UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
|
|
|
- Joshua Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb, Professor of Neurophysiology No.4 The pain and temperature system: Pain: Pain is a protective mechanism for the body, it is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual and potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. It is important that pain perception and reaction to pain is separated, this is particularly important for clinical pain because suffering is more heavily influenced by the reaction to pain than by actual pain intensity. Attention, motivation, past experience, and the meaning of the situation can influence the individual s reaction to pain. Thus pain involves anatomic structures, physiologic behaviors, and psychological, social, cultural, and cognitive factors. Some individuals are born insensitive to pain (congenital analgesia). TEST FOR PAIN SENSATION Peripheral receptors The pain and temperature system does not have specialized receptor organs. Instead, it uses free nerve endings throughout skin, muscle, bone, and connective tissue to perceive changes in temperature and pain peptides. Although pain will result from damage to a free nerve ending, in reality most pain is a result of substances released by damaged tissues: prostaglandins, histamine, and substance P. The free nerve ending has receptors for these substances and lets you know when tissue has been damaged. Axon diameters: Pain (and temperature) includes the third and fourth axon groups, Aδ and C fibers. There are two subtypes of pain. "Fast pain", carried by the Aδ fibers, is the instantaneous pain that makes your arm jerk back before you even realized you were burned. It is sharp and piercing and over quickly. "Slow pain" is carried by C fibers. C fibers are not only small, they are unmyelinated (the only sensory axons without myelin), so their 1
2 conduction velocity is quite slow. Slow pain is primarily mediated by those tissue-damage peptides listed above, and can go on indefinitely. It is distressing, it can be dull and aching, and it does not trigger withdrawal reflexes like the fast pain. A perfect example of slow pain is when you stub your toe on the coffee table. You feel the jolt of impact (proprioception and Pacinian corpuscles), and you have approximately a heartbeat to think, "This is really going to hurt." That heartbeat is the C-fiber travel time from your toe to your brain. When the signal hits, the pain is severe and lasts for quite a while. It is, however, a nice demonstration of the relative conduction velocities of Aά and C fibers. Types of Pain: 1. Fast pain: felt within 0.1 sec. after pain stimulus is applied. It's described as sharp, pricking, acute, electrical...etc it is localized to skin & not felt in most of the deeper structures. Receptors involved in fast pain are Free nerve endings. Stimulus type is either Mechanical or thermal. Transmitted in the peripheral nerves to the spinal cord by type Aδ fibers at velocities of 6-30 m / sec. Fast pain can be localized better than slow pain & when tactile receptors that excite the DC-ML system are also stimulated the localization can be nearly exact. NT involved in fast pain pathway is Glutamate. 2. Slow Pain: Felt after 1 sec. & increase slowly over many seconds or minutes. It is described as slow, burning, aching, throbbing, nauseous, chronic pain...it is localized to the skin & almost any deeper tissue or organ. Receptors involved in slow pain are Free nerve endings. Stimulus types are mechanical, thermal & chemical (like Bradykinin, Serotonin, Histamine, K +, acids, Acetylcholine & proteolytic enzymes). Slow pain is transmitted via type C fibers to SC at velocities between m / sec. 1 / 10 to 1 / 4 of the fibers terminate in Thalamus, other fibers will go to reticular nuclei of Pons, Medulla, & mesencephalon, tectal area of mesencephalon, & periaqueductal gray region then from here fibers will go to intralaminar & ventrolateral nuclei of Thalamus & Hypothalamus then to Somatic sensory cortex. Reticular nuclei & intralaminar nuclei are part of the "Arousal system" that is why person cannot sleep if he is in severe pain. The localization in this pathway is poor because of the multi-synaptic & diffuse connectivity of this pathway. Pain is perceived at sub-cortical level. Reticular formation & Thalamus can cause conscious perception of pain. Cortex plays an important role in interpreting the quality of pain. NT involved in slow pain is Substance P. In general tissue ischemia can lead to pain due to 2
3 accumulation of lactic acid from anaerobic metabolism & may be due to bradykinin & proteolytic enzyme accumulation too. Muscle spasm is the base for many clinical pain syndromes. Pain occurs in muscle spasm due to the direct effect of mechano-senstive pain receptors & also due to indirect effect through compressing blood vessels leading to ischemia & accumulation of metabolites. Pain & Temperature Pathway: As the dorsal root enters the cord (all sensory information comes in via the dorsal root, and all sensory cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglion), the fibers sort themselves out by diameter. The largest fibers enter the cord most medially, and the smallest fibers enter most laterally. Pain afferents (all of the following applies to temperature as well) enter the cord laterally, due to their small size, and synapse more or less immediately. "More or less", because they actually can travel one or two segments up or down the cord before synapsing. Lissauer's tract is the tract carrying these migrating axons, but they are only in the tract for a short time. Within one or two levels, they enter the dorsal horn and synapse. The dorsal horn is a multi-layered structure. The thin outermost layer is called the posterior marginalis layer. The wide pale second layer is called the substantia gelatinosa, and the layer deep to that is called the nucleus proprius. The layers continue into the ventral horn, but the two types of pain fibers enter different layers of the dorsal horn. Aδ fibers enter the posterior marginalis and (the nucleus proprius?), and synapse on a second set of neurons. These are the secondary afferents which will carry the signal to the thalamus. The secondary afferents from both layers cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord through the anterior commissure and ascend in a tract called the spinothalamic tract (Tracts are always labeled from beginning to end). The C fibers enter the substantia gelatinosa and synapse, but they do not synapse on secondary afferents. Instead they synapse on interneurons (neurons which do not project out of the immediate area).most of the signals then pass through one or more interneurons before entering mainly lamina V, also in the dorsal horn. Here the last neurons in the series give rise to long axons that mostly join fast pain fibers passing through the anterior commisure to the opposite side of the cord. The spinothalamic tract ascends the entire length of the cord, and the entire brainstem, staying in about the same location all the way up. By midbrain the spinothalamic tract appears to be continuous with the medial lemniscus. They will enter the VPL of the thalamus together. The spinothalamic system enters the VPL, synapses, and is finally carried to cortex by the thalamocortical neurons. Here is a schematic diagrams of the dorsal horn, the synapses and the entire pathway: 3
4 4
5 Clinical correlate; Because the pain and temperature information crosses almost as soon as it enters the spinal cord, any unilateral lesion of the spinothalamic tract in the spinal cord or brainstem will result in contralateral loss of pain and temperature. This is an extremely useful clinical sign because it means that if a patient presents with analgesia on one side of the trunk or limbs, the location of the lesion must be on the contralateral side of the spinal cord or brain stem. The analgesia begins 1-2 segments below the lesion and includes everything below that level. A note about generalizations: There is actually a fair amount of mixing that goes on between the tracts. Some light touch information travels in the spinothalamic tract, so that lesioning the dorsal columns will not completely knock out touch and pressure sensation. Some proprioception also travels in the dorsal columns, and follows the medial lemniscus all the way to the cortex, so there is conscious awareness of body position and movement. The pain 5
6 and temperature system, although it does ascend to somatosensory cortex, also has multiple targets in the brainstem and other areas. Pain control: Pain Analgesia System (Pain suppression system): It has been recognized for centuries that opium and related compounds (such as morphine) are powerful analgesics. Several decades ago scientists hunted down the opiate receptor which was responsible for the potent effects. They then reasoned that if there was such a receptor in the body, maybe the body used its own endogenous form of opium to control pain. (It has also been recognized for centuries that under certain circumstances, i.e. the heat of battle, a serious wound may not cause pain.) This hypothetical compound was named "endorphin", from endogenousmorphine. Soon after, an entire class of peptide neurotransmitters was discovered that interacted with the opiate receptor, and now includes endorphins, enkephalins, and dynorphins. Synthetic, exogenous forms of these compounds continue to be discovered, prescribed, and abused, and are classed under the general term, "narcotics". There are opiate receptors throughout the central nervous system. In the dorsal horn, they are located on the terminals of the primary afferents, as well as on the cell bodies of the secondary afferents. Opiate interneurons in the spinal cord can be activated by descending projections from the brainstem (especially the raphe nuclei and periaqueductal grey), and can block pain transmission at two sites. 1) They can prevent the primary afferent from passing on its signal by blocking neurotransmitter release, and 2) they can inhibit the secondary afferent so it does not send the signal up the spinothalamic tract. The reaction toward painful stimuli varies in different individuals. This results from the capability of brain itself to suppress the pain signals reaching it via pain control system (pain analgesia system), which include periaquiductal gray& periventricular areas of the mesencephalon & upper pons. Their neurons send signals to the Raphe magnus nucleus & nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis then signals send through the dorsolateral column to a pain inhibitory complex located in the dorsal horns of the SC. NT's involved in the analgesia system are Enkephalins from periaquductal & periventricular neurons & also from local SC neurons & Serotonin from Raphe magnus neurons (It has been shown that tricyclic antidepressant drugs, such as amitriptyline, which enhance the effects of serotonin by blocking its presynaptic uptake, have been found to be effective in the management of certain types of chronic pain). 6
7 Enkephalins cause pre-synaptic & post-synaptic inhibition to C & Aδ pain fibers where they synapse in dorsal horn. Pre-synaptic inhibition may be via blocking Ca +2 channels. Multiple areas in the brain especially the areas of analgesia system have shown to have opiate receptors. Around 12 different naturally occurring opiate substances have now been found in nervous system, the most important are β - Endorphines in Hypothalamus & pituitary gland & met - Enkephalins, Leu - Enkephalines & Dynorphin (in much lower quantities) in brainstem & SC (analgesia system). The opiate receptors are the site for action of morphine like drugs. Stimulation of type Aβ fibers from the peripheral tactile receptors can depress the transmission of pain signals e.g. rubbing the skin near painful area, or applying liniments is always helpful in relieving pain. 7
8 The same mechanism & the psychogenic excitation of the analgesia system are probably the basis of pain relief by (Acupuncture). 8
9 The Gate control Theory: Large & small fibers excite lamina V neurons that projects to the CNS. Neurons in the substantia gelatinosa inhibit transmission between large fibers & lamina 5 cells & those from small fibers & lamina 5 cells. Activation of large fibers excites substantia gelatinosa cells & therefore increases their inhibitory effect on the lamina 5 cells & closes the gate. Activation of small fibers inhibits substantia gelatinosa neurons & removes their inhibitory effect on lamina 5 neurons & therefore opens the gate. Pain & temperature sensation from the face ; The small diameter fibers carrying pain and temperature enter at mid pons, and then do something unusual - they turn down the brainstem. They travel down the pons and medulla until they reach the caudal medulla, which is where they finally synapse and cross. The tract that the descending axons travel in is called the spinal tract of V, and the long tail of a nucleus that they finally synapse in is called the spinal nucleus of V. These names come from the fact that they actually reach as far down as the upper cervical spinal cord. The spinal nucleus of V can be divided into three regions along its length; the region closest to the mouth is called subnucleus oralis, the middle region is called subnucleus interpolaris, and the region closest to the tail is called subnucleus caudalis. The pain fibers actually synapse in subnucleus caudalis, so you may hear that term used instead of the spinal nucleus of V. 9
10 The secondary afferents from subnucleus caudalis cross to the opposite side, and join the spinothalamic tract on its way to the thalamus. On to the thalamus: The somatosensory information from the face joins that from the body and enters the thalamus with it. Information from the face actually enters the ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPM). The thalamocortical afferents take all of the signals, whether from VPL or VPM, to primary somatosensory cortex. Once there, it is distributed in a somatotopic (body-mapped) fashion, with the legs represented medially, at the top of the head, and the face represented laterally. 10
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Chapter 16. Sense of Pain
 Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
*Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord.
 *somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
*somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
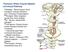 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
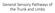 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
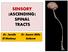 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Chapter 6. Gathering information; the sensory systems
 Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
PAIN MODULATION. numerical value. adjectives. DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH
 PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
Pain. Pain. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Psyc 2906: Sensation--Introduction 9/27/2006
 Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile
 Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways.
 Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Anatomy of the Spinal Cord Posterior spinal arteries Lateral corticospinal tract Dorsal column Spinothalamic tract Anterior spinal artery Anterior white commissure
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway
 Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
Unit VIII Problem 1 Physiology: Sensory Pathway - Process of sensation: Sensory receptors: they are specialized cells considered as biologic signal transducers which can detect stimuli and convert them
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center
 A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Chapter 15! Chapter 15 Sensory Pathways, Somatic Nervous System! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System!
 Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
The anatomy and physiology of pain
 The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Nervous System. Lab Exercise 29. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
Lab Exercise The Nervous System Objectives -You should be able to recognize a neuron and identify its components. - Be able to identify the principal components of the brain and be able to name at least
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D.
 Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D. Theodore Tzavaras MD2015 Eastern Virginia Medical School Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy 1. Discuss -- what is pain? 2. Outline the Anterolateral Quadrant (ALQ) pathway 3. Locate
Laurie L. Wellman Ph.D. Theodore Tzavaras MD2015 Eastern Virginia Medical School Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy 1. Discuss -- what is pain? 2. Outline the Anterolateral Quadrant (ALQ) pathway 3. Locate
How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? What must sensory systems encode? 9/8/2010. Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination
 Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Spatial Coding: Receptive Fields and Tactile Discrimination What must sensory systems encode? How strong is it? What is it? Where is it? When the brain wants to keep certain types of information distinct,
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Reasons for thinking so, according to von Frey:
 Reasons for thinking so, according to von Frey: The experiment consisted of sticking a pig bristle against the eye. Even with fairly light contact, the bristle was painful...... and a warm and cold bristle
Reasons for thinking so, according to von Frey: The experiment consisted of sticking a pig bristle against the eye. Even with fairly light contact, the bristle was painful...... and a warm and cold bristle
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Pain and impulse conduction
 1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW:
 NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM 1-2002 CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW: 1. Which of the following statements about CNS development is TRUE: A. the most likely time for a neural
NEUROSCIENCE and BEHAVIOR EXAM 1-2002 CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR EACH OF THE STATEMENTS BELOW: 1. Which of the following statements about CNS development is TRUE: A. the most likely time for a neural
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
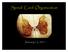 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture. Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs
 Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva, February 2009 A misunderstanding
Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva, February 2009 A misunderstanding
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
1. Somatosensory Pathways
 1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
Sensory Analgesia. Pain Definitions a distressing feeling due to disease, bodily injury or organic disorder. uneasiness of mind or grief.
 Sensory Analgesia Anesthesia- Analgesia- Partial or complete loss of sensation with or without loss of consciousness Relieving pain, being in a state without pain Pain Definitions a distressing feeling
Sensory Analgesia Anesthesia- Analgesia- Partial or complete loss of sensation with or without loss of consciousness Relieving pain, being in a state without pain Pain Definitions a distressing feeling
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Thalamus and Sensory Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To describe the functional divisions of thalamus. II: To state the functions of thalamus and the thalamic syndrome. III: To define the somatic sensory
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Nervous system. The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions
 Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
Nervous system The main regulation mechanism of organism's functions Questions Neuron The reflex arc The nervous centers Properties of the nervous centers The general principles of coordination Inhibition
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems
 CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
CNS part 2 & Intro to Sensory Systems Brain Function Important Concepts Functional areas of the cerebral cortex Sensory, Motor, Association Cerebral lateralization each hemisphere has functions not shared
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
Daniel J. Simons, Ph.D. I. Peripheral Nervous System THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM The somatosensory system consists of those components of the peripheral and central nervous systems that mediate sensations
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
