Michigan Ear Institute. Head Noise or Tinnitus.
|
|
|
- Joshua Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Michigan Ear Institute Head Noise or Tinnitus
2 DOCTORS Jack M. Kartush, MD Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Michael J. LaRouere, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent, MD, FACS Seilesh C. Babu, MD Eleanor Y. Chan, MD LOCATIONS Providence Medical Building Northwestern Highway Suite 101 Farmington Hills, MI Beaumont Medical Building 3535 W. Thirteen Mile Road Suite 444 Royal Oak, MI Oakwood Medical Building Oakwood Blvd. Suite 202 Dearborn, MI Providence Medical Center Providence Parkway Suite 130 Novi, MI phone fax 1
3 2
4 Welcome Welcome to the Michigan Ear Institute, one of the nation s leading surgical groups specializing in hearing, balance and facial nerve disorders. The Michigan Ear Institute is committed to providing you with the highest quality diagnostic and surgical treatment possible. Our highly experienced team of physicians, audiologists and clinical physiologists have established international reputations for their innovative diagnostic and surgical capabilities, and our modern, attractive facility has been designed with patient care and convenience as the foremost criteria. It is our privilege to be able to provide care for your medical problems and we will strive to make your visit to the Michigan Ear Institute a positive and rewarding experience. 3
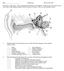
5 Head noise, or tinnitus, is common. It may be intermittent or constant, mild or severe, and vary from a low pitched roar to a high pitched type of sound like a whistle. It may be subjective (audible only to the patient) or objective (audible to others). It may or may not be associated with hearing impairment. Tinnitus is usually thought of as a symptom and not a disease. Just as pain in the arm or leg is a symptom and not a disease. Because the function of the auditory (hearing) nerve is to carry sound, when it is irritated from any cause, the brain interprets this impulse as noise. This phenomenon is similar to the sensation nerves elsewhere. A similar situation can occur in a patient who has pain from neuralgia. Their feeling of pain occurs because of irritation of the nerve and not because there is a problem where the nerve originates. Tinnitus may or may not be accompanied by a hearing impairment. Hearing is measured in decibels (db). A hearing level of 0 to 25 db is considered normal for conversational speech. HEARING MECHANISM In order to understand the possible causes of tinnitus, one must have some knowledge of the hearing mechanism. The mechanism is made up of five main divisions: the external ear, the middle ear, the inner ear, the nerve pathways and the brain. Right Ear Decibels Left Ear Decibels Conversion to degree of handicap 25 db 0% 55 db (Moderate) 45% 30 db (Mild) 8% 65 db (Severe) 60% 35 db (Mild) 15% 75 db (Severe) 75% 45 db (Moderate) 30% 85 db (Severe) 90% 4
6 External Ear The external ear consists of visible portion of the ear (auricle) and the external ear canal. These structures collect sound waves and transmit them to the eardrum. Middle Ear The middle ear lies between the eardrum and the inner ear. This air filled space contains three ossicles: the malleus, the incus and the stapes (hammer, anvil and stirrup). Vibrations of the eardrum are transmitted across the middle ear space by these three small bones. Movement of the stapes results in fluid waves in the inner ear. The middle ear chamber is lined by a membrane similar to the lining of the nose and contains secreting glands and blood vessels. This chamber is connected to the back of the nose by a narrow channel called the eustachian tube. The eustachian tube is usually closed but opens occasionally to maintain equal pressure between the middle ear chamber and the outside atmosphere, as evidenced by the popping sensation noted in the ear during altitude changes. 5
7 Inner Ear The inner ear is a fluid filled chamber enclosed in dense bone. It contains the tiny hearing cells and is lined by a delicate transparent membrane supplied by microscopic blood vessels. In the small chamber, fluid waves, resulting from movement of the stapes, are transformed into electrical impulses in the nerve. Nerve Pathways The electrical impulses created in the inner ear chamber are transmitted to the brain by the hearing nerve. The nerve pathways leading to the brain are enclosed in a small bony canal along with the nerve of balance and the nerve which stimulates movement of the facial muscle. Brain The hearing nerve pathways divide, as they reach the brain, into an inter-communicating system far more complex than the most extensive telephone exchange. Nerve impulses are then transformed into recognizable sound. Tinnitus Most tinnitus is audible only to the patient; this is called subjective tinnitus. Tinnitus audible to both the patient and others is called objective. Objective tinnitus may be due to muscle spasms in the middle ear or eustachian tube, or be due to abnormalities in the blood vessels surrounding the ear. Muscular Tinnitus Tinnitus may result from spasm of the two muscles attached to the hearing bones or from spasm of muscles attached to the eustachian tube, the channel which connects the middle ear to the back of the nose. There are two muscles in the middle ear: the stapedius, attached to the stapes bone (stirrup) and the tensor tympani, attached to the malleus bone 6
8 (hammer). These muscles normally contract briefly in response to very loud noise. On occasions one or both of these muscles may begin to contract rhythmically for no apparent reason, for brief periods of tone. Because the muscles are attached to one of the middle ear (hearing) bones these contractions may result in a repetitious sound in the ear. The clicking, although annoying, is harmless and usually subsides without treatment. Should the muscle spasm continue, medical treatment (muscle relaxants) or surgery (cutting the spastic muscle) may be necessary. Muscular tinnitus resulting from spasm from one of the various muscles of the throat attached to the eustachian tube is uncommon, but can also result in episodes of rhythmic clicking in the ear. This is called palatal myoclonus and usually responds to muscle relaxants. Vascular Tinnitus There are two large blood vessels intimately associated with the middle and inner ear; the jugular vein and the carotid artery. These are the major blood vessels supplying the brain. It is not uncommon to hear one s heart beat or to hear the blood circulating through these large vessels. This may be heard when an individual has a fever, a middle ear infection, or is engaging in strenuous exercise. The circulation sound in these instances is temporary and is not audible to others. On occasions the sound of blood circulation will become audible to others. This can be due to thickening of the blood vessel wall (a normal occurrence as one grows older), a kink in the vessel or an abnormal growth on the vessel wall. This pulsing sound can also be due to increased spinal fluid pressure. Further testing may be necessary to determine the cause and treatment indicated in these uncommon cases. 7
9 External Ear Tinnitus Obstruction of the external ear canal by wax, foreign bodies or swelling may produce a hearing impairment or pressure n the eardrum. This frequently results in a pulsating type of tinnitus. Middle Ear Tinnitus Disturbance of function of the middle ear may result from allergy, infection, injury, scar tissue or impaired motion of the three middle ear bones. These disturbances often result in hearing impairment and may lead to head noise. But there is no relationship between the degree of hearing loss and the intensity of the tinnitus Inner Ear Tinnitus Any condition which disturbs the inner ear chamber may produce head noise. This may be due to infection, allergy, or circulatory disturbances which produce changes not only in the fluid but also in the encasing membranes of the inner ear. Nerve Pathway Tinnitus The nerve pathways are the most delicate structures of the hearing mechanism. The small hair cells which serve to transform fluid waves into nerve impulses are analogous to the cells of the eye retina which transforms light waves into nerve impulses. The slightest swelling of interference with these delicate cells from any cause readily produces impairment of function and irritation. This may occur from a variety of causes: infection; allergic swelling; systemic diseases, either acute or chronic, with resultant toxic effects; sudden exposure to high noise levels in susceptible persons; certain drugs to which the patient may be sensitive; minute changes in the blood supply and changes in nutrition. Pressure changes may produce swelling both from outside and within the nerve as it transverses the 8
10 bony tunnel through which it passes to the brain. In these instances, the tinnitus occurs on one side of the head. The balance and facial nerves pass through this bony tunnel and can also be affected by the pressure. Rupture or spasm of one of the small blood vessels occurring anywhere in the auditory pathway produces pressure and interference with circulation. Consequently, sudden tinnitus, with or without partial or total loss of hearing function, may occur. If the blood clot is small it may absorb with little or no permanent changes. This condition, like the pressure phenomenon, occurs only on one side and because it has occurred once does not mean it would necessarily occur again either on the same or opposite side. Brain Tinnitus Any disturbance, whether due to swelling or pressure or interference with circulation, may occasionally involve one or more of the complex hearing pathways as they enter and terminate in the brain. In most of these instances the symptoms are localized to one ear, the other symptoms and signs develop which aid the doctor in determining the cause and location of the disturbance. HEARING IMPAIRMENT Head noise or tinnitus may or may not be associated with hearing impairment. After reviewing the many causes of this symptom it is easy to understand why the hearing may at times be affected when tinnitus is present. If a hearing loss co-exists with tinnitus, the severity of the head noise is not an index as to the future course of the hearing impairment. Many persons with tinnitus have the erroneous fear they are going to lose their hearing. This is an unnecessary fear. 9
11 TREATMENT If the examination reveals a local or general cause of the hear noise, correction of the problem may alleviate the tinnitus. In most cases, however, there is no medical or surgical treatment which will eliminate tinnitus. General Measures 1 Make every effort to avoid nervous anxiety, for this only stimulates an already tense auditory system. 2 Make every attempt to obtain adequate rest and avoid over fatigue. 3 The use of nerve stimulus is to be avoided. Therefore excessive amounts of coffee (caffeine) and smoking (nicotine) should be avoided. 4 Try to accept the existence of the head noise as an annoying reality and them promptly and completely ignore it as much as possible. 5 Tinnitus will not cause you to go deaf, will not result in your losing your mind or cause death, so immediately forget such distracting and terrifying thoughts. 6 Tinnitus is usually more marked after one goes to bed and his surroundings become quiet. Any noise in the room, such as a loud ticking clock or radio, will serve to mask the irritating head noise and make them much less noticeable. 7 If one sleeps in an elevated position with one or two pillows, less congestion to the head will result and the tinnitus may be less noticeable. 8 Sedatives of various types may be used occasionally for temporary relief. 10
12 Biofeedback Training Biofeedback training is effective in reducing the intensity of tinnitus in some patients. Treatment consists of biofeedback exercises, in hourly sessions, in which the patient learns to control circulation to various parts of the body and relax muscles attached to the head. When a patient is able to accomplish this type of relaxation tinnitus often subsides. Biofeedback exercises are not for all patients with tinnitus. Results of treatment have been good, however, in those individuals whose tinnitus is severe and interfering with daily activities or with sleep. Tinnitus Masking Tinnitus masking is based on the principle that an external noise can reduce or drown out the internal tinnitus. Sometimes common items such as radios or fans can be successful. Environmental sounds such as ocean waves or rainfall can be created by sound generators available at many stores. Specialized sound generators are available that create specific tones based on an individuals tinnitus. Tinnitus Adaptation Most of those affected by tinnitus will adapt over time and be much less aware of the sound. Specific techniques such as tinnitus retraining therapy are available to promote changes in perception over time. They can be very successful. Medications A variety of medications are available to treat tinnitus. Although none of these are true cures they can be beneficial in various situations. Some of the medications have direct effects on the tinnitus and some have indirect effects such as controlling frustration or sleep disruption associated with the tinnitus. 11
13 SUMMARY The auditory (hearing) pathway is one of the most delicate and sensitive mechanisms of the human body. Since it is directly associated with the general nervous system, its responses are in direct proportion to the anxiety of the person involved. In order for any treatment of tinnitus or head noise to be successful, it is imperative that the patient have a thorough understanding of this distressing symptom complex. 12
14 13
15 14
16 Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant Received by Patient Signature Date 15
17 16
18 For more information on the services and staff of the Michigan Ear Institute, call us at (248) or visit our web site at Michigan Ear Institute Providence Medical Building Northwestern Highway #101 Farmington Hills, MI (248) phone (248) fax Revised 08/2010
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Head Noise or Tinnitus www.michiganear.com 15-56111-089 BOOK Head Noise and Tinnitus.indd 1 2/13/18 10:41 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute Head Noise or Tinnitus www.michiganear.com 15-56111-089 BOOK Head Noise and Tinnitus.indd 1 2/13/18 10:41 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Otosclerosis www.michiganear.com 15-56111-109 BOOK Otosclerosis.indd 1 2/13/18 10:33 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent,
Michigan Ear Institute Otosclerosis www.michiganear.com 15-56111-109 BOOK Otosclerosis.indd 1 2/13/18 10:33 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS Eric W. Sargent,
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary
 X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
X-Plain Tinnitus Reference Summary Introduction Tinnitus causes a person to hear a persistent sound in the ear when no sound exists. According to the American Tinnitus Association, at least 12 million
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Chronic Ear Infections www.michiganear.com 15-56111-104 BOOK Chronic Ear Infections.indd 1 2/13/18 10:21 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute Chronic Ear Infections www.michiganear.com 15-56111-104 BOOK Chronic Ear Infections.indd 1 2/13/18 10:21 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Doctor, what causes the noise in my ear?
 Doctor, what causes the noise in my ear? What causes tinnitus? The noise in the ears that only you can hear is called tinnitus, a most common disorder. Some people hear a hissing in the ear, others a ringing
Doctor, what causes the noise in my ear? What causes tinnitus? The noise in the ears that only you can hear is called tinnitus, a most common disorder. Some people hear a hissing in the ear, others a ringing
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment
 INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
INTRODUCTION TO AUDIOLOGY Hearing Balance Tinnitus - Treatment What is Audiology? Audiology refers to the SCIENCE OF HEARING AND THE STUDY OF THE AUDITORY PROCESS (Katz, 1986) Audiology is a health-care
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com 15-56111-103 BOOK Cochlear Implant.indd 1 2/13/18 10:25 A WELCOME Welcome to the Michigan Ear Institute, one of the nation s leading surgical
Michigan Ear Institute Cochlear Implant www.michiganear.com 15-56111-103 BOOK Cochlear Implant.indd 1 2/13/18 10:25 A WELCOME Welcome to the Michigan Ear Institute, one of the nation s leading surgical
THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist
 WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
WHY AM I HERE? HEARING & THE BRAIN THE EAR Dr. Lily V. Hughes, Audiologist Fairbanks Hearing & Balance Center at the ENT Clinic 1 out of every 5 adults has hearing loss. That s more than 48 million people
The bloom guide to better hearing. Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide
 The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
The bloom guide to better hearing Find out what you need to know about hearing loss and hearing aids with this helpful guide Let us help you find the best solution for your hearing Coming to terms with
The ear: some applied basic science
 Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science The pinna The external ear or pinna is composed of cartilage with closely adherent perichondrium and skin. It is developed from six tubercles of the first
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Learning about Tinnitus
 Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals 4 What is that sound in your ears? 5 What causes tinnitus? 6 Tinnitus and your brain 7 What
Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals 4 What is that sound in your ears? 5 What causes tinnitus? 6 Tinnitus and your brain 7 What
Surgery for Conductive Hearing Loss
 THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
THE NEW YORK OTOLARYNGOLOGY GROUP, P.C. The Ear, Nose and Throat Specialists Neil M. Sperling, M.D. Otology/Neuro-Otology Diseases of the Ear Facial Nerve Balance Disorders Surgery for Conductive Hearing
Learning about Tinnitus
 Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals!........................................... 4 What s that ringing in my ears?........................................
Learning about Tinnitus Guide to help you understand and manage your tinnitus Content Your health and your goals!........................................... 4 What s that ringing in my ears?........................................
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
What is otosclerosis?
 What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
What is otosclerosis? The term otosclerosis describes a condition of abnormal growth in the tiny bones of the middle ear, which leads to a fixation of the stapes bone. The stapes bone must move freely
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing Loss. How does the hearing sense work? Test your hearing
 Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Hearing Loss You may have hearing loss and not even be aware of it. People of all ages experience gradual hearing loss, often due to the natural aging process or long exposure to loud noise. Other causes
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Ear Disorders and Problems
 Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Ear Disorders and Problems Introduction Your ear has three main parts: outer, middle and inner. You use all of them to hear. There are many disorders and problems that can affect the ear. The symptoms
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Presenter: Rytch Newmiller Accessibility Services Manager Grey Matters Conference 2015
 Presenter: Rytch Newmiller Accessibility Services Manager Grey Matters Conference 2015 Hearing Loss: More than Just an Inconvenience. Everything you need to know about Communicating with Seniors. Hearing
Presenter: Rytch Newmiller Accessibility Services Manager Grey Matters Conference 2015 Hearing Loss: More than Just an Inconvenience. Everything you need to know about Communicating with Seniors. Hearing
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA. Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002
 Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Pediatric Hearing Screening Training for the PCA Gouverneur Healthcare Services 227 Madison Street New York, NY 10002 Preface The purpose of any hearing screening program is to ensure early identification
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
Acquired Deafness Loss of hearing that occurs or develops sometime in the course of a lifetime, but is not present at birth.
 Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Page 1 of 5 URMC» Audiology Glossary of Terms A Acoustic Neuroma A tumor, usually benign, which develops on the hearing and balance nerves and can cause gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, and dizziness. Acquired
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Scrub In. What is the function of cerumen? Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal?
 Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Scrub In What is the function of cerumen? a. Keeps the ear canal from collapsing b. Helps transmit sound waves c. Protection d. Lubrication Which part of the ear collects sound waves and directs them into
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf
 Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Cochlear Implant The only hope for severely Deaf By: Dr. M. Sohail Awan, FCPS (ENT) Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi - Pakistan For centuries, people believed that only a miracle could restore hearing
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
THE MECHANICS OF HEARING
 CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
CONTENTS The mechanics of hearing Hearing loss and the Noise at Work Regulations Loudness and the A weighting network Octave band analysis Hearing protection calculations Worked examples and self assessed
The Human Ear. Grade Level: 4 6
 The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
The Human Ear Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Practice Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Give a blank sheet of paper,
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye. Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin
 Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
Two ears are better than one.
 Two ears are better than one. Two ears for a reason. Hearing with both ears, as nature intended, is called binaural hearing. It allows us to hear sounds accurately and more naturally. Especially in noisy
Two ears are better than one. Two ears for a reason. Hearing with both ears, as nature intended, is called binaural hearing. It allows us to hear sounds accurately and more naturally. Especially in noisy
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
The Sense Organs 10/13/2016. The Human Eye. 1. Sclera 2. Choroid 3. Retina. The eye is made up of three layers:
 The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
The human body gathers information from the outside world by using the five senses of: The Sense Organs 12.3 Sight Hearing Taste Smell Touch This information is essential in helping the body maintain homeostasis.
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
Hearing for life Facts about hearing. How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing
 Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
Hearing for life Facts about hearing How hearing works, how hearing fades and how to assist your hearing 3 Our hearing develops fully while we are still in the womb Our hearing is the only one of our senses
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
TASTE: Taste buds are the sense organs that respond to gustatory stimuli. Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals broken down from food in the saliva
 UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
3 Ear. Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance.
 3 Ear Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance. Common diseases of the ear In this chapter we will cover different
3 Ear Ear is a very important organ of human body which has two important roles comprising our organ of hearing and organ of balance. Common diseases of the ear In this chapter we will cover different
Hearing Aids. Bernycia Askew
 Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Hearing Aids Bernycia Askew Who they re for Hearing Aids are usually best for people who have a mildmoderate hearing loss. They are often benefit those who have contracted noise induced hearing loss with
Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871 Unit 4: Anatomy and physiology for health and social care Monday 15 January 2018 Morning Time allowed:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Level 3 Cambridge Technical in Health and Social Care 05831/05832/05833/05871 Unit 4: Anatomy and physiology for health and social care Monday 15 January 2018 Morning Time allowed:
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Audiology Lunch & Learn DR. BRANDI R. SHEPARD
 Audiology Lunch & Learn DR. BRANDI R. SHEPARD Professionally Practicing for 17 years Masters degree in 2003 I managed 5 hearing aid clinics 2005 Started my own Audiology Clinic 2007 Earned my doctorate
Audiology Lunch & Learn DR. BRANDI R. SHEPARD Professionally Practicing for 17 years Masters degree in 2003 I managed 5 hearing aid clinics 2005 Started my own Audiology Clinic 2007 Earned my doctorate
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Chapter Fourteen. The Hearing Mechanism. 1. Introduction.
 Chapter Fourteen The Hearing Mechanism 1. Introduction. 2. Hearing. 3. The Ear. 4. The External Ear. 5. The Inner Ear. 6. Frequency Discrimination. 7. The Organ of Corti. 8. Tests and Exrecises. 9. References.
Chapter Fourteen The Hearing Mechanism 1. Introduction. 2. Hearing. 3. The Ear. 4. The External Ear. 5. The Inner Ear. 6. Frequency Discrimination. 7. The Organ of Corti. 8. Tests and Exrecises. 9. References.
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Special Senses. Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition)
 Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
Special Senses Unit 6.7 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.7 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the five special senses. Identify the four general senses. Trace the pathway of light rays as they pass
LISTEN! You might be going deaf DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE
 LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
LISTEN! You might be going deaf OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH SERVICE 1 DEPARTMENT OF LABOUR TE TARI MAHI GET THE ANSWERS ABOUT HOW NOISE AFFECTS YOU. Issued by the Occupational Safety & Health Service,
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary
 photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
photo courtesy of Oticon Glossary 404.591.1884 www.childrensent.com American Sign Language (ASL): a manual language with its own word order and grammar, used primarily by people who are Deaf. Atresia (aural):
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Hearing Loss. Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions.
 Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Hearing Loss Understanding hearing loss, its effects and available solutions. Hearing loss is a very common health condition in adults but it is often unrecognised and untreated. Introduction Hearing loss
Glossary For Parents. Atresia: closure of the ear canal or absence of an ear opening.
 Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
Glossary For Parents This is not a complete or comprehensive glossary of audiologic and medical terms. It does include many technical and often unfamiliar terms that parents may hear used in connection
17.4 Sound and Hearing
 You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
You can identify sounds without seeing them because sound waves carry information to your ears. People who work in places where sound is very loud need to protect their hearing. Properties of Sound Waves
LESSON ASSIGNMENT , Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-9. TASK TAUGHT LESSON OBJECTIVES 081-833-0059, Irrigate an Obstructed Ear. After completing this lesson,
Speech Generation and Perception
 Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
Speech Generation and Perception 1 Speech Generation and Perception : The study of the anatomy of the organs of speech is required as a background for articulatory and acoustic phonetics. An understanding
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
HOW CAN I MANAGE MY TINNITUS?
 HOW CAN I MANAGE MY TINNITUS? Around 250 million people worldwide suffer from tinnitus. WHAT IS TINNITUS? Tinnitus is the perception of sounds or noise within the ears with no external sound source. These
HOW CAN I MANAGE MY TINNITUS? Around 250 million people worldwide suffer from tinnitus. WHAT IS TINNITUS? Tinnitus is the perception of sounds or noise within the ears with no external sound source. These
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss
 Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Diagnosing and Treating Adults with Hearing Loss Diana Callesano, Au.D., CCC-A Eric Nelson, Au.D., CCC-A Clinical Audiologists Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Hearing and Speech Services
Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise
 Department of Industrial Engineering Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise Learning outcomes After finishing this chapter, You should be able to Define the sound (physically) and how it
Department of Industrial Engineering Work Design and Industrial Ergonomics - Ear and Noise Learning outcomes After finishing this chapter, You should be able to Define the sound (physically) and how it
The Outer and Middle Ear PERIPHERAL AUDITORY SYSTEM HOW WE HEAR. The Ear in Action AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK. The 3 parts of the ear
 AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
AUDITORY NEUROPATHY: A CLOSER LOOK HOW WE HEAR The 3 parts of the ear The ear consists of three main parts: 1. The outer ear The part you see, which is called the auricle (ohr-a-kal). 2. The middle ear
managing safely Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23
 Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
Noise at Work Course Notes Mark Mallen Group Health and Safety Manager December 2005 Noise at Work: Version 1 Page 1 of 23 Course Content 1. What is noise? 2. Sound - Sound Waves 3. How do we hear? - The
Sensation and Perception. 8.2 The Senses
 Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Sensation and Perception 8.2 The Senses I. Introduction A. You probably think that you have just five senses: vision, hearing, taste, smell, and touch. In addition, people have two more internal senses:
Your ear consists of three parts that play a vital role in hearing-the external ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
 What is a Cochlear Implant? A cochlear implant is an electronic device that restores partial hearing to the deaf. It is surgically implanted in the inner ear and activated by a device worn outside the
What is a Cochlear Implant? A cochlear implant is an electronic device that restores partial hearing to the deaf. It is surgically implanted in the inner ear and activated by a device worn outside the
Senses- Ch. 12. Pain receptors- respond to tissue damage in all tissues except in the brain
 Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
