Quality of Life in Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Ileal Conduit: A Comparison of Women Versus Men
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Pearson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /invivo Quality of Life in Patients with Bladder Cancer Undergoing Ileal Conduit: A Comparison of Women Versus Men SALVATORE SIRACUSANO 1*, CAROLINA D ELIA 2*, MARIA ANGELA CERRUTO 1, OMAR SALEH 3, SERGIO SERNI 3, MAURO GACCI 3, STEFANO CICILIATO 4, ALCHIEDE SIMONATO 5, ANTONIO PORCARO 1, VINCENZO DE MARCO 1, RENATO TALAMINI 6, LAURA TOFFOLI 4, FRANCESCO VISALLI 4, MAURO NIERO 7, CRISTINA LONARDI 7, CIRO IMBIMBO 8, PAOLO VERZE 8, VINCENZO MIRONE 8, MARCO RACIOPPI 9, MASSIMO IAFRATE 10, GIOVANNI CACCIAMANI 1, DAVIDE DE MARCHI 1, PIERFRANCESCO BASSI 9 and WALTER ARTIBANI 1 1 Urology Department, and 7 TESIS Department, University of Verona, Verona, Italy; 2 Urology Department, Bolzano General Hospital, Bolzano, Italy; 3 Urology Department, Careggi Hospital, University of Florence, Florence, Italy; 4 Urology Department, Trieste University, Trieste, Italy; 5 Department of Urology, IRCSS San Martino IST, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy; 6 Unit of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, IRCCS_CRO, Aviano, Italy; 8 Urology Department, University of Naples, Federico II, Naples, Italy; 9 Urology Department, Foudazione Policlinico Gemelli, Catholic University of Rome, Rome, Italy; 10 Urology Department, University of Padua, Padua, Italy Abstract. Background/Aim: Studies comparing healthrelated quality of life (HR-QoL) between patients who underwent radical cystectomy (RC) and those who underwent a different form of urinary diversion has not reached yet univocal and reliable conclusions. The aim of our study was to evaluate bladder-specific long-term HR-QoL after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit. Patients and Methods: A multicenter study was carried out on 145 consecutive patients (112 males and 33 females) undergoing RC and ileal conduit (IC). HR-QoL assessment was conducted using Italian versions of European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30 and EORTC BLM-30 questionnaires. Results: Our data showed that women who underwent IC presented greater problems than men in cognitive functioning (mean score±sd: 77.3±27.9 vs. 87.8±18.6) as well in future perspective (score: 42.4±34.4 vs. This article is freely accessible online. *These Authors contributed equally to this study. Correspondence to: Carolina D Elia, M.D, F.E.B.U., Ph.D., Urology Department, Bolzano General Hospital, Via Lorenz Bohler 9, Bolzano, Italy. Mobile , Fax: , karolinedelia@gmail.com Key Words: Bladder cancer, quality of life, ileal conduit, orthotopic neobladder, radical cystectomy. 21.9±24.6). Nevertheless, men undergoing IC had more problems in sexual functioning than women (score: 23.3±24.5 vs. 7.0±20.3) (all p<0.05). Conclusion: In our series, female patients presented a greater burden than male patients in cognitive functioning as well in future perspective, but lower concerns with regard to sexual function. Bladder cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed types of cancer and Europe has the highest incidence rate of bladder cancer worldwide. Morevover, Spain and Italy have the highest incidence in men in Europe, at approximately 37/100,000 and 33/100,000. respectively, (1). Classically, according to European Association of Urology (EAU) Guidelines, radical cystectomy (RC) represents the gold standard treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer, T2- T4a, N0-Nx, M0 and for high-risk and recurrent superficial tumours (2). Unfortunately, no consensus has been reached about ideal age, timing and type of urinary diversion after RC. Options range from ileal conduit (IC) to orthotopic neobladder (ONB) reconstruction, with different outcomes, such as complication rates and health-related quality of life (HR-QoL). Studies comparing HR-QoL between radical cystectomy and different urinary diversion has not reached yet univocal and reliable conclusions. Nevertheless, in a recent meta-analysis of non-randomized comparative studies, Cerruto et al. demonstrated a significant advantage of ileal ONB compared to IC in terms of HR-QoL (3). On the other hand, a recent review conducted by Yang et al. failed to 139
2 demonstrate a significant difference between patients after IC and ONB, even showing a small benefit for physical health with IC (4). According to Cerruto et al., findings regarding IC show patient satisfaction seems to be related to the degree of adaptation to their new life with an IC, a new phase of life and not simply a deterioration (5). The aim of this study was to evaluate bladder-specific long-term HR-QoL after RC and IC and to assess whether HR-QoL outcomes differ between men and women. Patients and Methods A multicentre study was carried out on 145 consecutive patients (112 males and 33 females) undergoing RC and IC for bladder cancer at five Italian academic urological centres (Verona, Trieste, Naples Federico II, Padua and Rome Catholic University), from June 2007 to December Patients were invited to participate in the study at their follow-up medical consultation and gave their signed informed consent. All the patients included in our study underwent RC and IC due to oncological indication and were affected by muscle-invasive bladder cancer or had non-responding high-grade non-muscleinvasive bladder cancer according to EAU Guidelines (2). Moreover, all patients underwent RC with pelvic and iliac lymph node dissection with radical en bloc cystectomy as described by Skinner and Lieskovsky (6), and were between years of age, with a sufficient educational level and command of the italian language sufficient to understand and fill out a questionnaire. Patients who were not capable of completing a questionnaire, or had a history of psychiatric disorders, alcohol or substance abuse, difficulties in verbal or written communication, non-italian speakers, as well as those who had cognitive deterioration, were excluded from the study. Moreover, all the included patients had no evidence of disease recurrence and were actively followed-up. Data obtained from the retrospective review included age, gender, follow-up (months), pathological tumour (ptnm) stage as defined by the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) (7), grading, and adjuvant chemo- or radiotherapy. All these clinical, pathological as well as clinical outcome data were retrospectively analyzed and a comprehensive database was created. HRQoL assessment was conducted using italian versions of EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC BLM-30 questionnaires (8). The study was approved by local Ethics Committees at each center. Quality of life assessment. Patients were asked to complete both the following questionnaire: i) The EORTC-QLQ-C30 is a 30-item cancer-specific validated questionnaire, the most known tool for the QoL assessment. The versions we used were culturally validated in the italian language (male/female Italian version) and subjected to psychometric validation. This 30-item questionnaire has multi-item scales and single items reflecting the multidimensionality of the QoL construct. It comprises five functional scales covering physical, role, emotional, cognitive and social aspects, and one scale of global health status/qol. It also includes three multi-item symptom scales of fatigue, nausea/vomiting and pain, and six single items that deal with dyspnoea, insomnia, appetite loss, constipation, diarrhoea and financial difficulties caused by the disease or its treatment. The scores obtained were converted into a scale from 0 to 100 according to the provisions of the EORTC manual: aiming to obtain more useful and easily understandable statistical data. For functional and overall scales, higher scores represent a better QoL outcome, whereas for symptom and single-item scales, higher scores correspond to more problems and a reduced QoL. ii) The EORTC-QLQ-BLM30 (specific for muscle-invasive bladder cancer) is a module from the EORTC that specifically evaluates the impact of RC and reconstructive surgery in terms of HR-QoL. It is a 30-item questionnaire that includes questions related to general symptoms for all patients, a specific section with questions for patients with urinary diversion, questions on sexual function and a series of questions on the emotional state. For symptoms/single items, a higher score means a higher level of symptoms/problems. There is still no psychometric validation for this questionnaire and Italian linguistic validation has not been performed yet. Statistical analysis. Statistical analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.3 software (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Mean values with standard deviations (±SD) were computed and reported for age (years), follow-up (months), and for all items included in the EORTC. Wilcoxon two-sample test was used to verify differences between continuous variables, whereas Chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables. Statistical significance was achieved when the two-sided p-value was 0.05 or less. Results This multicentric study was conducted on 145 patients (112 males and 33 females) who underwent RC and IC in five urological academic centres. Patient characteristics are reported in Table I. The two groups were comparable with regard to the clinical and demographical variables. The EORTC- QLQ C30 data regarding our series are reported in Table II, and those for EORTC-QLQ BLM-30 are reported in Table III. Our data showed that women with IC presented significantly greater problems than men in cognitive functioning (higher score means better functionally: 77.3±27.9 vs. 87.8±18.6, respectively, p=0.04) as well in future perspective (lower score means a low level of symptomatology/problems: 42.4±34.4 vs. 21.9±24.6, respectively, p=0.001). Nevertheless, men undergoing IC had more problems in sexual functioning than women (23.3±24.5 vs. 7.0±20.3, respectively, p=0.001). Discussion In 1948, the World Health Organization defined health as being not only the absence of disease and infirmity, but also the presence of physical, mental and social well-being (9). Nevertheless. according to this definition, HR-QoL refers to a multidimensional concept, including physical, social and psychological wellbeing of the person, changing over time and influenced by expectations, concerns and experiences. 140
3 Siracusano et al: QoL After Ileal Conduit: Women vs. Men Table I. Centre, age and pathological and clinical characteristics of 145 patients with ileal conduit according to gender. Characteristic Males Females p-value a No. of patients Centre, n (%) Naples 30 (26.8) 2 (6.1) Padua 16 (14.3) 7 (21.2) Rome 25 (22.3) 5 (15.1) Trieste 15 (13.4) 6 (18.2) Verona 26 (23.2) 13 (39.4) ns Mean age (±SD), years 71.0 (±8.2) 70.5 (±8.7) ns Mean follow-up (±SD), months 41.8 (±34.4) 52.5 (±40.5) ns Stage (ptnm-uicc), n (%) Stage 0-I 38 (33.9) 11 (33.3) Stage II 34 (30.4) 7 (21.2) Stage III+IV 40 (35.7) 15 (45.5) ns Grading, n (%) Gx 1 (0.9) -- G1-2 8 (7.1) 2 (6.1) G (92.0) 31 (93.9) ns Adjuvant chemotherapy, n (%)* No 84 (77.8) 25 (75.8) Yes 24 (22.2) 8 (24.2) ns Adjuvant radiotherapy, n (%)* No 102 (92.7) 32 (97.0) Yes 8 (7.3) 1 (3.0) ns *Totals may not agree due to missing values. a Wilcoxon two-sample test or Chi-square test were used as appropriate (females vs. males). SD: standard deviation; ns: not significant (p>0.05). Every perturbance of the health status has a major impact on a patient s daily and personal life, leading to difficulty in social and working activities and to frustration. The duty of care of physicians is not limited to obtaining physical health, but also concerns maintaining a patient s capacity to fulfill family, social and working roles. The urological literature emphasizes the importance of HR- QoL in patients undergoing RC and urinary diversion; the ideal form of urinary diversion after RC should be easy to handle, presenting few complications, with low mortality and morbidity, protecting upper urinary tract function and e the ensuring the best possible HRQoL. Unfortunately, only few studies have compared HRQoL between female and male patients undergoing RC, who present different types of postoperative complications and impact on daily and personal life. In our series, at a mean ideal follow-up of 40 months, well after the time for stabilization of QoL hypothesized by Kulaksizoglu et al. (12 months), female patients undergoing RC and IC showed a more severe impact on cognitive function and future perspective, but a lower burden on their sexual life (10). Our results on sexual life in patients with IC agree with the literature data. Table II. Mean and standard deviation (±SD) of scores for the QLQ- C30 functional and single items according to gender of 145 patients with ileal conduit. Item Males Females p-value a (N=112) (N=33) Mean (±SD) Mean (±SD) Physical functioning* 73.9 (±25.2) 75.4 (±24.0) ns Role functioning* 78.4 (±28.9) 72.2 (±29.4) ns Emotional functioning* 80.5 (±23.0) 72.7 (±30.1) ns Cognitive functioning* 87.8 (±18.6) 77.3 (±27.9) 0.04 Social functioning* 84.7 (±22.8) 80.3 (±23.7) ns Fatigue 29.1 (±26.6) 31.0 (±30.1) ns Nausea and vomiting 5.2 (±14.5) 2.5 (±7.4) ns Pain 11.8 (±17.6) 13.1(±21.1) ns Dyspnoea 20.5 (±26.2) 21.2 (±31.0) ns Insomnia 19.3 (±27.8) 22.2 (±27.2) ns Appetite loss 15.2 (±28.3) 12.1 (±26.1) ns Constipation 33.3 (±34.7) 27.3 (±35.8) ns Diarrhoea 8.6 (±20.4) 10.1 (±27.0) ns Financial difficulties 15.6 (±26.8) 10.1 (±17.6) ns Global quality of life scale 62.5 (±24.3) 60.9 (±29.2) ns *A higher score represents a higher level of functioning. A higher score means a higher level of symptomatology/problems. a Wilcoxon twosample test (females vs. males). Ns: not significant (p>0.05). Table III. Mean and standard deviation (±SD) of scores for the QLQ- BLM30 items according to gender of 145 patients with ileal conduit. Item Males Females p-value a (N=112) (N=33) Mean (±SD) Mean (±SD) Future perspective 21.9 (±24,6) 42.4 (±34.4) Abdominal bloating and flatulence 24.7 (±24.9) 26.3 (±31.5) ns Body image 29.6 (±28.8) 28.3 (±33.1) ns Sexual functioning 23.3 (±24.5) 7.0 (±20.3) Sex life 80.8 (±33.7) 75.0 (±50.0) ns A higher score means a higher level of symptomatology/problems. a Wilcoxon two-sample test (females vs. males). Ns: not significant (p>0.05). In 2004, Protogerou et al. evaluated 108 recurrence-free patients undergoing RC and IC and S-pouch (with a control group) using the EORTC- QLQ C30 questionnaire. The patients of the IC group reported worse urinary function, but sexual dysfunction, similar for the groups, was less important in women compared with the male population (11), as reported in our series. These data were confirmed by Hedgepeteh et al., who evaluated 336 patients undergoing RC and IC or ONB or simple cystoscopy using the Bladder Cancer Index (12) and the EORTC Body Image Scale (13). 141
4 They documented higher sexual functional scores in female patients (p=0.021) and generally worse for patients with conduit (14). In our study, women reported better sexual function in comparison with male patients; female sexual function may be influenced by body perception and changes in body image, whereas male patients may experience problems in erectile function and ejaculatory function (15). The absence of ejaculation, obviously affecting only male patients, can deeply affect sexual QoL of the patients, as documented by Mak et al., comparing patients affected by muscle-invasive bladder cancer and treated with RC or bladder-sparing trimodal therapy (15). Moreover, in 2006, Allareddy et al. evaluated QoL in long-term surviving patients undergoing RC using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy (FACT-BL) instrument (16). At multivariate analysis, male patients had globally higher QoL life scores in comparison with female patients, but male patients had a worse social and well-being score in the stage II population (17). With regard to the concerns about future and cognitive function, no literature studies documented differences between male and female patients; nevertheless, Cerruto et al., in a systematic review of QoL after RC, showed that study populations with more than 65% of men had a better HR-QoL, but only in the ONB subgroup (5). Although not significant, 45% of the female patients vs. 35% of the male patients had clinical stage III-IV disease, which can negatively influence QoL and concerns about future perspective and future disease recurrence in this population. Our study presents several biases: a relatively limited number of patients, although our findings agree with literature data, and the absence of a baseline evaluation; nevertheless, the use of validated questionnaires make our results reliable and comparable. Larger and prospective studies using validated questionnaires are needed, with the aim of easily comparing QoL between men and women undergoing RC; in addition, the use of specific questionnaires, such as the IONB-PRO, should be encouraged in order to address the specific problems and concerns related to the type of urinary diversion (18). Conclusion In our series of 145 patients undergoing IC, female patients present greater burden than male patients in cognitive functioning, as well in future perspective, but lesser concerns with regard to sexual function. Larger and randomized studies are needed, with the aim of better understanding the aetiology of these differences. Conflict of Interest The Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. References 1 Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A and Bray F: Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recen trends. Eur Urol 71: , Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Compérat E, Sylvester RJ, Kaasinen E, Böhle A, Palou Redorta J, Rouprêt M: European Association of Urology EAU guidelines on non-muscle invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update Eur Urol 64: , Cerruto MA, D Elia C, Siracusano S, Gedeshi X, Mariotto A, Iafrate, Niero M, Lonardi C, Bassi P, Belgrano E, Imbimbo C, Racioppi M, Talamini R, Ciciliato S, Toffoli L, Rizzo M, Visalli F, Verze P and Artibani W: Systematic review and meta-analysis of non RCTs on health related quality of life after radical cystectomy using validated questionnaires: Better results with orthotopic neobladder versus ileal conduit. Eur J Surg Oncol 42: , Yang LS, Shan BL, Shan LL, Chin P, Murray S, Ahmadi N and Saxena A: A systematic review and meta-analysis of quality of life outcomes after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Surg Oncol 25: , Cerruto MA, D Elia C, Cacciamani G, De Marchi D, Siracusano S, Iafrate M, Niero M, Lonardi C, Bassi P, Belgrano E, Imbimbo C, Racioppi M, Talamini R, Ciciliato S, Toffoli L, Rizzo M, Visalli F, Verze P and Artibani W: Behavioural profile and human adaptation of survivors after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit. Health Qual Life Outcomes 12: 46, Skinner DG and Lieskovsky G: Management of invasive highgrade bladder cancer. In: Diagnosis and Management of Genitourinary Cancer. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co. vol 1, pp , Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, Seventh Edition. New York: Wiley-Liss, Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC: The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85: , World Health Organization. Available at 10 Kulaksizoglu H, Toktas G, Kulaksizoglu IB, Aglamis E, Unlüer E: When should quality of life be measured after radical cystectomy? Eur Urol. 4: , Protogerou V, Moschou M, Antoniou N, Varkarakis J, Bamias A and Deliveliotis C: Modified S-pouch neobladder vs. ileal conduit and a matched control population: a quality-of-life survey. BJU Int 94: , Gilbert SM, Wood DP, Dunn RL, Weizer AZ, Lee CT, Montie JE and Wei JT: Measuring health-related quality of life outcomes in bladder cancer patients using the Bladder Cancer Index (BCI). Cancer 109: ,
5 Siracusano et al: QoL After Ileal Conduit: Women vs. Men 13 Hopwood P, Fletcher I, Lee A, Al Ghazal S: A body image scale for use with cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 37: , Hedgepeth RC, Gilbert SM, He C, Lee CT, Wood DP Jr.: Body image and bladder cancer specific quality of life in patients with ileal conduit and neobladder. Urinary Diversions Urol 76: , Mak KS, Smith AB, Eidelman A, Clayman R, Niemierko A, Cheng JS, Matthews J, Drumm MR, Nielsen ME, Feldman AS, Lee RJ, Zietman AL, Chen RC, Shipley WU, Milowsky MI and Efstathiou JA: Quality of life in long-term survivors of muscleinvasive bladder cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96: , Cella DF, Tulsky DS, Gray G, Sarafian B, Linn E, Bonomi A, Silberman M, Yellen SB, Winicour P and Brannon J: The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale: development and validation of the general measure. J Clin Oncol 11: , Allareddy V, Kennedy J, West MM and Konety BR: Quality of life in long-term survivors of bladder cancer. Cancer 106: , Siracusano S, Niero M, Lonardi C, Cerruto MA, Ciciliato S, Toffoli L, Visalli F, Massidda D, Iafrate M, Artibani W, Bassi P, Imbimbo C, Racioppi M, Talamini R, D Elia C, Cacciamani G, De Marchi D, Silvestri T, Verze P and Belgrano E: Development of a questionnaire specifically for patients with ileal orthotopic neobladder (IONB). Health Qual Life Outcomes 12: 135, Received October 16, 2017 Revised November 19, 2017 Accepted November 29,
Point/Counterpoint: Quality of Life Considerations for Patients with Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Pro Trimodality Therapy
 Point/Counterpoint: Quality of Life Considerations for Patients with Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Pro Trimodality Therapy Kimberley S. Mak, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Boston Medical Center Boston University
Point/Counterpoint: Quality of Life Considerations for Patients with Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Pro Trimodality Therapy Kimberley S. Mak, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Boston Medical Center Boston University
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER
 GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
GUIDELINES ON NON-MUSCLE- INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER (Limited text update December 21) M. Babjuk, W. Oosterlinck, R. Sylvester, E. Kaasinen, A. Böhle, J. Palou, M. Rouprêt Eur Urol 211 Apr;59(4):584-94 Introduction
Reliability and Validity of the Taiwan Chinese Version of the EORTC QLQ-PR25 in Assessing Quality of Life of Prostate Cancer Patients
 Urol Sci 2010;21(3):118 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability and Validity of the Taiwan Chinese Version of the EORTC QLQ-PR25 in Assessing Quality of Life of Prostate Cancer Patients Wei-Chu Chie 1, Chih-Chieh
Urol Sci 2010;21(3):118 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability and Validity of the Taiwan Chinese Version of the EORTC QLQ-PR25 in Assessing Quality of Life of Prostate Cancer Patients Wei-Chu Chie 1, Chih-Chieh
Bladder Preservation Strategies for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Bladder Preservation Strategies for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Jeff M. Michalski, MD, MBA, FACR, FASTRO The Carlos A. Perez Distinguished Professor of Radiation Oncology Department of Radiation Oncology
Bladder Preservation Strategies for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Jeff M. Michalski, MD, MBA, FACR, FASTRO The Carlos A. Perez Distinguished Professor of Radiation Oncology Department of Radiation Oncology
Women s Health Development Unit, School of Medical Science, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia b
 The Malay Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC-QLQ C30): Reliability and Validity Study Yusoff N a, Low WY b and Yip CH c ORIGINAL
The Malay Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC-QLQ C30): Reliability and Validity Study Yusoff N a, Low WY b and Yip CH c ORIGINAL
Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems
 Syddansk Universitet Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems Lund Rasmussen, Charlotte; Johnsen, Anna Thit; Petersen,
Syddansk Universitet Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems Lund Rasmussen, Charlotte; Johnsen, Anna Thit; Petersen,
Development of a questionnaire specifically for patients with Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder (IONB)
 Siracusano et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2014, 12:135 RESEARCH Open Access Development of a questionnaire specifically for patients with Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder (IONB) Salvatore Siracusano
Siracusano et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2014, 12:135 RESEARCH Open Access Development of a questionnaire specifically for patients with Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder (IONB) Salvatore Siracusano
Behavioural profile and human adaptation of survivors after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit
 Cerruto et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2014, 12:46 RESEARCH Open Access Behavioural profile and human adaptation of survivors after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit Maria Angela Cerruto
Cerruto et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2014, 12:46 RESEARCH Open Access Behavioural profile and human adaptation of survivors after radical cystectomy and ileal conduit Maria Angela Cerruto
Prognostic features for quality of life after radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (6): 1109-1120, November - December, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0491 Prognostic features for quality of life after radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder Alexander
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (6): 1109-1120, November - December, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0491 Prognostic features for quality of life after radical cystectomy and orthotopic neobladder Alexander
Ileal orthotopic neo-bladder (IOB): how Quality of Life (QoL) of recipients can be measured. M.Niero (Dept of Education University of Verona ITA)
 Ileal orthotopic neo-bladder (IOB): how Quality of Life (QoL) of recipients can be measured S.Siracusano (Dip.of Urology University of Trieste ITA) M.Niero (Dept of Education University of Verona ITA)
Ileal orthotopic neo-bladder (IOB): how Quality of Life (QoL) of recipients can be measured S.Siracusano (Dip.of Urology University of Trieste ITA) M.Niero (Dept of Education University of Verona ITA)
Trimodality Therapy for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Trimodality Therapy for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Brita Danielson, MD, FRCPC Radiation Oncologist, Cross Cancer Institute Assistant Professor, Department of Oncology University of Alberta Edmonton,
Trimodality Therapy for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Brita Danielson, MD, FRCPC Radiation Oncologist, Cross Cancer Institute Assistant Professor, Department of Oncology University of Alberta Edmonton,
The outcome of non-muscle invasive urinary bladder tumour at Makassed General Hospital
 Makassed General Hospital The outcome of non-muscle invasive urinary bladder tumour at Makassed General Hospital Imad El Hajjar Department of surgery, Urology division Introduction Most common malignancy
Makassed General Hospital The outcome of non-muscle invasive urinary bladder tumour at Makassed General Hospital Imad El Hajjar Department of surgery, Urology division Introduction Most common malignancy
Eiji Kikuchi, Yutaka Horiguchi, Jun Nakashima, Takashi Ohigashi, Mototsugu Oya, Ken Nakagawa, Akira Miyajima and Masaru Murai
 Assessment of Long-Term Quality of Life Using the FACT-BL Questionnaire in Patients with an Ileal Conduit, Continent Reservoir, or Orthotopic Neobladder Eiji Kikuchi, Yutaka Horiguchi, Jun Nakashima, Takashi
Assessment of Long-Term Quality of Life Using the FACT-BL Questionnaire in Patients with an Ileal Conduit, Continent Reservoir, or Orthotopic Neobladder Eiji Kikuchi, Yutaka Horiguchi, Jun Nakashima, Takashi
MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
10 MUSCLE - INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER Recommendations from the EAU Working Party on Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer G. Jakse (chairman), F. Algaba, S. Fossa, A. Stenzl, C. Sternberg
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients with pathological Stage T3b and/or lymph node metastatic bladder cancer after radical cystectomy
 Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(10) 963 967 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv098 Advance Access Publication Date: 29 July 2015 Original Article Original Article Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(10) 963 967 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv098 Advance Access Publication Date: 29 July 2015 Original Article Original Article Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients
Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But...
 european urology 50 (2006) 1129 1138 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial 50th Anniversary Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But... Urs E. Studer
european urology 50 (2006) 1129 1138 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial 50th Anniversary Radical Cystectomy Often Too Late? Yes, But... Urs E. Studer
Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars
 IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org Conservative Treatment of Invasive Bladder Cancer Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org Conservative Treatment of Invasive Bladder Cancer Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation Oncology
Impact of invasive bladder cancer and orthotopic urinary diversion on general health-related quality of life: An SF-36 survey
 758 Impact of invasive bladder cancer and orthotopic urinary diversion on general health-related quality of life: An SF-36 survey MINGYING YANG 1,2*, HAIFENG WANG 2*, JIANSONG WANG 2 and MINGHUI RUAN 1
758 Impact of invasive bladder cancer and orthotopic urinary diversion on general health-related quality of life: An SF-36 survey MINGYING YANG 1,2*, HAIFENG WANG 2*, JIANSONG WANG 2 and MINGHUI RUAN 1
10th anniversary of 1st validated CaPspecific
 Quality of Life after Treatment of Localised Prostate Cancer Dr Jeremy Grummet Clinical Uro-Oncology Fellow May 28, 2008 1 Why? This is important May be viewed as soft science Until we know which treatment
Quality of Life after Treatment of Localised Prostate Cancer Dr Jeremy Grummet Clinical Uro-Oncology Fellow May 28, 2008 1 Why? This is important May be viewed as soft science Until we know which treatment
Body Image Following Radical Cystectomy and Ileal Neobladder or Conduit in Korean Patients
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.161 Original Article - Urological Oncology http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.161&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-03-17
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.161 Original Article - Urological Oncology http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.161&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-03-17
Prognostic value of changes in quality of life scores in prostate cancer
 Gupta et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:32 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2490/13/32 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prognostic value of changes in quality of life scores in prostate cancer Digant Gupta *, Donald
Gupta et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:32 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2490/13/32 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prognostic value of changes in quality of life scores in prostate cancer Digant Gupta *, Donald
Segmental ureterectomy does not compromise the oncologic outcome compared with nephroureterectomy for pure ureter cancer
 Int Urol Nephrol (2014) 46:921 926 DOI 10.1007/s11255-013-0514-z UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Segmental ureterectomy does not compromise the oncologic outcome compared with nephroureterectomy for pure ureter
Int Urol Nephrol (2014) 46:921 926 DOI 10.1007/s11255-013-0514-z UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Segmental ureterectomy does not compromise the oncologic outcome compared with nephroureterectomy for pure ureter
Radical Cystectomy in the Treatment of Bladder Cancer: Oncological Outcome and Survival Predictors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radical Cystectomy in the Treatment of Bladder Cancer: Oncological Outcome and Survival Predictors Chen-Hsun Ho, 1,2 Chao-Yuan Huang, 1 Wei-Chou Lin, 3 Shih-Chieh Chueh, 1 Yeong-Shiau
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radical Cystectomy in the Treatment of Bladder Cancer: Oncological Outcome and Survival Predictors Chen-Hsun Ho, 1,2 Chao-Yuan Huang, 1 Wei-Chou Lin, 3 Shih-Chieh Chueh, 1 Yeong-Shiau
RALP Registration Form (new registration)
 RALP Registration Form (new registration) RALP registration form new registration v2.0 1 RALP registration form new registration All fields are required, except those marked with an asterisk (*) Variables
RALP Registration Form (new registration) RALP registration form new registration v2.0 1 RALP registration form new registration All fields are required, except those marked with an asterisk (*) Variables
The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30): Validation study of the Thai version
 Quality of Life Research (2006) 15: 167 172 Ó Springer 2006 DOI 10.1007/s11136-005-0449-7 Brief communication The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire
Quality of Life Research (2006) 15: 167 172 Ó Springer 2006 DOI 10.1007/s11136-005-0449-7 Brief communication The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire
Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: oncologic outcome in 271 Chinese patients
 Original Article : oncologic outcome in 271 Chinese patients Zhi-Ling Zhang, Pei Dong, Yong-Hong Li, Zhuo-Wei Liu, Kai Yao, Hui Han, Zi-Ke Qin and Fang-Jian Zhou Abstract Few large scale studies have reported
Original Article : oncologic outcome in 271 Chinese patients Zhi-Ling Zhang, Pei Dong, Yong-Hong Li, Zhuo-Wei Liu, Kai Yao, Hui Han, Zi-Ke Qin and Fang-Jian Zhou Abstract Few large scale studies have reported
Optimal Timing of Radical Cystectomy for Patients with Invasive Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2002;32(1)14 18 Optimal Timing of Radical Cystectomy for Patients with Invasive Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder Isao Hara, Hideaki Miyake, Shoji Hara, Akinobu Gotoh, Hiroshi
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2002;32(1)14 18 Optimal Timing of Radical Cystectomy for Patients with Invasive Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder Isao Hara, Hideaki Miyake, Shoji Hara, Akinobu Gotoh, Hiroshi
Preoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Gastric Cancer
 pissn : 2093-582X, eissn : 2093-5641 J Gastric Cancer 2015;15(2):121-126 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2015.15.2.121 Original Article Preoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Gastric Cancer Hyoam
pissn : 2093-582X, eissn : 2093-5641 J Gastric Cancer 2015;15(2):121-126 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2015.15.2.121 Original Article Preoperative Quality of Life in Patients with Gastric Cancer Hyoam
Dr. Tareq Salah Ahmed,MD,ESMO. Lecturer of clinical oncology, Assiut faculty of medicine ESMO accreditation certificate
 Dr. Tareq Salah Ahmed,MD,ESMO Lecturer of clinical oncology, Assiut faculty of medicine ESMO accreditation certificate 1 st Assiut Urology department conference,marsa Alam 3 rd February 2015 Bladder cancer
Dr. Tareq Salah Ahmed,MD,ESMO Lecturer of clinical oncology, Assiut faculty of medicine ESMO accreditation certificate 1 st Assiut Urology department conference,marsa Alam 3 rd February 2015 Bladder cancer
Neoadjuvant vs. Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Neoadjuvant vs. Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Andrew J. Stephenson, MD, FRCSC, FACS Director, Urologic Oncology Associate Professor of Surgery Glickman Urological and Kidney
Neoadjuvant vs. Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Andrew J. Stephenson, MD, FRCSC, FACS Director, Urologic Oncology Associate Professor of Surgery Glickman Urological and Kidney
The Predictors of Local Recurrence after Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer
 The Predictors of Local Recurrence after Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer Hiroki Ide, Eiji Kikuchi, Akira Miyajima, Ken Nakagawa, Takashi Ohigashi, Jun Nakashima and Mototsugu
The Predictors of Local Recurrence after Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer Hiroki Ide, Eiji Kikuchi, Akira Miyajima, Ken Nakagawa, Takashi Ohigashi, Jun Nakashima and Mototsugu
Koji Ichihara Hiroshi Kitamura Naoya Masumori Fumimasa Fukuta Taiji Tsukamoto
 Int J Clin Oncol (2013) 18:75 80 DOI 10.1007/s10147-011-0346-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transurethral prostate biopsy before radical cystectomy remains clinically relevant for decision-making on urethrectomy in
Int J Clin Oncol (2013) 18:75 80 DOI 10.1007/s10147-011-0346-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transurethral prostate biopsy before radical cystectomy remains clinically relevant for decision-making on urethrectomy in
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Robotic Assisted Surgery for Bladder Cancer Reference: NHS England B14X08 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6
Old and New Radiation for Bladder and Upper Tract Cancers. Bridget Koontz Radiation Oncology Duke Cancer Institute
 Old and New Radiation for Bladder and Upper Tract Cancers Bridget Koontz Radiation Oncology Duke Cancer Institute Disclosures Janssen funded clinical research BlueEarth Diagnostics advisory board member
Old and New Radiation for Bladder and Upper Tract Cancers Bridget Koontz Radiation Oncology Duke Cancer Institute Disclosures Janssen funded clinical research BlueEarth Diagnostics advisory board member
QoL AFTER URINARY DIVERSION
 . JOURNAL COMPILATION 2008 BJU INTERNATIONAL Miscellaneous URINARY DIVERSION: EVIDENCE-BASED OUTCOMES AND DECISION-MAKING LEE and LATINI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Urinary diversion: evidence-based outcomes
. JOURNAL COMPILATION 2008 BJU INTERNATIONAL Miscellaneous URINARY DIVERSION: EVIDENCE-BASED OUTCOMES AND DECISION-MAKING LEE and LATINI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Urinary diversion: evidence-based outcomes
Bladder Sparing Treatment of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Bladder Sparing Treatment of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Pr Alexandre de la Taille CHU Mondor, Créteil INSERMU955Eq07 adelataille@hotmail.com High-Risk Invasive and Muscle-Invasive BCa Radical cystectomy
Bladder Sparing Treatment of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Pr Alexandre de la Taille CHU Mondor, Créteil INSERMU955Eq07 adelataille@hotmail.com High-Risk Invasive and Muscle-Invasive BCa Radical cystectomy
September 10, Dear Dr. Clark,
 September 10, 2015 Peter E. Clark, MD Chair, NCCN Bladder Cancer Guidelines (Version 2.2015) Associate Professor of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center Nashville, TN 37232 Dear Dr. Clark,
September 10, 2015 Peter E. Clark, MD Chair, NCCN Bladder Cancer Guidelines (Version 2.2015) Associate Professor of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center Nashville, TN 37232 Dear Dr. Clark,
Evaluation of the Physical and Psychosocial Domains among Patients Complaining Of Breast Cancer in Iraq
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 3 99.p- ISSN: 3 94 Volume, Issue Ver. III (Mar. - Apr. 6), PP -63 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Physical and Psychosocial Domains
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 3 99.p- ISSN: 3 94 Volume, Issue Ver. III (Mar. - Apr. 6), PP -63 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Physical and Psychosocial Domains
Early radical cystectomy in NMIBC Marko Babjuk
 Early radical cystectomy in NMIBC Marko Babjuk Dept. of Urology, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Hospital Motol, Praha, Czech Republic We Are The European Association of Urology We Are Urologists, residents,
Early radical cystectomy in NMIBC Marko Babjuk Dept. of Urology, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Hospital Motol, Praha, Czech Republic We Are The European Association of Urology We Are Urologists, residents,
Urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract how does UK practice compare with European guidelines: is there a difference?
 699543URO0010.1177/2051415817699543Journal of Clinical UrologyMoon et al. research-article2018 EAU Guidelines Urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract how does UK practice compare with European
699543URO0010.1177/2051415817699543Journal of Clinical UrologyMoon et al. research-article2018 EAU Guidelines Urothelial carcinomas of the upper urinary tract how does UK practice compare with European
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Debate: Adjuvant vs. Neoadjuvant Therapy for Urothelial Cancer
 Debate: Adjuvant vs. Neoadjuvant Therapy for Urothelial Cancer Kala Sridhar, MD, MSc, FRCPC Medical Oncologist, Princess Margaret Hospital GU Medical Oncology Site Group Head Associate Professor, University
Debate: Adjuvant vs. Neoadjuvant Therapy for Urothelial Cancer Kala Sridhar, MD, MSc, FRCPC Medical Oncologist, Princess Margaret Hospital GU Medical Oncology Site Group Head Associate Professor, University
Critical Evaluation of Early Post-operative Single Instillation Therapy in NMIBC
 Critical Evaluation of Early Post-operative Single Instillation Therapy in NMIBC Levent N. Türkeri MD, PhD Professor of Urology Acıbadem University Faculty of Medicine Istanbul Conflict of Interest No
Critical Evaluation of Early Post-operative Single Instillation Therapy in NMIBC Levent N. Türkeri MD, PhD Professor of Urology Acıbadem University Faculty of Medicine Istanbul Conflict of Interest No
A comparison of preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications between patients undergoing either open or robotic radical cystectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (4): 663-670, July - August, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0393 A comparison of preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications between patients undergoing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (4): 663-670, July - August, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0393 A comparison of preliminary oncologic outcome and postoperative complications between patients undergoing
Partial Cystectomy for Invasive Bladder Cancer
 European Urology Supplements European Urology Supplements 4 (2005) 67 71 Partial Cystectomy for Invasive Bladder Cancer Gerald H. Mickisch* Center of Operative Urology Bremen, Academic Hospital Bremen
European Urology Supplements European Urology Supplements 4 (2005) 67 71 Partial Cystectomy for Invasive Bladder Cancer Gerald H. Mickisch* Center of Operative Urology Bremen, Academic Hospital Bremen
Urological Oncology INTRODUCTION. M Hammad Ather, Masooma Zaidi
 Urological Oncology Predicting Recurrence and Progression in Non-Muscle- Invasive Bladder Cancer Using European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer Risk Tables M Hammad Ather, Masooma Zaidi
Urological Oncology Predicting Recurrence and Progression in Non-Muscle- Invasive Bladder Cancer Using European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer Risk Tables M Hammad Ather, Masooma Zaidi
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up
 Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
CHEMO-RADIOTHERAPY FOR BLADDER CANCER. Dr Darren Mitchell Consultant Clinical Oncologist Northern Ireland Cancer Centre
 CHEMO-RADIOTHERAPY FOR BLADDER CANCER Dr Darren Mitchell Consultant Clinical Oncologist Northern Ireland Cancer Centre AIMS Muscle invasive disease Current Gold-Standard Rationale behind Chemo-Radiotherapy
CHEMO-RADIOTHERAPY FOR BLADDER CANCER Dr Darren Mitchell Consultant Clinical Oncologist Northern Ireland Cancer Centre AIMS Muscle invasive disease Current Gold-Standard Rationale behind Chemo-Radiotherapy
Nutritional Counselling, cancer Outcome and Quality of Life!
 Nutritional Counselling, cancer Outcome and Quality of Life! Paula Ravasco p.ravasco@fm.ul.pt Unit of Nutrition and Metabolism, Institute of Molecular Medicine Faculty of Medicine of the University of
Nutritional Counselling, cancer Outcome and Quality of Life! Paula Ravasco p.ravasco@fm.ul.pt Unit of Nutrition and Metabolism, Institute of Molecular Medicine Faculty of Medicine of the University of
Upper urinary tract urothelial carcinomas (UTUC)
 Prognostic Role of Lymphovascular Invasion in Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of the Upper Urinary Tract Manel Mellouli 1 *, Slim Charfi 1, Walid Smaoui 2, Rim Kallel 1, Abdelmajid Khabir 1, Mehdi Bouacida
Prognostic Role of Lymphovascular Invasion in Patients with Urothelial Carcinoma of the Upper Urinary Tract Manel Mellouli 1 *, Slim Charfi 1, Walid Smaoui 2, Rim Kallel 1, Abdelmajid Khabir 1, Mehdi Bouacida
ROBOTIC VS OPEN RADICAL CYSTECTOMY
 ROBOTIC VS OPEN RADICAL CYSTECTOMY A REVIEW Colin Lundeen December 14, 2016 Objectives Review the history of radical cystectomy Critically analyze recent RCTs comparing open radical cystectomy (ORC) to
ROBOTIC VS OPEN RADICAL CYSTECTOMY A REVIEW Colin Lundeen December 14, 2016 Objectives Review the history of radical cystectomy Critically analyze recent RCTs comparing open radical cystectomy (ORC) to
Predictors of Quality of Life among Female Breast Cancer Survivors at Hospital Kepala Batas, Penang: A Pilot Study
 Academic Journal of Cancer Research 7 (3): 193-197, 2014 ISSN 1995-8943 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajcr.2014.7.3.8563 Predictors of Quality of Life among Female Breast Cancer Survivors
Academic Journal of Cancer Research 7 (3): 193-197, 2014 ISSN 1995-8943 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajcr.2014.7.3.8563 Predictors of Quality of Life among Female Breast Cancer Survivors
The quality of life in men after radical cystectomy with a continent cutaneous diversion or orthotopic bladder substitution: is there a difference?
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UK BJUBJU International1464-4096BJU International 90 2899 QOL AFTER RADICAL CYSTECTOMY AND BLADDER SUBSTITUTION Å. MÅNSSON et al. 10.1046/j.1464-4096.2002.02899.x Original
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UK BJUBJU International1464-4096BJU International 90 2899 QOL AFTER RADICAL CYSTECTOMY AND BLADDER SUBSTITUTION Å. MÅNSSON et al. 10.1046/j.1464-4096.2002.02899.x Original
Update on bladder cancer diagnosis and management
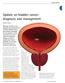 7 Update on bladder cancer diagnosis and management RICHARD T. BRYAN Although the basis of the diagnosis and management of urothelial bladder cancer has remained unchanged for two decades or more, there
7 Update on bladder cancer diagnosis and management RICHARD T. BRYAN Although the basis of the diagnosis and management of urothelial bladder cancer has remained unchanged for two decades or more, there
Health-Related Quality-of-Life Following Modified Ureterosigmoidostomy (Mainz Pouch II) as Continent Urinary Diversion
 European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 591 597 Health-Related Quality-of-Life Following Modified Ureterosigmoidostomy (Mainz Pouch II) as Continent Urinary Diversion Patrick J. Bastian a,*, Peter
European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 591 597 Health-Related Quality-of-Life Following Modified Ureterosigmoidostomy (Mainz Pouch II) as Continent Urinary Diversion Patrick J. Bastian a,*, Peter
QUALITY OF LIFE IN CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS A Practical Guide For. Research Staff
 QUALITY OF LIFE IN CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS A Practical Guide For Research Staff Contents What is Quality of Life?.. 1 QOL in Cancer Trials. 2 How is QOL Measured?....3 EORTC Questionnaires.....4 FACIT Questionnaires..
QUALITY OF LIFE IN CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS A Practical Guide For Research Staff Contents What is Quality of Life?.. 1 QOL in Cancer Trials. 2 How is QOL Measured?....3 EORTC Questionnaires.....4 FACIT Questionnaires..
UROTHELIAL CELL CANCER
 UROTHELIAL CELL CANCER Indications and regimens for neoadjuvant systemic treatment Astrid A. M. van der Veldt, MD, PhD, medical oncologist Department of Medical Oncology Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute
UROTHELIAL CELL CANCER Indications and regimens for neoadjuvant systemic treatment Astrid A. M. van der Veldt, MD, PhD, medical oncologist Department of Medical Oncology Erasmus Medical Center Cancer Institute
A Fourteen-Year Review of Radical Cystectomy for Transitional Cell Carcinoma Demonstrating the Usefulness of the Concept of Lymph Node Density
 Clinical Urology TCC of the Bladder and Lymph Node Density International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (5): 536-549, September - October, 2006 A Fourteen-Year Review of Radical Cystectomy for Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Clinical Urology TCC of the Bladder and Lymph Node Density International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (5): 536-549, September - October, 2006 A Fourteen-Year Review of Radical Cystectomy for Transitional Cell Carcinoma
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. World J Urol (2011) 29: DOI /s
 World J Urol (2011) 29:487 494 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0645-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concomitant carcinoma in situ as an independent prognostic parameter for recurrence and survival in upper tract urothelial
World J Urol (2011) 29:487 494 DOI 10.1007/s00345-011-0645-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concomitant carcinoma in situ as an independent prognostic parameter for recurrence and survival in upper tract urothelial
Ureteral orifice involvement by urothelial carcinoma: long term oncologic and functional outcomes
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (x): 2017 August 8.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0218 Ureteral orifice involvement by urothelial carcinoma: long term oncologic and functional outcomes Muammer
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (x): 2017 August 8.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0218 Ureteral orifice involvement by urothelial carcinoma: long term oncologic and functional outcomes Muammer
Breast cancer Can I still keep my breast?
 Bladder Cancer Organ-Sparing Approaches SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Urogenital Tumors September 15, 2012 Daniel R. Zwahlen, MD Radiation Oncology Breast cancer Can I still keep my breast? History
Bladder Cancer Organ-Sparing Approaches SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Urogenital Tumors September 15, 2012 Daniel R. Zwahlen, MD Radiation Oncology Breast cancer Can I still keep my breast? History
When to Integrate Surgery for Metatstatic Urothelial Cancers
 When to Integrate Surgery for Metatstatic Urothelial Cancers Wade J. Sexton, M.D. Senior Member and Professor Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer Center Case Presentation #1 67 yo male
When to Integrate Surgery for Metatstatic Urothelial Cancers Wade J. Sexton, M.D. Senior Member and Professor Department of Genitourinary Oncology Moffitt Cancer Center Case Presentation #1 67 yo male
Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Without Neoadjuvant or Adjuvant Therapy: Long-Term Results in 1100 Patients
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 61 (2012) 1039 1047 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Bladder Cancer Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Without Neoadjuvant
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 61 (2012) 1039 1047 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Bladder Cancer Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Without Neoadjuvant
Samantha J. Mason*, James W.F. Catto, Amy Downing*, Sarah E. Bottomley, Adam W. Glaser* and Penny Wright* Keywords. Introduction
 Evaluating patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) for bladder cancer: a systematic review using the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) checklist Samantha
Evaluating patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) for bladder cancer: a systematic review using the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments (COSMIN) checklist Samantha
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Outcome of Open Radical Cystectomy and Ileal Conduit: A Single Center Experience Mahesh Kalloli
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Outcome of Open Radical Cystectomy and Ileal Conduit: A Single Center Experience Mahesh Kalloli
Does the Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Improve Survival in Bladder Cancer?
 Does the Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Improve Survival in Bladder Cancer? Authors: Roderick Clark, 1 Kevin Wong, 2 Stacy Fan, 2 Joseph Chin, 1,3 Jonathan
Does the Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Improve Survival in Bladder Cancer? Authors: Roderick Clark, 1 Kevin Wong, 2 Stacy Fan, 2 Joseph Chin, 1,3 Jonathan
Factors influencing sexual function in patients with rectal cancer
 (5) 17, 231 238 & 5 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-99/5 $. www.nature.com/ijir Factors influencing sexual function in patients with rectal cancer CE Schmidt 1 *, B Bestmann 2,TKüchler
(5) 17, 231 238 & 5 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 955-99/5 $. www.nature.com/ijir Factors influencing sexual function in patients with rectal cancer CE Schmidt 1 *, B Bestmann 2,TKüchler
EORTC QLQ-C30 descriptive analysis with the qlqc30 command
 The Stata Journal (2015) 15, Number 4, pp. 1060 1074 EORTC QLQ-C30 descriptive analysis with the qlqc30 command Caroline Bascoul-Mollevi Biostatistics Unit CTD INCa, Institut régional du Cancer de Montpellier
The Stata Journal (2015) 15, Number 4, pp. 1060 1074 EORTC QLQ-C30 descriptive analysis with the qlqc30 command Caroline Bascoul-Mollevi Biostatistics Unit CTD INCa, Institut régional du Cancer de Montpellier
Cystectomies and bladder preservation: What you need to know
 Cystectomies and bladder preservation: What you need to know Robin Morash RN, BNSc, MHS Bladder Cancer Canada November 21, 2018 Presentation goals Review the options for treatment of muscle-invasive bladder
Cystectomies and bladder preservation: What you need to know Robin Morash RN, BNSc, MHS Bladder Cancer Canada November 21, 2018 Presentation goals Review the options for treatment of muscle-invasive bladder
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46: , 2015
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46: 381-388, 2015 Long-term health-related quality of life after curative treatment for prostate cancer: A regional cross-sectional comparison of two standard treatment
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46: 381-388, 2015 Long-term health-related quality of life after curative treatment for prostate cancer: A regional cross-sectional comparison of two standard treatment
2014 Best Papers in Robotic Cystectomy
 Klinik für Urologie Tübingen 2014 Best Papers in Robotic Cystectomy Dr Allen Sim Introduction! Over 100 publications since introduction of robotic cystectomy in 2003! 30+ publications in 2014 alone Important
Klinik für Urologie Tübingen 2014 Best Papers in Robotic Cystectomy Dr Allen Sim Introduction! Over 100 publications since introduction of robotic cystectomy in 2003! 30+ publications in 2014 alone Important
Lymph node dissection: how much is enough?
 1 Background Lymph node dissection: how much is enough? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology USC Keck School of Medicine Radical cystectomy is the gold standard for the treatment of invasive
1 Background Lymph node dissection: how much is enough? Eila C. Skinner, MD Professor of Clinical Urology USC Keck School of Medicine Radical cystectomy is the gold standard for the treatment of invasive
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, in press, accepted 26/02/2013.
 Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, in press, accepted 26/02/2013. The Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 (QLQ-C30) and Functional Assessment of Cancer - General (FACT-G) differ in responsiveness, relative
Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, in press, accepted 26/02/2013. The Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 (QLQ-C30) and Functional Assessment of Cancer - General (FACT-G) differ in responsiveness, relative
Chemotherapy and Bladder Cancer. Blayne Welk UBC Urology Grand Rounds June 4, 2008
 Chemotherapy and Bladder Cancer Blayne Welk UBC Urology Grand Rounds June 4, 2008 Outline Review of Incidence and Impact of bladder cancer Neoadjuvant chemotherapy Adjuvant chemotherapy Bladder preservation
Chemotherapy and Bladder Cancer Blayne Welk UBC Urology Grand Rounds June 4, 2008 Outline Review of Incidence and Impact of bladder cancer Neoadjuvant chemotherapy Adjuvant chemotherapy Bladder preservation
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up
 Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
Attachment #2 Overview of Follow-up Provided below is a general overview of follow-up and this may vary based on specific patient or cancer characteristics. Of note, Labs and imaging can be performed closer
INFORMATION AND SUPPORTIVE CARE NEEDS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH BLADDER CANCER
 INFORMATION AND SUPPORTIVE CARE NEEDS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH BLADDER CANCER ROBIN MORASH APN, URO-ONCOLOGY JUNE 23, 2018 www.ottawahospital.on.ca Affiliated with Affilié à PRESENTATION CONTENT Overview of
INFORMATION AND SUPPORTIVE CARE NEEDS OF INDIVIDUALS WITH BLADDER CANCER ROBIN MORASH APN, URO-ONCOLOGY JUNE 23, 2018 www.ottawahospital.on.ca Affiliated with Affilié à PRESENTATION CONTENT Overview of
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Mozhgan Patoo 1 *, Abbas Ali Allahyari 1 Ali Reza Moradi 2, Mehrdad Payandeh 3. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.9.3799 RESEARCH ARTICLE Persian Version of Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy- Breast (FACT-B) Scale: Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Psychometric Properties
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.9.3799 RESEARCH ARTICLE Persian Version of Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy- Breast (FACT-B) Scale: Confirmatory Factor Analysis and Psychometric Properties
Oral Communications & Posters
 Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
Efficacy of Bladder-Preserving Therapy for Patients with T3b, T4a, and T4b Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.525 Urological Oncology Efficacy of Bladder-Preserving Therapy for Patients with T3b, T4a, and T4b Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder Jaewoo Cheon, Hyunchul
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.8.525 Urological Oncology Efficacy of Bladder-Preserving Therapy for Patients with T3b, T4a, and T4b Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder Jaewoo Cheon, Hyunchul
Mapping EORTC QLQ-C30 onto EQ-5D for the assessment of cancer patients
 Kim et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2012, 10:151 RESEARCH Open Access Mapping EORTC QLQ-C30 onto EQ-5D for the assessment of cancer patients Seon Ha Kim 1, Min-Woo Jo 1*, Hwa-Jung Kim 2 and
Kim et al. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes 2012, 10:151 RESEARCH Open Access Mapping EORTC QLQ-C30 onto EQ-5D for the assessment of cancer patients Seon Ha Kim 1, Min-Woo Jo 1*, Hwa-Jung Kim 2 and
Quality Of Life Of The Patients With Ovarian Cancer
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Oncology Volume 7 Number 2 M Zamurovic, Z Perisic Citation M Zamurovic, Z Perisic.. The Internet Journal of Oncology. 2009 Volume 7 Number 2. Abstract PURPOSE: The goal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Oncology Volume 7 Number 2 M Zamurovic, Z Perisic Citation M Zamurovic, Z Perisic.. The Internet Journal of Oncology. 2009 Volume 7 Number 2. Abstract PURPOSE: The goal
Bone Metastases in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 18, No. 3, September: 03-08, 006 AZZA N. TAHER, M.D.* and MAGDY H. KOTB, M.D.** The Departments of Radiation Oncology* and Nuclear Medicine**, National Cancer
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 18, No. 3, September: 03-08, 006 AZZA N. TAHER, M.D.* and MAGDY H. KOTB, M.D.** The Departments of Radiation Oncology* and Nuclear Medicine**, National Cancer
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 14 (2005) 433 439 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominosacral resection, of recurrent rectal cancer, 202 215 Ablative techniques, image-guided,
Health-Related Quality of Life in Brain Tumor Patients Treated with Surgery: Preliminary Result of a Single Institution
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):87-93 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.87 Health-Related Quality of Life in Brain Tumor Patients Treated with
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):87-93 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.87 Health-Related Quality of Life in Brain Tumor Patients Treated with
receive adjuvant chemotherapy
 Women with high h risk early stage endometrial cancer should receive adjuvant chemotherapy Michael Friedlander The Prince of Wales Cancer Centre and Royal Hospital for Women The Prince of Wales Cancer
Women with high h risk early stage endometrial cancer should receive adjuvant chemotherapy Michael Friedlander The Prince of Wales Cancer Centre and Royal Hospital for Women The Prince of Wales Cancer
1. Introduction. 2. Methods. high-risk NMIBC in men with and without a prior history of RT for PC.
 ISRN Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 405064, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/405064 Research Article Radical Cystectomy after BCG Immunotherapy for High-Risk Nonmuscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in
ISRN Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 405064, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/405064 Research Article Radical Cystectomy after BCG Immunotherapy for High-Risk Nonmuscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in
The Impact of Blue Light Cystoscopy with Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) on Progression of Bladder Cancer ANewAnalysis
 Bladder Cancer 2 (2016) 273 278 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160048 IOS Press Research Report 273 The Impact of Blue Light Cystoscopy with Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) on Progression of Bladder Cancer ANewAnalysis Ashish
Bladder Cancer 2 (2016) 273 278 DOI 10.3233/BLC-160048 IOS Press Research Report 273 The Impact of Blue Light Cystoscopy with Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) on Progression of Bladder Cancer ANewAnalysis Ashish
Multidimensional fatigue and its correlates in hospitalized advanced cancer patients
 Chapter 5 Multidimensional fatigue and its correlates in hospitalized advanced cancer patients Michael Echtelda,b Saskia Teunissenc Jan Passchierb Susanne Claessena, Ronald de Wita Karin van der Rijta
Chapter 5 Multidimensional fatigue and its correlates in hospitalized advanced cancer patients Michael Echtelda,b Saskia Teunissenc Jan Passchierb Susanne Claessena, Ronald de Wita Karin van der Rijta
Tristate Lung Meeting 2014 Pro-Con Debate: Surgery has no role in the management of certain subsets of N2 disease
 Tristate Lung Meeting 2014 Pro-Con Debate: Surgery has no role in the management of certain subsets of N2 disease Jennifer E. Tseng, MD UFHealth Cancer Center-Orlando Health Sep 12, 2014 Background Approximately
Tristate Lung Meeting 2014 Pro-Con Debate: Surgery has no role in the management of certain subsets of N2 disease Jennifer E. Tseng, MD UFHealth Cancer Center-Orlando Health Sep 12, 2014 Background Approximately
Naviga2ng the Adverse Effects of ADT: Improving Pa2ent Outcomes
 Naviga2ng the Adverse Effects of ADT: Improving Pa2ent Outcomes E. David Crawford, M.D. Professor of Surgery/ Urology/ Radiation Oncology University of Colorado Greetings from Colorado Disclosures Consultant:
Naviga2ng the Adverse Effects of ADT: Improving Pa2ent Outcomes E. David Crawford, M.D. Professor of Surgery/ Urology/ Radiation Oncology University of Colorado Greetings from Colorado Disclosures Consultant:
Frequency and predictors of recurrence of bladder tumour on first check cystoscopy a tertiary care hospital experience
 2nd Annual Surgical Meeting 2016 S-125 UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency and predictors of recurrence of bladder tumour on first check cystoscopy a tertiary care hospital experience Muhammad Farhan, Syed
2nd Annual Surgical Meeting 2016 S-125 UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency and predictors of recurrence of bladder tumour on first check cystoscopy a tertiary care hospital experience Muhammad Farhan, Syed
Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital
 E-Da Medical Journal 20;():-5 Original Article Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital Wei-Ting Kuo, I-Wei Chang2, Kevin Lu, Hua-Pin Wang, Tsan-Jung u, Victor C.
E-Da Medical Journal 20;():-5 Original Article Rare Small Cell Carcinoma in Genitourinary Tract: Experience from E-Da Hospital Wei-Ting Kuo, I-Wei Chang2, Kevin Lu, Hua-Pin Wang, Tsan-Jung u, Victor C.
Highlighting Clinical Trials Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
 Highlighting Clinical Trials Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Part I: The Basics of MIBC Clinical Trials June 19, 2018 Presented by: Dr. Peter Black is a urologic oncologist at Vancouver General Hospital,
Highlighting Clinical Trials Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Part I: The Basics of MIBC Clinical Trials June 19, 2018 Presented by: Dr. Peter Black is a urologic oncologist at Vancouver General Hospital,
REVIEW. Patterns of recurrence of bladder carcinoma following radical cystectomy
 Cancer Imaging (2003) 3, 96 100 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2003.0009 CI REVIEW Patterns of recurrence of bladder carcinoma following radical cystectomy D M Koh and J E Husband Academic Department of Radiology,
Cancer Imaging (2003) 3, 96 100 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2003.0009 CI REVIEW Patterns of recurrence of bladder carcinoma following radical cystectomy D M Koh and J E Husband Academic Department of Radiology,
Some Seminal Studies. Chemotherapy Alone is Inadequate. Bladder Cancer Role of Radiation in Bladder Sparing. Primary Radiation for Bladder Cancer
 Bladder Cancer Role of Radiation in Bladder Sparing David C. Beyer M.D., FACR, FACRO, FASTRO Arizona Oncology Services Phoenix, Arizona Primary Radiation for Bladder Cancer No modern surgery / XRT randomized
Bladder Cancer Role of Radiation in Bladder Sparing David C. Beyer M.D., FACR, FACRO, FASTRO Arizona Oncology Services Phoenix, Arizona Primary Radiation for Bladder Cancer No modern surgery / XRT randomized
Oscillating pole treatment - An improved approach for Post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. A prospective randomised controlled trial
 Oscillating pole treatment - An improved approach for Post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. A prospective randomised controlled trial Marc Heydenreich 1, 2, Christian Puta 3, Holger Gabriel 3, Dirk-Henrik
Oscillating pole treatment - An improved approach for Post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. A prospective randomised controlled trial Marc Heydenreich 1, 2, Christian Puta 3, Holger Gabriel 3, Dirk-Henrik
Review Article Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: From Diagnosis to Survivorship
 Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 142135, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/142135 Review Article Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: From Diagnosis to Survivorship N. E. Mohamed, 1 M. A. Diefenbach, 1 H.
Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 142135, 10 pages doi:10.1155/2012/142135 Review Article Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: From Diagnosis to Survivorship N. E. Mohamed, 1 M. A. Diefenbach, 1 H.
Serum calcium is an independent predictor of quality of life in multiple myeloma
 Eur J Haematol 2006 doi:10.1111/j.0902-4441.2006.t01-1-ejh2887.x All rights reserved Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY Serum calcium is
Eur J Haematol 2006 doi:10.1111/j.0902-4441.2006.t01-1-ejh2887.x All rights reserved Ó 2006 The Authors Journal compilation Ó 2006 Blackwell Munksgaard EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY Serum calcium is
