Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC. Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC
|
|
|
- Percival Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Aco GCCCAACTGTGACTTCCATT GGCATGTAACCCGTAGCACT Agpat1 CACCCAGGATGTGAGAGTCTG CTGACAACGTCCAGGCGAGG Sqle CGCGCAGCGGTTACTCTGGT AGTCACGGCCGGGAACCTGT Mtp TGCGGGTCAACAGAGAGGCG CCTTGACCTTCCCCCGGACCA Gpat4 GGCAGAGGAGCTGGAGTC TGTTGTGGTACGTAATGATGG Dgat2 AGTGGCAATGCTATCATCATCGT AAGGAATAAGTGGGAACCAGATCA Fas GCTGCGGAAACTTCAGGAAAT AGAGACGTGTCACTCCTGGACTT Hmgcs GCCGTGAACTGGGTCGAA GCATATATAGCAATGTCTCCTGCAA Scd1 CCGGAGACCCCTTAGATCGA TAGCCTGTAAAAGATTTCTGCAACC Lipin1 GGTCCCCCAGCCCCAGTCCTT GCAGCCTGTGGCAATTCA Lipin2 AGTTGACCCCATCACCGTAG CCCAAAGCATCAGACTTGGT Srebp1 AGCAGCCCCTAGAACAAACAC CAGCAGTGAGTCTGCCTTGAT Srebp2 TGAAGGACTTAGTCATGGGGAC CGCAGCTTGTGATTGACCT ApoCIII AGGTACGTAGGTGCCATGC CGTCTTGGAGGCTTGTTCCA Pcsk9 CAGAGGTCATCACAGTCGGG GGGGCAAAGAGATCCACACA Hrpt TGACACTGGTAAAACAATGC AACACTTCGAGAGGTCCTTT Hmgcoar, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; Cyp7α, cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase; Cyp27a1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; Aco, Acyl coa carboxylase; Agpat1, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase; Sqle, Squalene monooxygenase; Mtp, Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein; Gpat, Glycerol-3- phosphate acyltransferase; Dgat, Diacylglycerol acyltransferase; Fas, Fatty acid synthase; Hmgcs, HMGcoA synthase; Scd1, Stearoyl-coA desaturase-1; Srebp, Sterol regulatory element binding protein; Apo, apolipoprotein; Pcsk9, Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/kexin type 9 ;Hrpt, Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase.
2 Supplement Table II: Effect of on major plasma lipid species in Ldlr -/- mice Plasma (nmol/ml) VLDL (nmol/apob) IDL/LDL (nmol/apob) Chol * CE ** DG # TG # PC *** Chol, cholesterol; CE, cholesteryl esters; DG, diacylglycerol; TG, triglyceride; PC, phosphatidyl choline. Lipid levels were determined by LC/MSMS. Data are presented as nmol/ml for plasma and expressed nmol lipid per apob content for VLDL and IDL/LDL fractions. ApoB content of VLDL and IDL/LDL particles was determined by Western blotting. Data is mean sem from 7-8 mice per group. # p<.5, *p<, **p<.1, ***p<.1 v ctrl.
3 Supplemental Table III: Lipidomics of VLDL and LDL in v -treated Ldlr -/- mice VLDL (nmol/apob) IDL/LDL (nmol/apob) Sphingomyelin Ceramide Dihydroceramide Monohexosylceramide Dihydrohexoceramide Trihexosylceramide G M3 ganglioside Lysophosphatidylcholine Lysoalkylphosphatyidylcholine Phosphatidylcholine Alkylphosphatidylcholine Alkenylphosphatidylcholine Lysophosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Alkylphosphatidylethanolamine Alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine Phosphatidylglycerol Lysophosphatidylinositol Phosphatidylinositol Phosphatidylserine Lipid levels were determined by LC/MSMS. Data are presented relative to apob content and represent mean sem from 7-8 mice per group.
4 Supplement Table IV: Lipidomics of SM species in VLDL and LDL in v -treated Ldlr -/- mice VLDL (nmol/pc) IDL/LDL (nmol/pc) SM 32:1 SM 33:1 SM 34:1 SM 34:2 SM 34:3 SM 36:1 SM 36:2 SM 36:3 SM 38:1 SM 38:2 SM 42:1 SM 31:1 SM 33:1 SM 35:1 SM 35:2 SM 37:2 SM 39:1 SM 41:1 SM 41: ** # * # * * * ** * *** * # ** * * * * * Levels of SM species were determined by LC/MSMS. Data is presented nmol per PC content and is mean sem from 7-8 mice per group. # p<.5, *p<, ** p<.1, ***p<.1.
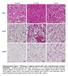
5 Figure I A wt Ldlr-/- B wt Ldlr-/- C wt Ldlr-/- Figure I: does not induce liver or kidney toxicity. Wt and Ldlr -/- mice were treated with 2mg/kg/day or vehicle () for 4 weeks via subcutaneous implanted Alzet Osmotic minipumps. Formalin-perfused livers (A) and kidneys (B) were paraffin embedded and stained with hematoxylin/eosin. Kidney sections were also stained with Periodic acid-schiff stain (C). Tissue sections shown were viewed using a 2x objective. Scale bar = 2µm. No significant difference was
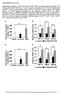
6 Figure II A B Blood glucose (mmol/l) AUC glucose (mmol/l x 12min) ** Time (min) Figure II: does not induce insulin resistance in LDLr -/- mice. LDLr -/- mice were treated with 2mg/kg/day or vehicle () for 4 weeks. Non-fasted insulin tolerance tests were performed as described in material and methods. (A) Blood glucose levels in response to i.p. injection of insulin and (B) Glucose area under the curve (AUC). Values are mean S.E.M. (n=1 per group). ** p<.
7 Figure III Hepatic mrna level (fold induction) Hmgcoar Fas Scd1 Srebp1 Srebp2 Figure III: does not affect hepatic mrna levels of genes involved in lipid synthesis. Wt mice were treated with 2mg/kg/day or vehicle () for 4 weeks. Hepatic mrna levels were determined by qpcr as described in Materials and Methods.
8 Figure IV VLDL particle size (nm) Figure IV: does not affect VLDL particle size in LDLr -/- mice. LDLr -/- mice were treated with 2mg/kg/day or vehicle () for 4 weeks. VLDL was isolated by density ultracentrifugation and VLDL particle size was determined using dynamic light scattering as described in Material and Methods.
9 Figure V wt Ldlr -/- [ 3 H] activity (% of injected dose) Liver Heart Spleen Kidney GonWAT ScWAT Muscle SolMuscle [ 3 H] activity (% of injected dose) Liver * Heart Spleen Kidney GonWAT ScWAT Muscle SolMuscle wt Ldlr -/- [ 14 C] activity (% of injected dose) Liver Heart Spleen Kidney GonWAT ScWAT Muscle SolMuscle Figure V: inhibits hepatic uptake of lipoprotein derived cholesteryl oleate in LDLr -/- mice. Wt and LDLr -/- mice were treated with 2 mg/kg/day or cremaphore vehicle () for 4 weeks. Mice were injected with VLDL-like particles, double-labeled with [ 3 H]TO and [ 14 C]CO. 3 H- and 14 C- uptake by organs and tissues were determined at 15 min for wt and 3 min for LDLr -/- after injection. Data are expressed as percentage 3 H- or 14 C-activity of the injected dose per total tissue, with the exception of kidney, white adipose tissue pads and muscle which were determined as uptake in 1 representative tissue. GonWAT, gonadal white adipose tissue, scwat, subcutaneous white adipose tissue. Values are mean S.E.M. (n=5-7 per group). * p<.5. [ 14 C] activity (% of injected dose) Liver * Heart Spleen Kidney GonWAT ScWAT Muscle SolMuscle
10 Figure VI Figure VI: Plasma PCSK9 levels are not increased by in wt mice Wt were treated with 2 mg/kg/day or vehicle () for 4 weeks. Plasma PSCK9 levels were determined by Western Blotting. A representative sample from Ldlr -/- mice is shown. No increase in PCSK9 was observed after treatment of wt mice.
Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR. Primer Sequence Primer Sequence Mouse Pcsk9-F TTGCAGCAGCTGGGAACTT Mouse Scd1-F CATCATTCTCATGGTCCTGCT Mouse Pcsk9-R CCGACTGTGATGACCTCTGGA Mouse
Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR. Primer Sequence Primer Sequence Mouse Pcsk9-F TTGCAGCAGCTGGGAACTT Mouse Scd1-F CATCATTCTCATGGTCCTGCT Mouse Pcsk9-R CCGACTGTGATGACCTCTGGA Mouse
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets. James M. Ntambi Ph.D
 Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Metabolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients
 Metaolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients Franck Chiappini, Audrey Coilly, Hanane Kadar, Philippe Gual, Alert Tran, Christophe Desterke, Didier
Metaolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients Franck Chiappini, Audrey Coilly, Hanane Kadar, Philippe Gual, Alert Tran, Christophe Desterke, Didier
The Addition of Ezetimibe to Statin therapy in. Patients with Homozygous Familial. Hypercholesterolaemia
 The Addition of Ezetimibe to Statin therapy in Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Submitted in fulfilment with the requirements for the degree Master in Medicine (MMed) Dr Adriano
The Addition of Ezetimibe to Statin therapy in Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Submitted in fulfilment with the requirements for the degree Master in Medicine (MMed) Dr Adriano
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Triacylglycerol and Fatty Acid Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM II. Triacylglycerol synthesis A. Overall pathway Glycerol-3-phosphate + 3 Fatty acyl-coa à Triacylglycerol + 3 CoASH B. Enzymes 1. Acyl-CoA synthase 2. Glycerol-phosphate
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at
 Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Zuhier Awan, MD, PhD, FRCPC
 Metabolism, Atherogenic Properties and Agents to Reduce Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins (TRL) The Fifth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 8-11, 2019 Zuhier
Metabolism, Atherogenic Properties and Agents to Reduce Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins (TRL) The Fifth IAS-OSLA Course on Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Risk Muscat, Oman, February 8-11, 2019 Zuhier
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Juxtapid. Juxtapid (lomitapide) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Juxtapid Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Juxtapid Description Juxtapid (lomitapide)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Juxtapid Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: September 20, 2018 Juxtapid Description Juxtapid (lomitapide)
Supplementary Figure S1
 Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Regulating Hepatic Cellular Cholesterol
 Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
 Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention
 Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity
 Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The LDL Receptor, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool I. Michael Brown and Joseph Goldstein A. Studied families with familial hypercholesterolemia. B. Defined the relationship
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM The, LDL Uptake, and the Free Cholesterol Pool I. Michael Brown and Joseph Goldstein A. Studied families with familial hypercholesterolemia. B. Defined the relationship
Supporting Information. Supporting Tables. S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Product size. Gene Primer pairs
 Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
Lipoproteins Metabolism
 Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc1,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD,!! Sébastien!M.!
 SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes
 Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes The major site of acetoacetate and 3-hydorxybutyrate production is in the liver. 3-hydorxybutyrate is the
Companion to Biosynthesis of Ketones & Cholesterols, Regulation of Lipid Metabolism Lecture Notes The major site of acetoacetate and 3-hydorxybutyrate production is in the liver. 3-hydorxybutyrate is the
The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome
 UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
PCs Acyl chain double bonds. PEs
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Male/Female ratio Male/Female ratio PCs 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0 1 2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Male/Female ratio Male/Female ratio PCs 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0 1 2
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol
 Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Supplementary Information. MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Cholesterol Metabolism
 Cholesterol Metabolism Lippincott s Illustrated Review Chapter 18 Steroid Nucleus 1 2 Cholesterol was isolated from gall bladder stones in 1774 3 Sources and Elimination of Cholesterol Synthesis: 1000
Cholesterol Metabolism Lippincott s Illustrated Review Chapter 18 Steroid Nucleus 1 2 Cholesterol was isolated from gall bladder stones in 1774 3 Sources and Elimination of Cholesterol Synthesis: 1000
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity
 ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
N-3 Fatty Acids Non-HDL-Cand LDL-C Thomas Dayspring MD, FACP
 Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Emerging science on omega-3: A lipidomic view of omega-3 in health and disease. Health benefits of omega 3 fatty acids
 Emerging science on omega-3: A lipidomic view of omega-3 in health and disease Peter Meikle 04 May 2017 Health benefits of omega 3 fatty acids Can lower plasma triacylglycerol can reduce the risk of metabolic
Emerging science on omega-3: A lipidomic view of omega-3 in health and disease Peter Meikle 04 May 2017 Health benefits of omega 3 fatty acids Can lower plasma triacylglycerol can reduce the risk of metabolic
Poly-unsaturated phospholipids WE (FA18:1) A B C D OAHFA 18:1/24:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:2 PS 38:4 C18:1C23:0 OAHFA 18:1/25:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:1
 Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice. Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health
 Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health Nightingale Health Ltd. Finnish biotech company specialized in comprehensive
Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health Nightingale Health Ltd. Finnish biotech company specialized in comprehensive
Chapter 1 The Lipid Droplet: a Dynamic Organelle, not only Involved in the Storage and Turnover of Lipids
 Chapter 1 The Lipid Droplet: a Dynamic Organelle, not only Involved in the Storage and Turnover of Lipids Sven-Olof Olofsson, Pontus Boström, Jens Lagerstedt, Linda Andersson, Martin Adiels, Jeanna Perman,
Chapter 1 The Lipid Droplet: a Dynamic Organelle, not only Involved in the Storage and Turnover of Lipids Sven-Olof Olofsson, Pontus Boström, Jens Lagerstedt, Linda Andersson, Martin Adiels, Jeanna Perman,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in. diabetic patients
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in diabetic patients Cubedo et al: ApoA-I truncated form in diabetes By Judit Cubedo a, Teresa Padró
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in diabetic patients Cubedo et al: ApoA-I truncated form in diabetes By Judit Cubedo a, Teresa Padró
Control 7 d cold 7 d CL
 Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Digestion, absorption, and transport of dietary lipids
 TG metabolism Utilization of dietary lipids Synthesis in liver and adipose tissue Fatty acid catabolism and synthesis Mobilization of TG to provide energetic needs β-oxidation of fatty acids De novo synthesis
TG metabolism Utilization of dietary lipids Synthesis in liver and adipose tissue Fatty acid catabolism and synthesis Mobilization of TG to provide energetic needs β-oxidation of fatty acids De novo synthesis
ALT (U/L) (Relative expression) HDL (mm) (Relative expression) ALT (U/L) (Relative expression)
 a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Cholesterol metabolism. Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia
 Cholesterol metabolism Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia - component of all cell membranes - precursor of bile acids steroid hormones vitamin D Cholesterol Sources: dietary
Cholesterol metabolism Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia - component of all cell membranes - precursor of bile acids steroid hormones vitamin D Cholesterol Sources: dietary
Supplemental Information. FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating. Antibody Act on the Nervous System. to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Disorders of Lipid Metabolism
 CHAPTER 37 Disorders of Lipid Metabolism CLAY F. SEMENKOVICH ANNE C. GOLDBERG IRA J. GOLDBERG Lipid Biochemistry and Metabolism, 1660 Nuclear Receptors and Lipid Metabolism, 1665 Plasma Lipoproteins, Apolipoproteins,
CHAPTER 37 Disorders of Lipid Metabolism CLAY F. SEMENKOVICH ANNE C. GOLDBERG IRA J. GOLDBERG Lipid Biochemistry and Metabolism, 1660 Nuclear Receptors and Lipid Metabolism, 1665 Plasma Lipoproteins, Apolipoproteins,
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity
 Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
Chapter 16 - Lipid Metabolism
 Chapter 16 - Lipid Metabolism Fatty acids have four major physiologic roles in the cell: Building blocks of phospholipids and glycolipids Added onto proteins to create lipoproteins, which targets them
Chapter 16 - Lipid Metabolism Fatty acids have four major physiologic roles in the cell: Building blocks of phospholipids and glycolipids Added onto proteins to create lipoproteins, which targets them
Cholesterol and its transport. Alice Skoumalová
 Cholesterol and its transport Alice Skoumalová 27 carbons Cholesterol - structure Cholesterol importance A stabilizing component of cell membranes A precursor of bile salts A precursor of steroid hormones
Cholesterol and its transport Alice Skoumalová 27 carbons Cholesterol - structure Cholesterol importance A stabilizing component of cell membranes A precursor of bile salts A precursor of steroid hormones
Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis. 1. Fatty acids 2. Eicosanoids 3. Triacylglycerols 4. Membrane phospholipids 5. Cholesterol, steroids, and isoprenoids
 Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis 1. Fatty acids 2. Eicosanoids 3. Triacylglycerols 4. Membrane phospholipids 5. Cholesterol, steroids, and isoprenoids 1. Fatty acid synthesis takes a different pathway from
Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis 1. Fatty acids 2. Eicosanoids 3. Triacylglycerols 4. Membrane phospholipids 5. Cholesterol, steroids, and isoprenoids 1. Fatty acid synthesis takes a different pathway from
Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions analysed by ESI-MS/MS
 Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations.
 Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
Hepatic insulin signaling regulates VLDL secretion and atherogenesis in mice
 Hepatic insulin signaling regulates VLDL secretion and atherogenesis in mice Seongah Han,, Domenico Accili, Alan R. Tall J Clin Invest. 2009;119(4):1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci36523. Research
Hepatic insulin signaling regulates VLDL secretion and atherogenesis in mice Seongah Han,, Domenico Accili, Alan R. Tall J Clin Invest. 2009;119(4):1029-1041. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci36523. Research
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS. Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of cysteine and methionine and then treated with 10 μm puromycin in depletion medium
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of cysteine and methionine and then treated with 10 μm puromycin in depletion medium
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Kynamro. Kynamro (mipomersen) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.40.02 Subject: Kynamro Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Kynamro Description Kynamro
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.40.02 Subject: Kynamro Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Kynamro Description Kynamro
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids. Martina Srbová
 Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride synthesis
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296: E1195 E1209, 2009. First published March 31, 2009; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90958.2008. Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296: E1195 E1209, 2009. First published March 31, 2009; doi:10.1152/ajpendo.90958.2008. Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination
 AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
Thematic review series: The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis
 thematic review Thematic review series: The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host 1 Weerapan
thematic review Thematic review series: The Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: mechanisms and consequences to the host 1 Weerapan
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol
 Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
GROWTH HORMONE AND PPARα IN THE REGULATION OF GENES INVOLVED IN HEPATIC LIPID METABOLISM. Caroline Améen
 GROWTH HORMONE AND PPARα IN THE REGULATION OF GENES INVOLVED IN HEPATIC LIPID METABOLISM Caroline Améen Department of Physiology and Wallenberg Laboratory for Cardiovascular Research Sahlgrenska Academy
GROWTH HORMONE AND PPARα IN THE REGULATION OF GENES INVOLVED IN HEPATIC LIPID METABOLISM Caroline Améen Department of Physiology and Wallenberg Laboratory for Cardiovascular Research Sahlgrenska Academy
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27
 Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Novel Reduction of PCSK9 Expression: Mechanistic Insights into the Anti-Atherosclerotic & Hypolipidemic Effects of Heat Shock Protein 27 Ed O Brien, Jean-Claude Bakala-N Goma, Chunhua Shi Cumming School
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
AN OVERVIEW OF FATTY ACID ETHYL ESTERS
 AN OVERVIEW OF FATTY ACID ETHYL ESTERS Michael Laposata, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Clinical Laboratories Massachusetts General Hospital Professor, Harvard Medical School OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Background
AN OVERVIEW OF FATTY ACID ETHYL ESTERS Michael Laposata, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Clinical Laboratories Massachusetts General Hospital Professor, Harvard Medical School OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Background
KSRP is critical in governing hepatic lipid metabolism
 KSRP is critical in governing hepatic lipid metabolism through controlling Per2 expression Chu-Fang Chou, 1, * Xiaolin Zhu, 1, Yi-Yu Lin, * Karen L. Gamble, W. Timothy Garvey, and Ching-Yi Chen 2, * Department
KSRP is critical in governing hepatic lipid metabolism through controlling Per2 expression Chu-Fang Chou, 1, * Xiaolin Zhu, 1, Yi-Yu Lin, * Karen L. Gamble, W. Timothy Garvey, and Ching-Yi Chen 2, * Department
Is it really that simple? Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics
 Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Optimising. membranes
 Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
Optimising Neuronal membranes Lipids are classified as 1. Simple lipids oils and fats 2. Complex lipids a) Phospholipids b) Glycosphingolipids containing a fatty acid, sphingosine and a CHO c) Lipoproteins
WILL ABSENCE OF GPAT1 IMPROVE DIET-INDUCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN APOE HETEROZYGOUS MICE? PEI-CHI WU
 WILL ABSENCE OF GPAT1 IMPROVE DIET-INDUCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN APOE HETEROZYGOUS MICE? PEI-CHI WU A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment
WILL ABSENCE OF GPAT1 IMPROVE DIET-INDUCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN APOE HETEROZYGOUS MICE? PEI-CHI WU A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment
Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
 Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Novel
Lipid Lowering in Patients at High Risk for Cardiovascular Disease Prof. John J.P. Kastelein, MD PhD FESC Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medical Center / University of Amsterdam The Netherlands Novel
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Cholesterol Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels
 Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Lipoprotein Formation, Structure and Metabolism: Balance and the Regulation of Plasma Lipid Levels David E. Cohen, MD, PhD Director of Hepatology, Gastroenterology Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids?
 Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Cellular control of cholesterol. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
