Session 2. Lung pathologies. Common cold (Gan Mao, 感冒 ) & influenza (Liu Gan, 流感 ) Chinese Medicine Department.
|
|
|
- Tyler Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Session 2 Lung pathologies Common cold (Gan Mao, 感冒 ) & influenza (Liu Gan, 流感 ) Chinese Medicine Department
2 o Briefly review: Session Content CM Lung physiology functions, pathway, acupoints & indication of Lung primary channel (and collaterals). Respiratory system physio-pathology. o Discuss Common Cold and Influenza (Gan Mao 感冒 & Liu gan 流感 ) mainly from CM perspective. o Practical: session topic relevant clinical skills practice and case study. Endeavour College of Natural Health 2
3 Session Rationale o This session includes the general TCM diagnostic tools & procedures, diagnostic differentiation and treatments for common cold and influenza. o There will be a practical tutorial for students to develop assessment, diagnosis and treatment skills. o The aim of this session for students is by applying TCM theoretical knowledge and skills to develop critical analysis and appropriate clinical perspective in the TCM assessment, diagnosis & differentiation, treatment and prognosis for common cold and influenza. Endeavour College of Natural Health 3
4 Session Learning outcomes o Understand in-depth TCM physiology and pathology of the Lung. o Define common cold / influenza, understand the differences between common cold and influenza. o Describe TCM etiology and pathogenesis of common cold and influenza. o Identify and differentiate the TCM patterns of common cold / influenza o Outline the TCM treatment (or management) for each pattern of Common Cold/ influenza and understand CM prevention for it. Endeavour College of Natural Health 4
5 Endeavour College of Natural Health 5
6 Functions of the Lung Zang o Governing qi and controlling respiration o Controlling disseminating and descending o Regulating the water passages o Controlling the skin and body hair o Opening into the nose Deadman 2007, p. 75 Endeavour College of Natural Health 6
7 The Lung (LU) Hand Tai Yin Primary Channel Regular Points 11 points Lung Connecting Zang Fu Large Intestine Stomach Main Channel Connections with other channels Nil Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 7
8 Pathway of the Lung Channel Lu-1 Lu-2 Throat Lu-5 Lu-9 Stomach Lungs Lu-11 Large Intestine Deadman, Al-Khafaji & Baker 2007, p. 73 Endeavour College of Natural Health 8
9 Main Acu-points on LU channel and Indications Main points & classification: LU1: Front-Mu point; the Crossing point of the LU&SP Meridian. LU7: Luo-Connecting point; Master Point of Ren Meridian (couple with KID 6);Command point of head and neck LU9:Yuan-Source point; Shu-Stream point of LU channel; Converging point of Vessels Main pathological changes/ main indications: Acupuncture points are indicated for throat, chest and lung ailments and for the other symptoms that are presented along the meridian s pathway Endeavour College of Natural Health 9
10 Clinical Uses of the Lung Channel Note Actions and indications of any channel are dictated by the channel pathway and the functions of the organs that the channel connects with internally. Endeavour College of Natural Health 10
11 Respiratory System 3D anatomy and physiology: c_entity%7cvideo_work%7c Endeavour College of Natural Health 11
12 Endeavour College of Natural Health 12
13 CMAC223 Session 2 Endeavour College of Natural Health 13
14 Bio-medical Perspective Cold & Flu Endeavour College of Natural Health 14
15 Common Cold VS Influenza o Both are upper respiratory illnesses mostly caused by different viruses. o It can be difficult to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone due to some similar symptoms: Runny nose, Nasal congestion Sore throat Red, watery eyes Loss of energy Cough o Endeavour College of Natural Health 15
16 F A C T S Fever Aches Chills Tiredness Sudden onset Bio-meds: Flu In general, Flu is worse than common cold and it can hit at any time of year with high trend of developing into a serious complication such as pneumonia, especially in young children, older adults, pregnant women, and people with immunocompromising health conditions (i.e. asthma, heart disease or diabetes) Endeavour College of Natural Health 16
17 Compare: cold and flu Cold Symptoms could build over 48 hours; Runny nose, watery eyes; Stuffy nose and congestion; Sneezing and coughing; Symptoms may last 3-10 days Flu Fast onset of symptoms; Fever and chills; Body aches and pains; Weakness and fatigue; Symptoms may last 7-14 days or may linger for up to 3 wks; (In general, the flu is worse than the common cold; Colds generally do not result in serious health problems, such as pneumonia, bacterial infections, etc.) Endeavour College of Natural Health 17
18 Cold and Flu Prevention and Management Bio-meds prevention & management/treatment (briefly): o Bio-meds prevention of common cold o Bio-meds treatment of common cold o Bio-meds prevention of influenza o Bio-meds treatment of influenza Endeavour College of Natural Health 18
19 Useful Links o o o ntent/about-pandemic-whatis o Endeavour College of Natural Health 19
20 Chinese Medicine Perspective Endeavour College of Natural Health 20
21 Common Cold- Gan Mao 感冒 o Define Common cold ( 感冒 ): is also called Wind-Injury, a frequently recurring disorder caused by attacks of exterior pathogenic wind. It manifests with nasal congestion, runny nose and sneezing, coughing, headache, aversion to cold, fever and general discomfort. The underlying pathologies are failure of Lung Qi to disperse and inability of protective Qi to consolidate the surface of the body. Endeavour College of Natural Health 21
22 Common Cold- Gan Mao 感冒 (cont.) o The pathway of Wind attack is the Lung system and the Defensive exterior, and the location of the illness is generally also limited to the Lung-Defensive level. o Mostly it results from strong exogenous Wind, but if the patient is exposed to Wind while the body is deficient the result may be an illness of root-deficiency and appearance/branch-strength. Liu, Zhanwen & Liu, Liang Essentials of Clinical Specialities in Chinese Medicine. Dordrecht : Springer ebook Collection (EBSCOhost) Endeavour College of Natural Health 22
23 Notes o Common cold is not a season specific, however it s more common in winter and spring; Generally it has a short course and rapid recovery. o In contrast, epidemic cold (Liu Gan, 流感 ) and cold in those with weak constitutions, such as the elderly and infants, tend to develop complications that make recovery difficult. o To a certain degree, common cold is contagious in that it may spread from one to another. Endeavour College of Natural Health 23
24 Etiological factor: External Wind The concept of Wind (Feng, 风 ) in Chinese medicine: o One of the six exterior pathogens, the chief of the six climatic pathogenic evils. o If the Righteous Qi is intact, exterior pathogens will not be able to penetrate through the Protective Qi o Exterior Wind invading into body may be combined with cold, heat, dampness and dryness o Exterior Wind penetrates via skin, nose and throat and interferes with the circulation of Defensive Qi (Wei Qi, 卫气 ) in the space between skin and muscle Endeavour College of Natural Health 24
25 Interior pathogens or preexisting deficiency o Lung Qi is Deficient which means that its function of impaired D & D Because if this impairment, the Wei Qi can not consolidate the surface o Phlegm Fire and Phlegm Damp Means that the Lung Qi can not regulate the Wei Qi Wei qi impairment allows exterior pathogens to easily invade via skin Endeavour College of Natural Health 25
26 Interior pathogens or pre-existing deficiency constitutional deficiency is associated with susceptibility to certain exterior pathogens. A person with pre-exiting Qi/Yang xu wind-cold attack propensity A person with pre-exiting Blood/Yin xu wind-heat attack propensity Endeavour College of Natural Health 26
27 o Fever ** Main manifestations of o Aversion to cold ** o Nasal congestion o Runny nose & sneezing o Cough o Headache o General discomfort Common cold o Short course, rapid recovery ** (it lasts 3 7 days. Its course seldom varies) ** key features of common cold Endeavour College of Natural Health 27
28 TCM etiology & Pathogenesis of Common Cold Endeavour College of Natural Health 28
29 Two Perspectives o Exterior (factors): Wind combines something (heat, cold, Damp, dryness, etc.) PLUS o Interior (factors): insufficient Wei Qi/ Righteous Qi Phlegm Fire/Heat and Phlegm Damp Endeavour College of Natural Health 29
30 Wind cold enters via skin closed pores & impaired Lu dispersing funct. External Pathogenic Wind combines with other pathogens Wind heat Wind dry via nose & throat (mouth) Wei Qi impaired open pores & impaired Lung descending function (Wei Qi Xu) Common cold Interior Pathogenic Influences; preexisting deficiency summer heatdampness Insufficient righteous qi Pre-existing phlegmfire; phlegm dampness in lung Lu Qi Xu; dispersing function impaired obstructs the clear Yang Wei qi fails to consolidate surface Lung unable to regulate Wei Qi Exterior pathogens invade Yang Xu Yin Xu Phlegm-damp Prone to wind-cold Prone to wind-heat; wind-dry Prone to damp invasion Endeavour College of Natural Health 30
31 Common Cold Etiology & Pathogenesis o Exterior wind combines with other exterior pathogens and invades via the skin, nose and throat into human body. o Although the main cause is the Wind evil, its development is closely related to the strength or weakness of the body s genuine Qi/ Righteous Qi. o Pathogens impairs Wei Qi & Lung D & D (descending & distributing) functions Endeavour College of Natural Health 31
32 Extra reading for students ( outside class): The Concept of Wind in Traditional Chinese Medicine Dashtdar, M., Dashtdar, M. R., Dashtdar, B., Kardi, K., & Shirazi, M. khabaz. (2016). The Concept of Wind in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Journal of Pharmacopuncture, 19(4), Endeavour College of Natural Health 32
33 Diagnosis and Treatments Endeavour College of Natural Health 33
34 Differential methods for Exterior Syndrome o Four levels differentiation o Six meridians (divisions)/ stages of exterior pathologies o ZangFu differentiation o Sanjiao/ Triple Energizer differentiation o Eight Principles differentiation Endeavour College of Natural Health 34
35 Diagnosis and Differentiation o Diagnosis (set text p4-5): 1) Identification of mild, severe and epidemic cold (see table in next slide) 2) Differentiation diagnosis of common cold and windwarm febrile disease: Have similar signs and symptoms Different fever nature Warm febrile disease diagnosis- Four levels (wei, qi, ying & Xue) diagnosis usually is applied o Basic patterns of common cold Endeavour College of Natural Health 35
36 TCM perspectives (set text P4): Common Cold VS Flu (Epidemic Cold) Common Cold Epidemic Cold (Flu, 流感 ) Pathogens Exterior pathogenic factors, primarily wind Epidemic contagious pathogens Season Severity Winter-spring; sporadic occurrence Mild and no significant systemic symptoms Non-seasonal; pandemic occurrence in local population Sever and systemic involvement Progress Mild and superficial with mild or no internal invasion Fast invasion into the interior with primary or secondary complications Endeavour College of Natural Health 36
37 Patterns of common cold o Wind-cold (WC) o Wind-heat (WH) o Summer-heat (damp heat)--sdh o Pre-existing Qi xu with External pathogens invasion o Pre-existing Yin xu with invasion of External pathogens Key Points of Analysis: Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat (cold/heat?) Accompanying Pathogenic Evils Strength and Deficiency (Shi and Xu/ excessive and deficient) *Lecturer please facilitate students fill the table below to do the patterns identification of Common cold. Endeavour College of Natural Health 37
38 Patterns Identification Patterns Main S&S Major accompanying S&S Wind-Cold Wind-Heat Summer heatdamp Qi Xu with exterior invasion Tongue Pulse Yin Xu with exterior invasion Endeavour College of Natural Health 38
39 Comparison of Wind-cold and Wind-Heat Wind-Cold Wind-Heat Pathology Wind-cold Wind-Heat Penetration of pathogenic factor Via skin Via nose & mouth Fever None/Light high Aversion to cold Pronounced slight Body aches severe slight Thirst none Slight-medium Headache Occipital Whole head sweating No/slight (head) Slight-medium Tongue & Pulse Thin-white coat; floating tight pulse Slightly red sides and thin-yellow coat; floatingrapid pulse See Table 48.1 on page 1319 Maciocia, G 2008, The practice of Chinese medicine: treatment of disease with acupuncture and Chinese herbs, 2nd edn, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh Endeavour College of Natural Health 39
40 Common Cold CM treatment (management) World Health Organisation (WHO) included certain upper respiratory tract & respiratory system disorders in it s 1979 list of amenable diseases to acupuncture: o Common cold o Acute bronchitis o Bronchial asthma Based on clinical experience more than controlled clinical research trials Endeavour College of Natural Health 40
41 CM Management Follow the principle that states For those pathogenic factors that stay in the superficial layer, induce sweating to release them. o The primary treatment for the common cold is to release the exterior by inducing sweating: WC: acrid and warm herbs to release the exterior WH: acrid and cold herbs to release the exterior SDH: Clear SH, expel damp, release exterior Exterior conditions with pre-exist deficiency: Support the righteous qi to release the exterior Endeavour College of Natural Health 41
42 Acupuncture and auxiliary treatment for Common Cold o Treatment principles: Release the exterior Expel wind Restore the diffusing and descending of Lung-Qi o Common treatment methods: Acupuncture Fire cupping/slide cupping Moxa Tuina/acupressure Endeavour College of Natural Health 42
43 Acu-prescription and Rationales What meridians and acu-points do you think most involved in the treatment for common cold? o LU7, LU9, LU5, LU1 o LI4, LI20 o BL12 (fengmen), BL13 o GB20 (fengchi), GV16(fengfu) o GV14, GV20 o KI7 reinformcing+li4 reducing to cause sweating Endeavour College of Natural Health 43
44 Acupuncture Treatment (Set text page 8 & 9) o Prophylactic measures: BL 12(Fengmen), ST36 (Zusanli) Moxibusion o Pattern differentiation treatments: Exterior wind-cold TX principle? Points: GV16, BL12, GB20,LU7,LI4 Manipulation: Reducing, Even method or moxa for deficiency Exterior wind-heat Exterior SDH Wind Invasion with Qi Xu TX principle? Points:GV14, LI11, TE5, LI4,LU10, LU11 TX principle? Points: LU6, LI4,ST36, CV12,TE6 TX principle? Points: ST36, BL13 + points for WC Manipulation: reducing Manipulation: reducing Manipulation: Reducing, Even method & moxa for Qi deficiency Invasion of Wind with Yin Xu TX principle? Points: KI7, BL43 + Manipulation: Reducing, Even method WH & reinforcing for Yin deficiency Endeavour College of Natural Health 44
45 A word on Wind Cold o This pattern exhibits the following symptoms: fever, chills (these are worse than the fever), inability to get warm, nasal or sinus congestion with clear mucus, cough with clear mucus, stiff neck and shoulders, occipital headache (back of head), and a slower-than-normal pulse that is more easily felt at the surface. Endeavour College of Natural Health 45
46 Ginger Tea for Wind cold Diaphoretic (sweating) therapy is especially helpful in this condition, since it warms the body and pushes the pathogen out through the pores. In the very early stages of this pattern, an effective remedy is miso soup with the white part of spring onion (cong bai) and fresh ginger (sheng jiang). For more severe or advanced cases, there is a full range of therapies, depending on the combination of symptoms. Endeavour College of Natural Health 46
47 Wind Heat o When treating cold or flu symptoms due to wind heat, the results are always more dramatic if the treatment begins at the earliest possible stage of the illness. o It is important to get adequate rest, a vacation from sources of stress, and good nutrition in the form of soups and fresh juices. o Sweets and stimulants (such as caffeinated beverages) cause a rapid progression in the severity of the illness since they tend to feed the pathogen. Why? Endeavour College of Natural Health 47
48 Tonifying herbs and Wind Heat / Wind Cold --yes or no? o People sometimes make the mistake of taking ginseng when they feel a cold coming on since they have heard that ginseng is good for the immune system. o Using ginseng in this case is a serious error since ginseng will powerfully feed the pathogen causing the illness, making the person feel much worse. This is traditionally known as "trapping the burglar. o While tonic herbs can be taken long-term, it is important to discontinue their use during a cold or flu. Then, after the pathogen has been expelled from the body, tonic herbs can be taken again to build up strength and vitality over the long-term. Endeavour College of Natural Health 48
49 TCM Perspectives to Flu see set text pages o Influenza (Flu) is different from common cold. o It is caused by exterior-wind attacking a person with deficient righteous Qi / inadequate resistance to exterior pathogens. o In Addition, constitutional strength plays an important role in the occurrence of flu. o Flu is mostly an excess condition, though a pattern of deficiency root with excess branch is apparent in those with deficient righteous Qi. Endeavour College of Natural Health 49
50 TCM Perspectives to Flu o It s usually named Liu Gan ( 流感 ), and viewed under the scope of epidemic cold disease due to its severity, pandemic nature and other Key S&S: A sudden and rapid onset Chills, High fever, headache, body aches Cough-productive or hacking, congested chest and dyspnoea o It could be referred to TCM differentiation and treatment for common cold and cough, based on the clinical manifestations. Endeavour College of Natural Health 50
51 TCM Diagnosis and Treatment of Flu o Four Levels differentiation is mostly used in the TCM pattern diagnosis of Flu o Analysis of primary symptoms: Fever: observe the characteristics of fever and the accompanying symptoms; clinic red flag Productive Cough, congested chest and dyspnoea: secondary symptoms due to heat accumulation inducing the failure of Lungs D&D functions; (can be referred to session 3 Cough learning content) Endeavour College of Natural Health 51
52 TCM Patterns of Flu o Basic patterns: 1) Wind-heat attacking the protective level 2) Pathogenic heat affecting both protective and qi levels 3) Heat accumulating in the lung 4) Heat lodged in the pericardium o Progression of Pattern (see details Set text P304) o Treatment Principles and methods o Relevant events or updated research articles o The role of Chinese Herbal medicine in Flu treatment Endeavour College of Natural Health 52
53 Extra herb formula: Gui Zhi Tang ( 桂枝汤 ) Cinnamon Twig Decoction Source: Shang Han Lun 伤寒论 Composition: Gui Zhi; Shao Yao; Zhi Gan Cao; Sheng Jiang; Da Zao Administration: Decoct all ingredients for oral administration (in Shang Han Lun, shortly after taking the first dose, having the warm, thin gruel and covering the body with a blanket to reinforce the sweating effect of the medicinal, also ideally just get light sweating (for example, the whole body is moist, not flowing sweating as water) ; if no sweating after taking decoction, take another dose according to the above method. ) Functions and indications: releases exterior; regulates nutritive (ying) qi and defensive (wei) qi; harmonizes the spleen and stomach. MacLean, W 2003 Exterior deficiency syndrome due to externally contracted wind-cold with the manifestations of headache, fever, sweating with aversion to cold, nasal hoarsenss, retching, white tongue coating, no thirst, floating and weak pulse. Biomedical Indications: Mild Diaphoretic, Antispasmodic Contraindications: Excess patterns, external cold with internal heat, wind heat, acute warm or damp heat, internal heat and yin deficiency Dosage (for patent medicine): : 8-12 pills (two to three times a day) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 53
54 Literature resource for Gui Zhi Tang: Shang Han Lun 伤寒论 Line 12 Tai yang zhong feng, yang fu er yin ruo, yang fu zhe, re zi fa, yin ruo zhe, han zi chu. Se se wu han, xi xi wu feng, xi xi fa re, bi ming gan ou zhe, gui zhi tang zhu zhi In great yang wind strike with floating yang and weak yin, floating yang is spontaneous heat effusion, and weak yin is spontaneous issue of sweat. If (there is) huddled aversion to cold, wetted aversion to wind, feather-warm heat effusion, noisy nose, and dry retching, Cinnamon Twig Decoction governs Mitchell, C, Ye, F & Wiseman, N 1999, Shang han lun, Paradigm Publications, Brookline, Massahusetts. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 54
55 Pinyin: Yin Qiao San ( 银翘散 ) English: Honeysuckle and Forsythia Powder Source: Wen Bing Tiao Bian 温病条辨 MacLean, W 2003 Composition: Yin Hua; Lian Qiao; Jie Geng; Bo He; Niu Bang Zi ; Jing jie (Sui); Dan Dou Chi; Lu Gen; Zhu Ye; Sheng Gan Cao Administration: oral administration. Functions : Release the exterior with acrid-cool; clear heat and remove toxic substances. Indications: Warm diseases at the early stage with symptoms of fever, slightly aversion to wind-cold, no sweat or non-smooth sweating, headache, thirst, cough, sore throat. Red tip of tongue, with thin white coating or thin yellowish coating; floating and rapid pulse. Contraindications: Wind-cold type cold or flu with dominant chills; muscle ache with absence of sweating Dosage (for patent medicine): 8 tablets (3-4 times per day) or in severe cases every two hours. Biomedical Indications: anti-pyretic, diaphoretic, anti-inflammatory, antiviral. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 55
56 Summary and Discussion o Summarise this session learning o Discuss Practical hints (Set Text Pg9-10) Differ wind-cold and wind-heat Avoid excessive diaphoresis Constitutional Xu is associated with susceptibility to certain exterior pathogens Prophylactic method for complications Endeavour College of Natural Health 56
57 Break Endeavour College of Natural Health 57
58 Practical Tutorial * Each student s attendance and performance in every practical section will be documented and graded according to Continuous Skill Development (Rubric-based) Assessment Guide (see details on LMS) Endeavour College of Natural Health 58
59 Case Study 1 o Jacqui, 48 years old, presents with a cold of 2 days duration. She has a severe distending headache and a fever 38.5 C. She tells you that although she s a bit warmer then usual, she does not like to go out in the wind. Her nose is congested and when she blows it (which makes her head aches worse) there is yellow discharge. She has a swollen sore throat and the beginnings of a barking cough. o Tongue: red with thin yellow coat o Pulse: rapid and floating Endeavour College of Natural Health 59
60 Case Study 2 A 19 years old men presents to your clinic suffering from the flu. He has a cough (non-productive, stuffy nose which is prone to running (clear watery mucous), sneezing and a strong aversion to cold (he is very rugged up when presenting at the consultation). He has also complained of headaches and general body aches. Clinical Assessments: Other: Pale Pulse: Floating and tight Tongue: Thin with a white coating Endeavour College of Natural Health 60
61 Case Study Questions Read the above case and answer all of the questions below: o o o o o o o What is the TCM diagnosis (Disease and Pattern)? Explain your answer. What is the TCM treatment principle? What TCM treatment methods will you choose to combine in the management for the patient s condition? Choose at least five acu-points for your acupuncture prescription to treat this condition based on your diagnosis. Give the rationale for the above acupuncture points & demonstrate your appropriate needling techniques and WH&S knowledge and skills. Recommend suitable lifestyle/dietary advice for this condition based on Chinese Medicine theory. How might be the progress of the patient s condition after a course of appropriate treatment has been applied? Endeavour College of Natural Health 61
62 Case Study based treatment Performance/Practice o Lets treat each other according to our diagnosis and treatment that we have figured out from our case study. o Demonstration and practice of the assessment, diagnosis and TCM treatment of Common cold and flu. o Demonstration of WH&S skills and sensitiveness of cultural differences. Endeavour College of Natural Health 62
63 Main References Shi, A. (2011). Essentials of Chinese medicine: Internal medicine. (2nd ed.). Walnut, CA: Bridge Publishing Group. Maciocia, G. (2008). The practice of Chinese medicine: Treatment of disease with acupuncture and Chinese herbs(2nd ed.). Edinburgh, Scotland: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone. [ebook available] Maclean, W., & Lyttleton, J. (1998). Clinical handbook of internal medicine: The treatment of disease with traditional Chinese medicine, volume one, lung, kidney, liver, heart. Sydney, NSW: University of Western Sydney. Maclean, W., & Lyttleton, J. (2002). Clinical handbook of internal medicine: The treatment of disease with traditional Chinese medicine, volume two, spleen and stomach. Sydney, NSW: University of Western Sydney. Maclean, W., & Lyttleton, J. (2010). Clinical handbook of internal medicine: The treatment of disease with traditional Chinese medicine, volume three, blood, fluid and channel disorders. Ulladulla, NSW: Pangolin Press. Endeavour College of Natural Health 63
64 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 64
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 )
 4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into
 Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Course: Diagnostics II Date: 9/26/07 Class #: 1
 Course: Diagnostics II Date: 9/26/07 Class #: 1 Theories of disease and symptom analysis to acquire differentiation. There are several tools and systems you can use to analyze symptoms and get form a differentiation
Course: Diagnostics II Date: 9/26/07 Class #: 1 Theories of disease and symptom analysis to acquire differentiation. There are several tools and systems you can use to analyze symptoms and get form a differentiation
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Respiratory diseases are extremely common and often respond very well to treatment with acupuncture and Chinese herbs. Both acute and respiratory diseases can be helped.
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Respiratory diseases are extremely common and often respond very well to treatment with acupuncture and Chinese herbs. Both acute and respiratory diseases can be helped.
Shang Han Lun - The Six Stages
 THE TREATMENT OF RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS Acute respiratory infections cannot be diagnosed and treated properly without a thorough understanding of the theory of the 6 Stages and particularly that of the
THE TREATMENT OF RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS Acute respiratory infections cannot be diagnosed and treated properly without a thorough understanding of the theory of the 6 Stages and particularly that of the
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities
 Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Single Herbs III / Quiz I
 Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Session 1. Subject Introduction. Tutorial: Academic Writing & Research Skills. Chinese Medicine Department.
 Session 1 Subject Introduction Tutorial: Academic Writing & Research Skills Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 1 Contents o 2-hour subject introduction Introduction to the subject
Session 1 Subject Introduction Tutorial: Academic Writing & Research Skills Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 1 Contents o 2-hour subject introduction Introduction to the subject
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10. Function in Formula. Disperse stagnation
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
INFLUENZA A (H1N1) Background
 INFLUENZA A (H1N1) Background The new strain of influenza A (H1N1) was first reported from Mexico this year (2009). The spectrum of disease caused by new influenza A (H1N1) virus infection ranges from
INFLUENZA A (H1N1) Background The new strain of influenza A (H1N1) was first reported from Mexico this year (2009). The spectrum of disease caused by new influenza A (H1N1) virus infection ranges from
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE I
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
Chapter 14 Warming interior
 Chapter 14 Warming interior [7. Herbs That Warm the Interior, 9] Fu Zi 附子 Gan Jiang 乾薑 Rou Gui 肉桂 Wu Zhu Yu 吳茱萸 Xiao Hui Xiang 小茴香 9 herbs Ding Xiang 丁香 Gao Liang Jiang 高良薑 Hua Jiao 花椒 Hu Jiao 胡椒 : Pungent,
Chapter 14 Warming interior [7. Herbs That Warm the Interior, 9] Fu Zi 附子 Gan Jiang 乾薑 Rou Gui 肉桂 Wu Zhu Yu 吳茱萸 Xiao Hui Xiang 小茴香 9 herbs Ding Xiang 丁香 Gao Liang Jiang 高良薑 Hua Jiao 花椒 Hu Jiao 胡椒 : Pungent,
Section Two. Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13)
 Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
Section Two Chapter 1 Herbs for relieving superficial syndrome (Biao Zheng) 解表藥 (23) A. Pungent & warm 辛溫解表 (13) Pungent, warm, SD of wind cold: no sweating, aversion to cold/fever, pain, sp/tense pulse
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae
 CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Two Release Exterior Chinese herbal medicine: warm pungent, cool pungent: o English name; Pin yin name o Composition; dosage and administration o Functions and indications
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Two Release Exterior Chinese herbal medicine: warm pungent, cool pungent: o English name; Pin yin name o Composition; dosage and administration o Functions and indications
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 10 Channel Diagnosis - 8 Principles Channels & Collaterals of the Bladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P.,
Lung and Large Intestine
 Course: Diagnostics II Date: October 17, 2007 Class #: 4 Homework For each zang or fu: make a small chart for each for symptoms. Do a chart per organ, later do a chart with combinations. See slide 9 from
Course: Diagnostics II Date: October 17, 2007 Class #: 4 Homework For each zang or fu: make a small chart for each for symptoms. Do a chart per organ, later do a chart with combinations. See slide 9 from
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
Influenza. Giovanni Maciocia
 Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding
 Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū
 Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
Course: Diagnostics II Date: Class #: 2
 Course: Diagnostics II Date: 10-03-07 Class #: 2 Eight principles cont d Know: what is true/what is false (true cold/false heat for example) Know yin deficiency symptoms Know exterior/interior dx. Note:
Course: Diagnostics II Date: 10-03-07 Class #: 2 Eight principles cont d Know: what is true/what is false (true cold/false heat for example) Know yin deficiency symptoms Know exterior/interior dx. Note:
Treatment Principle Basics
 Treatment Principle Basics Blood : Main TX: Nourish Blood + Tonify the Organ so: : Heart Blood Nourish Blood, tonify HT Calm Mind Pericardium Blood Nourish Blood, strengthen Heart and Pericardium Move
Treatment Principle Basics Blood : Main TX: Nourish Blood + Tonify the Organ so: : Heart Blood Nourish Blood, tonify HT Calm Mind Pericardium Blood Nourish Blood, strengthen Heart and Pericardium Move
CMPR121. Session 13. Small Intestine
 CMPR121 Session 13 Small Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Small Intestine o Separates the pure from the impure o Receives & transports food o Separates fluids o Is responsible
CMPR121 Session 13 Small Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Small Intestine o Separates the pure from the impure o Receives & transports food o Separates fluids o Is responsible
Medicated diet. Tonify the Qi
 Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Class 1 - Point Indication. Review of TCM theory. Yin / Yang ( / Yin and Yang are:
 Class 1 - Point Indication Review of TCM theory Yin / Yang ( / Yin and Yang are: 1. Counterbalanced They are the generalization of the relative opposite principles observed throughout all things 2. Inter-transforming
Class 1 - Point Indication Review of TCM theory Yin / Yang ( / Yin and Yang are: 1. Counterbalanced They are the generalization of the relative opposite principles observed throughout all things 2. Inter-transforming
Warms Jīng ( 经 ) and dispels Hán. Nourishes Xuè and opens Blood vessels. Hán obstruction in Jīng with Xuè Xū
 ormulas that Warm the Channels and Dispel Cold 1 Dāng Guī Sì Nì Tāng 当归四逆汤 Angelica rigid Extremities Decoction Warms Jīng ( 经 ) and dispels Hán. Nourishes uè and opens Blood vessels. Hán obstruction in
ormulas that Warm the Channels and Dispel Cold 1 Dāng Guī Sì Nì Tāng 当归四逆汤 Angelica rigid Extremities Decoction Warms Jīng ( 经 ) and dispels Hán. Nourishes uè and opens Blood vessels. Hán obstruction in
CMAC212. Session 9. Special point categories. Focusing on: Small & Large Intestine. Chinese Medicine Department.
 CMAC212 Session 9 Special point categories Focusing on: Small & Large Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 9 Today we shall: o Discuss point prescriptions for the take home
CMAC212 Session 9 Special point categories Focusing on: Small & Large Intestine Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 9 Today we shall: o Discuss point prescriptions for the take home
ALLERGIC RHINITIS 1. ALLERGIC RHINITIS IN WESTERN MEDICINE
 ALLERGIC RHINITIS we shall discuss the following topics: Allergic rhinitis in Western medicine; The theory of Bi Yuan in Chinese medicine; Differences between allergic rhinitis and Bi Yuan; A new theory
ALLERGIC RHINITIS we shall discuss the following topics: Allergic rhinitis in Western medicine; The theory of Bi Yuan in Chinese medicine; Differences between allergic rhinitis and Bi Yuan; A new theory
Tiredness/Fatigue Mild Moderate to severe, especially at onset of symptoms Head and Body Aches and Pains
 What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
What is the difference between a cold COLD FLU and the flu? How it starts Symptoms It s Cold and Flu Season in Snohomish County! Colds and Flu are respiratory illnesses caused by viruses. Our Immune Systems
CMCS121. Session 4. Interview Workshop/ Abdominal Pain. Chinese Medicine Department.
 CMCS121 Session 4 Interview Workshop/ Abdominal Pain Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Abdominal Pain o Maciocia, p 145-147, o Pain, p 255-259, 735-745 o Digestive symptoms p 262, o Asking
CMCS121 Session 4 Interview Workshop/ Abdominal Pain Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Abdominal Pain o Maciocia, p 145-147, o Pain, p 255-259, 735-745 o Digestive symptoms p 262, o Asking
Root & Branch Bulk Formula List
 An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses
 Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses and the people you support Is a major cause of unplanned hospitalizations. Usually occur in fall and winter. It is important for you to Help people
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses and the people you support Is a major cause of unplanned hospitalizations. Usually occur in fall and winter. It is important for you to Help people
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang. Shi Jue Ming ** Properties: Salty, mild cold LV. Actions: Suppress LV yang, clear eye heat
 C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
Single Herbs III / Quiz II
 Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 12 Channels & Collaterals of the Gallbladder Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman, P., Al-Khafaji, M., & Baker, K. (2007).
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease
 Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Session 5. Heart Pathologies. Sleep disorder: Chinese Medicine Department. Insomnia (Bu Mei / Shi Mian, 不寐 ) & Somnolence (Duo Mei, 多寐 )
 Session 5 Heart Pathologies Sleep disorder: Insomnia (Bu Mei / Shi Mian, 不寐 ) & Somnolence (Duo Mei, 多寐 ) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au o Sleep disorder: Session Content Insomnia(Shi
Session 5 Heart Pathologies Sleep disorder: Insomnia (Bu Mei / Shi Mian, 不寐 ) & Somnolence (Duo Mei, 多寐 ) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au o Sleep disorder: Session Content Insomnia(Shi
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE II
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment
 Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
The Vital Substances: Qì, Xuè, Jīn-Yè, Jīng and Shén
 Chapter 4 The Vital Substances:,, Jīn-Yè, Jīng and Shén Goals of this chapter Explain the concepts and functions of the Vital Substances. Learning Goals After this chapter you have to be able to: explain
Chapter 4 The Vital Substances:,, Jīn-Yè, Jīng and Shén Goals of this chapter Explain the concepts and functions of the Vital Substances. Learning Goals After this chapter you have to be able to: explain
1. CONNECTIONS AND DIFFERENCES BETWEEN EARLY-ONSET ALLERGIC ASTHMA AND XIAO- CHUAN
 ALLERGIC ASTHMA This newsletter is dedicated to the discussion of allergic asthma and especially that in children and young people. Asthma is a general term that may refer to quite different diseases and,
ALLERGIC ASTHMA This newsletter is dedicated to the discussion of allergic asthma and especially that in children and young people. Asthma is a general term that may refer to quite different diseases and,
Contents. Basic Theory of Acupuncture. (Page 1) Acupuncture Points. (Page 31) Side Effects of Acupuncture. (Page 51)
 VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020 Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Content Outline Effective January 1, 2020 Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who have met NCCAOM
CMAC212. Session 8. Special Point Categories. Focusing on Lung, Spleen & Stomach. Chinese Medicine Department.
 CMAC212 Session 8 Special Point Categories Focusing on Lung, Spleen & Stomach Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 8 Today we shall: o Explore points on the Lung channel o Explore points
CMAC212 Session 8 Special Point Categories Focusing on Lung, Spleen & Stomach Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session 8 Today we shall: o Explore points on the Lung channel o Explore points
Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs
 Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
Foundations of Traditional Chinese Medicine
 SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Foundations of Traditional Chinese Subject Code: CMPR113 SECTION 1 - GENERAL INFORMATION Award/s: Total Course Credit Points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Acupuncture)
SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Foundations of Traditional Chinese Subject Code: CMPR113 SECTION 1 - GENERAL INFORMATION Award/s: Total Course Credit Points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Acupuncture)
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses
 Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
FOUNDATIONS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SUBJECT STUDY GUIDE Semester 1, 2018
 FOUNDATIONS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SUBJECT STUDY GUIDE Semester 1, 2018 Last updated on 29-Jan-18 Page 1 of 18 FOUNDATIONS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SUBJECT STUDY GUIDE As students in the
FOUNDATIONS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SUBJECT STUDY GUIDE Semester 1, 2018 Last updated on 29-Jan-18 Page 1 of 18 FOUNDATIONS OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE SUBJECT STUDY GUIDE As students in the
FAMILIES OF REMEDIES
 FAMILIES OF REMEDIES This newsletter will present the main "families" of remedies grouped according to condition treated in a tabular form for quick reference. The "families" of remedies considered will
FAMILIES OF REMEDIES This newsletter will present the main "families" of remedies grouped according to condition treated in a tabular form for quick reference. The "families" of remedies considered will
Our ongoing interest in spirit
 Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
CMAC311. Session 4. Chinese Medicine Department MENSTRUATION DISORDERS. Pre-menstrual Syndrome (PMS) Dysmenorrhea (painful periods)
 CMAC311 Session 4 MENSTRUATION DISORDERS Pre-menstrual Syndrome (PMS) Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Contents o Explain the aetiology factors &
CMAC311 Session 4 MENSTRUATION DISORDERS Pre-menstrual Syndrome (PMS) Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au Session Contents o Explain the aetiology factors &
Introduction to Acupuncture
 Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: May 19, 2009 Class #: 6 12 D Tonify Yin and 13 Stabilize and Bind
 Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: May 19, 2009 Class #: 6 12 D Tonify Yin and 13 Stabilize and Bind Yin Tonics: know the channels for sure! Tian Dong This is the asparagus tuber, but not the same as the
Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: May 19, 2009 Class #: 6 12 D Tonify Yin and 13 Stabilize and Bind Yin Tonics: know the channels for sure! Tian Dong This is the asparagus tuber, but not the same as the
Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs
 Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs How many raw herbs are needed to make the concentrates? There are several possibilities to answer that question. The simplest answer is that 250
Frequently asked questions regarding concentrated herbs How many raw herbs are needed to make the concentrates? There are several possibilities to answer that question. The simplest answer is that 250
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS. Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac
 INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S17 Discussion on the Essentials of Pulse S18 Discussion on the Pulse Conditions of Healthy People
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM DIAGNOSIS METHODS Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S17 Discussion on the Essentials of Pulse S18 Discussion on the Pulse Conditions of Healthy People
Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages
 Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages 07 JUNE 2017 Researchers find acupuncture effective for the alleviation of chronic coughing. In a controlled clinical investigation, researchers determined
Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages 07 JUNE 2017 Researchers find acupuncture effective for the alleviation of chronic coughing. In a controlled clinical investigation, researchers determined
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL
 ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
Single Herbs II / Quiz II
 1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM TREATMENT PRINCIPLES. Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac
 INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM TREATMENT PRINCIPLES Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S5 Major Discussion on the Theory of Yin and Yang and the Corresponding Relationships Among
INTERNAL CANON OF THE YELLOW EMPEROR TCM TREATMENT PRINCIPLES Stanley Liang Ph.D., R.TCMP, R.Ac Text reading S5 Major Discussion on the Theory of Yin and Yang and the Corresponding Relationships Among
Term-End Examination December, 2009
 PGDACP - 01 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN ACUPUNCTURE (PGDACP) 00931 Term-End Examination December, 2009 PGDACP-01 : BASIC THEORIES OF ACUPUNCTURE/TCM DIAGNOSIS Time : 2 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : There
PGDACP - 01 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN ACUPUNCTURE (PGDACP) 00931 Term-End Examination December, 2009 PGDACP-01 : BASIC THEORIES OF ACUPUNCTURE/TCM DIAGNOSIS Time : 2 Hours Maximum Marks : 70 Note : There
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 9 Four Examination Methods in Channel Diagnosis Channels & Collaterals of the Kidney Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman,
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 9 Four Examination Methods in Channel Diagnosis Channels & Collaterals of the Kidney Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission. Deadman,
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences
 Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses
 Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
 1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
TONICS TO TONIFY OR TO EXPEL: THAT IS THE QUESTION
 TONICS "The three months of Autumn are the time of harvest. The energy of Heaven begins to blow swiftly and the energy of Earth begins to change colour. One should go to bed early and rise early: maintain
TONICS "The three months of Autumn are the time of harvest. The energy of Heaven begins to blow swiftly and the energy of Earth begins to change colour. One should go to bed early and rise early: maintain
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae
 CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Three Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Qi: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and indications
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Three Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Qi: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and indications
Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions
 Chapter 3 Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions 1 Characteristics of Luo Vessels Connect external/internal pairs Distribute qi throughout the body Harmonize circulation 2 In all, there are fifteen
Chapter 3 Luo Vessels, Cutaneous and Muscle Regions 1 Characteristics of Luo Vessels Connect external/internal pairs Distribute qi throughout the body Harmonize circulation 2 In all, there are fifteen
New and Improved 8 Principles in Clinical Practice: 3 Most Important Dichotomies. Bruce Ferguson, DVM, MS Holistic Veterinary Care
 New and Improved 8 Principles in Clinical Practice: 3 Most Important Dichotomies Bruce Ferguson, DVM, MS Holistic Veterinary Care www.naturalvet.org Introduction It is said that Chinese Medicine (TCVM)
New and Improved 8 Principles in Clinical Practice: 3 Most Important Dichotomies Bruce Ferguson, DVM, MS Holistic Veterinary Care www.naturalvet.org Introduction It is said that Chinese Medicine (TCVM)
HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE. Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands
 HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands Chinese Medical Theory Based on observation of phenomena and integrated with Chinese philosophy Chinese philosophy has
HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands Chinese Medical Theory Based on observation of phenomena and integrated with Chinese philosophy Chinese philosophy has
Sixfu organs: small intestine, gall bladder, stomach, Large intestine, urinary bladder
 Sixzang organs: heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, pericardium To manufacture and store essential substances including vital essence, qi (vital energy), blood, andbodyfluid Sixfu organs : small intestine,
Sixzang organs: heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, pericardium To manufacture and store essential substances including vital essence, qi (vital energy), blood, andbodyfluid Sixfu organs : small intestine,
YOUR ULTIMATE FLU SURVIVAL GUIDE CHICKEN SOUP, HERBAL REMEDIES, ANTIVIRAL DRUGS, OH MY! HERE S EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW.
 YOUR ULTIMATE FLU SURVIVAL GUIDE CHICKEN SOUP, HERBAL REMEDIES, ANTIVIRAL DRUGS, OH MY! HERE S EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW. IS IT THE FLU OR JUST A REALLY BAD COLD? The flu is a contagious respiratory
YOUR ULTIMATE FLU SURVIVAL GUIDE CHICKEN SOUP, HERBAL REMEDIES, ANTIVIRAL DRUGS, OH MY! HERE S EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW. IS IT THE FLU OR JUST A REALLY BAD COLD? The flu is a contagious respiratory
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae
 CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Four Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Xue; Qi and Xue: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and
CMHB221 Chinese Herbal Formulae Session Four Tonifying Chinese herbal formulae: Xue; Qi and Xue: o o o o o English name; Pin yin name and Chinese name Composition; dosage and administration Functions and
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory
 CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 2 Internal, external and secondary channels Lung, Pericardium & Heart Channels & Collateral Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission.
CMAC111 Acupuncture Channel Theory Session 2 Internal, external and secondary channels Lung, Pericardium & Heart Channels & Collateral Chinese Medicine Department All channel diagrams used with permission.
Chapter 15 Substances that Subdue Liver Yang and Extinguish Liver Wind
 Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: June 16, 2009 Class #: 9 Chapter 15: Sub LV Yang and Ext LV Wind Chapter 15 Substances that Subdue Liver Yang and Extinguish Liver Wind Already covered many herbs that
Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: June 16, 2009 Class #: 9 Chapter 15: Sub LV Yang and Ext LV Wind Chapter 15 Substances that Subdue Liver Yang and Extinguish Liver Wind Already covered many herbs that
Term-End Examination June, 2010
 00643 No. of Printed Pages : 12 PGDACP - 01 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN ACUPUNCTURE (PGDACP) Term-End Examination June, 2010 PGDACP-01 : BASIC THEORIES OF ACUPUNCTURE/TCM DIAGNOSIS Time : 2 Hours Maximum
00643 No. of Printed Pages : 12 PGDACP - 01 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN ACUPUNCTURE (PGDACP) Term-End Examination June, 2010 PGDACP-01 : BASIC THEORIES OF ACUPUNCTURE/TCM DIAGNOSIS Time : 2 Hours Maximum
The Herbalist s Corner
 Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic
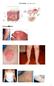 1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
Influenza. What Is Influenza?
 Flu is usually a mild, but uncomfortable disease. You can treat it yourself by staying home and drinking plenty of fluids. What Is?, often just called the flu, is the most common disease in the world,
Flu is usually a mild, but uncomfortable disease. You can treat it yourself by staying home and drinking plenty of fluids. What Is?, often just called the flu, is the most common disease in the world,
Treatment Strategy 1
 Treatment Strategy 1 5-12-06 Treatment Strategy 1...1 1. Wei Syndrome... 1 1.1. Wei Syndrome Types...1 1.1.1. Heat in Lung... 3 1.1.2. Dampness and heat... 4 1.1.3. LV & KD Yin Deficiency...5 1.1.4. Deficiency
Treatment Strategy 1 5-12-06 Treatment Strategy 1...1 1. Wei Syndrome... 1 1.1. Wei Syndrome Types...1 1.1.1. Heat in Lung... 3 1.1.2. Dampness and heat... 4 1.1.3. LV & KD Yin Deficiency...5 1.1.4. Deficiency
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING
 DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
Session 9. Abdominal pain (Fu tong, 腹痛 ) Nausea / vomiting. Chinese Medicine Department. SP, ST & Intestinal Pathologies
 Session 9 SP, ST & Intestinal Pathologies Abdominal pain (Fu tong, 腹痛 ) Abdominal Distension (Fu Zhang, 腹胀 ) Nausea / vomiting (E Xin/Ou Tu, 恶心 / 呕吐 ) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au o
Session 9 SP, ST & Intestinal Pathologies Abdominal pain (Fu tong, 腹痛 ) Abdominal Distension (Fu Zhang, 腹胀 ) Nausea / vomiting (E Xin/Ou Tu, 恶心 / 呕吐 ) Chinese Medicine Department www.endeavour.edu.au o
COMMON COLD & FLU PREVENTION
 COMMON COLD & FLU PREVENTION The arrival of winter means we see the prevalence of the common cold and flu on the rise here at Rosanna Traditional Chinese Medicine Centre. Most people don t realise just
COMMON COLD & FLU PREVENTION The arrival of winter means we see the prevalence of the common cold and flu on the rise here at Rosanna Traditional Chinese Medicine Centre. Most people don t realise just
Huang Qi Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang
 Huang Qi Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang Huang Qi Recorded in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of Materia Medica) as being used to treat welling-abscesses and flat abscesses,
Huang Qi Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang Huang Qi Recorded in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of Materia Medica) as being used to treat welling-abscesses and flat abscesses,
The Treatment of Infectious Diseases by Acupuncture (Part One) by Julian Scott
 The Treatment of Infectious Diseases by Acupuncture (Part One) by Julian Scott CONTENTS PART I Introduction Wind Diseases Internal and External Diseases Choice of Points Pulse Qualities Sources Respiratory
The Treatment of Infectious Diseases by Acupuncture (Part One) by Julian Scott CONTENTS PART I Introduction Wind Diseases Internal and External Diseases Choice of Points Pulse Qualities Sources Respiratory
 PROGRAMME CODE-UAC03 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ACUPUNCTURE - SYLLABUS FIRST YEAR CODE SUBJECT CREDITS UAC03-1 CLINICAL ACUPUNCTURE 8 CREDITS UAC03-2 TRADITIONAL ACUPUNCTURE 8 CREDITS UAC03-3 PRACTICAL-I 8 CREDITS
PROGRAMME CODE-UAC03 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ACUPUNCTURE - SYLLABUS FIRST YEAR CODE SUBJECT CREDITS UAC03-1 CLINICAL ACUPUNCTURE 8 CREDITS UAC03-2 TRADITIONAL ACUPUNCTURE 8 CREDITS UAC03-3 PRACTICAL-I 8 CREDITS
Ge Gen Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang
 Ge Gen Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang Ge Gen Recorded in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of Materia Medica) as being indicated for xiao ke (wasting-thirst disease), great fever,
Ge Gen Formula Family With Dr Huang Huang Ge Gen Recorded in the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing (Divine Husbandman s Classic of Materia Medica) as being indicated for xiao ke (wasting-thirst disease), great fever,
Julie Senko, MS, M.Ed, Registered Acupuncturist
 Treating Chronic Diseases with Asian Medicine By Misha R. Cohen, OMD, LAc Julie Senko, MS, M.Ed, Registered Acupuncturist West Chester Wellness Center 828 Paoli Pike West Chester, PA 19382 Tel: (610) 431
Treating Chronic Diseases with Asian Medicine By Misha R. Cohen, OMD, LAc Julie Senko, MS, M.Ed, Registered Acupuncturist West Chester Wellness Center 828 Paoli Pike West Chester, PA 19382 Tel: (610) 431
Differentiation in lung and L.I.
 Differentiation in lung and L.I. The main physiological function of the lung is in charge of breathing, supplements heart for blood circulation, and regulates the water metabolism. It s common manifestation
Differentiation in lung and L.I. The main physiological function of the lung is in charge of breathing, supplements heart for blood circulation, and regulates the water metabolism. It s common manifestation
Course: Meridians/energetics Date: 10/09/07 Class #: 3 Memorize bold/blue/underline on handout. Point Categories
 Course: Meridians/energetics Date: 10/09/07 Class #: 3 Memorize bold/blue/underline on handout 3 major groups of points. 1. Ashi points Point Categories Ashi in Chinese means oh yes. Not related to channels.
Course: Meridians/energetics Date: 10/09/07 Class #: 3 Memorize bold/blue/underline on handout 3 major groups of points. 1. Ashi points Point Categories Ashi in Chinese means oh yes. Not related to channels.
INFERTILITY Giovanni Maciocia
 INFERTILITY 馬 Giovanni Maciocia 萬 里 INFERTILITY Infertility is defined as the inability to produce offspring in a woman who has been trying for two years with a normal sexual life and, of course, the reproductive
INFERTILITY 馬 Giovanni Maciocia 萬 里 INFERTILITY Infertility is defined as the inability to produce offspring in a woman who has been trying for two years with a normal sexual life and, of course, the reproductive
URINARY DISORDERS: Lin Syndromes. Linda Boggie Eric Hartmann
 URINARY DISORDERS: Lin Syndromes Linda Boggie Eric Hartmann Lin Syndromes Painful Urination Syndromes Painful Frequent Short Urgent Dribbling A disruption in urine flow Often associated with or are an
URINARY DISORDERS: Lin Syndromes Linda Boggie Eric Hartmann Lin Syndromes Painful Urination Syndromes Painful Frequent Short Urgent Dribbling A disruption in urine flow Often associated with or are an
An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone
 An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin Zhi Zi Xiong Huang Honey Gold Leaf coating Zhen Zhu Chief Assistant Envoy Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin
An Gong Niu Huang Wan Calm the Palace Pill with Cattle Gallstone Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin Zhi Zi Xiong Huang Honey Gold Leaf coating Zhen Zhu Chief Assistant Envoy Niu Huang Huang Lian Huang Qin
H1N1 FLU H1N1 Influenza (Flu) 2009 H1N1 Flu in People. What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? Why is 2009 H1N1 flu sometimes called swine flu?
 2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
