Commonly recognized causes of sciatica include disk herniation
|
|
|
- Coleen Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published December 22, 2011 as /ajnr.A2813 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.M. Byun S.H. Ahn M.-W. Ahn Value of 3D MR Lumbosacral Radiculography in the Diagnosis of Symptomatic Chemical Radiculitis BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Radiologic methods for the diagnosis of chemical radiculitis associated with anular tears in the lumbar spine have been rare. Provocative diskography is one of the methods for diagnosing diskogenic chemical radiculitis but is invasive. A reliable imaging method for replacing provocative diskography and diagnosing chemical radiculitis is required. Our aim was to investigate the value of 3D MR radiculography depicted by rendering imaging in the diagnosis of symptomatic chemical radiculopathy associated with anular tears. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study population consisted of 17 patients (age range, years) with unilateral radiculopathy. Symptomatic chemical radiculopathy was confirmed with provocative CT diskography and/or provocative selective nerve root block for agreement of sides and levels. Through adhering to the principles of selective excitation (Proset imaging), we acquired 3D coronal FFE sequences with selective water excitation. Morphologic changes in the ipsilateral symptomatic nerve root caused by chemical radiculopathy were compared with those in the contralateral nerve root on 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography. RESULTS: Pain reproduction at the contrast-leak level during diskography (n 4) and selective nerve root injection (n 13) showed concordant pain in all patients. All patients with symptomatic chemical radiculopathy showed nerve root swelling in both ipsilateral levels and sides on 3D MR radiculography. The most common nerve root affected by the chemical radiculopathy was the L5 nerve root (n 13), while the most common segment exhibiting nerve root swelling was the exit nerve root (n 16). CONCLUSIONS: All patients with radicular leg pain caused by chemical radiculopathy showed nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography. We believe that in cases without mechanical nerve root compression caused by disk herniation or stenosis in the lumbar spine, nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography in patients with radiculopathy associated with an anular tear may be relevant in the diagnosis of symptomatic chemical radiculopathy. Received April 28, 2011; accepted after revision June 25. From the Departments of Diagnostic Radiology (W.M.B), Rehabilitation Medicine (S.H.A), and Orthopedic Surgery (M.-W.A), College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Namku, Daegu, Republic of Korea. This work was supported by the Yeungnam University research grants in Please address correspondence to Woo Mok Byun, MD, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, 317 1, Daemyungdong, Namku, Daegu , Republic of Korea; wmbyun@med.yu.ac.kr ABBREVIATIONS: DRG dorsal root ganglia; FFE fast-field echo; HIZ high-intensity zone; MPR multiplanar reformations; PLA2 phospholipase A2; SIR signal-intensity ratio of the nerve root to the paraspinal muscle Commonly recognized causes of sciatica include disk herniation and spinal stenosis; however, some patients presenting with radiculopathy can show no evidence of nerve root compression on MR imaging. Patients with anular tears may experience low back pain or radiation of pain into the lower extremity. Recently, it has been observed that introduction of the nucleus pulposus into the epidural space, in the absence of mechanical compression, induces pronounced morphologic and functional changes in the nerve roots. Chemical radiculitis is an inflammatory condition of the nerve root, which may result from the rupture of the anulus fibrosus and dissemination of disk fluid along the nerve root sheath. 1 The concept of radiculitis was first described by Lewin in 1943, when he discussed the condition of irritation of the lumbar and sacral nerve roots. 2 Muramoto et al 3 demonstrated that prostaglandin E2, a chemical mediator of inflammation, could provoke an ectopic eruption of impulses from the nerve roots in an in vitro canine model, indicating that it might play a role in irritation of the nerve roots. Also Peng et al 4 reported that leakage of chemical mediators or inflammatory cytokines, which are produced in the painful disk, into the epidural space through anular tears could lead to injury to adjacent nerve roots and that the leakage might constitute the primary pathophysiologic mechanism of radiating leg pain without disk herniation. Radiologic methods for the diagnosis of chemical radiculitis associated with anular tears in the lumbar spine have been rare. Diskography for the diagnosis of chemical radiculitis is controversial and poorly defined. Nevertheless, provocative diskography is one of the methods for diagnosing diskogenic chemical radiculitis. 5 Slipman et al 6 reported that inclusion criteria for the diagnosis of chemical radiculitis consisted of symptoms of extremity pain, MR imaging void of local nerve root pathology, an electromyographic study positive for an acute radiculopathy, and a positive fluoroscopically guided diagnostic selective nerve root block. Byun et al 7 showed that the perianular enhancement caused by chemical radiculitis on contrast lumbar MR imaging could cause radiculopathy. They suggested that perianular enhancement could be detected, in some cases, without any SPINE ORIGINAL RESEARCH Copyright 2011 by American Society of Neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
2 chemical radiculitis. However, morphologic evaluation of the nerve root caused by chemical radiculitis was not described. The aim of this study was to investigate the value of 3D MR radiculography depicted by rendering imaging in the diagnosis of symptomatic chemical radiculopathy associated with anular tears. Materials and Methods The study population consisted of 17 patients (age range, years; mean age, 56.6 years; 10 men, 7 women) with chemical radiculopathy. All patients with anular tears had unilateral pain localized to the leg or buttock. Patients with bilateral radiculopathy and disk herniation or spinal stenosis were excluded in our study. Also patients with tumor, synovial cyst, other intradural or extradural lesions, and peripheral neuropathy were excluded. Inclusion criteria in our study were the following: 1) unilateral radiculopathy without compressive lesions in the spinal canal and foraminal and extraforaminal zones of the lumbar spine on MR imaging, 2) an anular tear on MR images and/or CT diskography, 3) concordant pain during provocative CT diskography and/or provocative selective nerve root block for agreement of side and level, and 4) improvement of clinical symptoms after selective nerve root injection. Symptomatic nerve root was confirmed with provocative CT diskography (n 4) and/or provocative selective nerve root block (n 13) for agreement of side and level. Because diskography is more invasive compared with provocative selective nerve root block, selective nerve root block for confirmation and treatment in most of cases was performed. The presence of an anular tear was confirmed by CT diskography and/or MR imaging. A 3-month follow-up 3D MR radiculography after selective nerve root block was performed in 3 patients. A control group (10 subjects) for nerve root evaluation on 3D MR radiculography was included. Criteria for control group subjects were no radiculopathy, no disk herniation, and no spinal stenosis. MR imaging was performed by using a 1.5T scanner (Intera; Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) with a spine-array coil. With respect to spin-echo sequences, axial and sagittal T1- (TR/TE, 583/12 ms), turbo T2-weighted images (TR/TE, 3800/128 ms), and contrast-enhanced (gadopentetate dimeglumine, Magnevist; Schering, Berlin, Germany) axial T1-weighted images with fat suppression were obtained with the following parameters: 4-mm section thickness with a 0.4- to 0.7-mm overlapping section gap; FOV; 4 NEX; and a matrix. Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images were obtained in 14 patients with symptomatic chemical radiculopathy. The 3D coronal FFE sequence with selective water excitation adhering to the principles of the selective excitation technique (Proset imaging) was acquired under the following acquisition parameters: 1-mm section thickness without an overlapping section gap; 250-mm FOV; matrix; TR, 23.2 ms; TE, 13.8 ms; 8 flip angle; and 2 signal-intensity acquisitions. Forty coronal source FFE images for each subject were obtained. To obtain images of all lumbosacral nerve roots and DRG, we set the imaging plane to be parallel to the longitudinal axis of the lumbar spinal canal and centered on the level of the L3 vertebral body. One parallel regional saturation slab was added to suppress the signal intensity from the vessels. The resultant whole-imaging slab had an anteroposterior thickness of 4 cm, which fully covered the intervertebral foraminal region and extraforaminal zone from the anterior third of the vertebral body to the anterior margin of the spinous process. For image processing of direct volume rendering, an Aquarius 3D workstation equipped with commercially available automated analysis 3D rendering software (Tera- Recon, San Mateo, California) was used. Provocative diskography was performed in 4 patients. Diskography was performed in 1 or several intervertebral disk levels to confirm corresponding radiculopathy. Pain reproduction on injection of contrast medium during diskography was evaluated. CT was performed to identify the site of contrast leakage and the location of anular tears after diskography. Provocative selective nerve root block for confirmation of the radiculopathy was performed in 13 patients. All 14 patients demonstrated perianular enhancement caused by anular tears on contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted images with fat suppression. The spindle-shaped nerve root in the extraforaminal or foraminal zones was defined as DRG on Proset source images or 3D MR radiculography. In general, the nerve root that exited the spine at a particular level was referred to as the exiting nerve root. Another nerve root segment went across the disk and exited the spine at the next level below. It was called the traversing nerve root. On 3D MR radiculography, the nerve root in the extraforaminal zone beyond DRG was defined as the exit nerve. The proximal nerve segment between the thecal sac and DRG was defined as the transverse nerve root. Swelling of the DRG and nerve roots was defined as positive when either size was bigger than the normal contralateral side. Morphologic changes in the ipsilateral symptomatic nerve root caused by chemical radiculopathy were compared with those in the contralateral nerve root on 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography. The relationship between morphologic change in the symptomatic nerve root on 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography and provocative diskography or selective nerve root block for confirmation of the radiculopathy was analyzed. We evaluated the relationship between morphologic changes in the symptomatic nerve root on 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography and perianular enhancement on contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted images with fat suppression. Axial Proset MPR images were selected for quantitative analysis of signal intensity and width in the lumbar nerve roots. The width and signal intensity of the symptomatic nerve root were compared with those in the contralateral asymptomatic nerve root on axial Proset MPR images. The width of the transverse nerve root was measured at the midpoint perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. The width of the exit nerve root was measured at just 1 cm caudal to the distal end of the DRG. The width of the DRG was measured vertically at the midpoint perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the DRG. Three small regions of interest in each segment of ipsilateral and contralateral lumbar nerve roots were generated by an experienced radiologist by using the MR imaging console software. Placement of a region of interest generated a mean value for signal intensity of the pixels enclosed by the region of interest. The SIR of the nerve root to the paraspinal muscle was evaluated. 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography was interpreted by an experienced radiologist and spine physician. Interobserver and intraobserver variability of the nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography was assessed by using statistics. A value of 0.40 indicated poor agreement; , moderate agreement; , substantial agreement; and 0.81, almost perfect agreement. A paired t test was used to compare differences of width and signal intensity between symptomatic nerve roots and asymptomatic contralateral nerve roots. Statistical calculations were done with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, Version 19.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois). A P value.005 was statistically significant. All patients with symptomatic chemical radiculitis were treated with a selective nerve root block. Clinical symptom evaluation with 2 Byun AJNR
3 Table 1: Clinical symptoms and MR imaging findings of the patients with chemical radiculitis No Age (yr)/sex Symptoms NR Lesion Segment of Swelling Location of Perianular Enhancement ODI, Before VAS, After Provocation 1 51/M Lt buttock, calf pain Lt L5 DRG, exit For and extra SNI 2 53/M Lt leg pain Lt L5 Entire For and extra SNI 3 62/M Lt leg pain Lt L5 Entire , 3 SNI 4 49/F Rt buttock, lat thigh pain Rt L5 DRG, exit For and extra SNI 5 69/M Lt leg pain, numbness Lt L5 Entire For and extra Diskography 6 53/M Lt leg pain Lt L5 Exit For and extra SNI 7 62/M Rt leg pain Rt L5 Exit Extra SNI 8 35/M Rt leg pain, toe weakness Rt L5 Exit For and extra SNI 9 76/F Lt buttock, leg pain Lt L5 Entire For and extra Diskography 10 32/M Rt leg pain Rt L5 Exit Extra SNI 11 51/F Lt buttock, leg pain Lt L5 Exit SNI 12 56/F Lt buttock, leg pain Lt L5 Exit Extra SNI 13 69/F Rt buttock, leg pain Rt L5 Entire For and extra 54.6 No SNI 14 44/M Lt leg pain Lt L4 DRG, exit For and extra No 80% SNI 15 88/M Rt leg pain Rt L4 Entire For and extra SNI 16 54/F Rt anterior, lat leg pain Rt L4 Trans No 90% Diskography 17 59/F Lt leg pain Lt L2 Entire For and extra Diskography Note: NR indicates nerve root; ODI, Oswestry Disability Index; VAS, visual analogue sale; Rt, right; Lt, left; exit, exit nerve root; Trans, transverse nerve root; Entire, entire segments of nerve root; For, foraminal zone; extra, extraforaminal zone; lat, lateral; SNI, selective nerve root injection; No, no response of symptoms; Before, before treatment; After, after treatment; %, degree of symptom improvement;, no contrast study. Fig 1. A 69-year-old man with left leg pain. A, There is intermediate signal intensity (arrow) between the outer anulus and left L5 nerve root on the T2-weighted image. B, Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image with fat suppression shows abnormal enhancement at the left perianular extraforaminal zone (large arrow) and outer anulus (small arrow) in L5-S1. Pain reproduction at this level during diskography shows concordant pain. C, CT diskography shows an anular tear and left posterolateral extraforaminal leak (arrow) of the contrast media from an anular tear. There is contrast media (black arrow) at the extradural spinal canal. D, Diffuse swelling of the entire left L5 nerve root (thick arrow) including DRG (thin arrow) is demonstrated on 3D MR radiculography. E, Axial Proset MPR image demonstrates that the left L5 exit nerve root (long arrow) along the ventral surface of the sacral ala is larger and higher in signal intensity compared with the right L5 exit nerve root (thick arrow). the Oswestry Disability Index and the visual analog scale was performed after and before treatment. Our study was approved by the institutional review board of our hospital. Results The L5-S1 disk was involved in 13 patients with chemical radiculopathy, while the L4 5 disk was involved in 3. One case of chemical radiculopathy was detected at the L2 3 level. Pain reproduction at the contrast leak level during diskography showed concordant pain in all 4 cases. Pain reproduction during provocative selective nerve root injection showed concordant pain in all 13 patients. The clinical symptoms and MR imaging findings are summarized in Table 1. All patients with symptomatic chemical radiculopathy showed nerve root swelling in the ipsilateral level and side on 3D MR radiculography. Swelling of only the exit nerve root was observed in 6 patients, AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
4 Fig 2. A 51-year-old man with left buttock and calf pain. A and B, T1- (A) and T2-weighted (B) images show an anular tear (arrow) at the left lateral margin of the L5-S1 disk. There is intermediate signal intensity due to the fibrovascular and granulation tissue between the outer anulus and left L5 nerve root (short arrow). There is no apparent disk herniation. C, There is abnormal enhancement at the perianular extraforaminal zone (arrow) in L5-S1 on the contrast-enhanced T1-weighted image with fat suppression. D, Diffuse swelling of the left L5 dorsal root ganglion (arrow) and exit nerve root (thick arrow) is demonstrated on 3D MR radiculography. E, Axial Proset MPR image shows the left L5 exit nerve root (long arrow) along the ventral surface of the sacral ala to be larger and higher in signal intensity compared with the contralateral nerve root (short arrow). Star indicates the right S1 nerve root. F, Pain reproduction at this level (arrow) during a selective nerve root block (prone position) shows concordant pain. At 1 month after selective nerve root block at the left L5 nerve root, clinical symptoms are completely improved. G, However, a 3-month follow-up 3D MR radiculography reveals decreased swelling at the left L5 nerve root. while swelling of the entire segment of the nerve root was seen in 7 (Fig 1D). Swelling of the DRG and exit nerve root was found in 3 patients (Fig 2 D), and 1 patient had swelling of the transverse nerve root. Our study found that there was an apparent correlation between nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography and clinical symptoms, including provocative selective nerve root block and diskography. In 14 patients, perianular enhancement caused by chemical radiculitis demonstrated a thick and linear enhancement along margins of the anular tear on contrast-enhanced axial T1-weighted images with fat suppression (Figs 1B and 2C). Perianular enhancement on MR imaging study corresponded to nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography for level and side. Comparison between quantitative measurements of the symptomatic nerve roots and those of the contralateral asymptomatic nerve roots on axial Proset MPR images are summarized in Table 2. In all cases with chemical radiculitis, the width of DRG and the nerve roots was larger than those of the contralateral asymptomatic nerve roots on axial Proset MPR images (paired t test, P.005). The nerve/muscle SIR of the symptomatic nerve root was higher than that of the asymptomatic contralateral nerve root in segments of the DRG and exit nerve (Figs 1E and 2E) (paired t test, P.005). However, there was no statistical difference of SIR in the transverse segment. Although clinical symptoms were completely improved within 1 month, nerve root swelling caused by chemical radiculitis was improved to a decreased thickness at 3-month follow-up 3D MR radiculography in 3 patients (Fig 2F). In all control groups, a morphologic difference (thickness) of both sides of the DRG and nerve roots at the same levels was not detected. Agreement with respect to the recognition of the nerve root swelling was excellent ( values for intraobserver and interobserver 1.00 and 0.87). 4 Byun AJNR
5 Table 2: Comparison between quantitative measurements of the symptomatic nerve roots and those of the contralateral asymptomatic nerve roots on Proset images Mean Value of Nerve Root Diameter (mm) Mean Value of SIR a Side Transverse DRG Exit Transverse DRG Exit Ipsilateral Contralateral Note: Transverse indicates transverse nerve root; Exit, exit nerve root. a Width of the nerve roots with chemical radiculitis is larger than that of the contralateral asymptomatic nerve roots (paired t test, P.005). SIR of the DRG and exit nerve roots with chemical radiculitis is higher than that of the contralateral asymptomatic nerve roots (paired t test, P.005). Discussion Chemical radiculitis is an inflammatory condition of the nerve root, which may result from the rupture of the anulus fibrosus and dissemination of the disk fluid along the nerve root sheath. The nucleus pulposus has been demonstrated to induce axonal degeneration, myelin edema, and intravascular coagulation; increase endoneural fluid pressure; reduce intraneural blood flow; and reduce nerve root conduction velocity. 8,9 Several studies have been performed to understand the role of inflammation in radicular pain. Leukocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes have been found at the site of surgically created porcine disk protrusion in vivo. 10 Saal et al 11 found elevated levels of PLA2, the rate-limiting enzyme in the chemical cascade that liberates arachidonic acid, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes, in the disk material obtained from patients surgically treated for radiculopathy due to disk herniation. Further, Chen et al 12 demonstrated that PLA2 promoted loss of myelin, breakdown of myelin sheaths, and vacuolar degeneration, ultimately creating hypersensitive regions allowing ectopic discharges. Peng et al 13 investigated the histologic features of 19 specimens of lumbar intervertebral disks from 17 patients with diskogenic low-back pain during posterior lumbar interbody fusion. They suggested that the zone of granulation tissue with extensive innervations along the anular tears in the posterior part of the painful disk might be responsible for causing the pain of diskography and of diskogenic lowback pain. Also they reported that the adjacent tissues surrounding the anular tears were replaced by disorganized and vascularized granulation and scar tissue. One of our previous studies revealed that the perianular enhancement adjacent to anular tears on MR imaging may be relevant in the diagnosis of symptomatic chemical radiculitis. 7 In the current study, perianular enhancement on MR imaging corresponded with nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography for level and side. However, we suggest that perianular enhancement may be detected in asymptomatic patients without chemical radiculitis. On 3D MR radiculography, all patients with radiculopathy caused by chemical radiculopathy showed ipsilateral nerve root swelling. We suggest that nerve root swelling due to chemical radiculopathy may be caused by inflammation and granulation of adjacent tissues surrounding anular tears. We propose 3D MR radiculography as a helpful method for diagnosing chemical radiculopathy. Peng et al 4 reported that the L5 and S1 nerve roots were the most common nerve root lesions caused by chemical radiculitis. In our results, the most common nerve root lesion was at the L5 nerve root. Furthermore, the most common segment for nerve root swelling was the exit nerve root (n 16). We suggest a relationship between inflammatory perianular enhancement at the extraforaminal or foraminal zones and swelling of the exit nerve root. Anular tears manifest on MR imaging as HIZs. The presence of HIZs within the posterior anulus seen on T2-weighted MR imaging has aroused great interest and even controversy among many investigators, with respect to whether these HIZs are closely associated with a concordant pain response on awake diskography. 13,14 Although detection of symptomatic anular tears on MR imaging in patients with radiculopathy has been very important, nonspecific HIZs on T2-weighted images seem to be an unreliable marker of painful anular tears. Therefore, provocative diskography has become the criterion standard in the definitive diagnosis of diskogenic pain associated with anular tears; however, it is invasive. Slipman et al 6 mentioned that a biochemical etiology in chemical radiculitis associated anular tear is likely to play a significant role in radiculopathy and radicular pain. Patients with motor abnormalities, normal findings on MR imaging, positive findings on electromyography, and a positive diagnostic selective nerve root block were included. The study provided confirmatory clinical evidence and supported the existence of a nonstructural, biochemical mechanism by which radiculopathy can occur. In general, provocative diskography or diagnostic selective nerve root block or both are confirmatory for a chemical radiculopathy associated anular tear. To our knowledge, there are no noninvasive imaging techniques for diagnosing chemical radiculitis. There are several articles regarding the changes in spinal nerve roots by using 3D MR imaging. Kim et al 15 reported that DRG swelling and running course abnormality of the L5 exiting root on coronal source images of MR myelography were useful findings in diagnosing L5 root compression at the L5-S1 foramen or extraforamen. Furthermore, Kikkawa et al 16 studied gadolinium-enhanced 3D MR imaging fast low-angle shot in the evaluation of symptomatic lumbosacral nerve roots. They reported enhancement of the symptomatic nerve roots in patients with radiculopathy. However, morphologic changes in the nerve root in chemical radiculitis associated with anular tears by using 3D MR imaging had not yet been studied. Zhang et al 17 investigated the effectiveness of 3D highspatial-resolution diffusion-weighted MR neurography based on steady-state free precession in the diagnosis of sciatica. They mentioned that the presence of nerve root compression or increased T2 signal-intensity changes can be observed in all patients with sciatica. In patients with cervical radiculopathy, the signal intensity of the cervical spinal nerves on high-resolution MR neurogra- AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :
6 phy was evaluated by Erdem et al. 18 They reported that a markedly increased signal intensity in the distal portion of the affected spinal nerves was found. Nerve/muscle SIR measurements of the affected spinal nerves showed a significantly increased intensity compared with the noninvolved spinal nerves. In our study, nerve/muscle signal-intensity ratio on Proset MPR images showed significantly increased values compared with the contralateral nerve roots. We suggest that enlargement and increased signal intensity of the nerve root associated with chemical radiculitis indicate edema of the nerve root caused by inflammation and irritation associated with an anular tear. The Proset is a selective-excitation technique used to suppress either water or fat by exploiting the difference between water and fat resonance frequencies. With Proset, the signal intensity of fat has been completely suppressed and the details of the nerve root and DRG were delineated. 19 In our study, the nerve root and DRG are well-depicted on 3D MR rendering images by using source images based on Proset. Contrary to patients with chemical radiculopathy, the control group showed no definite swelling or abnormal thickness of nerve roots on 3D MR rendering imaging based on Proset. In cases with unilateral radiculopathy, spine MR imaging without compressive or stenotic lesions, and positive provocative diskography and/or diagnostic selective nerve block, abnormal nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography may suggest chemical radiculopathy. Conclusions All patients with radiculopathy caused by chemical radiculitis showed nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography. We believe that in cases without mechanical nerve root compression caused by disk herniation or stenosis in the lumbar spine, nerve root swelling on 3D MR radiculography in patients with radiculopathy may be relevant in the diagnosis of symptomatic chemical radiculitis. References 1. Marshall LL, Trethewie ER, Curtain CC. Chemical radiculitis: a clinical, physiological and immunological study. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1977: Lewin P. Backache and Sciatic Neuritis. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; Muramoto T, Atsuta Y, Iwahara T, et al. The action of prostaglandin E2 and triamcinolone acetonide on the firing activity of lumbar nerve roots. Int Orthop 1997;21: Peng B, Wu W, Li Z, et al. Chemical radiculitis. Pain 2007;127: Kloth D. Chemical radiculopathy. Pain physician 2003;6:139, author reply Slipman CW, Isaac Z, Lenrow DA, et al. Clinical evidence of chemical radiculopathy. Pain Physician 2002;5: Byun WM, Ahn SH, Ahn MW. Significance of perianular enhancement associated with anular tears on magnetic resonance imagings in diagnosis of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33: Olmarker K, Rydevik B, Nordborg C. Autologous nucleus pulposus induces neurophysiologic and histologic changes in porcine cauda equina nerve roots. Spine 1993;18: Otani K, Arai I, Mao GP, et al. Nucleus pulposus-induced nerve root injury: relationship between blood flow and motor nerve conduction velocity. Neurosurgery 1999;45:614 19, discussion Habtemariam A, Virri J, Gronblad M, et al. Inflammatory cells in full-thickness anulus injury in pigs: an experimental disc herniation animal model. Spine 1998;23: Saal JS, Franson RC, Dobrow R, et al. High levels of inflammatory phospholipase A2 activity in lumbar disc herniations. Spine 1990;15: Chen C, Cavanaugh JM, Ozaktay AC, et al. Effects of phospholipase A2 on lumbar nerve root structure and function. Spine 1997;22: Peng B, Hou S, Wu W, et al. The pathogenesis and clinical significance of a high-intensity zone (HIZ) of lumbar intervertebral disc on MR imaging in the patient with discogenic low back pain. Eur Spine J 2006;15: Lim CH, Jee WH, Son BC, et al. Discogenic lumbar pain: association with MR imaging and CT discography. Eur J Radiol 2005;54: Kim SB, Jang JS, Lee SH. Morphologic changes of L5 root at coronal source images of MR myelography in cases of foraminal or extraforaminal compression. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2009;46: Kikkawa I, Sugimoto H, Saita K, et al. The role of Gd-enhanced three-dimensional MRI fast low-angle shot (FLASH) in the evaluation of symptomatic lumbosacral nerve roots. J Orthop Sci 2001;6: Zhang Z, Song L, Meng Q, et al. Morphological analysis in patients with sciatica: a magnetic resonance imaging study using three-dimensional highresolution diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance neurography techniques. Spine 2009;34:E Erdem CZ, Erdem LO, Cagavi F, et al. High resolution MR neurography in patients with cervical radiculopathy [in Turkish]. Tani Girisim Radyol 2004;10: Shen J, Wang HY, Chen JY, et al. Morphologic analysis of normal human lumbar dorsal root ganglion by 3D MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006; 27: Byun AJNR
Original Article. Woo Mok Byun, MD, PhD, Jae Woon Kim, MD, Jae Kyo Lee, MD INTRODUCTION
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.403 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(4):403-411 Differentiation between Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Extraforaminal Stenosis
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.403 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(4):403-411 Differentiation between Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Extraforaminal Stenosis
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
A Comparative Evaluation of H-Reflex and MRI for Diagnosis of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
 Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 503-508 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.11.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Comparative Evaluation of H-Reflex and MRI for Diagnosis of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Sandip
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 3 (2015) 503-508 doi: 10.17265/2328-2150/2015.11.001 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Comparative Evaluation of H-Reflex and MRI for Diagnosis of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy Sandip
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica
 87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Low back pain, radiculopathy left leg icd 10 code
 Home Search Low back pain, radiculopathy left leg icd 10 code 2018 ICD - 10 code for Radiculopathy is M54.1. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for M54.1.. Low back pain ; M54.6 - Pain in thoracic
Home Search Low back pain, radiculopathy left leg icd 10 code 2018 ICD - 10 code for Radiculopathy is M54.1. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for M54.1.. Low back pain ; M54.6 - Pain in thoracic
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions
 Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Lumbar radicular pain, a common entity in clinical practice,
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH C. Cyteval N. Fescquet E. Thomas E. Decoux F. Blotman P. Taourel Predictive Factors of Efficacy of Periradicular Corticosteroid Injections for Lumbar Radiculopathy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH C. Cyteval N. Fescquet E. Thomas E. Decoux F. Blotman P. Taourel Predictive Factors of Efficacy of Periradicular Corticosteroid Injections for Lumbar Radiculopathy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002
 Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache
 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Spontaneous regression of extruded lumbar disc herniation: case report and its pathogenesis
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Spontaneous regression of extruded lumbar disc herniation: case report and its pathogenesis Prajapati Hanuman Prasad, Singh Deepak
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Spontaneous regression of extruded lumbar disc herniation: case report and its pathogenesis Prajapati Hanuman Prasad, Singh Deepak
RADICULOPATHY AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO RADICULOPATHY This booklet provides general information on radiculopathy. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO RADICULOPATHY This booklet provides general information on radiculopathy. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
Clinical Evaluation of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Gadolinium Enhancing Spinal Nerves Associated with Disc Herniation
 Pain Physician 2015; 18:E177-E185 ISSN 2150-1149 Observational Study Clinical Evaluation of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Gadolinium Enhancing Spinal Nerves Associated with
Pain Physician 2015; 18:E177-E185 ISSN 2150-1149 Observational Study Clinical Evaluation of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Gadolinium Enhancing Spinal Nerves Associated with
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS
 Indian J.Sci.Res. 4(2) : 205-209, 2013 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS a1 b c
Indian J.Sci.Res. 4(2) : 205-209, 2013 ISSN : 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN : 2250-0138 (Online) EFFECTIVENESS OF ROOT BLOCK AND RADIOFREQUENCY IN PROLAPSE INTERVERTEBRAL DISC AND LUMBAR CANAL STENOSIS a1 b c
The Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Grading Cervical Neural Foraminal Stenosis Based on Oblique Sagittal Images
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
In patients with degenerative lumbar disease, lumbar foraminal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Eguchi S. Ohtori S. Orita H. Kamoda G. Arai T. Ishikawa M. Miyagi G. Inoue M. Suzuki Y. Masuda H. Andou M. Takaso Y. Aoki T. Toyone A. Watanabe K. Takahashi Quantitative Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Eguchi S. Ohtori S. Orita H. Kamoda G. Arai T. Ishikawa M. Miyagi G. Inoue M. Suzuki Y. Masuda H. Andou M. Takaso Y. Aoki T. Toyone A. Watanabe K. Takahashi Quantitative Evaluation
Icd 9 lumbar radiculopathy
 Icd 9 lumbar radiculopathy Search Short description: Lumbar disc displacement. ICD - 9 -CM 722.10 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however.
Icd 9 lumbar radiculopathy Search Short description: Lumbar disc displacement. ICD - 9 -CM 722.10 is a billable medical code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis on a reimbursement claim, however.
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
Lumbar Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis: Prevalence and Patterns Abstract: Keywords: Introduction II. Materials And Methods
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VII (October. 2016), PP 27-32 www.iosrjournals.org Lumbar Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis:
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. VII (October. 2016), PP 27-32 www.iosrjournals.org Lumbar Spinal Epidural Lipomatosis:
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04
 Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at (sent 5/9/17) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy
 IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE
 The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery URMC Neurosurgery APP s Objectives Identify the most common pathology that leads to spine
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery URMC Neurosurgery APP s Objectives Identify the most common pathology that leads to spine
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal Cord without Evidence of Spinal Cord Herniation or an Intradural Mass
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
MEDICAL HISTORY CHIRO PHYSICAL
 Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
The Inflammatory Properties of the Intervertebral Disc
 The Inflammatory Properties of the Intervertebral Disc As we travel through the US and teach, it amazes us as a faculty, how few therapists are aware of the inflammatory issues of the intervertebral disc,
The Inflammatory Properties of the Intervertebral Disc As we travel through the US and teach, it amazes us as a faculty, how few therapists are aware of the inflammatory issues of the intervertebral disc,
Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain
 Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine
 703 High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine Peter J. Yang 1 Joachim F. Seeger1 Robert. Dzioba 2 Raymond F. Carmody 1 Todd. urt 1 Norman N. Komar 1 Janice R. Smith 1 Evaluation
703 High-Dose IV Contrast in CT Scanning of the Postoperative Lumbar Spine Peter J. Yang 1 Joachim F. Seeger1 Robert. Dzioba 2 Raymond F. Carmody 1 Todd. urt 1 Norman N. Komar 1 Janice R. Smith 1 Evaluation
Multidetector CT has enlarged our view of human vascular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.H. Heo Y.J. Cho S.H. Sheen M.S. Hong S.M. Cho S.H. Park 3D Reconstructions of Spinal Using CT Angiography: Applications in Minimally Invasive Spinal Procedures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.H. Heo Y.J. Cho S.H. Sheen M.S. Hong S.M. Cho S.H. Park 3D Reconstructions of Spinal Using CT Angiography: Applications in Minimally Invasive Spinal Procedures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Cervical radiculopathy: diagnostic aspects and non-surgical treatment Kuijper, B.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cervical radiculopathy: diagnostic aspects and non-surgical treatment Kuijper, B. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kuijper, B. (2011). Cervical
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cervical radiculopathy: diagnostic aspects and non-surgical treatment Kuijper, B. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kuijper, B. (2011). Cervical
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE
 The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery Diagnosis/Imaging/Surgery of Lumbar Spine Disorders Objectives Identify the most common
The ABC s of LUMBAR SPINE DISEASE Susan O. Smith ANP-BC University of Rochester Department of Neurological Surgery Diagnosis/Imaging/Surgery of Lumbar Spine Disorders Objectives Identify the most common
Innovative Techniques in Minimally Invasive Cervical Spine Surgery. Bruce McCormack, MD San Francisco California
 Innovative Techniques in Minimally Invasive Cervical Spine Surgery Bruce McCormack, MD San Francisco California PCF Posterior Cervical Fusion PCF not currently an ambulatory care procedure Pearl diver
Innovative Techniques in Minimally Invasive Cervical Spine Surgery Bruce McCormack, MD San Francisco California PCF Posterior Cervical Fusion PCF not currently an ambulatory care procedure Pearl diver
3D imaging reformation was obtained. The 3D color imaging reformation was reviewed in a different high resolution setting.
 POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 220-224, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.1010.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms Pius
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 220-224, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.1010.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms Pius
Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
 THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
Department of Radiology, Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine, Minami-kogushi, Ube, Yamaguchi , Japan 2
 11 Bull Yamaguchi Med Sch 62(1-2):11-19, 2015 Added Value of MR Myelography Using a Fat- Suppressed-Three Dimensional Coherent Oscillatory State Acquisition for the Manipulation of the Image Contrast Sequence
11 Bull Yamaguchi Med Sch 62(1-2):11-19, 2015 Added Value of MR Myelography Using a Fat- Suppressed-Three Dimensional Coherent Oscillatory State Acquisition for the Manipulation of the Image Contrast Sequence
REFERENCE DOCTOR Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean
Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean
Cox Technic Case Report #126 published at (sent December 2013 ) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #126 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent December 2013 ) 1 Cox Technic Decompression Spinal Manipulation Resolves Symptoms Associated with Disc Protrusion and S1 Radiculopathy,
Cox Technic Case Report #126 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent December 2013 ) 1 Cox Technic Decompression Spinal Manipulation Resolves Symptoms Associated with Disc Protrusion and S1 Radiculopathy,
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Consideration of proper operative route for interlaminar approach for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy
 Original Study Consideration of proper operative route for interlaminar approach for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy Juichi Tonosu 1,2,3,4, Yasushi Oshima 1,2,3, Ryutaro Shiboi 1,2, Akihiko Hayashi
Original Study Consideration of proper operative route for interlaminar approach for percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy Juichi Tonosu 1,2,3,4, Yasushi Oshima 1,2,3, Ryutaro Shiboi 1,2, Akihiko Hayashi
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Case Report Minimally Invasive Microendoscopic Resection of the Transverse Process for Treatment of Low Back Pain with Bertolotti s Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2014, Article ID 613971, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/613971 Case Report Minimally Invasive Microendoscopic Resection of the
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2014, Article ID 613971, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/613971 Case Report Minimally Invasive Microendoscopic Resection of the
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay
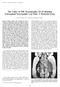 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:786 794, April 2001 The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay Kevin R. Moore, Jay S. Tsuruda, and Andrew T. Dailey Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:786 794, April 2001 The Value of MR Neurography for Evaluating Extraspinal Neuropathic Leg Pain: A Pictorial Essay Kevin R. Moore, Jay S. Tsuruda, and Andrew T. Dailey Summary:
The Role of Interventional Procedures in Sports Medicine
 The Role of Interventional Procedures in Sports Medicine Zacharia Isaac M.D. Director, Interventional Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Spinal Injections Localize Diagnosis
The Role of Interventional Procedures in Sports Medicine Zacharia Isaac M.D. Director, Interventional Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Spinal Injections Localize Diagnosis
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
An ESI for managing LBP is one of the most commonly
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.W. Lee H.I. Shin S.Y. Park G.Y. Lee H.S. Kang Therapeutic Trial of Fluoroscopic Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection for Axial Low Back Pain: Effectiveness and Outcome Predictors
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.W. Lee H.I. Shin S.Y. Park G.Y. Lee H.S. Kang Therapeutic Trial of Fluoroscopic Interlaminar Epidural Steroid Injection for Axial Low Back Pain: Effectiveness and Outcome Predictors
Evaluation of Canal Diameter by MRI in Sudanese Population
 American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS TASKFORCE
 NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS North American Spine Society 7075 Veterans Blvd. Burr Ridge, IL 60527 TASKFORCE Introduction North American
NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS North American Spine Society 7075 Veterans Blvd. Burr Ridge, IL 60527 TASKFORCE Introduction North American
Role of root block in lumbar spine radiculopathy
 2018; 2(2): 13-17 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(2): 13-17 Received: 05-02-2018 Accepted: 03-03-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry BJ medical College,
2018; 2(2): 13-17 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(2): 13-17 Received: 05-02-2018 Accepted: 03-03-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry BJ medical College,
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State
 Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
Case Studies, Impairment of the Spine in Washington State NAOEM at Skamania, 2015 25 Sep, 2015 Tim Gilmore, MD Several Slides from this Presentation Borrowed with permission from the Washington State Department
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Cox Distraction for Lumbar Discogenic Pain with Motor Weakness Increased by Lumbar Extension
 Cox Technic Case Report #129 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 3/11/14 ) 1 Cox Distraction for Lumbar Discogenic Pain with Motor Weakness Increased by Lumbar Extension submitted on December 5, 2013
Cox Technic Case Report #129 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 3/11/14 ) 1 Cox Distraction for Lumbar Discogenic Pain with Motor Weakness Increased by Lumbar Extension submitted on December 5, 2013
Spinal Pain Experienced as a Visceral Referral
 Spinal Pain Experienced as a Visceral Referral The lumbar spine is a frequent site of low back pain. Anatomy of the lumbar spine The lumbar spine is made up of 5 vertebrae, separated by intervertebral
Spinal Pain Experienced as a Visceral Referral The lumbar spine is a frequent site of low back pain. Anatomy of the lumbar spine The lumbar spine is made up of 5 vertebrae, separated by intervertebral
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
HERNIATED DISCS AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis
 Original Article New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/30862:2366 Radiology Section BINOJ VARGHESE v, ARUN C BABU ABSTRACT Introduction:
Original Article New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/30862:2366 Radiology Section BINOJ VARGHESE v, ARUN C BABU ABSTRACT Introduction:
Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up
 Chinese J. Pain 2009;19(1):08~16 Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up 1,4 3 2 2 1,4 Li Wei, Kung-Shing Lee, Man-Kit Siu, Yu-Ting Tai, Jia-Wei Lin, 1,4 1,4
Chinese J. Pain 2009;19(1):08~16 Outcomes of Epidural Neuroplasty to Treat Lumbar Discogenic Pain- One-Year Follow-Up 1,4 3 2 2 1,4 Li Wei, Kung-Shing Lee, Man-Kit Siu, Yu-Ting Tai, Jia-Wei Lin, 1,4 1,4
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Anatomy & Physiology II. Trunk
 Anatomy & Physiology II Trunk Bones and Landmarks of the Vertebral column 24 vertebrae Sacrum - consists of 5 vertebrae that fuse into one bone Median sacral crest Sacral hiatus 4 sacral foramina Coccyx
Anatomy & Physiology II Trunk Bones and Landmarks of the Vertebral column 24 vertebrae Sacrum - consists of 5 vertebrae that fuse into one bone Median sacral crest Sacral hiatus 4 sacral foramina Coccyx
Clinical Review Criteria Discography (Discogram) for Low Back Pain
 Clinical Review Criteria Discography (Discogram) for Low Back Pain Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington NOTICE: Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington and Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington
Clinical Review Criteria Discography (Discogram) for Low Back Pain Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington NOTICE: Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington and Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington
Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs
 Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs A CADAVER AND RADIOLOGICAL STUDY S. W. Suh, V. U. Shingade, S. H. Lee, J. H. Bae, C. E. Park, J. Y. Song From the University
Origin of lumbar spinal roots and their relationship to intervertebral discs A CADAVER AND RADIOLOGICAL STUDY S. W. Suh, V. U. Shingade, S. H. Lee, J. H. Bae, C. E. Park, J. Y. Song From the University
A Rare Case of Lumbar Traumatic Intradiscal Hematoma Followed by Repeatative Occupation Related Minor Trauma
 CASE REPORT J Trauma Inj 2018;31(1):38-42 http://doi.org/10.20408/jti.2018.31.1.38 JOURNAL OF TRAUMA AND INJURY A Rare Case of Lumbar Traumatic Intradiscal Hematoma Followed by Repeatative Occupation Related
CASE REPORT J Trauma Inj 2018;31(1):38-42 http://doi.org/10.20408/jti.2018.31.1.38 JOURNAL OF TRAUMA AND INJURY A Rare Case of Lumbar Traumatic Intradiscal Hematoma Followed by Repeatative Occupation Related
Nerve Ingrowth Into Diseased Intervertebral Disc in Chronic Back Pain. The Lancet July 19, 1997, Vol. 350, pp
 Nerve Ingrowth Into Diseased Intervertebral Disc in Chronic Back Pain 1 The Lancet July 19, 1997, Vol. 350, pp. 178-181 AJ Freemont, TE Peacock, P Goupille, JA Hoyland, J O Brien, MIV Jayson These authors
Nerve Ingrowth Into Diseased Intervertebral Disc in Chronic Back Pain 1 The Lancet July 19, 1997, Vol. 350, pp. 178-181 AJ Freemont, TE Peacock, P Goupille, JA Hoyland, J O Brien, MIV Jayson These authors
Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E445-E449 ISSN 2150-1149 Literature Review Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review Bin Zhu, MD,
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E445-E449 ISSN 2150-1149 Literature Review Transforaminal Endoscopic Decompression for a Giant Epidural Gas-Containing Pseudocyst: A Case Report and Literature Review Bin Zhu, MD,
Different operative findings of cases predicted to be symptomatic discal pseudocysts after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy
 Case Report Different operative findings of cases predicted to be symptomatic discal pseudocysts after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy Ryutaro Shiboi 1,2, Yasushi Oshima 1,2,3, Takeshi Kaneko
Case Report Different operative findings of cases predicted to be symptomatic discal pseudocysts after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy Ryutaro Shiboi 1,2, Yasushi Oshima 1,2,3, Takeshi Kaneko
Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 196~200, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.196 Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report Risa Utsunomiya,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 5, No. 3, pp 196~200, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2011.5.3.196 Hemorrhagic Facet Cyst in the Lumbar Spine Causing Contralateral Leg Symptoms: A Case Report Risa Utsunomiya,
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Epidural steroid injections have been used to treat lumbar
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.S. Lee S.H. Kim J.W. Lee S.H. Hong J.-Y. Choi H.S. Kang J.W. Song A.K. Kwon Comparison of the Temporary Diagnostic Relief of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection Approaches: Conventional
ORIGINAL RESEARCH I.S. Lee S.H. Kim J.W. Lee S.H. Hong J.-Y. Choi H.S. Kang J.W. Song A.K. Kwon Comparison of the Temporary Diagnostic Relief of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection Approaches: Conventional
MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS POLICY STATEMENT. Page: 1 of 8
 Page: 1 of 8 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title LUMBAR MICRODISCECTOMY Policy Number 7.01.98 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 06/21/18 Revised Date 12/20/18 Product
Page: 1 of 8 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title LUMBAR MICRODISCECTOMY Policy Number 7.01.98 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 06/21/18 Revised Date 12/20/18 Product
Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis
 Pain Physician 2018; 21:67-72 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Observational Study Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis Min Cheol
Pain Physician 2018; 21:67-72 ISSN 1533-3159 Prospective Observational Study Outcome of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection According to the Severity of Lumbar Foraminal Spinal Stenosis Min Cheol
Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at ( sent October 2013 ) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at www.coxtechnic.com ( sent October 2013 ) 1 5 th Lumbar Disc Herniation with Spondylolisthesis Treated with Cox Technic Flexion Distraction by Travis Cross BS,
Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at www.coxtechnic.com ( sent October 2013 ) 1 5 th Lumbar Disc Herniation with Spondylolisthesis Treated with Cox Technic Flexion Distraction by Travis Cross BS,
Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography
 Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography Policy #: 177 Latest Review Date: June 2011 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue
Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography Policy #: 177 Latest Review Date: June 2011 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue
Occult Lumbar Lateral Spinal Stenosis in Neural Foramina Subjected to Physiologic Loading
 Occult Lumbar Lateral Spinal Stenosis in Neural Foramina Subjected to Physiologic Loading Bruce H. Nowicki, Victor M. Haughton, Timothy A. Schmidt, Tae-Hong Lim, Howard S. An, Lee H. Riley III, Liyuan
Occult Lumbar Lateral Spinal Stenosis in Neural Foramina Subjected to Physiologic Loading Bruce H. Nowicki, Victor M. Haughton, Timothy A. Schmidt, Tae-Hong Lim, Howard S. An, Lee H. Riley III, Liyuan
