Two-Step Incision for Periarterial Sympathectomy of the Hand
|
|
|
- Bethany Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Two-Step Incision for Periarterial Sympathectomy of the Hand Seung Bae Jeon 1, Hee Chang Ahn 1, Yong Su Ahn 2, Matthew Seung Suk Choi 3 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Hanyang University Seoul Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul; 2 START Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 3 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea Original Article Background Surgical scars on the palmar surface of the hand may lead to functional and also aesthetic and psychological consequences. The objective of this study was to introduce a new incision technique for periarterial sympathectomy of the hand and to compare the results of the new two-step incision technique with those of a Koman incision by using an objective questionnaire. Methods A total of 40 patients (17 men and 23 women) with intractable Raynaud s disease or syndrome underwent surgery in our hospital, conducted by a single surgeon, between January 2008 and January Patients who had undergone extended sympathectomy or vessel graft were excluded. Clinical evaluation of postoperative scars was performed in both groups one year after surgery using the patient and observer scar assessment scale (POSAS) and the Wake Forest University rating scale. Results The total patient score was 8.59 (range, 6 15) in the two-step incision group and 9.62 (range, 7 18) in the Koman incision group. A significant difference was found between the groups in the total PS score (P-value=0.034) but not in the total observer score. Our analysis found no significant difference in preoperative and postoperative Wake Forest University rating scale scores between the two-step and Koman incision groups. The time required for recovery prior to returning to work after surgery was shorter in the two-step incision group, with a mean of days in the two-step incision group and days in the Koman incision group (P= 0.03). Conclusions Compared to the Koman incision, the new two-step incision technique provides better aesthetic results, similar symptom improvement, and a reduction in the recovery time required before returning to work. Furthermore, this incision allows the surgeon to access a wide surgical field and a sufficient exposure of anatomical structures. Keywords Raynaud disease / Sympathectomy Correspondence: Hee Chang Ahn Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Hanyang University Medical Center, 345 Wangsimni-gil, Sungdong-gu, Seoul 04763, Korea Tel: Fax: ahnhc@hanyang.ac.kr We are grateful to Jee Won Shin, medical illustrator, for the illustrations. This article was presented at the Research & Reconstructive Forum on April 3-4, 2014 in Busan, Korea. No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. Received: 13 May 2015 Revised: 28 Aug 2015 Accepted: 24 Sep 2015 pissn: eissn: Arch Plast Surg 2015;42: INTRODUCTION The treatment of Raynaud s symptoms of cold intolerance, pain, and ulceration that are refractory to oral medication is an extremely difficult clinical problem [1]. Historically, cervicothoracic sympathectomy was a common treatment if conservative Copyright 2015 The Korean Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited
2 Jeon SB et al. New incision method in the hand treatment of symptoms was unsuccessful [2]. However, this treatment provided only temporary improvement, and in 1980 Flatt et al. suggested the resection of the periarterial sympathetic fibers and digital nerve branches to the common and proper digital arteries. This technique has provided significant improvement in selected patients [3,4]. However, the associated incisions on the palmar surface of the hand typically lead to redness, pain, edema, tenderness, and aesthetic problems. Surgical scars on the palm may lead to not only functional but also aesthetic and psychological consequences, particularly if they are located in areas of the body that are actively moving and are exposed instead of covered by clothing [5,6]. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize scar formation by using appropriate incision techniques and performing a careful follow-up to check the healing process. Minimal incisions made for aesthetic purposes may lead to insufficient exposure of the operative field. Therefore, we have performed a new incision technique over several recent years in an attempt to obtain a sufficient operative field and improved aesthetic outcomes. The objective of this study was to introduce a new incision technique for periarterial sympathectomy of the hand and to compare the results of the new two-step incision technique with those of the Koman incision by using objective questionnaire. We hypothesized that periarterial sympathectomy of the palm performed with a two-step incision would result in a more aesthetically acceptable and functional scar, reduced postoperative pain, and earlier mobilization and discharge from the hospital. METHODS A total of 40 patients (17 men and 23 women) with intractable Raynaud s disease or syndrome underwent surgery in our hospital, conducted by a single surgeon, between January 2008 and January A retrospective study of periarterial sympathectomy, based on chart review, was designed and conducted. All patients had a diagnosis of Raynaud s disease or syndrome by a rheumatologist. They suffered from pain, ulcers, or gangrene in the affected digits and were unresponsive to pharmacologic or other conservative therapies. Pharmacologic interventions include alpha-blocking agents, beta-blocking agents, and calcium channel-blocking agents. We evaluated preoperative arteriography to assist with the decision for arterial reconstruction, and if possible, revascularization procedures were also performed. In all cases in our study, angiography showed multifocal arterial pathologic changes. A consecutive series of 40 Raynaud s patients managed with periarterial sympathectomy was comprised of patients receiving either a two-step incision or a Koman incision on the palm, as well as ulnar and radial incisions on the wrist. Patients who had undergone extended sympathectomy or vessel graft were excluded. The two-step incision technique was used in 28 selected patients between January 2008 and January The twelve patients who had a Koman incision served as the control group for comparison. All patients were admitted the day before surgery, which is the present practice at our institution. We analyzed the period that elapsed before return to work in order to evaluate the functional outcome. Incision methods In the Koman incision group, the incision was made in the middle of the palm as a single transverse line (Fig. 1A). In the twostep incision group, the incision consisted of two separate incisions in the proximal and distal palmar creases. The distal incision was made on the distal palmar crease from the proximal continuation of the center of the long finger to that of the little finger. The proximal incision was made on the proximal palmar crease from the proximal continuation of the radial side of the index finger to that of the ring finger. These incision lines can be modified to expose specific structures such as narrowed arteries (Fig. 1B). In all cases, longitudinal incisions were also made at the volar wrist over the radial and ulnar arteries. A straight skin incision over the ulnar artery, aligned with the crest of the ulna, was made from the proximal wrist crease to 5 cm more proximally (Fig. 1). Next, the fascia overlying the arteries was incised and flexor carpi ulnaris was retracted laterally and flexor digitorum superficialis was retracted medially. Another skin incision for the radial artery, aligned with the edge of the brachioradialis muscle, was extended from the proximal wrist crease to 5 cm Fig. 1. Incision method of periarterial sympathectomy (A) Incision method for periarterial sympathectomy in the hand. Koman incision (red), ulnar and radial incision (blue). (B) Incision method for periarterial sympathectomy in the hand. Two-step incision (red), ulnar and radial incision (blue). A B 762
3 Vol. 42 / No. 6 / November 2015 more proximally. Next, the fascia overlying the arteries was incised and brachioradialis was retracted laterally and flexor carpi radialis was retracted medially. Postoperative management Dressings were applied to minimize scar formation. Steri-strips were applied postoperatively along the sutured incision line after the application of antibiotic powder. Each strip was overlapped and attached without ointment so it could reinforce the subcuticular and simple interrupted sutures. After the stitches were removed, placement of strips was continued for six months. Patient and observer scar assessment scale Clinical evaluation of postoperative scars was performed in both groups one year after surgery and postoperative management with self-drying silicone gel and adhesive strips using the patient and observer scar assessment scale (POSAS). The POSAS consists of two subscales: the patient scale (PS) and the observer scale (OS). The PS was compiled by the patient, who rated scar pain, itch, color, stiffness, thickness, and surface. All items were evaluated on a numerical rating scale ranging from 1 to 10 (with 10 indicating the worst imaginable scar or sensation). The observer completed the OS using the same scale and rated scar vascularity, pigmentation, thickness, relief, pliability, and surface area (Table 1). The OS was evaluated based on clinical experience and on references in the literature such as the Vancouver scale. The total PS and OS scores were obtained by adding the scores of each of the six items (range, 6 60), with higher scores indicating the worst imaginable scar. Both the observer and the patient finally gave their overall opinion on the appearance of the scar, assigning a score ranging from 1 to 10 [7,8]. Wake Forest University rating scale Symptoms such as pain, numbness, and cold intolerance were assessed in each patient before and after undergoing periarterial sympathectomy using the Wake Forest University rating scale (0, none; 1, mild; 2, moderate; 3, severe), with a higher score indicating a greater intensity of symptoms. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using PASW ver (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the POSAS and Wake Forest University rating scale scores between the two groups. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for comparing preoperative and postoperative Wake Forest University rating scale scores in each group. An independent t-test was used to compare the periods of hospitalization and recovery before return to work between the two groups. A P-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Our patients were aged between 27 and 74 years, with a mean age of 53.1 years. The majority of them were in their sixth and seventh decades (33% and 30%, respectively). 42% of patients were male. The number of smokers was five (three in the twostep incision group and two in the Koman incision group). Table 1. The patient and observer scar assessment scale A. Patient scale Normal skin Worst scar imaginable Has the scar been painful the past few weeks? Has the scar been itching the past few weeks? Is the scar color different from the color of your normal skin at present? Is the stiffness of the scar different from your normal skin at present? Is the thickness of the scar different from your normal skin at present? Is the scar more irregular than your normal skin at present? Normal skin Worst scar imaginable Overall opinion B. Observer scale Normal skin Worst scar imaginable Vascularity Pigmentation Thickness Relief Pliability Surface area Normal skin Worst scar imaginable Overall opinion
4 Jeon SB et al. New incision method in the hand Patient and observer scar assessment scale The POSAS scores were lower on almost all of the items in the two-step incision group than in the Koman incision group. Of note, the total PS score was 8.59 (range, 6 15) in the two-step incision group, whereas it was 9.62 (range, 7 18) in the Koman incision group. The total OS score was (range, 7 20) in the two-step incision group and (range, 8 20) in the Koman incision group. A significant difference was found between the groups in total PS score (P = 0.034), but not in total OS score (P = 0.419) (Table 2). There were significant differences in PS scores on the parameters of pain (P = 0.028), color (P = 0.045), and overall opinion (P = 0.001) (Table 3) and in OS score in overall opinion (P = 0.003) (Table 4). The other parameters were not significantly different between groups. Table 2. Total POSAS scores in the Koman and two-step incision groups Scale Koman incision Two-step incision P-value Patient scale 9.62 (7 18) 8.59 (6 15) Observer scale (8 20) (7 20) Values are presented as the mean (range). POSAS, patient and observer scar assessment scale. Table 3. Total patient scale scores Variable Koman incision Two-step incision P-value Pain 2.34 (1 5) 1.31 (1 3) Itch 1.29 (1 4) 1.25 (1 3) Color 2.78 (1 7) 1.9 (1 4) Stiffness 1.56 (1 5) 1.49 (1 5) Thickness 1.34 (1 5) 1.35 (1 5) Surface 1.31 (1 4) 1.29 (1 4) Overall opinion 3.08 (1 7) 2.11 (1 4) Values are presented as the mean (range). Wake Forest University rating scale In the Koman incision group, evaluation of patient symptoms with the Wake Forest University rating scale indicated that patients experienced reduced pain (P < 0.001) and numbness (P = 0.038) after periarterial sympathectomy surgery. Cold intolerance, however, was not reduced significantly after the operation. In the two-step incision group, patients experienced reduced pain (P < 0.001) and numbness (P = 0.028) after the surgery, but cold intolerance was not significantly reduced. The preoperative scores under the Wake Forest University rating scale showed that the patients reported pain at a mean level of 2.41 in the Koman incision group and 2.27 in the two-step incision group. The mean numbness score was 1.75 in the Koman incision group and 1.82 in the two-step incision group, and the mean cold intolerance score was 2.23 in the Koman incision and 2.43 in the two-step incision group. Our analysis found no significant difference between the preoperative scores in the Koman and two-step incision groups. One year after sympathectomy, the Wake Forest University rating scale scores demonstrated that the patients reported pain at a mean level of 0.67 in the Koman incision group and 0.56 in the two-step incision group. The mean numbness score was 0.89 in the Koman incision group and 0.71 in the two-step incision group, and the mean cold intolerance score was 1.54 in the Koman incision group and 1.67 in the two-step incision group. There was no significant difference in postoperative scores between the Koman and two-step incision groups (Fig. 2). Period of hospitalization and return to work The average postoperative hospitalization period was days in the Koman incision group and days in the two- Fig. 2. Wake Forest University rating scale The Wake Forest University rating scale before and after the operation in both groups. Koman incision group (blue bars) and two-step incision group (orange bars). Pre-OP., preoperative; Post-OP., postoperative Koman incision Two-step incision Rating scale 3+= severe 2+= moderate 1+= mild 0= none Table 4. Total observer scale scores Variable Koman incision Two-step incision P-value Vascularity 1.34 (1 4) 1.44 (1 4) Pigmentation 4.23 (3 7) 4.14 (2 6) Thickness 1.27 (1 5) 1.26 (1 5) Relief 2.23 (1 6) 2.15 (1 6) Pliability 1.77 (1 4) 1.80 (1 5) Surface area 1 (1 1) 1 (1 1) Overall opinion 2.14 (2 5) 1.93 (1 4) Values are presented as the mean (range). Severity scale Pre-Op. Post-Op. Pre-Op. Post-Op. Pre-Op. Post-Op. Pain Numbness Cold intolerance 764
5 Vol. 42 / No. 6 / November 2015 step incision group, and these periods were not significantly different. The period of recovery prior to returning to work was different for the two groups, with a mean of days in the Koman incision group and days in the two-step incision group (P = 0.03) (Table 5). Case 1 A 64-year-old woman had been suffering from skin necrosis on her right second finger for several months. The patient had a history of Raynaud s syndrome, scleroderma, dermatomyositis and pulmonary fibrosis. Angiography showed multifocal stenosis over all proper digital arteries in the right hand. Conservative treatment was attempted without success. Periarterial sympathectomy was performed over the common digital arteries using the Koman incision and over the ulnar and radial arteries. Digital artery reconstruction with the superficial vein in the wrist was performed over the ulnar side of the right second finger. Cyanosis improved and the pain decreased post-surgery. Capillary refilling also improved. The patient was discharged on the Table 5. Mean duration for recovery before return to work in Koman incision and two-step incision groups Variable Koman incision Two-step incision P-value Period of hospitalization (2.34) (1.89) Period of recovery prior to (5.64) (4.68) return to work Values are presented as the mean (standard deviation). 13th postoperative day. The patient was treated according to the above-mentioned wound and scar care protocol for six months. The wound healed well but a clearly evident transverse scar was formed in the palm (Fig. 3). Case 2 A 36-year-old woman had been suffering from skin necrosis of the second and third digits for several years. The patient also suffered from sensitivity to cyanosis in cold temperatures. Periarterial sympathectomy was performed over the common digital arteries using the two-step incision and ulnar and radial incisions. Postoperatively, her symptoms were improved. The patient was discharged on the 11th postoperative day and treated according to the wound care protocol for six months. After one year, the scar was almost invisible and folded with the existing palmar crease (Fig. 4). DISCUSSION Digital ischemia with subsequent gangrene and tissue necrosis caused by Raynaud s syndrome remains a difficult treatment problem for rheumatologists and hand surgeons [9,10]. Although several pharmacologic agents have been used successfully to improve symptoms, some patients remain refractory to medical management [11,12]. During the past several decades, periarterial sympathectomy has been used as a treatment option for improving the quality of life for patients suffering from severe Raynaud syndrome [13,14]. Postoperative pain and scars Fig. 3. Koman incision method with ulnar and radial incision (A) Preoperative design by the Koman incision method on the palm and ulnar and radial incision on the wrist. (B) Postoperative results after three days. (C) Postoperative results after one year. A B C 765
6 Jeon SB et al. New incision method in the hand Fig. 4. Two-step incision method with ulnar and radial incision (A) Preoperative design by the two-step incision method on the palm and ulnar and radial incision on the wrist. (B) Postoperative results after three days. (C) Postoperative results after one year. A B C are known complications of the Koman incision for periarterial sympathectomy in the palm. These incisions leave a scar in the middle of the palm, an area subject to crease formation when making a fist. In some cases, an extra incision is required for visualizing the proximal common digital artery or proper digital artery. To the best of our knowledge, this retrospective study is the first to test whether periarterial sympathectomy in the palm performed through a two-step incision has any benefits over the Koman incision technique. To reduce confounding variables, a single surgeon performed all aspects of the procedure, using the same operative techniques and the same protocol for wound dressing and scar management in all patients. This is important, because methods of dressing and scar management significantly affect scar formation [7]. Compared with the Koman incision method, our method of incision on the palmar crease offers the following advantages. First, the two-step incision conceals the scar by being placed at the proximal and distal palmar crease. Traditional incision inevitably creates a scar that is visually distinct from the palmar crease. Second, our method involves two separate incisions, which allows more extensive exposure of anatomical structures than the Koman incision, especially of the superficial palmar arch and common digital arteries. Third, the two separated curved incisions disperse the vector of the scar in all directions, which can reduce its impact on the range of motion of the finger. Thus, as well as palmar spreading, the post-surgical outcome results in increased function and less pain when patients make a fist and unfold the palm. As there is therefore very little effect of hand movement on wound healing, the stitches can be removed early and patients can mobilize and return to work more quickly. In this study, wrist incision for ulnar and radial artery commenced from, and skin was preserved distal to, the proximal wrist crease. This was intended to reduce scar contracture and web formation in the wrist, and it did not interfere with the operative field. Although reduced pain is one of the benefits that have been cited for this surgical approach, none of the previously reported studies have directly measured pain as an outcome. For this reason, our two-step incision was objectively assessed using several parameters, including pain. The patient and observer scar assessment scale is reported in the literature as a verified tool for the evaluation of linear scars [15,16]. The incision method for the wrist does not differ between the two-step and Koman incision methods. The damaging effect of cigarette smoking on digital perfusion and wound healing has been reported in several studies [17,18]. Despite active counseling, five of 40 patients continued to smoke during the follow-up period in the present study (three in the two-step incision group and two in the Koman incision group). Three of these five patients had a healing period for a digital ulcer of more than six months duration (two in the twostep incision group and one in the Koman incision group). Two of these five patients had active ulcers at follow-up (one in each incision group). These results suggest a poor long-term out- 766
7 Vol. 42 / No. 6 / November 2015 come for patients who continue to smoke. We strongly encourage smoking cessation but will perform periarterial sympathectomy in patients who continue to smoke because we consider it to be a salvage procedure. The incidence of a single transverse palmar crease is 7% 10% in the general population [19]. Because this would be a confounding factor in our analysis, patients with a single transverse palmar crease were not included in this study. In these cases, a Koman incision was performed on the palmar crease, which was not effectively different to the procedure for a two-step incision, which is also performed on the palmar crease, and so it had a similar effect on scar formation. In the present study, patients in both groups reported decreased symptoms, most significantly in the area of pain and numbness. These changes were associated with significant improvement in digital micro-vascular perfusion, resulting in a resolution of ischemia. However, cold intolerance did not improve significantly in either group. The fact that cold intolerance, as assessed by the Wake Forest University rating scale, did not change after periarterial sympathectomy is not surprising when considering the unchanged total blood flow to the digits. Johnston et al. reported that cold intolerance persisted in spite of adequate sympathetic denervation [20]. This indicates that nutritional blood flow and cutaneous perfusion are not enough to improve cold intolerance following periarterial sympathectomy. An additional vessel graft could perhaps improve cold intolerance, although additional studies would be necessary to determine this. The postoperative outcomes in the Koman incision group and the two-step incision group were similar. We found that most patients wounds recovered well and symptoms subsided. Only two men (one in each incision group) reported no symptom reduction and continued to experience digital ulcers and substantial pain. None of the patients suffered from major complications. Taken together, these observations indicate that the twostep incision could replace the Koman incision method. Using the new incision technique, the scar at the palm was nearly invisible, being well integrated into the natural palmar crease at one year after surgery. Both patients and surgeons were more satisfied with the cosmetic appearance of the palm after wound healing with the two-step incision method than with the Koman incision method. In our experience, this new approach provides not only a more natural appearance, but also greater functional improvement. Furthermore, it results in sufficient exposure of anatomical structures and provides a wide surgical field. REFERENCES 1. Koman LA, Urbaniak JR. Ulnar artery insufficiency: a guide to treatment. J Hand Surg Am 1981;6: Miller LM, Morgan RF. Vasospastic disorders: etiology recognition, and treatment. Hand Clin 1993;9: Jones NF. Acute and chronic ischemia of the hand: pathophysiology, treatment, and prognosis. J Hand Surg Am 1991;16: Wilgis EF. Evaluation and treatment of chronic digital ischemia. Ann Surg 1981;193: Bruner JM. Optimum skin incisions for the surgical relief of stenosing tenosynovitis in the hand. Plast Reconstr Surg 1966;38: Bruner JM. The zig-zag volar-digital incision for flexor-tendon surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 1967;40: Bianchi FA, Roccia F, Fiorini P, et al. Use of Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale for evaluation of facial scars treated with self-drying silicone gel. J Craniofac Surg 2010; 21: Draaijers LJ, Tempelman FR, Botman YA, et al. The patient and observer scar assessment scale: a reliable and feasible tool for scar evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004;113: Drake DB, Kesler RW, Morgan RF. Digital sympathectomy for refractory Raynaud s phenomenon in an adolescent. J Rheumatol 1992;19: Barral X, Favre JP, Gournier JP, et al. Late results of palmar arch bypass in the treatment of digital trophic disorders. Ann Vasc Surg 1992;6: Ward WA, Van Moore A. Management of finger ulcers in scleroderma. J Hand Surg Am 1995;20: Landry GJ, Edwards JM, Porter JM. Current management of Raynaud s syndrome. Adv Surg 1996;30: Balogh B, Mayer W, Vesely M, et al. Adventitial stripping of the radial and ulnar arteries in Raynaud s disease. J Hand Surg Am 2002;27: Ortensi A, Salsano F, Trinchi S, et al. Microsurgical distal sympathectomy in chronic vasospastic syndromes of the hand. Int Surg 2005;90: van de Kar AL, Corion LU, Smeulders MJ, et al. Reliable and feasible evaluation of linear scars by the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale. Plast Reconstr Surg 2005;116: Durani P, McGrouther DA, Ferguson MW. Current scales for assessing human scarring: a review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2009;62: Fulcher SM, Koman LA, Smith BP, et al. The effect of trans- 767
8 Jeon SB et al. New incision method in the hand dermal nicotine on digital perfusion in reformed habitual smokers. J Hand Surg Am 1998;23: Morecraft R, Blair WF, Brown TD, et al. Acute effects of smoking on digital artery blood flow in humans. J Hand Surg Am 1994;19: Smallpeice PADV. The single transverse palmar crease in infants and children. Dev Med Child Neurol 1963;5: Johnston EN, Summerly R, Birnstingl M. Prognosis in raynaud s phenomenon after sympathectomy. Br Med J 1965;1:
Analysis of Frequency of Use of Different Scar Assessment Scales Based on the Scar Condition and Treatment Method
 Analysis of Frequency of Use of Different Scar Assessment Scales Based on the Scar Condition and Treatment Method Seong Hwan Bae, Yong Chan Bae Department of Plastic and Reconstructive, Pusan National
Analysis of Frequency of Use of Different Scar Assessment Scales Based on the Scar Condition and Treatment Method Seong Hwan Bae, Yong Chan Bae Department of Plastic and Reconstructive, Pusan National
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
The Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale: A Reliable and Feasible Tool for Scar Evaluation
 The Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale: A Reliable and Feasible Tool for Scar Evaluation Lieneke J. Draaijers, M.D., Fenike R. H. Tempelman, M.D., Yvonne A. M. Botman, M.D., Wim E. Tuinebreijer,
The Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale: A Reliable and Feasible Tool for Scar Evaluation Lieneke J. Draaijers, M.D., Fenike R. H. Tempelman, M.D., Yvonne A. M. Botman, M.D., Wim E. Tuinebreijer,
Vascular Disorders of the Hand Self-Assessment. Hand Vascular Disorders
 Vascular Disorders of the Hand Self-Assessment 1. The patency rate of repairing a radial artery laceration with an intact palmar arch using modern microsurgical techniques is: A. 20% B. 40% C. 60% D. 80%
Vascular Disorders of the Hand Self-Assessment 1. The patency rate of repairing a radial artery laceration with an intact palmar arch using modern microsurgical techniques is: A. 20% B. 40% C. 60% D. 80%
A Pilot Study to Investigate the Efficacy of Tobramycin Dexamethasone Ointment in Promoting Wound Healing
 Dermatol Ther (2012) 2:12 DOI 10.1007/s13555-012-0012-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Pilot Study to Investigate the Efficacy of Tobramycin Dexamethasone Ointment in Promoting Wound Healing Rachel Andrew Gwendolyn
Dermatol Ther (2012) 2:12 DOI 10.1007/s13555-012-0012-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Pilot Study to Investigate the Efficacy of Tobramycin Dexamethasone Ointment in Promoting Wound Healing Rachel Andrew Gwendolyn
Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap
 Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap June Seok Choi 1, Yong Chan Bae 1,2, Soo Bong Nam 1, Seong Hwan Bae 1, Geon Woo Kim 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan
Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap June Seok Choi 1, Yong Chan Bae 1,2, Soo Bong Nam 1, Seong Hwan Bae 1, Geon Woo Kim 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan
A new classification system of nasal contractures
 Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Original Article J Cosmet Med 2017;1(2):106-111 https://doi.org/10.25056/jcm.2017.1.2.106 pissn 2508-8831, eissn 2586-0585 A new classification system of nasal contractures Geunuck Chang 1, Donghak Jung
Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair
 Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger Flaps and Vigorous Postoperative Exercises
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects
 Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects Durga Karki, A. K. Singh Post Graduate Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article The distally-based island ulnar artery perforator flap for wrist defects Durga Karki, A. K. Singh Post Graduate Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Impact of Disturbed Wound Healing after Surgery on the Prognosis of Marjolin s Ulcer
 Impact of Disturbed Wound Healing after Surgery on the Prognosis of Marjolin s Ulcer Jae Yeon Choi, Yong Chan Bae, Su Bong Nam, Seong Hwan Bae Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan National
Impact of Disturbed Wound Healing after Surgery on the Prognosis of Marjolin s Ulcer Jae Yeon Choi, Yong Chan Bae, Su Bong Nam, Seong Hwan Bae Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan National
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features
 Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
What s New in Fingertip Injuries. Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City
 What s New in Fingertip Injuries Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City Goals of Treatment Durable Sensate Aesthetic Preserve Length Preserve Mobility Goals of Treatment Pain and Worker s Compensation are
What s New in Fingertip Injuries Gordon A. Brody, MD SOAR Redwood City Goals of Treatment Durable Sensate Aesthetic Preserve Length Preserve Mobility Goals of Treatment Pain and Worker s Compensation are
Interesting Case Series. Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects
 Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.181 The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.181 The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
Comparison between Intramedullary Nailing and Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone
 Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
The Surgical Release of Dupuytren s Contracture Using Multiple Transverse Incisions
 The Surgical Release of Dupuytren s Contracture Using Multiple Transverse Incisions Hyunjic Lee 1, Surak Eo 1, Sanghun Cho 1, Neil F. Jones 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dongguk
The Surgical Release of Dupuytren s Contracture Using Multiple Transverse Incisions Hyunjic Lee 1, Surak Eo 1, Sanghun Cho 1, Neil F. Jones 2 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dongguk
Interesting Case Series. Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female
 Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
Chapter 39. Volar surface incisions
 Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Disclosure. Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din. I do not have any potential conflict of interest
 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Hesham Aly Sharaf El-Din I do not have any potential conflict of interest Introduction 5% of patients with upper limb AVF develop ipsilateral hand ischemia, recently termed
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Syndactyly. What is syndactyly? Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
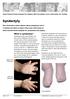 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Syndactyly This information sheet explains about syndactyly, how it is treated and what to expect when your child
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release
 Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Optimizing VAP scars after childhood cancer treatment de Bruijn, C. M. A.; Hoff, Fieke; Bruggeman-Westermann, M. M.; Terra, Jorrit; van Dijk, T. H.; de Bont, Evelina; Peek, A. M.
University of Groningen Optimizing VAP scars after childhood cancer treatment de Bruijn, C. M. A.; Hoff, Fieke; Bruggeman-Westermann, M. M.; Terra, Jorrit; van Dijk, T. H.; de Bont, Evelina; Peek, A. M.
Interesting Case Series. Dupuytren s Contracture
 Interesting Case Series Dupuytren s Contracture Aditya Sood, MD, Angie Paik, BA, and Edward Lee, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, Newark, NJ Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series Dupuytren s Contracture Aditya Sood, MD, Angie Paik, BA, and Edward Lee, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, Newark, NJ Correspondence:
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the Little Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery
 Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
Integra. SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Emile N. Brown, MD, and Scott D. Lifchez, MD
 Flexor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture After Volar Plating of a Distal Radius Fracture: Pronator Quadratus Plate Coverage May Not Adequately Protect Tendons Emile N. Brown, MD, and Scott D. Lifchez, MD
Flexor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture After Volar Plating of a Distal Radius Fracture: Pronator Quadratus Plate Coverage May Not Adequately Protect Tendons Emile N. Brown, MD, and Scott D. Lifchez, MD
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Failed Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon Transfer for Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture after Distal Radial Fracture
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
Boonlawat Homvises MD* * Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat University, Pathumthani, Thailand
 A Randomized Trial between Different Suture Materials (Polydioxanone vs. Poliglecaprone 25) and Different Suturing Techniques (Running Subcuticular Suture Alone vs. with Running Horizontal Mattress) in
A Randomized Trial between Different Suture Materials (Polydioxanone vs. Poliglecaprone 25) and Different Suturing Techniques (Running Subcuticular Suture Alone vs. with Running Horizontal Mattress) in
Trigger Finger Release
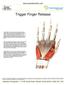 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease
 Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease Hand Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with Dupuytren s disease and who are considering surgical
Surgical treatment for Dupuytren s disease Hand Surgery Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with Dupuytren s disease and who are considering surgical
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials
 Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials Jae Jun Lee, Hyoung Joon Park, Hyun Gon Choi, Dong Hyeok Shin, Ki Il Uhm
Open Reduction of Proximal Interphalangeal Fracture-Dislocation through a Midlateral Incision Using Absorbable Suture Materials Jae Jun Lee, Hyoung Joon Park, Hyun Gon Choi, Dong Hyeok Shin, Ki Il Uhm
Dupuytrens disease. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Dupuytrens disease Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Dupuytrens Disease Dupuytren s disease is a thickening of the tissue in the palm of the hand which may result in progressive flexion contractures
Dupuytrens disease Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Dupuytrens Disease Dupuytren s disease is a thickening of the tissue in the palm of the hand which may result in progressive flexion contractures
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
미세수술을통하여수지신경을압박하는혈관종을성공적으로제거한증례보고. Microscopic Decompression of Digital Nerve Surrounded by Hemangioma: A Case Report
 Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):301-305. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.301 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 미세수술을통하여수지신경을압박하는혈관종을성공적으로제거한증례보고 고준걸ㆍ김준혁ㆍ나은영ㆍ이준용ㆍ유결ㆍ백상운
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(4):301-305. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.4.301 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 미세수술을통하여수지신경을압박하는혈관종을성공적으로제거한증례보고 고준걸ㆍ김준혁ㆍ나은영ㆍ이준용ㆍ유결ㆍ백상운
The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite grafts
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (1995), 48. 396-400 1995 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons BRITISH JOURNAL OF / PLASTIC SURGERY I Repair of complete syndactyly by tissue expansion and composite
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation
 Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation 7 th Congress of the Baltic Association of Rehabilitation Tallinn, Estonia September 2010 R. Scott Ward, PT, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Physical Therapy
Current Concepts in Burn Rehabilitation 7 th Congress of the Baltic Association of Rehabilitation Tallinn, Estonia September 2010 R. Scott Ward, PT, PhD Professor and Chair Department of Physical Therapy
Compartment Syndrome
 Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Compartment Syndrome Chapter 34 Compartment Syndrome Introduction Compartment syndrome may occur with an injury to any fascial compartment. The fascial defect caused by the injury may not be adequate to
Role and Rationale for Extended Periarterial Sympathectomy in the Management of Severe Raynaud Syndrome: Techniques and Results
 1 Role and Rationale for Extended Periarterial Sympathectomy in the Management of Severe Raynaud Syndrome: Techniques and Results Vascular Disorders Hand Clinics Wyndell H. Merritt, MD, FACS Synopsis There
1 Role and Rationale for Extended Periarterial Sympathectomy in the Management of Severe Raynaud Syndrome: Techniques and Results Vascular Disorders Hand Clinics Wyndell H. Merritt, MD, FACS Synopsis There
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Breast augmentation (enlargement)
 Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure that uses breast implants to enhance shape or increase the size of a woman s breast after body changes such as pregnancy, weight loss or from natural ageing.
Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure that uses breast implants to enhance shape or increase the size of a woman s breast after body changes such as pregnancy, weight loss or from natural ageing.
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist. Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury
 Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Flexor Tenorrhaphy Using Absorbable Suture Materials
 Flexor Tenorrhaphy Using Absorbable Suture Materials Hyung Joo Kang, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Sae Hwi Ki, Si Young Roh, Jae Won Yang Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Kwang-Myung Sung-Ae
Flexor Tenorrhaphy Using Absorbable Suture Materials Hyung Joo Kang, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Sae Hwi Ki, Si Young Roh, Jae Won Yang Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Kwang-Myung Sung-Ae
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx
 The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx Shao-Liang Chen, M.D., Trong-Duo Chou, M.D., Shyi-Gen Chen, M.D., Tian-Yeu Cheng, M.D., Tim-Mo Chen, M.D., and Hsian-Jenn Wang,
The Boomerang Flap in Managing Injuries of the Dorsum of the Distal Phalanx Shao-Liang Chen, M.D., Trong-Duo Chou, M.D., Shyi-Gen Chen, M.D., Tian-Yeu Cheng, M.D., Tim-Mo Chen, M.D., and Hsian-Jenn Wang,
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Sudqi A. Hamed 1, Falah Z. Harfoushi 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate prospectively the
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Sudqi A. Hamed 1, Falah Z. Harfoushi 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate prospectively the
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
A Patient's Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Traumatic Ulnar Artery Aneurysms In Children: A Case Report And Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 1 Number 2 Traumatic Ulnar Artery Aneurysms In Children: A Case Report And Review A Mason, H Fochler, B Micheal Citation A Mason, H Fochler, B Micheal..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 1 Number 2 Traumatic Ulnar Artery Aneurysms In Children: A Case Report And Review A Mason, H Fochler, B Micheal Citation A Mason, H Fochler, B Micheal..
Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report
 220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
220 Nasal septal reconstruction Case Report Fibular Bone Graft for Nasal Septal Reconstruction: A Case Report Yakup Cil1* Diyarbakır Military Hospital, Department of Plastic Surgery 21000 Diyarbakır, Turkey
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Intratendinous Ganglion of the Extensor Digitorum Tendon
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
T HE carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a clinical
 J Neurosurg 62:352-356, 1985 Complications of carpal tunnel surgery DEAN S. LOUIS, M.D., THOMAS L. GREENE, M.D., AND RAYMOND C. NOELLERT, Orthopaedic Hand Service, Department of Surgery, University of
J Neurosurg 62:352-356, 1985 Complications of carpal tunnel surgery DEAN S. LOUIS, M.D., THOMAS L. GREENE, M.D., AND RAYMOND C. NOELLERT, Orthopaedic Hand Service, Department of Surgery, University of
Digital Artery Perforator Adiposal Flaps to Cover Scarred Digital Nerves: a Preliminary Report
 Digital Artery Perforator Adiposal Flaps to Cover Scarred Digital Nerves: a Preliminary Report *Kiyohito Takamatsu 2) M.D., Ema Onode 1) M.D., Shouichirou Ooyama 1) M.D., Kousuke Shintani 1) M.D., Takuya
Digital Artery Perforator Adiposal Flaps to Cover Scarred Digital Nerves: a Preliminary Report *Kiyohito Takamatsu 2) M.D., Ema Onode 1) M.D., Shouichirou Ooyama 1) M.D., Kousuke Shintani 1) M.D., Takuya
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
DELSYS. Purpose. Hardware Concepts. Software Concepts. Technical Note 101: EMG Sensor Placement
 Technical Note 101: EMG Sensor Placement Purpose This technical note addresses proper placement technique for Delsys Surface EMG Sensors. The technique is demonstrated through an experiment in which EMG
Technical Note 101: EMG Sensor Placement Purpose This technical note addresses proper placement technique for Delsys Surface EMG Sensors. The technique is demonstrated through an experiment in which EMG
Comparison of the results of open
 1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System. SafeViewTM Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System SafeViewTM Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System Fully Disposable and Sterile Packaged Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System SafeView is packaged sterile with
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System SafeViewTM Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System Fully Disposable and Sterile Packaged Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release System SafeView is packaged sterile with
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care. Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017
 Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING)
 PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING) This is a guide for people who are considering having a nose re-shaping (Rhinoplasty) operation. We advise that you talk to a plastic
PROCEDURE FACT SHEET PLASTIC SURGERY RHINOPLASTY (NOSE RE-SHAPING) This is a guide for people who are considering having a nose re-shaping (Rhinoplasty) operation. We advise that you talk to a plastic
What is involved with breast reduction surgery
 1 Breast reduction is an operation in which your breasts are remodeled to reduce their size whilst maintaining an aesthetic breast shape. At the same time it is possible to lift the position of the nipple
1 Breast reduction is an operation in which your breasts are remodeled to reduce their size whilst maintaining an aesthetic breast shape. At the same time it is possible to lift the position of the nipple
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Manual Kirschner-Wire Insertion through the Soft Tissue for Finger Immobilization after Scar Contracture Release
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):8-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.8 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Manual Kirschner-Wire
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):8-14. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.8 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Manual Kirschner-Wire
