EBOLA PREPAREDNESS, PREVENTION AND RESPONSE COMMUNCATION PLAN APRIL 2014 GHANA
|
|
|
- Betty Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EBOLA PREPAREDNESS, PREVENTION AND RESPONSE COMMUNCATION PLAN APRIL 2014 GHANA Social Mobilisation and Risk Communication Thematic Group At the recent meeting on the preparation for and Ebola outbreak several thematic groups were formed. The following is a brief action plan developed by the Social Mobilisation and Risk Communication Thematic group. The group was mandated through a TOR to; Determine point(s) of communications, frequency, requirements and cost Develop key messages for the general public and for health workers and define best ways to communicate with cost Messages development Press release Media encounter (press briefing) Use of Media- Radio, TV, Print Posters, leaflets Establish advocacy requirements, tools and activities with cost Key Considerations During the development of this plan, it was identified that the following actions would have to be taken in order to support the prevention and control activities being undertaken. These included the following: Advocate for nationally coordinated action to address a comprehensive prevention strategy with an additional component looking into preparedness and response to; Initially provide information To address rumors and reduce panic, fear and stigmatization Address key at risk audience groups (such as people who consume bat meat, antelope, monkeys and other primates in other words bush meat, those who frequently travel across borders, those handling the sick and the dead if the outbreak occurs in Ghana) Address key risk behaviours (consumption/preparation of bush meat, and other habits such as shaking hands, handling dead bodies, treating the sick etc)
2 To ensure that the communication strategy is participatory to ensure that individuals, communities, organizations and policy makers are all active partners in achieving the change at the various levels. Strengthen capacity and skills of agencies and institutions responsible for Ebola response and prevention Support the frontline health workers including other frontline partners at the district and regional levels with appropriate communication materials including audio visuals to enable them carry out targeted activities to ensure that enough awareness is created about the disease to ensure that people minimise the risk of contracting and spreading the disease. Goal The main goal of this plan is to reduce the threat of an outbreak of Ebola in Ghana by addressing at risk groups and at risk behaviours among the Ghanaian population. The aim is to increase the level of knowledge on the causes, symptoms and modes of prevention of the disease including on what needs to be done if one suspects that they are ill with Ebola. As the strategy needs be of national scope with specific focus on key risk groups everybody in Ghana needs to be knowledgeable of a possible outbreak of Ebola in the country, and as such the total population in communities, become crucial actors in responding to mitigate such an outbreak. The priority behaviours that would be promoted are: Avoid hunting, handling or eating bush meat such as bats, antelope, monkeys, gorillas, chimpanzees etc. Washing hands with soap and plenty of water at key times After coming home (from work, school, market etc.) Treatment of Ebola during an outbreak Report to the nearest health facility/ or stay at home and inform the nearest health facility, when you have any of the following symptoms along with a sudden onset of high fever Vomiting Diarrhoea Headache Skin rash and red eyes Bleeding through the body openings, i.e eyes, nose, gums, ears and anus Care givers to protect themselves and avoid direct contact with the bodily fluids of sick individuals and keep children away from sick family members and do not share utensils and clothes of sick family members Traditional practices of touching, cleaning and caring for dead bodies to be avoided during an outbreak. The main actors to be targeted as agents of change are: Media Households All family members but particularly men and women and cares of the young. As them men engage in hunting while women engage in the handling and preparation of the meat. Other contact/carers of patients (who are normally left out of education/ hygiene promotion activities) e.g. taxi drivers who transport the patients to the hospitals/health centres Schools pupils, Teachers, SHEP Coordinators and Circuit Supervisors Food vendors (Chop Bars), restaurants, hoteliers and chop bar operators/cafeterias
3 Market traders especially market women who sell food smoked meat or bush meatboth seaters and roamers Hunters Community leaders /chiefs and queen mothers /religious leaders /assembly men Community Based organisations Organisers of Funerals and durbars and other gatherings (particularly in light of the upcoming Easter celebrations District Assemblies health services /environmental heath The Channels for the key messages are: Mass Media channels: such as television, radio, printed press, Institutional channels: including recognized public and private bodies such as the Government Ministries with outreach workers (e.g. MLGRD/EHSD, Ghana Health Service, Ministry of Education/GES, National Disaster Management Organisation etc), networks of development workers, NGOs, etc., for the dissemination of correct and timely information on Ebola towards a coordinated response including enforcement of regulations and by-laws. Social media channels: such as the use of the Internet, SMS text messages etc. Socio-traditional and socio-cultural channels: Opinion leaders (customary chiefs, queen mothers, religious leaders, notables, intellectuals, organized groups etc.) and other informal networks through the various forms and opportunities of traditional popular communication such as durbars, community/village meetings, collective work in the fields, vigils and wakes, talks, baptisms, markets, marriages, funerals, naming ceremonies, marriage ceremonies, journeys in public transports, churches and mosques etc. Inter personal communication (IPC) channels through Community Based Volunteers, CSOs e.g. Ghana Red Cross (GRC), Mothers Clubs and Assembly Agents in workshops, Group discussions, Forum Theatre, Door to door outreach, Peer to Peer outreach etc. Proximity Media channels: such as Community Information Centres (CIC) - PA systems, Mobile Vans videos and community outreach, Community Radio (Talk shows with phone-ins and Jingles, life presenter mentioning), Posters depicting key desirable behaviours and information. Communication Materials to be used for the campaign include: Posters Brochures Fact sheets SMS Radio/TV announcement Job aids (advocacy sheet for community leaders) Monitoring of the activities
4 Budget 1. Activity Description Qty. Amount (GHC) Amount (GHC)
5 ANNOUNCEMENTS (Text to be used on Media and through other communication Channels) This is an important message from the Ministry of Health: There is an outbreak of Ebola in some West African countries. Ebola is a serious disease that kills within a very short time. Signs and symptoms of Ebola include: a high temperature, abdominal pains, Diarrhoea and vomiting. Patients may also have other symptoms such as a body rash, blood spots in the eyes, blood in the vomit, bleeding from the nose, mouth, rectum, eyes and ears. One can get Ebola by coming into contact with body fluids like saliva, blood, urine, faeces and the sweat of an infected person, or by using sharp skin piercing instruments like razorblades and safety pins that have been used by an infected person or by coming into contact with bodies of persons who have died from Ebola. Ebola is also spread by animals infected with the virus. Consuming or coming into contact with bush meat such as bats, monkeys, antelope and other primates can infect people. So, STOP hunting and eating these animals until it is safe to do so again! To prevent Ebola: Avoid contact with bush animals including bats, monkeys, antelopes and porcupines Report a suspected case of Ebola to your nearest health centre as soon as possible Avoid contact with the person suspected to be suffering from Ebola Wash your hands frequently with soap, under running water and strong detergent after attending to a person suspected of suffering from Ebola Use strong detergents on any vomit or diarrhoea of a person suspected of suffering from Ebola before cleaning This Announce from the Ministry Of Health in collaboration with MoFA and NADMO. For Further information Please contact Telephone Numbers. XXX(GHS)
6 KEY MESSAGES AND SMS 1. Symptoms There is an Ebola outbreak in West Africa. Ebola is a serious disease that kills quickly. Signs & symptoms: high fever, stomach pain, diarrhoea & vomiting. There may also be bleeding from the nose, mouth, rectum, eyes & ears. 2. Spread Ebola spreads through contact with saliva, blood, urine, faeces & sweat from infected people. People with Ebola are most contagious in the later stages of the disease. BE SAFE avoid all contact 3. Spread Avoid contact with bush animals like bats, monkeys, antelopes & porcupines. Avoid buying or eating bush meat 4. Prevention To PREVENT Ebola: report suspected cases to health centre, limit contact, no contact with bush meat, wash hands frequently with soap & water. Use strong detergents on vomit or faeces of those infected 5. Prevention Follow infection-control procedures. Health workers must wear protective clothing e.g. gloves, masks, gowns & eye shields. Keep infected people isolated from others. 6. Prevention Don t handle remains. The bodies of people who have died of Ebola are still contagious. Special trained teams should bury the remains, using appropriate safety equipment. 7. Reporting Report all suspected Ebola cases to the District Health Officer (DHO)
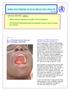
7 BROCHURE What you need to know about EBOLA Cause Transmission Signs and symptoms Prevention Introduction There is an outbreak of Ebola in some West African countries which are also closer to the boarders of Ghana. These countries have been affected and many people have been diagnosed with the disease and many of them have died. Although this disease is serious and kills in a short time, it can be prevented. This brochure provides information on what Ebola disease is, how it spreads and how it can be prevented. What is Ebola? Ebola is a killer disease caused by a virus. It spreads quickly from person to person, kills in a short time BUT can be prevented. How is Ebola spread? It is spread through; Direct contact with body fluids like blood, sweat, saliva, vomitus, urine, stool and wounds, of a person suffering from Ebola or splashing of such fluids from an infected person into another person s eyes Using skin piercing instruments such as needles, razors that have been used by an infected person Direct physical contact with a person who has died of Ebola Hunting, handling and Eating animals that carry the virus especially monkeys, bats, porcupine and antelope. What are the signs and symptoms of a person suffering from Ebola A person suffering from Ebola presents with sudden onset of high temperature or fever with any of the following: Vomiting Diarrhea Headache Skin rash and red eyes Bleeding through the body openings, i.e. eyes, nose, gums, ears, and anus may or may not be present.
8 What should be done to someone suffering from Ebola? Patients should be handled with care using protective wear like gloves, goggles, and masks The person should be taken to the nearest Health facility immediately for proper treatment and management. Clothing and beddings of the person should be disinfected with strong detergent to avoid infecting others in the house Who is at risk? Since the virus spreads through direct contact with blood and other body secretions of an infected person, people living with and caring for the patients are at a higher risk of getting infected. Where possible, use gloves when handling these patients to avoid contact with patients body fluids. During feeding, holding or caring for the patient, family members and friends should cover themselves properly with protective wear, such as gloves Persons who have died due to Ebola can also be infectious if not properly handled with the appropriate protective wear Hunters or those who come into contact with or eat bush meat such as bats, monkeys antelope are also at great risk. How can Ebola be prevented? Avoid direct contact with body fluids, blood, saliva, vomitus, urine, and stool of infected persons by wearing protective materials like gloves and goggles. Do not touch wounds of an infected person with unprotected hands Do not use skin piercing instruments that have been used on a patient suffering from Ebola Avoid hunting, handling and eating of bush animals like monkeys, bats porcupines and antelopes. Persons who have died of Ebola must be handled with strong protective wear and buried immediately to prevent spread of the disease; avoid feasting and the funeral should take place immediately after death After handling a patient suffering from Ebola, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap under running water. POINTS TO REMEMBER Ebola is a serious disease, it kills in a short time BUT can be prevented Ebola spreads from one person to another through physical contact with body fluids of an infected person Ebola can be prevented through: Reporting of any suspected cased of Ebola to the nearest health Facility Prompt management of all persons suffering from Ebola, by seeking early medical help Proper protection using gloves, goggles and masks where possible, when handling patients suffering from Ebola Regular washing of hands with soap and water after touching a suspected person Proper burying of people who have died of Ebola immediately after death Avoid communal washing of hands during funerals. Avoid hunting, handling and eating bush animals like monkeys, bats, antelope and porcupines. For further information contact * the nearest health facility or * the District Director of Health Services or * these Telephone numbers XXX (GHS)
9 JOB AID Ebola Fever JOB AID FOR COMMUNITY MOBILIZERS 1. What is Ebola Fever? Ebola Fever is a disease caused by the Ebola virus. It is transmitted through direct or indirect contact with an infected people and by contact with infected animals. Ebola Fever is responsible for the death of 50% to 90% of the sick individuals who show clinical symptoms No effective treatment or vaccine is currently available. The natural reservoir for this virus seems to be in the forests and savannahs of Central and West Africa. 2. What are the signs of a case of Ebola Fever? Ebola Fever develops 2 to 21 days after infection, its symptoms include: High fever, Headaches, Intense weakness, Joint or muscle pains, Sore throat, Nausea and vomiting, Diarrhea, Skin rash, Internal and external bleeding in the form of: nosebleed, bleeding gums, red eyes, vomiting of blood, bloody stools, red spots on the body, Impaired kidney and liver function. 3. How is Ebola Fever transmitted? Ebola virus is transmitted through direct contact with the blood, urine and stools, vomit and saliva, sperm, sweat and vaginal fluid of infected individuals. The disease can also be transmitted through contact with the soiled clothing or bed linens of a sick patient. It is therefore necessary to disinfect them before handling them. Funeral rituals, during which parents and friends come into contact with the corpse, play a critical role in the transmission. Ebola virus can be transmitted to humans when handling contaminated animals, alive or dead: bats, monkeys, chimpanzees, gorillas and forest antelope.
10 Transmission to health-care workers caring for sick patients has often happened where appropriate infection control measures were not observed and strict barrier nursing techniques and procedures were not implemented. 4. How do we avoid contamination by Ebola Fever? a. Avoid all contact with an Ebola patient or the corpse of a deceased patient, as well as with all bush meat found in the forest. Avoid all direct contact with blood, urine or stools, vomit and saliva, sperm, sweat, organs or biological fluids, soiled clothes or linens of sick individual by using protection. During the funeral of those who have died of Ebola: Do not wash, dress, apply make-up, touch or caress the body of the deceased Do not display the corpse on a bed or mat Do not sit around the corpse or lean over the coffin Do not handle or keep the deceased s everyday objects Do not wash hands in a common basin after the burial Do not keep the corpse, bury the body immediately using protective clothes Do not clip nails, cut hair or take off the clothes of the deceased to bring into the village Avoid transferring suspected cases and sick individuals from one health center to another Avoid all contact with suspected cases Isolate sick patients and rigorously implement strict barrier nursing techniques (wear protection equipment and disinfect equipment Avoid hunting, handling or eating meat bush meat such as monkeys, bats, antelopes and porcupines. b. Avoid traditional practices which favor transmission Avoid sacrifices involving animal blood Avoid multiple-use of rectal bulb syringe c. Follow general hygiene measures Wash hands regularly using soap under running water Use boiled water or sterilized with chorine tablets Use latrines always Burn or Dispose of household trash at the prescribed dump site Isolate suspected cases or people who have been in contact with the disease (in school, during events, etc.) NB: As the primary mode of person-to-person transmission is through contact with contaminated blood, bodily or biological fluids, all individuals who have had a physical contact with sick patients should be kept under a close watch: their temperature should be taken twice a day, with immediate hospitalization and strict isolation should a fever appear. All hospital personnel who have been in close contact with sick patients or contaminated material and who have not implemented strict barrier nursing techniques should be considered exposed and kept under strict medical surveillance. 5. What should community leaders do to promote health in the context of the Ebola Fever response? a. Mobilizing the community together
11 Activate and mobilise community members Accept and implement measure to fight the Ebola Fever epidemic as recommended by the epidemics response committee; Disseminate, exchange information on prevention using songs, theater, sketches and word of mouth; Mobilize local resources to support field interventions and workers; Strengthen community-based surveillance in collaboration with health professionals; Identify and quickly report any suspected cases, rumors, sick individuals or cases to the closest health center; Agree to stop all hunting activities; Avoid all social gatherings and meetings Welcome and accept volunteers to assist in the community Do not trust hurtful beliefs, and rumors, but follow the epidemics response committee s instructions and advice to stop the epidemics b. Support sick patients and their families Help maintain the nutritional status of sick patients by providing adequate food; Provide material assistance, and moral and psychosocial support to the affected families; Avoid exclusion, rejection and stigmatization of the healthy members of the affected families who are under surveillance; Improve knowledge on the disease, ease the reintegration of the members of families who have had cases of the disease;
12 FACT SHEET FOR MEDIA Facts About EBOLA What is Ebola? Ebola is a killer disease, which presents with high temperature and bleeding tendencies. It is very infectious, kills in a short time BUT can be prevented. The signs and symptoms of Ebola are High Temperature (Fever) Vomiting Diarrhea Abdominal pains Headache Measles like rash Red eyes Bleeding from body openings(nose, gums, ears and anus) may or may not be present How is it spread? Ebola is spread through direct physical contact with body fluids like blood, saliva, stool, vomitus, urine, and sweat of an infected person and soiled linen used by an infected patient Splashing of body fluids from an infected person into the eyes of another person It can also be spread through using skin piercing instruments that have been used by an infected person The Virus can also be gotten through contact with persons who have died of Ebola The virus can also be gotten through eating dead or infected animals especially monkeys, bats, antelope and porcupine that carried the Ebola virus. How can it be prevented? Avoid direct contact with body fluids of a person suffering from Ebola by using protective materials like gloves, goggles, and masks Disinfect the beddings and clothing of an infected person with Strong disinfectants Persons suspected to be suffering from Ebola should be taken to the nearest health facility immediately for prompt attention. Persons who have died of Ebola must be handled using strong protective wear and buried immediately; avoid feasting and funerals ceremonies Report any suspected cases of Ebola to the nearest health facility immediately
13 Wash your hands with soap under running water after handling a patient or the body of a person who has died of Ebola Avoid communal washing of hands during funeral rites Avoid hunting, handling and eating bush animals especially monkeys, bats, antelopes and porcupines. For further information contact:
14 INFECTION CONTROL POSTER
15 POSTER FOR COMMUNITIES (Needs to be translated)
EBOLA FACTS. During this outbreak, most of the disease has spread through human-to-human transmission.
 EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
saipem Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014
 Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
Ebola Virus Patient Advisory
 22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
Ebola Virus Diseases
 CDC/Dr F A Murphy Frequently Asked Questions on Ebola Virus Diseases Frequently asked questions on Ebola virus disease World Health Organization 2014 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or
CDC/Dr F A Murphy Frequently Asked Questions on Ebola Virus Diseases Frequently asked questions on Ebola virus disease World Health Organization 2014 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or
12 June The average EVD case fatality rate has been around 50 per cent.
 12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
Confronting Ebola. Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy
 Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
Media centre Ebola virus disease
 1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health
 Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health Joint WHO/ILO Briefing Note for Workers and Employers 25 August 2014 (update 5 September 2014) This briefing note is based on the existing WHO and ILO
Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health Joint WHO/ILO Briefing Note for Workers and Employers 25 August 2014 (update 5 September 2014) This briefing note is based on the existing WHO and ILO
EBOLA INFORMATION KIT 20 to 26 October 2014 MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP POPULAR ARTICLES
 HOME ABOUT PHASA MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP DOWNLOAD: PROFESSIONAL HUNTER STATUS SECTION 16A (click to download) DOWNLOADS NEWSLETTERS F.A.Q TWITTER FACEBOOK Home
HOME ABOUT PHASA MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP DOWNLOAD: PROFESSIONAL HUNTER STATUS SECTION 16A (click to download) DOWNLOADS NEWSLETTERS F.A.Q TWITTER FACEBOOK Home
Ebola Epidemic in Coastal West Africa Overall Situation
 Ebola Epidemic in Coastal West Africa Overall Situation Report given at Caritas Internationalis Briefing Meeting 05 November 2014 Dr and Deacon Timothy Flanigan MD Professor of Medicine and Infectious
Ebola Epidemic in Coastal West Africa Overall Situation Report given at Caritas Internationalis Briefing Meeting 05 November 2014 Dr and Deacon Timothy Flanigan MD Professor of Medicine and Infectious
Ebola Virus Disease. Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong. as of 13 August 2014
 Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone
 ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
Social mobilization: communicating with affected communities
 Short Course on Infectious Diseases in Humanitarian Emergencies LSHTM-WHO 3 April 2009 Social mobilization: communicating with affected communities Norma Johnston Session outline 09.00 09.30 An overview
Short Course on Infectious Diseases in Humanitarian Emergencies LSHTM-WHO 3 April 2009 Social mobilization: communicating with affected communities Norma Johnston Session outline 09.00 09.30 An overview
News in Review December 2014 Teacher Resource Guide EBOLA: A Deadly Virus Outbreak
 News in Review December 2014 Teacher Resource Guide EBOLA: A Deadly Virus Outbreak Note to Teachers The classroom must promote a safe place for students to discuss sensitive issues such as illness and
News in Review December 2014 Teacher Resource Guide EBOLA: A Deadly Virus Outbreak Note to Teachers The classroom must promote a safe place for students to discuss sensitive issues such as illness and
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus disease Updated 17 Oct 2014
 Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
Questions and Answers on Ebola
 Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information
 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Marburg virus disease
 Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA
 TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October EMS TB Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
 UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red
 Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red In this document: Summary Key Messages Ebola Cases and Deaths (West Africa) Ebola in U.S. Health Workers (in Liberia)
Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red In this document: Summary Key Messages Ebola Cases and Deaths (West Africa) Ebola in U.S. Health Workers (in Liberia)
What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS. They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids.
 What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
What are Universal Precautions? What employees should know about UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS They re work practices that help prevent contact with blood and certain other body fluids. Universal precautions are:
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE May 2004
 WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus
 THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH Introduction Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus Rotavirus infection is the leading cause of diarrhoea in children under 5 years of age worldwide.
THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH Introduction Rotavirus Factsheet What you need to know about Rotavirus Rotavirus infection is the leading cause of diarrhoea in children under 5 years of age worldwide.
PRESS STATEMENT ON MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE
 THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH PRESS STATEMENT ON MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE Hon. Dr. Jane Ruth Aceng Minister of Health October 19, 2017 PRESS STATEMENT ON MARBURG HEMORRHAGIC FEVER The Ministry
THE REPUBLIC OF UGANDA MINISTRY OF HEALTH PRESS STATEMENT ON MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE Hon. Dr. Jane Ruth Aceng Minister of Health October 19, 2017 PRESS STATEMENT ON MARBURG HEMORRHAGIC FEVER The Ministry
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA
 TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard
 Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Malaria prevention and control
 COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
COMMUNITY TOOLS Tool 1 Malaria prevention and control Point to first picture: What do you see in this picture? 1. A small child who looks very sick. The child is sweating and shaking. There are mosquitoes
Infection Control Handout
 Modes of Transmission Contact Routes Direct Contact Transmission Indirect Contact Transmission Droplet Transmission Indirect contact contamination Clothes Soiled bed linen Personal care products Personal
Modes of Transmission Contact Routes Direct Contact Transmission Indirect Contact Transmission Droplet Transmission Indirect contact contamination Clothes Soiled bed linen Personal care products Personal
Infection Prevention and Control
 Patient & Family Guide Infection Prevention and Control 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Prévention et contrôle des infections (FF85-1216) www.nshealth.ca Infection Prevention and Control Who are we?
Patient & Family Guide Infection Prevention and Control 2017 Aussi disponible en français : Prévention et contrôle des infections (FF85-1216) www.nshealth.ca Infection Prevention and Control Who are we?
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Chapter 11 PREVENTING INFECTION. Elsevier items and derived items 2010 by Mosby, Inc. an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
 Chapter 11 PREVENTING INFECTION Infection is a major safety and health hazard. The health team follows certain practices and procedures to protect patients, residents, visitors, and staff from infection.
Chapter 11 PREVENTING INFECTION Infection is a major safety and health hazard. The health team follows certain practices and procedures to protect patients, residents, visitors, and staff from infection.
U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus
 U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff - Sept. 09, 2014 1 2 3 4 To slow down the spread of the deadly virus Ebola, the United
U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff - Sept. 09, 2014 1 2 3 4 To slow down the spread of the deadly virus Ebola, the United
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
Prevention and Control of Healthcare-Associated Norovirus
 Purpose: Audience: Policy: To prevent healthcare-associated norovirus infections in patients, employees, contract workers, volunteers, visitors and students and to control and eradicate norovirus infections
Purpose: Audience: Policy: To prevent healthcare-associated norovirus infections in patients, employees, contract workers, volunteers, visitors and students and to control and eradicate norovirus infections
The presenter has no potential or actual conflicts of interest and no relevant financial relationships to maters regarding or related to Ebola.
 Leonard A. Levy, DPM, MPH Associate Dean of Research and Innovation Director, Institute for Disaster and Emergency Preparedness Professor of Public Health/Family Medicine/Biomedical Informatics Nova Southeastern
Leonard A. Levy, DPM, MPH Associate Dean of Research and Innovation Director, Institute for Disaster and Emergency Preparedness Professor of Public Health/Family Medicine/Biomedical Informatics Nova Southeastern
Genus Ebolavirus is 1 of 3 members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus), along with genus Marburgvirus and genus Cuevavirus.
 EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
Viral or Suspected Viral Gastroenteritis Outbreaks
 Viral or Suspected Viral Gastroenteritis Outbreaks Information for Directors and Staff of Early Childhood Education and Care Services Introduction Gastroenteritis outbreaks in early childhood education
Viral or Suspected Viral Gastroenteritis Outbreaks Information for Directors and Staff of Early Childhood Education and Care Services Introduction Gastroenteritis outbreaks in early childhood education
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS
 EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
Chapter 12. Preventing Infection. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. The health team follows certain practices and procedures to protect patients, residents, visitors, and staff from
Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. The health team follows certain practices and procedures to protect patients, residents, visitors, and staff from
Communicable Disease Policy
 Communicable Disease Policy Gastroenteritis (Diarrhoea and Vomiting), including Norovirus: Is easily spread and may lead to an outbreak (two or more cases) Outbreaks can be due to food poisoning or the
Communicable Disease Policy Gastroenteritis (Diarrhoea and Vomiting), including Norovirus: Is easily spread and may lead to an outbreak (two or more cases) Outbreaks can be due to food poisoning or the
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu)
 Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
Statements about Ebola: True or false? Part 1 Commented version for trainers only!
 Statements about Ebola: True or false? Part 1 Commented version for trainers only! The questions and answers are designed to revise key messages of the training. If necessary, you may adapt the questions
Statements about Ebola: True or false? Part 1 Commented version for trainers only! The questions and answers are designed to revise key messages of the training. If necessary, you may adapt the questions
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds What is Avian Influenza? The disease commonly referred to as bird flu is an animal infection caused by the H5N1 virus. The virus occurs naturally among
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1 Avian Influenza in Birds What is Avian Influenza? The disease commonly referred to as bird flu is an animal infection caused by the H5N1 virus. The virus occurs naturally among
Module 3 : Informing and mobilizing the community
 Module 3 : Informing and mobilizing the community Title Responsible/facilitators General Objective Informing and mobilizing the community Agency medical coordinator To foster behaviours that decrease the
Module 3 : Informing and mobilizing the community Title Responsible/facilitators General Objective Informing and mobilizing the community Agency medical coordinator To foster behaviours that decrease the
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Chapter 13. Preventing Infection. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 13 Preventing Infection Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 13.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Identify what microbes need to live and grow.
Chapter 13 Preventing Infection Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 13.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Identify what microbes need to live and grow.
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
MODULE B. Objectives. Infection Prevention. Infection Prevention. N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum
 DHSR/HCPR/CARE NAT I Curriculum - July 2013 1 N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum MODULE B Infection Prevention Objectives Relate the chain of infection to the work of a nurse aide in long-term care facilities.
DHSR/HCPR/CARE NAT I Curriculum - July 2013 1 N.C. Nurse Aide I Curriculum MODULE B Infection Prevention Objectives Relate the chain of infection to the work of a nurse aide in long-term care facilities.
What is hepatitis? What is hepatitis A? How is it spread? What are the symptoms? How soon do symptoms appear? How is hepatitis A diagnosed?
 Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Bloodborne Pathogens. Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager. ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018
 Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Bloodborne Pathogens Aaron Holmberg, Risk Manager ARM, MBA, OSHA Authorized Outreach Trainer February 2018 What s This About? Infectious microorganisms (viruses and diseases) found in blood and bodily
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees
 Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Bloodborne Pathogens For School Employees Waynesboro Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training and Annual Review Created on May 5, 2010 Reviewed/Revised April 6, 2017 Introduction In an educational
Norovirus. Causes. What causes infection with a norovirus? How is it spread?
 - Fact sheet - Public Health Agency of Canada es are a group of viruses that cause gastroenteritis, an illness that usually includes diarrhea and/or vomiting. es are commonly found throughout North America
- Fact sheet - Public Health Agency of Canada es are a group of viruses that cause gastroenteritis, an illness that usually includes diarrhea and/or vomiting. es are commonly found throughout North America
Pandemic Influenza A Matter of Time
 Pandemic Influenza A Matter of Time A Community Education Package Package developed by: Mary Smith Grampians Region Infection Control Consultant Department of Human Services What is Seasonal Influenza?
Pandemic Influenza A Matter of Time A Community Education Package Package developed by: Mary Smith Grampians Region Infection Control Consultant Department of Human Services What is Seasonal Influenza?
PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE
 PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE (Updated September 7, 2006) Information and concept courtesy Of the San Francisco Public Health Department Table of Contents Pandemic
PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE (Updated September 7, 2006) Information and concept courtesy Of the San Francisco Public Health Department Table of Contents Pandemic
EBOLA 101. Update for EMS System Stakeholders. Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014
 EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
Thank You to Our Partners. Law Enforcement Fire Services Emergency Management Public Health Behavioral/Mental Health
 Thank You to Our Partners Law Enforcement Fire Services Emergency Management Public Health Behavioral/Mental Health The School Safety Continuum Prevention Intervention Response Prevention & Intervention
Thank You to Our Partners Law Enforcement Fire Services Emergency Management Public Health Behavioral/Mental Health The School Safety Continuum Prevention Intervention Response Prevention & Intervention
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos.
 Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens. Pines Behavioral Health
 Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
Infection Control Blood Borne Pathogens Pines Behavioral Health Definition: Infection control is preventing the spread of germs that cause illness and infection. Infection control starts with understanding
Ebola Exposure (Version )
 Ebola Exposure (Version 10-28-14) Pediatric Office-Hours Version DEFINITION Exposure to a person with suspected or proven Ebola Travel to or living in an area with recent cases of Ebola. These are countries
Ebola Exposure (Version 10-28-14) Pediatric Office-Hours Version DEFINITION Exposure to a person with suspected or proven Ebola Travel to or living in an area with recent cases of Ebola. These are countries
Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus
 Fodder for young minds Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus By Meera Dolasia on September 29, 2014 CCSS NAS-6 Grades: 5-8 Word Search Every few years, a new pandemic hits the globe and sends shivers down everyone's
Fodder for young minds Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus By Meera Dolasia on September 29, 2014 CCSS NAS-6 Grades: 5-8 Word Search Every few years, a new pandemic hits the globe and sends shivers down everyone's
Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014
 Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014 With the announcement of the first confirmed case of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Dallas Texas, there could be interactions with individuals
Provider Health & Safety Alert Ebola Virus Disease September 30, 2014 With the announcement of the first confirmed case of Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Dallas Texas, there could be interactions with individuals
Module 1 : Influenza - what is it and how do you get it?
 Module 1 : Influenza - what is it and how do you get it? Responsible/facilitators General Objective Specific Objectives Methodology Agency medical coordinator Understand the mechanism how influenza is
Module 1 : Influenza - what is it and how do you get it? Responsible/facilitators General Objective Specific Objectives Methodology Agency medical coordinator Understand the mechanism how influenza is
EBOLA. Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014
 EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
Miami Dade County Public Schools
 Miami Dade County Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training 2017 ARTHUR J. GALLAGHER & CO. AJG.COM Objectives Introduction to bloodborne pathogens Types of bloodborne pathogens Who is at risk? Exposure
Miami Dade County Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Training 2017 ARTHUR J. GALLAGHER & CO. AJG.COM Objectives Introduction to bloodborne pathogens Types of bloodborne pathogens Who is at risk? Exposure
FACT SHEET. H1N1 Influenza phone
 www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
Bureau of Emergency Medical Services New York State Department of Health
 Swine Influenza A (H1N1) Advisory To: All EMS Agencies From: Disaster Preparedness Unit Date: April 28, 2009 Introduction The Bureau of Emergency Medical Services is providing the following update regarding
Swine Influenza A (H1N1) Advisory To: All EMS Agencies From: Disaster Preparedness Unit Date: April 28, 2009 Introduction The Bureau of Emergency Medical Services is providing the following update regarding
AIDS and hepatitis B are primarily spread by three types of body fluids: Blood Vaginal secretions Semen
 Bloodborne Pathogens Introduction In an educational environment, it s very important to know how to protect yourself and students from bloodborne diseases like AIDS and hepatitis B. At the same time it
Bloodborne Pathogens Introduction In an educational environment, it s very important to know how to protect yourself and students from bloodborne diseases like AIDS and hepatitis B. At the same time it
Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings
 Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings
 Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
Module C Epidemiology and Risk of Infection in outpatient Settings Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology (SPICE) UNC School of Medicine Objectives Discuss the infectious process through
21. Getting Tested for HIV
 21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
21. Getting Tested for HIV Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Describe the process of HIV testing. List reasons for getting tested for HIV. Background notes It is not
Infectious Diseases Prevention & Control Policy
 Document Title : Infectious Diseases Prevention & Control Policy Document Ref. RBS/SC/P001/14 Number : Issue Date: April 2017 Revision Date: April 2018 Section : School Clinic Version: 2 Prepared By: Pamela
Document Title : Infectious Diseases Prevention & Control Policy Document Ref. RBS/SC/P001/14 Number : Issue Date: April 2017 Revision Date: April 2018 Section : School Clinic Version: 2 Prepared By: Pamela
Assessing Public Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices, and Behaviors Relating to Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Sierra Leone. Preliminary Report
 Assessing Public Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices, and Behaviors Relating to Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Sierra Leone Preliminary Report 12 th September 2014 Table of Contents... 1 Executive Summary...
Assessing Public Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices, and Behaviors Relating to Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in Sierra Leone Preliminary Report 12 th September 2014 Table of Contents... 1 Executive Summary...
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
SCOTTISH AMBULANCE SERVICE Strategic Co-ordination Centre (SCC) Bulletin 01/ April Swine Flu-Information Sheet
 SCOTTISH AMBULANCE SERVICE Strategic Co-ordination Centre (SCC) Bulletin 01/09 Swine Flu-Information Sheet To date 2 cases of swine Influenza A (H1N1) have been confirmed in individuals in Scotland. Other
SCOTTISH AMBULANCE SERVICE Strategic Co-ordination Centre (SCC) Bulletin 01/09 Swine Flu-Information Sheet To date 2 cases of swine Influenza A (H1N1) have been confirmed in individuals in Scotland. Other
FIGHT INFECTIOUS BACTERIA AND VIRUSES MAKE HANDWASHING CONTAGIOUS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 FIGHT INFECTIOUS BACTERIA AND VIRUSES MAKE HANDWASHING CONTAGIOUS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! It s contagious!! HANDWASHING TO ATTACK NOROVIRUS!! HELP FIGHT INFECTIOUS BACTERIA AND VIRUSES MAKE HANDWASHING
FIGHT INFECTIOUS BACTERIA AND VIRUSES MAKE HANDWASHING CONTAGIOUS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! It s contagious!! HANDWASHING TO ATTACK NOROVIRUS!! HELP FIGHT INFECTIOUS BACTERIA AND VIRUSES MAKE HANDWASHING
UGANDA DECLARES END OF MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH PRESS STATEMENT UGANDA DECLARES END OF MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK 08 December 2017 Hon. Sarah Opendi Minister of State for Health General Duties HOLDING PORTFOLIO OF MINISTER OF
MINISTRY OF HEALTH PRESS STATEMENT UGANDA DECLARES END OF MARBURG VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK 08 December 2017 Hon. Sarah Opendi Minister of State for Health General Duties HOLDING PORTFOLIO OF MINISTER OF
Public Health Measures for Scaling up National Preparedness. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
 Public Health Measures for Scaling up National Preparedness Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Background Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is an acute respiratory illness caused by the novel
Public Health Measures for Scaling up National Preparedness Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Background Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is an acute respiratory illness caused by the novel
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]
![BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens] BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]](/thumbs/73/68341667.jpg) BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
Bloodborne Pathogens Training. July 26, 2012
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training July 26, 2012 Introduction As sure as the sun comes up every day, children end up with scraped knees, cuts, and bruises. Students of all ages hurt themselves on the playground,
Bloodborne Pathogens Training July 26, 2012 Introduction As sure as the sun comes up every day, children end up with scraped knees, cuts, and bruises. Students of all ages hurt themselves on the playground,
AMBULANCE DECONTAMINATION GUIDELINES SUSPECTED INFLUENZA PATIENT
 AMBULANCE DECONTAMINATION GUIDELINES SUSPECTED INFLUENZA PATIENT Reprinted with the Permission of John Hill, President Iowa EMS Association Following are general guidelines for cleaning or maintaining
AMBULANCE DECONTAMINATION GUIDELINES SUSPECTED INFLUENZA PATIENT Reprinted with the Permission of John Hill, President Iowa EMS Association Following are general guidelines for cleaning or maintaining
H1N1 (Swine) Influenza
 What is H1N1 influenza A? H1N1 (Swine) Influenza The new H1N1 influenza, also called swine flu, is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in 2009. This virus
What is H1N1 influenza A? H1N1 (Swine) Influenza The new H1N1 influenza, also called swine flu, is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new virus was first detected in 2009. This virus
Almost always Commonly Sometimes Fever. Nausea Cough Joint pain. Sore throat
 Preventing H1N1 Influenza (Flu) A Guideline for Homeless Shelters, Emergency Shelters and Transitional Facilities The purpose of this document is to help staff to prevent or reduce transmission of H1N1
Preventing H1N1 Influenza (Flu) A Guideline for Homeless Shelters, Emergency Shelters and Transitional Facilities The purpose of this document is to help staff to prevent or reduce transmission of H1N1
Flu Facts. January 2019
 Flu Facts January 2019 Seasonal influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses which circulate in all parts of the world. There are 4 types of seasonal influenza viruses, types
Flu Facts January 2019 Seasonal influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses which circulate in all parts of the world. There are 4 types of seasonal influenza viruses, types
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Infection Prevention Special Needs Shelters. Jacqueline Whitaker RN MS LHRM CPHQ CIC FAPIC
 Infection Prevention Special Needs Shelters Jacqueline Whitaker RN MS LHRM CPHQ CIC FAPIC Infection Prevention: Objectives and Your Role Know the client population and its impact on the special needs shelter
Infection Prevention Special Needs Shelters Jacqueline Whitaker RN MS LHRM CPHQ CIC FAPIC Infection Prevention: Objectives and Your Role Know the client population and its impact on the special needs shelter
OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. Universal Precautions
 Building a Safer Workplace OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Universal Precautions Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens are micro-organisms in the bloodstream that cause diseases. Bloodborne Pathogens
Building a Safer Workplace OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard Universal Precautions Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens are micro-organisms in the bloodstream that cause diseases. Bloodborne Pathogens
Influenza Fact Sheet
 What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Bloodborne Pathogens. Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety
 Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
There are four important ways in which frontline workers can work together with Peel Public Health to prevent illness due to outbreaks.
 Chapter 4 Outbreaks What is an outbreak? Preparing for an outbreak Identifying an outbreak Outbreak identification process Managing and controlling an outbreak 11 steps Outbreak control measures Outbreak
Chapter 4 Outbreaks What is an outbreak? Preparing for an outbreak Identifying an outbreak Outbreak identification process Managing and controlling an outbreak 11 steps Outbreak control measures Outbreak
Guideline Norovirus Outbreak
 POLICY: To control for the spread of the Norovirus infection & optimise the rehabilitation of those affected. www.hh.net.nz for Infection Control Policy [NZS: 4134: 2008] REFERENCE: A+ Guidelines for the
POLICY: To control for the spread of the Norovirus infection & optimise the rehabilitation of those affected. www.hh.net.nz for Infection Control Policy [NZS: 4134: 2008] REFERENCE: A+ Guidelines for the
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Communicable Diseases. Detection and Prevention
 Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Communicable Diseases Detection and Prevention Communicable Diseases Communicable Disease an infectious disease transmissible by direct contact (person to person) indirect means (body fluids, objects touched
Guidelines for the Control of a Suspected or Confirmed Outbreak of Viral Gastroenteritis (Norovirus) in an Assisted Living Facility or Nursing Home
 Guidelines for the Control of a Suspected or Confirmed Outbreak of Viral Gastroenteritis (Norovirus) in an Assisted Living Facility or Nursing Home The following is a summary of guidelines developed to
Guidelines for the Control of a Suspected or Confirmed Outbreak of Viral Gastroenteritis (Norovirus) in an Assisted Living Facility or Nursing Home The following is a summary of guidelines developed to
Norovirus in Healthcare Settings
 ST. JAMES HEALTHCARE DECEMBER 2012 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWSLETTER INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Norovirus in Healthcare Settings The Impacts of Unsafe Medical Injections in the U.S. Preparing Your Skin Before Surgery:
ST. JAMES HEALTHCARE DECEMBER 2012 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWSLETTER INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Norovirus in Healthcare Settings The Impacts of Unsafe Medical Injections in the U.S. Preparing Your Skin Before Surgery:
Chapter 9: Infection Control
 Chapter 9: Infection Control Chapter 9: Infection Control Page 9-1 Table of Contents for Chapter 9 1.0 Introduction 2.0 General Information on Influenza 2.1 Influenza 2.2 Modes of Transmission 2.3 Communicability
Chapter 9: Infection Control Chapter 9: Infection Control Page 9-1 Table of Contents for Chapter 9 1.0 Introduction 2.0 General Information on Influenza 2.1 Influenza 2.2 Modes of Transmission 2.3 Communicability
