Single-cuff forearm tourniquet in intravenous regional anaesthesia results in less pain and fewer sedation requirements than upper arm tourniquet
|
|
|
- Kathleen West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of Anaesthesia 111 (2): (2013) Advance Access publication 18 March doi: /bja/aet032 Single-cuff forearm tourniquet in intravenous regional anaesthesia results in less pain and fewer sedation requirements than upper arm tourniquet F. B. Chiao*, J. Chen, J. B. Lesser, F. Resta-Flarer and H. Bennett Department of Anesthesiology, St Luke s Roosevelt Hospital Center and Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, 1000 Tenth Avenue, New York, NY 10019, USA * Corresponding author. fchiao@gmail.com Editor s key points I.V. regional anaesthesia has a role in the management of upper limb surgery. The ideal position for tourniquet placement has not been determined in surgical populations. This study examined how differing positions of the tourniquet affected the efficacy of the analgesic technique. The forearm has advantages over upper limb tourniquet placement with improved analgesia and reduced opioid consumption. Background. A limitation of Bier s block or i.v. regional anaesthesia (IVRA) is tourniquet pain. We hypothesized that tourniquet placement on the forearm vs upper arm during IVRA for distal upper extremity surgery may result in less tourniquet pain, lower the need for analgesic interventions, and decrease post-anaesthesia care unit (PACU) admission. Methods. Patients for distal upper extremity surgery were randomized into upper or forearm single-cuff tourniquet placement. IVRA was either performed with 15 ml of 2% lidocaine and 20 mg ketorolac in the upper group or 8 ml of 2% lidocaine and 10 mg ketorolac in the forearm group. Vital signs and visual analogue scale (VAS) score were recorded. If VAS score was.4, 50 mg fentanyl was injected. If the patient had VAS scores.6 with fentanyl, deep sedation with propofol was administered. Results. Twenty-eight subjects were in each group. There were no significant differences in patient characteristics, tourniquet time, or pressure between the groups. Ten patients in the forearm vs 27 in the upper arm group had a VAS score.4. The mean fentanyl use was 30 mg in the forearm group vs 104 mg in the upper arm group. One patient in the forearm group required propofol vs 22 in the upper arm group. PACU bypass to phase 2 recovery occurred 19 times in the forearm group vs zero times in the upper arm group (P,0.0001). Conclusions. Our results indicate that the placement of the tourniquet on the forearm resulted in less discomfort, fewer sedation interventions, and greater likelihood of bypassing the PACU when compared with upper arm tourniquet. Keywords: Bier block; regional anaesthesia Accepted for publication: 27 December 2012 I.V. regional anaesthesia (IVRA) or Bier s block provides effective anaesthesia of the distal extremity of short duration and is particularly useful for ambulatory surgery procedures. IVRA requires the use of tourniquets that are applied to the extremity to sequester the local anaesthetic and to create a bloodless surgical field. 1 However, ischaemic pain due to tourniquet compression can occur. 2 As a result, IVRA may require sedation or additional parentally administered analgesia, which may impact postoperative cognitive function, nausea, vomiting, and time to discharge from the hospital. Although studies exist examining forearm tourniquets for IVRA, it has not been clearly demonstrated that pain is less than upper arm tourniquets. It also has not been studied in a surgical setting where parenteral sedative interventions were utilized. A few studies have reported success with forearm tourniquet for IVRA, but did not compare this group with an upper arm tourniquet. 3 4 Additional studies compared upper arm and forearm tourniquet groups. While some results showed no difference in pain scores, 5 7 others showed lower pain scores in the forearm group, 8 9 but did not have patients who were undergoing surgery. This left a knowledge gap that our study attempts to examine. Our study not only compares two tourniquet locations, but also has patients undergoing surgery with i.v. sedation which more closely resembles clinical practice. We hypothesized that single-cuff tourniquet placement on the forearm vs upper arm during IVRA for distal upper extremity surgery may result in less tourniquet pain, lower the need for i.v. adjuvants (fentanyl and propofol), and decrease postanaesthesia care unit (PACU) admission for patients undergoing distal upper extremity surgery. Post-Graduate Assembly in Anesthesiology 2011 awarded second place in the Current Research by New Investigators competition. & The Author [2013]. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Journal of Anaesthesia. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com
2 BJA Methods Patients having distal upper extremity surgery under IVRA were enrolled in the study which was approved by the IRB. Written informed consent was obtained. Patients were eligible to participate in the study if between age 18 and 70 and of ASA status I III with normal preoperative diagnostic studies. Patients with allergy to local anaesthetics, local infections, open wounds of the surgical hand, seizure disorder, severe coagulopathy, peripheral vascular disease, chronic opioid use, extremes of body weight, or pregnancy were excluded from the study. Patients were randomly assigned using a computer-based random number generator to one of the two study groups, either the upper arm tourniquet or forearm tourniquet placement. Sealed envelopes were opened before block placement. Before block placement, subjects were also educated in reporting the pain score using the visual analogue scale (VAS) score from 0 to 10; 0 representing no pain and 10 for the worst pain. A peripheral i.v. line was placed on the nonoperative arm in the holding area. In the operating theatre, standard monitoring included electrocardiography, oxygen saturation, end-tidal carbon dioxide, and non-invasive arterial pressure. A 22 G i.v. cannula was placed in the distal vein of the surgical hand and saline locked. The single-cuff pneumatic pressure tourniquet was placed immediately above or below the elbow crease and on the top of a circumferentially placed cotton cast padding before inflation. The patient s extremity to be operated on was then exsanguinated with an Esmarch bandage. The radial artery pulse was checked before and after the tourniquet inflation to ensure arterial occlusion. Next, we slowly injected medication into the i.v. cannula of the surgical hand. We used a dose of local anaesthetic for upper arm Bier block: 15 ml of 2% lidocaine as described by the New York School of Regional Anesthesia (NYSORA) and supplemented this with 20 mg ketorolac In the forearm group, we used 8 ml of 2% lidocaine supplemented with 10 mg ketorolac. Since, ketorolac has been shown to have beneficial effects in IVRA, it was added to the local anaesthetic solution at 20 mg for the upper arm group and 10 mg for the forearm group. 2 The adequacy of analgesia was then tested before surgery by the surgeon who tested sensation in the radial, median, and ulnar distributions. Thereafter, the patient s surgical arm was covered with a drape concealing the site of the tourniquet. The patients were constantly monitored and decisions made by an anaesthesiologist who was unaware of patient allocation, and was instructed by the protocol to only administer medications according to the VAS score by a predetermined schedule of administration. The patient s VAS score was assessed every 5 min until the tourniquet cuff was released. If the VAS score was.4, 50 mg fentanyl was injected i.v. Additional fentanyl was subsequently given if VAS score remained higher than four unless respiratory rate was,10 bpm, or reached a maximum allowable dose by protocol of 3 mg kg 21 of fentanyl. If the patient had VAS scores.6 under the treatment regimen of fentanyl, deep sedation with propofol was administered and VAS score was no longer recorded. After the procedure was finished, the tourniquet was deflated. Patients bypassed the PACU to phase 2 recovery, which refers to a step-down recovery unit of post-anaesthesia care with lower acuity and less monitoring, if they did not receive either propofol or fentanyl. All other patients went to the PACU. Statistical analyses were performed using the following methods. For an effect size of.30% on pain ratings per group, power analysis for 90%, and a set to 0.05, 54 patients were required. We considered VAS scores as ordinal. Data analysis for all pain ratings was by the Mann Whitney U. Group analysis was by parametric analysis for continuous variables and x 2 for categorical variables. P,0.05 was considered significant. Results Fifty-nine patients were enrolled in the study. Surgeries in each group were similar and were completed without complications. Surgeries included ganglion cyst excision, mass excision, digital nerve repair, metacarpal and digital fracture pinning, and ORIF, ruptured tendon repair, and palmar fasciotomy. Anaesthesia was satisfactory in all patients at the start of surgery. Patient characteristics in the upper and forearm groups did not differ significantly (Fig. 1; Table 1). However, there were significant differences between the groups in VAS scores, fentanyl and propofol requirements, and PACU admission frequency (Table 2). Patients who had the tourniquet placed on the forearm had lower pain scores than those who had the tourniquet placed on the upper arm. VAS score was.4 in 10 patients in the forearm group vs 27 patients in the upper arm group (Table 2). The mean VAS score was lower in the forearm group at all time intervals (Fig. 2). Accordingly, the use of analgesic interventions was lower in the forearm group when compared with the upper arm group (Table 2). For instance, three to four times more fentanyl was required in patients having an upper arm when compared with a forearm tourniquet, 104 mg when compared with 30 mg, respectively. In addition, 19 patients having a forearm tourniquet were able to bypass the PACU when compared with zero in the upper arm group. Moreover, propofol was required for only one patient in the forearm group compared with 22 patients in the upper arm group. No signs of local anaesthetic toxicity were noted in any study patients. Discussion Chiao et al. Our data indicate that placement of the tourniquet on the forearm rather than upper arm during IVRA for distal upper extremity surgery results in a greater proportion of patients with less tourniquet pain and as a by-product, less use of supplementary analgesia. This study is unique in that it compares two tourniquet locations in the surgical setting with supplementary sedation while demonstrating that the 272
3 Forearm tourniquet for IVRA BJA Enrolment Assessed for eligibility (n = 59) Excluded (n = 0) Not meeting inclusion criteria (n = 0) Declined to participate (n = 0) Other reasons (n = 0) Randomized (n = 59) Allocated to upper arm intervention (n = 29) Received allocated intervention (n = 28) Did not receive allocated intervention (give reasons) (n = 1) Protocol violation given narcotic during exsanguinations of arm Allocation Allocated to forearm intervention (n = 30) Received allocated intervention (n = 28) Did not receive allocated intervention (give reasons) (n = 2) 1. Protocol violation surgeon released tourniquet right after block placement 2. Protocol violation-given narcotic during exsanguinations of arm Follow-up Lost to follow-up (give reasons) (n = 0) Discontinued intervention (give reasons) (n = 0) Lost to follow-up (give reasons) (n = 0) Discontinued intervention (give reasons) (n = 0) Analysis Analysed (n = 28) Excluded from analysis (give reasons given narcotic during exsanguinations) (n = 1) Analysed (n = 28) Excluded from analysis (give reasons protocol violation surgeon released tourniquet right after block placement and given narcotic during exsanguinations) (n = 2) Fig 1 CONSORT forearm tourniquet is not equivocal to the upper arm tourniquet with respect to pain, sedation, and PACU bypass rates. In fact, the forearm location appears to be clearly less painful according to our results. For the study design, we utilized the single-cuff tourniquet for several reasons. The double tourniquet cuff size is different from the single-cuff size which makes their direct comparison difficult. We believe the double-cuff tourniquet size is too large for placement on the forearm as this interferes with the surgical field. Consequently, our study design compared the same single-cuff tourniquet on the forearm and upper arm (Fig. 2). All IVRAs in our study, regardless of where the tourniquet was placed, were successfully used for surgery. However, our results may be even more convincing because by design, we biased the results against the forearm tourniquet by using a lower dose of local anaesthetic in the forearm group. We used our Bier block dose in the upper arm based on external references The optimal dose for Bier block is not established, but in general, it should not be over 300 mg i.v In 273
4 BJA Chiao et al. Table 1 Upper arm and forearm group patient characteristics (n¼56) (95% confidence interval). *Range of ages Forearm Upper arm Female (%) Age (yr)* 40.8 (22 67) 40.1 (22 66) Body mass index (BMI) 24.7 (23 26) 26.4 (24 29) (kg m 22 ) Tourniquet duration (min) 49.1 (43 55) 47.9 (41 54) Tourniquet pressure (mm Hg) 270 ( ) 271 ( ) Mean visual analogue scale (VAS) Upper arm VAS Forearm VAS Pain vs tourniquet time Time (min) Table 2 Upper arm and forearm group patient results (n¼56). VAS, visual analogue scale; PACU, post-anaesthesia care unit Forearm Upper arm P-value VAS.4 (%) 10 (36%) 27 (96%), Average fentanyl (mg) , Fentanyl use (%) 8 (29%) 27 (96%), Propofol use (%) 1 (4%) 22 (79%), PACU bypass (%) 19 (68%) 0 (0%), our institute, we have used 300 mg of lidocaine for all patients on upper arm tourniquet Bier block for more than 20 yr without a single incidence of local anaesthetic toxicity. We empirically use half of this dose for forearm tourniquet Bier block due to the lower amount of tissue and venous capacity. This implies that the forearm group has a larger safety margin than the upper arm group because of the smaller lidocaine dose needed. Regardless of the differences in doses of local anaesthetic and ketorolac favouring the upper arm group, patients having the tourniquet placed on the forearm still had less tourniquet pain than the upper arm group. This is important because the use of narcotics may be associated with longer recovery, nausea and vomiting, and impaired cognition. Additionally, most patients in the forearm group did not require deep sedation with propofol and thereby avoided undesirable side-effects. There were no postoperative complications in our study and no signs or symptoms suggestive of local anaesthetic toxicity. We speculate that the difference in pain scores may be due to the anatomical differences between the upper arm and forearm. With the forearm technique, the tourniquet is placed around the radius and ulnar bones which creates a double pillar that potentially reduces muscle ischaemia by dissipating pressure more evenly when compared with when the tourniquet is placed on the upper arm, where only the humerus can absorb the pressure from the tourniquet. Other theories involve larger density of anaesthesia in the forearm. 8 Since both groups had similar tourniquet Fig 2 Mean VAS pain scores during tourniquet inflation. pressures and duration of inflation (Table 1), we feel pressure and duration contributed little to the difference in VAS scores between the two groups. Yet, forearm tourniquet placement has not been popular due to the theoretical risk of systemic leakage of the local anaesthetic via the interosseous vessels secondary to lower occlusion of the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries in the forearm However, recent studies have shown that forearm tourniquet use does not increase the risk of local anaesthetic leakage; as a matter of fact, due to a smaller dose requirement to achieve a comparable level of anaesthesia, forearm tourniquet has been shown to be as safe as using upper arm tourniquet In addition, forearm tourniquet position allows for preservation of some motor function of the long flexors and extensors of the wrist, which can be critical for some surgeries. A by-product of less tourniquet pain was that the majority of patients in the forearm group were able to bypass the PACU. We did not measure actual costs, but believe costsavings may be obtained by bypassing the PACU in most circumstances. Some may say that the criteria used in our study were too stringent in that any patients who received any fentanyl or propofol had to be admitted to the PACU. We could have used Aldrete s scoring system for PACU bypass, but our hospital policy dictates that patients receiving analgesics must visit the PACU even if for a brief period. Prior studies show PACU-bypass patients were discharged earlier than PACU-admitted patients. 18 In addition, fewer adverse events have been noted in PACU bypass groups and cost-savings may be possible. There may be some limitations to our study. First, we used standardized doses of lidocaine instead of weight-based which we believe better estimated the anaesthetic requirement based on anatomic differences. Indeed, all our patients had successful IVRAs and both groups were not given any more than the maximum study dose of lidocaine. In addition, it is possible that patients could have tolerated VAS.4 without the use of fentanyl or propofol. However, a VAS.4 274
5 Forearm tourniquet for IVRA BJA is a generally acceptable score for intervening with analgesics in the operating theatre and postoperative period. Lastly, patients were not blinded as to where the tourniquet was placed. For patients, though, it was not intuitive to assume more or less pain with the upper arm tourniquet vs the forearm tourniquet when reporting their scores. With greater popularity of ambulatory surgery, the ability to minimize the use of opioids and hypnotics is increasingly important. In this randomized prospective study, our results indicate that the placement of the tourniquet on the forearm resulted in less discomfort, fewer sedation requirements, and greater likelihood of bypassing the PACU when compared with upper arm tourniquet placement during IVRA for distal upper extremity surgery. The use of less local anaesthesia in the forearm group may also reduce the risk of systemic local anaesthetic toxicity with inadvertent tourniquet release. These contemporary characteristics of forearm tourniquet IVRA are particularly favourable in the office and ambulatory surgery centre where there are limited PACU facilities, or staff. We believe that the forearm tourniquet is a reassuring and safer alternative to IVRA. Acknowledgements The authors thank Dr Alan Santos, MD MPH, and Dr Admir Hadzic, MD PhD, for their critical review of the manuscript. Declaration of interest None declared. Funding The work was supported by the Department of Anesthesiology at St Luke s Roosevelt Hospital Center, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. References 1 Colbern E. The bier block for intravenous regional anesthesia: technic and literature review. Anesth Analg 1970; 49: Joshi G. Recent developments in regional anesthesia for ambulatory surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 1999; 12: Chan CS, Pun WK, Chan YM, Chow SP. Intravenous regional analgesia with a forearm tourniquet. Can J Anaesth 1987; 34: Karalezli N, Karalezli K, Iltar S, Cimen O, Aydogan N. Results of intravenous regional anesthesia with distal forearm application. Acta Orthop Belg 2004; 70: Odinsson A, Finsen V. The position of the tourniquet on the upper limb. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2002; 84: Edwards SA, Harper GD, Giddins GE. Efficacy of forearm versus upper arm tourniquet for local anaesthetic surgery of the hand. J Hand Surg Br 2000; 25: Chong AK, Tan DM, Ooi BS, Mahadevan M, Lim AY, Lim BH. Comparison of forearm and conventional Bier s blocks for manipulation and reduction of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Eur 2007; 32: Perlas A, Peng PW, Plaza MB, Middleton WJ, Chan VW, Sanandaji K. Forearm rescue cuff improves tourniquet tolerance during intravenous regional anesthesia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2003; 28: Hutchinson DT, McClinton MA. Upper extremity tourniquet tolerance. J Hand Surg Am 1993; 18: The New York School of Regional Anesthesia. New York School of Regional Anesthesia intravenous regional block Available from regional_blocks/3009-bier_block.html 11 Hadzic. Admir Hadzic s Peripheral Nerve Blocks and Anatomy for Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia, 2nd Edn. McGraw Hill, New York, Rosenberg PH, Veering BT, Urmey WF. Maximum recommended doses of local anesthetics: a multifactorial concept. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2004; 29: Lexi-Comp, Inc. (Lexi-Drugs TM ). Lidocaine (Systemic) (Lexi-Drugs). Lexi-Comp, Inc., Sanders R. The tourniquet, instrument or weapon? Hand 1973; 5: Coleman MM, Peng PW, Regan JM, Chan VW, Hendler AL. Quantitative comparison of leakage under the tourniquet in forearm versus conventional intravenous regional anesthesia. Anesth Analg 1999; 89: Plourde G, Barry PP, Tardif L, Lepage Y, Hardy JF. Decreasing the toxic potential of intravenous regional anesthesia. Can J Anaesth 1989; 36: Chow SP, Pun WK, Luk KD, So YC, Ip FK, Chan KC. Modified forearm intravenous regional analgesia for hand surgery. J Hand Surg Am 1989; 14: Apfelbaum JL, Walawander CA, Grasela TH, et al. Eliminating intensive postoperative care in same-day surgery patients using short-acting anesthetics. Anesthesiology 2002; 97: Williams BA, Kentor ML, Vogt MT, et al. Economics of nerve block pain management after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: potential hospital cost savings via associated postanesthesia care unit bypass and same-day discharge. Anesthesiology 2004; 100: Williams BA, Kentor ML, Williams JP, et al. PACU bypass after outpatient knee surgery is associated with fewer unplanned hospital admissions but more phase II nursing interventions. Anesthesiology 2002; 97:981 8 Handling editor: L. Colvin 275
The analgesic efficacy of intravenous regional anesthesia with a forearm versus conventional upper arm tourniquet: a systematic review
 Dekoninck et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2018) 18:86 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-018-0550-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The analgesic efficacy of intravenous regional anesthesia with a forearm versus conventional
Dekoninck et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2018) 18:86 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-018-0550-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The analgesic efficacy of intravenous regional anesthesia with a forearm versus conventional
Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
EVALUATION OF THE TOURNIQUET LEAK DURING FOREARM INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA
 EVALUATION OF THE TOURNIQUET LEAK DURING FOREARM INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA - Manual vs Automatic Pump Injection - Roshdi Roshdi Al-Metwalli * Summary Background: The present study was conducted to
EVALUATION OF THE TOURNIQUET LEAK DURING FOREARM INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA - Manual vs Automatic Pump Injection - Roshdi Roshdi Al-Metwalli * Summary Background: The present study was conducted to
Comparison of 0.5% Lignocaine with Tramadol and with Nalbuphine for Day Care IVRA in Upper Limb: an Interventional Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. VIII (September). 2016), PP 99-105 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of 0.5% Lignocaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. VIII (September). 2016), PP 99-105 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of 0.5% Lignocaine
Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture. WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC)
 Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC) Pre-operative Nursing Considerations for Surgery of Forearm Fracture 1. Patient s problems - Diagnosis: Clinical features, x-ray
Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC) Pre-operative Nursing Considerations for Surgery of Forearm Fracture 1. Patient s problems - Diagnosis: Clinical features, x-ray
Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5% Bupivacaine Plus Buprenorphine in Brachial Plexus Block
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
ABSTRACT TITLE: Near-OR Perioperative Interventions to Decrease Hospital Length
 ABSTRACT NUMBER: 020-0094 ABSTRACT TITLE: Near-OR Perioperative Interventions to Decrease Hospital Length of Stay AUTHORS: Mark J. Lenart, MD Vanderbilt University 1301 Medical Center Drive Nashville,
ABSTRACT NUMBER: 020-0094 ABSTRACT TITLE: Near-OR Perioperative Interventions to Decrease Hospital Length of Stay AUTHORS: Mark J. Lenart, MD Vanderbilt University 1301 Medical Center Drive Nashville,
Intra-articular Adjuvant Analgesics Following Knee Arthroscopy: Comparison between Dexmedetomidine and Fentanyl
 Intra-articular Adjuvant Analgesics Following Knee Arthroscopy: Comparison between Dexmedetomidine and Fentanyl 1 Mostafa El-Hamamsy, 2 Mohsen Dorgham 1 Anaesthesia Dept., Faculty of Medicine, El-Fayoum
Intra-articular Adjuvant Analgesics Following Knee Arthroscopy: Comparison between Dexmedetomidine and Fentanyl 1 Mostafa El-Hamamsy, 2 Mohsen Dorgham 1 Anaesthesia Dept., Faculty of Medicine, El-Fayoum
Chapter 39. Volar surface incisions
 Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Effectiveness of Low Dose Lidocaine With and Without Tramadol for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia: A Randomized Prospective Study
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, September: 665-669, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effectiveness of Low Dose Lidocaine With and Without Tramadol for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia:
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, September: 665-669, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effectiveness of Low Dose Lidocaine With and Without Tramadol for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia:
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman
 Questions CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman Web Editor Kirsten Fehrmann - kirstenfehrmann@hotmail.com 1) Why does a LA solution containing Epinephrine cause pain on injection and what can
Questions CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE BLOCK Author John Hyndman Web Editor Kirsten Fehrmann - kirstenfehrmann@hotmail.com 1) Why does a LA solution containing Epinephrine cause pain on injection and what can
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Setting The setting was tertiary care. The economic study appears to have been performed in Heidelberg, Germany.
 Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
(DOES INCLUDE MODERATE SEDATION PRIVILEGES)
 CAROLINAS HEALTHCARE SYSTEM CAROLINAS MEDICAL CENTERS - CHARLOTTE (Carolinas Medical Center, Carolinas Medical Center-University and Carolinas Medical Center Pineville) DEEP SEDATION WITH ANESTHESIA SPECIALTY
CAROLINAS HEALTHCARE SYSTEM CAROLINAS MEDICAL CENTERS - CHARLOTTE (Carolinas Medical Center, Carolinas Medical Center-University and Carolinas Medical Center Pineville) DEEP SEDATION WITH ANESTHESIA SPECIALTY
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 17 Mar 2019 16:13:06 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 09/05/2014 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 17 Mar 2019 16:13:06 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 09/05/2014 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan, BA a James Capon, BS, MS a Hayden Smith, BA a Alexandra Napoli, BS a Patrick Gaspar, MD b
 Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block
 A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block James T. Beckmann MD Stephen K. Aoki MD Stephen Guyette MD Jeffrey Swenson
A Staged Approach to Analgesia After Hip Arthroscopy Using Multimodal Analgesia & Elective Ultrasound Guided Fascia Iliaca Block James T. Beckmann MD Stephen K. Aoki MD Stephen Guyette MD Jeffrey Swenson
Intravenous Regional Anesthesia with Drug Combinations of Lidocaine, Ketamine, and Atracurium
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 1 Intravenous Regional Anesthesia with Drug Combinations of Lidocaine, Ketamine, and Atracurium G Mir, A Naqeeb, T Waani, A Shora Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 1 Intravenous Regional Anesthesia with Drug Combinations of Lidocaine, Ketamine, and Atracurium G Mir, A Naqeeb, T Waani, A Shora Citation
Type of intervention Anaesthesia. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Effect of Ketorolac on Pain Scores and Length of Stay in Post Anaesthetic Care Unit after Major Abdominal Surgery
 Effect of Ketorolac on Pain Scores and Length of Stay in Post Anaesthetic Care Unit after Major Abdominal Surgery Amanat Khan, Ghulam Sabir Iqbal, Azra Naseem, Mohammad Usman Ahmed, Omer Salahuddin Department
Effect of Ketorolac on Pain Scores and Length of Stay in Post Anaesthetic Care Unit after Major Abdominal Surgery Amanat Khan, Ghulam Sabir Iqbal, Azra Naseem, Mohammad Usman Ahmed, Omer Salahuddin Department
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government
 Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Bier s block is a frequently used intravenous regional. Original Article Journal of Kathmandu Medical College, Vol. 2, No. 1, Issue 3, Jan.-Mar.
 Original Article, Vol. 2, No. 1, Issue 3, Jan.-Mar., 2013 Tabdar S 1, Lama S 2, Kadariya ER 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College
Original Article, Vol. 2, No. 1, Issue 3, Jan.-Mar., 2013 Tabdar S 1, Lama S 2, Kadariya ER 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Lecturer, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College
S Kannan, Prem Kumar. Assistant Professor, Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Chennai.
 Original Article CLINICAL COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT VOLUMES OF 0.5% BUPIVACAINE FOR CLAVICULAR SURGERIES USING COMBINED INTERSCALENE AND SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK 2 S Kannan, Prem Kumar,2 Assistant
Original Article CLINICAL COMPARISON OF TWO DIFFERENT VOLUMES OF 0.5% BUPIVACAINE FOR CLAVICULAR SURGERIES USING COMBINED INTERSCALENE AND SUPERFICIAL CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK 2 S Kannan, Prem Kumar,2 Assistant
improve local aesthetic effects in Bier's Block? a double blind placebo controlled study".
 Title of the article: Does the use of nitro-glycerine patch improve local aesthetic effects in Bier's Block? a double blind placebo controlled study". Type of article: Original Ahmed Said Elgebaly, MD.
Title of the article: Does the use of nitro-glycerine patch improve local aesthetic effects in Bier's Block? a double blind placebo controlled study". Type of article: Original Ahmed Said Elgebaly, MD.
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIGNOCAINE 0.5% AND ROPIVACAINE 0.2% FOR INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA FOR ELECTIVE UPPER LIMB SURGERY
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIGNOCAINE 0.5% AND ROPIVACAINE 0.2% FOR INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA FOR ELECTIVE UPPER LIMB SURGERY S. Asrar 1, Devesh S 2, Vidushi S 3, Meenaxi S 4*, Anumeha J 5 Department
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIGNOCAINE 0.5% AND ROPIVACAINE 0.2% FOR INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA FOR ELECTIVE UPPER LIMB SURGERY S. Asrar 1, Devesh S 2, Vidushi S 3, Meenaxi S 4*, Anumeha J 5 Department
REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANESTESIOLOGIA
 Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2013;63(4):311-316 REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANESTESIOLOGIA Official Publication of the Brazilian Society of Anesthesiology www.sba.com.br SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparison of Lornoxicam and
Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2013;63(4):311-316 REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANESTESIOLOGIA Official Publication of the Brazilian Society of Anesthesiology www.sba.com.br SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparison of Lornoxicam and
FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1985), 5, 250-254 FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA W. S. NIMMO AND J. G. TODD is a synthetic opioid analgesic 50 times more potent than morphine, with
Br. J. Anaesth. (1985), 5, 250-254 FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA W. S. NIMMO AND J. G. TODD is a synthetic opioid analgesic 50 times more potent than morphine, with
THE EFFECT OF NITROGLYCERIN AS AN ADJUVANT TO LIDOCAINE IN INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA
 THE EFFECT OF NITROGLYCERIN AS AN ADJUVANT TO LIDOCAINE IN INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA Rahman Abbasivash *, Ebrahim Hassani *, Mir Moussa Aghdashi **, and Mohammad Shirvani *** Implication Statement
THE EFFECT OF NITROGLYCERIN AS AN ADJUVANT TO LIDOCAINE IN INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA Rahman Abbasivash *, Ebrahim Hassani *, Mir Moussa Aghdashi **, and Mohammad Shirvani *** Implication Statement
INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA (BIERS BLOCK);
 ; TO COMPARE THE ANALGESIC EFFECTS OF COMBINATION OF 0.5% LIDOCAINE PLUS KETROLAC IN INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA TECHNIQUE WITH THOSE OF LIDOCAINE 0.5 % ALONE TO PREVENT POST OPERATIVE PAIN ORIGINAL
; TO COMPARE THE ANALGESIC EFFECTS OF COMBINATION OF 0.5% LIDOCAINE PLUS KETROLAC IN INTRAVENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA TECHNIQUE WITH THOSE OF LIDOCAINE 0.5 % ALONE TO PREVENT POST OPERATIVE PAIN ORIGINAL
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine, fentanyl, tympanoplasty, monitored anaesthesia care. INTRODUCTION:
 13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. DOI: /sjams *Corresponding author Suresh T
 DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.7 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8A):2762-2766 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
DOI: 10.21276/sjams.2016.4.8.7 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(8A):2762-2766 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher
As laparoscopic surgeries are gaining popularity, Original Article. Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1. Introduction
 , Vol. 1, No. 1, Issue 1, Jul.-Sep., 2012 Original Article Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College,
, Vol. 1, No. 1, Issue 1, Jul.-Sep., 2012 Original Article Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair Richard E. Burney, MD; Mythili A. Prabhu, MD; Mary Lou V. H. Greenfield, MPH, MS; Amy Shanks,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair Richard E. Burney, MD; Mythili A. Prabhu, MD; Mary Lou V. H. Greenfield, MPH, MS; Amy Shanks,
Music medicine: A post-operative adjunct
 Music medicine: A post-operative adjunct Anesthesia Research Rounds January 8 th, 2013 Aaron Lau CC3 Marko Erak CC3 Outline Overview of current literature Identified research opportunity Proposed pilot
Music medicine: A post-operative adjunct Anesthesia Research Rounds January 8 th, 2013 Aaron Lau CC3 Marko Erak CC3 Outline Overview of current literature Identified research opportunity Proposed pilot
REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY
 REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY Jay B. Brodsky, MD Stanford University School of Medicine Jbrodsky@stanford.edu Potential Advantages Regional compared to General Anesthesia Minimal intra-operative
REGIONAL/LOCAL ANESTHESIA and OBESITY Jay B. Brodsky, MD Stanford University School of Medicine Jbrodsky@stanford.edu Potential Advantages Regional compared to General Anesthesia Minimal intra-operative
Methods. Anesthesiology, V 95, No 3, Sep Downloaded From: on 07/19/2018
 Anesthesiology 2001; 95:627 31 2001 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Ropivacaine 0.2% and Lidocaine 0.5% for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia in Outpatient
Anesthesiology 2001; 95:627 31 2001 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Ropivacaine 0.2% and Lidocaine 0.5% for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia in Outpatient
Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery
 (Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
(Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries. (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone
 Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block
 Tanta Medical Journal Vol. (6), April 2008 Original Article ABSTRACT Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Mohamed Samy Seddik Department of Anesthesia & Intensive Care,
Tanta Medical Journal Vol. (6), April 2008 Original Article ABSTRACT Dexamethasone Improves Outcome Of Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block Mohamed Samy Seddik Department of Anesthesia & Intensive Care,
TAP blocks vs wound infiltration in laparoscopic colectomies Results of a Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial
 TAP blocks vs wound infiltration in laparoscopic colectomies Results of a Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial Kim Gorissen Frederic Ris Martijn Gosselink Ian Lindsey Dept of Colorectal Surgery Dept of
TAP blocks vs wound infiltration in laparoscopic colectomies Results of a Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial Kim Gorissen Frederic Ris Martijn Gosselink Ian Lindsey Dept of Colorectal Surgery Dept of
The use of a muscle relaxant to supplement local anaesthetics for Bier's
 Archives of mergency Medicine, 1988, 5, 79-85 The use of a muscle relaxant to supplement local anaesthetics for Bier's blocks R. McGLON,1 F. HYS2 & P. HARRIS3 'The General Infirmary, Leeds, 2Accident and
Archives of mergency Medicine, 1988, 5, 79-85 The use of a muscle relaxant to supplement local anaesthetics for Bier's blocks R. McGLON,1 F. HYS2 & P. HARRIS3 'The General Infirmary, Leeds, 2Accident and
Impact of asystematic review on subsequent clinical research
 Impact of asystematic review on subsequent clinical research The case of the prevention of propofol injection pain Céline Habre 1,Martin R Tramèr 1,DanielM Pöpping 2, Nadia Elia 1,3 1 Division of Anaesthesiology,
Impact of asystematic review on subsequent clinical research The case of the prevention of propofol injection pain Céline Habre 1,Martin R Tramèr 1,DanielM Pöpping 2, Nadia Elia 1,3 1 Division of Anaesthesiology,
Tcases as 'day care' is increasing by the
 Review Article Choice of Anaesthesia for Day Care Surgery Shagufta Choudhary*, M.M. Begani**, Dheeraj Mulchandani*** Abstract Aims and Objectives: To review choice of anaesthesia and anaesthetic management
Review Article Choice of Anaesthesia for Day Care Surgery Shagufta Choudhary*, M.M. Begani**, Dheeraj Mulchandani*** Abstract Aims and Objectives: To review choice of anaesthesia and anaesthetic management
4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ANESTESHIA. Hosein Kimiaei Asadi I, Dariush Mehri II
 4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ANESTESHIA The analgesic effect of nitroglycerin added to lidocaine on quality of intravenous regional anesthesia in patients undergoing elective forearm and hand surgery 1 Hosein Kimiaei
4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ANESTESHIA The analgesic effect of nitroglycerin added to lidocaine on quality of intravenous regional anesthesia in patients undergoing elective forearm and hand surgery 1 Hosein Kimiaei
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome
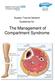 Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Sussex Trauma Network Guidelines for: The Management of Compartment Syndrome Management of Compartment Syndrome Control Page Version: 1 Category number: Approved by: Date approved: Name of author: and
Blood flow management in hand surgery using the S-MART TM device: a prospective randomized controlled study
 Blood flow management in hand surgery using the S-MART TM device: a prospective randomized controlled study E. Calif a, S. Stahl a Abstract Aim: Tourniquets are commonly used in ambulatory upper-limb surgery,
Blood flow management in hand surgery using the S-MART TM device: a prospective randomized controlled study E. Calif a, S. Stahl a Abstract Aim: Tourniquets are commonly used in ambulatory upper-limb surgery,
Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Gi-Soo Lee, Chan Kang*, You Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun
 Comparison of Postoperative Pain Control Methods After Bony Surgery In the Foot And Ankle Gi-Soo Lee, Chan Kang*, You Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine,
Comparison of Postoperative Pain Control Methods After Bony Surgery In the Foot And Ankle Gi-Soo Lee, Chan Kang*, You Gun Won, Byung-Hak Oh, June-Bum Jun Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine,
Alizaprideand ondansetronin the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled
 Alizaprideand ondansetronin the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. M. Smets N. Van Langenhove G. Dewinter Vrijdagochtendkrans22
Alizaprideand ondansetronin the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. M. Smets N. Van Langenhove G. Dewinter Vrijdagochtendkrans22
A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial P Ng, CW Kam, HH Yau Objectives: To compare
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial P Ng, CW Kam, HH Yau Objectives: To compare
The impact of Verapamil addition to Ketamine and Lidocaine Intravenous regional Anesthesia: A Randomized controlled study
 Original Research Article The impact of Verapamil addition to Ketamine and Lidocaine Intravenous regional Anesthesia: A Randomized controlled study Sarat Babu Chevuri 1*, Vijay Rekha 1 1 Associate Professor
Original Research Article The impact of Verapamil addition to Ketamine and Lidocaine Intravenous regional Anesthesia: A Randomized controlled study Sarat Babu Chevuri 1*, Vijay Rekha 1 1 Associate Professor
GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR
 GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR INTRODUCTION Regional block provides superior pain relief, compared
GUIDELINES FOR PERIPHERAL NERVE / PLEXUS BLOCK CATHETER MANAGEMENT DEPARTMENT OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY AND INTENSIVE CARE HOSPITAL KUALA LUMPUR INTRODUCTION Regional block provides superior pain relief, compared
Current evidence in acute pain management. Jeremy Cashman
 Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
Digital RIC. Rhode Island College. Linda M. Green Rhode Island College
 Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2013 The Relationship
Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2013 The Relationship
Practice Advisory on Pediatric Regional Anesthesia:
 ESRA/ASRA Joint Committee: Practice Advisory on Pediatric Regional Anesthesia: Giorgio Ivani Regina Margherita Children s Hospital Turin Italy gioivani@libero.it Why? Obsolete? Advances in Anesthesia
ESRA/ASRA Joint Committee: Practice Advisory on Pediatric Regional Anesthesia: Giorgio Ivani Regina Margherita Children s Hospital Turin Italy gioivani@libero.it Why? Obsolete? Advances in Anesthesia
COMPARISON OF ROPIVACAINE AND LIDOCAINE SENSORY AND MOTOR BLOCK AND POST OPERATIVE ANALGESIC REQUIREMENT IN INTRA- VENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA
 COMPARISON OF ROPIVACAINE AND LIDOCAINE SENSORY AND MOTOR BLOCK AND POST OPERATIVE ANALGESIC REQUIREMENT IN INTRA- VENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA Salah M. kamal Department of Anesthesia and Intensive care,
COMPARISON OF ROPIVACAINE AND LIDOCAINE SENSORY AND MOTOR BLOCK AND POST OPERATIVE ANALGESIC REQUIREMENT IN INTRA- VENOUS REGIONAL ANESTHESIA Salah M. kamal Department of Anesthesia and Intensive care,
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2008 Vol 2 No 2
 Randomized Clinical Trial of Periarticular Drug Injection used in combination Patient-Controlled Analgesia versus Patient-Controlled Analgesia Alone in Total Knee Arthroplasty MN Sabran, MBBS, AJM Talha*,
Randomized Clinical Trial of Periarticular Drug Injection used in combination Patient-Controlled Analgesia versus Patient-Controlled Analgesia Alone in Total Knee Arthroplasty MN Sabran, MBBS, AJM Talha*,
Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine
 1 Case report Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine Bastiaan M. Gerritse, M.D., Ph.D., Daan de Vos, R.N.A, Anton W. Visser, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Anesthesiology,
1 Case report Uneventful recovery following accidental epidural injection of dobutamine Bastiaan M. Gerritse, M.D., Ph.D., Daan de Vos, R.N.A, Anton W. Visser, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Anesthesiology,
A SAFE AND EFFECTIVE WAY TO OPTIMIZE ANESTHESIA DURING SURGERY
 Clinical Evidence Guide A SAFE AD EFFECTIVE WAY TO OPTIMIZE AESTHESIA DURIG SURGERY Bispectral Index (BIS) Complete Monitoring System This guide will help you review the clinical evidence that supports
Clinical Evidence Guide A SAFE AD EFFECTIVE WAY TO OPTIMIZE AESTHESIA DURIG SURGERY Bispectral Index (BIS) Complete Monitoring System This guide will help you review the clinical evidence that supports
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
 Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics
 Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
Dr Kelly Jones Anesthesiologist at Northwest Orthopedics Decrease narcotic use in the immediate post operative period. Better Pain Control Less side effects then General Anesthesia Sedation Post operative
Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent Option For Day Care Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group
 prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group 17 December 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
prilocaine hydrochloride 2% hyperbaric solution for injection (Prilotekal ) SMC No. (665/10) Goldshield Group 17 December 2010 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
DORIS DUKE MEDICAL STUDENTS JOURNAL Volume V,
 Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Silicone ring tourniquet versus pneumatic cuff tourniquet in carpal tunnel release: a randomized comparative study
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:131 135 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0223-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Silicone ring tourniquet versus pneumatic cuff tourniquet in carpal tunnel release: a randomized comparative study
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:131 135 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0223-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Silicone ring tourniquet versus pneumatic cuff tourniquet in carpal tunnel release: a randomized comparative study
Continuous interscalene infusion and single injection using levobupivacaine for analgesia after surgery of the shoulder
 Upper limb Continuous interscalene infusion and single injection using levobupivacaine for analgesia after surgery of the shoulder A DOUBLE-BLIND, RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL J. Kean, C. A. Wigderowitz,
Upper limb Continuous interscalene infusion and single injection using levobupivacaine for analgesia after surgery of the shoulder A DOUBLE-BLIND, RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL J. Kean, C. A. Wigderowitz,
The analgesic effect of lornoxicam when added to lidocaine for intravenous regional anaesthesia
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 97 (3): 408 13 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/ael170 Advance Access publication July 15, 2006 The analgesic effect of lornoxicam when added to lidocaine for intravenous regional
British Journal of Anaesthesia 97 (3): 408 13 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/ael170 Advance Access publication July 15, 2006 The analgesic effect of lornoxicam when added to lidocaine for intravenous regional
Peri operative pain control. Disclosure. Objectives 9/1/2011. No current conflicts of interest
 Peri operative pain control Chris Herndon, PharmD, FASHP Southern Illinois University Edwardsville Disclosure No current conflicts of interest Objectives Discuss studies evaluating the transformation of
Peri operative pain control Chris Herndon, PharmD, FASHP Southern Illinois University Edwardsville Disclosure No current conflicts of interest Objectives Discuss studies evaluating the transformation of
Patient Education Ulnar Collateral Ligament Reconstruction
 Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Overview is commonly referred to as Tommy John Surgery. Tommy John was a baseball pitcher who played for the Los Angeles Dodgers. He was the first person to have
Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Overview is commonly referred to as Tommy John Surgery. Tommy John was a baseball pitcher who played for the Los Angeles Dodgers. He was the first person to have
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
Dexamethasone combined with other antiemetics for prophylaxis after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
 Original Research Article Dexamethasone combined with other antiemetics for prophylaxis after laparoscopic cholecystectomy T. Uma Maheswara Rao * Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, Konaseema Institute
Original Research Article Dexamethasone combined with other antiemetics for prophylaxis after laparoscopic cholecystectomy T. Uma Maheswara Rao * Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, Konaseema Institute
A Comparison of Spinal, Epidural, and General Anesthesia for Outpatient Knee Arthroscopy
 AMBULATORY ANESTHESIA SECTION EDITOR PAUL F. WHITE SOCIETY FOR AMBULATORY ANESTHESIA A Comparison of Spinal, Epidural, and General Anesthesia for Outpatient Knee Arthroscopy Michael F. Mulroy, MD, Kathleen
AMBULATORY ANESTHESIA SECTION EDITOR PAUL F. WHITE SOCIETY FOR AMBULATORY ANESTHESIA A Comparison of Spinal, Epidural, and General Anesthesia for Outpatient Knee Arthroscopy Michael F. Mulroy, MD, Kathleen
Evaluation of the Injured Hand. Sanjay K. Sharma, M.D., F.A.C.S Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016
 Evaluation of the Injured Hand 2016 Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016 Disclosures Nothing relevant Outline General overview of Hand Trauma Anatomy/Examination Selected Cases History of Hand Surgery
Evaluation of the Injured Hand 2016 Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016 Disclosures Nothing relevant Outline General overview of Hand Trauma Anatomy/Examination Selected Cases History of Hand Surgery
Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 33 Number 1 Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia S Gautam, S Singh, R Verma, S Kumar,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 33 Number 1 Efficacy Of Ropivacaine - Fentanyl In Comparison To Bupivacaine - Fentanyl In Epidural Anaesthesia S Gautam, S Singh, R Verma, S Kumar,
Lidocaine use in ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block: what is the minimum effective anaesthetic concentration (MEAC 90 )?
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 110 (6): 1040 4 (2013) Advance Access publication 5 February 2013. doi:10.1093/bja/aes595 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Lidocaine use in ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block: what
British Journal of Anaesthesia 110 (6): 1040 4 (2013) Advance Access publication 5 February 2013. doi:10.1093/bja/aes595 REGIONAL ANAESTHESIA Lidocaine use in ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block: what
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story
 Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story Adela Hilda Onuţu, MD, PhD Cluj-Napoca, Romania adela_hilda@yahoo.com No conflict of interest Contents Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD)
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction a neverending story Adela Hilda Onuţu, MD, PhD Cluj-Napoca, Romania adela_hilda@yahoo.com No conflict of interest Contents Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD)
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 74/Dec 29, 2014 Page 15535
 RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
RANDOMISED CLINICAL TRIAL TO COMPARE THE EFFECT OF PRETREATMENT OF KETAMINE AND LIGNOCAINE ON PROPOFOL INJECTION PAIN Hanumanthappa V. Airani 1, Bhagyashree Amingad 2, Chandra Kumar B. M 3 HOW TO CITE
Original contribution. Department of Anesthesiology, Sapporo Medical University, School of Medicine, Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
 Session: L150 This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH Disclosures: This presenter has no financial relationships with
Session: L150 This Epidural Catheter Is Not Working Well. What Should I Do? Miguel A. Cruz, M.D. Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH Disclosures: This presenter has no financial relationships with
Ultrasound Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block versus Blind Landmark Technique for Breast Surgery. Does it Really Different?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 235-24, 216 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Ultrasound Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block versus Blind Landmark Technique for Breast Surgery. Does
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 235-24, 216 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Ultrasound Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block versus Blind Landmark Technique for Breast Surgery. Does
Intravenous lidocaine infusions. Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC
 Intravenous lidocaine infusions Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC Thank the organisers for inviting me. No conflicts or disclosures Lidocaine 1 st amide local anesthetic Synthesized in 1943 by Lofgren in Sweden.
Intravenous lidocaine infusions Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC Thank the organisers for inviting me. No conflicts or disclosures Lidocaine 1 st amide local anesthetic Synthesized in 1943 by Lofgren in Sweden.
JSLS. Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection
 Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection David M. B. Rosen, Alan M. Lam, Mark A. Carlton, Gregory M. Cario, Lindsay McBride 3 JSLS
Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection David M. B. Rosen, Alan M. Lam, Mark A. Carlton, Gregory M. Cario, Lindsay McBride 3 JSLS
Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds
 Original Article Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds Khaled Mohammed El-Radaideh, Mohammed Ahmed Al-Ghazo 1 and Kamal Eddin Bani-Hani, 2 Departments
Original Article Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds Khaled Mohammed El-Radaideh, Mohammed Ahmed Al-Ghazo 1 and Kamal Eddin Bani-Hani, 2 Departments
Table of Contents: CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Knife Assembly... Page 6 VERSION 2.2
 www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
www.s2ssurgical.com Table of Contents: Preparation... Page 1 Dissection... Page 2 Tunneling... Page 3 Release... Page 4 Closure... Page 6 Knife Assembly... Page 6 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES Priyesh Bhaskar, Mamta Harjai (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF THE ROLE OF DEXAMETHASONE AS AN ADJUVANT IN SUPRACLAVICULAR BLOCK FOR UPPER LIMB SURGERIES Priyesh Bhaskar, Mamta Harjai (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, March: 155-159, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Intravenous Caffeine for Adult Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Undergoing Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty:
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, March: 155-159, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Intravenous Caffeine for Adult Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Undergoing Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty:
Safety and efficacy of a new tourniquet system
 Sato et al. BMC Surgery 2012, 12:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Safety and efficacy of a new tourniquet system Junko Sato *, Yoshinori Ishii, Hideo Noguchi and Mitsuhiro Takeda Abstract Background: In
Sato et al. BMC Surgery 2012, 12:17 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Safety and efficacy of a new tourniquet system Junko Sato *, Yoshinori Ishii, Hideo Noguchi and Mitsuhiro Takeda Abstract Background: In
New Medicines Profile
 New Medicines Profile August 2008 Issue. 08/07 Lidocaine 70mg/tetracaine 70mg medicated plaster (Rapydan ) Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary
New Medicines Profile August 2008 Issue. 08/07 Lidocaine 70mg/tetracaine 70mg medicated plaster (Rapydan ) Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary
REGIONAL ANALGESIA FOR POST-OPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT INITIAL EXPERIENCE IN A LOW RESOURCE SETTING
 1 Ea s t Af r i c a n Me d i c a l Jo u r n a l March 212 East African Medical Journal Vol. 89 No. 3 March 212 REGIONAL ANALGESIA FOR POST-OPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT INITIAL EXPERIENCE IN A LOW RESOURCE
1 Ea s t Af r i c a n Me d i c a l Jo u r n a l March 212 East African Medical Journal Vol. 89 No. 3 March 212 REGIONAL ANALGESIA FOR POST-OPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT INITIAL EXPERIENCE IN A LOW RESOURCE
WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML)
 , 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
, 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
Citation British journal of anaesthesia, 104. pp ; 2010 is available onlin
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Laryngeal mask airway Supreme for a Author(s) Murata, Hiroaki; Nagaishi, Chikako; Citation British journal of anaesthesia, 104 Issue Date 2010-03 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24856
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Laryngeal mask airway Supreme for a Author(s) Murata, Hiroaki; Nagaishi, Chikako; Citation British journal of anaesthesia, 104 Issue Date 2010-03 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24856
All about your anaesthetic
 Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic Regional anaesthesia 4 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment entre This
Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic Regional anaesthesia 4 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment entre This
Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study
 Original article: Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study RajulSubhash Karmakar 1, ShishirRamachandra Sonkusale 1* 1Associate Professor,
Original article: Evaluation of the Effect of Magnesium Sulphate as Adjunct to Epidural Bupivacaine: An Institutional Based Study RajulSubhash Karmakar 1, ShishirRamachandra Sonkusale 1* 1Associate Professor,
Assistant Professor, Anaesthesia Department, Govt. General Hospital / Guntur Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
 The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Analgesic Effect of Ondansetron when Added to Lidocaine for Intravenous Regional Anesthesia
 International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: 2321-3124 Research Article Available at: http://ijmcr.com The Analgesic Effect of Ondansetron when Added to Lidocaine for Intravenous
International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research ISSN: 2321-3124 Research Article Available at: http://ijmcr.com The Analgesic Effect of Ondansetron when Added to Lidocaine for Intravenous
Closed-loop Double-pump Automated System Manual Boluses
 Closed-loop Double-pump Automated System versus Manual Boluses to treat Hypotension during Spinal Anaesthesia for Caesarean Section: randomised controlled trial Dr. Ban Leong SNG MBBS, MMED, FANZCA, FFPMANZCA,
Closed-loop Double-pump Automated System versus Manual Boluses to treat Hypotension during Spinal Anaesthesia for Caesarean Section: randomised controlled trial Dr. Ban Leong SNG MBBS, MMED, FANZCA, FFPMANZCA,
A Patient's Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
