Global Polio Eradication Initiative
|
|
|
- Berniece Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements as of January 2006 Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative
2 World Health Organization 2006 All rights reserved. Publications of the World Health Organization can be obtained from Marketing and Dissemination, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland (tel: ; fax: ; Requests for permission to reproduce or translate WHO publications whether for sale or for noncommercial distribution should be addressed to Publications, at the above address (fax: ; The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the World Health Organization concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. Dotted lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement. The mention of specific companies or of certain manufacturers products does not imply that they are endorsed or recommended by the World Health Organization in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. Errors and omissions excepted, the names of proprietary products are distinguished by initial capital letters. The World Health Organization does not warrant that the information contained in this publication is complete and correct and shall not be liable for any damages incurred as a result of its use. Printed in Switzerland Design & Layout: Paprika
3 WHO/POLIO/06.01 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements as of January 2006
4 Table of contents Acronyms and Abbreviations 3 Executive summary 4 Figure 1: Global Polio Eradication Initiative Annual Expenditure , Financial Resource Requirements, Contributions, Funding Gap, Table 1: Summary of external resource requirements by major category of activity, Figure 2: Countries with active transmission of wild poliovirus as of January Section 1: Overview of Global Polio Eradication Initiative Partnership 7 Table 2: Donor profile for Figure 3: External Financial Contributions and Funding Gap 9 Section 2: Financial requirements for Figure 4: Technical assistance to countries in polio-endemic regions 10 Table 3: Baseline supplementary immunization activities required for polio eradication, Section 3: Contingency Plans 13 Annex 1: Details of Country-Level External Funding Requirements for , as of January Table 4: Details of external funding requirements in polio-endemic and highest-risk 16 countries, Table 5: Surveillance and laboratory costs by country and region, Table 6: Technical assistance, country-level details, GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
5 Acronyms and Abbreviations AFP CDC GAVI GIVS IFFIm IHR mopv NIDs OPV SIAs SNIDs UNICEF WHO Acute Flaccid Paralysis US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization Global Immunization Vision and Strategy International Finance Facility for Immunization International Health Regulations monovalent oral polio vaccine national immunization days oral polio vaccine supplementary immunization activities subnational immunization days United Nations Children's Fund World Health Organization GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
6 Executive summary The feasibility of the international goal of global polio eradication in the near future was reaffirmed in the second half of In October, the Advisory Committee on Polio Eradication (ACPE), the independent oversight body of the Polio Eradication Initiative, concluded that strong advances toward polio eradication in 2005, as well as the recent introduction of a new monovalent oral polio vaccine type 1 (mopv1), had moved the polio eradication effort into its final phase in all countries but one. The ACPE stated that with sufficient resources and expanded use of mopv1, all polio-affected countries except Nigeria can stop this disease by mid It concluded that Nigeria will require at least an additional 12 months to finish the job. Advances included: the interruption of indigenous polio transmission in Egypt and Niger, thus reducing the number of polio-endemic countries from six to four; the interruption of polio transmission in 14 previously polio-free countries re-infected during the multi-country epidemic; and a two-thirds reduction of polio cases in Asia (India and Pakistan) during the August-October peak transmission period. Since nation-wide polio immunization resumed in late 2004 in Nigeria, there has been an increasing geographic restriction of polio transmission and a marked reduction in the genetic biodiversity of Nigerian poliovirus. The stage is set for more dramatic progress in the coming months, thanks to strong government commitment to polio eradication and routine immunization, together with a strengthened local-level system to improve immunization quality, intensified monitoring and an expected targeted introduction of mopv. Unprecedented levels of financial support from long-standing and new contributors in 2005 ensured that intensified polio campaigns in Africa and Asia could proceed as planned and that the polio eradication infrastructure was strengthened and continued to be used to strengthen the public health infrastructure in many countries, particularly in Africa. Financial Resource Requirements presents the estimated financial resources needed from external sources to interrupt the final chains of polio transmission world-wide, to contain all stocks of wild poliovirus and to prepare for certification and oral polio vaccine (OPV) cessation, using strategies outlined in the Global Polio Eradication Strategic Plan Following the executive summary, pages 7 to 9 provide an overview of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative partnership, summarizing financial contributions and pledges made to the Initiative as of January Pages 10 to 18 describe the activities planned for and the funding required to implement them. The first part of this period will concentrate on stopping polio transmission and maintaining polio-free status, with the focus shifting to the containment of wild polioviruses and preparation for certification and OPV cessation in the latter half of the period. There is a US$ 150 million funding gap for 2006 activities: of this, US$ 75 million is required by March, and US$ 75 million is required by July. An additional US$ 425 million must be made available for if planned activities are to be fully implemented. In this era of daily disasters, disease outbreaks, civil unrest and other bleak news, it would be all too easy to lose sight of the global victory over polio which is within our grasp. The timely availability of multi-year and flexible funding is vital to ensure that we deliver a polio-free world. 4 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
7 Figure 1: Global Polio Eradication Initiative, Annual Expenditure , Financial Resource Requirements, Contributions, Funding Gap, Total Expended: US$ 3.9 billion 2006 Funding Gap: US$ 150 million Intensification of SIAs US$ million Funding Gap: US$ 425 million Expenditure Funds Projected or Pledged Funding Gap Protecting the world's 17-year investment in polio eradication requires the international community to: 1) by July 2006, fill the US$ 150 million funding gap for 2006 activities (US$ 75 million of this is required by March 2006 for activities between April and September); and, 2) make multi-year pledges for to stop polio transmission, contain all stocks of wild polioviruses and implement certification and pre-opv cessation activities. Figure 2: Countries with active transmission of wild poliovirus as of January 2006 Indigenous poliovirus Imported poliovirus GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
8 Table 1: Summary of external financial requirements by major category of activity, (all figures are in US$ millions) Activity Category Oral polio vaccine $ $ $ - $ NIDs/SNIDs operations* $ $ $ - $ Emergency response / mopv $ $ $ $ evaluation Surveillance** $ $ $ $ Laboratory $ 8.44 $ 7.90 $ 6.72 $ Technical assistance*** $ $ $ $ Certification and containment $ 4.50 $ $ $ Product development for OPV $ $ 5.00 $ 5.00 $ cessation Vaccine for post-opv era stockpile $ $ $ $ (finished product and bulk) Total requirements $ $ $ $ 1, Contributions $ $ $ $ Funding Gap $ $ $ $ Funding Gap (rounded) $ $ $ $ * Operations costs include manpower and incentives, training and meetings, supplies and equipment, transportation, social mobilization and running costs. NIDs: national immunization days; SNIDs: subnational immunization days. ** Country-level surveillance and laboratory summary for 2006 are provided in Table 5. *** Technical assistance includes the cost of human resources deployed through UN agencies. Country-level breakdown for 2006 provided in Table 6. 6 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
9 Section 1: Overview of Global Polio Eradication Initiative Partnership The 17-year Global Polio Eradication Initiative, a public-private partnership spearheaded by the World Health Organization, Rotary International, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), includes governments of countries affected by polio; donor governments (e.g. Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Oman, Portugal, Qatar, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom and the United States of America); the European Commission; private foundations (e.g. United Nations Foundation, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the OPEC Fund and the AGFund); development banks (e.g. the World Bank and the African Development Bank); humanitarian and nongovernmental organizations (e.g. the International Red Cross and Red Crescent societies) and corporate partners (e.g. Sanofi Pasteur, De Beers, Wyeth). Table 2 highlights contributions/pledges by major donors to the Polio Eradication Initiative for Funding provided through external sources (including both multilateral and bilateral contributions) for the period totals more than US$ 4 billion. Forty-three private and public sector donors have contributed or pledged more than US$ 1 million each to polio eradication. Of these, 28 contributed US$ 5 million or more. Spearheading partner Rotary International has contributed more than US$ 500 million, a figure which will rise to more than US$ 600 million by the time the world is certified polio-free. G8 leaders meeting at Gleneagles, Scotland in July 2005 reaffirmed their commitment to finishing the job of polio eradication by pledging to "support the Polio Eradication Initiative for the post-eradication period in through continuing or increasing our own contributions towards the US$ 829 million target and mobilizing the support of others". The UK took immediate action, pledging 60 million for The polio partnership continued to expand in 2005: Sweden re-affirmed its long-standing commitment to children's health by making a US$ 30 million extraordinary contribution and several Organization of Islamic Conference (OIC) countries, including Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Turkey, joined Malaysia in taking action on polio resolutions made at the October 2003 OIC Summit in Putrajaya, Malaysia and at the June 2004 OIC Foreign Ministers' Meeting in Istanbul, Turkey. Spain and Monaco joined the Initiative and Iceland, the Czech Republic and Singapore also made their first polio eradication pledges in In a further affirmation of international commitment to polio eradication, the board of the Global Alliance of Vaccines and Immunization (GAVI) in July recommended that up to US$ 226.4* million be allocated from the International Finance Facility for Immunization (IFFIm) towards creation of a stockpile of mopvs for the post-eradication era. Funds are expected to be made available in * US$ 191 million in IFFIm funding was approved for the stockpile at the July 2005 GAVI Board meeting. GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
10 Table 2: Donor profile for Contribution Public Sector Development Private Sector (US$ million) Partners Banks Partners > 500 USA, United Kingdom Rotary International Japan World Bank European Commission, Canada, Germany, Netherlands, IFFIm Denmark, France, Norway, Sweden, UNICEF Regular Resources, WHO Regular Budget Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation United Nations Foundation Italy, Australia, Inter-American Sanofi Pasteur, IFPMA, 5-24 Russian Federation, Development Bank UNICEF National Ireland, Luxembourg Committees, American Red Cross Belgium, Spain, Switzerland, African 1-4 Malaysia, New Zealand, Saudi Development Arabia, United Arab Emirates Bank Advantage Trust (HK), De Beers, International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, Pew Charitable Trust, Wyeth, Shinnyo-en External contributions to countries' polio eradication efforts have been matched by national resources, including both financial expenditures and non-monetary commitments such as the time spent by volunteers, health workers and others in the implementation of supplementary immunization activities (SIAs). Funds are expended by governments, the private sector and non-governmental organizations at national, state/province, district and local community levels to cover petrol, social mobilization, training and other costs*. The world now has a tremendous opportunity to ensure that everyone shares equally in the benefits of a polio-free world. The economic justification is compelling. Regardless as to long-term polio immunization decisions, eradication would be cost-saving for low-income developing countries. Globally, the cost-effectiveness ratio of polio eradication would be an impressive US$ per disability-adjusted life year (DALY) saved. Failure to completely eradicate polio, on the other hand, would result in at least 10.6 million new cases of polio worldwide in the next 40 years, representing the loss of 60 million DALYs, nearly all in low-income developing countries*. * Aylward R, et al, Politics and practicalities of polio eradication, Global Public Goods for Health. Health Economic and Public Health Perspectives, eds Smith, R, Beaglehole R, Woodward D, Drager N, Oxford, Oxford University Press, GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
11 Budgets in this document were developed by ministries of health, WHO and UNICEF, and are based on the costs of implementing polio eradication strategies at the country level and the costs of managing the Global Polio Eradication Initiative through the United Nations implementing agencies (WHO and UNICEF) at the country, regional and global levels. Figure 2 summarizes the external financial contributions since 1988, as well as the funding gap. All donors highlighted in the pie chart have contributed more than US$ 25 million to the global polio eradication effort. Figure 3: External Financial Contributions and Funding Gap Multilateral Sector 22% IFFIm Japan Germany Canada France USAID USCDC G8 52% European Commission World Bank/India World Bank Investment Partnership for Polio UK UN Foundation Netherlands Denmark Gates Foundation Norway Rotary International (14%) Private Sector Sweden 18% Other Non-G8 OECD/Other 8% 2006 Funding Gap = US$ 150 million Funding Gap = US$ 425 million Note : Donor contributions of US$ 25 million or more are represented in the pie chart. Other includes: the Governments of Austria, Australia, Belgium, Czech Republic, Finland, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Monaco, New Zealand, Oman, Pakistan, Portugal, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates; African Development Bank; AG Fund; American Red Cross; De Beers, Inter-American Development Bank, International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, Oil for Food Programme, OPEC Fund, Sanofi Pasteur; Saudi Arabian Red Crescent Society, Smith Kline Biologicals, UNICEF National Committees, UNICEF Regular and Other Resources, United Arab Emirates Red Crescent Society, WHO Regular Budget and Wyeth. GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
12 Section 2: Financial requirements for PRIORITIES AND ACTIVITIES The highest priorities for the Global Polio Eradication Initiative and the focus for 2006 are : the rapid interruption of polio transmission in polio-endemic countries and in countries where polio was re-introduced following the major epidemic that originated in west Africa in 2003 ; and protecting the polio-free status of these countries while Nigeria finishes the job. In October 2005, the Initiative's independent oversight body concluded that Nigeria would take at least 12 months longer than anywhere else in the world to stop polio transmission. In 2006, 18 countries are expected to conduct 61 supplementary immunization activities aimed at reaching 342 million children under five years of age with multiple doses of oral polio vaccine. 201 countries will maintain Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) surveillance, 54 of them in polio-endemic regions requiring substantial technical assistance. Figure 3 shows the countries receiving technical support at the national, provincial and district levels. Figure 4: Polio-funded technical assistance by country National & Sub-national Technical Assistance National level support Regional office support Subregional office support Importantly, the polio infrastructure is also being used to detect and respond to outbreaks of other communicable diseases such as Cholera, Marburg Fever, Ebola and Yellow Fever. Countries are also using polio immunization campaigns for the systematic delivery of other health interventions, including Vitamin A, measles vaccine, malaria bed nets and anti-helminthics. The polio infrastructure underpinned the recent boosting of routine immunization coverage in the African region from 52% to 66% between 1999 and 2004, and strengthened micro planning and activities of the 'Reaching Every District' strategy. Other areas of reinforcement include renewal of the cold chain in many countries, development of more sustainable transportation for outreach activities, and the addition of external quality assessment programmes to public health laboratories. In , the polio infrastructure will also be used to help countries implement the revised International Health Regulations (IHR) and to build capacity for routine immunization as part of the Global Immunization Vision and Strategy (GIVS). 10 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
13 Realization of the full humanitarian and economic benefits of polio eradication requires not only the interruption of poliovirus transmission worldwide, but also containment of wild poliovirus stocks, completion of the certification processes, and the eventual cessation of OPV for routine immunization. Preparing for global certification requires sustained surveillance in all regions, rapid responses to circulating vaccinederived polioviruses (cvdpvs), and completion of appropriate poliovirus containment activities as detailed in the WHO Global Action Plan for Laboratory Containment of Wild Polioviruses, second edition (WHO/V&B/03.11). The following are prerequisites for cessation of OPV use: 1. Confirmation of interruption of transmission and appropriate containment of wild polioviruses; 2. Continued highly sensitive surveillance for poliovirus circulation; 3. Development of an international stockpile of mopv and response mechanisms; 4. Implementation of IPV requirements in bio-hazard settings; 5. International consensus on procedure for synchronous OPV cessation; 6. Appropriate biocontainment of Sabin polioviruses. The development of a third edition of the Global Action Plan for the Laboratory Containment of Wild Polioviruses (detailing final containment requirements for all polioviruses), as well as the development, licensing and stockpiling of 3 monovalent oral polio vaccines (mopv I, II, III) are included among the prerequisites outlined for policy-makers. A stockpile of mopv will be created to protect countries against the inadvertent reintroduction of polio after global cessation of routine immunization with OPV. A breakdown of the costs by major activity category can be found in Table 1 on page 6. FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS The financial resource requirements for 2006 are estimated at US$ 595 million, against which there is a funding gap of US$ 150 million. Of this, US$ 75 million is needed by March and US$ 75 million by July, to maintain the full programme of eradication work. The funding gap for is pegged at US$ 425 million. Table 3 summarizes the schedule of intensified supplementary immunization activity plans for 2006 and Supplementary immunization activities are the major cost driver for the Global Polio Eradication Initiative in (see Annex 1, Table 4 for details of planned costs by country for ). In addition to the planned activities summarized in Table 3, the Initiative requires US$ 90 million for emergency response to poliovirus importations in Emergency response activities will also be used for mopv evaluation as part of the development of the mopv stockpile for the post-eradication era. GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
14 Table 3: Baseline supplementary immunization activities required for polio eradication, as of January NID: National Immunization Day SNID: Subnational Immunization Day Activity NID SNID Region/Country Polio Endemic Afghanistan India Data % targeted % targeted Nigeria % targeted Pakistan % targeted WHO African Region Angola % targeted Benin % targeted Cameroon % targeted Chad % targeted Côte d Ivoire % targeted 100 Equ Guinea 1 % targeted Ethiopia % targeted Gabon 1 % targeted Niger % targeted WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region Egypt % targeted Somalia % targeted Sudan 2 % targeted Yemen % targeted 100 WHO South-East Asia Region Indonesia 3 % targeted Nepal % targeted J F M A M J J A S O N D J F M A M J J A S O N D Equatorial Guinea and Gabon postponed their 2005 Q4 SIAs to early In Sudan, SNID in August and September will take place in the South. 3 The Government of Indonesia will cover the cost of two NIDs, cost not reflected in country-level external funding requirements in Table 4 12 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
15 Section 3: Contingency Plans The external financial resource requirements for are based on the assumptions that polio transmission will be stopped in the Horn of Africa and in west and central Africa, with the exception of Nigeria, by the end of the first quarter of 2006; that polio transmission will be stopped in Asia by mid-2006; and that Nigeria will stop polio transmission by end Continued transmission of polio beyond that date would result in increased costs, as summarized below: Scenario 1: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in Nigeria until end-2007 Under this scenario, additional SIAs would be conducted through end-2008 in Nigeria, through end-2007 in Niger and through mid-2007 in Benin, Cameroon and Chad. Additional emergency response funding of US$ 30 million is also envisioned under this scenario. Financial implications: up to US$ million in additional costs for Scenario 1: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in Nigeria until end Region Country J F M A M J J A S O N D J F M A M J J A S O N AFRO Niger Base Contingency AFRO Nigeria Base Contingency AFRO Chad Base Contingency AFRO Cameroon Base Contingency AFRO Benin Base Contingency D 2008 J F M A M J J A S O N D GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
16 Scenario 2: Transmission of imported wild poliovirus continues in west and central Africa until the third quarter of 2006 Under this scenario, additional SIAs would be conducted in the second half of 2006 in Burkina Faso, the Central African Republic (CAR), Côte d'ivoire, and Mali (and in the first quarter of 2007 in Benin, Cameroon and Chad, as above). Financial implications: up to US$ 27.5 million in additional costs in Scenario 2: Transmission of imported wild poliovirus continues in west/central Africa until Q Region Country J F M A M J J A S O N D J F M A M J J A S O AFRO CAR Base Contingency AFRO Cote d'ivoire Base 100 Contingency AFRO Burkina Faso Base Contingency AFRO Mali Base Contingency N D Note: Other high-risk west/central African countries are reflected in Scenario 1 Scenario 3: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in the Horn of Africa until mid-2006 Under this scenario, additional SIAs would be conducted in 2006 in Sudan, Yemen, Eritrea and Ethiopia; and Somalia and south Sudan upto the first quarter of Financial implications: up to US$ 52 million in additional costs for Scenario 3: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in the Horn of Africa until mid Region Country J F M A M J J A S O N D J F M A M J J A S O EMRO Somalia Base Contingency EMRO Sudan Base Contingency EMRO Yemen Base Contingency AFRO Eritrea Base Contingency AFRO Ethiopia Base Contingency N D 14 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
17 Scenario 4: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in infected countries in Asia until end-2006 Under this scenario, additional SIAs would be conducted in Indonesia in 2006 and in Afghanistan, Pakistan and India in 2006 and Financial implications: up to US$ million in additional costs in Scenario 4: Transmission of wild poliovirus continues in infected countries in Asia until end Region Country J F M A M J J A S O N D J F M A M J J A S O EMRO Afghanistan Base Contingency EMRO Pakistan Base Contingency SEARO India Base Contingency SEARO Indonesia Base Contingency N D GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
18 Annex 1: Details of Country-Level External Funding Requirements for , as of January Table 4: Details of external funding requirements in polio-endemic and highest-risk countries, (all figures are in US$ millions) to 2007 AFP AFP AFP NIDs/ NIDs/ Surveillance NIDs/ NIDs/ Surveillance NIDs/ NIDs/ Surveillance Total Costs Country SNIDs: SNIDs: and Total Costs SNIDs: SNIDs: and Total Costs SNIDs: SNIDs: and 2006 to OPV Op Costs Laboratory 2006 OPV Op Costs Laboratory 2007 OPV Op Costs Laboratory 2007 Polio-Endemic Afghanistan $4.69 $9.93 $1.55 $16.17 $2.85 $5.50 $1.16 $9.51 $7.54 $15.43 $2.71 $25.68 India $95.06 $74.70 $5.72 $ $48.48 $43.18 $5.72 $97.38 $ $ $11.44 $ Nigeria $37.28 $46.46 $7.57 $91.31 $17.08 $20.72 $6.38 $44.19 $54.37 $67.18 $13.95 $ Pakistan $27.15 $15.72 $1.68 $44.55 $11.97 $6.41 $1.50 $19.88 $39.12 $22.13 $3.18 $64.43 WHO African Region Benin $0.70 $1.37 $0.23 $2.30 $0.00 $0.00 $0.19 $0.19 $0.70 $1.37 $0.42 $2.49 Cameroon $0.39 $0.55 $0.29 $1.23 $0.00 $0.00 $0.24 $0.24 $0.39 $0.55 $0.53 $1.48 Chad $0.77 $2.67 $0.38 $3.81 $0.00 $0.00 $0.32 $0.32 $0.77 $2.67 $0.70 $4.13 Côte d'ivoire $0.93 $1.11 $0.32 $2.36 $0.00 $0.00 $0.27 $0.27 $0.93 $1.11 $0.60 $2.63 Equatorial Guinea $0.02 $0.12 $0.02 $0.17 $0.00 $0.00 $0.02 $0.02 $0.02 $0.12 $0.04 $0.19 Ethiopia $2.13 $5.27 $2.76 $10.16 $0.00 $0.00 $2.33 $2.33 $2.13 $5.27 $5.10 $12.49 Gabon $0.07 $0.36 $0.11 $0.54 $0.00 $0.00 $0.10 $0.10 $0.07 $0.36 $0.21 $0.64 Niger $2.69 $7.88 $0.40 $10.98 $1.19 $3.26 $0.34 $4.78 $3.88 $11.14 $0.74 $15.76 South Eastern Mediterranean Region Egypt $3.64 $1.62 $0.37 $5.63 $0.00 $0.00 $0.37 $0.37 $3.64 $1.62 $0.74 $6.00 Somalia $1.55 $3.71 $0.86 $6.12 $0.00 $0.00 $0.68 $0.68 $1.55 $3.71 $1.54 $6.79 Sudan $3.23 $5.28 $1.55 $10.06 $0.00 $0.00 $1.25 $1.25 $3.23 $5.28 $2.81 $11.31 Yemen $0.63 $1.33 $0.18 $2.13 $0.00 $0.00 $0.18 $0.18 $0.63 $1.33 $0.35 $2.31 WHO South-East Asia Region Indonesia* $1.95 $4.78 $1.40 $8.13 $0.00 $0.00 $1.40 $1.40 $1.95 $4.78 $2.80 $9.53 Nepal $0.63 $0.37 $0.50 $1.50 $0.00 $0.00 $0.37 $0.37 $0.63 $0.37 $0.87 $1.87 Note: additional activities will be funded from emergency response funds. *The Government of Indonesia will cover OPV and operations cost for 2 NIDs in GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
19 Table 5: Surveillance and laboratory costs by country and region, 2006 (all figures are in US$ millions) WHO African Region 2006 Algeria $0.08 Angola $1.96 Benin $0.23 Botswana $0.10 Burkina Faso $0.28 Burundi $0.17 Cameroon $0.29 Cape Verde $0.05 Central African Republic $0.27 Chad $0.38 Comoros $0.06 Congo $0.20 Côte d'ivoire $0.32 Democratic Republic of Congo $2.40 Equatorial Guinea $0.02 Eritrea $0.14 Ethiopia $2.76 Gabon $0.11 Gambia $0.07 Ghana $0.47 Guinea $0.16 Guinea-Bissau $0.07 Kenya $0.50 Lesotho $0.06 Liberia $0.27 Madagascar $0.42 Malawi $0.20 Mali $0.22 Mauritania $0.18 Mauritius $0.04 Mozambique $0.85 Namibia $0.11 Niger $0.40 Nigeria $7.57 Rwanda $0.11 Sao Tome and Principe $0.01 Senegal $0.21 Seychelles $0.01 Sierra Leone $0.24 South Africa $0.07 Swaziland $0.06 Togo $0.09 Uganda $0.37 United Republic of Tanzania $0.24 Zambia $0.45 Zimbabwe $0.11 Regional surveillance and laboratory $3.26 Subtotal $26.65 WHO Region of the Americas 2006 Regional surveillance and laboratory $0.60 WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region 2006 Afghanistan $1.55 Djibouti $0.10 Egypt $0.37 Iraq $0.10 Pakistan $1.68 Somalia $0.86 Sudan $1.55 Yemen $0.18 Regional surveillance and laboratory $1.20 Subtotal $7.58 WHO South-East Asia Region 2006 Bangladesh $0.75 India $3.70 Indonesia $1.40 Myanmar $0.27 Nepal $0.50 Regional surveillance and laboratory $3.13 Subtotal $9.74 WHO European Region 2006 Armenia $0.003 Azerbaijan $0.01 Bosnia and Herzegovina $0.01 Bulgaria $0.01 Georgia $0.01 Kazakhstan $0.06 Kyrgystan $0.01 Republic of Moldova $0.01 Romania $0.01 Russian Federation $0.08 Tajikistan $0.08 Turkey $0.05 Turkmenistan $0.03 Ukraine $0.01 Uzbekistan $0.03 Serbia and Montenegro $0.01 Regional surveillance and laboratory $0.54 Subtotal $0.93 WHO Western Pacific Region 2006 Regional surveillance and laboratory $0.90 WHO/HQ 2006 $4.67 Global 2006 Total $51.06 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to
20 Table 6: Technical assistance, country-level details 2006 (all figures are in US$ millions) WHO African Region 2006 Angola $2.34 Benin $0.21 Botswana $0.01 Burkina Faso $0.24 Cameroon $0.07 Central African Republic $0.21 Chad $0.85 Congo $0.23 Côte d'ivoire $0.67 Democratic Republic of Congo $4.89 Equatorial Guinea $0.05 Eritrea $0.04 Ethiopia $1.40 Gabon $0.02 Gambia $0.02 Ghana $0.34 Guinea $0.19 Guinea-Bissau $0.05 Kenya $0.19 Lesotho $0.04 Liberia $0.29 Madagascar $0.09 Malawi $0.04 Mali $0.15 Mauritania $0.14 Mozambique $0.22 Namibia $0.20 Niger $1.11 Nigeria $16.13 Rwanda $0.19 Senegal $0.21 Sierra Leone $0.23 South Africa $0.16 Swaziland $0.08 Togo $0.16 Uganda $0.24 United Republic of Tanzania $0.31 Zambia $0.35 Zimbabwe $0.06 ICP-Central* $0.72 ICP-East* $0.73 ICP-South* $0.73 ICP-West* $0.76 Regional Office $3.68 Subtotal $39.02 WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region 2006 Afghanistan $1.71 Djibouti $0.14 Egypt $0.15 Iran $0.004 Iraq $0.17 Pakistan $4.56 Somalia $1.11 Sudan $2.95 Yemen $0.28 Regional Office $0.90 Subtotal $11.96 WHO South-East Asia Region 2006 Bangladesh $1.01 India $7.94 Indonesia $0.36 Myanmar $0.29 Nepal $0.51 Regional Office $2.00 Subtotal $12.11 WHO European Region 2006 Regional Office $0.82 Subtotal $0.82 WHO Western Pacific Region 2006 Cambodia $0.16 China $0.47 Fiji $0.16 Lao PDR $0.16 Philippines $0.16 Papua New Guinea $0.17 Viet Nam $0.31 Regional Office $0.93 Subtotal $2.50 WHO/HQ $7.34 UNICEF $10.40 Global 2006 Total $84.15 * ICP= Inter-country Programme 18 GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE FINANCIAL RESOURCE REQUIREMENTS 2006 to 2008
21
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2005 to 2008 as of April 2005 WHO Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2005 All rights reserved.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2005 to 2008 as of April 2005 WHO Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2005 All rights reserved.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2006-2008 as of September 2006 Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2006 All rights reserved.
Global Polio Eradication Initiative Financial resource requirements 2006-2008 as of September 2006 Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative World Health Organization 2006 All rights reserved.
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities
 Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information Document CONTENTS BACKGROUND PROGRESS MADE NEXT STEPS... 12
 5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
CONTENTS. Paragraphs I. BACKGROUND II. PROGRESS REPORT ON THE AFRICAN REGIONAL IMMUNIZATION STRATEGIC PLAN
 23 September 2013 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-third session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2 6 September, 2013 Agenda item 14 IMMUNIZATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT
23 September 2013 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-third session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2 6 September, 2013 Agenda item 14 IMMUNIZATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT
2. A statement on Rotary International's contribution to the polio eradication effort:
 UPDATE: July 2013 International PolioPlus Committee Statements on Current Facts and Figures Relative to Polio Eradication and the Role of Rotary International in the Global Effort For the sake of clarity
UPDATE: July 2013 International PolioPlus Committee Statements on Current Facts and Figures Relative to Polio Eradication and the Role of Rotary International in the Global Effort For the sake of clarity
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global Polio Eradication Initiative
 Global Polio Eradication Initiative Budgetary implications of the GPEI Strategic Plan and Financial resource requirements 2009-2013 As of January 2009 Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative
Global Polio Eradication Initiative Budgetary implications of the GPEI Strategic Plan and Financial resource requirements 2009-2013 As of January 2009 Partners in the Global Polio Eradication Initiative
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017
 THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
Eligibility List 2018
 The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges
 Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges European Conference on Post Polio Syndrome 31 August 2 September 2011, Copenhagen, Denmark Dr Rebecca Martin Vaccine Preventable
Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges European Conference on Post Polio Syndrome 31 August 2 September 2011, Copenhagen, Denmark Dr Rebecca Martin Vaccine Preventable
APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
ANNEX Page. AFR/RC61/11 4 July 2011 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA
 4 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 16 PROGRESS REPORT ON POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION
4 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 16 PROGRESS REPORT ON POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION
Ouagadougou Declaration
 Ouagadougou Declaration on Primary Health Care and Health Systems in Africa: Achieving Better Health for Africa in the New Millennium A declaration by the Members States of the WHO African Region 30 April
Ouagadougou Declaration on Primary Health Care and Health Systems in Africa: Achieving Better Health for Africa in the New Millennium A declaration by the Members States of the WHO African Region 30 April
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua. Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2
 Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan
 Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan SAGE Meeting 6 November 2012 Overview Process, Consultations, Development Eradication and Endgame Outcomes and Activities Legacy Planning
Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan SAGE Meeting 6 November 2012 Overview Process, Consultations, Development Eradication and Endgame Outcomes and Activities Legacy Planning
Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update
 1 of 5 12/07/2010 12:09 PM Google search this site contact links donate Home > Global Situation Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update 7 July 2010 Data as at 6 July 2010 Map of polio cases worldwide Wild poliovirus
1 of 5 12/07/2010 12:09 PM Google search this site contact links donate Home > Global Situation Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update 7 July 2010 Data as at 6 July 2010 Map of polio cases worldwide Wild poliovirus
POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information document EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 7 July 2006 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-sixth session Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 28 August 1 September 2006 Provisional agenda item 10.1 POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS
7 July 2006 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-sixth session Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 28 August 1 September 2006 Provisional agenda item 10.1 POLIO ERADICATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS
Malaria Funding. Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH. April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA
 Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
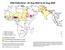 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Eradicating Polio: Why and How? Dr Roland Sutter, World Health Organization 20 September 2011
 Eradicating Polio: Why and How? Dr Roland Sutter, World Health Organization 20 Why? Polio Crippled for life Primarily affects children We have a historic opportunity. Preventable with vaccine 1955: polio
Eradicating Polio: Why and How? Dr Roland Sutter, World Health Organization 20 Why? Polio Crippled for life Primarily affects children We have a historic opportunity. Preventable with vaccine 1955: polio
PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR ACCELERATING THE ATTAINMENT OF THE MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS RELATED TO MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH IN AFRICA
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Global Measles and Rubella Update. April 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role. Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia
 Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen
 Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen (Copenhagen, Denmark, 27 June 2012) GAVI vaccine support Currently supported vaccines: pentavalent, pneumococcal, rotavirus, meningitis A, human papillomavirus (HPV), rubella,
Update from GAVI Aurelia Nguyen (Copenhagen, Denmark, 27 June 2012) GAVI vaccine support Currently supported vaccines: pentavalent, pneumococcal, rotavirus, meningitis A, human papillomavirus (HPV), rubella,
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP)
 COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011
 Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Polio. As of 1 September 2002 Draft copy for consultation. Estimated external financial resource requirements for
 HTP/Polio/02.09 RESTRICTED WHO Global Polio E r a d i c a t i o n I n i t i a t i v e Estimated external financial resource requirements for 2003 2005 as of 1 September 2002 Figures in this document were
HTP/Polio/02.09 RESTRICTED WHO Global Polio E r a d i c a t i o n I n i t i a t i v e Estimated external financial resource requirements for 2003 2005 as of 1 September 2002 Figures in this document were
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF),
 Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table. Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents.
 Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
TFI Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005
 January 2005 N 053 TFI 2004 - Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005 The 12th meeting of the Task Force on Immunization (TFI) in Africa and the 11th meeting of the Africa Regional Inter-
January 2005 N 053 TFI 2004 - Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005 The 12th meeting of the Task Force on Immunization (TFI) in Africa and the 11th meeting of the Africa Regional Inter-
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009
 Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Global Fund ARV Fact Sheet 1 st June, 2009 This fact sheet outlines the principles and approach in determining the number of people on antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) for HIV/AIDS treatment, with a breakdown
Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region
 Provisional agenda item 6(i) EUR/RC60/16 (+EUR/RC60/Conf.Doc./9) 23 July 2010 101614 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region WHO Regional Committee for Europe Sixtieth session
Provisional agenda item 6(i) EUR/RC60/16 (+EUR/RC60/Conf.Doc./9) 23 July 2010 101614 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region WHO Regional Committee for Europe Sixtieth session
MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Secretariat. Executive Summary
 16 June 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 13 MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY
16 June 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 13 MEASLES ELIMINATION BY 2020: A STRATEGY
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control
 The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio case
 Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
Rotavirus Vaccine: Supply & Demand Update. UNICEF Supply Division
 Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June Rotary s financial contribution to the polio eradication effort:
 International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June 2018 1. The goal of the PolioPlus program: The goal of the PolioPlus program is the global certification of polio eradication. By eradication,
International PolioPlus Committee PolioPlus Facts and Figures June 2018 1. The goal of the PolioPlus program: The goal of the PolioPlus program is the global certification of polio eradication. By eradication,
Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries
 EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
EMBARGOED until Monday, 20 October, 6am GMT HQ/2003/24 20 October 2003 CF/DOC/PR/2003-82 Maternal Deaths Disproportionately High in Developing Countries African women are 175 times more likely to die in
ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS. Note by the Executive Secretary * CONTENTS. Explanatory notes Tables. 1. Core budget
 UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
UNITED NATIONS Distr. GENERAL 13 October 1997 ENGLISH ONLY SUBSIDIARY BODY FOR IMPLEMENTATION Seventh session Bonn, 20-29 October 1997 Item 9 of the provisional agenda ADMINISTRATIVE AND FINANCIAL MATTERS
Global and Regional update on Polio Eradication Activities. Kenya Paediatric Association Pride Inn, Mombasa April 26, 2018
 Global and Regional update on Polio Eradication Activities Kenya Paediatric Association Pride Inn, Mombasa April 26, 2018 Presentation Outline 1. Background information 2. Poliovirus detection & interruption
Global and Regional update on Polio Eradication Activities Kenya Paediatric Association Pride Inn, Mombasa April 26, 2018 Presentation Outline 1. Background information 2. Poliovirus detection & interruption
Progress report on. Eradication of poliomyelitis
 Regional Committee for the EM/RC52/INF.DOC.2 Eastern Mediterranean August 2005 Fifty-second Session Original: Arabic Agenda item 4 (b) Progress report on Eradication of poliomyelitis Contents 1. Introduction...1
Regional Committee for the EM/RC52/INF.DOC.2 Eastern Mediterranean August 2005 Fifty-second Session Original: Arabic Agenda item 4 (b) Progress report on Eradication of poliomyelitis Contents 1. Introduction...1
IMMUNIZATION & VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASES
 IMMUNIZATION & VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASES MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION July-August 2015 (Vol 3, issue N 6 ) Special issue on WHO/UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage
IMMUNIZATION & VACCINE PREVENTABLE DISEASES MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION July-August 2015 (Vol 3, issue N 6 ) Special issue on WHO/UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN
 CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa
 Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
TT Procured by UNICEF
 TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
TT TT Procured by UNICEF 2001-08 250,000,000 200,000,000 150,000,000 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Routine SIA TT historical demand and forecast overview Upcoming Tender
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results
 Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
Global Fund Mid-2013 Results This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach in determining
BCG. and your baby. Immunisation. Protecting babies against TB. the safest way to protect your child
 BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
BCG and your baby Protecting babies against TB Immunisation the safest way to protect your child This leaflet is about the BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guerin) vaccination that is being offered to protect your
IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES
 No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries
 Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries Hamid Jafari, WHO Robert Linkins, CDC Independent Monitoring Board Meeting 7-8 May, 2013 Outline Non-Endemic Vulnerable & At-Risk Countries Recently infected countries
Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries Hamid Jafari, WHO Robert Linkins, CDC Independent Monitoring Board Meeting 7-8 May, 2013 Outline Non-Endemic Vulnerable & At-Risk Countries Recently infected countries
Market Updates: Routine Vaccine Introductions IPV. Vaccine Industry Consultation October 2018 UNICEF Supply Division
 Market Updates: Routine Vaccine Introductions IPV Vaccine Industry Consultation October 2018 UNICEF Supply Division Outline Review of rapid introduction of IPV Overview of the current situation for 2018
Market Updates: Routine Vaccine Introductions IPV Vaccine Industry Consultation October 2018 UNICEF Supply Division Outline Review of rapid introduction of IPV Overview of the current situation for 2018
HPV Vaccine Lessons Learned & New Ways Forward
 HPV Vaccine Lessons Learned & New Ways Forward The Gavi Alliance June 2016, Geneva www.gavi.org Overview 1 Background 2 Lessons learned 3 New Way Forward 2 1 Background 3 HPV Background HPV is responsible
HPV Vaccine Lessons Learned & New Ways Forward The Gavi Alliance June 2016, Geneva www.gavi.org Overview 1 Background 2 Lessons learned 3 New Way Forward 2 1 Background 3 HPV Background HPV is responsible
Financing malaria control
 Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Chapter 6. Financing malaria control The three major sources of funds for malaria control pro - grammes are national government spending, external assistance from donors and household or private out-of-pocket
Drug Prices Report Opioids Retail and wholesale prices * and purity levels,by drug, region and country or territory (prices expressed in US$ )
 1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers
 UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS
 ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
ICM: Trade-offs in the fight against HIV/AIDS 1 As the HIV/AIDS pandemic enters its 25 th year, both the number of infections and number of deaths due to the disease continue to rise. Despite an enormous
Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication. Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017
 Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017 Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategy 1. Poliovirus detection & interruption
Getting to Zero: On the Verge of Polio Eradication Ellyn Ogden, MPH USAID Worldwide Polio Eradication Coordinator May 17, 2017 Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategy 1. Poliovirus detection & interruption
GABON. Neglected tropical disease treatment report profile for mass treatment of NTDs
 GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes
 Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
 IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION AND POLIO UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION January February 2017 (Vol 5 issue N 1) District data completeness and coverage of DTP3 containing vaccine per
IMMUNIZATION VACCINE DEVELOPMENT MONTHLY IMMUNIZATION AND POLIO UPDATE IN THE AFRICAN REGION January February 2017 (Vol 5 issue N 1) District data completeness and coverage of DTP3 containing vaccine per
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria
 Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Progress has been made with respect to health conditions.
 health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
Global Polio. Estimated external financial resource requirements for as of 1 September WHO/Polio/01.05 DISTR.
 WHO/Polio/01.05 DISTR.: LIMITED Global Polio E r a d i c a t i o n I n i t i a t i v e Estimated external financial resource requirements for 2002 2005 as of 1 September 2001 Figures in this document were
WHO/Polio/01.05 DISTR.: LIMITED Global Polio E r a d i c a t i o n I n i t i a t i v e Estimated external financial resource requirements for 2002 2005 as of 1 September 2001 Figures in this document were
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality
 Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
Closing the loop: translating evidence into enhanced strategies to reduce maternal mortality Washington DC March 12th 2008 Professor Wendy J Graham Opinion-based decisionmaking Evidence-based decision-making
PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Information Document CONTENTS
 29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
1) SO1: We would like to suggest that the indicator used to measure vaccine hesitancy be DTP 1 to measles first dose dropout.
 To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
O c t o b e r 1 0,
 STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
STUDENT VOICES FROM THE FIELD: WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION GENEVA, SWITZERLAND O c t o b e r 1 0, 2 0 1 6 M o l l y P e z z u l o University at Albany School of Public Health MPH Epidemiology Candidate 17
EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT
 UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
UNICEF / Zar Mon Annexes EXPLANATION OF INDICATORS CHOSEN FOR THE 2017 ANNUAL SUN MOVEMENT PROGRESS REPORT This report includes nine nutrition statistics, as per the 2017 Global Nutrition Report. These
Tipping the dependency
 BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
BREAKING NEWS Meeting the investment challenge Tipping the dependency balance Domestic investments exceed international investments total reaching US$ 8.6 billion. 40 countries fund more than 70% of their
Poliomyelitis: successful and critical issues in the eradication process
 Vaccine Preventable Diseases in the Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: immunization strategies and coverage in the general population and the newly arrived migrants the ProVacMed project Poliomyelitis:
Vaccine Preventable Diseases in the Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: immunization strategies and coverage in the general population and the newly arrived migrants the ProVacMed project Poliomyelitis:
EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38)
 World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO
 CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO Dhaka, Bangladesh, 16 17 November 2011 Bangladesh, November 2011 Meningitis Incidence Children < 12 months Dhaka Shishu / Shishu Shahsta Catchment Area 2008 2011 1800
CEO Board report Seth Berkley MD CEO Dhaka, Bangladesh, 16 17 November 2011 Bangladesh, November 2011 Meningitis Incidence Children < 12 months Dhaka Shishu / Shishu Shahsta Catchment Area 2008 2011 1800
Certificate of Immunization
 Certificate of Immunization Required of all students (Page 1 of 5) QUESTIONS? 440-775-8180 or student.health@oberlin.edu (e-mail preferred) RETURN TO: Oberlin College Student Health Services 247 W. Lorain
Certificate of Immunization Required of all students (Page 1 of 5) QUESTIONS? 440-775-8180 or student.health@oberlin.edu (e-mail preferred) RETURN TO: Oberlin College Student Health Services 247 W. Lorain
Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
 Regional Committee for the Eastern Mediterranean Sixtieth session Provisional agenda item 3 (a) August 2013 Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
Regional Committee for the Eastern Mediterranean Sixtieth session Provisional agenda item 3 (a) August 2013 Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
FRAMEWORK CONVENTION ALLIANCE BUILDING SUPPORT FOR TOBACCO CONTROL. Smoke-free. International Status Report
 FRAMEWORK CONVENTION ALLIANCE BUILDING SUPPORT FOR TOBACCO CONTROL Smoke-free Environments International Status Report As December, 00 Smoke-free environments are a vital part combating the global tobacco
FRAMEWORK CONVENTION ALLIANCE BUILDING SUPPORT FOR TOBACCO CONTROL Smoke-free Environments International Status Report As December, 00 Smoke-free environments are a vital part combating the global tobacco
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING
 JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
JOINT TB AND HIV PROGRAMMING Haileyesus Getahun, WHO. On behalf of the Global Fund Interagency TB and HIV Working Group (Global Fund, PEPFAR, Stop TB Partnership, UNAIDS, WHO) I was admitted in a hospital
CALLING ABROAD PRICES FOR EE SMALL BUSINESS PLANS
 CALLING ABROAD PRICES FOR EE SMALL BUSINESS PLANS More information about out-of-bundle charges for our small business customers calling internationally from the UK using a small business price plan Page
CALLING ABROAD PRICES FOR EE SMALL BUSINESS PLANS More information about out-of-bundle charges for our small business customers calling internationally from the UK using a small business price plan Page
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of the material in this publication
FRAMEWORK FOR IMPLEMENTING THE GLOBAL STRATEGY TO ELIMINATE YELLOW FEVER EPIDEMICS (EYE), IN THE AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Secretariat
 13 June 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 20177 Provisional agenda item 11 FRAMEWORK FOR IMPLEMENTING
13 June 2017 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-seventh session Victoria Falls, Republic of Zimbabwe, 28 August 1 September 20177 Provisional agenda item 11 FRAMEWORK FOR IMPLEMENTING
Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions
 Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Review of decisions Debbie Adams
 Review of decisions Debbie Adams Geneva, Switzerland, Decision 1: Board/Committee member appointments (1/3) The GAVI Alliance Board: (a) Appointed the following Board members: Joan Awunyo-Akaba as Board
Review of decisions Debbie Adams Geneva, Switzerland, Decision 1: Board/Committee member appointments (1/3) The GAVI Alliance Board: (a) Appointed the following Board members: Joan Awunyo-Akaba as Board
1. Consent for Treatment This form must be completed in order to receive healthcare services in the campus clinic.
 HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
HEALTH & WELLNESS SERVICES INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE REQUIRED MEDICAL FORMS FOR: U.S. CITIZENS 18 YEARS OF AGE OR OLDER AT THE TIME THE FORMS ARE COMPLETED. THIS REQUIREMENT MUST BE COMPLETED WHETHER:
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets
 Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN
 UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
UNAIDS DATA TABLES 2011 Copyright 2011 Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) All rights reserved ISBN 978-92-9173-945-5 UNAIDS / JC2225E The designations employed and the presentation of
ANNEX 3: Country progress indicators
 : progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
: progress indicators 541 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS 2006 REPORT ON THE GLOBAL AIDS EPIDEMIC Annex 3 : COUNTRY PROGRESS INDICATORS As of March 2006, 115 countries had reported indicators on progress
Update from the GAVI Alliance Seth Berkley, MD Chief Executive Officer
 Update from the GAVI Alliance Seth Berkley, MD Chief Executive Officer SAGE meeting Geneva, 8-10 November 2011 Topics to cover Update on new vaccine introduction Introductions New approvals Co-financing
Update from the GAVI Alliance Seth Berkley, MD Chief Executive Officer SAGE meeting Geneva, 8-10 November 2011 Topics to cover Update on new vaccine introduction Introductions New approvals Co-financing
Poliovirus : éradication pour les prochaines JNI?
 Poliovirus : éradication pour les prochaines JNI? Bruno LINA CNR des entérovirus Laboratoire de virologie EST, GHE, HCL FRE 3011 CNRS UCBL, Lyon Polio Eradication Initiative 1 Polio Eradication Progress
Poliovirus : éradication pour les prochaines JNI? Bruno LINA CNR des entérovirus Laboratoire de virologie EST, GHE, HCL FRE 3011 CNRS UCBL, Lyon Polio Eradication Initiative 1 Polio Eradication Progress
VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation
 A report on current global access to new childhood vaccines VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation December 2016 INTERNAL VERSION Developed from data in VIEW-hub www.view-hub.org
A report on current global access to new childhood vaccines VIEW-hub Report: Global Vaccine Introduction and Implementation December 2016 INTERNAL VERSION Developed from data in VIEW-hub www.view-hub.org
