FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
|
|
|
- Alicia Gregory
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines PELVIC MRI Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 72195, 72196, Last Review Date: June 2015 NCD MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_037 Last Revised Date: June 2015 Responsible Department: Clinical Operations FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY Implementation Date: January 2016 NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING: Item/Service Description A. General 1. Method of Operation Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), formerly called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), is a non-invasive method of graphically representing the distribution of water and other hydrogen-rich molecules in the human body. In contrast to conventional radiographs or computed tomography (CT) scans, in which the image is produced by x-ray beam attenuation by an object, MRI is capable of producing images by several techniques. In fact, various combinations of MRI image production methods may be employed to emphasize particular characteristics of the tissue or body part being examined. The basic elements by which MRI produces an image are the density of hydrogen nuclei in the object being examined, their motion, and the relaxation times, and the period of time required for the nuclei to return to their original states in the main, static magnetic field after being subjected to a brief additional magnetic field. These relaxation times reflect the physicalchemical properties of tissue and the molecular environment of its hydrogen nuclei. Only hydrogen atoms are present in human tissues in sufficient concentration for current use in clinical MRI. 2. General Clinical Utility Overall, MRI is a useful diagnostic imaging modality that is capable of demonstrating a wide variety of soft-tissue lesions with contrast resolution equal or superior to CT scanning in various parts of the body. Among the advantages of MRI are the absence of ionizing radiation and the ability to achieve high levels of tissue contrast resolution without injected iodinated radiological contrast agents. Recent advances in technology have resulted in development and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of new paramagnetic contrast agents for MRI which allow even better visualization in some instances. Multi-slice imaging and the ability to image in multiple planes, especially sagittal and coronal, have provided flexibility not easily available with other modalities. Because cortical (outer layer) bone and metallic prostheses do not cause distortion of MR images, it has been possible to visualize certain lesions and body regions with greater certainty than has been possible with CT. The use of MRI on 1 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
2 certain soft tissue structures for the purpose of detecting disruptive, neoplastic, degenerative, or inflammatory lesions has now become established in medical practice. Indications and Limitations of Coverage B. Nationally Covered MRI Indications 1. MRI Although several uses of MRI are still considered investigational and some uses are clearly contraindicated (see subsection C), MRI is considered medically efficacious for a number of uses. Use the following descriptions as general guidelines or examples of what may be considered covered rather than as a restrictive list of specific covered indications. Coverage is limited to MRI units that have received FDA premarket approval, and such units must be operated within the parameters specified by the approval. In addition, the services must be reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of the specific patient involved. a) Effective November 22, 1985: a. MRI is useful in examining the head, central nervous system, and spine. b. Multiple sclerosis can be diagnosed with MRI and the contents of the posterior fossa are visible. c. The inherent tissue contrast resolution of MRI makes it an appropriate standard diagnostic modality for general neuroradiology. b) Effective November 22, 1985: a. MRI can assist in the differential diagnosis of mediastinal and retroperitoneal masses, including abnormalities of the large vessels such as aneurysms and dissection. b. When a clinical need exists to visualize the parenchyma of solid organs to detect anatomic disruption or neoplasia, this can be accomplished in the liver, urogenital system, adrenals, and pelvic organs without the use of radiological contrast materials. When MRI is considered reasonable and necessary, the use of paramagnetic contrast materials may be covered as part of the study. c. MRI may also be used to detect and stage pelvic and retroperitoneal neoplasms and d. to evaluate disorders of cancellous bone and soft tissues. e. It may also be used in the detection of pericardial thickening. f. Primary and secondary bone neoplasm and aseptic necrosis can be detected at an early stage and monitored with MRI. g. Patients with metallic prostheses, especially of the hip, can be imaged in order to detect the early stages of infection of the bone to which the prosthesis is attached. c) Effective March 22, 1994: a. MRI may also be covered to diagnose disc disease without regard to whether radiological imaging has been tried first to diagnose the problem. d) Effective March 4, 1991: a. MRI with gating devices and surface coils, and gating devices that eliminate distorted images caused by cardiac and respiratory movement cycles are now considered state of the art techniques and may be covered. Surface and other specialty coils may also be covered, as they are used routinely for high resolution 2 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
3 imaging where small limited regions of the body are studied. They produce high signal-to-noise ratios resulting in images of enhanced anatomic detail. C. Contraindications and Nationally Non-Covered Indications 1. Contraindications The MRI is not covered when the following patient-specific contraindications are present: MRI is not covered for patients with cardiac pacemakers or with metallic clips on vascular aneurysms unless the Medicare beneficiary meets the provisions of the following exceptions: Effective July 7, 2011, the contraindications will not apply to pacemakers when used according to the FDA-approved labeling in an MRI environment 2. Nationally Non-Covered Indications CMS has determined that MRI of cortical bone and calcifications, and procedures involving spatial resolution of bone and calcifications, are not considered reasonable and necessary indications within the meaning of section 1862(a)(1)(A) of the Act, and are therefore noncovered. D. Other Effective June 3, 2010, all other uses of MRI or MRA for which CMS has not specifically indicated coverage or non-coverage continue to be eligible for coverage through individual local MAC discretion. 3 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
4 NIA CLINICAL GUIDELINE FOR PELVIS MRI: INTRODUCTION: Magnetic resonance imaging of the pelvis is a noninvasive technique for the evaluation, assessment of severity, and follow-up of diseases of the male and female pelvic organs. MRI provides excellent contrast of soft tissues and provides multiplanar and 3D depiction of pathology and anatomy. Patients undergoing MRI do not have exposure to ionizing radiation or iodinated contrast materials. INDICATIONS FOR PELVIC MRI: For known or suspected prostate cancer and for recurrence workup: Initial treatment by radical prostatectomy: o Failure of PSA to fall to undetectable levels or PSA detectable and rising on at least 2 subsequent determinations Initial treatment radiation therapy: o Post-RT rising PSA or positive digital exam and is candidate for local therapy In patients without confirmed diagnosis of prostate cancer (with persistently elevated or rising PSA and prior negative biopsy. Prostatic cancer with: o PSA greater than twenty o Gleason score of seven or greater. Evaluation of suspicious known mass/tumors (unconfirmed diagnosis of cancer) for further evaluation of indeterminate or questionable findings: Initial evaluation of suspicious pelvic masses/tumors found only in the pelvis by physical exam or imaging study, such as Ultrasound (US). Surveillance: One follow-up exam to ensure no suspicious change has occurred in a tumor in the pelvic. No further surveillance unless tumor(s) are specified as highly suspicious, or change was found on last follow-up new/changing sign/symptoms or abnormal lab values. Evaluation of known cancer for further evaluation of indeterminate or questionable findings, identified by physical examination or imaging exams such as Ultrasound (US) and CT: Initial staging of known cancer: o All cancers, excluding the following: Excluding Basal Cell Carcinoma of the skin, Excluding Melanoma without symptoms or signs of metastasis. Three (3) month follow-up of known pelvic cancer undergoing active treatment within the past year. Six (6) month follow-up of known pelvic cancer undergoing active treatment within the past year. Follow-up of known cancer of patient undergoing active treatment within the past year. Known cancer with suspected pelvic metastasis based on a sign, symptom or an abnormal lab value. 4 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
5 Cancer surveillance: Once per year last test must be over ten (10) months ago before new approval for surveillance of known cancer. For evaluation of suspected infection or inflammatory disease: Suspected acute appendicitis (or severe acute diverticulitis) if pelvic pain and tenderness to palpation is present, with at LEAST one of the following: o WBC elevated o Fever o Anorexia or o Nausea and vomiting. Suspected complications of diverticulitis (known to be limited to the pelvis by prior imaging) with pelvic pain or severe tenderness, not responding to antibiotic treatment. Suspected infection in the pelvis. For evaluation of known infection or inflammatory disease follow up: Complications of diverticulitis with severe abdominal pain or severe tenderness, not responding to antibiotic treatment, (prior imaging study is not required for diverticulitis diagnosis). Known inflammatory bowel disease, (Crohn s or Ulcerative colitis) with recurrence or worsening signs/symptoms requiring re-evaluation. Any known infection that is clinically suspected to have created an abscess in the pelvis. Any history of fistula limited to the pelvis that requires re-evaluation, or is suspected to have recurred. Abnormal fluid collection seen on prior imaging that needs follow-up evaluation. Known infection in the pelvis. Pre-operative evaluation: For pelvic surgery or procedure. For post-operative/procedural evaluation: Follow-up of known or suspected post-operative complication involving the hips or the pelvis. A follow-up study to help evaluate a patient s progress after treatment, procedure, intervention or surgery. Documentation requires a medical reason that clearly indicates why additional imaging is needed. Indications for Musculoskeletal Pelvic MRI: Initial evaluation of suspicious mass/tumor of the bones, muscles or soft tissues of the pelvis found on an imaging study, and needing clarification, or found by physical exam and remains non-diagnostic after x-ray or ultrasound. Evaluation of suspected fracture and/or injury when initial imaging is inconclusive or needs further evaluation. For evaluation of known or suspected aseptic/avascular necrosis of hip(s). Sacroiliitis (infectious or inflammatory) Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: o Persistent back and/or sacral pain unresponsive to four (4) weeks of conservative treatment, receivedwithin the past six (6) months, including physical therapy or physician supervised home exercise plan (HEP). 5 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
6 Persistent Pain: o For evaluation of persistent pain unresponsive to four (4) weeks of conservative treatment received within the past six (6) months. Pelvic floor failure: o For evaluation of incontinence and anatomical derangements including, but not limited to uterine prolapse, rectocele, cystocele. o For further evaluation of congenital anomalies of the sacrum and pelvis and initial imaging has been performed. Indication for combination studies for the initial pre-therapy staging of cancer, OR ongoing tumor/cancer surveillance OR evaluation of suspected metastases: 5 concurrent studies to include CT or MRI of any of the following areas as appropriate depending on the cancer: Neck, Abdomen, Pelvis, Chest, Brain, Cervical Spine, Thoracic Spine or Lumbar Spine o Cancer surveillance excluding small cell lung cancer: Every six (6) months for the first two (2) years then annually thereafter. o Cancer surveillance small cell lung cancer: Up to every 3 months for the first two years then annually thereafter. Other Indications for a Pelvic MRI: For location or evaluation of undescended testes in adults and in children, including determination of location of testes, where ultrasound has been done previously. To provide an alternative to follow-up of an indeterminate pelvic CT when previous CT/Ultrasound was equivocal and needed to clarify a finding a CT could not. For evaluation and characterization of uterine and adnexal masses, (e.g., fibroids, ovaries, tubes and uterine ligaments), or congenital abnormality where ultrasound has been done previously. For evaluation of uterus prior to embolization. For evaluation of endometriosis. Prior to uterine surgery if there is abnormality suspected on prior ultrasound. For evaluation of known or suspected abnormality of the fetus noted on prior imaging and no prior pelvis MRI. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION RELATED TO PELVIC MRI: *Conservative Therapy - Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction should include a multimodality approach consisting of a combination of active and inactive components., Inactive components, such as rest, ice, heat, modified activities, medical devices, acupuncture and/or stimulators, medications, injections (epidural, facet, bursal, and/or joint, not including trigger point, and diathermy can be utilized.. Active modalities may consist of physical therapy, a physician supervised home exercise program**, and/or chiropractic care. **Home Exercise Program - (HEP) the following two elements are required to meet guidelines for completion of conservative therapy: Information provided on exercise prescription/plan AND Follow up with member with documentation provided regarding completion of HEP (after suitable 6 week period), or inability to complete HEP due to physical reasoni.e. increased pain, inability to physically perform exercises. (Patient inconvenience 6 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
7 or noncompliance without explanation does not constitute inability to complete HEP). MRI imaging Metal devices or foreign body fragments within the body, such as indwelling pacemakers and intracranial aneurysm surgical clips that are not compatible with the use of MRI, may be contraindicated. Other implanted metal devices in the patient as well as external devices such as portable O2 tanks may also be contraindicated. MRI and Undescended Testes The most common genital malformation in boys is undescended testis. The timely management of undescended testis is important to potentially minimize the risk of infertility and less the risk of malignancy. MRI is used as a diagnostic tool in the detection of undescended testes and can reveal information for both anatomic and tissue characterization. It is noninvasive, non-ionizing, and can obtain multiplanar images. MRI and Adnexal Masses MRI is used in the evaluation of adnexal masses in pregnancy. It can identify and characterize different neoplastic and nonneoplastic abnormalities, e.g., exophytic leiomyoma, endometrioma, dermoid cyst, and ovarian edema. It is a useful adjunct when sonography is inconclusive in the evaluation of adnexal masses in pregnancy. MRI and Endometriosis MRI manifestations of endometriosis vary including endometrioma, peritoneal endometrial implant, adhesion and other rare features. The data obtained from imaging must be combined with clinical data to perform preoperative assessment of endometriosis. MRI and Prostate Cancer Although prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer in men, the majority of cases do not lead to a prostate cancer related death. Aggressive treatment of prostate cancer can have side effects such as incontinence, rectal injury and impotence. It is very important to do an evaluation which will assist in making decisions about therapy or treatment. MRI can non-invasively assess prostate tissue, functionally and morphologically. MRI evaluation may use a large array of techniques, e.g., T1- weighted images, T2-weighted images, and dynamic contrast enhanced T1-weighted images. Prostate Cancer For symptomatic patients and/or those with a life expectancy of greater than 5 years, a bone scan is appropriate for patients with T1 to T2 disease who also have a PSA greater than 20ng/mL or a Gleason score of 8 or higher. Patients with a T3 to T4 disease or symptomatic disease should also receive a bone scan. Pelvic computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanning is recommended if there is T3 or T4 disease, or T1 or T2 disease and a nomogram indicates that there is greater than 20% chance of lymph node involvement, although staging studies may not be cost effective until the chance of lymph node positively reaches 45%. Biopsy should be considered for further evaluation of suspicious nodal findings. For all other patients, no addition imaging is required for staging. Men who suffer a biochemical recurrence following prostatectomy fall into two groups: (1) those whose PSA level fails to fall to undetectable levels after surgery, or (2) those who achieve an undetectable PSA after surgery with a subsequent detectable PSA level that increases on two or more laboratory determinations. Since PSA elevation alone does not necessary lead to clinical failure, the workup for both of these groups focuses on the 7 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
8 assessment of distant metastasis. The specific tests depend on the clinical history, but potentially include a bone scan, biopsy, PSA doubling time assessment, CT/MRI or radioimmunologic scintigraphy. (i.e. ProstaScint scan). Bone scans are appropriate when patients develop symptoms or when the PSA level is increasing rapidly. In one study, the probability of a positive bone scan for a patient not on ADT after radical prostatectomy was less then 5% unless the PSA increased to 40 to 45 ng/ml Further work up is indicated in patients who are considered candidates for local therapy. These patients include those with original clinical stage T1-2, a life expectancy of greater than 10 years, and a current PSA of less than 10ng/mL. Work up includes a prostate biopsy, bone scan and additional tests as clinically indicated such as abdominal/pelvic CT, MRI or radioimmunologic scintigraphy. (i.e. ProstaScint scan). A negative biopsy following post-radiation biochemical recurrence poses clinical uncertainties. Observation, ADT, or enrolling in clinical trials is viable options. Alternatively, the patients may undergo more aggressive workup, such as repeat biopsy, MR spectroscopy, and or endorectal MRI. Fusion imaging of multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and trasrectal ultrasound (TRUS) to guide prostate biopsy is not covered. MRI and Rectal Cancer MRI is used in the evaluation of rectal cancer to visualize not only the intestinal wall but also the surrounding pelvic anatomy. MRI is an excellent imaging technique due to its high soft-tissue contrast, powerful gradient system, and high resolution. It provides accurate evaluation of the topographic relationship between lateral tumor extent and the mesorectal fascia. 8 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
9 REFERENCES American College of Radiology. (2014). ACR Appropriateness Criteria Retrieved from American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. (2007). Prostate Cancer Guideline for the Management of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. Retrieved from tment+of+localized+prostate+cancer.pdf Bitti, G.T., Argiolas, G.M., Ballicu, N., Caddeo, E., Cecconi, M., Demurtas, G., Matta, G.,... Siotto, P. (2014). Pelvic Floor Failure: MR Imaging Evaluation of Anatomic and Functional Abnormalities. Radiographics, 34(2), doi: /rg Bloch, B.N., Lenkinski, R.E., & Rofskyk, N.M. (2008). The role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in prostate cancer imaging and staging at 1.5 and 3 tesla: the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) approach. Cancer Biomark, 4(4-5), Retrieved from Brandon, C.J., Jacobson, J.A., Fessell, D., Dong, Q., Morag, Y., Girish, G., & Jamadar, D. (2011). Pain beyond the hip: How anatomy predisposes to injury as visualized by musculoskeletal ultrasound and MRI. American Journal of Roentgenology, 197(5), doi: /AJR Durmus T, Stephan C, Grigoryev M, et al. Detection of prostate cancer by real-time MR/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy: 3T MRI and state of the art sonography. Rofo. 2013;185(5): Fritzsche, P.J., Hricak, H., Kogan, B.A., Winkler, M.L., & Tanagho, E.A. (1987). Undescended testis: Value of MR imaging. Radiology, 164, Retrieved from Hirsch, A.T., Haskal, Z.J., Hertzer, N.R., Bakal, C.W., Creager, M.A., Halperin, J.L, Roegel, B. (2006). ACC/AHA 2005 guidelines for the management of patients with peripheral arterial disease (lower extremity, renal, mesenteric, and abdominal aortic): executive summary a collaborative report from the American Association for Vascular Surgery/Society for Vascular Surgery, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society for Vascular Medicine and Biology, Society of Interventional Radiology, and the ACC/AHA Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Peripheral Arterial Disease) endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; Society for Vascular Nursing; TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus; and Vascular Disease Foundation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 47(6): Retrieved from Klessen, C., Rogalla, P., & Taupitz, M. (2007). Local staging of rectal cancer: The current role of MRI. European Radiology, 17, Retrieved from 9 NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
10 Koulouris, G. (2008). Imaging review of groin pain in elite athletes: An anatomic approach to imaging findings. American Journal of Roentgenology. 191, doi: /AJR Marks L, Young S, Natarajan S. MRI-ultrasound fusion for guidance of targeted prostate biopsy. Curr Opin Urol. 2013;23(1): Mueller, G.C., Hussain, H.K., Smith, Y.R., Quint, E.G., Carlos, R.C., Johnson, T.J. & DeLancey, J.O. (2007). Müllerian Duct Anomalies: Comparison of MRI diagnosis and clinical diagnosis. American Journal of Roentgenology, 189(6), Retrieved from Ostlere, S. (2011). How to image metal-on-metal prostheses and their complications. American Journal of Roengenology, 197, doi: /AJR Schilling D, Kurosch M, Mager R, et al. Fusion imaging in urology: Combination of MRI and TRUS for detection of prostate cancer. Urologe A. 2013;52(4): Shoji S, Hiraiwa S, Endo J, et al. Manually controlled targeted prostate biopsy with realtime fusion imaging of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and transrectal ultrasound: An early experience. Int J Urol Oct 14 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2005). Screening for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. AHRQ: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Yanny, S., Cahir, J.G., Barker, T., Wimhurst, J., Nolan, J.F., Goodwin, R.W., Marshall, T., & Toms, A.P. (2012). MRI of aseptic lymphocytic vasculitis associated lesions in metalon-metal hip replacements. American Journal of Roentgenology, 198, doi: /AJR NCD/NIA Pelvis MRI 2016 Proprietary
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT (TMJ) MRI Original Date: May 23, 2003 Page 1 of 5 CPT Code: 70336 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT (TMJ) MRI Original Date: May 23, 2003 Page 1 of 5 CPT Code: 70336 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines ORBIT MRI Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 7 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: August 2015 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines ORBIT MRI Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 7 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: August 2015 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date:
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (NCD 220.2)
 Policy Number 220.2 Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 05/14/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable to UnitedHealthcare Medicare
Policy Number 220.2 Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Committee Current Approval Date 05/14/2014 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This policy is applicable to UnitedHealthcare Medicare
Revision Date(s): In children under the age of 14, ultrasound should be the initial study performed for evaluation of abdominal pain.
 Subject: MRI Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 618 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Subject: MRI Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 618 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_301 Last Revised Date: March 2018 Responsible Department: Clinical Operations
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS (no U/S) CPT Codes: Cervical Thoracic Region: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492) Lumbar Sacral Region: 64493 (+64494, +64495)
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines PARAVERTEBRAL FACET JOINT INJECTIONS OR BLOCKS (no U/S) CPT Codes: Cervical Thoracic Region: 64490 (+ 64491, +64492) Lumbar Sacral Region: 64493 (+64494, +64495)
Implementation Date: January 2017 Clinical Operations FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guideline CERVICAL SPINE MRI Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 72141, 72142, 72156 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guideline CERVICAL SPINE MRI Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 72141, 72142, 72156 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Revision Date(s): In children under the age of 14, ultrasound should be the initial study performed for evaluation of abdominal pain.
 Subject: CT Abdomen Policy Number: MCR: 635 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Subject: CT Abdomen Policy Number: MCR: 635 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Revision Date(s): In children under the age of 14, ultrasound should be the initial study performed for evaluation of abdominal pain.
 Subject: CT Abdomen and Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 74176, 74177, 74178 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/07/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended
Subject: CT Abdomen and Pelvis Policy Number: MCR: 74176, 74177, 74178 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/07/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended
Staging Colorectal Cancer
 Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 72192 Computed tomography, pelvis; without contrast material 72193 with contrast material(s) 72194 without
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 72192 Computed tomography, pelvis; without contrast material 72193 with contrast material(s) 72194 without
POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET)
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Effective Utilization of Imaging. John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging
 Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
Effective Utilization of Imaging John V. Roberts, M.D. Premier Radiology Abdominal Imaging Safety Contrast and Radiation What to order Abdomen/Pelvis Brain/Spine Chest Musculoskeletal Ob/Gyn Head and Neck
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines CHEST CTA Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 71275 Last Review Date: August 2014 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
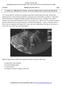 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/20/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 34 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guideline ABDOMEN/PELVIS CT COMBO Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 74176, 74177, 74178 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guideline ABDOMEN/PELVIS CT COMBO Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 74176, 74177, 74178 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March
Subject: Computed Tomography (CT) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar)
 04-70450-23 Original Effective Date: 09/15/09 Reviewed: 02/22/18 Revised: 08/23/18 Subject: Computed Tomography (CT) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
04-70450-23 Original Effective Date: 09/15/09 Reviewed: 02/22/18 Revised: 08/23/18 Subject: Computed Tomography (CT) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
PREAMBLE GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
 PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
PREAMBLE The General Diagnostic Radiology category is intended to cover the body of knowledge a practicing board certified Diagnostic Radiologist should know. Since the range of content relevant to the
Guideline Number: NIA_CG_057-4 Last Revised Date: August 2014 Responsible Department: Implementation Date: August 2014 Clinical Operations
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LOWER EXTREMITY MRI (Foot, Ankle, Knee, Leg or Hip MRI) CPT Codes: 73718, 73719, 73720, 73721, 73722, 73723 Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines LOWER EXTREMITY MRI (Foot, Ankle, Knee, Leg or Hip MRI) CPT Codes: 73718, 73719, 73720, 73721, 73722, 73723 Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of
Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144
 Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144 Objectives: Detection of prostate cancer the need for better imaging What
Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144 Objectives: Detection of prostate cancer the need for better imaging What
Revision Date(s): In children under the age of 14, ultrasound should be the initial study performed for evaluation of abdominal pain.
 Subject: MRI Abdomen Policy Number: MCR: 617 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Subject: MRI Abdomen Policy Number: MCR: 617 Revision Date(s): MHW Original Effective Date: 11/7/2017 Review Date: 8/23/2017 DISCLAIMER This Molina Clinical Review (MCR) is intended to facilitate the Utilization
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS
 JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013
 Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 7 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines ABDOMEN CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 74150, 74160, 74170 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
Magellan Healthcare Clinical guidelines ABDOMEN CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 10 CPT Codes: 74150, 74160, 74170 Last Review Date: May 2016 NCD 220.1 Last Effective Date: March 2008 Guideline
Alison Douglass Gillian Lieberman, MD. November. Colon Cancer. Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD
 November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
November Colon Cancer Alison Douglass, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient Mr. K. is a 67 year old man with no prior medical problems other than hemorrhoids which have caused occasional rectal
Stephen McManus, MD David Levi, MD
 Stephen McManus, MD David Levi, MD Prostate MRI Indications INITIAL DETECTION, STAGING, RECURRENT TUMOR LOCALIZATION, RADIATION THERAPY PLANNING INITIAL DETECTION Clinically suspected prostate cancer before
Stephen McManus, MD David Levi, MD Prostate MRI Indications INITIAL DETECTION, STAGING, RECURRENT TUMOR LOCALIZATION, RADIATION THERAPY PLANNING INITIAL DETECTION Clinically suspected prostate cancer before
11/10/2015. Prostate cancer in the U.S. Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. NIH estimates for 2015.
 Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar)
 04-70540-17 Original Effective Date: 07/01/07 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN
04-70540-17 Original Effective Date: 07/01/07 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
ADI Procedure Codes. August 2016 Revised April 2017 Page 1 of 7 ADI Procedure Codes
 Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: TRANSRECTAL ULTRASOUND (TRUS)
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: TRANSRECTAL ULTRASOUND 06/16/05, 05/18/06, 03/15/07, 02/21/08 PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: TRANSRECTAL ULTRASOUND 06/16/05, 05/18/06, 03/15/07, 02/21/08 PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526)
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
ADDITIONS. The following codes have been added.
 ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
ADDITIONS The following codes have been added. 99446 Interprofessional telephone/internet assessment and management service provided by treating/requesting physician or other qualified health care professional;
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/5/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 6 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 2/5/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 6 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy for prostate cancer. National Horizon Scanning Centre.
 Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Magnetic resonance spectroscopy for prostate cancer August 2006 This technology briefing is based on information available at the time
Horizon Scanning Technology Briefing National Horizon Scanning Centre Magnetic resonance spectroscopy for prostate cancer August 2006 This technology briefing is based on information available at the time
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes
 Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
MRI Based treatment planning for with focus on prostate cancer. Xinglei Shen, MD Department of Radiation Oncology KUMC
 MRI Based treatment planning for with focus on prostate cancer Xinglei Shen, MD Department of Radiation Oncology KUMC Overview How magnetic resonance imaging works (very simple version) Indications for
MRI Based treatment planning for with focus on prostate cancer Xinglei Shen, MD Department of Radiation Oncology KUMC Overview How magnetic resonance imaging works (very simple version) Indications for
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST
 HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
n Make tremendous difference in patients lives: n Diagnosing or excluding disease and injury n Evaluating response to therapy
 Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Imaging: Choosing the Appropriate Exam Rob Milman, MD Austin Radiological Association What is a Radiologist? A physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating disease and injury by using medical imaging
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging
 Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of Bone Marrow Blood Supply Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007 Last revised:
Clinical Appropriateness Guidelines: Advanced Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria: Imaging of Bone Marrow Blood Supply Effective Date: September 5, 2017 Proprietary Date of Origin: 05/21/2007 Last revised:
screening; including image post processing CT, heart; without contrast material; with Requires authorization
 0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Case Scenario 1. 4/19/13 Bone Scan: No scintigraphic findings to suggest skeletal metastases.
 Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management
 Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
Nonsurgical Interventional Treatments for Spinal Pain Management I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain
Special Instructions
 FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging
 Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging Jeffrey T. Yap, PhD http://catalyst.harvard.edu/ services/imagingconsulting.html Senior Diagnostic Physicist, Department of Imaging, DFCI Assistant Professor of Radiology,
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Imaging Jeffrey T. Yap, PhD http://catalyst.harvard.edu/ services/imagingconsulting.html Senior Diagnostic Physicist, Department of Imaging, DFCI Assistant Professor of Radiology,
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF MICHIGAN PRIOR AUTHORIZATION / PRE-SERVICE REVIEW GUIDE IMAGING CODES REQUIRING PRIOR AUTHORIZATION EFFECTIVE 1/1/2014
 70336 MRI MRI, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; with contrast material(s) 70470 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast
70336 MRI MRI, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; with contrast material(s) 70470 CT/CTA CT, head or brain; without contrast
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital
 Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu 1991 1997 Whole body MRI: multistation approach x z Isocenter: Table Move: Multiple Steps Whole body
Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale School of Medicine Yale-New Haven Hospital jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu 1991 1997 Whole body MRI: multistation approach x z Isocenter: Table Move: Multiple Steps Whole body
Introduction to Radiology
 Introduction - Lecture 1 436 Teams Introduction to Radiology Objectives Introduce the various Medical Imaging Modalities. Understand the basics of image generation. Relate imaging to gross anatomy. Appreciate
Introduction - Lecture 1 436 Teams Introduction to Radiology Objectives Introduce the various Medical Imaging Modalities. Understand the basics of image generation. Relate imaging to gross anatomy. Appreciate
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009
 Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER
 IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
IMAGING GUIDELINES - COLORECTAL CANCER DIAGNOSIS The majority of colorectal cancers are diagnosed on colonoscopy, with some being diagnosed on Ba enema, ultrasound or CT. STAGING CT chest, abdomen and
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body What is MRI of the Body? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MR imaging uses
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body What is MRI of the Body? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MR imaging uses
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections
 Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
Spinal and Trigger Point Injections I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will reimburse for nonsurgical interventional treatment for subacute and chronic spinal pain when determined to be medically
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body
 Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body What is MRI of the Body? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that physicians use to diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Scan for mobile link. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - Body What is MRI of the Body? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive medical test that physicians use to diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Pelvic Prolapse. A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
 Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
Pelvic Prolapse A Patient Guide to Pelvic Floor Reconstruction Pelvic Prolapse When an organ becomes displaced, or slips down in the body, it is referred to as a prolapse. Your physician has diagnosed
My Patient Has Pelvic Pain. David A. Kenny DO
 My Patient Has Pelvic Pain David A. Kenny DO Definition Of apparent pelvic origin Present most of the time for at least six months Severe enough to cause functional disability Requiring surgical or medical
My Patient Has Pelvic Pain David A. Kenny DO Definition Of apparent pelvic origin Present most of the time for at least six months Severe enough to cause functional disability Requiring surgical or medical
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Utilization Review Guideline MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE Guideline Number: URG-13.01 Effective Date: February 1, 2019 Table
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Utilization Review Guideline MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) AND COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT) SCAN SITE OF CARE Guideline Number: URG-13.01 Effective Date: February 1, 2019 Table
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography
 Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING PROSTATE/MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI EFFECTIVE DATE: 06/21/18
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide
 High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide 1 High Tech Imaging Authorizations may now be requested through our secure provider portal, BlueAccess. Getting Started Step 1: Log into BlueAccess from www.bcbst.com
High Tech Imaging Quick Reference Guide 1 High Tech Imaging Authorizations may now be requested through our secure provider portal, BlueAccess. Getting Started Step 1: Log into BlueAccess from www.bcbst.com
HIGHMARK Medicare Clinical Guidelines for Medical Necessity Review. Medicare - Pennsylvania
 HIGHMARK 2017 Medicare Clinical Guidelines for Medical Necessity Review Medicare - Pennsylvania Version: 1 Effective October 2016 2017 Magellan Health, Inc. Proprietary Page 1 of 31 Guidelines for Clinical
HIGHMARK 2017 Medicare Clinical Guidelines for Medical Necessity Review Medicare - Pennsylvania Version: 1 Effective October 2016 2017 Magellan Health, Inc. Proprietary Page 1 of 31 Guidelines for Clinical
PROSTATE MRI. Dr. Margaret Gallegos Radiologist Santa Fe Imaging
 PROSTATE MRI Dr. Margaret Gallegos Radiologist Santa Fe Imaging Topics of today s talk How does prostate MRI work? Definition of multiparametric (mp) MRI Anatomy of prostate gland and MRI imaging Role
PROSTATE MRI Dr. Margaret Gallegos Radiologist Santa Fe Imaging Topics of today s talk How does prostate MRI work? Definition of multiparametric (mp) MRI Anatomy of prostate gland and MRI imaging Role
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Codes Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (MSI): Updated 3/2014
 s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
s Requiring Authorization from MedSolutions (): Updated 3/2014 0042T Cerebral Perfusion Analysis using CT with contrast 0159T CAD, including computer algorithm analysis, BREAST MRI 0195T prepare interspace,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
ADVANCED CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation
 Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2551 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Matos, A. T. Almeida, A. Sanches; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT Keywords:
Endometriosis - MRI findings with anatomic-pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2551 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Matos, A. T. Almeida, A. Sanches; Vila Nova de Gaia/PT Keywords:
Coding Companion for OB/GYN. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for OB/GYN A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Skin...1 Pilonidal Cyst...11 Implant...12 Repair...14 Destruction...22
Coding Companion for OB/GYN A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion... i Skin...1 Pilonidal Cyst...11 Implant...12 Repair...14 Destruction...22
MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications
 MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org Acknowledgement Osman
MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org Acknowledgement Osman
Radiology Codes Requiring Authorization*
 70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
70336 Magnetic resonance (eg, proton) imaging, temporomandibular joint(s) 70450 Computed tomography, head or brain; without contrast material 70460 Computed tomography, head or brain; with contrast material(s)
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Chapter 5 Section 1.1. Diagnostic Radiology (Diagnostic Imaging)
 Radiology Chapter 5 Section 1.1 Issue Date: March 7, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(a), (b)(2)(x), (c)(2)(viii), (e)(14) and 32 CFR 199.6(d)(2) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 70010-72292, 73000-76499, 77071-77084,
Radiology Chapter 5 Section 1.1 Issue Date: March 7, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(a), (b)(2)(x), (c)(2)(viii), (e)(14) and 32 CFR 199.6(d)(2) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 70010-72292, 73000-76499, 77071-77084,
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Prostate Cancer Local or distant recurrence?
 Prostate Cancer Local or distant recurrence? Diagnostic flowchart Vanessa Vilas Boas Urologist VFX Hospital FEBU PSA - only recurrence PSA recurrence: 27-53% of all patients undergoing treatment with curative
Prostate Cancer Local or distant recurrence? Diagnostic flowchart Vanessa Vilas Boas Urologist VFX Hospital FEBU PSA - only recurrence PSA recurrence: 27-53% of all patients undergoing treatment with curative
UNMH Radiology Clinical Privileges. Name: Effective Dates: From To
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective April 28, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective April 28, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours. Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany
 PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
