A Short-term Clinical Evaluation of Immediately Restored Maxillary TiOblast Single-Tooth Implants. Michael R. Norton, BDS 1
|
|
|
- Harvey Archibald Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Short-term Clinical Evaluation of Immediately Restored Maxillary TiOblast Single-Tooth Implants Michael R. Norton, BDS 1 Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the short-term clinical outcome of single-tooth implants placed in the maxilla and immediately restored using cementless friction-fit temporary crowns. Materials and Methods: Twenty-five patients consecutively referred to a private specialist practice for the replacement of failing or missing maxillary teeth were treated by means of immediate temporization of their single-tooth implants. Where teeth were still present, implants were placed immediately following extraction. Provisional crowns were fabricated on a special friction-fit coping by means of autopolymerizing acrylic resin. Definitive crowns were placed a mean of 4.5 months after surgery. Implant survival was recorded along with the level of the marginal bone relative to a fixed reference point 1 year after placement. Any adverse soft tissue changes were also noted. Results: A total of 28 Astra Tech ST dental implants were placed. The overall survival rate at the end of the study was 96.4% for implants which were in function for periods ranging from 15.7 to 27 months. One patient, a smoker, lost 1 implant within 1 month of surgery. Mean marginal bone loss was 0.40 mm (range 0 to 1.53 mm) 1 year after placement of the implants. Many implants (37.5%) had no observed bone loss. No implants or crowns have been lost during the functional loading period. One implant was associated with an unfavorable recession of soft tissues; however, most maintained an esthetic gingival architecture. Eleven of 28 provisional restorations needed treatment; 6 required replacement during the temporization period, and 5 required cementation because of looseness. The ease of removal of the crowns allowed regular access for irrigation with chlorhexidine and thus maintenance of soft tissue health. Discussion: The need to provide provisional restorations for single-tooth gaps often presents challenges. An immediate temporary partial denture or adhesive prosthesis may be unacceptable or impractical. The current study describes a simple method for the immediate temporization of single-tooth implants. The results did not indicate any negative influence on osseointegration or shortterm survival once the implants were functionally loaded. Conclusion: Immediate temporization of maxillary single-tooth implants can be both safe and predictable, and it appears that the procedure can yield favorable soft tissue esthetics. INT J ORAL MAXILLOFAC IMPLANTS 2004;19: Key words: immediate placement, single-tooth implants, temporization The application of endosseous implants for the restoration of single missing teeth is widely accepted and has been reported in a number of studies 1 5 that suggest a predictable outcome. Some of these studies 2 5 have been published with longterm data, a basic criterion for demonstrating the success of an implant. 1 Specialist in Surgical Dentistry, Private Practice, London, United Kingdom; Visiting Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Marquette University School of Dentistry, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Correspondence to: Dr Michael R. Norton, 98 Harley Street, London W1G 7HZ, United Kingdom. Fax: drnorton@nortonimplants.com The option of implants for the replacement of teeth has been a valuable addition to established conventional methods; however, the time required for treatment, the need for additional surgical procedures, and particularly the need for indefinite periods of temporization are obstacles that occasionally result in patients deciding against implantbased treatment. Based on the aforementioned concerns, treatment of the edentulous mandible was advanced by the introduction of 1-stage surgery with an immediate loading protocol. Studies using this protocol 6 8 were able to demonstrate success rates ranging from 85% to 100%. These studies emphasized the need for cross-arch splinting to provide protection against micromotion of the implants, which can result in early failure. However, in subsequent investigations 274 Volume 19, Number 2, 2004
2 Table 1 Individual Patient Data Time between Tooth surgery and final Immediate/ Time since Mo in Bone loss Patient Age Sex position* restoration (mo) healed surgery (mo) function (mm) Complications DF 58 M 7 (12) 3 I Recession VW 30 F 6 (13) 2 H SH 33 F 8 (11) 5 H KC 41 F 10 (22) 3 H TE 58 M 10 (22) 4 I HW 67 F 7 (12) 7 I JS1 61 F 12 (24) 4 H (25) I NS 46 M 8 (11) 3 I MH 37 M 8 (11) 5 H CB 39 F 10 (22) 4 I JS2 51 F 8 (11) 3 H BC 42 M 8 (11) 6 H TB 62 M 8 (11) 7 H (21) I OG 65 F 5 (14) 4 H CM 40 M 9 (21) 3 I JH1 50 F 7 (12) 5 H (21) I VM 72 F 9 (21) 3 I BB 58 F 9 (21) H Failure MD 33 M 8 (11) 4 I JH2 45 M 9 (21) 8 I SZ 41 F 8 (11) 7 H LC 36 F 9 (21) 5 I DH 27 M 8 (11) 5 I EI 70 F 7 (12) 4 I AP 42 F 10 (22) 4 I Mean Total number of implants = 28 (16 immediate, 12 healed); total number of patients = 25 (10 men, 15 women). *Universal tooth numbering system used with FDI system numbers in parentheses. Immediately loaded/healed site. Congenitally absent. Excluded from the calculation of the mean data. evaluating the outcome for individual unsplinted implants with respect to immediate restoration, 9 12 implant survival rates ranged from 80% to 100% with up to 5 years of follow-up. Interpretation of these studies, however, requires careful assessment of the reported results. Although a majority of these studies have included the words immediate loading or immediately loaded in their titles, the implants in these studies have not been subjected to direct functional loading, since all fixed provisional restorations were carefully relieved of both centric and excursive occlusal contacts. It is therefore misleading to describe these implants as being immediately loaded. A more accurate description would be immediately restored or immediately temporized. Nonetheless, unsplinted implant-supported restorations are still potentially subject to micromotion, and in this respect, these studies are of considerable interest. The current study was designed to take advantage of the standard components of the Astra Tech implant system (Astra Tech, Lexington, MA), in which friction-fit copings could provide retentive cores for provisional restorations. The implant system used for this study has been well documented using conventional protocols, 3,5 with reported survival rates up to 100%. The primary objective of this study was to investigate a quick and relatively inexpensive technique to allow for the fabrication of nonfunctional but esthetic provisional restorations for the immediate temporization of implants. The survival rate and marginal bone response were determined. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients were recruited between June 2000 and November Individual patient data are shown in Table 1. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 275
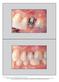
3 Fig 1 Surgery can be performed through the socket without raising a mucoperiosteal flap. Fig 2 For healed sites, a palatocrestal-scalloped incision was used to recreate the gingival architecture. The prospective inclusion criteria for the study were: Systemic health Absence of local purulent infection Teeth for extraction not be tender to percussion Adequate bone volume to receive an implant mm 5 mm bone apical to the extraction socket Grafting limited to circumferential socket defects Primary fixation at 25 Ncm Twenty-five patients were consecutively treated. All had acceptable systemic health. Patients diagnosed with diabetes were excluded, but smokers were included. Ten men and 15 women with a mean age of 48.2 years (range of 27 to 72 years) were referred for the replacement of missing teeth and/or extraction of failing teeth, typically the result of periodontal disease, endodontic failure, root fracture, or trauma. Sixteen teeth required extraction. The other 12 sites in the sample were completely healed. Ten were the sites of previous extractions (n = 10); 2 of the sites were congenitally absent of teeth (Table 1). All patients, after being informed about the treatment protocol, signed an informed consent form. The experimental nature of the protocol was emphasized. When requested by the patient, surgery was conducted under intravenous sedation; otherwise, all procedures were conducted under local anesthetic. Amoxicillin (or an equivalent for penicillin-allergic patients) was used as an antibiotic prophylaxis. Patients were given 3 g preoperatively and then 250 mg 3 times daily for 5 days postoperatively. All patients were asked to rinse with a 0.2% wt/vol chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash (Corsodyl; GlaxoSmithKline, Maidenhead, United Kingdom) for 1 minute preoperatively and then twice a day for 1 minute for 1 week postoperatively. Extractions were facilitated by means of a periotome and gentle elevation, and every effort was made to ensure maintenance of the labial cortical plate. All extraction sockets were thoroughly debrided with aggressive curettage prior to the immediate placement of implants. The implant osteotomy was performed through an apicopalatal aspect to avoid perforation of the labial/buccal plate. Limited flap elevation or flapless surgery (Fig 1) was employed whenever possible. However, if a labial/buccal concavity was noted clinically or there was a concern for breach of the integrity of the cortical plate, a mucoperiosteal flap was elevated to allow visual inspection during osteotomy preparation. Similar parameters were employed in healed sites, where a minimal flap design involved a palatocrestal scalloped incision with sulcular relief, allowing careful elevation of the intact papillae to expose the ridge crest and create a scalloped architecture on the labial aspect (Fig 2). For healed sites, osteotomy preparation followed the manufacturer s protocol, as previously described. 1 For extraction sites, the conical drill was employed only when the socket diameter was less than the diameter of the head of the implant (diameter 4.5 mm, n = 18; diameter 5.0 mm, n = 10). In some patients, the palatal location of the implant required flaring of the palatal cortical plate only. The preparation was completed to ensure that the top of the implant could be located approximately 0.5 to 1.0 mm below the crestal bone, approximately 4.0 mm below the free gingival margin. Implants were self-tapping. The osteotomy was prepared with a diameter 0.3 mm less than the diameter of the apical portion of the implant so that the implant compressed the bone slightly. A torque driver set at 25 Ncm was used to evaluate primary stability 276 Volume 19, Number 2, 2004
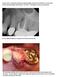
4 Fig 3a The prefabricated Astra Tech ST abutment in situ, with visible retention grooves and anti-rotational octagon. Fig 3b The friction-fit plastic impression coping was used as a core for the temporary crown. The retention tags have been cut off. Fig 3c This clinical photograph was taken 1 week postoperatively and demonstrates the temporary crown in the maxillary left central incisor position made from a denture tooth bonded to the core with autopolymerizing acrylic resin. Fig 3d The definitive restoration at the 1-year review. of the implant. This torque was based upon a small test series of 3 implants using the resonance frequency analysis instrument (Ostell; Integration Diagnostics, Göteborg, Sweden), which indicated that when inserted with a torque of 25 Ncm, the implant stability quotient (ISQ) value of these implants was equivalent to that expected for an osseointegrated implant (ISQ 60). It was also the level of torque that the manufacturer recommended be applied to the abutment screw when seating the prefabricated single-tooth abutment (Astra Tech) (Fig 3a). To detect and prevent unfavorable rotation of the implant, the abutment was secured through a mounting sleeve that allowed manual detection of rotation. Any implants found to have rotational stability less than 25 Ncm were excluded from the study. After abutment connection, a prefabricated friction-fit plastic coping was reduced and shaped to create a core, which was placed over the abutment, engaging the octagon for mechanical retention (Fig 3b). A provisional autopolymerized acrylic resin crown could then be fabricated over the coping. Initially, this procedure involved the use of shell- Fig 3e One-year review radiograph of implant. Note the bone level at the top of the implant, which is close to the microgap on the distal aspect. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 277
5 Fig 4 The definitive all-ceramic Procera crown at the site of the maxillary right canine in patient VW at the 1-year review. formers filled with Trim acrylic resin (Harry J. Bosworth, Skokie, IL). However, due to degradation of the esthetic appearance of these crowns over a period of 4 months, this technique was discontinued in favor of using carefully matched denture teeth, hollow ground to create veneers, which were then bonded to the coping with the Trim acrylic resin (Fig 3c). The denture veneer maintained a long-lasting luster and resisted staining. Staining had been a problem with the autopolymerized provisional restorations. The provisional crowns were carefully contoured and polished to achieve proper emergence profile and adaptation to the gingival tissues, to ensure congruence with the scalloped gingival architecture, and to provide the appropriate support to the interdental papillae. Furthermore, the occlusion was adjusted to relieve all centric and excursive contacts, thus avoiding any direct functional loading. Patients were advised of the vulnerability of the implants during the first 2 months postplacement and were strongly advised to refrain from applying loading force to them. Sutures were avoided whenever possible, but when indicated a 6/0 Prolene monofilament was employed (Ethicon W8005; Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson, Somerville, NJ). Patients were examined 1 week postoperatively to remove sutures and to assess the stability of both the provisional crowns and the implants. Subsequently, all patients were seen 1 month postoperatively and monthly thereafter for removal of the friction-fit crown to allow direct assessment of implant stability and to provide the opportunity to irrigate the submucosal peri-implant sulcus with 0.2% wt/vol chlorhexidine solution. In addition, a 1% chlorhexidine gel (Corsodyl; GlaxoSmithKline) was applied to the inside of the crowns, which were then reseated. This gel can leach out over time, helping to enhance the health of the peri-implant tissues. All patients were either referred back to their dental practitioner for restoration or restored by the author approximately 4.5 months after surgery with either a metal-ceramic or an all-ceramic crown (Procera; Nobel Biocare, Göteborg, Sweden) (Figs 3 and 4). Standardized intraoral radiographs were taken using a Rinn device (Dentsply-Rinn, Elgin, IL) prior to the cementing of the definitive restoration and again at the annual recall. Only the most recent radiograph was used to record the change in bone levels, which was measured under 8 magnification from the reference point at the top of the implant, which coincides with the microgap at the implantto-abutment junction. Measurements to the bone crest at the mesial and distal points of the implant were facilitated by the knowledge that this reference point is 0.7 mm from the first Microthread and that the pitch of the Microthread is mm. The mesial and distal bone loss figures were averaged for each implant, and the mean for the total group data was calculated. RESULTS The time to complete the same-day procedures, including extractions where indicated, implant placement, and temporary crown fabrication ranged from 60 to 90 minutes. Implant lengths ranged from 11 to 17 mm, with the majority (79%) being 13 or 15 mm in length. The abutment length selected was the shortest available (Astra notation = 0.0 mm) in all but one case (patient AP received a 1.0-mm abutment), yielding a crown margin 1.0 mm above the top of the implant. For the 25 patients in the study, abutments were tightened to 25 Ncm, and all received an esthetically acceptable provisional restoration fabricated on the same day. For an additional 8 patients, it was not possible to achieve rotational stability at 25 Ncm, and these patients and their implants were excluded from the study. One patient presented at the 1-month review complaining of mobility. She habitually protruded her mandible and thus had difficulty avoiding loading the provisional crown. The implant was assessed as being both rotationally and axially unstable and was subsequently removed. This implant was successfully replaced and restored using a 2-stage submerged protocol. 278 Volume 19, Number 2, 2004
6 Twelve all-ceramic and 16 metal-ceramic definitive crowns were placed a mean of 4.5 months after surgery (range from 2 to 8 months), with any delayed placement resulting from the appointment schedule of the referring dental practitioner or patients scheduling conflicts. Definitive crowns have been in function for a mean of 15.7 months (range 8 to 27 months); implants have been in situ for a mean of 20.3 months (range 13 to 30 months). No further implant failures were detected during the study period, yielding a survival rate of 96.4%. Two patients permanently relocated and were lost to follow-up. However, both patients received their definitive crowns. A radiograph taken at the time of crown insertion showed no evidence of marginal bone loss. These 2 implants, along with the 1 implant failure and 1 implant in a patient unable to attend her 1-year review because of illness, have been excluded from the mean marginal bone loss data. For the remaining 24 implants in 21 patients, radiographs taken at least 1 year after surgery were available for assessment (Fig 3e). The mean marginal bone loss from the time of implant placement, as measured from the reference point at the top of the implant, was 0.40 mm (range 0 to 1.53 mm). Bone loss occurred with 62.5% of the implants. Bone was recorded at or even above the implantabutment junction in more than one third of the implants. Any positive bone levels with respect to the reference level were recorded as zero bone loss so as to not positively influence the data. The only other adverse event to be recorded during the study was an undesirable recession of the soft tissues and gingival margin from around 1 implant and the juxtaposing teeth in 1 patient. This was attributed to the deep placement of the implant and an unfavorable labial inclination of the implant/crown complex, which may have resulted in an unacceptable amount of pressure on the labial soft tissues. Although the esthetic result was poor, both the marginal bone levels and the implant stability remained unchanged. DISCUSSION With increasing awareness of dental implants, more patients are demanding treatment with implantsupported restorations over conventional alternatives. The only significant obstacles perceived by the patients to this treatment have been the long treatment times, the need for multiple surgical procedures and in some cases, the inconvenience of an undesirable temporary restoration and cost. The relatively recent introduction of an immediate loading protocol has removed many of these obstacles, since the typical delay to placement of an implantsupported restoration is effectively eliminated, only 1 surgical procedure is required, and the patient benefits from not having to wear a removable or bonded provisional restoration. Many of the early studies on immediate loading were based upon restoration of the edentulous mandible, where bone density is known to be favorable and cross-arch splinting is possible to minimize micromovement, which can be a principal cause of early implant failure. 6 8 The desire to overcome these obstacles has also led to further studies investigating the outcome for immediately loaded implants in the maxilla for both splinted and unsplinted implants. 13 Other studies have also reported specifically on the survival of single-tooth implants with provisional restorations placed on the day of surgery These implants, the majority of which were placed in the maxilla, were not splinted and were therefore potentially subject to micromovement and overload. Although many of these articles misleadingly imply in their titles that the implants were immediately loaded, close scrutiny of the methodology reveals that in most cases the provisional restorations were kept clear of functional contacts. This current report supports the small group of studies confirming that it is possible to obtain short-term implant survival equivalent to that reported using 2-stage conventional protocols (96.4%). The marginal bone change at 24 implants was evaluated from radiographs taken a minimum of 1 year (range 13 to 30 months) after implant placement, and a mean of 15.7 months after insertion of the definitive crowns (range 8 to 27 months). The bone level was measured relative to the location of the reference point at the top of the implant, which was always placed at or just below the crest of the ridge. Bone loss was measured this way because implants were not subject to a second surgical procedure. Any initial changes in bone levels were not the result of further surgical trauma such as occurs between the time of exposure and definitive crown placement, but were the result of the physiologic response to the immediate restoration of the implants and any microbial influence through the peri-implant sulcus or microgap. The change represents the total change in bone height over the short-term healing period and is therefore a more exacting evaluation of the marginal bone response around this implant, which the manufacturer claims has specific bone-maintaining features, ie, the TiOblast surface and the Microthread, The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 279
7 which are applied to the entire length of the implant. 14 Certainly the high frequency of implants with no recorded marginal bone loss (37.5%) and the low mean marginal bone loss (0.40 mm) would seem to support this claim, especially when all positive bone levels with respect to the reference level were recorded as zero. These findings contribute to the controversy surrounding the current theory that bone cannot be maintained closer than 1 to 2 mm from the microgap, 15 since the reference point for Astra Tech implants is at the level of the microgap. The empirical use of torque to determine the suitability of an implant for a same-day restoration technique, from the perspective of immediate primary stability, was based upon a small test series of 3 implants using a resonance frequency analysis instrument (Ostell, Integration Diagnostics). In this test it was noted that when an implant was resistant to rotation at 25 Ncm, the ISQ was 60, which is close to that reported for an osseointegrated implant. 16 The ability to fabricate a simple yet esthetically effective provisional crown was appreciated by all the patients, since no impressions were required, no laboratory time or cost was incurred, and in all but 1 patient, an esthetic outcome was obtained. It was apparent that the contour of the provisional crown could be used to maintain the gingival architecture and ensure appropriate support of the free gingival margin and the interdental papillae. The use of autopolymerizing resin intraorally did not appear to cause any adverse reactions by the soft tissues. The use of a friction-fit coping proved invaluable, since this eliminated the need for cementation and allowed the regular removal of the crown for submucosal irrigation with chlorhexidine and ongoing assessment of the supporting implant. In addition, the adjunctive application of a chlorhexidine gel inside the temporary crown proved beneficial for the maintenance of tissue health between visits. However, it was noted that 6 crowns required replacement because the plastic coping split over time, and another 5 crowns were eventually cemented in place as the result of persistent looseness. At no time did any crown become so loose that aspiration was a risk; however, this 39% complication rate is cause for some concern. A small amount of temporary cement used at insertion of the provisional crown could have reduced this figure. The implants in the current study were definitively restored a mean of 4.5 months after surgery, 12 with all-ceramic Procera crowns (Nobel Biocare). No complications have occurred with any of the definitive crowns. CONCLUSION In this patient population, using this treatment approach, the Astra Tech ST implant system was reliable and predictable for immediate implant placement and restoration with provisional acrylic resin crowns in the short term. The use of a friction-fit acrylic resin provisional crown fabricated chairside allowed for close adaptation to the gingival architecture and optimal tissue health, related in part to the ability to regularly remove the crown for submucosal irrigation with chlorhexidine. The close relationship between the marginal bone level and the so-called microgap warrants further investigation and consideration. The application of a rough surface and retention elements to the top of this implant contrasts with the designs of other implants, which have a smooth, machined collar. In combination with the Astra internal conical connection, this may explain the maintenance of crestal bone. With a survival rate of 96.4% and a mean marginal bone loss of 0.40 mm after a mean of 15.7 months in function, the clinical survival rate is comparable to short-term results achieved using the more conventional 2-stage implant protocol. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The author is a consultant to Astra Tech, Mölndal, Sweden. The present study, however, was carried out as an independent, nonfunded study. REFERENCES 1. Norton MR. The Astra Tech single tooth implant system: A report on 27 consecutively placed and restored implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997;17: Henry P, Laney W, Jemt T, et al. Osseointegrated implants for single-tooth replacement: A prospective 5-year multicenter study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1996;11: Palmer RM, Palmer PJ, Smith BJ. A 5-year prospective study of Astra single tooth implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 2000;11: Andersson B, Ödman P, Lindvall A-M, Brånemark P-I. Cemented single crowns on osseointegrated implants after 5 years. Results from a prospective study on CeraOne. Int J Prosthodont 1998;11: Norton MR. Biologic and mechanical stability of singletooth implants: 4- to 7-year follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2001;3: Randow K, Ericsson I, Nilner K, Petersson A, Glantz P-O. Immediate functional loading of Brånemark implants. An 18-month clinical follow-up study. Clin Oral Implants Res 1999;10: Volume 19, Number 2, 2004
8 7. Schnitman PA, Wöhrle PS, Rubenstein JE, Da Silva JD, Wang N-H. Ten-year results of Brånemark implants immediately loaded with fixed prostheses at implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Tarnow DP, Emtiaz S, Classi A. Immediate loading of threaded implants at stage 1 surgery in edentulous arches: Ten consecutive case reports with 1- to 5-year data. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Ericsson I, Nilson H, Lindh T, Nilner K, Randow K. Immediate functional loading of Brånemark single tooth implants. An 18 months clinical pilot follow-up study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2000;11: Chaushu G, Chaushu S, Tzohar A, Dayan D. Immediate loading of single-tooth implants: Immediate versus nonimmediate implantation. A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Cooper L, Felton DA, Kugelberg CF, et al. A multicenter 12-month evaluation of single-tooth implants restored 3 weeks after 1-stage surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Andersen E, Haanaes HR, Knutsen BM. Immediate loading of single-tooth ITI implants in the anterior maxilla: A prospective 5-year pilot study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2002; 13: Becker W, Becker BE, Israelson H, et al. One-step surgical placement of Brånemark implants: A prospective clinical multicenter study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Hansson S. The implant neck: Smooth or provided with retention elements. A biomechanical approach. Clin Oral Implants Res 1999;10: Tarnow DP, Cho SC, Wallace SS. The effect of interimplant distance on the height of the inter-implant bone crest. J Periodontol 2000;71: Balleri P, Cozzolino A, Momicchioli G, Varriale A. Stability measurements of osseointegrated implants using Ostell in partially edentulous jaws after 1 year of loading: A pilot study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2002;4: The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 281
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Hiron Andreaza da Cunha, MS 1 /Carlos Eduardo Francischone, DMD 2 /Hugo Nary Filho, DDS 3 / Rubelisa Cândido Gomes de Oliveira, BDS 4
 A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation
 Clinical Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation Pär-Olov Östman 1 Immediate implant loading has become an attractive option for meeting
Clinical Using immediate implant placement to address aesthetic and biomechanical challenges: A clinical presentation Pär-Olov Östman 1 Immediate implant loading has become an attractive option for meeting
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
Initial findings and treatment plan
 12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
Providing patients with optimal esthetics remains
 Volume 78 Number 4 Case Series Optimizing the Esthetic Potential of Implant Restorations Through the Use of Immediate Implants With Immediate Provisionals Brien V. Harvey* Background: Few things in clinical
Volume 78 Number 4 Case Series Optimizing the Esthetic Potential of Implant Restorations Through the Use of Immediate Implants With Immediate Provisionals Brien V. Harvey* Background: Few things in clinical
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Immediate function or immediate
 Immediate function with dental implants Immediate function or immediate loading is defined as the placement of a dental implant fixture, abutment and functional (provisional) restoration all at stage one
Immediate function with dental implants Immediate function or immediate loading is defined as the placement of a dental implant fixture, abutment and functional (provisional) restoration all at stage one
Areview of recent studies concerning molar. Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report
 Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5
 Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Case Series. Early Functional Loading at 5 Days for Brånemark Implants Placed into Edentulous Mandibles: A Prospective, Open-Ended, Longitudinal Study
 Early Functional Loading at 5 Days for Brånemark Implants Placed into Edentulous Mandibles: A Prospective, Open-Ended, Longitudinal Study William Becker,* Burton E. Becker, and Scott Huffstetler Background:
Early Functional Loading at 5 Days for Brånemark Implants Placed into Edentulous Mandibles: A Prospective, Open-Ended, Longitudinal Study William Becker,* Burton E. Becker, and Scott Huffstetler Background:
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study
 immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Rehabilitating Anterior Ridge Defect with Implant Supported Prosthesis Using Bone Graft and Customized Abutment
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Rehabilitating Anterior Ridge Defect with Implant Supported Prosthesis Using Bone Graft and Customized Abutment
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space
 C A S E R E P O R T Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space Michael Kristensen 1 This case report describes the application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9 mm implant
C A S E R E P O R T Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space Michael Kristensen 1 This case report describes the application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9 mm implant
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Special reprint from
 Special reprint from Copyright 2007 by Quintessence Publ Co, Inc Volume 27 Number 5 October 2007 451 Fig 1d (left) View of the 1.3-mm twist drill preparing the osteotomy for implant placement. Fig 1e
Special reprint from Copyright 2007 by Quintessence Publ Co, Inc Volume 27 Number 5 October 2007 451 Fig 1d (left) View of the 1.3-mm twist drill preparing the osteotomy for implant placement. Fig 1e
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
Implant dentistry has provided predictable
 Inside CONTINUING EDUCATION ENDODONTICS RESTORATIVE Unique Benefits of Immediate Implants with Immediate Provisional Restoration Outcome analytics from 26 years of documentation David A. Gelb, DDS ABSTRACT
Inside CONTINUING EDUCATION ENDODONTICS RESTORATIVE Unique Benefits of Immediate Implants with Immediate Provisional Restoration Outcome analytics from 26 years of documentation David A. Gelb, DDS ABSTRACT
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Immediate Loading of Brånemark System Implants Following Placement in Edentulous Patients: A Clinical Report
 Immediate Loading of Brånemark System Implants Following Placement in Edentulous Patients: A Clinical Report Katsuhiro Horiuchi, DDS, PhD 1 /Hiroya Uchida, DDS 2 / Kazuhiko Yamamoto, DDS, PhD 3 /Masahito
Immediate Loading of Brånemark System Implants Following Placement in Edentulous Patients: A Clinical Report Katsuhiro Horiuchi, DDS, PhD 1 /Hiroya Uchida, DDS 2 / Kazuhiko Yamamoto, DDS, PhD 3 /Masahito
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
INTRODUCTION. General Information. Important Warning
 S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
The CMC approved a motion to accept all editorial action requests that remain on the consent calendar 21 Yea / 0 Nay / 0 Abstain
 PAGE 1 OF 14 Editorial Actions One or more member organizations requested that the following editorial action submissions be removed from the consent calendar and addressed individually: #s 4, 7, 8, 9,
PAGE 1 OF 14 Editorial Actions One or more member organizations requested that the following editorial action submissions be removed from the consent calendar and addressed individually: #s 4, 7, 8, 9,
SCD Case Study. The ability of the integrated implant to bear a load must be greater than the anticipated load during function.
 SCD Case Study Dental implants offer an effective and predictable way to replace teeth. Function, aesthetics and phonetics are regained. The long-term success clinically and aesthetically depends upon
SCD Case Study Dental implants offer an effective and predictable way to replace teeth. Function, aesthetics and phonetics are regained. The long-term success clinically and aesthetically depends upon
While the protocol for direct bone-to-implant
 Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
INTRODUCTION. Jun-Won Hong 1, DDS, MS, Seung-Geun Ahn 1, DDS, PhD, Dae-Ho Leem 2, DDS, PhD, Jae-Min Seo 1 *, DDS, MS
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1045 CASE REPORT Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 Mitha M Shetty, 2 Akshai KR Shetty, 3 N Kalavathy,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1045 CASE REPORT Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 Mitha M Shetty, 2 Akshai KR Shetty, 3 N Kalavathy,
MINI System CASE REPORT. Name: Dr. Achraf Souayah Na<on: Tunisia
 MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Case Report Early Loading of Single-Piece Implant for Partially Edentulous Posterior Arch: A Prospective One-Year Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 854062, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/854062 Case Report Early Loading of Single-Piece Implant for Partially Edentulous Posterior Arch: A Prospective
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 854062, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/854062 Case Report Early Loading of Single-Piece Implant for Partially Edentulous Posterior Arch: A Prospective
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodonticstown. Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites. clinical. Table I
 Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Hex-Lock Abutment System. Restorative Manual
 System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly.
 Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations
 Clinical A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations Pär-Olov Östman 1 Prosthetic rehabilitation of the edentulous patient with implant-supported restorations is a commonly
Clinical A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations Pär-Olov Östman 1 Prosthetic rehabilitation of the edentulous patient with implant-supported restorations is a commonly
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
NobelActive. Quick start page 5. Surgical procedures page 8. Prosthetic procedures page 28. Appendix IV cleaning and. sterilization page 66
 NobelActive PROCEDURES AND PRODUCTS Quick start page 5 Surgical procedures page 8 Prosthetic procedures page 28 Appendix IV cleaning and sterilization page 66 Product catalog page 68 Important aspects
NobelActive PROCEDURES AND PRODUCTS Quick start page 5 Surgical procedures page 8 Prosthetic procedures page 28 Appendix IV cleaning and sterilization page 66 Product catalog page 68 Important aspects
SURGICAL MANUAL. Step By Step Techniques
 SURGICAL MANUAL Step By Step Techniques TABLE OF CONTENTS PRE-SURGICAL 1 8 MEASUREMENT OF BONE.......................... 2 BONE CLASSIFICATION........................... 3 IMPLANT SIZE SELECTION.........................
SURGICAL MANUAL Step By Step Techniques TABLE OF CONTENTS PRE-SURGICAL 1 8 MEASUREMENT OF BONE.......................... 2 BONE CLASSIFICATION........................... 3 IMPLANT SIZE SELECTION.........................
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients
 52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Surgical Manual. Step By Step Techniques
 Surgical Manual Step By Step Techniques Table of Contents Pre-Surgical 1 8 Measurement of Bone 2 Bone Classification 3 Implant Size Selection 4 5 Surgical Template Fabrication 6 8 Instrumentation 9 11
Surgical Manual Step By Step Techniques Table of Contents Pre-Surgical 1 8 Measurement of Bone 2 Bone Classification 3 Implant Size Selection 4 5 Surgical Template Fabrication 6 8 Instrumentation 9 11
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
INTRODUCTION. long-term results in the restoration of both totally and partially
 CLINICAL RESTORATION OF THE SOFT-TISSUE MARGIN IN SINGLE-TOOTH IMPLANT IN THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Jamil Awad Shibli, DDS, MS, PhD Susana d Avila, DDS, MS KEY WORDS Dental implants Subepithelial connective
CLINICAL RESTORATION OF THE SOFT-TISSUE MARGIN IN SINGLE-TOOTH IMPLANT IN THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Jamil Awad Shibli, DDS, MS, PhD Susana d Avila, DDS, MS KEY WORDS Dental implants Subepithelial connective
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Immediate Loading of Single-Tooth Implants in the Posterior Region
 Immediate Loading of Single-Tooth Implants in the Posterior Region Marcus Abboud, Dr Med Dent 1 /Bernd Koeck, Prof Dr Med Dent 2 /Helmut Stark, Prof Dr Med Dent 3 / Gerhard Wahl, Prof Dr Med Dent 4 /Roswitha
Immediate Loading of Single-Tooth Implants in the Posterior Region Marcus Abboud, Dr Med Dent 1 /Bernd Koeck, Prof Dr Med Dent 2 /Helmut Stark, Prof Dr Med Dent 3 / Gerhard Wahl, Prof Dr Med Dent 4 /Roswitha
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
One-Piece Immediate-Load Post-Extraction Implant In Maxillary Central Incisor
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. XIII (March. 2017), PP 78-83 www.iosrjournals.org One-Piece Immediate-Load Post-Extraction
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. XIII (March. 2017), PP 78-83 www.iosrjournals.org One-Piece Immediate-Load Post-Extraction
NARROW DIAMETER implant
 ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
ND NARROW DIAMETER implant TABLE OF CONTENTS ND - NARROW DIAMETER implant Implant characteristics page 04 Dental implant page 05 Open Tray Impression Transfer page 06 Titanium Abutments page 07 O-Ball
MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants
 A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP, Glenn J. Wolfinger, DDS, FACP, Daniel Wulc, & Stephen F. Balshi, MBE Institute for Facial Esthetics,
A Prospective Analysis of Immediate Provisionalization of Single Implants Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, FACP, Glenn J. Wolfinger, DDS, FACP, Daniel Wulc, & Stephen F. Balshi, MBE Institute for Facial Esthetics,
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
soft-tissue regrowth. Pre-treatment. Implants placed with surgical guide for cemented crowns through the incisal edges.
 Extraction of #7 and 8 with Immediate Astra A discussion among dental professionals on the message boards of Dentaltown.com. A terrific case from Dr. Scott Erikson that takes you through the entire process
Extraction of #7 and 8 with Immediate Astra A discussion among dental professionals on the message boards of Dentaltown.com. A terrific case from Dr. Scott Erikson that takes you through the entire process
Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement
 Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement By Robert Margeas, DDS Research on the preservation of the tissue architecture, reduction of surgical sequences and greater aesthetic
Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement By Robert Margeas, DDS Research on the preservation of the tissue architecture, reduction of surgical sequences and greater aesthetic
Case Report - Dr. Arthur Weiss
 High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
