The City School. Prep Section. PAF Chapter. Science. 2 nd Term. Class 8. Worksheets for Intervention Classes
|
|
|
- Emma Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The City School PAF Chapter Prep Section Science 2 nd Term Class 8 Worksheets for Intervention Classes
2 Science Class 8 RESPIRATION AND CIRCULATION Q1. What is respiration? What are the types of respiration? Q2. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Q3. What is the chemical equation to summarize aerobic respiration? Q4. What is the pathway of inhaled air? Q5. State the three features of alveoli. Q6. What happens to the diaphragm when one inhales and exhales air? Q7. Differentiate between inhaled and exhaled air. Q8. Define the mechanism of breathing? Q9. What is the blood circulatory system made up of? Q10. What are the three main kind of blood vessels which carry blood? Q11. What is the blood made up of? Q12. What is the function of the red blood cells in the body? Q13. What is the function of pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein? The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 2 of 10
3 The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 3 of 10
4 The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 4 of 10
5 Ecology Q1. What is a habitat? Q2. What is a population? Q3. What is a community? Q4. What is an abiotic environment made up of? Describe any three factors. Q5. What is hibernation? Q6. What is migration? Q7. What does aestivation mean? Q8. Why do organisms need to compete with each other? Q9. Why is co-operation important for organisms to survive? Q10. How do organism camouflage themselves? Q11. State and describe the kind of relationship that exists between a. Flea and dog b. Sea gull and turtle c. Strangler fig and host tree Q12. What is meant by the environment of an organism? Q13. Why do organism use mimicry? Q14. Define the following with examples a. Symbiosis b. Mutualism c. Parasitism Q15write down three ways in which the plants and animals in forest ecosystem interact with one another. The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 5 of 10
6 Food chains and Food webs Q1. What do you understand when you look at a food chain? Q2. Study the food chain below. Grass Cow lion (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) In which habitat will you find such a food chain? Name the producer. Where does it get its energy from? Name the prey and predator in the food chain. What does the arrow in the food chain represent? Q3. What is a food web? Q4. What does a food web show? Q5. Energy is being transferred in the form of food. Does the amount of energy transferred increase, decrease or remain the same along afood chain? Q6. What does the pyramid of number show? Q7. What are decomposers? Q8. What are the examples of decomposers? Q9. How do decomposers help the environment? Q10. What are producers and consumers? The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 6 of 10
7 Man s impact on the ecosystem Q1. State those human activities which can cause air pollution. Q2. What are the bad effects caused by pollution? Q3. What do you understand by global warming? Q4. What can be the consequences of global warming? Q5. There are different types of water pollutants. State the four types. Q6. Define the following terms (i) (ii) (iii) Acid rain Green house effect Global warming Q7. How will global warming affect you personally? What can be done to reduce the effects of global warming? Q8. How will the damaged fur and feathers affect the survival of certain animals? Q9. If litter is thrown in water, would that create problems for the marine animals? How? Q10. What can be done to reduce the amount of rubbish been thrown away? Q11. If a new species is introduced in a habitat, would that create any problems? If so why would that happen? Q12. Define the following: (a) Over-hunting (b) Deforestation (c) Excessive use of energy Q13. What are the negative effects of deforestation? Q14. How can energy be conserved? Q15. How can we keep our environment clean and green? The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 7 of 10
8 MAGNETISM WORKSHEET 1 1. How would you label pole 1? 2. How would you label pole 2? Why? 3. How would you label poles 5 and 6? Why? 4. How could you use iron filings to tell which of two bar magnets is stronger? 5. What generalization can you make about the reaction between like poles? 6. What generalization can you make about the reaction between unlike poles? 7. The magnetic field is strongest near (the poles/the center) of a bar magnet. 8. Materials that can become magnetized include steel and (copper/iron). 9. The needle of a compass lines up with Earth's magnetic field and points to (Earth's poles/earth's equator). 10. Magnetic field lines that curve toward each other show (repulsion/attraction). Directions: Match the following terms with the correct descriptions below. a) Compass b) electromagnet c) magnetism d) magnetic field 12. imaginary lines of force around a magnet 13. a force created through a magnetic field 14. a magnetic needle that is free to turn 15. a current-carrying wire wrapped around an iron core The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 8 of 10
9 Worksheet for Sound & Hearing Internal Structure of the Human Ear Pinna the outer portion of the external ear: sound travels through the outer ear to the ear canal. Auditory Canal the open passage through which sound waves travel to the middle ear. Eardrum a taut, circular piece of skin that vibrates when hit by sound waves. Malleus (Hammer), Incus (Anvil), Stapes (Stirrup) tiny bones that vibrate to amplify sound waves. These are the smallest bones in the body. Eustachian Tube the passageway that connects the ear to the back of the nose to maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum. Cochlea coiled, fluid-filled structure of the inner ear that contains hair cells called cilia. Cilia sway in response to sound waves, transmitting signals toward the brain. Semicircular Canals fluid-filled structures in the inner ear that detect movement and function as balance organs. Auditory Nerve bundle of nerve cells that carry signals from the sensory fibers to the brain. Read the above passage thoroughly and answer the following questions: Q1. Where is the malleus found? (middle ear) Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Where can cilia be found? (cochlea) What's the most important part of the ear for maintaining balance? (semicircular canal) What structures vibrate in response to sound waves? (eardrum, incus) Our ears "pop" on airplanes because of pressure changes. What structure makes it possible for the pressure inside our ears to return to normal? (eustachian tube) What structure transmits sound signals to the brain? (auditory nerve) The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 9 of 10
10 Starter activity for Sound & Hearing #1 Demonstrate how the eardrum works with this simple activity. Have students stretch plastic wrap tightly over the opening of a large bowl or pot and sprinkle a teaspoon of rice over the plastic. Ask students to clap their hands close to the plastic wrap. They may also try to create louder noises (such as banging a metal cookie sheet or pan). What happens to the rice? #2 Explain that sounds travel in waves. Those waves make the plastic wrap vibrate, similar to the way that your eardrum vibrates in response to sound. The rice "jumps" when the plastic wrap vibrates. Like the rice, the tiny bones of the middle ear move in response to vibrations in the eardrum. #3 Tell students that they will begin putting together their ear accordion models. The first step is cutting the three pieces of paper along the black lines. Your students will then tape or glue the pieces together to make one strip (III.#1). Afterward, the students should fold the paper like an accordion along the dotted lines so that the outer ear is at the top. The City School /PAF Chapter / Prep Section / Worksheet for Intervention Class /Science/Class 8 Page 10 of 10
Draw a cross section of the human ear and label its parts.
 Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
Human Ear 1. Open the Human Ear session and follow the instructions. 2. Complete the Human Ear worksheet as you progress through the session. Draw a cross section of the ear and label its parts. 3. Using
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
AND THE EARS HAVE IT! (1 Hour)
 (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
(1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 3 Grade Range: K-2 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will explore the nature of human hearing by attempting to determine the location at different locations
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
2 Sensing the Environment
 CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
CHAPTER 17 2 Sensing the Environment SECTION Communication and Control California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.5.g, 7.6.b BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE
 2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
2. Drumming on My Ear BUILD KNOWLEDGE INTRODUCTION What Students Do in this Activity Students learn more about the form that sound waves take and how humans hear sound. They build a model of a human eardrum
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
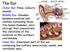 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye. Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin
 Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT
 HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? - UNDERSTANDING HUMAN SENSORS AND COMPARING THEM WITH THOSE IN A ROBOT (50 MINUTES) PRE/POST- ASSESSMENT SHEET HOW DO HUMAN SENSORS WORK? 1. What sensors or senses do we humans
Norwood Science Center
 Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Norwood Science Center Energy Grade 5 Background Information: The sense of hearing involves the ear, the auditory nerve, and a special center within the brain. We hear because our ears respond to vibrations
Essential questions. What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2
 Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears.
 Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Sound Travels How sound travels is explained and demonstrated using a spoon and some string to get the vibrations, then sound, to the students ears. Grade Level Used This activity was done with 4 th graders.
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Physics
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 Index No:- 1) Which is necessary for producing a sound? a) air
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 Index No:- 1) Which is necessary for producing a sound? a) air
Unit 3 Lesson 3 How Do Cells Work Together? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
How Cells Are Organized Cells are organized to work together so the body functions smoothly. How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 1 How do cells work together? Classwork 1: Question 2 Organ
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
 Chapter 50 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 50 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Sound Workshop. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum
 Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Sound Workshop a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. What is sound Longitudinal Waves Frequency and pitch Hearing ranges Sounds in solids, liquids and gases Sound in a vacuum Echoes Ultrasound Loudspeakers
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab
 Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
is the clear, transparent part at the front of the eye. It allows light to enter the eye and it also refracts (focuses) the light onto the retina.
 Senses- Vision Light is a small part (1/70th) of the total electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The EM band extends from radio waves at one extreme to x-rays at the other. The eye detects light and converts
Senses- Vision Light is a small part (1/70th) of the total electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The EM band extends from radio waves at one extreme to x-rays at the other. The eye detects light and converts
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
The Nature of Sound. Section 1: What Is Sound? (p. 534)
 CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
CHAPTER 21 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET The Nature of Sound As you read Chapter 21, which begins on page 532 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Would You Believe...? (p. 532) 1. What did Marco
Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations
 secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
Our Sense Organs Ears
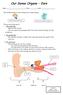 Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Our Sense Organs Ears Name: Class: Date: Ears enable people to hear things and to keep balance. This boy can hear with his ear. This boy s ears help him to balance. The ear has three parts: 1. The Outer
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Sound. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 _ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
_ Sound Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. _ 1. Sound is a disturbance that travels through a medium as a a. longitudinal wave. b. surface wave.
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY
 Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Become a good listener LESSON PLAN / MARCH 2015 SPONSORED BY WHO KNOWS WHAT HEARING IS? Hearing, auditory perception, or audition is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations, changes in the
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871 Unit 4: Anatomy and physiology for health and social care Monday 15 January 2018 Morning Time allowed:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871 Unit 4: Anatomy and physiology for health and social care Monday 15 January 2018 Morning Time allowed:
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date
 Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date Study Guide You must know: The location and function of several types of sensory receptors. How skeletal muscle contracts. Cellular events that lead
Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date Study Guide You must know: The location and function of several types of sensory receptors. How skeletal muscle contracts. Cellular events that lead
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees. Leader s Guide ERI Safety Videos
 3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
3882 Hearing Conservation Training for Employees Leader s Guide 2008 ERI Safety Videos HEARING CONSERVATION TRAINING FOR EMPLOYEES This easy-to-use Leader s Guide is provided to assist in conducting a
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
LESSON ASSIGNMENT , Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the:
 Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Sound Waves. Making Sound Waves
 Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Benchmarks SC.B.1.3.6 Annually Assessed (pp. 195, 197): The student knows the properties of waves; that each wave consists of a number of crests and troughs; and the effects of different media on waves;
Sensing the Environment
 2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
2 Sensing the Environment Key Concept Your organ systems have specialized structures and functions to sense and gather information. What You Will Learn Pressure, temperature, pain, and vibration are four
FUNNELS OF SOUND. Activity Pack. Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears. Neurosciences and Mental Health
 FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
FUNNELS OF SOUND Activity Pack Description: Duration of Activity: Age: Topic: Key words: Resources: Related Activities: Explore how sound travels using ear defenders and funnels to create giant ears No
Sound and hearing 2 The outside of the ear. Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears
 Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
Sound and hearing 1 How sounds get to our ears 1. What are some of the sounds you would hear if you were camping on a quiet night? 2. How would you feel if you couldn t hear anything? When you listen to
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Speech Generation and Perception
 Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Senses- Ch. 12. Pain receptors- respond to tissue damage in all tissues except in the brain
 Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Sound Waves. Sound waves can only travel through matter. The energy carried by a sound wave is transferred by the collisions between the
 Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Sound Waves Making Sound Waves How does the motion of a drummer s drumsticks produce sound waves? The impact of the sticks on the head of a drum causes the drum head to vibrate. These vibrations transfer
Producing and Detecting Sound
 Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Sound Producing and Detecting Sound What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
What is otosclerosis?
 What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
TASTE: Taste buds are the sense organs that respond to gustatory stimuli. Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals broken down from food in the saliva
 UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Chapter 2. The Senses
 Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Chapter 2. The Senses 2.1 Sensory Receptors (p.25-27) sensory receptors - specialized nerve cells whose function is to collect information about changes in the surrounding environment. sensory organs -
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA. Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002
 Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Hearing Conservation for Children
 Hearing Conservation for Children How Loud is too Loud? 160 db Jet Airplane DANGER ZONE 150 db Helicoptor 140 db Rock Concert 130 db Ambulance Siren 120 db School Dance 110 db Power Saw 100 db Cement Mixer
Hearing Conservation for Children How Loud is too Loud? 160 db Jet Airplane DANGER ZONE 150 db Helicoptor 140 db Rock Concert 130 db Ambulance Siren 120 db School Dance 110 db Power Saw 100 db Cement Mixer
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri
 JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
JEOPARDY How do Human Sensors Work? Center for Computational Neurobiology, University of Missouri Robot Router Sensors Modes Touch Human WAN WAN Router Sight Sound & Sensors Encapsulation Services Basics
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
Biological Psychology Unit Two AE Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Vision How do our brains make 3-D images out of 2-D inputs? We live in a 3-dimensional world, but each of our eyes is only capable
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION
 SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
SENSATION & PERCEPTION Sensation and perception result from a symphony of sensory receptors and the neurons those receptors communicate with. The receptors and neurons fire in different combinations and
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Treatment of glue ear with grommets
 Treatment of glue ear with grommets Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about glue ear, how it can be treated using grommets and
Treatment of glue ear with grommets Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust This leaflet explains about glue ear, how it can be treated using grommets and
