Outline Pretransplant Essential data Why comorbidities are important? For patients with cancer For patients given allogeneic HCT
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Emerald Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comorbidities before Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) The HCT-specific Comorbidity Index (HCT-CI) Mohamed Sorror, M.D., M.Sc. FHCRC Seattle, WA Outline Pretransplant Essential data Why comorbidities are important? For patients with cancer For patients given allogeneic HCT What is the HCT-CI? How to collect comorbidities per the HCT-CI? How the HCT-CI scores could be utilized? Outcome prediction Comparing trials at different institutions Causes of death Other pretransplant risk factors Pre-Transplant Essential Data 1
2 Why comorbidities are important? For patients with cancer Background Comorbidity Any distinct additional clinical entity that has existed or may occur during the clinical course of a patient with an index disease. (Feinstein. J Chronic Dis. 1970; 23:455) Relevant in the prognosis of cancer patients. Physiological burden of chronic disease and its interaction with cancer and cancer treatment Increased severity of comorbidities leads to increased risks of toxicities to specific therapies Clinical impacts Prognosis Quality of care Choice of therapy Tolerability to therapy Mortality Quality of life (QOL) Comorbidities and Cancer Statistical impact Confounder Effect modifier Predictor of study outcome One comprehensive measure de Groot V. J. Clin. Epidemiol.,
3 Comorbidities and Cancer Solid Tumors ± Lymphoma Major predictors of quality of life Age Comorbidities (scores or numbers) Cancer site ± Symptom severity Age did not constitute a difference (<45, 45-65, >65) Comorbidities caused age-related differences Greimel ER. British J Cancer, 1997 Comorbidities and Hematological Malignancies Lymphoma Leukemia Impact survival Death from comorbidities Contraindications to specific therapy Reduction of specific-therapy dose Treatment-related complications Lymphoma: van Spronsen DL. Euro. J Cancer, 2005 Leukemia: Pinto A. Critical Reviews, 2001 Why comorbidities are important? For patients given allogeneic HCT 3
4 Allogeneic HCT for hematological malignancies Myeloablative conditioning regimens: High-dose chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy Potentially curative treatment Relatively high NRM Young healthy patients with limited prior treatment history Nonmyeloablative or reduced-intensity conditioning regimens: Milder regimen-related toxicity and mortality Enroll older patients Enroll more patients with comorbidities Allogeneic HCT for hematological malignancies Available literature focuses on studying individual comorbidities No data on the impact of increasing number and severity of comorbidities on HCT outcomes No comorbidity objective measures are available to determine which patients: Could tolerate myeloablative conditioning Would benefit from nonmyeloablative conditioning Would not benefit from either kind of conditioning Initial experiences with comorbidity indices in allogeneic HCT The Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) 4
5 The CCI Developed from Number and severity of comorbid diseases An inception cohort of 604 medical patients Admitted for a 1 month period at NY hospital One-year follow up data Comorbidity weighted index (training population): Relative risks of each comorbidity for 1-year mortality Adjusted for All other comorbidities Illness severity Reason for admission Employed as weights for different comorbidities Charlson et al, J Chronic Dis., 1987;104: % of patients Seattle experience CCI scores and grade IV toxicity: URD Score 3 Score 1-2 Score 0 Nonmyeloablative (n=60) Myeloablative (n=74) p= % 38% 21% p=0.1 89% 66% Days after HCT Days after HCT Sorror ML et al, Blood. 2004, 104(4): Seattle experience CCI scores and NRM: URD Nonmyeloablative (n=60) Score 3 Score 1-2 Score 0 Myeloablative (n=74) % of patients p=0.1 36% 19% 14% p= % 28% Months after HCT Months after HCT Sorror ML et al, Blood. 2004, 104(4):
6 Seattle experience CCI scores and survival: URD Score 0 Score 1-2 Score 3 Nonmyeloablative (n=60) Myeloablative (n=74) % of patients p= % 47% 9% p= % 22% Months after HCT Months after HCT Sorror ML et al, Blood. 2004, 104(4): Houston experience CCI scores and outcomes: AML/MDS Outcomes for all patients Scores 0-2 (n = 28) Scores >2 (n = 50) P % 2yrs % 2yrs % NRM Day % NRM Day Giralt S et al, Tandem BMT Meeting 2004 The HCT-CI Sorror et al, Blood. 2005, 106(8):
7 Limitations of the CCI for HCT Some CCI comorbidities were rarely identified among HCT patients Pulmonary and hepatic comorbidities Some comorbidities were not represented in the CCI Infections and depression Lack of sensitivity Scores 1 in 35% of patients Particularly low in myeloablative patients (12%) Aims Better define comorbidities using laboratory data Pulmonary, hepatic, cardiac, and renal comorbidities Investigate additional comorbidities among HCT patients All new comorbidities Establish comorbidity scores suited for HCT Other comorbidities as originally defined Design: 1055 patients Nonmyeloablative = 294 Myeloablative = 761 Transplanted between for related recipients for unrelated recipients Malignant or non-malignant hematological diseases Database pre-hct lab values Bilirubin, AST, ALT, creatinine, EF, DLco, FEV 1 Retrospective chart review 7
8 Developing the new HCT-CI All patients were randomly divided into two populations Training set (n=708) Validation set (n=347) Refining some comorbidity definitions Comorbidity Pulmonary: Mild Moderate Severe Cardiac Old definition CCI Dyspnea grade II Dyspnea grade III Dyspnea grade IV Heart failure & myocardial infarction Added definition HCT-CI DLco/ FEV1 >80% DLco/ FEV % DLco/ FEV1 65% EF 50% Refining some comorbidity definitions Comorbidity Hepatic: Old definition CCI Added definition HCT-CI Mild Moderate/severe Renal: Mild Moderate/severe Hepatitis or cirrhosis Portal hypertension ± bleeding varices Creatinine 2-3 mg/dl Creatinine >3 mg/dl, renal dialysis/transplant Hepatitis, bilirubin (1.5 ULN), or AST/ALT (2.5 ULN) Cirrhosis, bilirubin (>1.5 ULN), or AST/ALT (>2.5 ULN) Creatinine >1.2-2 mg/dl Creatinine >2mg/dl 8
9 The added new comorbidities New comorbidity Bleeding Migraine/headache Osteoarthritis Osteoprosis Depression/anxiety Obesity Infection Prevalence 1% 4% 1% 1% 9% 2% 4% Development of the scores Training set 28 comorbidities Calculation of unadjusted HR of each comorbidity for NRM At 2-years Adjustment of HRs for All other comorbidities Disease risk Type of conditioning Age Adjusted HR were employed as weights: HR 1.2 = score 0 HR = score 1 HR = score 2 HR = score 3 New scores and prediction of NRM Scores 0 Training set (n = 708) # Pts, % 38 NRM, % 9 HR* 1 Validation set (n = 346) # Pts, % 38 NRM, % 14 HR* *Adjusted for age, disease risk and type of conditioning 9
10 HCT-CI The validation set CCI Percent NRM Score 3 (28%) Score 1-2 (34%) Score 0 (38%) Score 2 (3%) Score 1 (10%) Score 0 (87%) Percent survival Months after HCT HCT-CI Scoring comorbidities Cardiovascular Arrhythmia: Atrial fibrillation (AF) Atrial flutter Ventricular arrhythmias (Tachycardia or fibrillation) Sick sinus syndrome Cardiac problems: Coronary artery disease Myocardial infarction Congestive heart failure Ejection fraction (EF) 50% Valvular disease Any proven valve stenosis or malfunction with the exception of asymptomatic mitral valve prolapse Prosthetic aortic or mitral valves 10
11 Gastrointestinal Inflammatory bowel disease Ulcerative colitis Crohn s disease Peptic ulcer Previously required treatment Previously bled from ulcer Endocrine Diabetes Type I Type II requiring treatment with oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin Neurology Cerebro-vascular disease History of transient ischemic attacks History of a cerebro-vascular accident 11
12 Obesity Patients with body mass index of >35 (weight in kg/ height x height in m) Infection Documented or suspected and requiring treatment before, during, and after start of conditioning regimen Psychiatric disturbances Depression Anxiety Previously diagnosed and receiving specific treatment Diagnosed and started treatment at the time of HCT Renal Serum creatinine >2 mg/dl On dialysis Had prior renal transplantation Preceding solid malignancy Requiring treatment Excluding non-melanoma skin cancer 12
13 Rheumatologic Systemic lupus erythmatosis (SLE) Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Polymyositis Mixed connective tissue disease Polymyalgia rheumatica Hepatic Mild Chronic hepatitis Bilirubin >upper limit of normal (ULN)-1.5 x ULN AST or ALT >ULN-2.5 x ULN Or Moderate-severe Cirrhosis or fibrosis proved by liver biopsy Bilirubin >1.5 x ULN AST or ALT >2.5 x ULN Pulmonary Moderate Diffusion capacity of CO (DLco) 80%-66% FEV1 80%-66% Shortness of breath on exertion Or Severe DLco 65% FEV1 65% Shortness of breath at rest Requiring supplemental oxygen 13
14 Current and future applications of the HCT-CI Predict HCT outcomes Determine how patients tolerate different conditioning regimens Correlation with Conditioning Intensity Patients diagnosed with MDS or AML Sorror ML et al, ASH
15 HCT-CI scores % of patients Nonablativ Nonmyeloablative e Ablative Myeloablative HCT-CI scores Risk factors HCT-CI scores of 2 Multivariate analysis Risk factors for NRM HR 3.32 P < High-risk disease Unrelated donor Recipient age 50 years Marrow myeloablative conditioning Recipient CMV positive Patients with high-risk MDS/AML and HCT-CI scores of 2 Adjusted* P = % NRM myeloablative nonmyeloablative Years after HCT *Adjusted for age, diagnosis, stem cell source, donor type, prior HCT, and CMV serostatus 15
16 Patients with high-risk MDS/AML and HCT-CI scores of 2 % Overall survival Adjusted* P = 0.01 nonmyeloablative myeloablative Years after HCT *Adjusted for age, diagnosis, stem cell source, donor type, prior HCT, and CMV serostatus Summary Patients with high-risk MDS or AML and HCT-CI scores of 2 receiving nonablative conditioning: Less NRM Survival benefit More data are needed for patients with: Low-risk MDS or AML Low HCT-CI scores HCT-CI should be considered among other risk factors: Prospective trials Patient counseling Correlation with Conditioning Intensity Lymphoid malignancies Sorror ML et al, ASH
17 Characteristics Median age, years Median (range) # of prior regimens Diagnoses NHL CLL HD URD G-PBMC Prior HCT Refractory/untreated relapse Nonablative (n=152) 52 3 (0-10) % /13 Ablative (n=68) 40 2 (0-8) % /3 HCT-CI score 0: Adjusted outcomes Myeloablative Nonmyeloablative Nonmyeloablative (adjusted) NRM* *HR: 0.92, p = 0.93 Survival* *HR: 0.95, p = 0.91 % Years after HCT *Adjusted for age, stem cell source, diagnoses, CMV sero-status, prior regimens, donor type, and disease chemo-sensitivity HCT-CI score 1: Adjusted outcomes Myeloablative Nonmyeloablative Nonmyeloablative (adjusted) NRM* *HR: 0.19, p< Survival* *HR: 0.33, p= % Years after HCT *Adjusted for age, stem cell source, diagnoses, CMV sero-status, prior regimens, donor type, and disease chemo-sensitivity 17
18 Summary and future directions Lymphoid malignancies Patients with no comorbidities: At 3-years NRM of 15%-18% regardless of conditioning Patients with comorbidities receiving nonablative compared to ablative conditioning: Less NRM Better survival Prospective randomized studies for patients: NO comorbidities Age 60 years Comparing patients at different institutions MD Anderson Cancer Center Patients with AML in 1 st complete remission Sorror ML et al, Tandem BMT 2006 AML in first complete remission Characteristics FHCRC (n=177) MDACC (n=67) Age, median (range) years Interval from Dx to HCT, months 41 (19 75) (19 67) 5.1 Donors Matched related 68% 78% Mismatched related 4% 7% Unrelated 28% 15% G-PBMC 35% 42% 18
19 Conditioning regimens FHCRC (n=177), % MDACC (n=67), % Myeloablative TBI-based Non TBI-based Reduced intensity* 2 22 Nonablative *Includes fludarabine/alkylating agent-based regimens Includes 2 Gy TBI-based regimen or fludarabine/ara-c/idarubucin HCT-CI scores FHCRC MDACC % of patients HCT-CI scores Individual comorbidities FHCRC MDACC % of patients Pulmonary Lung Hepatic Malignancy Liver Cancer Cardiac Obesity Infection DM DM Depression Rheumatology Psych 19
20 2-year NRM stratified by HCT-CI scores FHCRC Score 3 Score 1-2 Score 0 MDACC Percent NRM Years after HCT 2-year survival stratified by HCT-CI scores FHCRC Score 0 Score 1-2 Score 3 MDACC Percent survival Years after HCT High Early Mortality Palliative Care Discussion Programs 20
21 Conditioning Group 1 Myeloablative Group 2 Nonmyeloablative Relapse-risk High* High* HCT-CI scores 3 6 *All except AML in 1 st CR, CML in 1 st chronic phase, MDS-RA or RARS Patients with High-risk for relapse Myeloablative HCT-CI scores 3 Nonmyeloablative HCT-CI scores 6 % Years after HCT Correlation with causes of death HCT-CI and acute GVHD Sorror ML et al, Tandem BMT
22 Patients Hematological malignancies myeloablative conditioning CSP/MTX GVHD prophylaxis Characteristics Related (n=709) Unrelated (n=249) Median age, years Disease-risk Low 54% 58% Stem cell source Marrow 67% 77% HCT-CI scores 1 53% 56% Conditioning BU/CY CY/TBI 66% 34% 17% 83% Factors analyzed Recipient age Donor age Recipient/donor sex Type of donor TBI versus no TBI Dose of TBI HCT-CI Disease risk Year of HCT Marrow vs. G-PBMC Full vs. reduced dose: CSP MTX 22
23 Multivariate analysis Risk factors for grades II-IV acute GVHD Risk factors HR P HCT-CI scores TBI Yes 1.71 < CSP dose reduction < 80% Recipient age > Donor Unrelated 1.85 < Multivariate analysis Risk factors for grades III-IV acute GVHD Risk factors HR P HCT-CI scores < Disease-risk High CSP dose reduction < 80% MTX dose reduction < 80% Donor Unrelated 2.60 <.0001 Correlation between age, comorbidity and CSP dose reduction Recipient age P < 20 years 20 years HCT-CI scores of 0 68% 46% CSP dose reduction 34% 73% <
24 Grades III-IV acute GVHD HCT-CI scores Probability if GVHD Related Unrelated Score 5 Score 4 Score 1-3 Score 0 Days after HCT Summary The age related reductions of CSP dosing were likely due to increasing comorbidities with increasing age. Patients with high comorbidity scores or advanced disease should be stratified in future clinical trials for GVHD prophylaxis. Interaction with other pretransplant risk factors HCT-CI and Performance Status Nonmyeloablative Conditioning Sorror ML et al, ASH
25 Correlation between HCT-CI and KPS scores r = HCT-CI scores KPS scores NRM HR: 2.91 HR: 1.64 P< P = 0.04 Percent NRM HCT-CI scores 3 HCT-CI scores KPS 80% KPS >80% Years after HCT Survival HR: 2.46 HR: 1.58 P< P = 0.01 Percent survival HCT-CI scores 0-2 HCT-CI scores KPS >80% KPS 80% Years after HCT 25
26 Risk Groups Consolidated HCT-CI and KPS Definitions HCT-CI KPS Patients (n=341) % Low 0-2 >80% 38 Intermediate I % 16 II 3 >80% 25 High 3 80% 21 Consolidated HCT-CI and KPS Impact on Survival % of patients P < Low 68 Intermediate I 58 Intermediate II 41 High 32 Years after HCT Conclusion: HCT-CI One measure for different comorbidities Higher performance Stratify patients Nonmyeloablative versus myeloablative Prognostic Compare trial results at different institutions Impact on GVHD prophylaxis regimens Consolidated with Performance Status 26
27 Future Aims Multi-institutional validation Inter-rater reliability Interaction with aging Post-HCT toxicities and quality of life Causes of death Simplifying assessment Different methods Education program 27
Comorbidities prior to Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
 Who is fit for transplant? Comorbidities prior to Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MS CIBMTR Medical College of Wisconsin Outline Clinical relevance of studying risk factors
Who is fit for transplant? Comorbidities prior to Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Marcelo C. Pasquini, MD, MS CIBMTR Medical College of Wisconsin Outline Clinical relevance of studying risk factors
Workshop I: Patient Selection Current indication for HCT in adults. Shinichiro Okamoto MD, PhD Keio University, Tokyo, Japan
 Workshop I: Patient Selection Current indication for HCT in adults Shinichiro Okamoto MD, PhD Keio University, Tokyo, Japan Factors to Take into Account with Recommending HCT Patient & disease factors
Workshop I: Patient Selection Current indication for HCT in adults Shinichiro Okamoto MD, PhD Keio University, Tokyo, Japan Factors to Take into Account with Recommending HCT Patient & disease factors
CONSIDERATIONS IN DESIGNING ACUTE GVHD PREVENTION TRIALS: Patient Selection, Concomitant Treatments, Selecting and Assessing Endpoints
 CONSIDERATIONS IN DESIGNING ACUTE GVHD PREVENTION TRIALS: Patient Selection, Concomitant Treatments, Selecting and Assessing Endpoints CENTER FOR INTERNATIONAL BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT RESEARCH Potential
CONSIDERATIONS IN DESIGNING ACUTE GVHD PREVENTION TRIALS: Patient Selection, Concomitant Treatments, Selecting and Assessing Endpoints CENTER FOR INTERNATIONAL BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT RESEARCH Potential
Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care AF symptoms Tachycardia
 Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Survivorship After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Monitoring, Management and Quality of Life
 1 Survivorship After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Monitoring, Management and Quality of Life Stephanie J. Lee, MD, MPH Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center April 16, 2016 (40 min) Hematopoietic
1 Survivorship After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Monitoring, Management and Quality of Life Stephanie J. Lee, MD, MPH Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center April 16, 2016 (40 min) Hematopoietic
RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
 RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Rainer Storb, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, WA Disclosure Grant Support: NIH grants
RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Rainer Storb, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, WA Disclosure Grant Support: NIH grants
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Di Riley Associate Director Clinical Outcomes Programme
 Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Di Riley Associate Director Clinical Outcomes Programme Co-morbidity in cancer Definition:- Co-morbidity is a disease or illness affecting a cancer patient
Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Di Riley Associate Director Clinical Outcomes Programme Co-morbidity in cancer Definition:- Co-morbidity is a disease or illness affecting a cancer patient
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation
 An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa
 Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa Objectives Provide brief review of marrow failure Re emphasize the importance of predictions
Bone Marrow Transplantation in Myelodysplastic Syndromes An overview for the Myelodysplasia Support Group of Ottawa Objectives Provide brief review of marrow failure Re emphasize the importance of predictions
HCT for Myelofibrosis
 Allogeneic HSCT for MDS and Myelofibrosis Sunil Abhyankar, MD Professor Medicine, Medical Director, Pheresis and Cell Processing University of Kansas Hospital BMT Program April 27 th, 213 HCT for Myelofibrosis
Allogeneic HSCT for MDS and Myelofibrosis Sunil Abhyankar, MD Professor Medicine, Medical Director, Pheresis and Cell Processing University of Kansas Hospital BMT Program April 27 th, 213 HCT for Myelofibrosis
Jacqueline C. Barrientos, Nicole Meyer, Xue Song, Kanti R. Rai ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 2015:3301
 Characterization of atrial fibrillation and bleeding risk factors in patients with CLL: A population-based retrospective cohort study of administrative medical claims data in the U.S. Jacqueline C. Barrientos,
Characterization of atrial fibrillation and bleeding risk factors in patients with CLL: A population-based retrospective cohort study of administrative medical claims data in the U.S. Jacqueline C. Barrientos,
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Protecting Your Health After Transplant (Adults)
 Protecting Your Health After Transplant (Adults) Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, Health Services Research, National Marrow Donor Program Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine, University of
Protecting Your Health After Transplant (Adults) Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, Health Services Research, National Marrow Donor Program Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine, University of
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation
 Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016
 What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
Donatore HLA identico di anni o MUD giovane?
 Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
Review of Stem Cell Collection Data 2016 Ronan Foley, Professor, Director Stem Cell Laboratory, McMaster University
 1 Review of Stem Cell Collection Data 2016 Ronan Foley, Professor, Director Stem Cell Laboratory, McMaster University Objectives 2 Review our national apheresis-based stem cell registry To evaluate the
1 Review of Stem Cell Collection Data 2016 Ronan Foley, Professor, Director Stem Cell Laboratory, McMaster University Objectives 2 Review our national apheresis-based stem cell registry To evaluate the
KEY WORDS: Comorbidity index, Reduced-intensity conditioning stem cell transplantation, Allo-RIC, HCT-CI, Mortality INTRODUCTION
 Comparison of Two Pretransplant Predictive Models and a Flexible HCT-CI Using Different Cut off Points to Determine Low-, Intermediate-, and High-Risk Groups: The Flexible HCT-CI Is the Best Predictor
Comparison of Two Pretransplant Predictive Models and a Flexible HCT-CI Using Different Cut off Points to Determine Low-, Intermediate-, and High-Risk Groups: The Flexible HCT-CI Is the Best Predictor
Samples Available for Recipient Only. Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
Samples Available for Recipient Only. Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Samples Available for Recipient and Donor
 Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
Unrelated HCT Research Sample Inventory - Summary for First Allogeneic Transplants in CRF and TED with biospecimens available through the CIBMTR Repository stratified by availability of paired samples,
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Michael Chapman Research Programme Manager
 Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Michael Chapman Research Programme Manager Co-morbidity in cancer Definition:- Co-morbidity is a disease or illness affecting a cancer patient in addition
Why is co-morbidity important for cancer patients? Michael Chapman Research Programme Manager Co-morbidity in cancer Definition:- Co-morbidity is a disease or illness affecting a cancer patient in addition
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Late Effects after Transplantation for Pediatric Severe Aplastic Anemia. Jean E. Sanders, M.D.
 Late Effects after Transplantation for Pediatric Severe Aplastic Anemia Jean E. Sanders, M.D. Patient Characteristics Acquired Fanconi Number 137 15 Gender F:M 63:74 9:6 Etiology: Idiopathic Hepatitis
Late Effects after Transplantation for Pediatric Severe Aplastic Anemia Jean E. Sanders, M.D. Patient Characteristics Acquired Fanconi Number 137 15 Gender F:M 63:74 9:6 Etiology: Idiopathic Hepatitis
Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup
 Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Director, Blood & Marrow Transplant Program, Cleveland Clinic Professor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Director, Blood & Marrow Transplant Program, Cleveland Clinic Professor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML 2011 Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders Report on EHA/ICML 2011 presentations Efficacy and safety of bendamustine plus
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML 2011 Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders Report on EHA/ICML 2011 presentations Efficacy and safety of bendamustine plus
MUD SCT. Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
 MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
 ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Corey Cutler, MD MPH FRCPC Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA HCT Outcomes - MDS 2001-2011
ADVANCES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES Corey Cutler, MD MPH FRCPC Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA HCT Outcomes - MDS 2001-2011
Stem cell transplantation in elderly, but fit multiple myeloma patients
 Stem cell transplantation in elderly, but fit multiple myeloma patients Mohamad MOHTY, MD, PhD Clinical Hematology and Cellular Therapy Dpt. Université Pierre & Marie Curie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine INSERM
Stem cell transplantation in elderly, but fit multiple myeloma patients Mohamad MOHTY, MD, PhD Clinical Hematology and Cellular Therapy Dpt. Université Pierre & Marie Curie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine INSERM
Long-Term Outcomes After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
 Long-Term Outcomes After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Conflicts of Interest No relevant financial conflicts of interest Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, NMDP Assistant Scientific Director,
Long-Term Outcomes After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Conflicts of Interest No relevant financial conflicts of interest Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, NMDP Assistant Scientific Director,
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Kidney Transplantation
 Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Kidney Transplantation Version 3.0 Trillium Gift of Life Network Adult Kidney Transplantation Referral & Listing Criteria PATIENT REFERRAL CRITERIA: The
Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Kidney Transplantation Version 3.0 Trillium Gift of Life Network Adult Kidney Transplantation Referral & Listing Criteria PATIENT REFERRAL CRITERIA: The
Late effects after HSCT
 Late effects after HSCT Yves Chalandon Hematology Division, University Hospital of Geneva (HUG) Switzerland Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Company name Disclosures of: Yves Chalandon Research support
Late effects after HSCT Yves Chalandon Hematology Division, University Hospital of Geneva (HUG) Switzerland Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Company name Disclosures of: Yves Chalandon Research support
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Clinical Outcome in Patients with Aortic Stenosis
 Clinical Outcome in Patients with Aortic Stenosis Is the Prognosis Worse in Patients with Low-Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis? Yoel Angel BSc, Shemy Carasso MD, Diab Mutlak MD, Jonathan Lessick MD Dsc,
Clinical Outcome in Patients with Aortic Stenosis Is the Prognosis Worse in Patients with Low-Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis? Yoel Angel BSc, Shemy Carasso MD, Diab Mutlak MD, Jonathan Lessick MD Dsc,
Late complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplant in adult patients
 Late complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplant in adult patients Gérard Socié, MD, PhD Hematology/Transplantation, Hospital Saint Louis, Paris, France Synopsis H S C T Allogeneic HSCT activity
Late complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplant in adult patients Gérard Socié, MD, PhD Hematology/Transplantation, Hospital Saint Louis, Paris, France Synopsis H S C T Allogeneic HSCT activity
Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Pancreas-After- Kidney Transplantation
 Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Pancreas-After- Kidney Transplantation Version 2.0 Trillium Gift of Life Network Adult Pancreas-After-Kidney Transplantation Referral & Listing Criteria
Ontario s Referral and Listing Criteria for Adult Pancreas-After- Kidney Transplantation Version 2.0 Trillium Gift of Life Network Adult Pancreas-After-Kidney Transplantation Referral & Listing Criteria
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD
 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Causes of Death. J. Douglas Rizzo, MD MS February, New11_1.ppt
 Causes of Death J. Douglas Rizzo, MD MS February, 2012 New11_1.ppt Overview Attribution of COD important for research purposes Frequently not correctly coded or completely reported Source of confusion
Causes of Death J. Douglas Rizzo, MD MS February, 2012 New11_1.ppt Overview Attribution of COD important for research purposes Frequently not correctly coded or completely reported Source of confusion
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris
 Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris 18th ESH - EBMT Training Course on HSCT 8-10 May 2014, Vienna,
Myeloablative and Reduced Intensity Conditioning for HSCT Annalisa Ruggeri, MD, Hôpital Saint Antoine Eurocord- Hôpital Saint Louis, Paris 18th ESH - EBMT Training Course on HSCT 8-10 May 2014, Vienna,
Late Complications. Objectives. Long-term Survival after HCT. Long-term Survival and Late Complications after HCT. Long-term Survival after HCT
 Objectives Late Complications Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Review late complications in hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients Review screening and prevention guidelines for HCT survivors Review upcoming
Objectives Late Complications Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Review late complications in hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients Review screening and prevention guidelines for HCT survivors Review upcoming
Late Complications. Navneet Majhail, MD, MS
 Late Complications Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, Health Services Research, NMDP Assistant Scientific Director, CIBMTR Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Objectives
Late Complications Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Medical Director, Health Services Research, NMDP Assistant Scientific Director, CIBMTR Adjunct Associate Professor of Medicine University of Minnesota Objectives
Late effects, health status and quality of life after hemopoietic stem cell
 Late effects, health status and quality of life after hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) THE 13th ESH-EBMT TRAINING COURSE ON BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION EBMT Slide template Barcelona 7
Late effects, health status and quality of life after hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) THE 13th ESH-EBMT TRAINING COURSE ON BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION EBMT Slide template Barcelona 7
BMT CLINICAL TRIALS NETWORK RIC vs. MAC Protocol # 0901 Version 5.0 dated March 3, 2014
 Core Study Participants: Baylor College of Medicine (Methodist ) BMT at Northside Hospital Case Western Reserve University Consortia Cleveland Clinic Foundation Oregon Health and Science University University
Core Study Participants: Baylor College of Medicine (Methodist ) BMT at Northside Hospital Case Western Reserve University Consortia Cleveland Clinic Foundation Oregon Health and Science University University
EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT :29 Pagina 454 CHAPTER 30. HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults. A. Sureda
 EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 454 * CHAPTER 30 HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults A. Sureda EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 455 CHAPTER 30 HL in adults 1. Introduction
EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 454 * CHAPTER 30 HSCT for Hodgkin s lymphoma in adults A. Sureda EBMT2008_22_44:EBMT2008 6-11-2008 9:29 Pagina 455 CHAPTER 30 HL in adults 1. Introduction
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
Blood Cancers. Blood Cells. Blood Cancers: Progress and Promise. Bone Marrow and Blood. Lymph Nodes and Spleen
 Blood Cancers: Progress and Promise Mike Barnett & Khaled Ramadan Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Providence Health Care & UBC Blood Cancers Significant health problem Arise from normal cells
Blood Cancers: Progress and Promise Mike Barnett & Khaled Ramadan Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Providence Health Care & UBC Blood Cancers Significant health problem Arise from normal cells
Table S1: Diagnosis and Procedure Codes Used to Ascertain Incident Hip Fracture
 Technical Appendix Table S1: Diagnosis and Procedure Codes Used to Ascertain Incident Hip Fracture and Associated Surgical Treatment ICD 9 Code Descriptions Hip Fracture 820.XX Fracture neck of femur 821.XX
Technical Appendix Table S1: Diagnosis and Procedure Codes Used to Ascertain Incident Hip Fracture and Associated Surgical Treatment ICD 9 Code Descriptions Hip Fracture 820.XX Fracture neck of femur 821.XX
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
Field Underwriting Quickview
 Field Underwriting Quickview For a selected list of medical conditions, the Field Underwriting Quickview outlines possible classifications and the circumstances when coverage may not be. For coverage provided
Field Underwriting Quickview For a selected list of medical conditions, the Field Underwriting Quickview outlines possible classifications and the circumstances when coverage may not be. For coverage provided
AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy?
 AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy? 1960 s: Importance of HLA type in Animal Models Survival of Dogs Given 1000 RAD TBI and a Marrow Infusion from a Littermate Matched or Mismatched for Dog Leucocyte Antigens
AML:Transplant or ChemoTherapy? 1960 s: Importance of HLA type in Animal Models Survival of Dogs Given 1000 RAD TBI and a Marrow Infusion from a Littermate Matched or Mismatched for Dog Leucocyte Antigens
Disclosures. Investigator-initiated study funded by Astellas
 Disclosures Investigator-initiated study funded by Astellas 1 Background Widespread use of preemptive therapy strategies has decreased CMV end-organ disease to 5-8% after HCT. Implications for development
Disclosures Investigator-initiated study funded by Astellas 1 Background Widespread use of preemptive therapy strategies has decreased CMV end-organ disease to 5-8% after HCT. Implications for development
AIH, Marseille 30/09/06
 ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
ALLOGENEIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION FOR MYELOID MALIGNANCIES Transplant and Cellular Therapy Unit Institut Paoli Calmettes Inserm U599 Université de la Méditerranée ée Marseille, France AIH, Marseille
KEY WORDS: Allogeneic, Hematopoietic cell transplantation, Graft-versus-host disease, Immunosuppressants, Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus
 A Retrospective Comparison of Tacrolimus versus Cyclosporine with Methotrexate for Immunosuppression after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation with Mobilized Blood Cells Yoshihiro Inamoto, 1
A Retrospective Comparison of Tacrolimus versus Cyclosporine with Methotrexate for Immunosuppression after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation with Mobilized Blood Cells Yoshihiro Inamoto, 1
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma. Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy
 Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
Haploidentical Transplants for Lymphoma Andrea Bacigalupo Universita Cattolica Policlinico Gemelli Roma - Italy HODGKIN NON HODGKIN Non Myelo Ablative Regimen Luznik L et al BBMT 2008 Comparison of Outcomes
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION. Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore
 THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore Introduction Radiotherapy is the medical use of ionising radiation. TBI or Total Body Irradiation
THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore Introduction Radiotherapy is the medical use of ionising radiation. TBI or Total Body Irradiation
PERFORMANCE AFTER HSCT Mutlu arat, md ıstanbul bilim un., dept. hematology ıstanbul, turkey
 PERFORMANCE AFTER HSCT Mutlu arat, md ıstanbul bilim un., dept. hematology ıstanbul, turkey Joint Educational Meeting of the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anaemia, Late Effects and Autoimmune Diseases Working Parties
PERFORMANCE AFTER HSCT Mutlu arat, md ıstanbul bilim un., dept. hematology ıstanbul, turkey Joint Educational Meeting of the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anaemia, Late Effects and Autoimmune Diseases Working Parties
Reduced-Intensity Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Reduced-Intensity Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation Session Chair: Claudio Anasetti, MD Speakers: Brenda M. Sandmaier, MD; Issa F. Khouri, MD; and Franco Locatelli, MD Outcomes with Myeloid Malignancies
Reduced-Intensity Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation Session Chair: Claudio Anasetti, MD Speakers: Brenda M. Sandmaier, MD; Issa F. Khouri, MD; and Franco Locatelli, MD Outcomes with Myeloid Malignancies
Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Myelofibrosis. Outline
 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Myelofibrosis H.Joachim Deeg MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center & University of Washington, Seattle WA Great Debates, NY, 4/28/2012 Outline Rationale for hematopoietic
Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Myelofibrosis H.Joachim Deeg MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center & University of Washington, Seattle WA Great Debates, NY, 4/28/2012 Outline Rationale for hematopoietic
Supplementary Materials for
 Supplementary Materials for A Clinical Trial for Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Syndromes Not Eligible for Standard Clinical Trials Table of Contents Content Page Supplementary
Supplementary Materials for A Clinical Trial for Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Syndromes Not Eligible for Standard Clinical Trials Table of Contents Content Page Supplementary
Pretransplant Predictors and Posttransplant Sequels of Acute Kidney Injury after Allogeneic. stem cell transplantation
 Pretransplant Predictors and Posttransplant Sequels of Acute Kidney Injury after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Yuki Kagoya, 1 Keisuke Kataoka, 1 Yasuhito Nannya, 1 Mineo Kurokawa 1,2 Acute kidney
Pretransplant Predictors and Posttransplant Sequels of Acute Kidney Injury after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Yuki Kagoya, 1 Keisuke Kataoka, 1 Yasuhito Nannya, 1 Mineo Kurokawa 1,2 Acute kidney
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Summary of Changes Page BMT CTN 1205 Protocol Amendment #4 (Version 5.0) Dated July 22, 2016
 Page 1 of 8 Date: July 22, 2016 Summary of Changes Page BMT CTN 1205 Protocol #4 Dated July 22, 2016 The following changes, and the rationale for the changes, were made to the attached protocol in this
Page 1 of 8 Date: July 22, 2016 Summary of Changes Page BMT CTN 1205 Protocol #4 Dated July 22, 2016 The following changes, and the rationale for the changes, were made to the attached protocol in this
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Steinhubl SR, Waalen J, Edwards AM, et al. Effect of a home-based wearable continuous electrocardiographic monitoring patch on detection of undiagnosed atrial fibrillation
Supplementary Online Content Steinhubl SR, Waalen J, Edwards AM, et al. Effect of a home-based wearable continuous electrocardiographic monitoring patch on detection of undiagnosed atrial fibrillation
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. Cranial Health History Form
 WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Cranial Health History Form Welcome to the Neurosurgery Department at Washington University. To help us treat you, please fill this form out completely. Your Name:
WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Cranial Health History Form Welcome to the Neurosurgery Department at Washington University. To help us treat you, please fill this form out completely. Your Name:
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
 Version 3-30-2009 Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Authors: Hirohisa Nakamae, 1 Katharine A. Kirby, 1 Brenda M. Sandmaier, 1,2
Version 3-30-2009 Effect of Conditioning Regimen Intensity on CMV Infection in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Authors: Hirohisa Nakamae, 1 Katharine A. Kirby, 1 Brenda M. Sandmaier, 1,2
KEY WORDS: CRp, Platelet recovery, AML, MDS, Transplant
 Platelet Recovery Before Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Predicts Posttransplantation Outcomes in Patients with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Gheath Alatrash, Matteo Pelosini,
Platelet Recovery Before Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Predicts Posttransplantation Outcomes in Patients with Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Gheath Alatrash, Matteo Pelosini,
Late effects and long-term survivorship after HSCT
 Late effects and long-term survivorship after HSCT André Tichelli What are late effects? Why is it of importance? How to proceed in daily routine? 59-year old male survivor 22 years after allogeneic HSCT
Late effects and long-term survivorship after HSCT André Tichelli What are late effects? Why is it of importance? How to proceed in daily routine? 59-year old male survivor 22 years after allogeneic HSCT
Outcome of patients with hematologic malignancy admitted to the ICU
 Outcome of patients with hematologic malignancy admitted to the ICU Geeta Mehta MD, FRCPC Mount Sinai Hospital Toronto, Canada CCCF November 2, 2016 Disclosures Hematologic Malignancy Advances in diagnostics,
Outcome of patients with hematologic malignancy admitted to the ICU Geeta Mehta MD, FRCPC Mount Sinai Hospital Toronto, Canada CCCF November 2, 2016 Disclosures Hematologic Malignancy Advances in diagnostics,
Indication for unrelated allo-sct in 1st CR AML
 Indication for unrelated allo-sct in 1st CR AML It is time to say! Decision of allo-sct: factors to be considered Cytogenetic risk status Molecular genetics FLT3; NPM1, CEBPA. Response to induction Refractoriness
Indication for unrelated allo-sct in 1st CR AML It is time to say! Decision of allo-sct: factors to be considered Cytogenetic risk status Molecular genetics FLT3; NPM1, CEBPA. Response to induction Refractoriness
TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Community Acquired Influenza (v 1.2. Dec 2005) TIBDN ID :
 TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Community Acquired Influenza (v 1.2. Dec 2005) TIBDN ID : 1) Patient Initials 2) Sex: Male Female 4) Hospital: 3) DOB: (dd/month/yyyy) 5) Postal code: INFLUENZA ONSET
TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Community Acquired Influenza (v 1.2. Dec 2005) TIBDN ID : 1) Patient Initials 2) Sex: Male Female 4) Hospital: 3) DOB: (dd/month/yyyy) 5) Postal code: INFLUENZA ONSET
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Busulfan/Cyclophosphamide (BuCy) versus Busulfan/Fludarabine (BuFlu) Conditioning Regimen Debate
 Busulfan/Cyclophosphamide (BuCy) versus Busulfan/Fludarabine (BuFlu) Conditioning Regimen Debate Donald Hutcherson, RPh Clinical Pharmacy Specialist BMT Emory University Hospital/Winship Cancer Institute
Busulfan/Cyclophosphamide (BuCy) versus Busulfan/Fludarabine (BuFlu) Conditioning Regimen Debate Donald Hutcherson, RPh Clinical Pharmacy Specialist BMT Emory University Hospital/Winship Cancer Institute
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
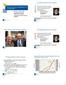 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD
 Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in adult ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart failure being the most common conditions
Chapter 9: Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With ESRD Cardiovascular disease is common in adult ESRD patients, with atherosclerotic heart disease and congestive heart failure being the most common conditions
HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0
 CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
CIC: HSCT - Minimum Essential Data - A REGISTRATION - DAY 0 Centre Identification EBMT Code (CIC): Contact person: Hospital: Email: Unit: Patient Data Date of this report: First transplant for this patient?:
Medical Reference Library Table of Contents
 Medical Reference Library Table of Contents Alcoholism Anemia Anxiety Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Asthma Atrial Fibrillation Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Barrett s Esophagus Bipolar Disorder
Medical Reference Library Table of Contents Alcoholism Anemia Anxiety Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Asthma Atrial Fibrillation Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Barrett s Esophagus Bipolar Disorder
The role of liposomal doxorubicin in DLBCL lymphomas. Michele Spina Aviano
 The role of liposomal doxorubicin in DLBCL lymphomas Michele Spina Aviano Disclosures of Michele Spina Company name Research support Employee Consultant Stockholder Speakers bureau Advisory board Other
The role of liposomal doxorubicin in DLBCL lymphomas Michele Spina Aviano Disclosures of Michele Spina Company name Research support Employee Consultant Stockholder Speakers bureau Advisory board Other
ASBMT and Marrow Transplantation
 Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19 (2013) 784e791 Analysis of Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Manifestations on Major Outcomes: A Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Consortium
Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 19 (2013) 784e791 Analysis of Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Manifestations on Major Outcomes: A Chronic Grant-versus-Host Disease Consortium
A NEW METHOD OF CLASSIFYING PROGNOSTIC COMORBIDITY IN LONGITUDINAL STUDIES: DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION
 J Chron Dis Vol. 40, No. 5, pp. 373-383, 1987 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0021-9681/87 53.00 + 0.00 Copyright 0 1987 Pergamon Journals Lid A NEW METHOD OF CLASSIFYING PROGNOSTIC COMORBIDITY
J Chron Dis Vol. 40, No. 5, pp. 373-383, 1987 Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0021-9681/87 53.00 + 0.00 Copyright 0 1987 Pergamon Journals Lid A NEW METHOD OF CLASSIFYING PROGNOSTIC COMORBIDITY
Transplants for MPD and MDS
 Transplants for MPD and MDS The question is really who to transplant, with what and when. Focus on myelofibrosis Jeff Szer Royal Melbourne Hospital Myelodysplasia Little needs to be said Despite new therapies
Transplants for MPD and MDS The question is really who to transplant, with what and when. Focus on myelofibrosis Jeff Szer Royal Melbourne Hospital Myelodysplasia Little needs to be said Despite new therapies
TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Hospital Acquired Influenza (v.1.2. Dec, 2005)
 TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Hospital Acquired Influenza (v.1.2. Dec, 2005) TIBDN ID: 1) Patient Initials 2) Sex: Male Female 4) Hospital: 3) DOB: (dd/month/yyyy) 5) Postal code: INFLUENZA ONSET AND
TIBDN INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE FORM Hospital Acquired Influenza (v.1.2. Dec, 2005) TIBDN ID: 1) Patient Initials 2) Sex: Male Female 4) Hospital: 3) DOB: (dd/month/yyyy) 5) Postal code: INFLUENZA ONSET AND
