Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
|
|
|
- Warren Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.! Cells arise from the division of preexisting cells.! Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions.! Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level.! Organismal homeostasis reflects combined, coordinated action of many cells.! 2 1!
2 The Diversity of Cells in the Human Body! Somatic cells! Sex cells! 3 Anatomy of a Representative Cell! Spotlight Figure 3-1! 4 2!
3 A Typical Cell! Is surrounded by extracellular fluid! Has a cell (plasma) membrane separates cell from its environment! Has a large surface area to volume ratio! 5 Why are cells small?! Surface area to volume ratio limits cell size.! Surface area! 1-mm cube! 6 sides x 1 2 =! 6 mm 2! 6-mm cube! 6 sides x 6 2 =! 216 mm 2! Volume! 1 3 = 1 mm 3! 6 3 = 216 mm 3! Surface area to! Volume ratio! 6/1 (6:1)! 1/1 (1:1)! 6 3!
4 ! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Importance of Surface Area to Volume Ratio! Surface area to volume ratio limits cell size because:! Cell volume determines metabolic demands! Volume increases with r 3! Cell surface area determines amount of exchange with environment (e.g. supply of O 2, nutrients)! Surface area increases with r 2! Look at the previous slide until you understand this.! Ask me again if you still don t see it.! 7 Surface area to volume ratio - 2! The bottom line is supply vs. demand:! As cell size increases, volume increases.! ü But volume increases more rapidly that surface area. ( X 3 vs. X 2 )! ü Therefore, the surface area to volume ratio decreases.! At some cell size, demand becomes greater than supply. A cell can t survive this way!! 8 4!
5 SECTION 3-1! The plasma membrane separates the cell from its surrounding environment and performs various functions! 9 Cell Membrane Functions! Physically isolates cell from environment! Regulates of exchange with the environment (semipermeable)! Recognizes/responds to environment (sensitivity)! Catalyzes chemical reactions! Provides structural support! Cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer =! Fluid Mosaic Model of the cell membrane! 10 5!
6 The Cell (Plasma) Membrane Figure 3-2! Phospholipid bilayer with proteins, lipids and carbohydrates! 11 Membrane Lipids! By weight, lipid:protein ratio about 40%:60%! Phospholipids (about 70% - review Figure 2-18)! Polar molecules! Hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails! Cholesterol (about 20% - review Figure 2-17)! Increases stiffness of membrane! Glycolipids (very low %) ( glyco- = sugar)! On extracellular surface only! Adhesion molecules, identity markers! 12 6!
7 Membrane Protein Types! Positional classification:! Integral proteins! Peripheral proteins! Functional classification:! Anchoring proteins! Recognition proteins (e.g. MHC)! Enzymes! Receptor proteins (bind ligands)! Carrier proteins! Channel proteins! 13 The Cell Membrane Review of Figure 3-2! 14 7!
8 Membrane Carbohydrates Form the Glycocalyx! Types! Proteoglycans! Glycolipids! Glycoproteins (MHCs)! Functions! Lubrication and protection (structure)! Anchoring and locomotion! Reception - binding specificity! Recognition! 15 SECTION 3-2! Organelles within the cytoplasm perform particular functions! 16 8!
9 The Cytoplasm! Cytoplasm = cytosol = intracellular fluid! Varies in viscosity (thickness)! Plasmasol Plasmagel! Contains organelles and inclusions! 17 Intra- vs. Extracellular Fluid! Compared to extracellular fluid, intracellular fluid has:! A higher [K + ]! A lower [Na + ]! A higher suspended [proteins] (30% of cell weight)! Reserves! e.g., CH 2 Os, amino acids, lipids! Insoluble inclusions! glycogen granules, lipid droplets, pigments! 18 9!
10 ! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Organelles! Nonmembranous organelles are not enclosed by a membrane! e.g. Cytoskeleton, centrioles, ribosomes! Membranous organelles are surrounded by lipid membranes! e.g. Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, nucleus! 19 Anatomy of a Representative Cell Figure 3-1! 20 10!
11 Cytoskeleton Provides Strength and Flexibility! Functions! Structural support, cell shape! Cell movement! Organelle movement!! Types thinnest to thickest! Microfilaments! Intermediate filaments! Microtubules! Thick filament! 21 The Cytoskeleton Figure 3-3! 22 11!
12 !! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Microfilaments! Composed of actin! Functions:! Anchor cytoskeleton to integral proteins - mechanical support! Determine consistency of cytoplasm plasmagel (lots of microfilaments) plasmasol (fewer microfilaments)! Phagocytosis and cell movement/ contraction (with myosin)! 23 Intermediate Filaments! Composed of different proteins in different cells! e.g. Keratin in epithelial cells (chapter 5)! Functions: Cell shape and structure! Stabilize organelles! Cell-cell junctions! e.g. desmosomes, keratin! 24 12!
13 Microtubules! Composed of tubulin! Extend outward from centrosome! Functions:! Support, anchoring! Cell shape - movement! Organelle movement - Molecular motors! dynein, kinesins! Centrioles and spindle apparatus (cell division)! Cilia! 25 Centrioles, Centrosome and Cilia (microtubules)! Centrioles! Direct the movement of chromosomes during cell division! Organize the cytoskeleton! Centrosome = cytoplasm surrounding the centrioles! Cilia (singular = cilium)! Anchored by a basal body! Beat rhythmically to move fluids across cell surface (e.g. Respiratory system)! 26 13!
14 ! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Centrioles and Cilia Microtubules Figure 3-4! Very cool mechanism! 27 Thick Filaments! Composed of myosin! Found in muscle cells! Function: Part of contractile mechanism (Chapter 10)! Videos on my Links Page! 28 14!
15 Ribosomes! Sites of protein synthesis (translation)! Composed of a large and a small ribosomal subunit! Contain ribosomal RNA (rrna) + protein! Types:! Free ribosomes: suspended (free) in cytoplasm make proteins for use within cell cytoplasm Fixed ribosome: attached to endoplasmic reticulum protein functions listed under rough ER! 29 Proteasomes! Barrel-shaped molecules - several polypeptides! Contain proteases (enzymes)! Remove and break down damaged or abnormal proteins! Proteins to be recycled tagged with ubiquitin (An entire class of enzymes does this tagging)! Proteins amino acids, small peptides! 30 15!
16 The Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Figure 3-5! 31 ER: Overall Functions! 1. Synthesis! Lipids, CH 2 Os, proteins! 2. Storage! 3. Transport within cell! 4. Detoxification! 32 16!
17 Rough ER Functions! Rough ER contains fixed ribosomes! Major functions:! Make proteins for! Export from cell (secretion)! Inclusion in cell membranes! Inclusion in lysosomes! Other functions:! Intracellular transport! Temporary storage! 33 Smooth ER Functions! Smooth ER does not contain ribosomes! Vesicles transport proteins to Golgi apparatus! Synthesizes lipids (phospholipids, cholesterol, steroid hormones)! Storage area! Calcium stored inside, especially in muscle cells! Glycogen granules stored on surface! Surface area for enzymatic reactions! Glycogen free glucose! Detoxification reactions! 34 17!
18 The Golgi Apparatus Figure 3-6! Transport vesicles! from ER! 35 Golgi Apparatus Functions! Acts like the Post Office! Sorts, packages, delivers molecules Forms secretory vesicles! Discharged by exocytosis! Forms new membrane components! Packages enzymes into lysosomes! 36 18!
19 Functions of the Golgi Apparatus Figure 3-7! e.g. Natural Killer cell secreting perforin 37 Lysosomes! Contain digestive enzymes used in:! Digestion following phagocytosis or endocytosis - kiss and run, fusion! Autophagy (recycling) kiss and run, fusion! Autolysis (after cell damage, death)! (Not involved in programmed cell death : British Society for Cell Biology, January 2011)! Enzymes:! Hydrolases - digest all types of macromolecules! Maximum activity at ph near 5! Inactive in primary lysosomes, activated in secondary lysosomes! 38 19!
20 Lysosome Functions Figure 3-8! Autophagy! Autolysis! Digestion! 39 Mitochondrion (Mitochondria) Figure 3-9! All derived from mother! Contain their own DNA! Responsible for ATP production through aerobic respiration! Matrix = fluid contents of mitochondria! Cristae = folds in inner membrane! 40 20!
21 SECTION 3-3! The nucleus contains DNA and enzymes essential for controlling cellular activities! 41 The Nucleus is the Brain of the Cell! Surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane)! Communicates with cytoplasm through nuclear pores! Contents of the nucleus (nucleoplasm):! Nuclear matrix! Enzymes, nucleotides (DNA, RNA), ions, etc.! One or more nucleoli! Chromatin! DNA bound to histones! Chromosomes! 42 21!
22 The Nucleus Figure 3-10! 43 Chromosome Structure Figure 3-11! 44 22!
23 ! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! The Nucleolus (Nucleoli)! Region containing DNA, rrna, enzymes, histones! Synthesize ribosomal RNA (rrna)! Assemble ribosomal subunits (small and large)! Carriers transport subunits to nuclear pores! Nucleolus Nucleus 45 SECTION 3-4! DNA controls protein synthesis, cell structure, and cell function! 46 23!
24 The Genetic Code! Triplet code! Three nucleotides in sequence along a DNA strand code for one amino acid that will be added to a growing polypeptide! A gene contains all the triplets needed to code for a specific polypeptide! 47 Protein Synthesis Overview! transcription! translation! DNA! RNA! Protein! (Nucleotides)! (Nucleotides)! (Amino acids)! Transcription:! Information stays in the same language (base pair sequence)! Translation:! Information is translated from base pair sequence to amino acid sequence 48 24!
25 Gene Activation and Protein Synthesis! Gene activation begins with RNA polymerase binding to the gene (DNA) at a promoter region! Transcription is the formation of mrna from DNA! mrna carries instructions from the nucleus to the ribosome in the cytoplasm! 49 Making Proteins Requires:! Be absolutely certain that you know this slide and the next slide before you worry about other details.! 1. Instructions:! Genes on DNA in nucleus! 2. An assembly site:! Ribosomes = rrna (ribosomal RNA) + proteins in cytoplasm! And! 50 25!
26 Making Protein Requires (2)! 3. Federal Express :! mrna (messenger RNA) takes instructions from nucleus to assembly site in cytoplasm! 4. Raw materials:! Amino acids in cytoplasm! 5. Transport of raw materials to assembly site:! trna (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to ribosome! 51 DNA vs. RNA Base Pairing! mrna DNA polymerase! makes new DNA! RNA polymerase makes RNA from DNA! 52 26!
27 !! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Some Important Terms! Code - DNA! Three (3) nucleotide bases in sequence along a gene (DNA) code for one amino acid! Codon - mrna! Complementary to DNA sequence for a protein (made from DNA template strand)! Three (3) nucleotide bases along an mrna molecule code for one amino acid Anticodon - trna! Anticodon determines which amino acid the trna molecule can carry! Complementary to mrna codon(s)! 53 More Important Terms! Coding strand - DNA strand that specifies the sequence of amino acids in the new polypeptide! Template strand - DNA strand that is read by RNA polymerase to produce mrna! The template strand is complementary to the coding strand! 54 27!
28 DNA Triplets Table 3-1! AUG = START; UAA, UAG and UGA = STOP 55 Transcription! Overview slide, not from your text 56 28!
29 RNA Polymerase - 1! 57 RNA Polymerase - 2! Transcription direction DNA coils back up CODING STRAND DNA unwinds Newly-formed mrna TEMPLATE STRAND DNA template strand being read, mrna forming 58 29!
30 RNA Polymerase - 3! = RNA polymerase 59 Transcribed mrna! At end of gene:! mrna transcript is released from RNA polymerase ( Release Factor inserted)! Post-transcriptional modification occurs 60 30!
31 ! Chapter 3 Part 2 Organelles! Post-transcriptional Modifications to mrna! Introns = intervening sequences! Cut out while mrna is in nucleus! Not expressed in protein! May be evolutionary baggage! Exons = expressed portion of mrna! Spliced together after introns cut out! 61 Post-transcriptional Modifications - 2! 5ʹ cap = modified G (guanine) nucleotides! Protects mrna from digestion (for a while)! Says attach here to ribosome! Poly-A tail = adenines! Protects mrna from digestion! May help guide mrna out of nucleus! 62 31!
32 The Triplet Code! Transcription by RNA Polymerase! Amino acid 1 Amino acid 2 Amino acid 3 Amino acid 4 Amino acid 5 63 Translation! The mrna codon (nucleotide sequence) is translated into a polypeptide (amino acid sequence)! Takes place in cytoplasm! Involves:! mrna (codon)! Ribosome (assembly site)! trnas (anticodons)! Amino acids! 64 32!
33 Transfer RNAs (trnas)! Composed of nucleotides (like all RNAs)! Carry amino acids to ribosome! Which amino acid is carried is determined by a trna s anticodon! Anticodon is complementary to specific mrna codon(s)! 65 In-class Protein Synthesis! The bringing together of all of these parts is a synthesis of its own.! Starting with a gene (DNA), we will go through the steps of protein protein synthesis on the board in lecture room.! You may also want to look at the diagrams in the text, pp ! Protein synthesis links from Links Page:! Protein synthesis animation on YouTube! Transcription and translation video! 66 33!
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
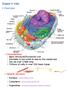 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Modern Cell Theory. Plasma Membrane. Generalized Cell Structures. Cellular Form and Function. Three principle parts of a cell
 Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
Cellular Form and Function Concepts of cellular structure Cell surface Membrane transport Cytoplasm Modern Cell Theory All living organisms are composed of cells. the simplest structural and functional
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of
Cytology. Cell Anatomy. Cell Theory - A good place to start! The generalized cell contains: Cell membrane Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytosol Organelles
 Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
Cytology The key to every biological problem must finally be sought in the cell, for every living organism is, or at some time has been, a cell. E.B. Wilson, 1925 Cell Theory - A good place to start! Cell
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
basic unit structure and function
 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
Chapter 3 Cells Introduction The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells vary in their shape, size, and arrangements, but all cells have similar components with a particular
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
CELLS.
 CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
CELLS http://www.aimediaserver.com/studiodaily/harvard/harvard.swf INTERESTING FACTS The longest cells in the human body are the motor neurons. They can be up to 1.37 meters long and go from the spinal
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Don t Freak Out. Test on cell organelle on Friday!
 Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Cell Structure 1 Don t Freak Out Test on cell organelle on Friday! This test should be a buffer test and help raise your overall test score. All information will come from this week! 2 Cells Provide Compartments
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 7
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS
 CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
CH 03 CELLS: THE LIVING UNITS This chapter provides a review of critical information regarding cells the basic units of structure and function of all living things. CELL THEORY The cell theory resulted
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life
 Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY
 BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
BIOLOGY 12 - CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION: Chapter Notes THE CELL THEORY 1. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of life 3. All cells come from the division
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
10/5/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
The Cell Biology 102 Fundamental unit of life Smallest unit that displays all the basic elements of life Lecture 5: Cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells Cell Theory 2. The
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE
 LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
LECTURE 3 CELL STRUCTURE HISTORY The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 examining very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that remarked looked like the walled compartments
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Chapter 2: The Cell. Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College
 Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
11/1/2014. accumulate in brain.
 EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
EU 4.A: Interactions within biological systems lead to complex properties. EU 4.B: Competition and cooperation are important aspects of biological systems. EU 4.C: Naturally occurring diversity among and
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Fungal cell walls are rigid with less flexibility due to a combination of more sugar (more chitin) and protein flexibility.
 Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Homeostatic Control Systems
 Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS. Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles
 Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
Organelles in EUKARYOTIC CELLS Pages 4 5: cell membrane, cytoplasm/cytosol, cytoskeleton, nucleus, chromatin/chromosomes, and centrioles Use the info on the following slides to complete pages 4 5 in your
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
