1 of 6 10/02/ :03
|
|
|
- Maximilian Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 6 10/02/ :03 Brief Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Evidence-based guidelines for the management of Lyme disease. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Evidence-based guidelines for the management of Lyme disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2004;2(1 Suppl):S1-13. [66 references] GUIDELINE STATUS This is the current release of the guideline. ** REGULATORY ALERT ** FDA WARNING/REGULATORY ALERT Note from the National Guideline Clearinghouse: This guideline references a drug(s) for which important revised regulatory and/or warning information has been released. September 11, 2007, Rocephin (ceftriaxone sodium): Roche informed healthcare professionals about revisions made to the prescribing information for Rocephin to clarify the potential risk associated with concomitant use of Rocephin with calcium or calcium-containing solutions or products. May 2, 2007, Antidepressant drugs: Update to the existing black box warning on the prescribing information on all antidepressant medications to include warnings about the increased risks of suicidal thinking and behavior in young adults ages 18 to 24 years old during the first one to two months of treatment. ** REGULATORY ALERT ** RECOMMENDATIONS EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE RECOMMENDATIONS IDENTIFYING INFORMATION AND AVAILABILITY DISCLAIMER BRIEF SUMMARY CONTENT Go to the Complete Summary RECOMMENDATIONS MAJOR RECOMMENDATIONS Highlights of Guidelines Since there is currently no definitive test for Lyme disease, laboratory results should not be used to exclude an individual from treatment. Lyme disease is a clinical diagnosis and tests should be used to support rather than supersede the physician s judgment. The early use of antibiotics can prevent persistent, recurrent, and refractory Lyme disease. The duration of therapy should be guided by clinical response, rather than by an arbitrary (i.e., 30 day) treatment course. The practice of stopping antibiotics to allow for delayed recovery is not recommended for persistent Lyme disease. In these cases, it is reasonable to continue treatment for several months after clinical and laboratory abnormalities have begun to resolve and symptoms have disappeared. Diagnostic Concerns The most important method for preventing chronic Lyme disease is recognition of the early manifestations of the disease. Atypical Early Presentations Early Lyme disease classically presents with a single erythema migrans (EM or "bull s-eye") rash. The EM rash may be absent in over 50% of Lyme disease cases, however. Patients should be made aware of the significance of a range of rashes beyond the classic EM, including multiple, flat, raised, or blistering rashes. Central clearing was absent in over half of a series of EM rashes. Rashes can also mimic other common presentations including a spider bite, ringworm, or cellulitis. Physicians should be aware that fewer than 50% of all Lyme disease patients recall a tick bite. Early Lyme disease should also be considered in an evaluation of "off-season" onset when flu-like symptoms, fever, and chills occur in the summer and fall. Early recognition of atypical early Lyme disease presentation is most likely to occur when the patient has been educated on this topic. New Chronic Lyme Disease Presentations A detailed history may be helpful for suggesting a diagnosis of chronic Lyme disease. Headache, stiff neck, sleep disturbance, and problems with memory and concentration are findings frequently associated with neurologic Lyme disease. Other clues to Lyme disease have been identified, although these have not been consistently present in each patient: numbness and tingling, muscle twitching, photosensitivity, hyperacusis, tinnitus, lightheadedness, and depression. Most patients diagnosed with chronic Lyme disease have an indolent onset and variable course. Neurologic and rheumatologic symptoms are characteristic, and increased severity of symptoms on wakening is common. Neuropsychiatric symptoms alone are more often seen in chronic than acute Lyme disease. Although many studies have found that such clinical features are often not unique to Lyme disease, the striking association of musculoskeletal and neuropsychiatric symptoms, the variability of these symptoms, and their recurrent nature may support a diagnosis of the disease. The Limitations of Physical Findings A comprehensive physical examination should be performed, with special attention to neurologic, rheumatologic, and cardiac symptoms associated
2 2 of 6 10/02/ :03 with Lyme disease. Physical findings are nonspecific and often normal, but arthritis, meningitis, and Bell s palsy may sometimes be noted. Available data suggest that objective evidence alone is inadequate to make treatment decisions, because a significant number of chronic Lyme disease cases may occur in symptomatic patients without objective features on examination or confirmatory laboratory testing. Factors other than physical findings, such as a history of potential exposure, known tick bites, rashes, or symptoms consistent with the typical multisystem presentation of Lyme disease, must also be considered in determining whether an individual patient is a candidate for antibiotic therapy. Sensitivity Limitations of Testing Treatment decisions should not be based routinely or exclusively on laboratory findings. The two-tier diagnostic criteria, requiring both a positive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and western blot, lacks sensitivity and leaves a significant number of individuals with Lyme disease undiagnosed and untreated. These diagnostic criteria were intended to improve the specificity of tests to aid in identifying well-defined Lyme disease cases for research studies. Though arbitrarily chosen, these criteria have been used as rigid diagnostic benchmarks that have prevented individuals with Lyme disease from obtaining treatment. Diagnosis of Lyme disease by two-tier confirmation fails to detect up to 90% of cases and does not distinguish between acute, chronic, or resolved infection. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers a western blot positive if at least 5 of 10 immunoglobulin G (IgG) bands or 2 of 3 immunoglobulin M (IgM) bands are positive. However, other definitions for western blot confirmation have been proposed to improve the test sensitivity. In fact, several studies showed that sensitivity and specificity for both the IgM and IgG western blot range from 92 to 96% when only two specific bands are positive. Lumbar puncture has also been disappointing as a diagnostic test to rule out concomitant central nervous system infection. In Lyme disease, evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid is unreliable for a diagnosis of encephalopathy and neuropathy because of poor sensitivity. For example, pleocytosis was present in only one of 27 patients (sensitivity 3%) and with only seven cells. The antibody index was positive (>1) in only one of 27 patients (sensitivity 3%). An index is the ratio between Lyme ELISA antibodies in the spinal fluid and Lyme ELISA antibodies in the serum. The proposed index of 1.3 would be expected to have even worse sensitivity. Several additional tests for Lyme disease have been evaluated. These include antigen capture, urine antigen, and po lymerase chain reaction. Each has advantages and disadvantages in terms of convenience, cost, assay standardization, availability, and reliability. These tests remain an option to identify people at high risk for persistent, recurrent, and refractory Lyme disease but have not been standardized. Seronegative Lyme Disease A patient who has tested seronegative may have a clinical presentation consistent with Lyme disease, especially if there is no evidence to indicate another illness. Although many individuals do not have confirmatory serologic tests, surveillance studies show that these patients may have a similar risk of developing persistent, recurrent, and refractory Lyme disease compared with the seropositive population. Continued Importance of Differential Diagnosis The differential diagnosis of Lyme disease requires consideration of both infectious and noninfectious etiologies. Among noninfectious causes are thyroid disease, degenerative arthritis, metabolic disorders (vitamin B12 deficiency, diabetes), heavy metal toxicity, vasculitis, and primary psychiatric disorders. Infectious causes can mimic certain aspects of the typical multisystem illness seen in chronic Lyme disease. These include viral syndromes, such as parvovirus B19 or West Nile virus infection, and bacterial mimics, such as relapsing fever, syphilis, leptospirosis, and mycoplasma. The clinical features of chronic Lyme disease can be indistinguishable from fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome. These illnesses must be closely scrutinized for the possibility of etiological Borrelia burgdorferi infection. Clinical Judgment Clinical judgment remains necessary in the diagnosis of late Lyme disease. A problem in some studies that relied on objective evidence was that treatment occurred too late, leaving the patient at risk for persistent and refractory Lyme disease. As noted, time-honored beliefs in objective findings and two-tier serologic testing have not withstood close scrutiny. Lyme disease should be suspected in patients with newly acquired or chronic symptoms (headaches, memory and concentration problems, and joint pain). Management of patients diagnosed on the basis of clinical judgment needs to be tested further in prospective trials, and diagnostic reproducibility must be verified. Testing for Coinfection Polymicrobial infection is a new concern for individuals with Lyme disease, and coinfection is increasingly reported in critically ill individuals. Although B. burgdorferi remains the most common pathogen in tick-borne illnesses, coinfections including Ehrlichia and Babesia strains are increasingly noted in patients with Lyme disease, particularly in those with chronic illness. Bartonella is another organism that is carried by the same ticks that are infected with B. burgdorferi, and evidence suggests that it is a potential coinfecting agent in Lyme disease. Recent animal and human studies suggest that Lyme disease may be more severe and resistant to therapy in coinfected patients. Thus, concurrent testing and treatment for coinfection is mandatory in Lyme disease patients. Treatment Considerations Since Lyme disease can become persistent, recurrent, and refractory even in the face of antibiotic therapy, evaluation and treatment must be prompt and aggressive. Prompt Use of Antibiotics Although no well designed studies have been carried out, the available data support the prompt use of antibiotics to prevent chronic Lyme disease. Antibiotic therapy may need to be initiated upon suspicion of the diagnosis, even without definitive proof. Neither the optimal antibiotic dose nor the duration of therapy has been standardized, but limited data suggest a benefit from increased dosages and longer treatment, comparable to the data on tuberculosis and leprosy which are caused by similarly slow-growing pathogens. Choosing an Antibiotic In acute Lyme
3 3 of 6 10/02/ :03 disease, the choice of antibiotics should be tailored to the individual and take into account the severity of the disease as well as the patient s age, ability to tolerate side effects, clinical features, allergy profile, comorbidities, prior exposure, epidemiologic setting, and cost. Conversely, persistent and refractory Lyme disease treatment is more likely to include intravenous and/or intramuscular antibiotics. The choices depend in part on the patient s response to antibiotic therapy and on the success of antibiotics in treating other Lyme disease patients. Therapy usually starts with oral antibiotics, and some experts recommend high dosages. The choice of antibiotic therapy is guided by weighing the greater activity of intravenous antibiotics in the central nervous system against the lower cost and easy administration of oral antibiotics for B. burgdorferi. Oral Antibiotic Options For many Lyme disease patients, there is no clear advantage of parenteral therapy. Along with cost considerations and pressure to treat patients with Lyme disease with the least intervention, there is growing interest in the use of oral therapy. First-line drug therapies for Lyme disease may include (in alphabetical order): oral amoxicillin, azithromycin, cefuroxime, clarithromycin, doxycycline, and tetracycline. These antibiotics have similar favorable results in comparative trials of early Lyme disease. Intravenous Antibiotic Options It is common practice to consider intravenous antibiotics upon failure of oral medications in patients with persistent, recurrent, or refractory Lyme disease, and as the first line of therapy for certain conditions, (i.e., encephalitis, meningitis, optic neuritis, joint effusions, and heart block). Ideally, the intravenous antibiotic should be selected on the basis of in vitro sensitivity testing or clinical experience. Intravenous antibiotics are also justified by concern for penetration into the central nervous system. Until recently, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and penicillin were the only intravenous antibiotics routinely studied for use in Lyme disease. Intravenous imipenem, azithromycin, and doxycycline have an adequate antispirochetal spectrum of activity and may represent suitable alternative therapies. However, the latter two drugs are often considered for intravenous use only if they are not tolerated orally. Intramuscular Antibiotic Options Intramuscular benzathine penicillin (1.2 to 2.4 million units per week) is sometimes effective in patients who do not respond to oral and intravenous antibiotics. If intramuscular benzathine penicillin is used, long-term therapy may be necessary due to the low serum concentration of this form of penicillin. Benzathine penicillin has mainly been used in patients who have had multiple relapses while receiving oral or intravenous antibiotic therapy or who are intolerant of oral or intravenous antibiotics. Combination Antibiotic Treatment Combination therapy with two or more antibiotics is now increasingly used for refractory Lyme disease and has also been given as initial therapy for some chronic presentations. This approach is already used for another tick-borne illness, babesiosis. Oral amoxicillin, cefuroxime, or (more recently) cefdinir combined with a macrolide (azithromycin or clarithromycin) are examples of combination regimens that have proven successful in clinical practice, although controlled clinical trials are lacking in persistent, recurrent, and refractory Lyme disease. Combination therapy in patients with Lyme disease raises the risk of adverse events. This risk must be weighed against the improved response to combination therapy in Lyme disease patients failing single agents. Sequential Treatment Clinicians increasingly use the sequence of an intravenous antibiotic followed by an oral or intramuscular antibiotic. In two recent case series that employed combination therapy and sequential therapy, most patients were successfully treated. A logical and attractive sequence would be to use intravenous therapy first (e.g., intravenous ceftriaxone), at least until disease progression is arrested and then follow with oral therapy for persistent and recurrent Lyme disease. Dosage Increasingly, clinicians recommend that certain drugs used for Lyme disease be given at higher daily doses: for example, 3,000 6,000 mg of amoxicillin, mg doxycycline, and mg of azithromycin. Some clinicians prescribe antibiotics using blood levels to guide higher doses. Close monitoring of complete blood counts and chemistries are also required with this approach. With higher doses, there may be an increase in adverse events in general and gastrointestinal problems in particular. Acidophilus has reportedly reduced the incidence of Clostridium difficile colitis and non-c. difficile antibiotic-related diarrhea. Serious adverse effects of antibiotics, however, were less common than previous estimates. In a recent clinical trial of chronic Lyme disease, the overall serious adverse event rate was 3% after three months of antibiotics, including 1 month of intravenous antibiotics. Clinicians who have experience with higher dose antibiotic therapy must balance the benefit of higher drug levels achieved with this therapy against the modest risk of gastrointestinal and other side effects. Duration of Therapy Because of the disappointing long-term outcome with shorter courses of antibiotics, the practice of stopping antibiotics to allow for a delayed recovery is no longer recommended for patients with persistent, recurrent, and refractory Lyme disease. Reports show failure rates of 30 62% within 3 years of short-course treatment using antibiotics thought to be effective for Lyme disease. Conversely for neurologic complications of Lyme disease, doubling the length of intravenous ceftriaxone treatment from 2 to 4 weeks improved the success rate from 66 to 80%. The management of chronic Lyme disease must be individualized, since patients will vary according to severity of presentation and response to previous treatment. Concurrent risk factors (i.e., coinfections, previous treatment failures, frequent relapses, neurologic involvement, or previous use of corticosteroids) or evidence of unusually severe Lyme disease should lead to the initiation of prolonged and/or intravenous antibiotic treatment. Physicians should always assess the patient s response to treatment before deciding on appropriate duration of therapy (i.e., weeks versus months). Empiric Treatment
4 4 of 6 10/02/ :03 The importance of establishing the diagnosis of Lyme disease is heightened in light of increasing concern about antibiotic overuse. After an appropriate history, physical examination, and laboratory testing are completed, empiric antimicrobial therapy should be initiated on the basis of clinical clues, the severity of the patient s acute illness, underlying disease, and the likelihood of B. burgdorferi infection. The International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society (ILADS) working group recommends that empiric treatment be considered routine for patients with a likely diagnosis of Lyme disease. Persistent Lyme Disease Persistent Lyme disease is more resistant to treatment and more likely to produce a relapse. Although persistent Lyme disease may resolve without additional therapy, many experts believe that this condition should be treated with repeated and prolonged antibiotics. Physicians should extend the duration of antibiotics to prevent or delay recurrent and refractory Lyme disease. Recurrent Lyme Disease Despite previous antibiotic treatment, Lyme disease has a propensity for relapse and requires careful follow-up for years. The data suggest that failure to eradicate the organism may be the reason for a recurrence of symptoms. Early and aggressive treatment with antibiotics is indicated for recurrent Lyme disease. The ultimate impact from retreating each episode of recurrent Lyme disease is currently unclear. Refractory Lyme Disease Refractory Lyme disease is a devastating condition that usually affects patients with persistent symptomatology and long-term disability. Prompt and aggressive institution of antibiotic therapy may be essential to prevent refractory disease. Increasing evidence shows that antibiotics have a beneficial effect on the course of refractory Lyme disease even in cases where the patient is intolerant of antibiotics or when a previous regimen has failed. Several months of therapy are often required to produce clear evidence of improvement. During this time, symptomatic treatment may be combined with antibiotic treatment. Treatment Failure When patients fail to respond or their conditions deteriorate after initiation of empiric therapy, a number of possibilities should be considered other than Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. These include adverse events that limit treatment, allergic history to medication, inappropriate or inadequate dosing regimen, compliance problems, incorrect medication, immune sequelae, and sequestering of the organism (e.g., in the central nervous system). An alternative diagnosis or coinfection should also be considered. Symptomatic Treatment Although there may be a potential role for symptomatic treatment in chronic Lyme disease, this approach has little support due to the strong possibility of persistent infection. Owing to the potential hazard of immunosuppression and the poor outcome in one study, steroid therapy is not recommended. Surgical synovectomy is associated with significant morbidity and does not address neurologic presentations; it should be reserved for knee pain failing antibiotic treatment. Intra-articular steroid injection may be useful as a temporizing procedure in patients with persistent knee pain but this runs the risk of masking persistent infection. Symptomatic therapy (particularly anti-inflammatory medications, tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors, and hydroxychloroquine) may be useful in concert with antibiotics and in individuals failing antibiotics. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is under study but is not recommended for routine therapeutic use. Other treatments, including cholestyramine (CSM), antifungal therapy, and antiviral agents require further study. Since patients are becoming more interested in alternative therapies (e.g., traditional Chinese medicine, anti-oxidants, hyperthermia, bee venom, naturopathy and homeopathy), physicians should be prepared to address questions regarding these topics. Fibromyalgia The outcome of treating fibromyalgia secondary to Lyme disease with nonantibiotic regimens has been poor. The most encouraging clinical trial showed success in only one of 15 patients and only modest improvement in 6 of 15 individuals with fibromyalgia despite 2 years of treatment. Antibiotic therapy has been much more effective than supportive therapy in symptomatic patients with fibromyalgia secondary to Lyme disease. Fibromyalgia treatment alone without antibiotics raises the risk of conversion to refractory chronic Lyme disease and/or exacerbation of an undiagnosed persistent infection and is not recommended. Increasingly, clinicians do not feel comfortable treating fibromyalgia in Lyme disease without antibiotics. Decision to Stop Antibiotics Several studies of patients with Lyme disease have recommended that antibiotics be discontinued after 30 days of treatment. Complicating the decision to stop antibiotics is the fact that some patients present with disease recurrence after the resolution of their initial Lyme disease symptoms. This is consistent with incomplete antibiotic therapy. Although the optimal time to discontinue antibiotics is unknown, it appears to be dependent on the extent of symptomatology, the patient s previous response to antibiotics, and the overall response to therapy (see below). Rather than an arbitrary 30-day treatment course, the patient s clinical response should guide duration of therapy. Patients must therefore be carefully evaluated for persistent infection before a decision is made to withhold therapy. The decision to discontinue antibiotics should be made in consultation with the patient and should take into account such factors as the frequency and duration of persistent infection, frequency of recurrence, probability of refractory Lyme disease, gains with antibiotics, the importance to the patient of discontinuing antibiotics, and potential for careful follow-up. The ideal approach would be to continue therapy for Lyme disease until the Lyme spirochete is eradicated. Unfortunately there is currently no test available to determine this point. Therefore, the clinician must rely on the factors outlined above to decide on the length of antibiotic therapy for chronic Lyme disease. Alternative Antibiotics There is compelling evidence that Lyme disease can result in serious and potentially refractory illness. Use of alternative antibiotics to treat early Lyme disease with erythema migrans is generally not indicated unless coinfection is suspected. The ILADS Working Group believes that the risk of alternative antibiotics is acceptable in selected Lyme disease patients presenting with chronic
5 5 of 6 10/02/ :03 Lyme disease. Alternative antibiotics include less commonly used oral antibiotics (cefixime, cefdinir, metronidazole) and intravenous antibiotics (imipenem, azithromycin). The role of alternative antibiotics in low-risk patients is less certain and there is less consensus among the guideline developers as to whether the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Therapy for Coinfection Therapy for polymicrobial infection in Lyme disease is a rapidly changing area of clinical practice. Uncomplicated Lyme disease may be managed without addressing coinfection by means of standard oral or parenteral antibiotic therapy. Some but not all experts recommend therapy for subclinical or chronic coinfection with Ehrlichia, Babesia, or Bartonella on the basis of their belief that responses are more prompt with this approach. The dose, duration, and type of treatment for coinfections have not been defined. Published reports of coinfection are limited to a small number of patients treated in open-label, nonrandomized studies. Doxycycline has been indicated for Ehrlichia. A recently published randomized trial determined that treatment of severe Babesia microti with the combination of atovaquone and azithromycin was as effective as the use of standard oral therapy with clindamycin and quinine. The decision to use alternative antibiotics should be based on the individual case, including a careful assessment of the patient s risk factors and personal preferences. Patients managed in this way must be carefully selected and considered reliable for follow-up. Further controlled studies are needed to address the optimal antimicrobial agents for coinfections and the optimal duration of therapy. CLINICAL ALGORITHM(S) None provided EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE RECOMMENDATIONS TYPE OF EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE RECOMMENDATIONS The type of supporting evidence is not specifically stated for each recommendation. IDENTIFYING INFORMATION AND AVAILABILITY BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Evidence-based guidelines for the management of Lyme disease. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2004;2(1 Suppl):S1-13. [66 references] ADAPTATION Not applicable: The guideline was not adapted from another source. DATE RELEASED 2004 GUIDELINE DEVELOPER(S) International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society - Disease Specific Society SOURCE(S) OF FUNDING International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society GUIDELINE COMMITTEE The ILADS Working Group COMPOSITION OF GROUP THAT AUTHORED THE GUIDELINE Working Group Members: Daniel Cameron, MD, MPH, Internal Medicine and Epidemiology, Mt. Kisco, New York; Andrea Gaito, MD, Rheumatology, Basking Ridge, New Jersey; Nick Harris, PhD, Immunology, Pal Alto, California; Gregory Bach, DO, Family and Integrative Medicine, Colmar, Pennsylvania; Sabra Bellovin, MD, Family Practice, Portsmouth, Virginia; Kenneth Bock, MD, Family Practice, Rhineback, New York; Steven Bock, MD, Family Practice, Rhineback, New York; Joseph Burrascano, MD, Internal Medicine, East Hampton, New York; Constance Dickey, RN, Registered Nurse, Hampden, Maine; Richard Horowitz, MD, Internal Medicine, Hyde Park, New York; Steven Phillips, MD, Internal Medicine, Ridgefield, Connecticut; Laurence Meer-Scherrer, MD, Internal Medicine, Flamatt, Switzerland; Bernard Raxlen, MD; Psychiatry, Greenwich, Connecticut; Virginia Sherr, MD, Psychiatry, Holland, Pennsylvania; Harold Smith, MD, Emergency Medicine, Danville, Pennsylvania; Pat Smith, President, Lyme Disease Association, Inc., Jackson, New Jersey; Raphael Stricker, MD, Hematology and Immunotherapy, San Francisco, California FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES/CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Not stated GUIDELINE STATUS This is the current release of the guideline. GUIDELINE AVAILABILITY Electronic copies: Not available at this time. Print copies: Available from the International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society, PO Box , Bethesda, Maryland ; Phone: (301) ; Fax: (301) ; lymedocs@aol.com AVAILABILITY OF COMPANION DOCUMENTS None available PATIENT RESOURCES None available NGC STATUS This NGC summary was completed by ECRI on August 26, The information was verified by the guideline developer on October 13, This
6 6 of 6 10/02/ :03 summary was updated by ECRI Institute on October 3, 2007 following the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advisory on Rocephin (ceftriaxone sodium). This summary was updated by ECRI Institute on November 6, 2007, following the U.S. Food and Drug Administration advisory on Antidepressant drugs. COPYRIGHT STATEMENT This NGC summary is based on the original guideline, which may be subject to the guideline developer's copyright restrictions. DISCLAIMER NGC DISCLAIMER The National Guideline Clearinghouse (NGC) does not develop, produce, approve, or endorse the guidelines represented on this site. All guidelines summarized by NGC and hosted on our site are produced under the auspices of medical specialty societies, relevant professional associations, public or private organizations, other government agencies, health care organizations or plans, and similar entities. Guidelines represented on the NGC Web site are submitted by guideline developers, and are screened solely to determine that they meet the NGC Inclusion Criteria which may be found at NGC, AHRQ, and its contractor ECRI make no warranties concerning the content or clinical efficacy or effectiveness of the clinical practice guidelines and related materials represented on this site. Moreover, the views and opinions of developers or authors of guidelines represented on this site do not necessarily state or reflect those of NGC, AHRQ, or its contractor ECRI, and inclusion or hosting of guidelines in NGC may not be used for advertising or commercial endorsement purposes. Readers with questions regarding guideline content are directed to contact the guideline developer.
Tick Talk: What s new in Lyme Disease. May 5 th, 2017 Cristina Baker, M.D., M.P.H.
 Tick Talk: What s new in Lyme Disease May 5 th, 2017 Cristina Baker, M.D., M.P.H. Dr. Baker indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. She does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Tick Talk: What s new in Lyme Disease May 5 th, 2017 Cristina Baker, M.D., M.P.H. Dr. Baker indicated no potential conflict of interest to this presentation. She does not intend to discuss any unapproved/investigative
Medical Review Criteria Lyme/Tick-Borne Diseases: Use of Parenteral Antibiotics
 Medical Review Criteria Lyme/Tick-Borne Diseases: Use of Parenteral Antibiotics Subject: Lyme/Tick-Borne Diseases: Use of Parenteral Antibiotics Authorization: Prior authorization is required for ALL parenteral
Medical Review Criteria Lyme/Tick-Borne Diseases: Use of Parenteral Antibiotics Subject: Lyme/Tick-Borne Diseases: Use of Parenteral Antibiotics Authorization: Prior authorization is required for ALL parenteral
LYME DISEASE Last revised May 30, 2012
 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Communicable Disease Surveillance Guideline LYME DISEASE Last revised May 30, 2012 I. IDENTIFICATION A. CLINICAL DESCRIPTION: A multi-systemic
Wisconsin Department of Health Services Division of Public Health Communicable Disease Surveillance Guideline LYME DISEASE Last revised May 30, 2012 I. IDENTIFICATION A. CLINICAL DESCRIPTION: A multi-systemic
LYME DISEASE. Page. Lyme Disease: Medical Policy (Effective 10/01/2013)
 MEDICAL POLICY LYME DISEASE Policy Number: 2013T0351K Effective Date: October 1, 2013 Table of Contents COVERAGE RATIONALE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... BACKGROUND... CLINICAL EVIDENCE... U.S. FOOD AND
MEDICAL POLICY LYME DISEASE Policy Number: 2013T0351K Effective Date: October 1, 2013 Table of Contents COVERAGE RATIONALE... BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... BACKGROUND... CLINICAL EVIDENCE... U.S. FOOD AND
STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT GROUP (IDEG) DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND WELLNESS STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT GROUP (IDEG) DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND WELLNESS STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Practice parameter: thymectomy for autoimmune myasthenia gravis (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology.
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Practice parameter: thymectomy for autoimmune myasthenia gravis (an evidence-based review). Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology.
Update on Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin for Providers and Laboratories
 Update on Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin for Providers and Laboratories Christopher Steward Division of Public Health Wisconsin Department of Health Services 04/10/14 Protecting and promoting the
Update on Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin for Providers and Laboratories Christopher Steward Division of Public Health Wisconsin Department of Health Services 04/10/14 Protecting and promoting the
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy for Lyme Disease File Name: intravenous_antibiotic_therapy_for_lyme_disease Origination: 3/2006 Last CAP Review: 2/2017 Next CAP Review: 2/2018 Last
Corporate Medical Policy Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy for Lyme Disease File Name: intravenous_antibiotic_therapy_for_lyme_disease Origination: 3/2006 Last CAP Review: 2/2017 Next CAP Review: 2/2018 Last
Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness. Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia
 Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia 2018 Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia 2018 Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
Acute Lyme disease is a well known and recognized infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochete and associated tick borne organisms.
 Acute Lyme disease is a well known and recognized infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochete and associated tick borne organisms. It is endemic to much of the United States and Europe and
Acute Lyme disease is a well known and recognized infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochete and associated tick borne organisms. It is endemic to much of the United States and Europe and
A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease
 A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Practice parameter: immunotherapy for Guillain-Barre syndrome: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology.
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Practice parameter: immunotherapy for Guillain-Barre syndrome: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S)
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Practice parameter: immunotherapy for Guillain-Barre syndrome: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S)
Guideline Summary NGC-5582
 Guideline Summary NGC-5582 Guideline Title Antiviral therapy and prophylaxis for influenza in children. Bibliographic Source(s) American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases. Antiviral
Guideline Summary NGC-5582 Guideline Title Antiviral therapy and prophylaxis for influenza in children. Bibliographic Source(s) American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases. Antiviral
Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin Christopher Steward Division of Public Health Wisconsin Department of Health Services 04/10/2014
 Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin Christopher Steward Division of Public Health Wisconsin Department of Health Services 04/10/2014 Protecting and promoting the health and safety of the people of Wisconsin
Lyme Disease Surveillance in Wisconsin Christopher Steward Division of Public Health Wisconsin Department of Health Services 04/10/2014 Protecting and promoting the health and safety of the people of Wisconsin
Announcements. Please mute your phones and DO NOT place us on hold. Press *6 to mute your phone.
 Announcements Register for the Epi-Tech Trainings: 1. Log-on or Request log-on ID/password: https://tiny.army.mil/r/zb8a/cme 2. Register for Epi-Tech Surveillance Training: https://tiny.army.mil/r/dvrgo/epitechfy14
Announcements Register for the Epi-Tech Trainings: 1. Log-on or Request log-on ID/password: https://tiny.army.mil/r/zb8a/cme 2. Register for Epi-Tech Surveillance Training: https://tiny.army.mil/r/dvrgo/epitechfy14
A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease
 A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Lyme Disease 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Lyme Disease, an Infectious Diseases Perspective
 Lyme Disease, an Infectious Diseases Perspective Lyme: Pretest 1. The pathognomonic finding of Lyme disease is: 1. An indurated lesion, measuring ~ 2 cm in diameter with a central, necrotic eschar. 2.
Lyme Disease, an Infectious Diseases Perspective Lyme: Pretest 1. The pathognomonic finding of Lyme disease is: 1. An indurated lesion, measuring ~ 2 cm in diameter with a central, necrotic eschar. 2.
Lyme Disease. By Farrah Jangda
 Lyme Disease By Farrah Jangda Disease Name: Lyme Disease Lyme disease is a common tick-borne bacterial infection transmitted from the bite of a tick in United States and Europe (2). It is caused by the
Lyme Disease By Farrah Jangda Disease Name: Lyme Disease Lyme disease is a common tick-borne bacterial infection transmitted from the bite of a tick in United States and Europe (2). It is caused by the
Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease. Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP)
 Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP) Lyme Disease Most common vectorborne illness in the United States Caused by the tick-transmitted spirochete
Seroprevalence of Babesia microti in Individuals with Lyme Disease Sabino R. Curcio, M.S, MLS(ASCP) Lyme Disease Most common vectorborne illness in the United States Caused by the tick-transmitted spirochete
** REGULATORY ALERT **
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Fibromyalgia. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Fibromyalgia. Philadelphia (PA): Intracorp; 2004. Various p. GUIDELINE STATUS This is the current release of the guideline. All Intracorp
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Fibromyalgia. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Fibromyalgia. Philadelphia (PA): Intracorp; 2004. Various p. GUIDELINE STATUS This is the current release of the guideline. All Intracorp
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE. Cervical cytology screening. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S)
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Cervical cytology screening. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Cervical cytology screening. Washington (DC): American
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Cervical cytology screening. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Cervical cytology screening. Washington (DC): American
Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists Position Statement
 04-ID-01 Committee: Title: Infectious Disease Revision of the National Surveillance Case Definition of Diseases Caused by Neurotropic Domestic Arboviruses, Including the Addition to the NNDSS of Non-Neuroinvasive
04-ID-01 Committee: Title: Infectious Disease Revision of the National Surveillance Case Definition of Diseases Caused by Neurotropic Domestic Arboviruses, Including the Addition to the NNDSS of Non-Neuroinvasive
MULTI-SYSTEMIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE SYNDROME SYMPTOM QUESTIONNAIRE
 MULTI-SYSTEMIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE SYNDROME SYMPTOM QUESTIONNAIRE SECTION 1: SYMPTOM FREQUENCY SCORE Select the frequency of each of the following symptoms. 0 = None 1 = Mild 2 = Moderate 3 = Severe 1.
MULTI-SYSTEMIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE SYNDROME SYMPTOM QUESTIONNAIRE SECTION 1: SYMPTOM FREQUENCY SCORE Select the frequency of each of the following symptoms. 0 = None 1 = Mild 2 = Moderate 3 = Severe 1.
Do you think you have Lyme Disease? Fill out The Horowitz MSIDS Questionnaire (HMQ)
 Do you think you have Lyme Disease? Fill out The Horowitz MSIDS Questionnaire (HMQ) Answer the following questions as honestly as possible. Think about how you have been feeling over the previous month
Do you think you have Lyme Disease? Fill out The Horowitz MSIDS Questionnaire (HMQ) Answer the following questions as honestly as possible. Think about how you have been feeling over the previous month
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Lyme disease stakeholder scoping workshop
 1.1 Who is the focus: Groups that will be covered: Adults and children with a suspected or confirmed diagnosis of Lyme disease 1.2. Settings All setting where NHS care The group suggested that the following
1.1 Who is the focus: Groups that will be covered: Adults and children with a suspected or confirmed diagnosis of Lyme disease 1.2. Settings All setting where NHS care The group suggested that the following
Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis!
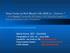 Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis! Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June
Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis! Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June
STEVEN E. PHILLIPS, MD
 STEVEN E. PHILLIPS, MD 944 Danbury Road Wilton, CT 06897 203-544-0005 EDUCATION YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 6/96 Greenwich Hospital, Greenwich CT Internal Medicine Residency Program SUNY HEALTH
STEVEN E. PHILLIPS, MD 944 Danbury Road Wilton, CT 06897 203-544-0005 EDUCATION YALE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 6/96 Greenwich Hospital, Greenwich CT Internal Medicine Residency Program SUNY HEALTH
LYME DISEASE: NEW OPTIONS FOR TREATMENT
 LYME DISEASE: NEW OPTIONS FOR TREATMENT Lyme disease prevalence is on the rise, arguably more now than any time in human history. Millions of people have been diagnosed with this debilitating illness,
LYME DISEASE: NEW OPTIONS FOR TREATMENT Lyme disease prevalence is on the rise, arguably more now than any time in human history. Millions of people have been diagnosed with this debilitating illness,
Technical Bulletin No. 121
 CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory Technical Bulletin No. 121 January 31, 2014 Lyme Blot, IgG and IgM - Now Performed at CPAL Contact: J. Matthew Groeller, 717.851.1416 Operations Manager, Clinical
CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory Technical Bulletin No. 121 January 31, 2014 Lyme Blot, IgG and IgM - Now Performed at CPAL Contact: J. Matthew Groeller, 717.851.1416 Operations Manager, Clinical
Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung disease in preterm infants.
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung disease in preterm infants. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung disease in preterm infants. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Postnatal corticosteroids to treat or prevent chronic lung
Public Statement: Medical Policy Statement:
 Medical Policy Title: Lyme Disease, Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 and Associated Diagnostic Testing Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0235 Revision Date: Code(s):
Medical Policy Title: Lyme Disease, Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 and Associated Diagnostic Testing Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0235 Revision Date: Code(s):
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@dhhs.nh.gov June 01, 2017, 1100 EDT (11:00 AM EDT) NH-HAN 20170601 Emerging Tickborne Diseases in New Hampshire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@dhhs.nh.gov June 01, 2017, 1100 EDT (11:00 AM EDT) NH-HAN 20170601 Emerging Tickborne Diseases in New Hampshire
Lyme Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
 Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.57a Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.57a Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi Years after Active Lyme Disease
 MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10 20 Years after Active Lyme Disease Robert A. Kalish, 1 Gail McHugh, 1 John Granquist, 1 Barry
MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10 20 Years after Active Lyme Disease Robert A. Kalish, 1 Gail McHugh, 1 John Granquist, 1 Barry
My Case Study Solution
 My Case Study Solution By Chiara Corey Amy and John, recent newlyweds and hiking enthusiasts from California, completed a backpacking road trip across the United States for their honeymoon. They started
My Case Study Solution By Chiara Corey Amy and John, recent newlyweds and hiking enthusiasts from California, completed a backpacking road trip across the United States for their honeymoon. They started
Lyme disease conference
 Lyme disease conference Epidemiology of Lyme in England and Wales Robert Smith, Public Health Wales 9 October 213 Lyme disease in England and Wales Dr Robert Smith Health Protection Division Public Health
Lyme disease conference Epidemiology of Lyme in England and Wales Robert Smith, Public Health Wales 9 October 213 Lyme disease in England and Wales Dr Robert Smith Health Protection Division Public Health
Addressing Tick Borne Diseases in Ireland. Dr. John Lambert - Professor of Medicine and Infectious Diseases, Mater Hospital & UCD School of Medicine
 Meeting of the Joint Oireachtas Committee on Health (28 th November 2018) Addressing Tick Borne Diseases in Ireland Dr. John Lambert - Professor of Medicine and Infectious Diseases, Mater Hospital & UCD
Meeting of the Joint Oireachtas Committee on Health (28 th November 2018) Addressing Tick Borne Diseases in Ireland Dr. John Lambert - Professor of Medicine and Infectious Diseases, Mater Hospital & UCD
SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency
 FROM: 530 229 8447 TO: 15302293984 08/06/14 12:30 Pg 1 of 5 especially SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency Public Health 2650RreslauerWay Redding, CA 96001-4297 (530) 229-8484 FAX (530) 225-3743
FROM: 530 229 8447 TO: 15302293984 08/06/14 12:30 Pg 1 of 5 especially SHASTA COUNTY Health and Human Services Agency Public Health 2650RreslauerWay Redding, CA 96001-4297 (530) 229-8484 FAX (530) 225-3743
Tickborne Diseases: Challenges and Controversies
 Tickborne Diseases: Challenges and Controversies JENNIFER HANRAHAN, D.O. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, CWRU DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION METROHEALTH MEDICAL CENTER Disclosures I have been on Advisory Boards
Tickborne Diseases: Challenges and Controversies JENNIFER HANRAHAN, D.O. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, CWRU DIRECTOR OF INFECTION PREVENTION METROHEALTH MEDICAL CENTER Disclosures I have been on Advisory Boards
Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis HEADACHE AND FEVER. What is the best initial approach for fever, headache, meningisums?
 Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine HEADACHE AND FEVER What is the best initial approach for fever,
Dilemmas in the Management of Meningitis & Encephalitis Paul D. Holtom, MD Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine HEADACHE AND FEVER What is the best initial approach for fever,
Working Group Practices and Composition
 November 26, 2018 Tickborne Disease Working Group Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 200 Independence Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20201 Dear Tickborne
November 26, 2018 Tickborne Disease Working Group Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 200 Independence Avenue, SW Washington, DC 20201 Dear Tickborne
Fatigue, persistence after Lyme borreliosis 196, 197 Francisella tularensis, see Tularemia
 Subject Index Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA) antibiotic therapy 121, 122 Borrelia induction 13 clinical characteristics 64, 65, 82 diagnosis 65, 66 differential diagnosis 66 etiology 62 frequency
Subject Index Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA) antibiotic therapy 121, 122 Borrelia induction 13 clinical characteristics 64, 65, 82 diagnosis 65, 66 differential diagnosis 66 etiology 62 frequency
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Feder HM Jr, Johnson BJB, O Connell S, et al. A critical appraisal
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Feder HM Jr, Johnson BJB, O Connell S, et al. A critical appraisal
Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza. Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09)
 Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09) 1 Outline Clinical assessment Diagnostic testing Antiviral medications
Clinical Guidance for 2009 H1N1 Influenza and Seasonal Influenza Barbara Wallace, MD New York State Department of Health (Updated 10/8/09) 1 Outline Clinical assessment Diagnostic testing Antiviral medications
Horowitz Lyme-MSlDS Questionnaire
 Horowitz Lyme-MSlDS Questionnaire The Horowitz Lyme-MSlDS Questionnaire is not intended to replace the advice of your own physician or other medical professional. You should consult a medical professional
Horowitz Lyme-MSlDS Questionnaire The Horowitz Lyme-MSlDS Questionnaire is not intended to replace the advice of your own physician or other medical professional. You should consult a medical professional
Marie Kroun, MD Denmark. Presentation in York, UK June 2004
 Pilot project Case 1 Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June 2004 LymeRICK lots of info on TBI: http://lymerick.net Project website (Danish): http://kroun.ulmarweb.dk ILADS Website: http://www.ilads.org
Pilot project Case 1 Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June 2004 LymeRICK lots of info on TBI: http://lymerick.net Project website (Danish): http://kroun.ulmarweb.dk ILADS Website: http://www.ilads.org
Not currently the time of year, but spring is around the corner. Seems to be in the news every other week. Task forces being formed.
 1 2 3 Not currently the time of year, but spring is around the corner. Seems to be in the news every other week. Task forces being formed. Elizabeth May has been a big proponent. Avril Lavigne has come
1 2 3 Not currently the time of year, but spring is around the corner. Seems to be in the news every other week. Task forces being formed. Elizabeth May has been a big proponent. Avril Lavigne has come
Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND
 Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND 603-610-8882 Patient Name: DOB: Section A Do you remember being bitten by a tick? Yes No. If yes, when? Do you remember having the "bulls eye" rash? Yes No Do
Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND 603-610-8882 Patient Name: DOB: Section A Do you remember being bitten by a tick? Yes No. If yes, when? Do you remember having the "bulls eye" rash? Yes No Do
Two Standards of Care
 Two Standards of Care ILADS and IDSA guidelines reflect deeply divided opinions about treatment approaches, clinical judgment and patient preferences By Lorraine Johnson, JD, MBA Medically recognized standards
Two Standards of Care ILADS and IDSA guidelines reflect deeply divided opinions about treatment approaches, clinical judgment and patient preferences By Lorraine Johnson, JD, MBA Medically recognized standards
 Page 1 de 6 Brief Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Neck and upper back (acute & chronic). BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Work Loss Data Institute. Neck and upper back (acute & chronic). Corpus Christi (TX): Work Loss
Page 1 de 6 Brief Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Neck and upper back (acute & chronic). BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Work Loss Data Institute. Neck and upper back (acute & chronic). Corpus Christi (TX): Work Loss
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Emerging Issues in STDs and Resistance
 Emerging Issues in STDs and Resistance Toye H. Brewer, MD Asst. Professor of Clinical Medicine University of Miami School of Medicine Co-Director- Fogarty International Training Program Outline Syphilis-
Emerging Issues in STDs and Resistance Toye H. Brewer, MD Asst. Professor of Clinical Medicine University of Miami School of Medicine Co-Director- Fogarty International Training Program Outline Syphilis-
Fluoroquinolone-Associated Disability (FQAD) Cases in Patients Being Treated for Uncomplicated Sinusitis, Bronchitis, and/or Urinary Tract Infection
 Joint Meeting of the Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee November 5, 2015 FDA s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Review: Fluoroquinolone-Associated
Joint Meeting of the Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee and the Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee November 5, 2015 FDA s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Review: Fluoroquinolone-Associated
NO DISCLOSURES. Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies. Willie Burgdorfer, Ph.D. ( ) RM Lab in Hamilton, MT 1/20/2017
 Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies Richard A. Jacobs, M.D., PhD. NO DISCLOSURES Willie Burgdorfer, Ph.D. (1925 2014) RM Lab in Hamilton, MT Polly Murray who first reported an outbreak of arthritis
Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies Richard A. Jacobs, M.D., PhD. NO DISCLOSURES Willie Burgdorfer, Ph.D. (1925 2014) RM Lab in Hamilton, MT Polly Murray who first reported an outbreak of arthritis
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: West Nile Virus Illness Revised March 2017 West Nile Virus Illness
Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: West Nile Virus Illness Revised March 2017 West Nile Virus Illness
Guideline Summary NGC-3246
 NGC banner Guideline Summary NGC-3246 Guideline Title Metatarsalgia/intractable plantar keratosis/tailor's bunion. Bibliographic Source(s) Academy of Ambulatory Foot and Ankle Surgery. Metatarsalgia/intractable
NGC banner Guideline Summary NGC-3246 Guideline Title Metatarsalgia/intractable plantar keratosis/tailor's bunion. Bibliographic Source(s) Academy of Ambulatory Foot and Ankle Surgery. Metatarsalgia/intractable
SITE NAVIGATION. Also read about...
 1 of 11 16/11/2008 20:09 SITE NAVIGATION Home Career Center About Us Publishing Staff Author Guidelines Contact Us Subscription Info Advertising Info NP Organizations PA Organizations Issue Archives Also
1 of 11 16/11/2008 20:09 SITE NAVIGATION Home Career Center About Us Publishing Staff Author Guidelines Contact Us Subscription Info Advertising Info NP Organizations PA Organizations Issue Archives Also
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis
 Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
Lyme disease Overview
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 21 Lyme Disease Learning Objectives 1. Describe the agent and vector of Lyme Disease 2. Identify the geographic and temporal patterns
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 21 Lyme Disease Learning Objectives 1. Describe the agent and vector of Lyme Disease 2. Identify the geographic and temporal patterns
Appendix I (a) Human Surveillance Case Definition (Revised July 4, 2005)
 Section A: Case Definitions Appendix I (a) Human Surveillance Case Definition (Revised July 4, 2005) The current Case Definitions were drafted with available information at the time of writing. Case Definitions
Section A: Case Definitions Appendix I (a) Human Surveillance Case Definition (Revised July 4, 2005) The current Case Definitions were drafted with available information at the time of writing. Case Definitions
Evidence Supporting the Recommendations. Implementation of the Guideline. Benefits/Harms of Implementing the Guideline Recommendations
 1 / 6 Surgical safety checklist in obstetrics and gynaecology Guideline Developer(s) Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada Date Released 2013 Jan Full Text Guideline Surgical safety checklist
1 / 6 Surgical safety checklist in obstetrics and gynaecology Guideline Developer(s) Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada Date Released 2013 Jan Full Text Guideline Surgical safety checklist
Editors Note: These guidelines are written by Dr. Burrascano, who is regarded as being the grandfather of Lyme disease treatment.
 Editors Note: These guidelines are written by Dr. Burrascano, who is regarded as being the grandfather of Lyme disease treatment. Although dated (last revised in 2008) and some of the information may be
Editors Note: These guidelines are written by Dr. Burrascano, who is regarded as being the grandfather of Lyme disease treatment. Although dated (last revised in 2008) and some of the information may be
Diagnostic Testing Difficulties. Testing for Borreliosis
 Diagnostic Testing Difficulties! Antibody development! Immune system deficiencies! Persistence: cystic forms and biofilms of Borrelia! False negative ELISA tests! No Western Blot if ELISA negative in Canada,
Diagnostic Testing Difficulties! Antibody development! Immune system deficiencies! Persistence: cystic forms and biofilms of Borrelia! False negative ELISA tests! No Western Blot if ELISA negative in Canada,
Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Lyme Disease
 10-ID-06 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Lyme Disease I. tatement of the Problem: CTE position statement 07-EC-02 recognized the need to develop
10-ID-06 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Lyme Disease I. tatement of the Problem: CTE position statement 07-EC-02 recognized the need to develop
Guideline Summary NGC-3241
 NGC banner Guideline Summary NGC-3241 Guideline Title Ingrown toenails. Bibliographic Source(s) Academy of Ambulatory Foot and Ankle Surgery. Ingrown toenails. Philadelphia (PA): Academy of Ambulatory
NGC banner Guideline Summary NGC-3241 Guideline Title Ingrown toenails. Bibliographic Source(s) Academy of Ambulatory Foot and Ankle Surgery. Ingrown toenails. Philadelphia (PA): Academy of Ambulatory
If these vaccines haven t been given, please follow guidelines below for emergency procedures.
 MANAGEMENT OF PATIIENTS POST SPLENECTOMY & HYPOSPLENIIC PATIIENTS Splenectomised and hyposplenic patients are at increased risk of life-threatening infections due to encapsulated micro-organisms such as
MANAGEMENT OF PATIIENTS POST SPLENECTOMY & HYPOSPLENIIC PATIIENTS Splenectomised and hyposplenic patients are at increased risk of life-threatening infections due to encapsulated micro-organisms such as
Lyme disease: diagnosis and management
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Final Lyme disease: diagnosis and management [L] Evidence review for the management of ongoing symptoms related to Lyme disease NICE guideline 95 Evidence
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Final Lyme disease: diagnosis and management [L] Evidence review for the management of ongoing symptoms related to Lyme disease NICE guideline 95 Evidence
Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary
 Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, NetResults F series and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
Benlysta (belimumab) Prior Authorization Criteria Program Summary This prior authorization applies to Commercial, NetResults A series, NetResults F series and Health Insurance Marketplace formularies.
Lyme disease Overview
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, Dr.PH) Lecture 22 Lyme Disease Learning Objectives 1. Describe the agent and vector of Lyme Disease 2. Identify the geographic and temporal patterns
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, Dr.PH) Lecture 22 Lyme Disease Learning Objectives 1. Describe the agent and vector of Lyme Disease 2. Identify the geographic and temporal patterns
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities
 Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Case Report Early Disseminated Lyme Disease with Carditis Complicated by Posttreatment Lyme Disease Syndrome
 Hindawi Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2017, Article ID 5847156, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5847156 Case Report Early Disseminated Lyme Disease with Carditis Complicated by Posttreatment
Hindawi Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2017, Article ID 5847156, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5847156 Case Report Early Disseminated Lyme Disease with Carditis Complicated by Posttreatment
PE1662/E Lyme Disease Action submission of 27 October 2017
 PE1662/E Lyme Disease Action submission of 27 October 2017 We support the petitioners calls for action to improve the position with regard to awareness, diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. We would
PE1662/E Lyme Disease Action submission of 27 October 2017 We support the petitioners calls for action to improve the position with regard to awareness, diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease. We would
A New Look at The Role of HBOT in Neurovascular & Rheumatic Diseases: Borrelia, Bartonella, & Parasitic Infections
 A New Look at The Role of HBOT in Neurovascular & Rheumatic Diseases: Borrelia, Bartonella, & Parasitic Infections HBOT 2012 Long Beach, CA AUGUST 12, 2012 B Robert Mozayeni, MD Translational Medicine
A New Look at The Role of HBOT in Neurovascular & Rheumatic Diseases: Borrelia, Bartonella, & Parasitic Infections HBOT 2012 Long Beach, CA AUGUST 12, 2012 B Robert Mozayeni, MD Translational Medicine
Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection
 Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Introduction In 1999, West Nile Virus (WNV), an Old World flavivirus, producing a spectrum of disease including severe meningoencephalitis, appeared
Clinical Information on West Nile Virus (WNV) Infection Introduction In 1999, West Nile Virus (WNV), an Old World flavivirus, producing a spectrum of disease including severe meningoencephalitis, appeared
West Nile Virus. Syndrome. (Family: Flaviviridae) Severe Manifestations (Typically >50 years of age) NEUROLOGICAL (Meningoencephalitis >Meningitis)
 Severe Manifestations (Typically >50 years of age) Syndrome NEUROLOGICAL (Meningoencephalitis >Meningitis) CSF WBC Protein Glucose-WNL Confusion Change in Sensorium Stupor Seizures Ataxia Cranial Nerve
Severe Manifestations (Typically >50 years of age) Syndrome NEUROLOGICAL (Meningoencephalitis >Meningitis) CSF WBC Protein Glucose-WNL Confusion Change in Sensorium Stupor Seizures Ataxia Cranial Nerve
Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND
 Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND 603-610-8882 Patient Name: DOB: Section A Do you remember being bitten by a tick? Yes No. If yes, when? Do you remember having the "bulls eye" rash? Yes No Do
Nicole Schertell, ND, CCT Johanna Mauss, ND 603-610-8882 Patient Name: DOB: Section A Do you remember being bitten by a tick? Yes No. If yes, when? Do you remember having the "bulls eye" rash? Yes No Do
Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy and Associated Diagnostic Testing for Lyme Disease
 Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy and Associated Diagnostic Testing for Lyme Disease Policy Number: 5.01.08 Last Review: 01/2018 Origination: 1/2009 Next Review: 01/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Intravenous Antibiotic Therapy and Associated Diagnostic Testing for Lyme Disease Policy Number: 5.01.08 Last Review: 01/2018 Origination: 1/2009 Next Review: 01/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
The objectives of this presentation are; to increase awareness of the issue of antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea, and to inform primary care and
 1 Antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea is an emerging public health threat that needs to be addressed. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is able to develop resistance to antimicrobials quickly. Effective antibiotic stewardship
1 Antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea is an emerging public health threat that needs to be addressed. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is able to develop resistance to antimicrobials quickly. Effective antibiotic stewardship
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults
 Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Peter J. Weina, PhD, MD, FACP, FIDSA. Colonel, Medical Corps, US Army Deputy Commander Walter Reed Army Institute of Research
 Peter J. Weina, PhD, MD, FACP, FIDSA Colonel, Medical Corps, US Army Deputy Commander Walter Reed Army Institute of Research Background Most common vector-borne disease in U.S. First described in Lyme,
Peter J. Weina, PhD, MD, FACP, FIDSA Colonel, Medical Corps, US Army Deputy Commander Walter Reed Army Institute of Research Background Most common vector-borne disease in U.S. First described in Lyme,
2/7/2018. Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies. Richard A. Jacobs, M.D., PhD. NO DISCLOSURES
 Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies Richard A. Jacobs, M.D., PhD. NO DISCLOSURES 1 Willie Burgdorfer, Ph.D. (1925 2014) RM Lab in Hamilton, MT Polly Murray who first reported an outbreak of arthritis
Lyme Disease Convention and Controversies Richard A. Jacobs, M.D., PhD. NO DISCLOSURES 1 Willie Burgdorfer, Ph.D. (1925 2014) RM Lab in Hamilton, MT Polly Murray who first reported an outbreak of arthritis
Case Classification West Nile Virus Neurological Syndrome (WNNS)
 WEST NILE VIRUS Case definition Case Classification West Nile Virus Neurological Syndrome (WNNS) CONFIRMED CASE West Nile Virus Neurological Syndrome (WNNS) Clinical criteria AND at least one of the confirmed
WEST NILE VIRUS Case definition Case Classification West Nile Virus Neurological Syndrome (WNNS) CONFIRMED CASE West Nile Virus Neurological Syndrome (WNNS) Clinical criteria AND at least one of the confirmed
Lyme Disease: The Unknown Epidemic
 Lyme Disease: The Unknown Epidemic by D. J. Fletcher and Tom Klaber Millions of people who are diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, fibromyalgia, Alzheimer's, chronic fatigue syndrome and other degenerative
Lyme Disease: The Unknown Epidemic by D. J. Fletcher and Tom Klaber Millions of people who are diagnosed with multiple sclerosis, fibromyalgia, Alzheimer's, chronic fatigue syndrome and other degenerative
To develop guidelines for the use of appropriate antibiotics for adult patients with CAP and guidance on IV to PO conversion.
 Page 1 of 5 TITLE: COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA (CAP) EMPIRIC MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS AND IV TO PO CONVERSION GUIDELINES: These guidelines serve to aid clinicians in the diagnostic work-up, assessment
Page 1 of 5 TITLE: COMMUNITY-ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA (CAP) EMPIRIC MANAGEMENT OF ADULT PATIENTS AND IV TO PO CONVERSION GUIDELINES: These guidelines serve to aid clinicians in the diagnostic work-up, assessment
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities
 Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS): Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities A REMS is a program required by the FDA to manage known or potential serious risks associated with
Lyme Disease. 1. DISEASE REPORTING A. Purpose of Reporting and Surveillance
 1. DISEASE REPORTING A. Purpose of Reporting and Surveillance Lyme Disease 1. To determine the incidence of Lyme disease, the degree of endemicity, and potential risk of contracting Lyme disease in Washington
1. DISEASE REPORTING A. Purpose of Reporting and Surveillance Lyme Disease 1. To determine the incidence of Lyme disease, the degree of endemicity, and potential risk of contracting Lyme disease in Washington
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21004 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Burgel, Nathalie Daniëlle van Title: Host-pathogen interactions in Lyme disease
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21004 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Burgel, Nathalie Daniëlle van Title: Host-pathogen interactions in Lyme disease
Syphilis Treatment Protocol
 STD, HIV, AND TB SECTION Syphilis Treatment Protocol CLINICAL GUIDANCE FOR PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SYPHILIS AND LATENT SYPHILIS www.lekarzol.com (4/2016) Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents Description... 3 Stages
STD, HIV, AND TB SECTION Syphilis Treatment Protocol CLINICAL GUIDANCE FOR PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SYPHILIS AND LATENT SYPHILIS www.lekarzol.com (4/2016) Page 1 of 8 Table of Contents Description... 3 Stages
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013
 Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent. 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens
 Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
Choosing an appropriate antimicrobial agent Consider: 1) the host 2) the site of infection 3) the spectrum of potential pathogens 4) the likelihood that these pathogens are resistant to antimicrobial agents
** REGULATORY ALERT **
 Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Attaining optimal asthma control: a practice parameter. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters. Attaining optimal asthma control: a practice parameter.
Complete Summary GUIDELINE TITLE Attaining optimal asthma control: a practice parameter. BIBLIOGRAPHIC SOURCE(S) Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters. Attaining optimal asthma control: a practice parameter.
West Nile Virus in Maricopa County
 West Nile Virus in Maricopa County Maricopa County Department of Public Health Office of Epidemiology July 21 January 1, 29 December 31, 29 Commentary West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that
West Nile Virus in Maricopa County Maricopa County Department of Public Health Office of Epidemiology July 21 January 1, 29 December 31, 29 Commentary West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus that
West Nile Virus in Maricopa County
 West Nile Virus in Maricopa County Maricopa County Department of Public Health Office of Epidemiology July 2009 January 1, 2008 December 31, 2008 Commentary West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus
West Nile Virus in Maricopa County Maricopa County Department of Public Health Office of Epidemiology July 2009 January 1, 2008 December 31, 2008 Commentary West Nile virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne virus
Necrotizing Granulomatous Hepatitis as an Unusual Manifestation of Lyme Disease
 Dig Dis Sci (2007) 52:2629 2632 DOI 10.1007/s10620-006-9405-9 Necrotizing Granulomatous Hepatitis as an Unusual Manifestation of Lyme Disease Antonela C. Zanchi Alan R. Gingold Neil D. Theise Albert D.
Dig Dis Sci (2007) 52:2629 2632 DOI 10.1007/s10620-006-9405-9 Necrotizing Granulomatous Hepatitis as an Unusual Manifestation of Lyme Disease Antonela C. Zanchi Alan R. Gingold Neil D. Theise Albert D.
Cimzia (certolizumab pegol) Data Showed Broad and Rapid Relief From Burden of Symptoms In Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
 Cimzia (certolizumab pegol) Data Showed Broad and Rapid Relief From Burden of Symptoms In Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Rapid, sustained and clinically meaningful improvement in wideranging patient-reported
Cimzia (certolizumab pegol) Data Showed Broad and Rapid Relief From Burden of Symptoms In Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Rapid, sustained and clinically meaningful improvement in wideranging patient-reported
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP
 Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Influenza A H1N1 Swine Flu Update:
 Influenza A H1N1 Swine Flu Update: Pandemic Influenza Planning for the Workplace Current as of August 2009 Georgia Tech OSHA Consultation Program This course does not necessarily reflect the views or policies
Influenza A H1N1 Swine Flu Update: Pandemic Influenza Planning for the Workplace Current as of August 2009 Georgia Tech OSHA Consultation Program This course does not necessarily reflect the views or policies
A D V A N C E D T O P I CS I N L Y M E D ISE ASE
 A D V A N C E D T O P I CS I N L Y M E D ISE ASE D I A G N OS T I C H I N T S A N D T R E A T M E N T G U I D E L I N ES F O R L Y M E A N D O T H E R T I C K B O R N E I L L N ESSES Sixteenth Edition
A D V A N C E D T O P I CS I N L Y M E D ISE ASE D I A G N OS T I C H I N T S A N D T R E A T M E N T G U I D E L I N ES F O R L Y M E A N D O T H E R T I C K B O R N E I L L N ESSES Sixteenth Edition
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF CHRONIC LYME DISEASE FIFTY ONE CASE REPORTS AND ESSAYS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF CHRONIC LYME DISEASE FIFTY ONE CASE REPORTS AND ESSAYS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 treatment of chronic lyme disease fifty one case reports and essays treatment of
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREATMENT OF CHRONIC LYME DISEASE FIFTY ONE CASE REPORTS AND ESSAYS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 treatment of chronic lyme disease fifty one case reports and essays treatment of
