Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education
|
|
|
- Eustace Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New Jersey Department of Health, Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Frequently Asked Questions Please note that throughout this document, we will be referring to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention as the CDC and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices as the ACIP. NJ Immunization Requirements Q: What are the minimum immunization requirements for preschool/child care, school, and college entry in New Jersey? A: Please visit Age-Appropriate Vaccinations for Licensed Child Care Centers/Pre-School [word 25k] [pdf 20k] Minimum Immunization Requirements Table For School Attendance In New Jersey [word 34k] [pdf 29k] Immunization Regulations can be accessed at: Instructions for accessing NJ Immunization Requirements: Q: Are NJ Immunization Requirements in accordance with the CDC/ACIP guidelines? A: Yes, New Jersey s immunization requirements are in accordance with the guidelines of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the American Academy of Family Physicians, and CDC/Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). However NJ establishes the minimum vaccine requirements for child-care centers, preschool, and school entry and attendance. For example, NJ requires every child born on or after January 1, 1998 to receive one dose of a varicella virus containing vaccine. The CDC/ACIP schedule recommends 2 doses of varicella vaccine. A child would only be required to receive one dose of a varicella virus containing vaccine for 1
2 attendance in NJ, but two doses would be recommended for optimal protection. The New Jersey Department of Health (NJDOH) recommends following the CDC/ACIP schedule, as periodically revised, for optimal protection Child Care Pre-School Requirements Influenza Vaccine Q: Is the seasonal influenza vaccine a requirement for child care and preschool? A: Yes, it is a requirement as per N.J.A.C. 8: unless the Commissioner or his or her designee temporarily suspends the requirement due to limited vaccine availability. As per N.J.A.C. 8: , children six months through 59 months of age attending any licensed child care center, or preschool facility on or after September 1, 2008, shall annually receive at least one dose of influenza vaccine between September 1 and December 31 of each year. Q: How many doses of the seasonal influenza vaccine are required for preschool/child care attendance? A: Per NJAC 8: , only 1 dose of seasonal flu vaccine is required for children 6-59 months of age attending child care/preschool. However, the CDC/ACIP recommends two doses given at least four weeks apart for children aged 6 months through 8 years of age who are getting a flu vaccine for the first time. Please see the Vaccination Dosage section for further guidance. Q: Why did the state health department make the influenza vaccine requirement only apply to preschool and licensed child care facilities? A: Flu seasons are unpredictable and can be severe. Over a period of 30 years, between 1976 and 2006, estimates of flu-associated deaths range from a low of about 3,000 to a high of about 49,000 people. Hospitalization rates for influenza for children 12 months of age and younger are comparable to rates of persons 65 years and older. Among children 0 to 4 years of age, hospitalization rates due to influenza have varied from 100 per 100,000 healthy children to as high as 500 per 100,000 for children with underlying medical conditions. To reduce the risk of hospitalization from complications of influenza, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the CDC recommend routine annual influenza vaccination of all children 6 months of age and older. However, annual vaccination of all children aged 6 months--4 years (59 months) and older children with conditions that place 2
3 them at increased risk for complications from influenza should continue to be a primary focus of vaccination efforts. With regard to the influenza vaccine, a study in The American Journal of Epidemiology supports the recommendation to vaccinate all preschool children. The study tracked influenza cases by age groups and found that preschoolers were the first to be seen in flu-related doctor visits, with sick adults following about 29 days later. The findings revealed that flu-like illness in children under age five, compared with all other age groups, was the most predictive of pneumonia and influenza deaths in the general population. Q: Is the flu vaccine required after January 1st for children coming in at that time or had not gotten it between Sept. 1- Dec. 31 of the prior year? A: Yes, the flu vaccine is still required for children after January 1. As we all know, the flu season may not peak until February. The flu season can also extend until May in some cases. So getting a flu vaccine even late in the season is protective. Q: Why then do the regulations specify a specific time frame? A: Most flu vaccine is distributed to health care providers (HCPs) by October and November each year so most HCPs should have their supplies at that time. We also know that public requests for flu vaccine peaks around September to December. If we can get a majority of children immunized within that four month timeframe, it will make monitoring the immunization status of a large number of children more manageable by the school or public health agency. Q: How much time after December 31 of a given year do I have to get my child vaccinated with the flu vaccine? A: Students who do not receive the vaccine by December 31 will be excluded from school for the duration of influenza season (through March 31) or until they receive at least one dose of the influenza vaccine. Q: How should a school enforce the flu vaccine regulation for those students who have not received the flu shot after December 31? A: Students who have not received the flu vaccine by December 31 must be excluded from school for the duration of influenza season (through March 31), until they receive at least one dose of the influenza vaccine or until they turn 60 months of age. 3
4 Q: Is the flu vaccine required for children who just turned 6 months of age in January since they were not age-eligible to receive the vaccine between Sept. 1- Dec. 31 of the prior year? A: Yes, once the child becomes age-eligible the flu vaccine is still required until the end of flu season in New Jersey (through March 31). As we all know, the flu season may not peak until February. The flu season can also extend until May in some cases. So getting a flu vaccine even late in the season is protective. Q: What if I am enrolling my child in January of the following year, is my child exempt from getting the mandatory flu vaccine? A: No, the flu vaccine is still required for children after January 1. Flu season may not peak until February and can also extend until May in some cases. Getting a flu vaccine even late in the season is still protective. If you enroll your child after December 31, you must provide documentation that your child received the flu vaccine prior to entering school. Q: Is flu vaccine required after March? A: No, students enrolling in school after March 31 are not required to get vaccinated; however, flu season may extend until May and therefore getting a flu vaccine even late in the season is still protective. Q: Is it acceptable for a child to receive flu vaccine in August when the regulations specifically state to receive one flu dose between September 1 to December 31 of each year? A: Children who get vaccinated with the seasonal flu vaccine prior to September 1, will be considered compliant and these vaccinations will be accepted to meet the requirement as long as the vaccine is for the respective flu season. Please note most seasonal flu vaccines expire on June 30. Q: Where can a family go to get the flu vaccine if the pediatrician does not have any more flu vaccine? A: The influenza vaccine is now recommended for all individuals > 6 months. Discuss with your health care provider (HCP) what plans are in place to ensure an adequate supply of flu vaccine for all eligible clients at the practice. 4
5 If a national flu vaccine shortage has not been declared and your HCP cannot guarantee an adequate supply of flu vaccine, other alternatives must be sought by the family. Options include: 1. Asking your child s HCP to assist with arranging for vaccination through another healthcare provider 2. Seeking out another HCP who can administer flu vaccine to children; 3. Checking with your local health department to see if they will administer flu vaccine to children less than 18 years of age; 4. Contacting your local public health clinic/federally Qualified Health care Centers (FQHCs): (Note: anyone is eligible to receive service at a local public health clinic); 5. Checking your local newspaper for flu clinic listings and verifying that they have flu vaccine available that is appropriate for your child s age. As a reminder, local health departments and FQHCs purchase flu vaccine through the Vaccine for Children (VFC) Program. A child must qualify to receive VFC vaccine; to view those eligibility requirements, go to the NJ VFC brochure for health care providers: 6. Checking the HealthMap Vaccine Finder at for vaccine availability at local health departments, pharmacies, and other locations. Q: What if there is a flu vaccine shortage or a flu vaccine distribution problem? A: The influenza vaccine regulation states that children six months through 59 months of age enrolling in or attending a child-care center or preschool facility on of after September 1, 2008, shall annually receive at least one dose of influenza vaccine between September 1 and December 31 of each year. After December 31, a student will be considered delinquent. As far as distribution and shortages are concerned, the NJ regulations state the following: In the event of a national or state vaccine supply shortage, as determined by the CDC and Commissioner, respectively, the Commissioner or his or her designee may temporarily suspend the immunization requirement for the particular immunization affected by the supply shortage, after provision of notice to the public via print and electronic news media, NJ Local Information Network and Communications System (NJ LINCS), electronic posting on the Department's website, etc. Q: What will be included in the flu vaccine? A: The seasonal flu vaccine protects against three influenza viruses that research indicates will be most common during the upcoming season. 5
6 The influenza vaccine will protect against the following 3 viruses: an A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like; AND an A/Victoria/361/2011/(H3N2)-like; AND a B/Wisconsin/1/2010-like (Yamagata lineage) antigens. While the H1N1 virus used to make the flu vaccine is the same virus that was included in the vaccine, the recommended influenza H3N2 and B vaccine viruses are different from those in the influenza vaccine for the Northern Hemisphere. Q: What is the H3N2 variant virus? Pigs can be infected with their own influenza viruses (called swine influenza) that are usually different from human flu viruses. While rare, influenza can spread from pigs to people and from people to pigs. However, sporadic human infections with influenza viruses that normally circulate in swine and not people have occurred. When this happens, these viruses are called variant viruses. A number of human infections with a variant influenza A H3N2 virus ("H3N2v") have been detected in the United States since August This virus is related to human flu viruses from the 1990s, so adults should have some immunity against these viruses, but young children probably do not. Early steps to make a vaccine against H3N2v have been taken, but no decision to mass produce such a vaccine has been made. The seasonal vaccine is not designed to protect against H3N2v. There are currently no cases of human infections with H3N2v in New Jersey. Public health authorities are watching this situation closely. Q: What types of flu vaccines are available? A: There are two types of flu vaccine available. The first is an inactivated (killed) vaccine given as a shot, which has been used for many years. It is also known as a trivalent influenza vaccine (TIV). The flu shot is approved for use in people 6 months of age and older, including healthy people and people with chronic medical conditions. The second is a live, attenuated (weakened) vaccine, which is sprayed into the nose and was licensed in It is also known as a live, attenuated, influenza vaccine (LAIV). The brand name for the LAIV is FluMist. The LAIV is not for everyone. LAIV is approved for use in healthy people 2 through 49 years of age who are not pregnant. 6
7 Check with your health care provider to see if your child can receive the LAIV flu vaccine. Q: What is the intradermal flu shot? A: "Fluzone Intradermal " was licensed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the United States for the flu season. The intradermal flu vaccine is a shot that is injected into the skin instead of the muscle. The intradermal shot uses a much smaller needle than the regular flu shot, and it requires less antigen to be as effective as the regular flu shot. Antigen is the part of the vaccine that helps your body build up protection against flu viruses. The intradermal vaccine has been approved by the FDA for use in adults 18 through 64 years of age. For more information, please visit: Q: What is the high dose flu vaccine? A: Fluzone High-Dose is an influenza vaccine designed specifically for people 65 years and older. Fluzone High-Dose vaccines contain 4 times the amount of antigen (the part of the vaccine that prompts the body to make antibody) contained in regular flu shots. A higher dose of antigen in the vaccine is supposed to give older people a better immune response and therefore better protection against flu. For more information, please visit: Q: How effective is the flu vaccine in children? A: It is recommended that all individuals > 6 months be vaccinated. The flu vaccine can prevent 66% or more influenza infections in young children, with even higher estimates for older children, when the vaccine strains are wellmatched to the flu viruses causing illness. Vaccinating close contacts of children can also help decrease children s risk of getting the flu. Children younger than 6 months of age are most at risk for having complications from the flu. However, they are too young to get the flu vaccine. In addition, vaccinated people who are elderly or ill may not develop antibody levels as well as healthy people. To protect these infants and other vulnerable individuals within our communities, it is very important that their household members, out-of-home caregivers and other close contacts be vaccinated against the flu. 7
8 Q: How is the flu season defined? A: Based on trend analysis of influenza seasons in New Jersey over the past five years, influenza and/ or influenza-like illness (ILI) have been confirmed to be present during the months of November through to the end of March with the peak occurrence during January and February. However, cases of influenza can be seen at any time of the year. Q: Is there flu vaccine available that does not contain the preservative thimerosal? A: Most single dose vials or syringes of influenza vaccine do not contain the preservative thimerosal. The live, attenuated, influenza vaccine, (Brand Name: FluMist) given intra-nasally, is thimerosal-free. A listing of thimerosal content in seasonal flu vaccines, can be accessed at: Q: Should I be concerned about thimerosal in my child s vaccines? A: Thimerosal is a mercury-containing preservative used in some vaccines and other products since the 1930s. There is no scientific evidence of harm caused by the low doses of thimerosal in vaccines, except for minor reactions like redness and swelling at the injection site. However, in July 1999, the Public Health Service agencies, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and vaccine manufacturers agreed that thimerosal should be reduced or eliminated in vaccines as a precautionary measure. Since 2001, with the exception of some influenza (flu) vaccines, thimerosal is not used as a preservative in routinely recommended childhood vaccines. For more information about vaccine safety and thimerosal, go to: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Q: Although the flu vaccine, Afluria, is licensed for those aged 5 years and older, why is the CDC/ACIP only recommending it for those who are aged 9 years and older? A: The CDC/ ACIP is recommending that Afluria not be used in children aged 5-8 years because of increased reports of febrile seizures in this age group. If no other age-appropriate, licensed inactivated seasonal influenza vaccine is available for a child aged 5-8 years who has a medical condition that increases the child's risk for influenza complications, Afluria can be used; however, providers should discuss with the parents or caregivers the 8
9 benefits and risks of influenza vaccination with Afluria before administering this vaccine. Afluria may be used in persons aged 9 years. Below is a complete listing of influenza vaccines: TABLE. Influenza vaccine information, by age group United States, influenza season* Vaccine Trade name Manufacturer Presentation Mercury content (µg Hg per 0.5 ml dose) Ovalbumin content (µg per 0.5mL dose) Age group No. of doses Route TIV Fluzone Sanofi Pasteur 0.25 ml prefilled syringe mos 1 or 2 IM** 0.5 ml prefilled syringe mos 1 or 2 IM** 0.5 ml vial mos 1 or 2 IM** 5.0 ml multidose vial mos 1 or 2 IM** TIV Agriflu Novartis Vaccines 0.5 ml prefilled syringe 0 < yrs 1 IM** TIV Fluvirin Novartis Vaccines 0.5 ml prefilled syringe yrs 1 or 2 IM** 5.0 ml multidose vial TIV Fluarix GlaxoSmithKline 0.5 ml prefilled syringe yrs 1 or 2 IM** TIV FluLaval ID Biomedical Corporation of Quebec (distributed by GlaxoSmithKline) 5.0 ml multidose vial < yrs 1 IM** TIV Afluria CSL Biotherapies (distributed by Merck) 0.5 ml prefilled syringe yrs 1 IM** 5.0 ml multidose vial TIV highdose Fluzone High- Dose Sanofi Pasteur 0.5 ml prefilled syringe yrs 1 IM** 9
10 TIV intraderm al Fluzone Intrader mal Sanofi Pasteur 0.1 ml prefilled microinjection system 0.0 (per 0.1 ml) yrs 1 ID LAIV FluMist* ** MedImmune 0.2 ml prefilled intranasal sprayer 0.0 (per 0.2 ml) <0.24 (per 0.2mL) 2 49 yrs 1 or 2 IN Abbreviations: TIV = trivalent inactivated vaccine; LAIV = live-attenuated influenza vaccine; IM = intramuscular; ID = intradermal; IN = intranasal. * Vaccination providers should consult Food and Drug Administration approved prescribing information for influenza vaccines for the most updated information, including indications, contraindications, and precautions. Data on maximum ovalbumin content is supplied in package inserts of certain vaccines. Persons with a history of mild allergy to egg (specifically, those who experience only hives) should receive TIV with additional precautions (Figure 2). Information is not included in package insert but is available upon request from the manufacturer, Sanofi Pasteur, by contacting or mis. s@sanofipasteur.com. Figure 1 describes two approaches for determining the number of doses needed for children aged 6 months through 8 years. ** For adults and older children, the recommended site of vaccination is the deltoid muscle. The preferred site for infants and young children is the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. Age indication per package insert is 5 years; however, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommends that Afluria not be used in children aged 6 months through 8 years because of increased risk for febrile reactions noted in this age group with CSL's 2010 Southern Hemisphere TIV. If no other age-appropriate, licensed inactivated seasonal influenza vaccine is available for a child aged 5 through 8 years who has a medical condition that increases the child's risk for influenza complications, Afluria can be used; however, vaccination providers should discuss with the parents or caregivers the benefits and risks of influenza vaccination with Afluria before administering this vaccine. Afluria may be used in persons aged 9 years. A 0.5-mL dose contains 60 µg of each vaccine antigen (180 µg total). A 0.1-mL dose contains 9 µg of each vaccine antigen (27 µg total). *** A new quadrivalent formulation of FluMist was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in February It is anticipated that this formulation will replace the currently available seasonal trivalent LAIV formulation for the season. FluMist is shipped refrigerated and stored in the refrigerator at 35 F 46 F (2 C 8 C) after arrival in the vaccination clinic. The dose is 0.2 ml divided equally between each nostril. Health-care providers should consult the medical record, when available, to identify children aged 2 through 4 years with asthma or recurrent wheezing that might indicate asthma. In addition, to identify children who might be at greater risk for asthma and possibly at increased risk for wheezing after receiving LAIV, parents or caregivers of children aged 2 through 4 years should be asked, "In the past 12 months, has a health-care provider ever told you that your child had wheezing or asthma?" Children whose parents or caregivers answer "yes" to this question and children who have asthma or who had a wheezing episode noted in the medical record within the past 12 months should not receive FluMist. Insufficient data available for use of LAIV in egg-allergic persons. Flumist is indicated for healthy, nonpregnant persons aged 2 through 49 years. Persons who care for severely immunosuppressed persons who require a protective environment should not receive FluMist given the theoretical risk for transmission of the live-attenuated vaccine virus. If you suspect a severe side effect after receiving any type of vaccination, you may ask your health care provider to report the reaction to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), a national vaccine safety surveillance program co-sponsored by the CDC and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Anyone can file a VAERS report, including health care providers, manufacturers, and vaccine recipients. You can find information about submitting a VAERS report at the following website: 10
11 Q: Aside from the flu vaccination requirement for children 6-59 months, who else should get vaccinated for flu? A: The CDC/ACIP currently recommends everyone 6 months and older to receive a flu vaccine each year. The purpose of Universal flu vaccination in the U.S. is to expand protection against the flu to more people. While everyone should get a flu vaccine each flu season, it s especially important that certain people get vaccinated either because they are at high risk of having serious flu-related complications or because they live with or care for people at high risk for developing flu-related complications. Those who are at high risk for flu complications include: Children younger than 5, but especially children younger than 2 years old Adults 65 years of age and older Pregnant women American Indians and Alaskan Natives seem to be at higher risk of flu complications People who have medical conditions including: o o o o o o o o o o o o Asthma (even if it s controlled or mild) Neurological and neurodevelopmental conditions [including disorders of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerve, and muscle such as cerebral palsy, epilepsy (seizure disorders), stroke, intellectual disability (mental retardation), moderate to severe developmental delay, muscular dystrophy, or spinal cord injury] Chronic lung disease (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD] and cystic fibrosis) Heart disease (such as congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure and coronary artery disease) Blood disorders (such as sickle cell disease) Endocrine disorders (such as diabetes mellitus) Kidney disorders Liver disorders Metabolic disorders (such as inherited metabolic disorders and mitochondrial disorders) Weakened immune system due to disease or medication (such as people with HIV or AIDS, or cancer, or those on chronic steroids) People younger than 19 years of age who are receiving long-term aspirin therapy People who are morbidly obese (Body Mass Index [BMI] of 40 or greater) Other people for whom vaccination is especially important are: People who live in nursing homes and other long-term care facilities 11
12 People who live with or care for those at high risk for complications from flu, including: o Health care workers o Household contacts of persons at high risk for complications from the flu o Household contacts and caregivers of children younger than 5 years of age with particular emphasis on vaccinating contacts of children younger than 6 months of age (children younger than 6 months are at highest risk of flu-related complications but are too young to get vaccinated) Use of the Nasal Spray Seasonal Flu Vaccine Vaccination with the nasal-spray flu vaccine is an option for healthy people 2 through 49 years of age who are not pregnant. Even people who live with or care for those in a high risk group (including health care workers) can get the nasal-spray flu vaccine as long as they are healthy themselves and are not pregnant. The one exception is health care workers who care for people with severely weakened immune systems who require a special protected hospital environment (like those who had a bone marrow transplant); these people should get the inactivated flu vaccine (flu shot). Who should not be vaccinated against seasonal flu? Some people should not be vaccinated without first consulting a physician. They include: People who have a severe allergy to chicken eggs. People who have had a severe reaction to an influenza vaccination in the past. Children younger than 6 months of age (influenza vaccine is not approved for use in this age group). People who have a moderate or severe illness with a fever should wait to get vaccinated until their symptoms lessen. People with a history of Guillain-Barré Syndrome (a severe paralytic illness, also called GBS) that occurred after receiving influenza vaccine and who are not at risk for severe illness from influenza should generally not receive vaccine. Tell your doctor if you ever had Guillain- Barré Syndrome. Your doctor will help you decide whether the vaccine is recommended for you. If you have questions about whether you should get a flu vaccine, consult your health care provider. 12
13 Q: Can individuals with egg allergies now receive the flu vaccine? A: For the season, there is a more permissive influenza vaccination recommendation for persons with egg allergies. Based on a thorough review of several recent studies, administration of trivalent flu vaccine has been tolerated by people with egg allergies, without serious reactions. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends that for the influenza season, people who have experienced only hives from consuming eggs can receive TIV intramuscularly as long as they are treated by a health care provider who is familiar with the potential manifestations of egg allergies and can be observed by a health care professional for at least 30 minutes after receiving each dose. LAIV (nasal spray) should not be used in these patients. Additional information about vaccinating people with egg allergy is available in the 2012 ACIP recommendations, which can be accessed at Health care providers should use the following algorithm when a patient reports allergy to eggs. 13
14 Recommendations regarding influenza vaccination for persons who report allergy to eggs Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, influenza season * Persons with egg allergy might tolerate egg in baked products (e.g., bread or cake). Tolerance to egg-containing foods does not exclude the possibility of egg allergy. Please contact your health care provider for more information. Q: Will NJ continue to accept an allergy to eggs as a valid medical exemption for receiving the flu vaccine? A: The NJDOH has received numerous inquiries from school health officials and parents regarding vaccination of persons with egg allergies. The current ACIP recommendation includes an algorithm for healthcare providers to manage patients with egg allergies. Since egg allergies range in severity, school health officials may find it difficult to determine the validity of influenza vaccine medical exemptions. 14
15 After careful consideration, the DOH has made a decision to continue to accept egg allergy as a valid medical contraindication for the school year and will continue to evaluate the feasibility of implementing this ACIP recommendation in the future. Please see the Egg Allergies and Flu Vaccination Update for further information: In the interim, we continue to encourage healthcare providers to follow ACIP s guidelines and screening protocols to determine whether their patient can receive flu vaccine. For the complete ACIP influenza recommendations, please visit Q: Who should NOT get the nasal mist flu vaccine? A: The following people should receive the inactivated vaccine instead: Adults 50 years of age and older or children from 6 through 23 months of age (Children younger than 6 months should not get either influenza vaccine). Children younger than 5 years with asthma or one or more episodes of wheezing within the past year. Pregnant women Anyone with a long-term health problem such as: Heart disease Lung disease Asthma Kidney or liver disease Metabolic disease such as diabetes Anemia and other blood disorders Anyone with certain muscle or nerve disorders (such as cerebral palsy) that can lead to breathing or swallowing problems Anyone with a weakened immune system. Anyone in close contact with someone whose immune system is so weak they require care in a protected environment (such as a bone marrow transplant unit). Close contacts of other people with a weakened immune system (such as those with HIV) may receive LAIV. Healthcare personnel in neonatal intensive care units or oncology clinics may receive LAIV. Children or adolescents on long-term aspirin treatment Please note: Anyone with a nasal condition serious enough to make breathing difficult, such as a very stuffy nose, should get the flu shot instead. 15
16 Q: How long after I get a flu vaccine will I become immune to the flu virus? A: Flu vaccines cause antibodies to develop in the body. These antibodies provide protection against infection with the viruses that are in the vaccine. Once you get vaccinated, your body makes protective antibodies in about two weeks. Q: Why do I need to receive a flu vaccine every year? A: A flu vaccine is needed every year because flu viruses are constantly changing. It s not unusual for new flu viruses to appear each year. The flu vaccine is formulated each year to keep up with the flu viruses as they change. In addition, multiple studies conducted over different seasons and across vaccine types and influenza virus subtypes have shown that the body s immunity to influenza viruses (acquired either through natural infection or vaccination) declines over time. Getting vaccinated each year provides the best protection against influenza throughout flu season. Q: Does getting a flu vaccine early in the season mean that I will not be protected later in the season? A: No. Flu vaccination provides protection against the influenza strains contained in the seasonal vaccine for the entire season. Everyone six months of age and older should be vaccinated as soon as the flu vaccine becomes available. Q: Can flu vaccines be given at the same time as other vaccines? A: Nasal mist (live) flu vaccines can be given at the same time as killed vaccines (e.g., pneumococcal or meningococcal vaccine) or any other live injectable vaccine (e.g., MMR, MMRV, varicella, yellow fever). If not given at the same time, nasal mist (live) flu vaccines and other live vaccines should be separated by at least 4 weeks. The injectable (killed) flu vaccine can be given at the same time as any other killed or live vaccine. Tell your health care provider if you received any other vaccines within the past month or plan to get any within the next month. 16
17 Vaccination Dosage Q: How do you determine the number of doses of flu vaccine recommended for children 6 months through 8 years? A: All children ages 6 months through 8 years who receive a seasonal influenza vaccine for the first time should be given 2 doses administered a minimum of 4 weeks apart to optimize immune response. Children who received seasonal influenza vaccine before the season but did not receive a vaccine containing 2009(H1N1) antigen (either seasonal vaccine since July 2010 or monovalent 2009[H1N1] vaccine) are recommended to receive 2 doses this season, even if 2 doses of seasonal influenza vaccine were received before the season. This is illustrated in two approaches for determining the number of doses required for children aged 6 months through 8 years, both of which are acceptable: Influenza vaccine dosing algorithm for aged children 6 months through 8 years Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, influenza season * Doses should be administered at least 4 weeks apart. For simplicity, this algorithm takes into consideration only doses of seasonal influenza vaccine received since July 1, As an alternative approach in settings where vaccination history from before July 1, 2010, is available, if a child aged 6 months through 8 years is known to have received at least 2 seasonal influenza vaccines during any previous season, and at least 1 dose of a 2009(H1N1)-containing vaccine (i.e., either or seasonal vaccine or the monovalent 2009[H1N1] vaccine), then the child needs only 1 dose for Using this approach, children aged 6 months through 8 years need only 1 dose of vaccine in if they have received any of the following: 1) 2 or more doses of seasonal influenza vaccine since July 1, 2010; 2) 2 or more doses of seasonal influenza vaccine before July 1, 2010, and 1 or more doses of monovalent 2009(H1N1) 17
18 vaccine; or 3) 1 or more doses of seasonal influenza vaccine before July 1, 2010, and 1 or more doses of seasonal influenza vaccine since July 1, Children for whom one of these conditions is not met require 2 doses in Q: Will it be necessary for the first and second dose to be given by the same provider? A: No. Patients should be given written documentation of the doses administered that can be presented to any health care provider in the future. Q: Can the first dose be nasal mist and the second dose be injectable (and vice versa)? A: Yes, but when feasible, the same brand and type of vaccine (live attenuated or inactivated) should be used. Q: Will it be necessary for the first and second dose to be the same product? A: When feasible, the same brand of vaccine should be used in a two dose schedule, but any vaccine FDA-approved for the age of the patient can be used to complete the series. Q: If my child gets the 2 nd dose more than 4 weeks after the 1 st one, how does that affect his protection against the flu? Is my child protected against the flu with just one dose? A: The span of 4 weeks between doses is a minimum time. With just one dose, your child has some protection against the flu, but for full protection a second dose should be administered. The level of protective immunity will not be affected by a delay in receiving the 2 nd dose. Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Q: According to the regulations, your pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) requirements of 1-2 doses (depending on age) does not provide sufficient protection from the disease with the current available formulation. Can you explain this? A: Our regulations reflect the minimum requirements for vaccines needed to attend school in NJ. They do not, however, comprise the full immunization series recommended by the CDC. It is the state's intention that parents will seek to meet their vaccination requirements for school and then begin a dialogue with their HCP who would educate them about the importance of completing the full vaccination series to achieve full protection from vaccine 18
19 preventable diseases and set up subsequent appointments with the intention of giving them the age-appropriate vaccines at the next visit. (This answer also applies to the haemophilus Influenzae b (Hib) vaccine as well). Q: If a child entered pre-school/child care at the age of two and has received 4 doses of PCV before 12 months of age, does this child need additional doses? A: Yes, even though PCV is a 4 dose series, children are still required by NJ Regulations to receive one dose after twelve months of age. (This answer also applies to the haemophilus Influenzae b (Hib) vaccine as well). Q: If my child did not attend child care, preschool, or prekindergarten, is my child required to receive a dose of PCV when he/she enters kindergarten if my child did not receive these vaccines after his/her first birthday? A: If your child is at least 5 years old, he/she is not required to receive PCV prior to entry into kindergarten. NJ does not require PCV after the age of 59 months. (This answer also applies to the haemophilus Influenzae b (Hib) vaccine as well). Q: Why is pneumococcal vaccination required for child care/ preschool entry? A: The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine protects against the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. This bacterium is the most common cause of: lung infections (pneumonia), blood infections (bacteremia) and infection of the covering of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis). Two to five percent of children who get pneumococcal meningitis will die. Of those who survive, 25% to 35% will have hearing loss, mental retardation or paralysis. Streptococcus pneumoniae is also the most common cause of ear infections (otitis media) in young children. Children under two years of age average more than one middle ear infection each year, many of which are caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae infections. Young children are much more likely than older children and adults to get pneumococcal disease. Children in child care settings are two- to-three times at greater risk for pneumococcal disease. For more pneumococcal vaccine information, go to: 19
20 Hib Vaccine Q: According to the regulations, the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine requirements of 1-2 doses (depending on age) does not provide sufficient protection from the disease with the current available formulation. Can you explain this? A: Our regulations reflect the minimum requirements for vaccines needed to attend school in NJ. They do not however, comprise the full immunization series recommended by the CDC. It is the state's intention that parents will seek to meet their vaccination requirements for school and then begin a dialogue with their HCP who would educate them about the importance of completing the full vaccination series to achieve full protection from vaccine preventable diseases and set up subsequent appointments with the intention of giving them the age-appropriate vaccines at the next visit. (This answer also applies to the PCV as well). Q: If a child entered pre-school/child care at the age of two and has received 4 doses of Hib vaccine before 12 months of age, does this child need additional doses? A: Yes, even though Hib is a 3 or 4 dose series (depending on brand of vaccine), children are still required by NJ Regulations to receive one dose after twelve months of age. (This answer also applies to the PCV as well). Q: If my child did not attend child care, preschool, or prekindergarten, is my child required to receive a dose of Hib when he/she enters kindergarten if my child did not receive these vaccines after his/her first birthday? A: If your child is at least 5 years old, he/she is not required to receive Hib prior to entry into kindergarten. NJ does not require Hib after the age of 59 months. (This answer also applies to the PCV as well). Hib Vaccine Shortage Q: Is my child required to receive the Hib booster dose after the first birthday for preschool/child care attendance? A: Yes, NJDOH lifted the waiver and reinstated the Hib vaccine mandate effective September
21 Since it has been almost 2 years since the shortage has been lifted, NJDOH is now enforcing the booster dose after the first birthday. Please see the following link announcing the reinstatement of the Hib booster dose: GRADE SIX REQUIREMENTS Tdap Vaccine Q: Why did the state health department make Tdap a requirement for sixth grade entry? A: Acellular pertussis antigen is given as part of the Tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid vaccine. Pertussis, an acute, infectious cough illness, remains endemic in the United States despite routine childhood pertussis vaccination for more than half a century and high coverage levels in children for more than a decade. A primary reason for the continued circulation of Bordetella pertussis is that immunity to pertussis wanes approximately 5 10 years after completion of childhood pertussis vaccination, leaving adolescents and adults susceptible to pertussis. Among the diseases for which universal childhood vaccination has been recommended, pertussis is the least well-controlled reportable bacterial vaccine-preventable disease in the United States. Since the 1980s, the number of reported pertussis cases has been steadily increasing, especially among adolescents and adults. Possible reasons for the increase in reported pertussis cases include a true increase in the burden of disease and an increase in the detection and reporting of cases; the relative contribution of each of these factors to the increase observed is unclear. B. pertussis is primarily transmitted from person-to-person through large respiratory droplets generated by coughing or sneezing. Persons with pertussis are most infectious during the catarrhal and early paroxysmal phases of illness. The disease is highly communicable, with attack rates as high as 80% 90% among nonimmune household contacts. Q: There are two vaccines for Tdap. Can you please clarify the difference between these vaccines? A: The Tdap vaccines are made by two different manufacturers and are licensed for different age groups. Boostrix by Glaxo Smith Kline is licensed for ages 10 and older. Adacel by Sanofi Pasteur is licensed for ages The Tdap vaccine provides protection from pertussis as immunity to pertussis wanes over time. 21
22 Q: Some 6th graders will not be 11 years old. I m guessing that a 10 year old would not have to be in compliance with the 6 th grade Tdap requirement until he or she reaches 11, is that correct? A: Yes, a 10 year old would not be required to receive the Tdap vaccine until 11 years of age per NJ s Immunization Regulations. Note that while Boostrix is approved for 10 year olds, Adacel is not (11 to 64 years). If the child's physician only carries Adacel then the child will not be required to receive it until 11 years of age. If the physician carries Boostrix then we encourage them to use it for their 10 year olds and this would fulfill NJ s school immunization requirements. However, either brands of Tdap vaccine may be administered at the same visit when they turn 11. Q: NJ s regulations for Tdap states that a dose is required for students entering or attending Grade Six, or a comparable age level special education program with an unassigned grade. What if a child is 11 years old, but has the mental abilities of a 5-year-old, would he still need to receive the vaccine for Tdap? A: Yes, the child would still need to follow NJ s immunization requirements and receive one dose of Tdap vaccine. The vaccine recommendations refer to the age-appropriate grade for the child s biological age, and not the child s mental capacity. (This answer also applies to all NJ Immunization Requirements). Q: If a student was inadvertently overlooked for the 6 th grade Tdap requirement, would he/she still need to meet this requirement in the higher grade levels? A: Yes, all children born after January 1, 1997 attending or transferring into a NJ school at grade six or higher grade level from another state or country are subject to the Tdap requirement provided at least five years have elapsed from the last documented Td dose. (This answer also applies to the meningococcal vaccine requirement). Q: Since the CDC/ACIP has new age recommendations for Tdap, will this effect NJ s immunization requirements? A: In an effort to protect more people from pertussis, the CDC/ACIP recently expanded the Tdap recommendations. For more information about the broadened recommendations, please visit: NJ immunization regulations remain the same and reflect the minimum requirements for vaccines needed to attend school in NJ. 22
23 Q: I understand the importance of the pertussis booster. But why should I give a Tetanus toxoid and diphtheria toxoid booster? A: Just as with pertussis, immunity to tetanus and diphtheria wanes with time so it is important to get regularly scheduled vaccines, such as receiving the Tdap vaccine to maintain protective immunity. There is no licensed vaccine that just provides protection against pertussis at this time. Q: If a child is medically contraindicated from receiving pertussis vaccine, would receiving the Td vaccination suffice for the new 6 th grade Tdap requirement? A: The New Jersey immunization requirement is for all sixth graders to receive the Tdap vaccine. The purpose of this requirement is to provide protection to this age cohort whose immunity to pertussis wanes from their last DTaP vaccination at 4-6 years of age. If a child cannot receive the pertussis component then they cannot receive Tdap and therefore would need to provide a medical exemption from their health care provider. In this circumstance, the Td vaccine is not a required vaccine for sixth grade entry; the Td vaccine is recommended to be given 10 years after their last DT as long as they have received at least three doses of DT. Meningococcal Vaccine Q: Why did the state health department make meningococcal disease a requirement for sixth grade entry? A: Meningococcal disease is a severe infection of the blood or the meninges (the covering of the brain and spinal cord). It is caused by a bacterium (germ) called Neisseria meningitidis. Each year, about 3,000 people in the U.S. get the disease. Adolescents die about 10 percent of the time, and one in four survivors has long-term disability, such as a loss of an arm or leg, deafness, nervous system problems, or even brain damage. Anyone can get meningococcal disease, but pre-teens and teens are at greater risk of contracting the disease. According to the CDC, pre-teens and teens account for nearly 30 percent of all cases of reported meningococcal infection in the U.S. and death rates are up to five times higher among 15-to 24-year olds compared with other age groups. The disease is spread by exchange of respiratory droplets and close, personal contact with infected persons, such as through kissing, uncovered face-to-face coughing and sneezing, sharing eating utensils, food or drink or 23
24 living in the same household or living quarters, such as a sleep-away camp or dormitory. The ACIP goal is routine vaccination of all adolescents with MCV4 beginning at age 11 years. ACIP and partner organizations, including the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Academy of Family Physicians, American Medical Association, and Society for Adolescent Medicine, recommend children aged years receive the recommended vaccinations and indicated preventive services at that adolescent health care visit. This visit is the optimal time for adolescents to receive MCV4. In addition, because the incidence of meningococcal disease increases during adolescence, healthcare providers should vaccinate previously unvaccinated persons aged years with MCV4 at the earliest possible health-care visit. College freshmen living in dormitories are at increased risk for meningococcal disease and should be vaccinated with MCV4 before college entry if they have not been vaccinated previously. Because of difficulties in targeting freshmen in dormitories, colleges may elect to target their vaccination campaigns to all matriculating freshmen. Source: Q: There are different vaccines for meningococcal disease. Can you please clarify the difference between these vaccines? A: The meningococcal vaccine protects against the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. There are two types of meningococcal vaccines: the meningococcal polysaccharide (MPSV4, brand name, Menomune) and the meningococcal conjugate vaccine (MCV4, brand names, Menactra and Menveo). Both vaccines are about 90% effective in protecting against four strains (A,C,Y and W-135) of meningococcal disease, including all but one of the most common strains found in the United States. Meningococcal conjugate vaccine (also known as MCV4) is currently preferred because it provides longer lasting immunity. A Meningococcal and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine (brand name, Menhibrix) was FDA-approved this year. This vaccine protects against two strains (C and Y) of meningococcal disease and is licensed for children 6 weeks through 18 months of age. Q: Some 6th graders will not be 11 years old. I m guessing that a 10 year old would not have to be in compliance with the 6 th grade meningococcal vaccine requirement until he or she reaches 11, is that correct? A: Yes, a 10 year old entering sixth grade will not be required to receive the Meningococcal containing vaccine until they turn 11 years of age. 24
Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education
 New Jersey Department of Health, Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Frequently Asked Questions
New Jersey Department of Health, Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Frequently Asked Questions
Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education
 New Jersey Department of Health (NJDOH), Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Frequently Asked
New Jersey Department of Health (NJDOH), Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Frequently Asked
Influenza Clinical Bulletin # 3: October 8, 2009 Vaccination Guidelines for Patients for Influenza
 The purpose of this document is to provide NYP providers with the most current recommendations regarding influenza vaccination for their patients. It is important to recognize that guidance reflects optimal
The purpose of this document is to provide NYP providers with the most current recommendations regarding influenza vaccination for their patients. It is important to recognize that guidance reflects optimal
INFLUENZA 2009 H1N1. INACTIVATED (the flu shot ) W H A T Y O U N E E D T O K N O W. 1 What is 2009 H1N1 influenza? H1N1 influenza vaccine
 2009 H1N1 INFLUENZA INACTIVATED (the flu shot ) VACCINE W H A T Y O U N E E D T O K N O W Many Vaccine Information Statements are available in Spanish and other languages. See http://www.immunize.org/vis.
2009 H1N1 INFLUENZA INACTIVATED (the flu shot ) VACCINE W H A T Y O U N E E D T O K N O W Many Vaccine Information Statements are available in Spanish and other languages. See http://www.immunize.org/vis.
Protecting Infants and Children from Pertussis and Influenza
 September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
Andrew Kroger, MD, MPH National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases MCH & Immunization Conference Anchorage, AK September 28, 2010
 2010 Immunization Update Andrew Kroger, MD, MPH National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases MCH & Immunization Conference Anchorage, AK September 28, 2010 Disclosures No financial conflict
2010 Immunization Update Andrew Kroger, MD, MPH National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases MCH & Immunization Conference Anchorage, AK September 28, 2010 Disclosures No financial conflict
Key Facts about Seasonal Flu Vaccine from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Key Facts about Seasonal Flu Vaccine from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Why should people get vaccinated against the flu? Influenza is a serious disease that can lead to hospitalization
Key Facts about Seasonal Flu Vaccine from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Why should people get vaccinated against the flu? Influenza is a serious disease that can lead to hospitalization
CAPE MAY COUNTY DEPARTMENT of HEALTH
 GERALD M. THORNTON Freeholder KEVIN L. THOMAS, M.A. Health Officer Public Health Coordinator JOSEPH R.TORDELLA, D.O. Medical Director CAPE MAY COUNTY DEPARTMENT of HEALTH 4 Moore Road Cape May Court House,
GERALD M. THORNTON Freeholder KEVIN L. THOMAS, M.A. Health Officer Public Health Coordinator JOSEPH R.TORDELLA, D.O. Medical Director CAPE MAY COUNTY DEPARTMENT of HEALTH 4 Moore Road Cape May Court House,
Immunization Update: New CDC Recommendations. Blaise L. Congeni M.D. 2012
 Immunization Update: New CDC Recommendations Blaise L. Congeni M.D. 2012 Polysaccharide Vaccines Vaccine Hib capsule polysaccharide PRP (polyribose ribitol phosphate) Not protective in infants
Immunization Update: New CDC Recommendations Blaise L. Congeni M.D. 2012 Polysaccharide Vaccines Vaccine Hib capsule polysaccharide PRP (polyribose ribitol phosphate) Not protective in infants
These slides are the property of the presenter. Do not duplicate without express written consent.
 Cancer Survivorship Protecting Against Vaccine Preventable Diseases Heidi Loynes BSN, RN Immunization Nurse Educator Michigan Department of health and Human Services (MDHHS) loynesh@michigan.gov Are Vaccine-Preventable
Cancer Survivorship Protecting Against Vaccine Preventable Diseases Heidi Loynes BSN, RN Immunization Nurse Educator Michigan Department of health and Human Services (MDHHS) loynesh@michigan.gov Are Vaccine-Preventable
ACIP Meeting Update, New Recommendations and Pending Influenza Season
 ACIP Meeting Update, New Recommendations and Pending Influenza Season February 17 th 2011 www.immunizetexas.com ACIP Upcoming Agenda and New Recommendations ACIP (February 23-24 th 2011) Topics for meeting
ACIP Meeting Update, New Recommendations and Pending Influenza Season February 17 th 2011 www.immunizetexas.com ACIP Upcoming Agenda and New Recommendations ACIP (February 23-24 th 2011) Topics for meeting
Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education
 New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services, Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Immunization
New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services, Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Questions and Answers on Immunization Regulations Pertaining to Children Attending School/ Higher Education Immunization
Mandates and More. Julie Morita, M.D. Deputy Commissioner Chicago Department of Public Health. Chicago Department of Public Health
 Mandates and More Julie Morita, M.D. Deputy Chicago Department of Public Health Why are vaccines required for school entry? School Vaccine Requirements Small pox vaccine required in Massachusetts 1855
Mandates and More Julie Morita, M.D. Deputy Chicago Department of Public Health Why are vaccines required for school entry? School Vaccine Requirements Small pox vaccine required in Massachusetts 1855
Influenza Virus. Influenza A virus. Influenza B virus. Influenza C virus
 Outline Influenza Virus Population Data Vaccination Rates 2010-11 Influenza Vaccines Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV) High-Dose Trivalent Inactivated Vaccine (HD TIV) Influenza Virus Influenza
Outline Influenza Virus Population Data Vaccination Rates 2010-11 Influenza Vaccines Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV) High-Dose Trivalent Inactivated Vaccine (HD TIV) Influenza Virus Influenza
GENERAL SAFETY ISSUES September 18, 2009
 Is the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine safe? GENERAL SAFETY ISSUES September 18, 2009 We expect the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine to have a similar safety profile as seasonal flu vaccines, which have a very
Is the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine safe? GENERAL SAFETY ISSUES September 18, 2009 We expect the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine to have a similar safety profile as seasonal flu vaccines, which have a very
Meningococcal Disease and College Students
 MASSACHUSETTS PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Meningococcal Disease and College Students May 2018 Page 1 of 4 What is meningococcal disease? Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria
MASSACHUSETTS PUBLIC HEALTH FACT SHEET Meningococcal Disease and College Students May 2018 Page 1 of 4 What is meningococcal disease? Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria
Immunization Guidelines For the Use of State Supplied Vaccine July 1, 2011
 DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
Disclosures. No support One off-label recommendation
 Seasonal Influenza John B. Murphy, MD Professor of Medicine and Family Medicine Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Executive Vice President for Physician Affairs, Lifespan 8/21/14 Disclosures
Seasonal Influenza John B. Murphy, MD Professor of Medicine and Family Medicine Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Executive Vice President for Physician Affairs, Lifespan 8/21/14 Disclosures
What You Need to Know About the Flu
 Thursday, August 16, 018 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com SIENNA PLANTATION EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive
Thursday, August 16, 018 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com SIENNA PLANTATION EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive
Immunization Guidelines for the Use of State Supplied Vaccine April 18, 2013
 DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines Antigens Vaccine Approved Age Daptacel Diphtheria, Tetanus, and acellular Pertussis (DTaP)
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines Antigens Vaccine Approved Age Daptacel Diphtheria, Tetanus, and acellular Pertussis (DTaP)
Immunization Guidelines for the Use of State Supplied Vaccine May 17, 2015
 DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
DTaP / DT DTaP/IPV/Hep B Combination (Pediarix ) Children from 6 weeks of age up to the 7 th birthday Children from 2 months of age up to the 7th birthday: Indicated for the primary doses of DTaP, IPV,
Influenza: Questions and Answers
 Influenza: Questions and Answers Information about the disease and vaccines What causes influenza? Viruses cause influenza. There are two basic types, A and B. Their genetic material differentiates them.
Influenza: Questions and Answers Information about the disease and vaccines What causes influenza? Viruses cause influenza. There are two basic types, A and B. Their genetic material differentiates them.
What You Need to Know About the Flu
 Thursday, August 16, 018 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com CYPRESS EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive the flu
Thursday, August 16, 018 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com CYPRESS EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive the flu
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women
 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women March 2012 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MARCH 2012 Risk
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women March 2012 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MARCH 2012 Risk
Vaccinations for Adults
 Case: Vaccinations for Adults Lisa Winston, MD University of California, San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital A 30-year old healthy woman comes for a routine visit. She is recently married and
Case: Vaccinations for Adults Lisa Winston, MD University of California, San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital A 30-year old healthy woman comes for a routine visit. She is recently married and
2/16/2015 IMMUNIZATION UPDATE Kelly Ridgway, RPh February 21, Today s Overview NEW RECOMMENDATIONS
 IMMUNIZATION UPDATE 2015 Kelly Ridgway, RPh February 21, 2015 Today s Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 Pneumococcal Vaccine Recommendations Meningococcal Vaccine Recommendations HPV Vaccine Recommendations Patient
IMMUNIZATION UPDATE 2015 Kelly Ridgway, RPh February 21, 2015 Today s Overview 1 2 3 4 5 6 Pneumococcal Vaccine Recommendations Meningococcal Vaccine Recommendations HPV Vaccine Recommendations Patient
UPDATE ON IMMUNIZATION GUIDELINES AND PRACTICES
 DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IMMUNIZATION GUIDELINES AND PRACTICES Nothing to disclose Kylie Mueller, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Specialist, Infectious Diseases Spartanburg Regional Medical Center LEARNING OBJECTIVES
DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IMMUNIZATION GUIDELINES AND PRACTICES Nothing to disclose Kylie Mueller, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Specialist, Infectious Diseases Spartanburg Regional Medical Center LEARNING OBJECTIVES
COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT
 1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women
 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women April 2013 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) April 2013 Risk
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women April 2013 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) April 2013 Risk
MERCURY-FREE VACCINE ACT EXEMPTION DECLARATION
 ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH MERCURY-FREE VACCINE ACT EXEMPTION DECLARATION NOW COMES, the Department of Public Health (hereinafter, the Department ), by and through LaMar Hasbrouck, Director,
ILLINOIS DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH MERCURY-FREE VACCINE ACT EXEMPTION DECLARATION NOW COMES, the Department of Public Health (hereinafter, the Department ), by and through LaMar Hasbrouck, Director,
Needle Facts: Immunization Update Mirada Wilhelm, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor SIUE School of Pharmacy
 Needle Facts: Immunization Update 2015 Mirada Wilhelm, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor SIUE School of Pharmacy Objectives Pharmacists At the conclusion of this program, the pharmacist will be able
Needle Facts: Immunization Update 2015 Mirada Wilhelm, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor SIUE School of Pharmacy Objectives Pharmacists At the conclusion of this program, the pharmacist will be able
Novel H1N1 Influenza Vaccine
 Novel H1N1 Influenza Vaccine Vaccine Supply and Distribution 1) When will the 2009 novel H1N1 influenza vaccine be available? Limited amounts of the novel H1N1 vaccine are expected to be available in mid-
Novel H1N1 Influenza Vaccine Vaccine Supply and Distribution 1) When will the 2009 novel H1N1 influenza vaccine be available? Limited amounts of the novel H1N1 vaccine are expected to be available in mid-
FLU Clinic. Children 6 months through 18 years October 26 th, p.m. to 6 p.m. At the Milbank High School Lobby
 FLU Clinic Children 6 months through 18 years October 26 th, 2016 2 p.m. to 6 p.m. At the Milbank High School Lobby MUST BRING: Insurance/Medicaid Cards All others please inquire. INFLUENZA 2016-2017 INACTIVATED
FLU Clinic Children 6 months through 18 years October 26 th, 2016 2 p.m. to 6 p.m. At the Milbank High School Lobby MUST BRING: Insurance/Medicaid Cards All others please inquire. INFLUENZA 2016-2017 INACTIVATED
General Questions and Answers on 2009 H1N1 Influenza Vaccine Safety
 General Questions and Answers on 2009 H1N1 Influenza Vaccine Safety October 5, 2009, 12:00 PM ET Will the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccines be safe? We expect the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine to have a similar
General Questions and Answers on 2009 H1N1 Influenza Vaccine Safety October 5, 2009, 12:00 PM ET Will the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccines be safe? We expect the 2009 H1N1 influenza vaccine to have a similar
HELP PREVENT THE FLU WITH FLUMIST QUADRIVALENT
 HELP PREVENT THE FLU WITH FLUMIST QUADRIVALENT THE NEEDLE-FREE INTRANASAL QUADRIVALENT FLU VACCINE Inf luenza Vaccine Live, Attenuated, Intranasal TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 What is FluMist Quadrivalent? 3 How
HELP PREVENT THE FLU WITH FLUMIST QUADRIVALENT THE NEEDLE-FREE INTRANASAL QUADRIVALENT FLU VACCINE Inf luenza Vaccine Live, Attenuated, Intranasal TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 What is FluMist Quadrivalent? 3 How
APEC Guidelines Immunizations
 Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Kenneth McCall, BSPharm, PharmD Associate Professor UNE President Maine Pharmacy Association
 Kenneth McCall, BSPharm, PharmD Associate Professor UNE President Maine Pharmacy Association Objectives Discuss the gap between current rates and Healthy People 2020 goals for vaccinations. Categorize
Kenneth McCall, BSPharm, PharmD Associate Professor UNE President Maine Pharmacy Association Objectives Discuss the gap between current rates and Healthy People 2020 goals for vaccinations. Categorize
Influenza Update. Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH Influenza Division, CDC. NAICP Call 6 October 2015
 Influenza Update Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH Influenza Division, CDC NAICP Call 6 October 2015 National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Influenza Division Overview Surveillance update ACIP
Influenza Update Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH Influenza Division, CDC NAICP Call 6 October 2015 National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Influenza Division Overview Surveillance update ACIP
PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS. PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS These codes do not have a diagnosis code requirement for preventive benefits to apply.
 An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
Influenza can cause: fever, sore throat, cough, headache, chills, muscle aches
 Influenza Vaccine: What You Need to Know From the U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Immunization Program 1. Why get vaccinated? Influenza is
Influenza Vaccine: What You Need to Know From the U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Immunization Program 1. Why get vaccinated? Influenza is
Update on Adult Immunization
 Update on Adult Immunization Paul J. Carson, MD, FACP Sanford Health, Infectious Disease NDSU Master of Public Health Program UND School of Medicine and Health Sciences When meditating over a disease,
Update on Adult Immunization Paul J. Carson, MD, FACP Sanford Health, Infectious Disease NDSU Master of Public Health Program UND School of Medicine and Health Sciences When meditating over a disease,
Influenza Backgrounder
 Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS. PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS These codes do not have a diagnosis code requirement for preventive benefits to apply.
 An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
Immunization with Influenza Vaccine (Inf)
 Immunization with Influenza Vaccine (Inf) Background Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by either the type A or type B influenza viruses, and occurs in populations worldwide. Although it is generally
Immunization with Influenza Vaccine (Inf) Background Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by either the type A or type B influenza viruses, and occurs in populations worldwide. Although it is generally
REQUIRED IMMUNIZATIONS
 REQUIRED IMMUNIZATIONS Pre-Kindergarten 4 DTP/DTaP/TD, 3 OPV (Polio), 1 MMR, 3 HEP B, 2 HEP A, 1 VARICELLA Kindergarten-6 th Grade 5 DTP/DTaP/TD, 4 OPV (Polio), 2 MMR, 3 HEP B, 2 HEP A, 1 VARICELLA All
REQUIRED IMMUNIZATIONS Pre-Kindergarten 4 DTP/DTaP/TD, 3 OPV (Polio), 1 MMR, 3 HEP B, 2 HEP A, 1 VARICELLA Kindergarten-6 th Grade 5 DTP/DTaP/TD, 4 OPV (Polio), 2 MMR, 3 HEP B, 2 HEP A, 1 VARICELLA All
Health Care Personnel Vaccination in the Long Term Care Setting
 Health Care Personnel Vaccination in the Long Term Care Setting Jennifer Heath, DNP, MPH, RN Objectives Interpret current influenza recommendations as they pertain to health care personnel (HCP) in the
Health Care Personnel Vaccination in the Long Term Care Setting Jennifer Heath, DNP, MPH, RN Objectives Interpret current influenza recommendations as they pertain to health care personnel (HCP) in the
Patient Immunization FAQ Sheet
 Patient Immunization FAQ Sheet Shingles Vaccine: Q: Who should get the shingles vaccine (Zostavax )? A: Anyone 60 years of age or should get the shingles (herpes zoster) vaccine. There is no maximum age
Patient Immunization FAQ Sheet Shingles Vaccine: Q: Who should get the shingles vaccine (Zostavax )? A: Anyone 60 years of age or should get the shingles (herpes zoster) vaccine. There is no maximum age
School-based Seasonal Influenza (flu) Vaccinations Frequently Asked Questions Parents/Guardians
 School-based Seasonal Influenza (flu) Vaccinations Frequently Asked Questions Parents/Guardians 1) Why are school children being offered free flu vaccine? The Hawai i State Department of Health (DOH) believes
School-based Seasonal Influenza (flu) Vaccinations Frequently Asked Questions Parents/Guardians 1) Why are school children being offered free flu vaccine? The Hawai i State Department of Health (DOH) believes
Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly
 Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious illness that can be severe and life threatening, especially for
Training Your Caregiver: Flu Prevention and Treatment for Disabled and the Elderly Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious illness that can be severe and life threatening, especially for
16 November 2017 National Immunisation Advisory Committee Recommendations for the 2017/2018 Influenza Vaccination Campaign
 16 November 2017 National Immunisation Advisory Committee Recommendations for the 2017/2018 Influenza Vaccination Campaign Please note the National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has updated the
16 November 2017 National Immunisation Advisory Committee Recommendations for the 2017/2018 Influenza Vaccination Campaign Please note the National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has updated the
Thank you for scheduling your influenza immunization clinic with Bloomington Public Health. We have your clinic(s) scheduled for:
 Thank you for scheduling your influenza immunization clinic with Bloomington Public Health. We have your clinic(s) scheduled for: Southpoint Office Center Wednesday, 10/4/2017 10:00 am 1:00 pm Please let
Thank you for scheduling your influenza immunization clinic with Bloomington Public Health. We have your clinic(s) scheduled for: Southpoint Office Center Wednesday, 10/4/2017 10:00 am 1:00 pm Please let
Immunization Update Richard M. Lampe M.D.
 Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
Immunization Update: What s New in 2013? Thursday, August 15, :30 a.m. 12:30 p.m.
 Immunization Update: What s New in 2013? Thursday, August 15, 2013 11:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. Presented by: Lynn Trefren, RN Nurse Manager, Tri-County Health Department Deb Zambrano, PHNC Vaccines for Children
Immunization Update: What s New in 2013? Thursday, August 15, 2013 11:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. Presented by: Lynn Trefren, RN Nurse Manager, Tri-County Health Department Deb Zambrano, PHNC Vaccines for Children
Meningococcal Update. Disclosure. Meningococal and Influenza Vaccines Update! Robert Wittler, MD Sept 12, 2014 KAAP Fall CME Meeting
 1 Meningococal and Influenza Vaccines Update! Robert Wittler, MD Sept 12, 2014 KAAP Fall CME Meeting 2 Disclosure Speakers Bureau: Sanofi Pasteur Vaccines and Novartis! I do not intend to discuss an unapproved/
1 Meningococal and Influenza Vaccines Update! Robert Wittler, MD Sept 12, 2014 KAAP Fall CME Meeting 2 Disclosure Speakers Bureau: Sanofi Pasteur Vaccines and Novartis! I do not intend to discuss an unapproved/
What You Need to Know About the Flu
 Wednesday, August 0, 017 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com CYPRESS EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive the flu
Wednesday, August 0, 017 BLUE P FISH E D I A T R I C S www.bluefishmd.com CYPRESS EDITION Biannual Newsletter In This Issue Find Out: Who should receive the flu vaccine? Who should NOT receive the flu
SEASONAL INFLUENZA VACCINE INFORMATION FOR IMMUNIZATION PROVIDERS
 2015-2016 SEASONAL INFLUENZA VACCINE INFORMATION FOR IMMUNIZATION PROVIDERS Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Communicable Disease Control Branch Immunization Program August 2015 Table of Contents
2015-2016 SEASONAL INFLUENZA VACCINE INFORMATION FOR IMMUNIZATION PROVIDERS Office of the Chief Medical Officer of Health Communicable Disease Control Branch Immunization Program August 2015 Table of Contents
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers
 What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers Stanley E. Grogg, DO, FACOP, FAAP he Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends the childhood vaccination
What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers Stanley E. Grogg, DO, FACOP, FAAP he Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends the childhood vaccination
CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology
 VOLUME XXXIII NUMBER 4 September 2018 CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology Influenza Vaccination Suchitra Rao, MBBS and Jason Child, PharmD New influenza vaccines have arrived. It is important
VOLUME XXXIII NUMBER 4 September 2018 CONTAGIOUS COMMENTS Department of Epidemiology Influenza Vaccination Suchitra Rao, MBBS and Jason Child, PharmD New influenza vaccines have arrived. It is important
Serum Institute of India Ltd. The Nasal-Spray Flu Vaccine (Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine [LAIV])
![Serum Institute of India Ltd. The Nasal-Spray Flu Vaccine (Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine [LAIV]) Serum Institute of India Ltd. The Nasal-Spray Flu Vaccine (Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine [LAIV])](/thumbs/89/100792695.jpg) Nasovac The Nasal-Spray Flu Vaccine (Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine [LAIV]) Questions & Answers Who can be vaccinated with the nasal-spray flu vaccine LAIV (Nasovac )? LAIV (Nasovac ) is approved for
Nasovac The Nasal-Spray Flu Vaccine (Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine [LAIV]) Questions & Answers Who can be vaccinated with the nasal-spray flu vaccine LAIV (Nasovac )? LAIV (Nasovac ) is approved for
The Advisory Committee on Immunization
 Need-to-know information for the 2016-2017 flu season ACIP now advises against using the LAIV nasal spray. In addition, 2 new vaccines are available and 2 more may soon be approved. Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Need-to-know information for the 2016-2017 flu season ACIP now advises against using the LAIV nasal spray. In addition, 2 new vaccines are available and 2 more may soon be approved. Doug Campos-Outcalt,
ACIP Recommendations
 ACIP Recommendations Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH Influenza Division National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Influenza Vaccine Summit May
ACIP Recommendations Lisa Grohskopf, MD, MPH Influenza Division National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Influenza Vaccine Summit May
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Committee on Infectious Diseases
 Early Release 8/8/08 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Committee on Infectious Diseases POLICY STATEMENT Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health
Early Release 8/8/08 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Committee on Infectious Diseases POLICY STATEMENT Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the Health
3 rd dose. 3 rd or 4 th dose, see footnote 5. see footnote 13. for certain high-risk groups
 Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
H1N1 Vaccine Based on CDCs ACIP Meeting, July 29, 2009
 August 6, 2009 H1N1 Vaccine Based on CDCs ACIP Meeting, July 29, 2009 CDC s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), a panel made up of medical and public health experts, met July 29, 2009,
August 6, 2009 H1N1 Vaccine Based on CDCs ACIP Meeting, July 29, 2009 CDC s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), a panel made up of medical and public health experts, met July 29, 2009,
2/20/2019. The need for adult vaccinations. Update on Adult Immunizations. The Need for Adult Vaccinations. Objectives:
 The need for adult vaccinations Update on Adult Immunizations Objectives: Recall the latest recommendations on adult vaccinations Detail the importance of adult vaccinations I m not a kid.. Why are you
The need for adult vaccinations Update on Adult Immunizations Objectives: Recall the latest recommendations on adult vaccinations Detail the importance of adult vaccinations I m not a kid.. Why are you
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Tel [203] Tel [203]
![NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Tel [203] Tel [203] NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Tel [203] Tel [203]](/thumbs/83/87667716.jpg) NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-3782 September 18, 2017 For Immediate Release
NEWS RELEASE FOR INFORMATION CONTACT: Caroline Calderone Baisley Deborah C. Travers Director of Health Director of Family Health Tel [203] 622-7836 Tel [203] 622-3782 September 18, 2017 For Immediate Release
8: Applicability
 Chapter 14 New Jersey State Sanitary Code Immunization of Pupils in Schools (New Jersey Administrative Code Citation 8:57-4.1 to 8:57-4.20) (Readopted with amendments September 20, 2003. Effective Date:
Chapter 14 New Jersey State Sanitary Code Immunization of Pupils in Schools (New Jersey Administrative Code Citation 8:57-4.1 to 8:57-4.20) (Readopted with amendments September 20, 2003. Effective Date:
For Residence Hall Students Only
 Immunization Record 2016-2017 Please print all information. PLEASE MAIL OR FAX COMPLETED FORMS (TWO PAGES) TO: Mount St. Joseph University, Wellness Center, 5701 Delhi Road, Cincinnati, OH 45233-1670 ATTN:
Immunization Record 2016-2017 Please print all information. PLEASE MAIL OR FAX COMPLETED FORMS (TWO PAGES) TO: Mount St. Joseph University, Wellness Center, 5701 Delhi Road, Cincinnati, OH 45233-1670 ATTN:
2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine. Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC
 2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC National Influenza Vaccine Summit April 19, 2007 Recommendation Changes for Influenza Vaccination:
2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC National Influenza Vaccine Summit April 19, 2007 Recommendation Changes for Influenza Vaccination:
FluMist Update (Influenza Virus Vaccine Live, Intranasal)
 FluMist Update (Influenza Virus Vaccine Live, Intranasal) National Influenza Vaccine Summit Kathleen Coelingh, PhD Senior Director, Medical and Scientific Affairs June 29, 2009 Dallas, TX 2009-10 Seasonal
FluMist Update (Influenza Virus Vaccine Live, Intranasal) National Influenza Vaccine Summit Kathleen Coelingh, PhD Senior Director, Medical and Scientific Affairs June 29, 2009 Dallas, TX 2009-10 Seasonal
Hemagglutinin Neuraminidase
 Evolving Vaccine Guidance: Influenza, Meningococcal & HPV Vaccines H. Cody Meissner, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Tufts University School of Medicine Maine Chapter AAP Bar Harbor, Maine October 16, 2016
Evolving Vaccine Guidance: Influenza, Meningococcal & HPV Vaccines H. Cody Meissner, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Tufts University School of Medicine Maine Chapter AAP Bar Harbor, Maine October 16, 2016
School Year IN State Department of Health School Immunization Requirements Updated March to 5 years old
 2013 2014 School Year IN State Department of Health School Immunization Requirements Updated March 2013 3 to 5 years old Kindergarten Grades 1 to 5 Grades 6 to 10 Grades 11 to 12 (Hepatitis B) 4 DTaP (Diphtheria,
2013 2014 School Year IN State Department of Health School Immunization Requirements Updated March 2013 3 to 5 years old Kindergarten Grades 1 to 5 Grades 6 to 10 Grades 11 to 12 (Hepatitis B) 4 DTaP (Diphtheria,
Novel H1N1 Influenza A Update. William Muth MD 2 Oct 2009
 Novel H1N1 Influenza A Update William Muth MD 2 Oct 2009 Novel H1N1 Influenza A Update Epidemiology Treatment Chemoprophylaxis Vaccine Infection Prevention Novel H1N1 Influenza A International Epidemiology
Novel H1N1 Influenza A Update William Muth MD 2 Oct 2009 Novel H1N1 Influenza A Update Epidemiology Treatment Chemoprophylaxis Vaccine Infection Prevention Novel H1N1 Influenza A International Epidemiology
NJ Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program
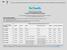 FOR LOCAL HEALTH DEPARTMENTS AND HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS: CHILD CARE/PRESCHOOL REQUIREMENTS FOR LOCAL HEALTH DEPARTMENTS AND HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS CHILD CARE/PRESCHOOL REQUIREMENTS NJ Department of Health
FOR LOCAL HEALTH DEPARTMENTS AND HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS: CHILD CARE/PRESCHOOL REQUIREMENTS FOR LOCAL HEALTH DEPARTMENTS AND HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS CHILD CARE/PRESCHOOL REQUIREMENTS NJ Department of Health
THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE
 THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE The following content is provided for informational purposes only. PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF INFLUENZA Lisa McHugh, MPH Influenza can be a serious
THIS ACTIVITY HAS EXPIRED. CME CREDIT IS NO LONGER AVAILABLE The following content is provided for informational purposes only. PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF INFLUENZA Lisa McHugh, MPH Influenza can be a serious
Lana Hudanick RN, BSN Public Health Consultant Nurse Bureau of Immunization Assessment and Assurance Missouri Department of Health and Senior
 Lana Hudanick RN, BSN Public Health Consultant Nurse Bureau of Immunization Assessment and Assurance Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Identify the appropriate vaccines and the Advisory
Lana Hudanick RN, BSN Public Health Consultant Nurse Bureau of Immunization Assessment and Assurance Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services Identify the appropriate vaccines and the Advisory
Washtenaw County Community Mental Health HEALTH CARE PERSONNEL (HCP) VACCINES (RECOMMENDED EMPLOYEE IMMUNIZATIONS)
 Washtenaw County Community Mental Health HEALTH CARE PERSONNEL (HCP) VACCINES (RECOMMENDED EMPLOYEE IMMUNIZATIONS) PURPOSE To reduce the risk of exposure of Washtenaw County Community Mental Health (CMH)
Washtenaw County Community Mental Health HEALTH CARE PERSONNEL (HCP) VACCINES (RECOMMENDED EMPLOYEE IMMUNIZATIONS) PURPOSE To reduce the risk of exposure of Washtenaw County Community Mental Health (CMH)
New Jersey Dept. of Health and Senior Services Public Information. Date: September 22, 2009 Time: 12:00 AM. H1N1 Vaccination Program
 2009 H1N1 INFLUENZA New Jersey Dept. of Health and Senior Services Public Information Date: September 22, 2009 Time: 12:00 AM H1N1 Vaccination Program 1. What is novel H1N1 (swine flu)? Novel H1N1 (referred
2009 H1N1 INFLUENZA New Jersey Dept. of Health and Senior Services Public Information Date: September 22, 2009 Time: 12:00 AM H1N1 Vaccination Program 1. What is novel H1N1 (swine flu)? Novel H1N1 (referred
Immunization Update 2016 Clinical Learning Day. Tamara Sheffield, MD, MPA, MPH
 Immunization Update 2016 Clinical Learning Day Tamara Sheffield, MD, MPA, MPH Disclosure I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests I am a Medical Director employed
Immunization Update 2016 Clinical Learning Day Tamara Sheffield, MD, MPA, MPH Disclosure I do not have any relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests I am a Medical Director employed
School Immunization Requirements IN State Department of Health School Year FAQ s
 Requirements & Compliance School Immunization Requirements IN State Department of Health 2014-2015 School Year FAQ s 1. Are there any new required immunizations for the 2014-2015 school year? Yes. Two
Requirements & Compliance School Immunization Requirements IN State Department of Health 2014-2015 School Year FAQ s 1. Are there any new required immunizations for the 2014-2015 school year? Yes. Two
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy
 Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Routine Immunizations Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 3 References... 7 Effective Date... 4/15/2018
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Routine Immunizations Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 3 References... 7 Effective Date... 4/15/2018
In the United States, flu season runs from October to May, with most cases occurring between late December and early March.
 Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
Partners in Pediatrics, PC 7110 Forest Ave Suite 105 Richmond, VA 23226 804-377-7100 Influenza (Flu) Influenza, commonly known as "the flu," is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract.
Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedu...ates, January - December 2000, NP Central
 Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule United States, January - December 2000 Vaccines 1 are listed under routinely recommended ages. Solid-colored bars indicate range of recommended ages for immunization.
Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule United States, January - December 2000 Vaccines 1 are listed under routinely recommended ages. Solid-colored bars indicate range of recommended ages for immunization.
Prevention of Influenza: Recommendations for Influenza Immunization of Children,
 POLICY STATEMENT Prevention of Influenza: Recommendations for Influenza Immunization of Children, 2007 2008 Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the
POLICY STATEMENT Prevention of Influenza: Recommendations for Influenza Immunization of Children, 2007 2008 Organizational Principles to Guide and Define the Child Health Care System and/or Improve the
NOTE: The above recommendations must be read along with the footnotes of this schedule.
 Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
 135 Forsyth Building Northeastern University 360 Huntington Avenue Boston, MA 02115 617.373.2772 (voice) 617.373.2601 (fax) 617.373.5973 (TTY) uhcs@northeastern.edu Health Report Massachusetts law requires
135 Forsyth Building Northeastern University 360 Huntington Avenue Boston, MA 02115 617.373.2772 (voice) 617.373.2601 (fax) 617.373.5973 (TTY) uhcs@northeastern.edu Health Report Massachusetts law requires
WESTFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS 5320 IMMUNIZATION
 WESTFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS PUPILS WESTFIELD, NEW JERSEY 5320 Regulations follow Page 1 of 1 5320 IMMUNIZATION In order to safeguard the school community from the spread of certain communicable diseases and
WESTFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS PUPILS WESTFIELD, NEW JERSEY 5320 Regulations follow Page 1 of 1 5320 IMMUNIZATION In order to safeguard the school community from the spread of certain communicable diseases and
Overview 10/3/2011. Vaccines for Life: 2011 Updates for ADULT SCHEDULE WHAT S NEW? Adult Immunization Schedules
 Vaccines for Life: 2011 Updates for Adult Immunizations George T. DiFerdinando, Jr, MD, MPH,FACP Co Director, NY NY Preparedness and Emergency Response Learning Center Director, NJCPHP at UMDNJ SPH Overview
Vaccines for Life: 2011 Updates for Adult Immunizations George T. DiFerdinando, Jr, MD, MPH,FACP Co Director, NY NY Preparedness and Emergency Response Learning Center Director, NJCPHP at UMDNJ SPH Overview
Frequently Asked Questions About the Flu Vaccine Policy
 Frequently Asked Questions About the Flu Vaccine Policy How has the CHWC new flu vaccine policy changed since last year? CHWC s new flu vaccine policy requires all CHWC employees, volunteers, medical staff,
Frequently Asked Questions About the Flu Vaccine Policy How has the CHWC new flu vaccine policy changed since last year? CHWC s new flu vaccine policy requires all CHWC employees, volunteers, medical staff,
Benefit Interpretation
 Benefit Interpretation Subject: Part B vs. Part D Vaccines Issue Number: BI-039 Applies to: Medicare Advantage Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Attachments: Part B Vaccines Diagnosis Code Limits Table of Contents
Benefit Interpretation Subject: Part B vs. Part D Vaccines Issue Number: BI-039 Applies to: Medicare Advantage Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Attachments: Part B Vaccines Diagnosis Code Limits Table of Contents
TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH
 TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH SERIES 95 IMMUNIZATION REQUIRMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NEW SCHOOL ENTERERS 64-95-1. General. 1.1. Scope.
TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH SERIES 95 IMMUNIZATION REQUIRMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NEW SCHOOL ENTERERS 64-95-1. General. 1.1. Scope.
Frequently Asked Questions Vaccine for Teens Program
 Frequently Asked Questions Vaccine for Teens Program Overall Are there new immunization requirements for the 2010 2011 school year? Yes, Students entering grades 6 12 must have appropriate documentation
Frequently Asked Questions Vaccine for Teens Program Overall Are there new immunization requirements for the 2010 2011 school year? Yes, Students entering grades 6 12 must have appropriate documentation
Objectives. Immunity. Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children 12/22/2015
 Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
Health Care Worker Vaccinations, 2011: EXTENDED CARE FACILITIES
 Health Care Worker Vaccinations, 2011: EXTENDED CARE FACILITIES Karen K Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA. Clinical Instructor, Division of Infectious Diseases University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Associate
Health Care Worker Vaccinations, 2011: EXTENDED CARE FACILITIES Karen K Hoffmann, RN, MS, CIC, FSHEA. Clinical Instructor, Division of Infectious Diseases University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Associate
Flu Vaccine Access Via Pharmacy Vaccine Network
 Re: Flu Vaccine Access Via Pharmacy Vaccine Network Effective 9/15/2016, IEHP Medi-Cal and Medicare DualChoice Cal MediConnect (IEHP Direct) Members who are over 18 years old may obtain Flu Vaccines through
Re: Flu Vaccine Access Via Pharmacy Vaccine Network Effective 9/15/2016, IEHP Medi-Cal and Medicare DualChoice Cal MediConnect (IEHP Direct) Members who are over 18 years old may obtain Flu Vaccines through
Immunization Update Disclosures. Candice Robinson, MD, MPH Medical Officer Immunization Services Division 5/12/2017
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Immunization Update 2017 Candice Robinson, MD, MPH Medical Officer Immunization Services Division Western
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Immunization Update 2017 Candice Robinson, MD, MPH Medical Officer Immunization Services Division Western
February 10, Dear Colleague,
 February 10, 2016 Dear Colleague, The New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) urges you to strongly recommend and administer the second (booster) dose of vaccine against meningococcal serogroups A,
February 10, 2016 Dear Colleague, The New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH) urges you to strongly recommend and administer the second (booster) dose of vaccine against meningococcal serogroups A,
IMMUNIZATION OF PUPILS IN SCHOOL
 R 5320 IMMUNIZATION A. Immunizations on Admission IMMUNIZATION OF IN SCHOOL 1. No Principal shall knowingly admit or retain any pupil who has not submitted acceptable evidence of immunization according
R 5320 IMMUNIZATION A. Immunizations on Admission IMMUNIZATION OF IN SCHOOL 1. No Principal shall knowingly admit or retain any pupil who has not submitted acceptable evidence of immunization according
