Neuropathic pain in patients with haemophilia, that is the question
|
|
|
- Helena Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original article S Neuropathic pain in patients with haemophilia, that is the question S. Krüger; T. Hilberg Lehrstuhl für Sportmedizin, Bergische Universität Wuppertal Keywords Haemophilia, neuropathic, nociceptive, pain Summary Chronic pain caused by recurrent joint bleedings affects a large number of patients with haemophilia (PwH). The basis of this pain, nociceptive or neuropathic, has not been investigated so far. In other pain-related chronic disorders such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, initial studies showed nociceptive but also neuropathic pain features. 137 PwH and 33 controls (C) completed the paindetect-questionnaire (pdq), which identifies neuropathic components in a person s pain profile. Based on the pdq results, a neuropathic pain component is classified as positive, negative or unclear. A positive neuropathic pain component was found in nine PwH, but not in C. In 20 PwH an unclear pdq result was observed. In comparison to C the allocation of pdq results is statistically significant (p 0.001). Despite various pdq results in PwH and C a similar appraisal pain quality, but on a different level, was determined. Summarising the results, there is a potential risk to misunderstand underlying pain mechanisms in PwH. In chronic pain conditions based on haemophilic arthopathy, a differential diagnosis seems to be unalterable for comprehensive and individualised pain management in PwH. Correspondence to: Prof. Thomas Hilberg Bergische Universität Wuppertal / Lehrstuhl für Sportmedizin, Pauluskirchstraße Wuppertal hilberg@uni-wuppertal.de Schlüsselwörter Hämophilie, neuropathisch, nozizeptiv, Schmerz Zusammenfassung Personen mit Hämophilie (PmH) leiden aufgrund rezidivierender Gelenkblutungen oft unter chronischen Schmerzen. Die Schmerz - ursache, nozizeptiv oder neuropathisch, wurde bisher nicht untersucht. Bei anderen Erkrankungen mit chronischen Schmerzen, wie Arthrose oder rheumatoide Arthritis, konnten Studien neuropathische Schmerzkomponenten nachweisen. 137 PmH und 33 Kontrollen (K) beantworteten den paindetect-fragebogen (pdq), der neuropathische Schmerzen identifizieren kann. Basierend auf dem pdq kann ein neuropathischer Schmerz als positiv, negativ oder unklar klassifiziert werden. Ein positives pdq-ergebnis war bei neun PmH vorhanden, bei 20 PmH war das pdq-ergebnis unklar. Der Vergleich PwH zu K war statistisch signifikant (p 0,001). Die Bewertung der Schmerzqualität zeigt bei PmH und K ähnliche Muster, allerdings mit unterschiedlicher Intensität. Bei PmH besteht ein potenzielles Risiko, von einer falschen Schmerz ursache auszugehen. Bei chronischen Schmerzen, bedingt durch eine hämophilie Arthropathie, scheint eine differenzierte Diagnose unabdingbar, um ein umfassendes und individualisiertes Schmerzmanagement bei PwH zu gewährleisten. Neuropathischer Schmerz bei Hämophilie- Patienten, das ist die Frage Hämostaseologie 201; 3 (Suppl 1): S S9 received: January 29, 201 accepted in revised form: May 4, 201 Haemophilia is an x-linked recessive coagulopathy characterised by bleeding episodes which mostly affect the ankles, knees and elbows. Recurring haemarthrosis leads to adverse changes in the synovial tissue and the articular cartilage (1, 2). Pain plays a central role in the life of patients with haemophilia (PwH) (3 ). Caused by recurrent joint bleedings acute pain conditions may shift to chronic pain due to synovitis, enhanced cartilage damage and bone destruction (3). Pain becomes an autonomous disorder through this shift. In contrast, the knowledge about pain in PwH is very restricted to visual analogue scales or different pain questionnaires (6). In a previous study we have shown that pain thresholds are altered in people with haemophilia (3). We were able to determine reduced pressure pain thresholds at the knee and elbow joints of PwH in comparison to control subjects. This increased pain sensitivity is related to the severity of joint pathology. Non-joint structures like sternum and forehead showed no different pain thresholds between PwH and controls. These results were confirmed by the study of Teyssler et al. (7). They also verified reduced pain thresholds in PwH. Currently, the cause of increased pain sensitivity cannot be answered adequately. It is assumed that an acute increase of intra-articular pressure due to acute bleeding (3) and/or synovial inflammatory changes (1) may lead to these altered pain thresholds. Pain conditions in PwH seem to be based on nociceptive pain mechanisms. Nevertheless, a neuropathic pain component in the pain profile of PwH should be taken into account, which on the one hand can occur as an autonomous mechanism and on the other hand may interact with a nociceptive component. So far, neuropathic pain as an underlying mechanism for the pain condition in PwH has not been investigated nor discussed. Schattauer 201 Hämostaseologie 4a/201
2 S6 S. Krüger; T. Hilberg: Neuropathic pain parameter age (years) height (cm) weight (kg) people with haemophilia ± (19 80) 178 ± 7.6 ( ) 82 ± 14.3 (4 130) Nociceptive and neuropathic pain arise from diverse mechanisms. Nociceptive pain mechanisms are classified into nociceptive (physiologic) and inflammatory pain (pathophysiologic). While inflammatory pain is characterised by tissue damage and inflammation, neuropathic pain is induced by a dysfunction or lesion of the peripheral or central nervous system (8). In inflammatory pain, inflammatory mediators sensitize nociceptors leading to allo dynia and hyperalgesia. Nociceptive pain describes a suprathreshold activation of nociceptors, i. e. the classical warning symptom. The function of both mechanisms is to protect the organism from tissue damage (9). In contrast, neuropathic pain originates from damage or dysfunction within the nervous system, which may or may not be associated with potential or actual tissue damage (10). Further, plasticity changes of the peripheral or central nervous system may lead to an irreversible, autonomous pathology (9). For the pain management in PwH it is of major importance to distinguish between nociceptive and neuropathic pain mechanisms because of different treatment interventions. Up to now, pain caused by haemophilic arthropathy has been attributed to osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis pain conditions and is managed similarly (2, 13). Although there are initial studies, which identified features of neuropathic pain in unspecific joint pain conditions (14), osteoarthritis (1 17) or rheumatoid arthritis (18), neuropathic pain components in PwH also have to be determined. Moreover, haemophilia s specific comorbidities such as HIV or hepatitis already comprises the option for a neuropathic pain condition by itself (19 21). Apart from other comprehensive neurological screening tools, the paindetect questionnaire (pdq) is a patient-based questionnaire, which identifies neuropathic pain mechanisms (22). control subjects ± 16 (22 76) 179 ± 7 ( ) 81.7 ± 13.9 (6 0) The aim of this study was to detect if there is a neuropathic pain component in the pain profile of PwH. We hypothesised that non-neuropathic pain is present in PwH mainly, but that there are also patients with a neuropathic pain component. Patients and methods Subjects p = Tab. 1 Anthropometric data as mean ± standard deviation (min-max) of people with haemophilia and control subjects In total, we contacted 287 persons with severe and moderate haemophilia by mail. Beside an information letter, a statement of agreement and a general questionnaire, the pdq was annexed. 137 responses including Tab. 2 Clinical characteristics of people with haemophilia ( 137) parameter type of haemophilia severity HIV hepatitis most affected joint data A B severe moderate yes no yes HBV HCV HAV & HCV HBV & HCV HAV & HBV & HCV unavailable no knee ankle elbow other none a written informed consent returned to our department. In addition 7 male control subjects without any blood coagulation or joint diseases were also contacted out of which 33 persons answered. All participants were recruited by our internal database. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of good clinical and ethical practice (Declaration of Helsinki). Pain questionnaire paindetect The pdq is a one page patient-based screening tool, which identifies neuropathic components in a person s pain profile and has been developed by the German Research Network On Neuropathic Pain (Deutscher Forschungsverbund Neuropathischer Schmerzen, DFNS) (22). The pdq is based on characteristic clinical neuropathic symptoms and can easily be applied fully by the patient without any prior physical examination by medical personnel (22). The questionnaire is composed of four parts whereby three of them (part 2 4) were used for the final analysis. In the first part, current pain rating, worst pain rating within the last four weeks and mean pain ratings within the last four weeks were gathered by a visual analogue scale ranging form 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain imaginable). The second part of the pdq displayed different pictures which asked for the course of pain (e. g. persistent pain with slight fluctuations or pain attacks with pain between them). Thus, patients were able to distinguish between various pain progressions. In addition, the third part queried if the pain radiated to other regions of the body. Patients were requested to mark the main area of pain on a body image as well as the direction of pain radiation. Seven questions that concern the quality of neuropathic pain syndromes constitute the last pdq part (e. g. Do you have sudden pain attacks in the area of your pain, like electric shocks?). Each of the seven questions were graded from 0 (never) to (very strongly). Previous answers were scored for a final screening-result also. The issue on pain-course pattern was graded from 1 to +1. In addition, score points re- Hämostaseologie 4a/201 Schattauer 201
3 S. Krüger; T. Hilberg: Neuropathic pain S7 garding pain radiation, graded 0 for no radiation or +2 for radiating pain, were awarded finally (22). Based on a score-range from 0 to 38, a neuropathic pain component was evaluated as negative (a neuropathic pain component is unlikely (<1%); score: 0 to ), unclear (neuropathic pain component can be present; score: 13 to 18) or positive (neuropathic pain component is likely (>90%); score: 19 to 38). The pdq was evaluated in 392 patients with back pain and indicated a sensitivity of 8% and specificity of 80%. A complete description of the pdq including a score manual is published by Freynhagen et al. (22). Statistics Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS 22 (Chicago, IL, USA) for Windows. Normal distribution of data was tested by Kolmogorov Smirnov tests. As the data were not distributed normally, statistical group comparison between PwH and controls was done by Mann-Whitney U test for score points and by chi-square tests for the final result. The alpha level for all tests was set at p 0.0. Tab. 3 Results of the pain - DETECT-questionnaire in people with haemo - philia and controls positive negative pdq result negative unclear positive in total people with haemophilia / 78.8% SP:.9 ± 3.2 (0 ) 20 / 14.6% SP: 1.8 ± 1.8 (13 18) 9 / 6.6% SP: 23.0 ± 4.9 (19 33) SP: 8.4 ± 6.1 (0 33) paindetect results controls Data presented as absolute/percentage and additionally as score points (SP) mean ± standard deviation (min-max) / 97.0% SP: 3.9 ± 3.7 (0 ) 1 / 3.0% SP: 14 0 / 0 % SP: -- SP: 4.2 ± 4.0 (0 14) Results Anthropometric data of PwH and controls are shown ( Tab. 1), clinical characteristics of PwH are listed ( Tab. 2). PwH attained in percentage more often an unclear or positive pdq-result based on higher score points (PwH: 8.4 vs. controls: 4.2), as seen ( Tab. 3). This allocation is statistically significant for the scores (p 0.001) as well as for the pdq-results (p = 0.006). The single results of the pdq in PwH are shown ( Fig. 1). On the basis of this mapping the distribution of particular results became apparent. In the majority of PwH, a neuropathic pain component was unlikely. Even so some results pointed out a neuropathic or an almost neuropathic pain component. Overall, pain ratings (1 st part of pdq) via numeric pain scale were scored significantly higher in PwH as in controls when current pain (PwH: 2. vs. controls: 1.2) (p Fig. 1 Single results of the paindetect-questionnaire (pdq-results) in people with haemophila (PwH) ( 137), including score points, cut-off values and final results negative: neuropathic pain component unlikely; positive: neuropathic pain component likely prevalence burning sensation tingling, prickling sensation light touch sudden pain attacks cold or heat painful Fig. 2 Results of questions responding to quality of neuropathic pain syndromes in controls, people with haemophilia (PwH) ( 137), people with haemopilia and a paindetect screening result positive (PwH-pDq-positive), unclear (PwH-pDq-unclear) and negative (PwH-pDq-negative) on a scale 0 (never) (very strongly). sensation of numbness slight pressure Controls PwH PwH-pDq-positive PwH-pDq-unclear PwH-pDq-negative Schattauer 201 Hämostaseologie 4a/201
4 S8 S. Krüger; T. Hilberg: Neuropathic pain 0.01), worst pain ratings (PwH:.8 vs. controls: 3.9) (p 0.001) or mean pain ratings (PwH: 3. vs. controls: 2.4) (p 0.0) within the last four weeks were questioned. Pain ratings in controls resulted in most cases from low back pain (data not shown). The findings of the seven questions responding to the quality of neuropathic pain syndromes are presented ( Fig. 2). PwH conceived their pain more often in a quality of neuropathic pain. Regarding the conception of pain, PwH showed significant differences in relation to controls in terms of burning sensation (p 0.01), tingling/prickling sensation (p 0.0), sudden pain attacks (p 0.01) and slight pressure (p 0.001). Discussion In accordance to other studies our results provide evidence for an increased pain status in PwH when compared to controls (3, 23 24). Inflammatory conditions seem to play a major role for pain complaints in PwH. Regarding to molecular pathologic changes caused by haemophilic arthropathy, Acharya named some proinflammatory cytokines, which are involved in the development of haemophilic synovitis (2). In general, proinflammatory cytokines are typical triggers in osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis pain, as described in different studies. Schaible et al. showed that especially the tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β and IL-6 play an important part in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis related pain, causing an increase sensitivity of the joint nociceptors (17, 26). These exact cytokines are involved in the destructive process during the development of haemophilic arthropathy (). However, further studies have to analyse in greater detail the role of molecular causes of pain conditions in PwH. As we hypothesised, our findings verified that non-neuropathic pain in PwH is prominent. On the basis of pdq results, non-neuropathic pain is verified in 79% of our patients. A peripheral increased excitability of C-fibres evoked by bleeding events, may lead to a secondary sensitisation and/or an increased activity of central nociceptive neurons in PwH. In this study, we detect that a neuropathic pain component is likely in approximately seven percent of our patients and appears as frequent as in the general population in Europe (27). Furthermore, one has to consider an unclear pdq result for almost 1% of our patients where additional diagnostic measures should be realised. Therefore, there is a latent risk to estimate chronic pain in PwH by means of increased nociceptive sensitivity per se and to under-recognise neuropathic pain components. The distribution of divergent results ( Fig. 1) points out the risk of misunderstanding underlying pain mechanisms and verifies a very heterogeneous pain profile in PwH. Moreover, pain mechanisms still remain unknown in 1% of the patients cohort. Also, these data may suggest another capability concerning a side-by-side combination of nociceptive and neuropathic pain mechanisms. Nevertheless, the pdq provides the possibility to identify neuropathic pain mechanisms simply, but also effectively and should be included in the routine pain diagnostics in PwH. Our findings are accompanied with recent studies, which proved that a neuropathic pain condition might also be present in osteoarthritis (1 16, 28) or rheumatoid arthritis (18). The prevalence of neuropathic pain components in osteoarthritis pain ranged from % (16) to 34% (1). Sim et al. found neuropathic pain mechanisms in 33% of their patients with rheumatoid arthritis and neurologic symptoms (18). However, data of PwH are still missing. To sum up, joint pain caused by haemophilia, rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, can no longer be attributed to nociceptive pain mechanisms only. Complicated by limited evidence on pain assessment and management in PwH, an individualised pain management cannot be realised. A distinct pain diagnostic in PwH, which is still non-existent, is absolutely essential to tailor specific pain treatment based on particular pain mechanisms. According to the type of pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs/paracetamol (inflammatory pain) or opioids, anticonvulsants and/or antidepressants (neuropathic pain) must be prescribed (27). A false pain diagnostic and subsequently an incorrect pain medication may lead to an insufficient pain treatment regime, as often described (4, 29). The development of evidence-based guidelines, as mentioned by many authors (4, 7, 24), is of upmost importance and should include specific recommendations for the treatment of neuropathic pain in PwH. Only then can it be ensured that suitable medication is used for a specific type of pain. We evaluated a small number of controls to also gain awareness about pain pattern in persons with common pain in contrast to pain modalities in PwH. Between the different pdq result-groups, a comparable pattern in the pain character could be determined. Despite similar pain experience in all scanned persons, there is a big gap with respect to the subjective prevalence of pain quality ( Fig. 2). The general questionnaire was re-examined in order to identify feasible common features in PwH with a likely neuropathic pain component. Because of small subgroup numbers, additional statistical analyses were not carried out. No PwH with a pdq-score 19 points had a total endoprosthesis or synovectomy, while the occurrence of arthroscopy, bone fracture and arthrocentesis arose once. On the basis of the raw data, it seems that either accompanying diseases such as HIV, hepatitis or other diseases such as diabetes or rheumatism influence the pdq result. Thus, out of nine PwH with a likely neuropathic pain component, only one had HIV and four had hepatitis. Furthermore, the allocation of HIV and hepatitis was nearly equal with a prevalence of % persons who had HIV in the positive pdq result group versus 16% in the negative pdq result group. The difference of hepatitis was 2% between these two groups. However, larger surveys may verify the impact of HIV or hepatitis on neuropathic pain in PwH in more detail. In all PwH with a positive pdq result, severe haemophilia A was present. Also, attention has been paid to the age pattern of the nine PwH with a positive pdq result, but no age effect can be assumed. PwH with a positive pdq aged between 2 and 7 years (mean ± standard deviation: 44 ± years). Thus, we cannot conclude that with rising age in the course of age a positive pdq result is more presumable. There are some other limitations of the study based on a sheer questionnaire and Hämostaseologie 4a/201 Schattauer 201
5 S. Krüger; T. Hilberg: Neuropathic pain S9 cross-section elicitation. We are not able to verify if a more impaired joint is associated with a higher pdq-result. Also we cannot conclude a relation between the numbers of joint bleeding events and the pdq result. Further studies should clarify if these factors may influence the pdq result. As a consequence of these data, it is necessary to investigate the pathogenesis of haemophilia related pain. As recently as the mechanisms of pain development and pain processing will be understood, evidencebased guidelines must be generated to cope the heterogeneity of pain in PwH adequately. Conclusion Although inflammatory pain is a central theme in PwH, neuropathic pain is present in approximately seven percent of the patients based on our study and may be a reason of an unsuccessful classical pain treatment in these patients. The pdq is a sensitive and specific tool to differ between the underlying pain mechanisms and should be included into a comprehensive pain diagnostic and treatment. Acknowledgements The authors thank Priv.-Doz. Dr. U. F. Wehmeier and Priv.-Doz. Dr. M. K. Böttger for their scientific and linguistic input on the manuscript. Conflict of interest The authors stated that they had no interests which might be perceived as posing a conflict or bias. References 1. Jansen NWD, Roosendaal G, Lafeber FPJG. Understanding haemophilic arthropathy: an exploration of current open issues. Br J Haematol 2008; 143: Raffini L, Manno C. Modern management of haemophilic arthropathy. Br J Haematol 2007; 136: Hilberg T, Czepa D, Freialdenhoven D, Boettger MK. Joint pain in people with hemophilia depends on joint status. Pain 20; : Young G, Tachdjian R, Baumann K, Panopoulos G. Comprehensive management of chronic pain in haemophilia. Haemophilia 2014; 20: e3 e0.. Elander J. A review of evidence about behavioural and psychological aspects of chronic joint pain among people with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2014; 20: Humphries TJ, Kessler CM. The challenge of pain evaluation in haemophilia: can pain evaluation and quantification be improved by using pain instruments from other clinical situations? Haemophilia 2013; 19: Teyssler P, Kolostova K, Bobek V. (2014). Assessment of pain threshold in haemophilic patients. Haemophilia 2014; 20: Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN et. al. Neuropathic pain Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 2008; 70: Scholz J, Woolf CJ. Can we conquer pain? Nature Neuroscience 2002; Suppl Segall SK, Maixner W, Belfer I et al. Janus molecule I: dichotomous effects of COMT in neuropathic vs nociceptive pain modalities. CNS Neurological Disord Drug Targets 20; : Valentino LA. Blood-induced joint disease: the pathophysiology of hemophilic arthropathy. J Thromb Haemost 2010; 8: Soroa VE, del Huerto Velázquez Espeche M, Giannone C et al. Effects of radiosynovectomy with p-32 colloid therapy in hemophilia and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 200; 20: Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Musculoskeletal complications of hemophilia. HSS J 2010; 6: Soni A, Batra RN, Gwilym SE et al. Neuropathic features of joint pain: a community-based study. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 6: Hochman JR, French MR, Bermingham SL, Hawker GA. The nerve of osteoarthritis pain. Arthritis Care Res 2010; 62: Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamashita M et al. Existence of a neuropathic pain component in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Yonsei Med J 20; 3: Schaible H. Mechanisms of chronic pain in osteoarthritis. Current rheumatology reports 20; 14: Sim MK, Kim D, Yoon J et al. Assessment of peripheral neuropathy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who complain of neurologic symptoms. Ann Rehabil Med 2014; 38: Hao S. The molecular and pharmacological mechanisms of HIV-related neuropathicpain. Curr Neuropharmacol 2013; : Keltner JR, Fennema-Notestine C, Vaida F et al. HIV-associated distal neuropathic pain is associated with smaller total cerebral cortical gray matter. J Neurovirol 2014; 20: Chin RL, Sander HW, Brannagan TH et al. Demyelinating neuropathy in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis 2010; : Freynhagen R, Baron R, Gockel U, Tölle TR. pain DETECT. Curr Med Res Opin 2006; 22: Goodyear MD, Poon M. Pain management issues in haemophilia. Haemophilia 20; 18: e81 e Holstein K, Klamroth R, Richards M et al. Pain management in patients with haemophilia: a European survey. Haemophilia 20; 18: Acharya SS. Exploration of the pathogenesis of haemophilic joint arthropathy: understanding implications for optimal clinical management. Br J Haematol 20; 16: Schaible H G, von Banchet GS, Boettger MK et al. The role of proinflammatory cytokines in the generation and maintenance of joint pain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010; 93: Attal N, Cruccu G, Baron R et al. EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol 2010; 17: 13 e Gwilym SE, Keltner JR, Warnaby CE et al. Psychophysical and functional imaging evidence supporting the presence of central sensitization in a cohort of osteoarthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 61: Witkop M, Lambing A, Divine G et al. A national study of pain in the bleeding disorders community: a description of haemophilia pain. Haemophilia 20; 18: e e9. Schattauer 201 Hämostaseologie 4a/201
Risk Factors of Neuropathic Pain after Total Hip Arthroplasty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.226 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Risk Factors of Neuropathic Pain after Total Hip Arthroplasty Kazumasa Maeda, MD, Motoki Sonohata,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.4.226 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Risk Factors of Neuropathic Pain after Total Hip Arthroplasty Kazumasa Maeda, MD, Motoki Sonohata,
Diagnosis of Neuropathic Pain. Didier Bouhassira
 Diagnosis of Neuropathic Pain Didier Bouhassira INSERM U-792 Centre d Evaluation et de Traitement de la Douleur Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne-Billancourt FRANCE BPS, June 7, Brussels Definition Pain
Diagnosis of Neuropathic Pain Didier Bouhassira INSERM U-792 Centre d Evaluation et de Traitement de la Douleur Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne-Billancourt FRANCE BPS, June 7, Brussels Definition Pain
INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS
 INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS Pathophysiology What is pain? Pathophysiology Does everyone feel pain the same way? Pathophysiology From a practical point of view, how do you classify pain? Pathophysiology What
INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS Pathophysiology What is pain? Pathophysiology Does everyone feel pain the same way? Pathophysiology From a practical point of view, how do you classify pain? Pathophysiology What
Haemophiliac joints in adults: can we preserve them from (further) damage.
 Haemophiliac joints in adults: can we preserve them from (further) damage. Dr Anne Powell Consultant Rheumatologist Alfred hospital, Melbourne HAEMOPHILIA@alfred.org.au. No Conflict of Interest to declare.
Haemophiliac joints in adults: can we preserve them from (further) damage. Dr Anne Powell Consultant Rheumatologist Alfred hospital, Melbourne HAEMOPHILIA@alfred.org.au. No Conflict of Interest to declare.
THE JOINTS OF CHILDREN WITH HAEMOPHILIA: CAN WE PRESERVE THEM? A/PROF PJ MANNERS MD FRACP SCHOOL OF PAED AND CHILD HEALTH UWA
 THE JOINTS OF CHILDREN WITH HAEMOPHILIA: CAN WE PRESERVE THEM? A/PROF PJ MANNERS MD FRACP SCHOOL OF PAED AND CHILD HEALTH UWA COORDINATOR GRAD CERT OF PAED RHEUMATOLOGY UWA pmanners@meddent.uwa.edu.au
THE JOINTS OF CHILDREN WITH HAEMOPHILIA: CAN WE PRESERVE THEM? A/PROF PJ MANNERS MD FRACP SCHOOL OF PAED AND CHILD HEALTH UWA COORDINATOR GRAD CERT OF PAED RHEUMATOLOGY UWA pmanners@meddent.uwa.edu.au
Prevalence of Neuropathic Pain According to the IASP Grading System in Patients with Chronic Non-Malignant Pain
 bs_bs_banner Pain Medicine 2014; 15: 120 127 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Prevalence of Neuropathic Pain According to the IASP Grading System in Patients with Chronic Non-Malignant Pain Henrik Bjarke Vaegter,
bs_bs_banner Pain Medicine 2014; 15: 120 127 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Prevalence of Neuropathic Pain According to the IASP Grading System in Patients with Chronic Non-Malignant Pain Henrik Bjarke Vaegter,
Haemophilia. Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View. Epidemiology of Haemophilic joint disease
 Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
Hemofílie. MUDr.Ivan Vonke, MBA OKH, Nemocnice České Budějovice, a.s.
 Hemofílie e MUDr.Ivan Vonke, MBA OKH, Nemocnice České Budějovice, a.s. Hemophilia Incidence: Hemopilia A (deficiency of factor VIII): 1-2 of 10 000 male newborns in all ethnic groups Hemophilia B (deficiency
Hemofílie e MUDr.Ivan Vonke, MBA OKH, Nemocnice České Budějovice, a.s. Hemophilia Incidence: Hemopilia A (deficiency of factor VIII): 1-2 of 10 000 male newborns in all ethnic groups Hemophilia B (deficiency
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
p. 70 p. 94 p. 102 p. 105 p. 108
 European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
Gaining insight into the complexity of pain in patients with haemophilia: State- of- the- art review on pain processing
 Accepted: 10 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/hae.13509 REVIEW ARTICLE Gaining insight into the complexity of pain in patients with haemophilia: State- of- the- art review on pain processing N. A. Roussel Medicine
Accepted: 10 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/hae.13509 REVIEW ARTICLE Gaining insight into the complexity of pain in patients with haemophilia: State- of- the- art review on pain processing N. A. Roussel Medicine
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Is mindfulness meditation an appropriate therapy in patients presenting with chronic pain?
 Is mindfulness meditation an appropriate therapy in patients presenting with chronic pain? Background Chronic pain affects between one-third and one-half of the UK adult 10.4% to 14.3% of cases being moderate-severely
Is mindfulness meditation an appropriate therapy in patients presenting with chronic pain? Background Chronic pain affects between one-third and one-half of the UK adult 10.4% to 14.3% of cases being moderate-severely
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
 Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE
 PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE TERM DEFINITION HOW TO USE CLINICALLY Acute Pain Pain that is usually temporary and results from something specific, such as a surgery, an injury, or an infection Addiction A chronic
PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE TERM DEFINITION HOW TO USE CLINICALLY Acute Pain Pain that is usually temporary and results from something specific, such as a surgery, an injury, or an infection Addiction A chronic
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Frequently Asked Questions: Table of Contents What clinical clues help distinguish between nociceptive and neuropathic pain? Can I combine treatments? Why should the treatment
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS Frequently Asked Questions: Table of Contents What clinical clues help distinguish between nociceptive and neuropathic pain? Can I combine treatments? Why should the treatment
Using screening tools to identify neuropathic pain
 Using screening tools to identify neuropathic pain Michael I. Bennett a,*, Nadine Attal b, Miroslav M. Backonja c, Ralf Baron d, Didier Bouhassira b, Rainer Freynhagen e, Joachim Scholz f, Thomas R. Tölle
Using screening tools to identify neuropathic pain Michael I. Bennett a,*, Nadine Attal b, Miroslav M. Backonja c, Ralf Baron d, Didier Bouhassira b, Rainer Freynhagen e, Joachim Scholz f, Thomas R. Tölle
Pre-op Interventions to Mitigate Post-op Acute and Chronic Pain
 Pre-op Interventions to Mitigate Post-op Acute and Chronic Pain H A R S H A S H A N T H A N N A. M D, M S C A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F A N E S T H E S I A C H R O N I C
Pre-op Interventions to Mitigate Post-op Acute and Chronic Pain H A R S H A S H A N T H A N N A. M D, M S C A S S O C I A T E P R O F E S S O R D E P A R T M E N T O F A N E S T H E S I A C H R O N I C
Sharon A Stephen, PhD, ARNP, ACHPN. September 23, 2014
 Sharon A Stephen, PhD, ARNP, ACHPN September 23, 2014 Case-based presentation selected to discuss: Pain assessment Barriers to adequate pain relief Pharmacologic interventions Non-Pharmacologic interventions
Sharon A Stephen, PhD, ARNP, ACHPN September 23, 2014 Case-based presentation selected to discuss: Pain assessment Barriers to adequate pain relief Pharmacologic interventions Non-Pharmacologic interventions
Prevalence and characteristics of neuropathic pain in the people affected by leprosy in China
 Lepr Rev (2012) 83, 195 201 Prevalence and characteristics of neuropathic pain in the people affected by leprosy in China SHUMIN CHEN, JINLONG QU & TONGSHENG CHU Shandong Provincial Institute of Dermatology,
Lepr Rev (2012) 83, 195 201 Prevalence and characteristics of neuropathic pain in the people affected by leprosy in China SHUMIN CHEN, JINLONG QU & TONGSHENG CHU Shandong Provincial Institute of Dermatology,
Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: What Does the Evidence Say? or Just the Facts Ma am
 Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: What Does the Evidence Say? or Just the Facts Ma am Tim R Brown, PharmD, BCACP, FASHP Director of Clinical Pharmacotherapy Cleveland Clinic Akron General Center for Family
Treatment of Neuropathic Pain: What Does the Evidence Say? or Just the Facts Ma am Tim R Brown, PharmD, BCACP, FASHP Director of Clinical Pharmacotherapy Cleveland Clinic Akron General Center for Family
Desmopressin testing in haemo - philia A patients and carriers Results of a multi centre survey
 Original article Schattauer 202 27 Desmopressin testing in haemo - philia A patients and carriers Results of a multi centre survey R. Knöfler ; J. Koscielny 2 ; J. T. Tauer ; B. Huhn ; A. Gneuss ; E. Kuhlisch
Original article Schattauer 202 27 Desmopressin testing in haemo - philia A patients and carriers Results of a multi centre survey R. Knöfler ; J. Koscielny 2 ; J. T. Tauer ; B. Huhn ; A. Gneuss ; E. Kuhlisch
Answers to Self Assessment Questions
 Answers to Self Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following findings is supportive of the diagnosis of multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN): A. Absence of conduction block (CB) on nerve conduction studies
Answers to Self Assessment Questions 1. Which of the following findings is supportive of the diagnosis of multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN): A. Absence of conduction block (CB) on nerve conduction studies
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Evidence / Title of article
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Evidence / Title of article Sensory findings after stimulation of the thoracolumbar fascia with hypertonic saline suggest its contribution to low back pain Schilder A et
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Evidence / Title of article Sensory findings after stimulation of the thoracolumbar fascia with hypertonic saline suggest its contribution to low back pain Schilder A et
Arthritis of the Shoulder
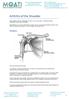 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
The Treatment of Flexion Contracture of the Knee Joint in Hemophilic Patients Using Gradual Manipulation and Serial Casting
 THE FLEXION IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CONTRACTURE MEDICAL IN HEMOPHILIC JOURNAL PATIENTS VOL. 13,NO.3, 2014 The Treatment of Flexion Contracture of the Knee Joint in Hemophilic Patients Using Gradual Manipulation
THE FLEXION IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CONTRACTURE MEDICAL IN HEMOPHILIC JOURNAL PATIENTS VOL. 13,NO.3, 2014 The Treatment of Flexion Contracture of the Knee Joint in Hemophilic Patients Using Gradual Manipulation
HILOTHERAPY. The thermal procedure, controllable to the nearest degree. Rheumatism HILOTHERAPY
 HILOTHERAPY The thermal procedure, controllable to the nearest degree HILOTHERAPY Rheumatism WHAT IS HILOTHERAPY? HILOTHERAPY is a form of thermal healing treatment that promotes the healing process for
HILOTHERAPY The thermal procedure, controllable to the nearest degree HILOTHERAPY Rheumatism WHAT IS HILOTHERAPY? HILOTHERAPY is a form of thermal healing treatment that promotes the healing process for
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion
 Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT
 Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Author s response to reviews Title: Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor. A case report
 Author s response to reviews Title: Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor. A case report Authors: Rubén Cuesta-Barriuso (ruben.cuestab@gmail.com) Roberto O Trelles
Author s response to reviews Title: Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor. A case report Authors: Rubén Cuesta-Barriuso (ruben.cuestab@gmail.com) Roberto O Trelles
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes
 The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
The biochemical origin of pain: The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response: Inflammatory profile of pain syndromes 1 Medical Hypothesis 2007, Vol. 69, pp. 1169 1178 Sota Omoigui
Syllabus. Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain
 Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain Syllabus A. Epidemiology 1. Pain as a public health problem with social, ethical, legal and economic consequences 2.
Questions may appear on any of the topics below: I. Multidimensional Nature of Pain Syllabus A. Epidemiology 1. Pain as a public health problem with social, ethical, legal and economic consequences 2.
Investigation of knee pain in osteoarthritic and neuropathic pain awareness
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 639-646 ORIGINAL STUDY Investigation of knee pain in osteoarthritic and neuropathic pain awareness Umut Hatay Gölge, Halil Murat Şen, Ersin Kuyucu, Hacer Şen, Ferdi Göksel,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 639-646 ORIGINAL STUDY Investigation of knee pain in osteoarthritic and neuropathic pain awareness Umut Hatay Gölge, Halil Murat Şen, Ersin Kuyucu, Hacer Şen, Ferdi Göksel,
3/7/2018. IASP updated definition of pain. Nociceptive Pain. Transduction. (Nociceptors) Transmission. (Peripheral nerve) Modulation
 IASP updated definition of pain The Pain of Trauma and The Trauma of Pain: The Opioid Crisis is Not What You Think. Bennet Davis, M.D. Many people report pain in the absence of tissue damage or any likely
IASP updated definition of pain The Pain of Trauma and The Trauma of Pain: The Opioid Crisis is Not What You Think. Bennet Davis, M.D. Many people report pain in the absence of tissue damage or any likely
o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% o Other studies predict up to 3.48 million TKA o 17% adults over age 45 have symptomatic OA
 NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF KNEE ARTHRITIS DAVID M SCHALL MD Knee Arthritis o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% to 1.26 million procedures per year by 2030 o Other studies predict up to 3.48
NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF KNEE ARTHRITIS DAVID M SCHALL MD Knee Arthritis o Total knee arthroplasty is projected to grow 85% to 1.26 million procedures per year by 2030 o Other studies predict up to 3.48
Musculo-Skeletal Complications of Hemophilia
 Review Elmer Press Musculo-Skeletal Complications of Hemophilia E. Carlos Rodriguez-Merchan Abstract Prophylactic treatment from ages 2 to 18 years could avoid the development of hemophilic arthropathy
Review Elmer Press Musculo-Skeletal Complications of Hemophilia E. Carlos Rodriguez-Merchan Abstract Prophylactic treatment from ages 2 to 18 years could avoid the development of hemophilic arthropathy
Wrist Ganglion. Did not notice Suddenly. Over several hours Over several days Over several weeks Over several months
 Onset, Duration and Frequency Are you left handed or right handed? Left Right Both Which side of your body is affected? Left Right Both If both, which side is more severe? Left Right Varies About the same
Onset, Duration and Frequency Are you left handed or right handed? Left Right Both Which side of your body is affected? Left Right Both If both, which side is more severe? Left Right Varies About the same
BIOM Pharmacodynamics 4 Types of Antagonism
 BIOM2009 2.1 - Pharmacodynamics 4 Types of Antagonism 1. Chemical Antagonism 2. Pharmacokinetic Antagonism 3. Physiological Antagonism 4. Pharmacological Antagonism Where two drugs bind to each other,
BIOM2009 2.1 - Pharmacodynamics 4 Types of Antagonism 1. Chemical Antagonism 2. Pharmacokinetic Antagonism 3. Physiological Antagonism 4. Pharmacological Antagonism Where two drugs bind to each other,
Pathophysiological Classification of Pain
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
pc oral surgery international
 pc oral surgery international Evidence-based TMJ Surgery 2013 Professor Paul Coulthard BDS FGDP(UK) MDS FDSRCS FDSRCS(OS) PhD evidence-based practice? - the integration of best research evidence with clinical
pc oral surgery international Evidence-based TMJ Surgery 2013 Professor Paul Coulthard BDS FGDP(UK) MDS FDSRCS FDSRCS(OS) PhD evidence-based practice? - the integration of best research evidence with clinical
paindetect: a new screening questionnaire to identify neuropathic components in patients with back pain
 Current Medical Research and Opinion ISSN: 0300-7995 (Print) 1473-4877 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/icmo20 paindetect: a new screening questionnaire to identify neuropathic
Current Medical Research and Opinion ISSN: 0300-7995 (Print) 1473-4877 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/icmo20 paindetect: a new screening questionnaire to identify neuropathic
MANAGEMENT OF CRPS. Brachial Neuralgia n = 81 patients. CRPS type II n = 126 patients CONTENTS. Neuropathic Pain. Introduction.
 MANAGEMENT OF CRPS Paradoxical Hypoaesthetic Skin, Painful to Touch: A Target to relieve Neuropathic Pain Spicher, C.J. et al. (2010) Paris: Sauramps medical Paradoxical Hypoaesthetic Skin, Painful to
MANAGEMENT OF CRPS Paradoxical Hypoaesthetic Skin, Painful to Touch: A Target to relieve Neuropathic Pain Spicher, C.J. et al. (2010) Paris: Sauramps medical Paradoxical Hypoaesthetic Skin, Painful to
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS. Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement
 Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement 2 as 20 Experts published and leaders in their respective field 12 month lead in
Prof Wayne Derman MBChB,BSc (Med)(Hons) PhD, FFIMS Pain Management in the Elite Athlete: The 2017 IOC Consensus Statement 2 as 20 Experts published and leaders in their respective field 12 month lead in
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Common and New Orthopaedic/Physical Therapy Recommendations. Mauricio Silva MD
 Common and New Orthopaedic/Physical Therapy Recommendations Mauricio Silva MD Hemophilia Journal WFH Website Recommendations regarding the clinical management of people with hemophilia Practice statements
Common and New Orthopaedic/Physical Therapy Recommendations Mauricio Silva MD Hemophilia Journal WFH Website Recommendations regarding the clinical management of people with hemophilia Practice statements
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION
 NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION MISSION Neurofix aims to discover and develop innovative therapies for the treatment of neurological disorders. Our main focus now is Spinal Cord Injury. VISION Spinal Cord
NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION MISSION Neurofix aims to discover and develop innovative therapies for the treatment of neurological disorders. Our main focus now is Spinal Cord Injury. VISION Spinal Cord
Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs
 University of Groningen Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
University of Groningen Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture
 Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Pain and Touch. Academic Press. Edited by Lawrence Kruger. Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California
 Pain and Touch Edited by Lawrence Kruger Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California San Diego New York Sydney Academic Press London Boston Tokyo Toronto Contributors
Pain and Touch Edited by Lawrence Kruger Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California San Diego New York Sydney Academic Press London Boston Tokyo Toronto Contributors
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Prevention Diagnosis Assessment Prescription and /or application of wide range of interventions and PRM program management
 OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS
 1. Medical Condition MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS Musculoskeletal conditions including those arising from injuries are common in sport. In this setting of sport, we traditionally classify injury according
1. Medical Condition MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS Musculoskeletal conditions including those arising from injuries are common in sport. In this setting of sport, we traditionally classify injury according
Lin s Bone Setting and Massage Therapy in Lingnan Area for Waist-Induced Knee Pain. ZHANG Wanqing MA Weidong LI Liang ISOA P > 0.05 ISOA P < 0.
 2017 6 49 6 113 510130 76 2 38 2 ISOA P > 0.05 P > 0.05 ISOA P < 0.01 P > 0.05 ISOA P < 0.01 P < 0.05 2 ISOA P < 0.01 2 P < 0.01 2 ISOA R681.5 + 7 A 0256-7415 2017 06-0113- 05 DOI 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2017.06.039
2017 6 49 6 113 510130 76 2 38 2 ISOA P > 0.05 P > 0.05 ISOA P < 0.01 P > 0.05 ISOA P < 0.01 P < 0.05 2 ISOA P < 0.01 2 P < 0.01 2 ISOA R681.5 + 7 A 0256-7415 2017 06-0113- 05 DOI 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2017.06.039
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points. Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine
 Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine Objectives Discuss why this topic is pertinent to our practices Review diagnostic criteria
Myofascial Pain Syndrome and Trigger Points Paul S. Sullivan, Do Trinity Health Care New England - Family Medicine Objectives Discuss why this topic is pertinent to our practices Review diagnostic criteria
Management of Neuropathic pain
 Management of Neuropathic pain Ravi Parekodi Consultant in Anaesthetics and Pain Management 08/04/2014 Ref: BJA July2013, Map of Medicine2013, Pain Physician 2007, IASP 2012, Nice guideline 2013 Aims Highlight
Management of Neuropathic pain Ravi Parekodi Consultant in Anaesthetics and Pain Management 08/04/2014 Ref: BJA July2013, Map of Medicine2013, Pain Physician 2007, IASP 2012, Nice guideline 2013 Aims Highlight
Intent to Consider the Appropriate Classification of Hyaluronic Acid Intra-articular Products
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 12/18/2018 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2018-27351, and on govinfo.gov 4164-01-P DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 12/18/2018 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2018-27351, and on govinfo.gov 4164-01-P DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Contents Introduction...3 What is rheumatoid arthritis?...4 Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis... 5 What causes rheumatoid arthritis?... 10 The role of genes and family
Clot waveform analysis in patients with haemophilia A
 Original article S Clot waveform analysis in patients with haemophilia A T. Siegemund 1 ; U. Scholz 2 ; R. Schobess 2 ; A. Siegemund 2 1 The Scripps Research Institute, Department of Molecular and Experimental
Original article S Clot waveform analysis in patients with haemophilia A T. Siegemund 1 ; U. Scholz 2 ; R. Schobess 2 ; A. Siegemund 2 1 The Scripps Research Institute, Department of Molecular and Experimental
Iowa Methodist Medical Center Transplant Center. Informed Consent for Kidney Transplant Recipient
 Iowa Methodist Transplant Center Iowa Methodist Medical Center Transplant Center 1215 Pleasant Street, Suite 506 Des Moines, IA 50309 515-241-4044 Phone 515-241-4100 Fax Iowa Methodist Medical Center Transplant
Iowa Methodist Transplant Center Iowa Methodist Medical Center Transplant Center 1215 Pleasant Street, Suite 506 Des Moines, IA 50309 515-241-4044 Phone 515-241-4100 Fax Iowa Methodist Medical Center Transplant
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Impact of zoledronic acid on control of metastatic spinal cord compression
 Strahlenther Onkol 2012 188:910 916 DOI 10.1007/s00066-012-0158-4 Received: 16 May 2012 Accepted: 30 May 2012 Published online: 18. August 2012 Springer-Verlag 2012 D. Rades 1 S.G. Hakim 2 A. Bajrovic
Strahlenther Onkol 2012 188:910 916 DOI 10.1007/s00066-012-0158-4 Received: 16 May 2012 Accepted: 30 May 2012 Published online: 18. August 2012 Springer-Verlag 2012 D. Rades 1 S.G. Hakim 2 A. Bajrovic
Annex IV Scientific conclusions
 Annex IV Scientific conclusions 56 Scientific conclusions On 7 June 2017, the European Commission (EC) was informed of a fatal case of fulminant liver failure in a patient treated with daclizumab in an
Annex IV Scientific conclusions 56 Scientific conclusions On 7 June 2017, the European Commission (EC) was informed of a fatal case of fulminant liver failure in a patient treated with daclizumab in an
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
young adult patients with advanced haemophilic arthropathy
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 3883-3888, 2018 Clinical outcomes of arthroscopic synovectomy for adolescent or young adult patients with advanced haemophilic arthropathy TING ZHANG, SIHUA HUANG,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: 3883-3888, 2018 Clinical outcomes of arthroscopic synovectomy for adolescent or young adult patients with advanced haemophilic arthropathy TING ZHANG, SIHUA HUANG,
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
Short Screening for the Presence of Neuropathic Pain Component What the Clinical Nurses Need to Know
 International Journal of Caring Sciences 2014 May-August Vol 7 Issue 2 670. O R I G I N A L P A P E R.r. Short Screening for the Presence of Neuropathic Pain Component What the Clinical Nurses Need to
International Journal of Caring Sciences 2014 May-August Vol 7 Issue 2 670. O R I G I N A L P A P E R.r. Short Screening for the Presence of Neuropathic Pain Component What the Clinical Nurses Need to
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Is Topical Clonazepam More Effective Than Oral Clonazepam in Treatment of Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS)?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Is Topical Clonazepam More Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Is Topical Clonazepam More Effective
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Passive Motion in the Home Setting File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_passive_motion_in_the_home_setting 9/1993 6/2018
Arthritis among Patients Attending GMC Hospital, Ajman, UAE: A cross sectional survey
 Arthritis among Patients Attending GMC Hospital, Ajman, UAE: A cross sectional survey Abdullah Ahmed 1, Amin Rigi 1, Feras Emaddin Kokash 1*, Osman Abdul Samad 1, Isaa Al Sebae 1, Rizwana Burhanuddin Shaikh
Arthritis among Patients Attending GMC Hospital, Ajman, UAE: A cross sectional survey Abdullah Ahmed 1, Amin Rigi 1, Feras Emaddin Kokash 1*, Osman Abdul Samad 1, Isaa Al Sebae 1, Rizwana Burhanuddin Shaikh
Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Arthroses
 R. Kausch 1, U. Lahne 2, R. Thomas 3, C. Kipshoven 4, M. Schuld 4 Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Arthroses From the Bad Neuenahr, Bad Neuenahr-Ahrweiler Clinics (Medical Director: Dr.
R. Kausch 1, U. Lahne 2, R. Thomas 3, C. Kipshoven 4, M. Schuld 4 Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Arthroses From the Bad Neuenahr, Bad Neuenahr-Ahrweiler Clinics (Medical Director: Dr.
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Icd 10 code paresthesia of right arm
 Icd 10 code paresthesia of right arm The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 code paresthesia of right arm 2018 ICD-10 code for Paresthesia of skin is R20.2. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for R20.2.
Icd 10 code paresthesia of right arm The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 code paresthesia of right arm 2018 ICD-10 code for Paresthesia of skin is R20.2. Lookup the complete ICD 10 Code details for R20.2.
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care
 Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb
 Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
Referral Criteria: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Feb 2019 1 5.2. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Background Carpal tunnel syndrome present with non-traumatic tingling of the fingers due to compression of the median nerve
Effects of Acupuncture on Chinese Adult Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study
 Effects of Acupuncture on Chinese Adult Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study Peiyi Chen 1, Tiantian Xin 2* and Yingchun Zeng 3,4 1 School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese
Effects of Acupuncture on Chinese Adult Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study Peiyi Chen 1, Tiantian Xin 2* and Yingchun Zeng 3,4 1 School of Nursing, Guangzhou University of Chinese
Pathophysiological Classifica\on of Pain
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Freynhagen R, Baron R. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2009; 13(3):185-90; Jensen TS et al. Pain 2011; 152(10):2204-5; Julius D et al. In: McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M (eds). Wall and Melzack s Textbook
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Freynhagen R, Baron R. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2009; 13(3):185-90; Jensen TS et al. Pain 2011; 152(10):2204-5; Julius D et al. In: McMahon SB, Koltzenburg M (eds). Wall and Melzack s Textbook
Cost-effectiveness analysis of alternative factor VIII products in treatment of haemophilia A Hay J W, Ernst R L, Kessler C M
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of alternative factor VIII products in treatment of haemophilia A Hay J W, Ernst R L, Kessler C M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets
Cost-effectiveness analysis of alternative factor VIII products in treatment of haemophilia A Hay J W, Ernst R L, Kessler C M Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets
Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis
 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis You may think that arthritis is a single condition, but there are many forms of arthritis. Each type can be caused by different
Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arthritis Rheumatism Psoriasis You may think that arthritis is a single condition, but there are many forms of arthritis. Each type can be caused by different
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Management of Pain in Older People Aza Abdulla, Margaret Bone, Nicola Adams, Alison M.
 Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Management of Pain in Older People Aza Abdulla, Margaret Bone, Nicola Adams, Alison M. Elliott, Derek Jones, Roger Knaggs, Denis Martin, Elizabeth L. Sampson,
Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Management of Pain in Older People Aza Abdulla, Margaret Bone, Nicola Adams, Alison M. Elliott, Derek Jones, Roger Knaggs, Denis Martin, Elizabeth L. Sampson,
Role of Imaging in Management of Hemophilic Patients
 Pediatric Imaging Ng et al. Imaging of Hemophilic Patients W. H. Ng 1 W. C. W. Chu 1 M. K. Shing 2 W. W. M. Lam 1 K. W. Chik 2 C. K. Li 2 C. K. Li 3 S. C. Ling 3 Ng WH, Chu WCW, Shing MK, et al. Received
Pediatric Imaging Ng et al. Imaging of Hemophilic Patients W. H. Ng 1 W. C. W. Chu 1 M. K. Shing 2 W. W. M. Lam 1 K. W. Chik 2 C. K. Li 2 C. K. Li 3 S. C. Ling 3 Ng WH, Chu WCW, Shing MK, et al. Received
METHODOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS OF EMG-BASED BIO-MECHANICAL MOTION ANALYSIS. Thomas Jöllenbeck Bergische Universität - Gesamthochschule Wuppertal, Germany
 METHODOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS OF EMG-BASED BIO-MECHANICAL MOTION ANALYSIS Thomas Jöllenbeck Bergische Universität - Gesamthochschule Wuppertal, Germany The purpose of the present study was to investigate
METHODOLOGICAL LIMITATIONS OF EMG-BASED BIO-MECHANICAL MOTION ANALYSIS Thomas Jöllenbeck Bergische Universität - Gesamthochschule Wuppertal, Germany The purpose of the present study was to investigate
1 von , 04:42
 1 von 37 06.10.2017, 04:42 2 von 37 06.10.2017, 04:42 Christine Charité - Universitätsme christine.holmberg@cha Effect of a Website That Presents Patients Experiences on Self-Efficacy and Patient Competence
1 von 37 06.10.2017, 04:42 2 von 37 06.10.2017, 04:42 Christine Charité - Universitätsme christine.holmberg@cha Effect of a Website That Presents Patients Experiences on Self-Efficacy and Patient Competence
Stadien der Progression bei CKD
 Stadien der Progression bei CKD Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR Kidney failure CKD death Screening for CKD risk factors CKD risk reduction; Screening for CKD Diagnosis & treatment; Treat
Stadien der Progression bei CKD Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR Kidney failure CKD death Screening for CKD risk factors CKD risk reduction; Screening for CKD Diagnosis & treatment; Treat
Pain and endometriosis: How to optimize the medical management?
 Pre-congress course Endometriosis sand pelvic pain 1st Society for endometriosis and uterine Disorders Meeting Paris, 7-9 May 2015 Pain and endometriosis: How to optimize the medical management? J. FAIDHERBE
Pre-congress course Endometriosis sand pelvic pain 1st Society for endometriosis and uterine Disorders Meeting Paris, 7-9 May 2015 Pain and endometriosis: How to optimize the medical management? J. FAIDHERBE
Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): Application of surface (transcutaneous) neurostimulator
 ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 64550 Application of surface (transcutaneous) neurostimulator Medical Policy Title: Electrical Stimulation, Transcutaneous
ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 64550 Application of surface (transcutaneous) neurostimulator Medical Policy Title: Electrical Stimulation, Transcutaneous
DIABETIC NEUROPATHY ASSESSED AT TWO TIME POINTS FIVE YEARS APART
 1 University Department of Neurology, Sarajevo Clinical Center, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Zenica Cantonal Hospital, Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina 3 Department of Hemodialysis, Sarajevo Clinical
1 University Department of Neurology, Sarajevo Clinical Center, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Zenica Cantonal Hospital, Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina 3 Department of Hemodialysis, Sarajevo Clinical
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Department of Paediatric and Adult Movement Disorders and Neuropsychiatry, Institute of Neurogenetics, University of Luebeck, Luebeck, Germany
 Quantitative Sensory Testing in adults with Tourette syndrome Odette Schunke 1 *, Wiebke Grashorn 1 *, Ursula Kahl 1, Daniel Schöttle 6, Patrick Haggard 2, Alexander Münchau 3, Ulrike Bingel 5, Christos
Quantitative Sensory Testing in adults with Tourette syndrome Odette Schunke 1 *, Wiebke Grashorn 1 *, Ursula Kahl 1, Daniel Schöttle 6, Patrick Haggard 2, Alexander Münchau 3, Ulrike Bingel 5, Christos
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts
 Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor
 Cuesta-Barriuso and Trelles-Martínez BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:26 DOI 10.1186/s12891-018-1934-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor
Cuesta-Barriuso and Trelles-Martínez BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:26 DOI 10.1186/s12891-018-1934-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Manual therapy in the treatment of patients with hemophilia B and inhibitor
