(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
|
|
|
- Hugo Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US 2008O154260A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 HOOF (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 26, 2008 (54) SUTURE MANAGEMENT AND TENSIONING DEVICES AND METHODS FOR SOFT TISSUE RECONSTRUCTION OR BONE-TO-BONE FXATION (75) Inventor: JORDAN A. HOOF, Phoenix, AZ (US) Correspondence Address: STOUT, UXA, BUYAN & MULLINS LLP 4 VENTURE, SUITE 300 IRVINE, CA (73) Assignee: Cayenne Medical, Inc., Scottsdale, AZ (US) (21) Appl. No.: 11/943,566 (22) Filed: Nov. 20, 2007 Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional application No. 60/860,533, filed on Nov. 21, Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. A6B 7/56 ( ) A6B I7/04 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /53;606/232 (57) ABSTRACT An adjustable, stand-alone tensioning system requires no additional fixturing, weights, or bone Surface modification, and allows a single practitioner to provide an adjustable and repeatable tension to a soft tissue graft, and to install the final fixation implant. Its design facilitates introduction of the Suture component of the graft into the tensioning process by simplifying retention of the Suture. An even, regulated and reproducible tension is easily achieved without requiring the practitioner to manually pull on the Suture strands to maintain graft tension.
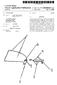
2 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 1 of 7 US 2008/O A1
3 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 2 of 7 US 2008/O A1
4 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 3 of 7 US 2008/O A1
5 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 4 of 7 US 2008/O A1
6 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 5 of 7 US 2008/O A1
7 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 6 of 7 US 2008/O A1
8 Patent Application Publication Jun. 26, 2008 Sheet 7 of 7 US 2008/ A1 A. I me E. y/atle== on 82
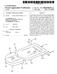
9 US 2008/O A1 Jun. 26, 2008 SUTURE MANAGEMENT AND TENSIONING DEVICES AND METHODS FOR SOFT TISSUE RECONSTRUCTION OR BONE-TO-BONE FXATION This application claims the benefit under 35 U.S.C. 119(e) of the filing date of Provisional U.S. Application Ser. No. 60/ , entitled Suture Management and Tensioning Device for Soft Tissue Reconstruction or Bone-to-Bone Fixa tion, filed on Nov. 21, 2006, which application is expressly and entirely incorporated herein by reference. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002 The present invention relates generally to devices, systems and methods for material fixation, and, more particu larly, to Suture management and tensioning devices used dur ing soft tissue reconstruction or bone-to-bone fixation that will assist in the repair of many soft tissue injuries, such as in the reconstruction of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Prior to completing the final steps of fixation during an ACL repair, the reconstructed ligament must be tensioned in order to establish joint stability. Current devices used to establish ligament pretension require the practitioner to apply and maintain a manual tensile force of the graft during tibial fixation. Devices relying on this technique have proven to be cumbersome, and oftentimes require time consuming steps to prepare the Suture component of the tensioning process. These devices also require unnecessary physical exertion, and often require an additional assistant during the final phases of graft fixation. Still other ligament tensioning devices require external fixturing and/or modification of the bone surface to Support the tensioning process Studies have shown that the magnitude of tension affects characteristics such as the maximal anterior transla tion or subluxation of the joint. In one study, it was found that a higher graft pretension significantly reduced postoperative anterior-posterior knee laxity. However, optimal tensioning of the reconstructed ligament may be related to graft stiffness, and different ligament reconstruction systems and graft tissue types create different stiffness values. Additionally, the opti mal graft tension for men and women may be different. According to a second study, too high of an initial tension may increase the anterior-posterior knee laxity in women though the specific effects of differing graft tensions between gen ders is unknown. Further research in this area may find an optimal pretension value for each sex The tendons of the Gracilis and Semitendinosus muscles are commonly harvested for use in ACL reconstruc tion. The tendons are doubled over to create a four strand graft complex. During ACL reconstruction the strands are sutured to form a paired complex of either of two strands sutured together. The strength and stiffness of the graft complex typi cally surpass that of the native ACL, and both characteristics are optimized when a relatively even tension is applied to each of the four tendon strands The ConMedTM Linvatec Stress Equalization (SETM) Graft Tensioning System is a soft tissue graft tension ing system with the ability to apply different tensions to either of two sides of a graft in order to equalize stress in grafts of non-uniform diameter. The system requires multiple acces sories and additional drill holes to fixate the system within the bone so that tension can be established The DePuy Mitek Tie Tensioner is a soft tissue graft tensioning device that requires the user to manually apply and maintain a force distal to the patient. Even tension can be achieved with this device, but requires that the suture ends be tied together to form two loops of equal length. Furthermore, limitations in the range of motion of the device's Swiveling Suture slide can prohibit true equality in graft strand tension. The Bio-INTRAFIX Surgical Technique manual specifies that the Tie Tensioner be used to manually apply a force of approximately 40 lbs. to the sutures while the knee is cycled to eliminate graft creep. This level of exertion often requires an additional assistant to pull the Tie Tensioner while the knee is cycled. After cycling the knee, the Surgeon must maintain a force of at least 10 lbs. while the Intrafix sheath is inserted and screwed into place. Furthermore, the sheath must usually be hammered into place while tension is maintained, often requiring the assistance of an additional technician. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The inventive device is an adjustable, standalone tensioning system that requires no additional fixturing, weights, or bone surface modification, and allows a single operator to provide an adjustable and repeatable tension to a Soft tissue graft, and to install the final fixation implant. Its design facilitates introduction of the Suture component of the graft into the tensioning process by simplifying retention of the Suture. An even, regulated and reproducible tension is easily achieved without requiring the user to manually pull on the suture strands to maintain graft tension. Furthermore, the benefits of the device's Suture management system, coupled with its ability to maintain tension on the graft, minimizes obstructions Surrounding the installation site and eases instal lation of the final fixation implant. Therefore, most Surgeons will be able to use the device without requiring additional assistance during the tensioning and final fixation procedure The present invention is a device that is easy to use, requires no additional accessories, uses only one drill hole, and can be implanted by one practitioner. A primary goal of the inventive system and methods is to provide a means of applying a repeatable, selectable graft tension without caus ing additional patient trauma and to minimize the number of steps and time required to complete the soft tissue graft fixa tion. The device requires fewer steps and less time to operate than current state-of-the-art devices in use Another primary goal of the inventive device is to minimize the probability that an additional assistant be required to complete the fixation of the soft tissue graft. The device is designed so that a high initial tension can be used by a single operator to cycle the knee and eliminate graft creep, then released and reset to another value if desired for final fixation More particularly, in one aspect of the invention, there is provided a Suture management device for use during an orthopedic procedure, which comprises a body. The device body has structure for accommodating a length of Suture and a surface for engaging a portion of a patient s body for stabi lizing the Suture management device relative to a procedural site within the patient s body. Additionally, the body com prises a Suture tensioning spring and a Suture tensioning con trol, preferably a rotatable knob, engaged with the suture tensioning spring, for retracting the length of Suture to place soft tissue to which the suture is attached in tension The suture management device as described above preferably further comprises a force level indicator for assist
10 US 2008/O A1 Jun. 26, 2008 ing an operator in setting a desired tensioning level. A stop is provided for limiting a distance through which the Suture may be retracted, in order to limit tension imposed on the suture to a desired amount. A channel disposed in the body is provided for accommodating a tool for performing steps of the ortho pedic procedure In one embodiment of the invention, the above men tioned surface comprises an outer surface of the body. The body comprises a center portion for channeling the length of suture between the soft tissue to be tensioned and the suture tensioning control. The body further comprises a first tension ingapparatus connected to the centerportion and extending in a first direction, and a second tensioning apparatus connected to the center portion and extending in a second opposed direction. The first tensioning apparatus includes the above noted Suture tensioning spring and Suture tensioning control, and the second tensioning apparatus includes a second Suture tensioning spring and a second Suture tensioning control. The center body portion preferably comprises a curved Surface and a pair of posts for retaining the Suture in the center body portion Preferably, each of the first tensioning apparatus and the second tensioning apparatus further comprise a sliding Suture cleat for receiving an end of a Suture length opposed to the end connected to the soft tissue to be tensioned, wherein the sliding suture cleat slides responsive to actuation of the Suture tensioning control In another embodiment of the invention, the surface is disposed on a force displacement arm which extends dis tally of the body. A force displacement tube is connected to a proximal end of the force displacement arm. A proximal end of the force displacement tube engages the Suture tensioning spring. The device further comprises a rotatable suture spool for accommodating a portion of the length of Suture as the Suture is retracted by the Suture tensioning control In another aspect of the invention, there is disclosed a method of tensioning a portion of soft tissue during an orthopedic procedure at an operative site in a patient's body. The disclosed method comprises steps of positioning a body of a Suture management device at a desired location in prox imity to the operative site, and attaching a first end of a length of suture to a portion of soft tissue to be tensioned, wherein the second end of said length of Suture is attached to a Suture retaining member disposed within the Suture management device body. A Suture tensioning control is actuated to retract the length of suture into the body, thereby tensioning the portion of soft tissue, and the tension applied to the portion of soft tissue is limited to a desired level In one variant of the method, the tension limiting step is performed by pre-setting a tension level using a tension adjusting control on the device. In another method variant, the tension limiting step is performed by actuating the Suture tensioning control until a force gauge indicates that the desired tension level has been applied The method disclosed above comprises an addi tional step of inserting a tool through a channel in the body to deploy an implant. Then, the device is removed from the patient's body The invention, together with additional features and advantages thereof, may best be understood by reference to the following description taken in conjunction with the accompanying illustrative drawing. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0020 FIG. 1A is an isometric exploded view of an embodiment of a device constructed in accordance with the principles of the present invention; (0021 FIG. 1B is a detailed view of the portion of FIG. 1A delineated by circle 1B: 0022 FIG. 2 is an isometric view of the assembled device of FIG. 1A: 0023 FIG. 3A is a view from one side of the device of FIGS. 1 and 2: 0024 FIG. 3B is a view of the device of FIG. 3A from an orientation 90 degrees rotated from that of FIG. 3A: 0025 FIG.3C is a view from one end of the device of FIG. 3A: (0026 FIG. 3D is a view from the opposed end of the device of FIG. 3A; 0027 FIG. 4A is an isometric view illustrating a clinical application of the device of FIGS. 1-3: (0028 FIG. 4B is a detailed view of the portion of FIG. 4A delineated by the circle B, taken from the side; (0029 FIG. 5 is a perspective view of a modified embodi ment of the Suture tensioning device of the present invention; 0030 FIG. 6 is an exploded view of the suture tensioning device of FIG. 5: 0031 FIG. 7 is a detailed view of the portion of FIG. 6 which is delineated by circle 7; and 0032 FIG. 8 is a view illustrating a clinical application of the device of FIG. 5. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT 0033 Referring now more particularly to the drawings, there is shown in FIGS. 1-3 a suture tensioning device 10 comprised of a body 12. The device 10 comprises a force displacement arm 14, which functions to fix the device 10 against the wall of a tibial tunnel 15 (FIG. 4A), as will be described hereinbelow. The force displacement arm 14 is shaped to flexibly accommodate different topographies with acceptable clearance for both the final fixation implant and any installation tools. With slight modification of the design, the force displacement arm 14 maybe made removable and replaceable so that the tensioning device 10 can be either a single use device or reusable Proximal to the force displacement arm 14 is a suture guide knob 16. Fasteners 18 (FIG. 1A) secure the force displacement arm 14 to a force displacement tube 20 within the suture guide knob 16. The device 10 further comprises a plurality of suture drawers 22. Pins 24 are adapted for inser tion through pin apertures 26 in the suture drawers 22. A rotatable suture spool 28 is provided, on which are disposed a plurality of thumb levers Fasteners 32 extend through a flange 34 on the rotat able suture spool 28, for attaching the flange 34 to a ratchet gear 36, through apertures 38. A spring collar stop 40 and a tensioner spring 42 are disposed within the rotatable Suture spool 28, as shown in FIG. 1A. Slidable about a proximal end of the tensioner spring 42 is a spring collar slide 44. A pawl 46 and a ratchet torsion spring 48 are provided, wherein the
11 US 2008/O A1 Jun. 26, 2008 ratchettorsion spring 48 is disposed about an adjustment slide rod 50. An adjustment lock 52 and a sliding stop 54 are also provided, as shown At a proximal end of the device 10, there is provided a tensioning knob 56. Within the tensioning knob 56 are disposed, in cooperating relationship, an adjustment cover 58, a washer retainer 60, and a gauged cover plate 62. Fas teners 64 assist in securing the adjustment cover 58, washer retainer 60, and gauged cover plate 62 within the tensioning knob 56. A tension adjust button 66 extends proximally from the adjustment cover, and is connected to an adjustment spring 68 and a spring Support washer 70, which, in turn, are operatively disposed on a proximal end of the adjustment slide rod Now with reference to FIGS. 4A and 4B, a method for using the device 10 will be described. In this particular example, the Suture tensioning device 10 is used in the per formance of an ACL repair, of the types disclosed in U.S. Patent Application Publication No. 2006/ , entitled Devices, Systems, and Methods for Material Fixation, in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 1 1/725,981, entitled Devices, Sys tems, and Methods for Material Fixation, filed on Mar. 20, 2007, and in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 1 1/923,526, entitled Methods & Systems for Material Fixation, filed on Oct. 24, All of these prior applications are commonly assigned with the present application, and are herein expressly incorporated by reference, in their entirety. This particular procedure is exemplary only, as the device 10 and methods of the present invention may be used in a variety of procedures during which it is necessary or desirable to ten sion portions of the tissue Illustrated are the femur 72 and tibia 74 of a patient. As graft tendons 76 are pulled proximally and become ten Sioned, displacement is constrained by the design to occur at the force displacement arm 14, whose load is transferred to the force displacement tube 20, spring collar stop 40, and tensioner spring 42. The displacement of these components is adjustably limited by the sliding stop 54. This component controls the maximum displacement of the tensioner spring by preventing further displacement once it is in contact with the spring collar stop 40. The tensioner spring 42 is housed within the spring collar slide 44 and is so constrained. The tensile force imposed on the tendons 76 can be estimated by multiplying the tensioner spring constant by the displacement distance traveled by the tensioner spring Known values of force or a qualitative scale can be marked on the adjustment cover 58 or the force displacement tube 20. The position of the tension adjust button 66 indicates the tension setting and relates the circumferential position of the sliding stop 54 to a displacement tangential along the spring collar slide 44. The tensioning device is adjusted by depressing the tension adjust button 66 and sliding it to the desired tension force marked on the adjustment cover 58. The tension adjust button 66, adjustment spring 68, spring Support washer 70, and adjustment slide rod 50 slide along an aligned track 76a (FIG.2) formed by the adjustment cover 58, washer retainer 60, and gauged cover plate 62. Depressing the tension adjust button 66 compresses the adjustment spring 68, lowers the adjustment slide rod 50, and thus disengages the adjust ment lock 52 from a mated hole on the perimeter of the gauged cover plate 62 corresponding to a specific tension setting. Consequently, the pawl 46 disengages from the ratchetgear 36. As the adjustment slide rod 50 moves circum ferentially around the aligned track formed by the adjustment cover 58, the washer retainer 60, and the gauged cover plate 62, it rotates the sliding stop 54 around the perimeter of the spring collar slide 44. A spiral shaped cut translates circum ferential movement of the sliding stop 54 into a tangential motion along the length of the spring collar slide 44, thereby adjustably limiting the maximum possible displacement for the force displacement arm 14, force displacement tube 20, spring collar stop 40, and thus the tensioner spring Once the desired tension is set, the tension adjust button 66 is released, allowing the adjustment spring 68 to return the adjustment slide rod 50 and to re-engage the adjust ment lock 52 into a mated hole of the gauged cover plate 62, which corresponds to the desired tension setting. Simulta neously, the pawl 46 re-engages with the ratchet gear 36 assisted by the angle-chamfered teeth of the lower half of the ratchet gear Once the force displacement arm 14 is properly positioned, after the desired tension is set, suture 77 can be loaded into the suture drawers 22. Optionally, the device may be packaged with the Suture drawers in a state ready for loading, and in this configuration, any potential displacement of the force displacement arm 14 is prohibited by the inter ference created between lower portions of the suture drawers 22 and the suture guide knob 16. Two or more suture drawers 22 contain a Suture slot feature which can accommodate multiple strands of a plurality of suture sizes. Moreover, the Suture guide knob 16 also contains two or more Suture slot features 78 (FIG. 4B) which provide channels for the suture strands to be guided within and removed from hindrance. Thumb levers 30 are attached to the rotatable suture spool 28 by pins 24. Slots in the thumb levers 30 allow movement of the pin 24 press fit through the suture drawer 22. When the thumb lever 30 is depressed inwardly toward the rotatable suture spool 28, the suture drawers 22 retract into a cavity within the rotatable suture spool 28. The width of the suture drawers 22 steps down at the location of the suture slots 78 to accommodate the width of the suture as it retracts into the cavity. Once the suture drawers 22 are retracted, the interfer ence between the cavity walls of the rotatable suture spool 28, the Suture strands, and the Suture drawers constrains the suture strands 77 from moving When the suture strands 77 of approximately equal length have been passed through the Suture guide knob 16, after the desired tension level has been set, and loaded into the suture drawers 22, the device is ready to tension the suture Strands and soft tissue graft, to which the Suture Strands are connected. The operator simply grasps the Suture guide knob 16 with one hand while rotating the tensioning knob 56 in a clockwise motion with the other hand. During the tensioning process, the device is held parallel to the graft tunnel. The tensioning knob 56 is rotated until it stops. At this point, the desired tension has been reached and the sliding stop 54 has come into contact with the spring collar stop 40, thereby prohibiting further displacement of the tensioner spring 42. Tension is achieved as the suture strands 77, whose ends are constrained within the Suture drawers 22, wrap and accumu late around the rotatable suture spool 28. The load propagates along the Suture strands, equally tensioning each Strand of the soft tissue graft The tensioning knob 56 rotates the ratchet gear 36 and the rotatable suture spool 28. The inner components of the device are prevented from rotating as they are fixed in relation to the Suture guide knob 16. A keyway internal to the spring collar slide 44 and the spring collar stop 40 prohibits rotation
12 US 2008/O A1 Jun. 26, 2008 of the spring collar slide 44 and its attached components. The pawl 46 is therefore fixed in place relative to the suture guide knob 16. As the ratchet gear 36 rotates clockwise around the inner components, the pawl 46 alternately moves in a clicking fashion along and opposite to the tangential vector of ratchet gear rotation. The ratchet torsion spring 48 returns the pawl 46 to its original position between the teeth of the ratchet gear 36. Motion of the tensioning knob 56 is restricted to the clockwise direction by a feature on the side of the pawl 46 that interferes with one edge of the sliding stop 54. If motion is attempted in the counter-clockwise direction, the pawl 46 is obstructed from moving by the sliding stop 54 and the ratchet gear 36 is prevented from rotating. The ratcheting mechanism of this device is not limited to the description provided herein, but may also constitute similarly functional configurations utilizing a variety or a plurality of pawls, gears, teeth or grooves. it is also within the scope of the present invention to utilize a one-way (Sprag freewheel type) rotational bearing in place of the above described ratcheting mechanism. 0044) If used during the course of a ligament reconstruc tion procedure. Such as that described in co-pending U.S. application Ser. No. 1 1/725,981, already expressly incorpo rated by reference herein, the soft tissue graft is first located in a tunnel drilled through the tibia, and a femoral anchor is deployed to secure a distal end of the graft in a socket drilled into the femur. Then, the proximal end of the soft tissue graft is extended proximally through the tibial tunnel and through receiving portions of a tibial anchor. Before the tibial anchor is deployed, the graft is tensioned by pulling it taut, using the device 10. After tensioning of the soft tissue graft has been completed, the device can be held with one hand while the joint (knee) is cycled to eliminate graft creep. Afterwards, the tension can be readjusted to a lower value for final fixation by holding the Suture guide knob 16, and while disengaging the ratchet mechanism by pressing the tension adjust button 66. rotating the tensioning knob 56 counter-clockwise to unwind some or all suture from the suture spool 28. The new tension can be assessed by looking at where gauged markings on the force displacement tube 20 align with the edge of the suture guide knob 16 or by releasing all tension and repeating the tensioning procedures with the newly desired value. Once the desired final fixation tension is reached, the implant is posi tioned and an implant installation tool 79 is inserted and operated through the center of the tensioning device, as illus trated in FIGS. 4A and 4B. The device is removed from patient contact by either cutting the Suture Strands, thus sepa rating the device 10 from the soft tissue grafts, or by opening the suture drawers 22 using the thumb levers A second, modified embodiment of the device of the present invention is illustrated in FIGS In this embodi ment, like elements to those illustrated in FIGS. 1-4 are delin eated by like reference numerals. The embodiment of FIG. 5 differs from the FIG. 1 embodiment in that the tendon bundles 76 are tensioned laterally to the tibial tunnel 15 (FIG.8) rather than axially. Instead of pushing off of a cortical bone surface, the device 10 of FIG. 5 rests on the surrounding bone and/or tissue during the tensioning procedure. The device 10 com prises two tensioning assemblies 80, 82 that are symmetric about the center of the tensioner body 12. A centerportion 84 of the tensioner body 12 is filleted with a large radius to provide a smooth transition for the tensile force to translate around the bend of the suture strands to the tendon bundles within the tibial tunnel. The C-shaped centerportion 84 of the tensioner body 12 is left open, allowing the suture strands 77 (FIG. 8) to be passed over the filleted edges of the center portion of the tensioner body 12 rather than being threaded through an otherwise closed portion. The open center portion 84 also facilitates implant insertion and installation. The tibial tunnel 15 (FIG. 8) is angled with respect to the surface of the knee (tibia 74), so the inclusion of two posts 86 at the edges of the C-shaped center portion 84 of the tensioner body 12 prevents the sutures 77 from sliding off of the edge of the tensioner body during the tensioning procedure The patient contact side of the tensioner body 12 has two sliding suture cleats 88 (FIGS. 6 and 7) located at each end of the device, that fixate the suture strands of the soft tissuegraft for tensioning. Each tensioning knob 56 is fixed to a force translation screw 90. When the knob is rotated, a threaded force translation nut 92 moves linearly along the length of the tensioner body 12. The tensioning nut 92 is prevented from rotating relative to the tensioner body 12 by the extruded portion of the nut that slides within a channel on the top surface of the tensioner body The tensioning knob 56 and force translation screw 90 are constrained within the cylindrical cavity of the ten sioner body by the outside diameter of the tensioning knob shaft, which lies partly inside the slightly larger inner diam eter of the tensioner body, allowing for rotation of the ten sioning knob 56. The end of the force translation screw 90 opposite to the tensioning knob 56 has a notch machined into it so that it can be installed through a keyhole snap within the tensioner body 12. The keyhole snap retains the opposite end of the force translation screw and allows only rotational movement of the screw As the tensioning knob 56 is rotated in the appro priate direction, the force translation nut 92 moves away from the center of the tensioner body and begins to compress the tensioning spring 42, which is press fit over the force trans lation nut 92 and sliding suture cleat 88, maintaining the motion of the force translation nut and the sliding Suture cleat relative to one another. Each end of the tensioning assembly is designed to remove any slack from the tendon bundles and Suture Strands by the allowance for a displacement distance beyond the combined length of the assembly of the tensioning spring 42, force translation nut 92, and sliding suture cleat 88. Rotating the tensioning knob 56 will remove any slack in the tendon bundles within this allowance prior to establishing tension The tensioning spring 42 directs the compressive force created by the linear displacement of the translation nut to the sliding suture cleat 88 which is constrained from move ment by the cleated suture strands leading into the tibial tunnel. Each force translation screw 90 and force translation nut 92 may be threaded oppositely to one another, allowing the force translation nuts 92 to compress the tensioning springs 42 while rotating the tensioning knobs 56 in the same direction, instead of in opposing directions. An indicator pin or other marking on the force translation nut 92 moves either underneath or relative to a slot on the sliding Suture cleat/ force gauge 88 which may be translucent, for purposes of reading the force indicator mark of the force translation nut 92 if the post and slot configuration is not used The sliding suture cleat/force gauge 88 has linear gradient markings which relate displacement of the tension ing spring 42 to force in either lbf or N. A typical tensioning range for each tendon bundle may be from 0 to 30 lbf (0 to N). However, the tension on either side of the device may be set to any value within this range by rotating the
13 US 2008/O A1 Jun. 26, 2008 tensioning knob until the desired tension is reached. The design of the device allows tension to be set and maintained without requiring the physician to physically hold the ten Sioning knobs. Therefore, the device can be used by a single physician without additional assistance The device is designed so that once tension is estab lished, the physician can have both hands free to complete the installation of the final fixation implant. In the example cited above, involving the repair of an ACL as described in the co-pending 981 application, the final fixation implant is the tibial anchor, the femoral anchor having already been installed prior to tensioning. Similar to the ConMed Linvatec SETM (Stress Equalization) Graft Tensioning System, the dis closed device permits the physician to independently tension each tissue graft bundle to normalize stress between bundles of differing cross-sectional area, but with fewer steps, greater ease, and less time. Moreover, the design of the tensioning device assists implant installation by separating and spread ing the tendon bundles to the edges of the tibial tunnel, thus facilitating the process of inserting the tibial implant between the tendons. Once the implant is installed, the device is removed from patient contact by either cutting or unwinding the Suture Strands from the Suture cleats Accordingly, although an exemplary embodiment of the invention has been shown and described, it is to be understood that all the terms used herein are descriptive rather than limiting, and that many changes, modifications, and Substitutions may be made by one having ordinary skill in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the inven tion. What is claimed is: 1. A suture management device for use during an orthope dic procedure, comprising: a body, having structure for accommodating a length of Suture; a Surface for engaging a portion of a patient's body for stabilizing the Suture management device relative to a procedural site within the patient's body; a Suture tensioning spring; and a Suture tensioning control engaged with said Suture ten sioning spring, for retracting the length of suture to place soft tissue to which the suture is attached in tension. 2. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, and further comprising a force level indicator for assisting an operator in setting a desired tensioning level. 3. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, wherein the device comprises a stop for limiting a distance through which the suture may be retracted, in order to limit tension imposed on the Suture to a desired amount. 4. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, and further comprising a channel disposed in said body for accommodating a tool for performing steps of the orthopedic procedure. 5. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, wherein said Suture tensioning control comprises a rotatable knob. 6. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, wherein said Surface comprises an outer Surface of said body. 7. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, wherein said body comprises a center portion for channeling said length of suture between the soft tissue to be tensioned and the Suture tensioning control. 8. The Suture management device as recited in claim 7. wherein said body further comprises a first tensioning appa ratus connected to the center portion and extending in a first direction, and a second tensioning apparatus connected to the center portion and extending in a second opposed direction. 9. The suture management device as recited in claim 8. wherein the first tensioning apparatus includes said Suture tensioning spring and said Suture tensioning control, and said second tensioning apparatus includes a second Suture ten Sioning spring and a second Suture tensioning control. 10. The suture management device as recited in claim 7. wherein said center body portion comprises a curved surface and a pair of posts for retaining the Suture in the center body portion. 11. The suture management device as recited in claim 9. wherein each of said first tensioning apparatus and said sec ond tensioning apparatus further comprise a sliding Suture cleat for receiving an end of a Suture length opposed to the end connected to the Soft tissue to be tensioned, the sliding Suture cleat sliding responsive to actuation of the Suture tensioning control. 12. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, wherein said Surface is disposed on a force displacement arm which extends distally of said body. 13. The Suture management device as recited in claim 12, and further comprising a force displacement tube connected to a proximal end of the force displacement arm, a proximal end of the force displacement tube engaging said Suture ten Sioning spring. 14. The Suture management device as recited in claim 1, and further comprising a rotatable Suture spool for accommo dating a portion of the length of Suture as the Suture is retracted by the Suture tensioning control. 15. A method of tensioning a portion of soft tissue during an orthopedic procedure at an operative site in a patient's body, comprising: positioning a body of a Suture management device at a desired location in proximity to the operative site; attaching a first end of a length of suture to a portion of soft tissue to be tensioned, wherein the second end of said length of Suture is attached to a Suture retaining member disposed within said Suture management device body; actuating a Suture tensioning control to retract the length of suture into the body, thereby tensioning the portion of Soft tissue; and limiting the tension applied to the portion of soft tissue to a desired level. 16. The method as recited in claim 15, wherein the tension limiting step is performed by pre-setting a tension level using a tension adjusting control on said device. 17. The method as recited in claim 15, wherein the tension limiting step is performed by actuating the Suture tensioning control until a force gauge indicates that the desired tension level has been applied. 18. The method as recited in claim 15, and further com prising a step of inserting a tool through a channel in said body to deploy an implant. 19. The method as recited in claim 18, and further com prising a step of removing the device from the patient's body. c c c c c
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,796,977 B2
 USOO6796977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,796,977 B2 Yap et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2004 (54) VARIABLE GRAFTTENSIONER 5,397.357 * 3/1995 Schmieding et al.... 606/86 5,415,651
USOO6796977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,796,977 B2 Yap et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 28, 2004 (54) VARIABLE GRAFTTENSIONER 5,397.357 * 3/1995 Schmieding et al.... 606/86 5,415,651
AFX. Femoral Implant. System. The AperFix. AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide. with the. The AperFix System with the AFX Femoral Implant
 The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
Berry (43) Pub. Date: May 6, (76) Inventor: Bret Berry, Cordova, TN (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
The AperFix II System
 The AperFix II System A Complete Anatomic Solution Transtibial Surgical Technique 2 AperFix II System Transtibial Surgical Technique Figure 1 A Complete Anatomic Solution The Cayenne Medical AperFix and
The AperFix II System A Complete Anatomic Solution Transtibial Surgical Technique 2 AperFix II System Transtibial Surgical Technique Figure 1 A Complete Anatomic Solution The Cayenne Medical AperFix and
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1
 USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH PINN-ACL CROSSPIN SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The ConMed Linvatec Pinn-ACL CrossPin System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH PINN-ACL CROSSPIN SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The ConMed Linvatec Pinn-ACL CrossPin System
Technique Guide. *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System
 Technique Guide *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System N8TIVE ACL System The N8TIVE ACL Anatomic Reconstruction System provides a novel and simple approach to ACL repair. The N8TIVE
Technique Guide *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System N8TIVE ACL System The N8TIVE ACL Anatomic Reconstruction System provides a novel and simple approach to ACL repair. The N8TIVE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
Tibial Fixation. with TunneLoc Device. Surgical Technique by Mark J. Albritton, M.D. and Sherwin Ho, M.D.
 Tibial Fixation with TunneLoc Device Surgical Technique by Mark J. Albritton, M.D. and Sherwin Ho, M.D. Table of Contents Surgical Technique... 4 Ordering Information... 11 Indications For Use... 12 Contraindications...
Tibial Fixation with TunneLoc Device Surgical Technique by Mark J. Albritton, M.D. and Sherwin Ho, M.D. Table of Contents Surgical Technique... 4 Ordering Information... 11 Indications For Use... 12 Contraindications...
Alternative Design Report
 Alternative Design Report Novel Polysaccharide-derived Fixation Device for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Team 13 Derek Holyoak Alexander Werne Benjamin Roberts Clients: Dr. Krystyna Gielo-Perczak
Alternative Design Report Novel Polysaccharide-derived Fixation Device for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Team 13 Derek Holyoak Alexander Werne Benjamin Roberts Clients: Dr. Krystyna Gielo-Perczak
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2
 US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
SE CE. E. E. C. alignment.
 USOO6478799B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,478,799 B1 Williamson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) INSTRUMENTS AND METHODS FOR USE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS N PERFORMING KNEE SURGERY
USOO6478799B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,478,799 B1 Williamson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) INSTRUMENTS AND METHODS FOR USE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS N PERFORMING KNEE SURGERY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
Double Bundle PCL Reconstruction. Surgical Technique
 Double Bundle PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Double Bundle PCL Reconstruction With recent interest in double tunnel endoscopic PCL reconstruction, Arthrex has created a series of Femoral PCL Drill
Double Bundle PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Double Bundle PCL Reconstruction With recent interest in double tunnel endoscopic PCL reconstruction, Arthrex has created a series of Femoral PCL Drill
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Clark et al. USOO6306138B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,306,138 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) ACL FIXATION PIN AND METHOD (75) Inventors: Ron Clark, Pleasant Grove, UT (US);
(12) United States Patent Clark et al. USOO6306138B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,306,138 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 2001 (54) ACL FIXATION PIN AND METHOD (75) Inventors: Ron Clark, Pleasant Grove, UT (US);
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
Transtibial PCL Reconstruction. Surgical Technique. Transtibial PCL Reconstruction
 Transtibial PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Transtibial PCL Reconstruction The Arthrex Transtibial PCL Reconstruction System includes unique safety features for protecting posterior neurovascular
Transtibial PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Transtibial PCL Reconstruction The Arthrex Transtibial PCL Reconstruction System includes unique safety features for protecting posterior neurovascular
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
TWISTR TM Retrograde Reamer & Cruciate+ Instruments Surgical Technique
 TWISTR TM Retrograde Reamer & Cruciate+ Instruments Surgical Technique Guide Carriage Suture Passing Pin Step 1: Set the TWISTR TM Retrograde Reamer to drill the desired socket / tunnel diameter by twisting
TWISTR TM Retrograde Reamer & Cruciate+ Instruments Surgical Technique Guide Carriage Suture Passing Pin Step 1: Set the TWISTR TM Retrograde Reamer to drill the desired socket / tunnel diameter by twisting
ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and. ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System. *smith&nephew. Knee Series Technique Guide ENDOBUTTON CL
 Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Thomas D. Rosenberg, MD ACL Reconstruction
Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Thomas D. Rosenberg, MD ACL Reconstruction
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
(12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
Torn ACL Hamstring Graft
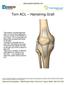 Torn ACL Hamstring Graft The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects the femur to the tibia.
Torn ACL Hamstring Graft The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects the femur to the tibia.
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
(12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
United States Patent (19) McGuire
 United States Patent (19) McGuire 54 76 21 22 63 51 (52) 58) 56 BONE-CUTTING GUDE Inventor: David A. McGuire, 3418 Lakeside Dr., Anchorage, Ak.99515 Appl. No.: 622,615 Filed: Mar 26, 1996 Related U.S.
United States Patent (19) McGuire 54 76 21 22 63 51 (52) 58) 56 BONE-CUTTING GUDE Inventor: David A. McGuire, 3418 Lakeside Dr., Anchorage, Ak.99515 Appl. No.: 622,615 Filed: Mar 26, 1996 Related U.S.
ACL Reconstruction for BTB Grafts
 Transtibial ACL Reconstruction System for BTB Grafts Surgical Technique Designed in conjunction with John C. Garrett, M.D., Atlanta, GA ACL Reconstruction for BTB Grafts Reference Anatomical Constants
Transtibial ACL Reconstruction System for BTB Grafts Surgical Technique Designed in conjunction with John C. Garrett, M.D., Atlanta, GA ACL Reconstruction for BTB Grafts Reference Anatomical Constants
GENERAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 GENERAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE PRODUCT OVERVIEW The Eclipse Soft Tissue Anchor employs MedShape s shape memory PEEK Altera technology for soft tissue fixation procedures in the shoulder, elbow, knee, hand & wrist,
GENERAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE PRODUCT OVERVIEW The Eclipse Soft Tissue Anchor employs MedShape s shape memory PEEK Altera technology for soft tissue fixation procedures in the shoulder, elbow, knee, hand & wrist,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
Bio-TransFix ACL Reconstruction. Surgical Technique
 Bio-TransFix ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Bio-TransFix ACL Reconstruction 1 Semitendinosus and gracilis tendon autografts or tibialis tendon allografts are mounted on the GraftPro workstation.
Bio-TransFix ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Bio-TransFix ACL Reconstruction 1 Semitendinosus and gracilis tendon autografts or tibialis tendon allografts are mounted on the GraftPro workstation.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003
 US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
U2 PSA. Revision Knee. Surgical Protocol
 U2 PSA TM Revision Knee Surgical Protocol Table of Contents 1 Component Removal... 1 2 Tibial Preparation... 1 2.1 Tibial Canal Preparation... 1 2.2 Proximal Tibial Resection... 2 2.3 Non Offset Tibial
U2 PSA TM Revision Knee Surgical Protocol Table of Contents 1 Component Removal... 1 2 Tibial Preparation... 1 2.1 Tibial Canal Preparation... 1 2.2 Proximal Tibial Resection... 2 2.3 Non Offset Tibial
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique
 ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique Surgical Technique Lonnie E. Paulos, MD Salt Lake City, Utah 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 201 831 5000 www.stryker.com A surgeon should always rely on
ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique Surgical Technique Lonnie E. Paulos, MD Salt Lake City, Utah 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 201 831 5000 www.stryker.com A surgeon should always rely on
RIGIDfix. Soft Tissue. Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction PRODUCTS. Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. TISSUE SOFT.
 RIGIDfix A C L C R O S S P I N S Y S T E M Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. Toledo, Ohio SOFT TISSUE Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction Soft Tissue PRODUCTS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RIGIDfix A
RIGIDfix A C L C R O S S P I N S Y S T E M Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. Toledo, Ohio SOFT TISSUE Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction Soft Tissue PRODUCTS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RIGIDfix A
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009629579B2 (10) Patent No.: Volkmuth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) LANCING DEVICE FOR TAKING BLOOD (58) Field of Classification Search SAMPLES CPC... A61 B
(12) United States Patent US009629579B2 (10) Patent No.: Volkmuth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) LANCING DEVICE FOR TAKING BLOOD (58) Field of Classification Search SAMPLES CPC... A61 B
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
BioRCI Screw System. Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts
 BioRCI Screw System Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Using the BioRCI Screw System The Smith & Nephew BioRCI cruciate
BioRCI Screw System Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Using the BioRCI Screw System The Smith & Nephew BioRCI cruciate
GraftLink All-Inside ACL
 Surgical Technique GraftLink All-Inside ACL GraftLink All-Inside ACL Reconstruction with ACL TightRope ABS GraftLink Minimally Invasive ACL Reconstruction The GraftLink technique provides the ultimate
Surgical Technique GraftLink All-Inside ACL GraftLink All-Inside ACL Reconstruction with ACL TightRope ABS GraftLink Minimally Invasive ACL Reconstruction The GraftLink technique provides the ultimate
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
Knee Preservation System
 Knee Preservation System Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System
Knee Preservation System Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0149040 A1 Haines et al. US 2005O149040A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR ORTHOPEDIC
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0149040 A1 Haines et al. US 2005O149040A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR ORTHOPEDIC
Surgical Technique. CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System
 Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
Surgical Technique CONQUEST FN Femoral Neck Fracture System Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Indications... 3 Product Overview... 4 Surgical Technique... 5 Patient Positioning... 5 Reduce the Fracture...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0281578 A1 Spencer US 20090281578A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) PROXMAL HUMERAL FRACTURE REDUCTION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0281578 A1 Spencer US 20090281578A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) PROXMAL HUMERAL FRACTURE REDUCTION
CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL
 CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL INTRODUCTION The RIGIDFIX Curve Cross Pin System is designed specifically for use with the anteromedial (AM) portal approach to achieve a more anatomic soft tissue
CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL INTRODUCTION The RIGIDFIX Curve Cross Pin System is designed specifically for use with the anteromedial (AM) portal approach to achieve a more anatomic soft tissue
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation
 Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
FIXED PERFORMANCE. Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction
 ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System is an innovative technology
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System is an innovative technology
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 2 (8144 Rev 2)
 1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction
 Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects
Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects
AcUMEDr. Olecranon Threaded Compression Rod
 AcUMEDr Olecranon Threaded Compression Rod Olecranon Threaded Compression Rod Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their
AcUMEDr Olecranon Threaded Compression Rod Olecranon Threaded Compression Rod Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray
 Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique
 1 TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INTERCONDYLAR RESECTION...... page FEMORAL STEM...... page NON CEMENTED FEMORAL STEM...... page TRIAL FEMORAL COMPONENTS...... page
1 TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INTERCONDYLAR RESECTION...... page FEMORAL STEM...... page NON CEMENTED FEMORAL STEM...... page TRIAL FEMORAL COMPONENTS...... page
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual
 Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide
 KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide Table of Contents Step 1 System Assembly... 1 Step 2 System Assembly... 2 Step 3 System Assembly... 2 Step 4 System Assembly... 2 Step 5 Sensor Pairing... 2 Step
KneeAlign System Surgical Technique Guide Table of Contents Step 1 System Assembly... 1 Step 2 System Assembly... 2 Step 3 System Assembly... 2 Step 4 System Assembly... 2 Step 5 Sensor Pairing... 2 Step
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
Technique Guide. *smith&nephew SPEEDSCREW Fully Threaded Knotless Implant
 Technique Guide *smith&nephew SPEEDSCREW Fully Threaded Knotless Implant SPEEDSCREW system Fully threaded knotless implant system The SPEEDSCREW system is specifically designed for rotator cuff repair
Technique Guide *smith&nephew SPEEDSCREW Fully Threaded Knotless Implant SPEEDSCREW system Fully threaded knotless implant system The SPEEDSCREW system is specifically designed for rotator cuff repair
Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation
 Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE
 ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE RIGIDLOOP ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL SYSTEM The RIGIDLOOP
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE RIGIDLOOP ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL SYSTEM The RIGIDLOOP
Knee Preservation System
 Knee Preservation System Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch Surgical Technique Multiple continuous stitches for repair of any size meniscal tear. COMMITTED TO INNOVATION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sequent
Knee Preservation System Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch Surgical Technique Multiple continuous stitches for repair of any size meniscal tear. COMMITTED TO INNOVATION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The Sequent
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160081727A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0081727 A1 Munday et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION (52) U.S. Cl. SCREW
US 20160081727A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0081727 A1 Munday et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION (52) U.S. Cl. SCREW
Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics
 MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer
 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
Visit Linvatec.com today to learn more. Surgical Technique: Sequential Meniscal Running Stitch
 ORDERING INFORMATION Sequent Meniscal Repair System MR004S MR007S MR004C MR007C SC047D Straight Needle, 4 Implants Straight Needle, 7 Implants Curved Needle, 4 Implants Curved Needle, 7 implants Sequent
ORDERING INFORMATION Sequent Meniscal Repair System MR004S MR007S MR004C MR007C SC047D Straight Needle, 4 Implants Straight Needle, 7 Implants Curved Needle, 4 Implants Curved Needle, 7 implants Sequent
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
Arcos Interlocking Distal Stem. Surgical Technique Addendum to the Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System
 Arcos Interlocking Distal Stem Surgical Technique Addendum to the Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
Arcos Interlocking Distal Stem Surgical Technique Addendum to the Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized
United States Patent (19) Andelin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Andelin et al. 54 BONE MARROW BIOPSY NEEDLE AND METHOD FOR USING THE SAME 76 Inventors: John B. Andelin, 4940 140 Ave., N.W., Lot 62, Williston, N. Dak. 58801-8605; Martin T.
United States Patent (19) Andelin et al. 54 BONE MARROW BIOPSY NEEDLE AND METHOD FOR USING THE SAME 76 Inventors: John B. Andelin, 4940 140 Ave., N.W., Lot 62, Williston, N. Dak. 58801-8605; Martin T.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0160728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0160728A1 Blitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION NAIL AND RELATED METHOD
(19) United States US 2011 0160728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0160728A1 Blitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION NAIL AND RELATED METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,744,043 B2
 USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O156474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0156474 A1 Wack et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) POLYAXIAL LOCKING PLATE (76) Inventors: Michael
(19) United States US 2002O156474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0156474 A1 Wack et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2002 (54) POLYAXIAL LOCKING PLATE (76) Inventors: Michael
ACL Reconstruction with Flipped BTB Graft Surgical Technique
 ACL Reconstruction with Flipped BTB Graft Surgical Technique Flipped BTB Graft "Based on the clinical success of GraftLink soft tissue grafts*, I wanted to develop a technique using the same tensioning
ACL Reconstruction with Flipped BTB Graft Surgical Technique Flipped BTB Graft "Based on the clinical success of GraftLink soft tissue grafts*, I wanted to develop a technique using the same tensioning
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft
 Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft By Stephen M. Howell, MD Maury L. Hull, PhD. Sacramento, CA The method of tensioning a soft tissue ACL graft is controversial, because surgeons do not agree on how much
Tensioning a Soft Tissue ACL Graft By Stephen M. Howell, MD Maury L. Hull, PhD. Sacramento, CA The method of tensioning a soft tissue ACL graft is controversial, because surgeons do not agree on how much
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact)
 STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
OSS Orthopedic Salvage System Compress Device. Surgical Technique
 OSS Orthopedic Salvage System Compress Device Surgical Technique Table of Contents Quick Reference Guide... 2 Device Description... 3 Resection... 4 No Face Adapter Provisional Construct... 4 Canal Preparation...
OSS Orthopedic Salvage System Compress Device Surgical Technique Table of Contents Quick Reference Guide... 2 Device Description... 3 Resection... 4 No Face Adapter Provisional Construct... 4 Canal Preparation...
Surgical Technique. Targeter Systems Overview
 Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,865,834 McGuire (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 1999
 USOO5865834A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McGuire (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 1999 54). CORING REAMER 5,205,685 4/1993 Herbert... 408/204 5,320,115 6/1994 Kenna...... 128/898 76 Inventor:
USOO5865834A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: McGuire (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 1999 54). CORING REAMER 5,205,685 4/1993 Herbert... 408/204 5,320,115 6/1994 Kenna...... 128/898 76 Inventor:
Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis using Cortical Buttons Surgical Technique
 Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis using Cortical Buttons Surgical Technique Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis using Cortical Buttons Introduction Subpectoral biceps tenodesis using cortical
Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis using Cortical Buttons Surgical Technique Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis Subpectoral Biceps Tenodesis using Cortical Buttons Introduction Subpectoral biceps tenodesis using cortical
PCL GraftLink Surgical Technique
 PCL GraftLink Surgical Technique PCL GraftLink GraftLink Minimally Invasive PCL Reconstruction The GraftLink technique provides the ultimate in anatomic, minimally invasive, and reproducible PCL reconstruction
PCL GraftLink Surgical Technique PCL GraftLink GraftLink Minimally Invasive PCL Reconstruction The GraftLink technique provides the ultimate in anatomic, minimally invasive, and reproducible PCL reconstruction
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY SYSTEM 90-SRK-700000 B.0 0 Contents 1. Implant Sizing 2. Surgical Technique a. Incision and Exposure b. Distal Femoral Resection c. Tibial Resection d. Femoral
Introduction to the Taylor Spatial Frame Hardware. Trademark of Smith & Nephew. Certain marks Reg. US Pat. & TM Off.
 Introduction to the Taylor Spatial Frame Hardware Trademark of Smith & Nephew. Certain marks Reg. US Pat. & TM Off. What is the Taylor Spatial Frame? Next generation circular fixator capable of 6 axes
Introduction to the Taylor Spatial Frame Hardware Trademark of Smith & Nephew. Certain marks Reg. US Pat. & TM Off. What is the Taylor Spatial Frame? Next generation circular fixator capable of 6 axes
ACL Primary Repair Surgical Technique
 ACL Primary Repair Surgical Technique ACL Primary Repair ACL Primary Repair BioComposite SwiveLock and Labral Scorpion Suture Passing Technology There has been a recent resurgence of interest in the possibility
ACL Primary Repair Surgical Technique ACL Primary Repair ACL Primary Repair BioComposite SwiveLock and Labral Scorpion Suture Passing Technology There has been a recent resurgence of interest in the possibility
Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique
 Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique VALENCIA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Indications for Use Surgical Technique 1. Pedicle Preparation 2. Screw Insertion 3. Rod Placement 4. Locking
Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique VALENCIA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Indications for Use Surgical Technique 1. Pedicle Preparation 2. Screw Insertion 3. Rod Placement 4. Locking
52 U.S. Cl /137, 482/100; 482/139 component, when the four bar linkage mechanisms are
 US006056678A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,056,678 Giannelli et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54). ARM CURLAPPARATUS FOR EXERCISING 5,562,577 10/1996 Nichols, Sr. et al.... 482/137
US006056678A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,056,678 Giannelli et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 2, 2000 54). ARM CURLAPPARATUS FOR EXERCISING 5,562,577 10/1996 Nichols, Sr. et al.... 482/137
Twin Tail TightRope System
 Open Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation using the Twin Tail TightRope System Surgical Technique Twin Tail TightRope System Open Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
Open Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation using the Twin Tail TightRope System Surgical Technique Twin Tail TightRope System Open Stabilization of Acute Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
