Kobe University Repository : Kernel
|
|
|
- Mae Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Alpha E- and Alpha N-catenin Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglia and Spinal Cord Shibuya, Yasuyuki / Murata, Maho / Munemoto, Sachiko / Masago, Hiroshi / Takeuchi, Jyunichirou / Wada, Keinoshin / Yokoo, Satoshi / Umeda, Masahiro / Komori, Takahide The Kobe journal of the medical sciences,49(3/4): Departmental Bulletin Paper / 紀要論文 publisher JaLCDOI / URL PDF issue:
2 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 4, pp , 2003 Alpha E- and Alpha N-catenin Expression in Dorsal Root Ganglia and Spinal Cord YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, MAHO MURATA, SACHIKO MUNEMOTO, HIROSHI MASAGO, JYUNICHIROU TAKEUCHI, KEINOSHIN WADA, SATOSHI YOKOO, MASAHIRO UMEDA, and TAKAHIDE KOMORI Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine Received 31 October 2003/ Accepted 24 December 2003 Key words: Intercellular adhesion molecule; Cadherin; Catenin; Dorsal root ganglion; Spinal cord The localization of alpha E- and alpha N-catenin in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord was examined immunocytochemically. Alpha E- and alpha N-catenin appeared to be co-localized in cell bodies of neurons in dorsal root ganglia, but alpha N-catenin was not expressed in cell bodies of neurons in the ventral horn that showed alpha E-catenin expression. These findings indicate the possibility that the type of alpha catenin expressed in neurons differs with its functional property (e.g. sensory or motor). Cadherins constitute a superfamily of calcium-dependent intercellular adhesion molecules (22) and are thought to play a role in cell recognition and segregation, morphogenetic regulation, and tumor suppression (21)(22)(5)(3)(4). Cadherin is a transmembrane glycoproteins and link to catenin at its cytoplasmic domain. Catenins are classified into alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenins (13), and alpha E- and alpha N-catenins have been identified as subtypes of alpha-catenin (6)(5)(7)(11). Cadherin is linked directly to one or two molecules of beta-catenin, and to one molecule of alpha-catenin via beta-catenin (15)(8)(14). Gamma-catenin is associated loosely with the alpha- and beta-catenin complex (13)(14). These proteins combine and form the cadherin-catenin complex that can bind to actin filaments, thus influencing the cytoskeletal system correlated to intercellular adhesion (15). Recently, proteins of the p120 family have been identified as a regulator of cadherin-based cell adhesion, and those are also binding to the cytoplasmic domain of cadherins (1)(2)(16)(23). At present, it is known that alpha E-catenin can associate with N- and P-cadherins in addition to E-cadherin, and alpha N-catenin with E-cadherin as well as N-cadherin. In previous studies, we identified the localization of N-cadherin and alpha N-catenin in the normal unmyelinated and regenerating chick sciatic nerve (19)(20). Alpha E-catenin can also bind to N-cadherin, and we have clarified the nature of alpha E-catenin expression in the peripheral nerve (data not shown). The parent cell bodies of sciatic nerve fibers are located in the dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord, but their alpha E- and alpha N-catenin expression has not yet been clarified. In the study presented here, the distribution patterns of alpha E- and alpha N-catenin were therefore examined in the dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord at the lumbar level where sciatic nerves originate. The results showed that alpha E- and alpha N-catenin are co-localized in the dorsal root ganglia and dorsal horn of the spinal cord. On the other hand, alpha E- and alpha N-catenin showed a different distribution in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. Alpha E-catenin was expressed in the cell bodies of neurons in the Phone: Fax: shibuya@med.kobe-u.ac.jp 93
3 Y. SHIBUYA et al. ventral horn where alpha N-catenin was absent. These findings suggest that catenin expression may be differentially regulated depending on the functional properties of neurons such as sensory or motor properties. MATERIALS AND METHODS Materials White Leghorn chickens (female, 11~27 days of age) were obtained from a commercial poultry farm (Kakogawa City, Japan). All animal experiments were conducted according to the Guidelines for Animal Experimentation at Kobe University School of Medicine. The animals were anesthetized with halothane and fixed by transcardiac perfusion with a fixative containing 3% paraformaldehyde in 0.15 M NaCl and 100 mm phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at ph 7.5 supplemented with 1 mm CaCl 2, and 8% sucrose. The spinal cord of the lumbar level where sciatic nerves derived was excised with dorsal root ganglia and immersed in the same fixative as described above for 4 h at 4 o C. This segment was cryoprotected through a range of increasing sucrose concentrations (10, 15, 20 and 25%) in 0.2 M NaCl and 50 mm Tris-buffered saline (TBS) at ph 7.5, embedded in OCT compound, quick-frozen, and sectioned 8-µm thick in a cryostat. Immunohistochemistry The frozen sections mounted on slides were washed in TBS supplemented with 1 mm CaCl 2 (TBS-Ca) and incubated with TBS-Ca containing 5% skimmed milk for 30 min. These sections were incubated for 24 h at 4 o C with a rat monoclonal anti-alpha E-catenin antibody, alpha-18 (12), or a rat monoclonal anti-alpha N-catenin antibody, NCAT-2 (6) diluted 1:200 with TBS-Ca containing 1% skimmed milk. As a control, sections were incubated with rat serum instead of alpha-18 or NCAT-2. After washing three times with TBS-Ca, the sections were incubated for 24 h at 4 o C with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled sheep anti-rat IgG antibody [species-specific F(ab ) 2 fragment (Amersham)] at a final dilution of 1:20. After washing with TBS-Ca, the sections were incubated for 30 min in 50 µm Tris buffer containing 0.05% 3,3 -diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (DAB solution), and then incubated for 10 min in the DAB solution with 0.01% H 2 O 2 added. The sections were embedded with 50% glycerine in TBS-Ca and examined by light microscopy. RESULTS Control As control for non-specific labeling by the alpha-18 antibody or the NCAT-2 antibody, frozen sections were stained in an identical manner with normal rat serum being substituted for the monoclonal antibody. In these control sections no labeling was observed by light microscopy. Dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord immunostained with alpha-18 and NCAT-2 Immunoreactions of both alpha-18 and NCAT-2 in dorsal root ganglia were distributed throughout the cytoplasm of neuron cell bodies (Fig.1). In the spinal cord intense immunoreactivities for both alpha-18 and NCAT-2 were found in Rexed s laminae I and II of the dorsal horn (Fig.2). In the ventral horn, on the other hand, immunoreactivity for alpha-18 was observed in neuron cell bodies that seemed to be motor neurons where no immunoreactivity for NCAT-2 was seen (Fig.2). In general, there was no indication of accumulation of catenin beneath the plasmalemma of neuron cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia and ventral horn. 94
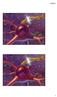
4 ALPHA E/N-CATENIN IN DRG AND SPINAL CORD Figure 1. a. The dorsal root ganglion immunostained with alpha-18. Immunoreaction is shown throughout the cytoplasm of neuron cell bodies including nucleus. This immunoreaction is distributed uniformly in general but concentrated under plasmalemma at a few intercellular contacts (arrowhead). Some of the satellite cells also show immunoreactivity (arrows). Figure 1. b. The dorsal root ganglion immunostained with NCAT-2. Distribution pattern of NCAT-2 immunoreactive products is almost the same as alpha-18. The intense immunoreactivity is occasionally found under plasmalemma at a few intercellular contacts (arrowheads). 95
5 Y. SHIBUYA et al. 2a 2b I II I II Figure 2. a. The spinal cord of the lumber level immunostained with alpha-18. The intense immunoreactivity is observed in the cytoplasm of neuron cell bodies in the ventral horn (inset). The neuropile in the Rexed s laminae I and II of the dorsal horn also shows alpha-18 immunoreactivity (arrows). Figure 2. b. The spinal cord of the lumber level immunostained with NCAT-2. The neuropile in the Rexed s laminae I and II of the dorsal horn shows NCAT-2-immunoreactivity (arrows), but there is no immunoreactivity in cell bodies of neurons in the ventral horn (inset). DISCUSSION Our study has demonstrated that cell bodies of sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia express not only alpha E-catenin but also alpha N-catenin, whereas motor neurons in the ventral horn have alpha E-catenin without alpha N-catenin expression. This finding indicates the possibility that the motor fibers in sciatic nerves can be distinguished from the sensory fibers by their immunoreactivity for anti-alpha N-catenin antibody. If the sensory nerve consists of unmyelinated fibers, this hypothesis is supported by our previous findings that alpha N-catenin is expressed not in myelinated but in unmyelinated nerve fibers (20). However, it is doubtful that all sensory nerves are unmyelinated. Considering that cadherins were not present in myelinated fibers based on our previous finding and that catenins are used to link to cadherins, there is no need for myelinated fibers to express catenins even in sensory neurons. On the contrary, the Rexed s laminae I and II of the dorsal horn are shown to be intense immunoreactive region for anti-alpha E- and alpha N-catenin antibodies, since this area is rich in unmyelinated fibers. Our previous studies also indicated that cadherins and alpha N-catenin are present in some of the growth cones sprouting from myelinated fibers. These findings imply that growth cones without myelinization need cadherins and alpha catenin which function at the axon-axon or axon-schwann cell interaction. Once myelination has started, cadherins and alpha N-catenin of growth cones are likely to disappear. Even among growth cones, there are those with intense immunoreaction and very faint immunoreaction to anti-alpha N-catenin antibody. It is hypothesized that the former may be derived from the sensory and the latter from the motor neurons. 96
6 ALPHA E/N-CATENIN IN DRG AND SPINAL CORD During the development, the general somatic sensory nerve, like the trigeminal nerve, shows N-cadherin expression at embryonic days 6 to 11, while R-cadherin is expressed in the visceral motor fibers of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves (17). Fibers expressing the same type of cadherins can adhere to each other for fasciculation so that this difference in cadherin expression is thought to have a nerve sorting function (18). Catenins could also affect intercellular adhesion by forming complexes with cadherins and may contribute indirectly to nerve fasciculation. It is thus hypothesized that the different expression patterns of alpha N-catenin in the spinal cord may be associated with peripheral nerve sorting during development or regeneration. Another hypothesis is that alpha N-catenin may not be distributed uniformly in the motor neurons: the alpha N-catenin expression is concentrated in the neurites or under the plasmalemma but not in the perikaryon. However, this hypothesis argues against the observation of alpha N-catenin in the dorsal root ganglion. Since Mizoguchi et al. detected that alpha N-catenin is located under the plasmalemma in the central nerve (10), further study at the electron microscopical level will be required before any definite conclusions can be reached. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This study was supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology [No (2002)]. REFERENCES 1. Chen, X., Kojima S., Borisy G.G., Green K.J P120 catenin associates with kinesin and facilitates the transport of cadherin-catenin complexes to intercellular junctions. J Cell Biol 163: Davis, M.A., Ireton R.C., Reynolds A.B A core function for p120-catenin in cadherin turnover. J Cell Biol 163: Geiger, B., Ayalon, O Cadherins. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8: Grunwald, G.B The structural and functional analysis of cadherin calcium-dependent cell adhesion molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5: Herrenknecht, K., Ozawa, M., Eckerskorn, C., Lottspeich, F., Lenter, M., Kemler, R The uvomorulin-anchorage protein alpha catenin is a vinculin homologue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88: Hirano, S., Kimoto, N., Shimoyama, Y., Hirohashi, S., Takeichi, M Identification of a neural alpha-catenin as a key regulator of cadherin function and multicellular organization. Cell 70: Johnson, K.R., Lewis, J.E., Li, D., Wahl, J., Soler, A.P., Knudsen, K.A., Wheelock, M.J P- and E-cadherin are in separate complexes in cells expressing both cadherins. Exp Cell Res 207: Knudsen, K.A., Wheelock, M.J Plakoglobin, or an 83-kD homologue distinct from beta catenin, interacts with E-cadherin and N-cadherin. J Cell Biol 118: Magee, A.I., Buxton, R.S Transmembrane molecular assemblies regulated by the greater cadherin family. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3: Mizoguchi, A., Nakanishi, H., Kimura, K., Matsubara, K., Ozaki-Kuroda, K., Katata, T., Honda, T., Kiyohara, Y., Heo, K., Higashi, M., Tsutsumi, T., Sonoda, S., Ide, C., Takai, Y Nectin: an adhesion molecule involved in formation of synapses. J Cell Biol 156: Nagafuchi, A., Takeichi, M., Tsukita, S The 102 kd cadherin-associated protein: similarity to vinculin and posttranscriptional regulation of expression. Cell 65: 97
7 Y. SHIBUYA et al Nagafuchi, A., Tsukita, S The loss of the expression of alpha catenin, the 102 kd cadherin associated protein, in central nervous tissues during development. Dev Growth Differ 36: Ozawa, M., Baribault, H., Kemler, R The cytoplasmic domain of the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin associates with three independent proteins structurally related in different species. EMBO J 8: Ozawa, M., Kemler, R Molecular organization of the uvomorulin-catenin complex. J Cell Biol 116: Ozawa, M., Ringwald, M., Kemler, R Uvomorulin-catenin complex formation is regulated by a specific domain in the cytoplasmic region of the cell adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87: Peifer M., Yap A.S Traffic control: p120-catenin acts as a gatekeeper to control the fate of classical cadherins in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 163: Redies, C., Inuzuka, H., Takeichi, M Restricted expression of N- and R-cadherin on neurites of the developing chicken CNS. J Neurosci 12: Redies, C Cadherins and the formation of neural circuitry in the vertebrate CNS. Cell Tissue Res 290: Shibuya, Y., Mizoguchi, A., Takeichi, M., Shimada, K., Ide, C Localization of N-cadherin in the normal and regenerating nerve fibers of the chicken peripheral nervous system. Neuroscience 67: Shibuya, Y., Yasuda, H., Tomatsuri, M., Mizoguchi, A., Takeichi, M., Shimada, K., Ide, C alpha N-catenin expression in the normal and regenerating chick sciatic nerve. J Neurocytol 25: Takeichi, M The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis. Development 102: Takeichi, M Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science 251: Xiao K., Allison D.F., Buckley K.M., Kottke M.D., Vincent P.A., Faundez V., Kowalczyk A.P Cellular levels of p120 catenin function as set point for cadherin expression levels in microvascular endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 163:
Ultrastructural Localization of Alpha E-catenin in the Rat Sciatic Nerve
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 77-84 2006 Ultrastructural Localization of Alpha E-catenin in the Rat Sciatic Nerve MAHO MURATA, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, SACHIKO MUNEMOTO, JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, MASAKI KOBAYASHI,
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 77-84 2006 Ultrastructural Localization of Alpha E-catenin in the Rat Sciatic Nerve MAHO MURATA, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, SACHIKO MUNEMOTO, JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, MASAKI KOBAYASHI,
Expression of Beta-catenin and Integrin-linked Kinase in the Mouse Sciatic Nerve
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 4, pp. E217-E226, 2008 Expression of Beta-catenin and Integrin-linked Kinase in the Mouse Sciatic Nerve JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, MAHO MURATA and TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 4, pp. E217-E226, 2008 Expression of Beta-catenin and Integrin-linked Kinase in the Mouse Sciatic Nerve JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, MAHO MURATA and TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Treatment and Diagnosis of Panner's Disease : A Report
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Treatment and Diagnosis of Panner's Disease : A Report
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Agreement of Rebound Tonometer in Measuring
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Agreement of Rebound Tonometer in Measuring
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Osteochondritis of Hallux Sesamoid Bone
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Osteochondritis of Hallux Sesamoid Bone
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Expression of S-100 Protein and Neuron-Specific
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Expression of S-100 Protein and Neuron-Specific
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Possible Roles of Schwann Cells in Peripheral
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Possible Roles of Schwann Cells in Peripheral
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Establishment of a quantitative evaluation of wrist
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Establishment of a quantitative evaluation of wrist
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI The Effect of Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Instructions
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI The Effect of Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Instructions
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights An integration of color and motion information in visual
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights An integration of color and motion information in visual
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI URL Macroscopic Observations on Human Lower Leg Muscles
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI URL Macroscopic Observations on Human Lower Leg Muscles
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Stress fracture of the olecranon in an
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Stress fracture of the olecranon in an
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Relation of Aortic Distensibility and Pulse
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Relation of Aortic Distensibility and Pulse
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Ultrasound treatment of nonunion of the
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Ultrasound treatment of nonunion of the
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Bilateral Hip Fractures in a Patient with
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Bilateral Hip Fractures in a Patient with
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
The developmental history of a sensory ganglion cell
 (bozza v1, luglio 2016 per VC) The developmental history of a sensory ganglion cell by Brian Freeman, School of Medical Sciences, UNSW (b.freeman@unsw.edu.au) The sensory ganglion cell (e.g., in spinal
(bozza v1, luglio 2016 per VC) The developmental history of a sensory ganglion cell by Brian Freeman, School of Medical Sciences, UNSW (b.freeman@unsw.edu.au) The sensory ganglion cell (e.g., in spinal
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more
 Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Nervous system Nervous system is the most complex system in our body. It is formed by a network of more than 100 million nerve cells (neurons) assisted by many more glial cells. Devoid from connective
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Proximal translation of the radius following
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Proximal translation of the radius following
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Introduction to Nervous Tissue
 Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
NERVOUS TISSUE. 1. Functional units of the nervous system; receive, process, store and transmit information to other neurons, muscle cells or glands.
 NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
NERVOUS TISSUE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Characterize and contrast the structure of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and axons 2. List the classification of synapses and identify the basic structures of a
Nervous Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Nervous Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Plasma Cell Leukemia with Acute Renal Failure
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Plasma Cell Leukemia with Acute Renal Failure
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
8.2. Types of Neurons
 Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Chapter 8 Nervous Tissue The neuron is the functional and the structural unit of the nervous system. It displays two highly developed physiological traits: 1. Irritability - the capacity to generate a
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
PNS and ANS Flashcards
 1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
1. Name several SOMATIC SENSES Light touch (being touched by a feather), heat, cold, vibration, pressure, pain are SOMATIC SENSES. 2. What are proprioceptors; and how is proprioception tested? PROPRIOCEPTORS
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Nervous system The nervous system is responsible for communication between different regions of the body, it is divided into: CNS (central nervous system) = brain + spinal cord
Fig The C.S. of the Spinal Cord A ganglion is a term for a collection of perikarya located outside of the CNS. In certain regions of the spinal
 Chapter 9 Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two components: The CNS - the brain and spinal cord and the PNS - the nerves emanating from the spinal cord and brain that distribute to other
Chapter 9 Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two components: The CNS - the brain and spinal cord and the PNS - the nerves emanating from the spinal cord and brain that distribute to other
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI JaLCDOI URL Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Autonomic Nervous System. Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 14 Autonomic Nervous System Lecture 21 1 Autonomic (Visceral) Nervous System CNS PNS 2 Autonomic Nervous System functions without conscious
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI STUDIES ON THE PERMEATION OF UREA INTO LEAF CELLS :
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI STUDIES ON THE PERMEATION OF UREA INTO LEAF CELLS :
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous system. 1. Neurons :
 Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Nervous system nervous system is composed of billions of cells, the most essential being the nerve cells or neurons. There are estimated to be as many as 100 billion neurons in our nervous system. Two
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Anatomy of a Neuron. Copyright 2000 by BSCS and Videodiscovery, Inc. Permission granted for classroom use. Updated Master 2.
 Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact with Other Neurons through Synapses Master 2.2 Name Date Due Cells of the Nervous System Learning Target: Identify and state the function of the components
Anatomy of a Neuron Master 2.1 Neurons Interact with Other Neurons through Synapses Master 2.2 Name Date Due Cells of the Nervous System Learning Target: Identify and state the function of the components
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Effects of Calcium Phosphate Cement on the Peripheral Nerve Fibers
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 55, No. 4, pp. E98-E105, 2009 Effects of Calcium Phosphate Cement on the Peripheral Nerve Fibers SACHIKO MUNEMOTO, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, MAHO MURATA, JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, NORIKO IKEHATA,
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 55, No. 4, pp. E98-E105, 2009 Effects of Calcium Phosphate Cement on the Peripheral Nerve Fibers SACHIKO MUNEMOTO, YASUYUKI SHIBUYA, MAHO MURATA, JUNICHIRO TAKEUCHI, NORIKO IKEHATA,
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat
 Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
Sheet: microscopic structures of the ns Done by: Rasha Rakan and Nisreen Obiedat Lecture Objectives Classify the types of neurons. Describe the structure of the different parts of neurons. Describe the
LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER
 ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
 C h a p t e r 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing. Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2
 ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
ABSTRACT Neural stem cells and the neurobiology of ageing Chen Siyun 1, Dawe G.S. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, National University of Singapore 10 Kent Ridge Road, Singapore 117546 The
The Nervous System 7PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART A Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Classification of the nervous system. Prof. Dr. Nikolai Lazarov 2
 1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
1 1. Formation and general organization 2. Spinal ganglia 3. Zonal and segmental innervation 4. Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves 5. Ventral rami of the spinal nerves 6. Cervical plexus Classification of
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance
 Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
9.01 Midterm Examination NAME October 27, 2003
 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
10.1: Introduction. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial cells) Dendrites.
 10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
10.1: Introduction Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Cell types in neural tissue: Neurons Neuroglial cells (also known as neuroglia, glia, and glial
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Pearson Education, Inc.
 13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
13 The Nervous System: Neural Tissue Introduction Nervous System Characteristics Controls and adjust the activity of the body Provides swift but brief responses The nervous system includes: Central Nervous
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Abnormally Shaped-Polyclonal Hypergammaglobulinemia
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Abnormally Shaped-Polyclonal Hypergammaglobulinemia
Collin County Community College BIOL Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure
 (3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
(3) Chemical synapse ---structure LM: in silver preparation dark brown color button-liked on the surface of cell body and dendrites called synaptic button LM: synaptic button (3) Chemical synapse ---structure
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
Chapter 9 The Nervous System: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms acetylcholine motor presynaptic action potential nerve
The Nervous System SBI4U
 SBI4U The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS): consists of the brain and spinal cord Acts as the coordinating centre for incoming and outgoing information Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): consists
SBI4U The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS): consists of the brain and spinal cord Acts as the coordinating centre for incoming and outgoing information Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): consists
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Teacher Key. Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body.
 Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Big Idea Different types of neurons compose the nervous tissue that forms the communication system within the body. Introduction to Neurons An individual s survival and reproductive success depends upon
Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet
 The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
The Nervous System Week 7 and 8 Master Worksheet 1. Complete the chart regarding the 3 functions of the nervous system: Sensory input What does it do? Integration Motor output 2. Complete the chart: Component
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
OpenStax-CNX module: m56161 1 Derived copy of Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System * Stephanie Fretham Based on Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
A. Subdivisions of the Nervous System: 1. The two major subdivisions of the nervous system:
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Ch 10 A Ch 10 B CHAPTER 10 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1 BASIC STRUCTURE and FUNCTION Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
