(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,065 B2 Kopelman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006
|
|
|
- Jonathan Cox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent US B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,065 B2 Kopelman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR DEFINING A FINISH LINE 5,372,502 A 12/1994 Massen et al. OF A DENTAL PROSTHESIS 5,417,572 A 5/1995 Kawai et al. 5,880,962 A 3/1999 Andersson et al. (75) Inventors: Avi Kopelman, Ramat Chen (IL); E. f ck : eral TOOf 163 W-1 OS 3. Eldad Taub, Reut (IL) 6,575,751 B1 6/2003 Lehmann et al. (73) Assignee: Cadent Ltd., Or Yehuda (IL) 2003/ A1* 11/2003 der Zel ,223 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this WO WO , 1997 past l S.S. yed under 35 W. WOOOO8415 2, 2000 * cited by examiner (21) Appl. No.: 10/623,707 Primary Examiner Cary E. O'Connor (22) Filed: Jul. 22, 2003 (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Nath & Associates PLLC; Gregory B. Kang: Derek Richmond (65) Prior Publication Data 57 ABSTRACT US 2005/ A1 Apr. 14, 2005 (57) A computer-based prosthodontic method is provided, for Related U.S. Application Data enabling a dental practitioner to define a finish line of a (60) Provisional application No. 60/397672, filed on Jul. dental prosthesis of at least one tooth to be fitted over a tooth 22, sy as preparation. The method comprises the following steps: s providing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data relating to (51) Int. Cl. the patient s dentition, the 3D data includes data represen A6C 5/II ( ) tative of the Surface topology of the preparation and its (52) U.S. Cl A213 Surroundings; generating first finish line data representative (58) Field of Classification Search 433/213 of at least a portion of the finish line and Superimposing an "433/ image of the finish line on an image of the dentition; See application file for complete search histo s obtaining second finish line data determined on the basis of pp p ry. input received from a dental practitioner; and using the (56) References Cited second finish line data to update the first finish line data and U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Superimposing the updated data on the dentition image ,928 A * 7/1990 van der Zel... 29, Claims, 4 Drawing Sheets Provide 3D teeth model 510 Generate partial/complete finish line 520 Receive dentist input 530 Update Finish line and 3D teeth model 550 Generate virtual Crown data 560
2
3 U.S. Patent US 7,112,065 B2 JOSS000Jeff 09ZOZ JOSS30OJE
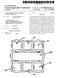
4 U.S. Patent Sep. 26, 2006 Sheet 3 of 4 US 7,112,065 B2 Provide 3D teeth model 310 Generate partial/complete finish line 320 Receive dentist input 330 Update Finish line and 3D teeth model 340 F.G. 3 72A 72B 70 FG. 4
5 U.S. Patent Sep. 26, 2006 Sheet 4 of 4 US 7,112,065 B2 Provide 3D teeth model 510 Generate partial/complete finish line 520 Receive dentist input 530 Update Finish line and 3D teeth model 550 Generate virtual Crown data 560 F.G. 5
6 1. METHOD FOR DEFINING A FINISH LINE OF A DENTAL PROSTHESIS This application claims benefit of U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 60/ filed Jul. 22, 2002, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety. FIELD OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to the filed of prosthodontics. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION An artificial dental prosthesis such as a crown covers portions of a tooth surface and is normally fabricated away from the patient s mouth, in a lab, and then installed in the mouth by the dentist. The artificial crowns are prepared based on a working cast (also known by the term master cast'). It is on the cast that all the technical steps leading to the completed restoration must be performed. In preparing artificial crowns, best mechanical compatibility between the abutment tooth (here inafter referred to as the preparation) and the crown is desired, to ensure complete imperviousness of the restored structure. Thus, the more precisely the working cast repro duces the anatomy of the mouth in the areas to be treated, the more accurate will be the spatial position as will be the static and dynamic relationships within the mouth after treatment. An accurate working cast is thus important to produce a biomechanically acceptable restoration. The precision of the cast depends on several factors, including, inter alia, the accuracy of the impressions and wax bites, the material from which the cast is constructed, and the identification of the anatomic contours and of the finish line (also referred to at times by the term chamfer line' and marginal line'), etc. The finish line, by definition, is the apical limit of the abutment tooth model (the preparation') and the margin of the reconstruction must end on it, i.e. it represents the point of transition between the biologic and artificial parts. Being able to identify the Zone that is apical to the finish line in absolute precision is fundamentally important for two reasons: (1) it allows to define the preparation limit with certainty, and (2) being intact, it maintains the anatomic characteristics of that tooth. According to current practice, after diagnosing that a patient needs a crown, the dentist cuts the tooth to be reconstructed and prepares two impressions and a wax bite of the patient's jaws. Based on the impressions, wax bite and on written instructions of the dentist, a technician prepares in a lab the corresponding cast, and the relevant tooth within the preparation is temporary separated from the plaster so that the area with the anatomic information (the area defin ing the anatomic contour) and the finish line are exposed. At this point, the finish line is manually marked by the lab technician in ink on the preparation, and this finish line is an important parameter used in constructing the crown. Alter natively, a virtual three-dimensional (3D) image of the working cast is obtained e.g. in a manner as described in international publication No. WO97/03622, or in interna tional publication No. WO00/08415, and the lab technician marks the finish line in the three dimensional environment. U.S. Pat. No. 5,417,572 discloses a computer-based method for extracting a finish line for designing an artificial crown. Amounts of variation of data representing the shape of an abutment tooth are determined, and a train of points is US 7,112,065 B extracted from the amounts of variation. Then a developed view of the surface shape of the abutment tooth is displayed, and the obtained train of points is also displayed in the developed view. The finish line for designing the artificial crown is determined, based on thus displayed train of points. There are times when the finish line is not clear and the transition between the cut area to the biological area is not well defined. In such cases the technician either estimate himself where the line is or returns the cast (or the 3D virtual model) to the dentist for him to complete the finish line. In other cases, the boundaries between the cut area and the natural area of the tooth are blurred such that only the dentist himself is able to assess the cut area (the so-called knife edges), and to define the finish line. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION According to one of its aspects, the present invention provides a computer-based prosthodontic method for enabling a dental practitioner (e.g. a dentist) to define a finish line of a dental prosthesis of at least one tooth to be fitted over a tooth preparation, comprising: (a) providing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data relating to the patient s dentition, the 3D data includes data representative of the Surface topology of said preparation and its Surroundings; (b) generating first finish line data representative of at least a portion of said finish line and Superimposing an image of said finish line on an image of said dentition; (c) obtaining second finish line data determined on the basis of input received from a dental practitioner, and (d) using said second finish line data to update said first finish line data and Superimposing the updated data on the dentition image. The updating of the first finish line data comprises defin ing a portion of the finish line not defined in the first finish line data or changing a portion of said first finish line data. According to another aspect, the present invention pro vides a computer-based method for constructing a crown to be fitted on a tooth preparation in a subject. The method comprises defining a finish line on the preparation to obtain finish line data and employing the finish line data in con structing the crown. The finish line is determined in a manner as defined above. The present invention is best implemented over a com puter network. Thus, according to yet another aspect, the present invention provides a computer-based system for enabling a dental practitioner to define a finish line of a dental prosthesis of at least one tooth to be fitted over a tooth preparation. The system comprises one or more central server utilities and a plurality of practitioner computerized machines connected to the server utility through a computer network, e.g. through the Internet. Said server utility comprises: (a) a processor, (b) a memory coupled to the processor for storing a three dimensional (3D) digital data relating to the patients dentition, the 3D data including data representative of the Surface topology of the preparation and its Surroundings; (c) a dedicated utility coupled to or integrated with the processor for generating a first finish line data represen tative of at least a portion of said finish line and Super imposing an image of said finish line on an image of said dentition; (d) a network interface coupled to the processor for trans mitter to a dental practitioner computerized device at least a portion of the 3D digital data and the first finish line data
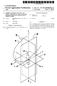
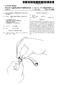
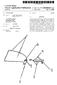
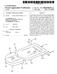
7 3 and for receiving from the practitioner device data rep resentative of a second finish line determined on the basis of practiotioner input, wherein the second finish line data is used to update the first finish line data. Said practitioner machine comprises: (a) a processor; (b) a display coupled to the processor for presenting digital data relating to the patient's dentition, the digital data includes data representative of the Surface topology of the preparation and its Surroundings and a first finish line data representative of at least a portion of a finish line. Such that the first finish line data is superimposed on the dentition image; (c) a user interface coupled to the processor for allowing entry of a dental practitioner input for the determination of a second finish line data, the second finish line data being used to update the first finish line data; and (d) a communication port coupled to the processor for receiving said digital data from a remote server utility and for conveying to the remote utility data relating to said updated first finish line data. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS In order to understand the invention and to see how it may be carried out in practice, preferred embodiments will now be described, by way of non-limiting examples only, with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. 1 shows, by way of a block diagram, a generalized system architecture in accordance with an embodiment of the invention. FIG. 2 shows, by way of a block diagram, a generalized system architecture in accordance with another embodiment of a system of the invention. FIG. 3 is a schematic flow chart of a method for defining and displaying a finish line in accordance with an embodi ment of the invention. FIG. 4 shows a three-dimensional virtual image con structed in accordance with the invention with a finish line shown on the applicable portion of a tooth preparation. FIG. 5 is a schematic representation of a flow chart showing the virtual construction of a crown to obtain digital crown data. FIG. 6 shows a three dimensional virtual image, similarly as FIG. 4, with an added crown. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The present invention provides a prosthodontic method that permits a dental practitioner (e.g. a dentist) to define a finish line on a tooth preparation. FIG. 1 is a general and schematic illustration of a computer-based system in accor dance with an embodiment of the present invention. The system 10 includes a server computer 100 and a number of client machines such as 110, which can be personal com puters. Each client computer communicates to the server computer 100 through a computer network 120 (e.g. Inter net, Intranet) or through a dedicated communication link. The server 100 includes, inter alia, a processor 130 and memory 140, which is coupled to the processor 130 for storing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data relating to the patient s dentition. The 3D data includes data representative of the Surface topology of the preparation and its Surround ings. A software utility 150 is further coupled to processor 130 or integrated with it, for generating data representative of at least a portion of said finish line. US 7,112,065 B Rather than drawing or marking by a lab technician the finished line on a working cast or in the virtual 3D envi ronment, the finish line is generated in the service center 100 and is conveyed, via the computer network 10, to the dentist 1 computer 110. Computer 110 includes, inter alia, a pro cessor 170, a display 180 and a user interface 190 for allowing presentation of the dentition image and for allow ing entry of the dentist input regarding the finish line, for updating the digital data. The updated data is then conveyed back to the service center 100 and is used by the crown construction utility 160 for the digital and physical construc tion of the desired crown. The construction and fabrication of the crown can be done in a CAD/CAM (Computer-aided design/computer-aided-manufacture) environment, utiliz ing for example, a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) device. The present invention is not limited to the exemplary architecture of FIG. 1 and other configurations can be implemented, for example as described in FIG. 2 in which like components to those shown in FIG. 1 are given same reference numerals shifted by 100. The main difference between the system 20 of FIG. 2 and system 10 of FIG. 1 is that the finish line utility 250 is integrated in the client computer. Such architecture, for example, allows the dentist (or his assistant) to obtain at the clinic, the 3D data that relates to the patient s dentition. The dentist is then able to view on the spot, an image of the patient s dentition and to define the finish line immediately or at a later stage. Accord ing to this scenario, the service center 200 is provided with the 3D data of the patient s dentition including the definition of the finish line. This data is then used to construct the COW. In both examples, the service center is provided with a finish line that is best defined by the dentist in accordance with his professional considerations, in a novel and a very efficient manner, without the need for further iterations between the lab technician and the dentist, as typically occurring in the hitherto working methodology. Reference is now being made to FIG. 3 showing, by way of a schematic blocked diagram, the steps for defining a finish line in a virtual three-dimensional teeth model. Fol lowing start, in step 310 a 3D teeth model of at least a portion of the teeth that includes the tooth preparation on which a crown is to be constructed is inputted. Then at 320 a first finish line is generated on the tooth preparation in a manual or a semi-automated or a fully automated manner. The first finish line is Superimposed on the dentition image and is displayed on a Suitable display medium. FIG. 4 shows an example of such a display. A tooth preparation 70 is seen with its neighboring teeth 72A and 72B with a finish line 74 drawn as a continuous line on the apical limit of tooth preparation. In addition to general physical structure of such a teeth model, the colors of the neighboring teeth 72A and 72B may be determined by the dentist and also be recorded to permit the technician to produce a crown that has a color resembling that of the neighboring teeth. In addition to general physical structure of Such a teeth model, the colors of the neighboring teeth 72A and 72B may be determined by the dentist and also recorded to permit the technician to produce a crown that has a color resembling that of the neighboring teeth. Turning back to FIG. 3, a second finish line data is obtained, after receiving the dentist input, at step 330. The second finish line data is used, in 340, for updating the first finish line data. The updating comprises defining a portion of the finish line not defined in the first finish line (for example,
8 5 in a knife edge case) or changing a portion of the first finish line. The updated data is further imposed on the dentition image. The three dimensional virtual teeth model includes at least the preparation, preferably the preparation with neighboring teeth. Typically, however, although not exclusively, the virtual teeth model includes also teeth of the jaw opposite the preparation region. Occasionally, although not necessar ily, the virtual teeth model may also include all teeth of both JaWS. The teeth model, and particularly the region thereof that includes the preparation, is typically manipulable Such that the virtual teeth model may be displayed and visualized from different angles. The data for the virtual teeth model may be obtained by a variety of methods, such as that described in PCT Appli cation No. PCT/IL96/00036 (publication No. WO97/03620) and in PCT Application No. PCT/IL99/00431 (publication No. WO00/08415). The virtual three-dimensional image may be manipulated, for example, in a manner described in PCT Application No. PCT/IL99/00577 (publication No. WO00/25677). The generation of the finish line data can be obtained in any of the known manners. For example, the finish line may be drawn by moving a cursor, by moving a stylus on a touch-sensitive screen or pad, etc. By another example, the line may be drawn by indicating a series of dots while the Software then automatically connects the dots into one continuous finish line. The finish line data can be also obtained in a fully automated manner, for example as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,417,572. Based on data indicating the 3D shape of the Surface of the preparation, a train of points in the margin area is determined by calculations, and the finish line is deter mined by plotting the train of points on a developed view of the Surface. In determining the train of points, a reference line (e.g. a central axis 22 of the 3D shape of the preparation is determined. Several crossing lines between the surface that includes the reference line and the curved plane con stituting the shape of the preparation are considered, and the distances between the reference line and corresponding points onto the crossing lines are calculated. Then the inclination between the adjacent points of the adjacent crossing lines is determined. Based on the above-explained calculation, the margin area is defined at a point where the variation of the inclination exceeds a certain value. Be the method of generating the finish line as it may be, the visual representation of the finish line data is associated with the visual representation of the 3D model such that the digital image of the model will include the finish line data. The dentist is then provided with a digital image of the patient s dentition that includes the generated finish line. This visual model can be rendered to the dentist in several manners. For example, the dentist is provided with a 3D image of the preparation and its Surroundings wherein the finish line is marked, for example, by a colored line. The dentist can be allowed to enlarge the image and to manipu late it for better viewing of the model. The dentist can further be provided with 2D images of cross-sections of the prepa ration. The dentist can input his instructions for example by moving a cursor to draw the finish line, by moving a stylus on a touch-sensitive screen or pad, etc. By another example, the dentist can indicates a series of dots onto the 3D or the 2D images, while the software then automatically connects the dots into one continuous finish line. US 7,112,065 B The finish line obtained according to the present invention may serve as an input in constructing a physical crown, preferably in a CAD/CAM environment. For example, the virtual image with the drawn finish line may be electroni cally transmitted to the lab that constructs the physical crown and when such image is displayed to the technician and based on Such a display, the technician may then identify the finish line on the working cast before him. The display is typically a computerized display provided with software permitting the technician to visualize the virtual image from different angles. As will be appreciated, the invention is not limited to any specific display means and any means for presenting the image Such as, for example, in a printed format, on a computer display screen, etc., may be employed in accordance with the invention. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, the technician may use a virtual model with the finish line marked therein by the dentist to construct a virtual crown to be fitted over the virtual tooth preparation. Once a good crown fitting is determined, the virtual crown so obtained may be used as guidance for constructing a real life physical crown. The guidance may be a visual guidance, although, in accordance with one embodiment, digital data representative of the three dimensional structure of the virtual crown is generated and this may be fed into a computer-controlled apparatus that automatically constructs the crown based on Such data. Reference is now being made to FIG. 5 showing, by way of a schematic blocked diagram, a method for the construc tion of a virtual crown to generate digital data representative of such a virtual crown. In FIG. 5, elements with the same function as in FIG. 3 were given the same reference numeral shifted by 200. After a finish line is defined by the dentist, (at 530) and associated with the 3D model (at 550), a virtual crown is constructed (at 550). This may be done manually, according to some embodiments, or may be an automatic procedure carried out by a dedicated software utility. Fol lowing Such construction, a virtual crown data is generated (at 560) and such data may then be exported to a CNC device for constructing a physical crown. Reference is now being made to FIG. 6. The same reference numerals used in FIG. 4 shifted by 20 are used to designate like components. As can be seen in FIG. 6, a virtual crown 96 is fitted on preparation 90. It should be understood that the methods of the present invention, as exemplified with reference to FIGS. 3 and 5. are best implemented in distributed systems, like the ones shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, but are not limited to the archi tectures shown hereto. It will also be understood that the system according to the invention may be a suitably programmed computer. Like wise, the invention contemplates a computer program being readable by a computer for executing the method of the invention. The invention further contemplates a machine readable memory tangibly embodying a program of instruc tions executable by the machine for executing the method of the invention. The invention claimed is: 1. A computer-based prosthodontic method for enabling a dental practitioner to define a finish line of a dental pros thesis of at least one tooth to be fitted over a tooth prepa ration, comprising: (One) providing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data relating to the patient s dentition, said 3D data includes data representative of the Surface topology of said preparation and its Surroundings;
9 US 7,112,065 B2 7 8 (Two) generating first finish line data representative of at employing said digital data to construct a physical crown least a portion of said finish line and Superimposing an for fitting on a tooth preparation in a patient. image of said finish line on an image of said dentition; 10. A server utility of a computer-based system, for (Three)obtaining second finish line data determined on enabling a dental practitioner to define a finish line of a the basis of input received from a dental practitioner; 5 dental prosthesis of at least one tooth to be fitted over a tooth and preparation, said utility comprising: (Four) using said second finish line data to update said (a) a processor; first finish line data and Superimposing the updated data on the dentition image. (b) a memory coupled to the processor for storing a 2. A method according to claim 1, wherein the updating of 10 three-dimensional (3D) digital data relating to the the first finish line data comprises defining a portion of the patient s dentition, the 3D data including data repre finish line not defined in said first finish line data or changing sentative of the Surface topology of the preparation and its Surroundings; a portion of said first finish line data. 3. A method according to claim 1, wherein the second (c) a dedicated utility coupled to or integrated with the finish line data is generated by virtually drawing a line at the 15 processor for generating a first finish line data repre apical limit of the preparation. sentative of at least a portion of said finish line and 4. A method according to claim 3, wherein the line is Superimposing an image of said finish line on an image drawn in a continuous fashion. of said dentition; and 5. A method according to claim 3, wherein the line is (d) a network interface coupled to the processor for drawn by marking dots in Small intervals and then forming 20 transmitter to a dental practitioner computerized device a line by automatically connecting the dots to one another. at least a portion of the 3D digital data and the first 6. A method according to claim 1, wherein the defined finish line data and for receiving from the practitioner finish line is used as an input in constructing a crown. device data representative of a second finish line deter 7. A computer-based method for constructing a crown to mined on the basis of practiotioner input, wherein the be fitted on a tooth preparation in a subject, the method 25 second finish line data is used to update the first finish comprising defining a finish line on said preparation to line data. obtain finish line data and employing said data in construct- 11. A computer-based program storage device readable by ing the crown; the method being characterized in that machine, tangibly embodying a program of instructions defining the finish line comprises: executable by the machine to perform method steps for (One) providing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data 30 constructing a crown to be fitted on a tooth preparation in a relating to the patient s dentition, said 3D data includes Subject, the method comprising defining a finish line on said data representative of the surface topology of said preparation to obtain finish line data and employing said preparation and its surroundings; data in constructing the crown; the method being character (Two) generating first finish line data representative of at ized in that defining the finish line comprises: least a portion of said finish line and Superimposing an 35 (a) providing a three-dimensional (3D) digital data relat image of said finish line on an image of said dentition; ing to the patient s dentition, said 3D data includes data (Three) obtaining second finish line data on a finish line representative of the Surface topology of said prepara determined on the basis of input received from a dental tion and its Surroundings; practitioner, and (b) generating first finish line data representative of at (Four) using said second finish line data to update said 40 first finish line data and Superimposing the updated data least a portion of said finish line and Superimposing an on the dentition image. image of said finish line on an image of said dentition; 8. A method according to claim 7, wherein a virtual image (c) obtaining second finish line data on a finish line of the preparation with a defined finish line is presented on determined on the basis of input received from a dental a suitable display medium. 45 practitioner, and 9. A method according to claim 7, comprising: (d) using said second finish line data to update said first constructing a virtual crown and virtually fitting said finish line data and superimposing the updated data on.. crown on said preparation in said virtual teeth; generating digital data representing the three dimensional the dentition image. structure of the virtual crown; k..
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8454.364B2 (12) United States Patent Taub et al. () Patent No.: US 8.454,364 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 4, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR PREPARING A
USOO8454.364B2 (12) United States Patent Taub et al. () Patent No.: US 8.454,364 B2 (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 4, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR PREPARING A
IHIH IIII. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,417, Date of Patent: May 23, Kawai et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KOpelman et al. USOO684.5175B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) DENTAL IMAGE PROCESSING METHOD 5,278,756 A 1/1994 Lemchen et al. AND SYSTEM 5,318,441.
(12) United States Patent KOpelman et al. USOO684.5175B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) DENTAL IMAGE PROCESSING METHOD 5,278,756 A 1/1994 Lemchen et al. AND SYSTEM 5,318,441.
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,049,743 Baba (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 11, 2000
 US006049743A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Baba (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 11, 2000 54 METHOD OF DESIGNING DENTAL Dental Materials and Appliances, vol. 8, Special Issue 14 PROSTHESIS MODEL
US006049743A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Baba (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 11, 2000 54 METHOD OF DESIGNING DENTAL Dental Materials and Appliances, vol. 8, Special Issue 14 PROSTHESIS MODEL
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.289,276 B2
 US009289276B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.289,276 B2 Fisker et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 22, 2016 (54) TOOLS FOR CUSTOMIZED DESIGN OF (52) U.S. Cl. DENTAL RESTORATIONS CPC... A61C
US009289276B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.289,276 B2 Fisker et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 22, 2016 (54) TOOLS FOR CUSTOMIZED DESIGN OF (52) U.S. Cl. DENTAL RESTORATIONS CPC... A61C
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(12) United States Patent
 US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
(12) United States Patent Clapp et al. US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 US B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1
 USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120258416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0258416A1 Tong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD TO DEFINE, MEASURE, AND Publication Classification
US 20120258416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0258416A1 Tong (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 11, 2012 (54) METHOD TO DEFINE, MEASURE, AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Hofmeister et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004O220691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hofmeister et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 700/98 CONSTRUCTING
(19) United States US 2004O220691A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hofmeister et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 4, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 700/98 CONSTRUCTING
United States Patent (19) Annoni
 United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160337769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0337769 A1 Siddhartha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) A METHOD FOR FITTING A HEARING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE AS WELL
(19) United States US 20160337769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0337769 A1 Siddhartha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) A METHOD FOR FITTING A HEARING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE AS WELL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
1 ADJUSTMENT THRESHOLD-N. United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. 5,660,184. Aug. 26, 1997 PATIENT'S HEARTBEAT PACEMAKEREVENT QRS DETECTION THRESHOLD
 United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060105287A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Wilburn (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2006 (54) DO-IT-YOURSELF ORTHODONTIC KIT AND Publication Classification METHOD (51)
(19) United States US 20060105287A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Wilburn (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2006 (54) DO-IT-YOURSELF ORTHODONTIC KIT AND Publication Classification METHOD (51)
United States Patent (19) Martin
 United States Patent (19) Martin 54 DENTAL INSTRUMENT 76 Inventor: James A. Martin, Wieand Rd., P.O. Box 77, Milford Square, Pa. 18935 21 Appl. No.: 831,321 22 Filed: Feb. 20, 1986 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Martin 54 DENTAL INSTRUMENT 76 Inventor: James A. Martin, Wieand Rd., P.O. Box 77, Milford Square, Pa. 18935 21 Appl. No.: 831,321 22 Filed: Feb. 20, 1986 Related U.S. Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2
 US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
III. United States Patent (19) Hess et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,584,802 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Hess et al. (54) ELASTIC KNEE-JOINT BANDAGE (75) Inventors: Heinrich Hess, Saarlouis; Wolfgang Krause, Kassel; Hans B. Bauerfeind, Kempen, all of Germany 73) Assignee: Bauerfeind
United States Patent (19) Hess et al. (54) ELASTIC KNEE-JOINT BANDAGE (75) Inventors: Heinrich Hess, Saarlouis; Wolfgang Krause, Kassel; Hans B. Bauerfeind, Kempen, all of Germany 73) Assignee: Bauerfeind
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1
 (19) United States US 2004O267527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1 Creamer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2004 (54) VOICE-TO-TEXT REDUCTION FOR REAL TIME IM/CHAT/SMS
(19) United States US 2004O267527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1 Creamer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2004 (54) VOICE-TO-TEXT REDUCTION FOR REAL TIME IM/CHAT/SMS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1. Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006
 US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
TEPZZ 85_Z 4A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8_Z 4A_T (11) EP 2 81 034 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (21) Application number: 1022.2 (1) Int Cl.: A61C /02 (06.01) A61C 19/04 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8_Z 4A_T (11) EP 2 81 034 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (21) Application number: 1022.2 (1) Int Cl.: A61C /02 (06.01) A61C 19/04 (06.01)
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee
 Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
(12) United States Patent
 US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
Simplant. Immediate Smile. featuring Atlantis Abutment, Clinical and laboratory procedures
 Simplant Immediate Smile featuring Atlantis Abutment, Clinical and laboratory procedures Contents Immediate Smile featuring Atlantis Abutment Product description 4 Advantages 5 Process at a glance 6 When?
Simplant Immediate Smile featuring Atlantis Abutment, Clinical and laboratory procedures Contents Immediate Smile featuring Atlantis Abutment Product description 4 Advantages 5 Process at a glance 6 When?
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
(51) Int Cl.: A61C 9/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7 6448B_T (11) EP 2 736 448 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.09.1 Bulletin 1/39 (21) Application number: 12747898.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 7 6448B_T (11) EP 2 736 448 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.09.1 Bulletin 1/39 (21) Application number: 12747898.0 (22)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2
 US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150254235A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254235 A1 Whitley (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) SIGN LANGUAGE TRANSLATION (57) ABSTRACT The instant
US 20150254235A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254235 A1 Whitley (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) SIGN LANGUAGE TRANSLATION (57) ABSTRACT The instant
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
(12) United States Patent Li et a].
![(12) United States Patent Li et a]. (12) United States Patent Li et a].](/thumbs/82/84922623.jpg) US008700126B2 (12) United States Patent Li et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COMPUTER AIDED SEPTAL DEFECT DIAGNOSIS AND SURGERY FRAMEWORK (75) Inventors:
US008700126B2 (12) United States Patent Li et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COMPUTER AIDED SEPTAL DEFECT DIAGNOSIS AND SURGERY FRAMEWORK (75) Inventors:
Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow
 Mirero Dental Clinic Dr. Jaemin Lee Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Patient, 32-year
Mirero Dental Clinic Dr. Jaemin Lee Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Patient, 32-year
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O156638A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0156638A1 Gantes (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2012 (54) ASSISTED DENTAL IMPLANT TREATMENT (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/29:
(19) United States US 2012O156638A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0156638A1 Gantes (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2012 (54) ASSISTED DENTAL IMPLANT TREATMENT (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/29:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113348 A1 Douskey et al. US 2015O113348A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) IMPLEMENTING MISR COMPRESSION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113348 A1 Douskey et al. US 2015O113348A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) IMPLEMENTING MISR COMPRESSION
3D Printing Technology ----Applications in Dentistry
 3D Printing Technology ----Applications in Dentistry Xingzhe Ding April 25, 2015 Agenda Introduction of - 3D printing technology - Dentistry Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry Challenges and Opportunities
3D Printing Technology ----Applications in Dentistry Xingzhe Ding April 25, 2015 Agenda Introduction of - 3D printing technology - Dentistry Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry Challenges and Opportunities
Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
(51) Int Cl.: A61C 11/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_8B_T (11) EP 1 18 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.11.12 Bulletin 12/46 (1) Int Cl.: A61C 11/00 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ Z_8B_T (11) EP 1 18 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.11.12 Bulletin 12/46 (1) Int Cl.: A61C 11/00 (06.01) (21) Application
Case Presentation PROSTHETIC PHASE
 Case Presentation This gentleman presents with the Chief complaint I don't like the space between my teeth and fact that my teeth aren't visible when I smile. I am also concerned that my teeth are wearing
Case Presentation This gentleman presents with the Chief complaint I don't like the space between my teeth and fact that my teeth aren't visible when I smile. I am also concerned that my teeth are wearing
76 Inventors: late Stella YErin, 5,479,944 1/1996 Petruson /858
 USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
4,883,072 11/1989 Bessler. 1288so mouth available for food and reducing the food intake.
 USOO5924.422A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,422 Gustafson (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54) ORAL DEVICE TO AID WEIGHT CONTROL Attorney, Agent, or Firm Donald A. Kettlestrings 76
USOO5924.422A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,924,422 Gustafson (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 1999 54) ORAL DEVICE TO AID WEIGHT CONTROL Attorney, Agent, or Firm Donald A. Kettlestrings 76
E. }2. E. 156/578 X mountant on the Slide to Spread evenly over the Slide with a
 USOO.5989386A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,989,386 Elliott (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54 COVERSLIPPICK-UP AND LAYDOWN 4,428,793 1/1984 Sato et al.. APPARATUS 4,455,188 6/1984 Stormby.
USOO.5989386A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,989,386 Elliott (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54 COVERSLIPPICK-UP AND LAYDOWN 4,428,793 1/1984 Sato et al.. APPARATUS 4,455,188 6/1984 Stormby.
Implant Studio Patient Case
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
(12) United States Patent
 USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1
 USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
&S 36 IHHHHHHHHHII 38' United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,240,414 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 31, Thompson
 United States Patent (19) Thompson 54 METHOD FOR SHADE SELECTION IN RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY 76 Inventor: Charles C. Thompson, Rt. 4, Box, Ellisville, Miss. 39437 (21) Appl. No.: 855 22 Filed: Jan. 5, 1993
United States Patent (19) Thompson 54 METHOD FOR SHADE SELECTION IN RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY 76 Inventor: Charles C. Thompson, Rt. 4, Box, Ellisville, Miss. 39437 (21) Appl. No.: 855 22 Filed: Jan. 5, 1993
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2
 USOO691.6338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2 Speziali (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SYNTHETIC LEAFLETS FOR HEART VALVE (51) Int. Cl."... A61F 2/06 REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT
USOO691.6338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2 Speziali (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SYNTHETIC LEAFLETS FOR HEART VALVE (51) Int. Cl."... A61F 2/06 REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008022721 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0227210 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) HOME TEST FOR GLYCATED ALBUMIN IN Publication Classification
US 2008022721 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0227210 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) HOME TEST FOR GLYCATED ALBUMIN IN Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) Tooth preparation for anterior fi xed partial denture (FPD)
 CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
inm sity aawaayawasa United States Patent (19) -l', all \ 2 27 Bl Cinquin 11 Patent Number: 5,865,171 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, g co m 2 BO
 United States Patent (19) Cinquin 54 NEBULIZER WITH PRESSURE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Gérard Cinquin, Villeneuve-sur-Lot, France 73 Assignee: System Assistance Medical, Villeneuve-Sur-Lot, France 21 Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Cinquin 54 NEBULIZER WITH PRESSURE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Gérard Cinquin, Villeneuve-sur-Lot, France 73 Assignee: System Assistance Medical, Villeneuve-Sur-Lot, France 21 Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0346.064A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0346064 A1 Schulhof et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR PRODUCING AONE-PIECE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016.0346.064A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0346064 A1 Schulhof et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 1, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR PRODUCING AONE-PIECE (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003
 US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
See the end from the beginning
 Staub Cranial See the end from the beginning with Staub Cranial Recently a new technology was introduced to the United States that will revolutionize the way our industry restores teeth. The Staub Cranial
Staub Cranial See the end from the beginning with Staub Cranial Recently a new technology was introduced to the United States that will revolutionize the way our industry restores teeth. The Staub Cranial
Case study for quality control & quality assurance in metal additive manufacturing: A dental bridge
 Case study for quality control & quality assurance in metal additive manufacturing: A dental bridge Keywords: Dental bridge, quality in dentistry Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Product description...
Case study for quality control & quality assurance in metal additive manufacturing: A dental bridge Keywords: Dental bridge, quality in dentistry Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Product description...
FULL DENTURE SYSTEM THE INHOUSE MOVEMENT
 EN FULL DENTURE SYSTEM THE INHOUSE MOVEMENT 2 FULL DENTURE PROSTHETICS ACCORDING TO DENTAL TECHNOLOGY LOGIC. PRECISE, CUSTOMISED, AESTHETIC. Ceramill FDS (Full Denture System) describes a completely continuous
EN FULL DENTURE SYSTEM THE INHOUSE MOVEMENT 2 FULL DENTURE PROSTHETICS ACCORDING TO DENTAL TECHNOLOGY LOGIC. PRECISE, CUSTOMISED, AESTHETIC. Ceramill FDS (Full Denture System) describes a completely continuous
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080283526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0283526 A1 Buchanan (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) ATTACHABLE PACKAGES FOR THIN, (52) U.S. Cl.... 220/234
(19) United States US 20080283526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0283526 A1 Buchanan (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) ATTACHABLE PACKAGES FOR THIN, (52) U.S. Cl.... 220/234
Patient Case. Source: Tero Rakkolainen
 Patient Case The manufacture of dental implants with CAD/CAM technology raises many questions among laboratory technicians. Unfortunately, if a technician is not familiar with CAD/CAM technology, he/she
Patient Case The manufacture of dental implants with CAD/CAM technology raises many questions among laboratory technicians. Unfortunately, if a technician is not familiar with CAD/CAM technology, he/she
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
(12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
About Dental Wings. DWOS Dental Wings Digital Dentistry Platform
 About Dental Wings Dental Wings is a leading provider of dental CAD / CAM solutions. The company is specialized in the development of 3D scanners and CAD software dedicated to different dental market segments.
About Dental Wings Dental Wings is a leading provider of dental CAD / CAM solutions. The company is specialized in the development of 3D scanners and CAD software dedicated to different dental market segments.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
(19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0193020 A1 Krissman et al. US 2014O193020A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) HEADPHONE ASSEMBLY Applicant: THE KETCHUM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0193020 A1 Krissman et al. US 2014O193020A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) HEADPHONE ASSEMBLY Applicant: THE KETCHUM
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
US 8,287,508 B1. Oct. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: VACUUM PUMP URINE RESERVOIR. Sanchez
 US008287508B1 (12) United States Patent Sanchez () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2012 (54) USING MOISTURE-WICKING ARTICLE WRAPPED OVER OPENINGS IN AN ELONGATED URINE COLLECTING CONTAINER FOR
US008287508B1 (12) United States Patent Sanchez () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2012 (54) USING MOISTURE-WICKING ARTICLE WRAPPED OVER OPENINGS IN AN ELONGATED URINE COLLECTING CONTAINER FOR
Reinvent Your Practice and Your TEAM through 3D Guided Implantology By Patrick Hayden, M.Ed
 Reinvent Your Practice and Your TEAM through 3D Guided Implantology By Patrick Hayden, M.Ed The Dental Market In 2011 there were over half a billion missing teeth in adults 18-65*. Two million of those
Reinvent Your Practice and Your TEAM through 3D Guided Implantology By Patrick Hayden, M.Ed The Dental Market In 2011 there were over half a billion missing teeth in adults 18-65*. Two million of those
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,405,401 B1. Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002
 USOO6405401B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH HAVING A BRISTLE D364,740 S : 12/1995 Loew PATTERN WHICH PROVIDES ENHANCED D372.584
USOO6405401B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Hellerud et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH HAVING A BRISTLE D364,740 S : 12/1995 Loew PATTERN WHICH PROVIDES ENHANCED D372.584
Scan & Design. Features. Features. Additional licenses include:
 Scan & Design Preciso S200 Scanner Preciso CAD Software The Preciso S200 Scanner is a precise and highly accurate dental scanner which serves as your fully open gateway to Digital Workflows. Utilizes blue
Scan & Design Preciso S200 Scanner Preciso CAD Software The Preciso S200 Scanner is a precise and highly accurate dental scanner which serves as your fully open gateway to Digital Workflows. Utilizes blue
Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide
 Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
User Case Production of titanium abutments with inlab MC X5. dentsplysirona.com March 2017
 User Case Production of titanium abutments with inlab MC X5 dentsplysirona.com March 2017 01 Custom titanium abutments made in your own laboratory As links between implants and superstructures, abutments
User Case Production of titanium abutments with inlab MC X5 dentsplysirona.com March 2017 01 Custom titanium abutments made in your own laboratory As links between implants and superstructures, abutments
75 Inventors: Ulrik Nosted, Lyngby; Jan Torstensen, 55. o1. Rho 206/364
 US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993
 United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5222902A Patent Number: 5,222,902 Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993 54 INTERLOCKING BLOCKS 3,890,738 6/1975 Bassani... 44.6/1 3,900,985 8/1975 Yoen... 44.6/124
United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5222902A Patent Number: 5,222,902 Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993 54 INTERLOCKING BLOCKS 3,890,738 6/1975 Bassani... 44.6/1 3,900,985 8/1975 Yoen... 44.6/124
TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P P P P
 Full Smile Solution TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-11 P. 12-13 P. 14-15 P. 16-17 FULL SMILE SOLUTION MGUIDE PROCESS ADVANTAGES CUSTOM SOLUTIONS MGUIDE SURGICAL SETS MCENTER REQUIRED SOURCES
Full Smile Solution TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-11 P. 12-13 P. 14-15 P. 16-17 FULL SMILE SOLUTION MGUIDE PROCESS ADVANTAGES CUSTOM SOLUTIONS MGUIDE SURGICAL SETS MCENTER REQUIRED SOURCES
BIOTECH DENTAL GROUP, 2.0 DENTAL OFFICE PARTNER.
 BROCHURE BIOTECH DENTAL GROUP, 2.0 DENTAL OFFICE PARTNER. Since its creation in 1987, Biotech Dental has been committed to develop a strong relationship of trust with dental surgeons and dental technicians.
BROCHURE BIOTECH DENTAL GROUP, 2.0 DENTAL OFFICE PARTNER. Since its creation in 1987, Biotech Dental has been committed to develop a strong relationship of trust with dental surgeons and dental technicians.
KAREN O. From Failure to Fantastic
 KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,744,043 B2
 USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0310236A1 Kopelman et al. US 20160310236A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) DIRECT FABRICATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0310236A1 Kopelman et al. US 20160310236A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) DIRECT FABRICATION
(51) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 ( ) A61B 6/00 ( ) A61B 6/08 ( ) A61B 6/04 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 123 223 A1 (43) Date of publication: 2.11.09 Bulletin 09/48 (21) Application number: 081649.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 (06.01) A61B 6/00 (06.01) A61B 6/08
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 123 223 A1 (43) Date of publication: 2.11.09 Bulletin 09/48 (21) Application number: 081649.7 (1) Int Cl.: A61B 6/14 (06.01) A61B 6/00 (06.01) A61B 6/08
(12) United States Patent
 USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
CPD Article ISSUE 59. Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future
 CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
