invented in 1600 s - Robert Hooke observed cork in 1665 and described them as little boxes he called cells - Hooke did not
Cell membranes. Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102
 Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC. Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
10/28/2013. Double bilayer of lipids with imbedded, dispersed proteins Bilayer consists of phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids
 Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries
 Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Chapter 7-3 Cell Boundaries The Plasma Membrane: Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Provides protection and support. Highly selective barrier!!!! What the plasma membrane is made
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes. Reading Assignments. Selective and Semi-permeable Barriers
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter 15 regarding Endocytosis and Exocytosis Read Chapter 20 (Cell
Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang
 Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Today s Agenda: I. Review of organelles II. More important organelles III. Plasma membrane structure IV. Diffusion and transport Delve AP Biology Lecture 4: 10/9/11 Melissa Ko and Anne Huang I. Review
Name 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of
 Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Name _ 4 A Tour of the Cell Test Date Study Guide You must know: The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. The
Cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Euakryotic cells are generally one to one hundred times bigger than prokaryotic cells
 Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Cell Theory Cells 1. All living things are composed of one or more cell 2. Cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division of pre-existing cells Cells are divided into 2 categories:
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
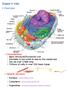 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell
 Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell Honors Biology 2011 1 The History of the Microscope and Cell Theory 1665 - Robert Hooke uses a simple microscope to look at cork. 1668 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed single celled
Chapters 4 & 5: The Cell Honors Biology 2011 1 The History of the Microscope and Cell Theory 1665 - Robert Hooke uses a simple microscope to look at cork. 1668 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek observed single celled
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Biology 12 Chapter 4
 Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
Transport: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Biology 12 Chapter 4 FLUID-MOSAIC MODEL OF MEMBRANE STRUCTURE The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipid molecules (bilayer)
