Original Article. Abstract. Introduction. N Tuloglu, S Bayrak. Key words: Apical barrier, BioAggregate, mineral trioxide aggregate
|
|
|
- Thomasine McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Comparative evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate and bioaggregate as apical barrier material in traumatized nonvital, immature teeth: A clinical pilot study N Tuloglu, S Bayrak Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey Abstract Background: Clinical research examining the use of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) as an apical barrier material are limited, and no studies have so far examined the clinical performance of BioAggregate as apical barrier material in nonvital immature teeth. Aim: This study was aimed to provide a comparative evaluation of the clinical and radiographic success of MTA and BioAggregate as an apical barrier material in children with traumatized nonvital, immature permanent maxillary incisors. Subjects and Methods: A total of 26 maxillary incisor teeth in 20 children aged 7 11 were chosen for this study. Teeth were randomly divided into two groups according to the material to be applied, and the apical barrier was performed. Following treatment, for 24 month, teeth were clinically and radiographically evaluated once every 3 and 6 month, respectively. Results: All teeth treated with MTA and BioAggregate were clinically and radiographically successful throughout the 24 month follow up period. Conclusions: Similar success was achieved in the apical barrier that using BioAggregate and MTA. BioAggregate would be considered suitable materials for apical barrier technique and can be used as an alternative to MTA. Key words: Apical barrier, BioAggregate, mineral trioxide aggregate Date of Acceptance: 31-May-2015 Introduction Completion of root development and apex closure occurs from 1 to 4 years after the emergence of the tooth in the oral cavity. [1] In teeth with an open apex, proper root filling cannot be achieved if endodontic treatment is needed as a result of dental trauma or caries. [1 3] Thus, the clinician is faced with the challenge of creating an apical stop or constriction in order to achieve a hermetically sealed root canal filling. [4] Various treatment options exist to manage nonvital immature teeth which include apexification, apical barrier technique, and regenerative endodontic procedures. [2 5] Up to now, mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) has been popularly employed as a suitable material in apical barrier technique, [2 11] as it combines good tissue biocompatibility, low solubility, ability to induce mineralized tissue formation, and bacteriostatic action with favorable sealing ability. [2,5,12] Despite these excellent properties, MTA also possesses several undesirable characteristics such as long setting time, [12] difficulties in manipulation and insertion, [13] high costs, [14] and potential of discoloration. [7,8] In order to overcome these limitations, various alternative formulations have been developed. Quick Response Code: Access this article online Website: Address for correspondence: Dr. N Tuloglu, Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, 26480, Eskisehir, Turkey. E mail: nuraytuloglu@yahoo.com DOI: / PMID: Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1
2 Recently, a modified version of MTA, the calcium silicate based nanoparticles sized bioceramic BioAggregate (DiaRoot BioAggregate, Innovative BioCeramix Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada) has emerged on the dental market. [15] Unlike MTA, BioAggregate does not contain aluminum oxide and bismuth oxide. [15,16] Recent studies reported that BioAggregate is more biocompatible, [17 19] better sealing ability, [20,21] higher fracture, [22] and acidic resistance [23] than MTA. In light of the information presented above, BioAggregate represents a reasonable alternative to MTA for apical barrier material in nonvital immature teeth. However, to our knowledge, no published study has investigated the clinical performance of BioAggregate as an apical barrier material in nonvital immature teeth. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the clinical and radiographical success of MTA and BioAggregate as an apical barrier material in children with traumatized nonvital, immature permanent maxillary incisors. Subjects and Methods Subject selection The study population consisted of good general healthy (having no history of systemic diseases or hospitalization) and cooperative children applying for treatment at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Samsun, Turkey from November 2009 to December This clinical pilot study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Council (2009/3), and informed consent was obtained from the parents of all study participants. Medical and dental histories were obtained during the initial evaluation of each patient, and clinical and radiographic examinations were performed to assess tooth vitality. The following clinical signs and symptoms were recorded: Acute pain, need for analgesics for pain control, tenderness to percussion, tenderness to palpation, sinus tract, a bad taste in the mouth, discoloration, luxation injury, and crown fracture. Clinical examinations also included electric pulp testing (Digitest, Parkell Electronics Division, Farmingdale, USA) and cold stimulation testing (Chloraethyl, Wehr, Baden, Germany). Radiographic examinations were conducted using an anterior film holder and periapical radiolucencies, periodontal ligament thickness and root resorption were recorded. A total of 62 teeth were assessed for eligibility from November 2009 to December 2010, 36 teeth were excluded for not meeting inclusion criteria (n = 32) and declined to participate (n = 4). Following clinical and radiographic examinations, 26 immature incisor teeth with evidence of pulp necrosis as a result of previous dental trauma in 20 children aged 7 11 were selected for inclusion in this study. Inclusion and exclusion criteria are given in Table 1. Treatment procedures All treatment procedures were performed by the same pediatric dentist (NT) using the same protocol. In the first appointment, local anesthesia (Ultracaine DS Fort Ampul, Sanofi Aventis Ilaclari Ltd. Sti., Istanbul, Turkey) was administered, and teeth were isolated with a rubber dam (Ash Rubber Dam Kit, Dentsply International Inc., Milford, USA). A round diamond burr (801H016, Hager and Meisinger GmBH, Heisinger, Germany) was used to prepare an appropriate access cavity to allow removal of all necrotic tissue. The necrotic pulp was extirpated and working length was determined from a radiograph taken with a film holder. Canals were prepared to 2 mm short of the radiographic apex with K files (Diadent Group International Inc., Canada) using a gentle, circumferential motion, and copious irrigation with 2.5% sodium hypochlorite to maximize cleansing and minimize dentin removal. After biomechanical preparation, canals were irrigated using a sterile saline solution and dried with sterile paper points (Spident, SPI Dental Mfg. Inc., Korea). Calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH) ] paste (Kalsin, Aktu Tic., Izmir, 2 Turkey) was placed in the canal using a lentulo spiral (Mani Inc., Tochigi, Japan), and a radiograph was exposed to determine the degree of the Ca(OH) filling. If found 2 to be adequate, the endodontic access cavity was sealed with cotton pellets and reinforced with zinc oxide eugenol cement (IRM, Dentsply International Inc., Milford, USA). Patients were recalled for a second appointment after 7 days, at which time the root canal was re accessed, the Ca(OH) 2 dressing was removed with reamers and the canal was irrigated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid followed by 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. After minor instrumentation, canals were irrigated with sterile saline solution and dried with sterile paper points. Teeth were then randomly divided into treatment groups (n = 13) for apical barrier with MTA or BioAggregate (randomization was achieved by coin throwing). Patients were blinded to the type of materials used. Materials were mixed in line with the manufacturers instructions, inserted into the apical third of the root canal using a carrier, and gently condensed using pluggers premeasured to 4 mm short of the working length. A conventional periapical radiograph was taken to confirm the appropriate placement of the material, a cotton pellet moistened with sterile water was placed over the apical plug, followed by a dry cotton pellet, and the endodontic access cavity was sealed with IRM. After 4 days, patients were recalled for a third appointment. The cotton pellets were removed, and a reamer was used to check the apical plug for set and hardness. Canals were then obturated with Gutta percha (Spident, SPI Dental Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1 53
3 Mfg. Inc., Korea) and a resin based root canal sealer (AH plus, Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany) using the lateral condensation technique. If the apical plug hardness was unsatisfactory, procedures were repeated, and the final obturation was delayed to a later visit. Once obturation was completed, a periapical radiograph taken was used to evaluate the root filling. After the root canal filling was determined to be adequate, teeth were restored with glass ionomer liner material (Fuji IX, GC Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and composite resin (Grandio, Voco, Cuxhaven, Germany). Clinical and radiographic examinations All preoperative, immediate postoperative, and recall radiographs were taken with a beam guiding device using the paralleling technique. All radiographic films were exposed and processed conventionally under similar conditions and analyzed under standardized conditions (darkened room, magnification). Clinical and radiographic evaluations were performed by two different investigators (NT and SB). Kappa Cohen test used for examiner calibration showed complete agreement between the two investigators. Following treatment, study participants were recalled at 3 month intervals for the 24 month follow up period. The following clinical parameters were assessed: Pain or discomfort at any time following root canal obturation Use of any analgesics for pain relief Tenderness to palpation or obvious signs of abscess formation (sinus tract, etc.) Tenderness to percussion. Treatment was recorded as a clinical failure if any of the above parameters were met. The following radiographic parameters were also assessed once every 6 month: Normal periodontal ligament space Reduction in the size of the periapical lesion as compared to preoperative radiographs No evidence of inflammatory external root resorption. Treatment was recorded as a radiographical success when all three of the above parameters were met. In cases where a locally widened periodontal ligament space remained after healing of an extensive periapical lesion, this defect was considered to be scar tissue rather than a sign of persisting disease, and in such situations, apical barrier material was classified as a success. In cases where no reduction was observed in the size of the periapical radiolucency, the success of apical barrier materials were deemed inconclusive. Radiographical evidence of failure included enlargement of an existing periapical lesion, the formation of a new lesion after placement of the root filling, and signs of root resorption or hypercementosis. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 12.0 software program (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) with the level of significance set at Intra examiner calibration was measured using Kappa Cohen test. Results This study was conducted with 26 incisor teeth in 20 healthy and cooperative children (10 girls, 10 boys) aged 7 11 years (mean age: 8.7 ± 1.5 years; mean age of girls: 8.50 ± 1.72 years; mean age of boys: 8.90 ± 1.1). The demographic and baseline data for each group are presented in Table teeth included in this study were evaluated for the 24 month Table 1: Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the teeth Inclusion criteria Table 2: Demographic and baseline characteristics for each group MTA (n=13) BioAggregate (n=13) Age (years) 8.69± ±0.45 Sex Male 5 6 Female 8 7 Tooth MTA=Mineral trioxide aggregate a Restorable tooth Possibility of rubber dam isolation Root formation at stage 8 (two thirds of root completed) or 9 (root almost completed open apex), in according to Nolla [24] Nonvital immature permanent incisor requiring endodontic therapy Exclusion criteria Pathological external or internal root resorption Horizontal or vertical root fracture Pulp calcification Ankylosis Severe luxation injury b Figure 1: Radiographs of tooth 11 treated with mineral trioxide aggregate (a) Preoperative radiograph (b) Postoperative radiograph (c) 12-month follow-up (d) 24-month follow-up c d 54 Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1
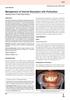
4 Table 3: Clinical findings of the 13 teeth in each group Clinical parameters Materials Posttreatment interval 3 month 6 month 9 months 12 month 15 months 18 months 21 months 24 month No pain MTA No tenderness to percussion MTA No tenderness to palpation MTA No swelling or sinus tract MTA MTA=Mineral trioxide aggregate Table 4: Radiographic findings of the 13 teeth in each group Radiographic parameters Materials Posttreatment interval 6 month 12 month 18 months 24 month Normal periodontal ligament MTA BioAggregate No external root resorption MTA BioAggregate No enlargement of an existing periapical lesion MTA 8* BioAggregate 9* *Preoperative radiographic periapical lesions were observed 8 teeth in MTA group and 9 teeth in BioAggregate group. MTA=Mineral trioxide aggregate a b Figure 2: Radiographs of tooth 11 treated with BioAggregate (a) Preoperative radiograph (b) Postoperative radiograph (c) 12-month follow-up (d) 24-month follow-up follow up period. No patients were lost during the follow up period. The clinical and radiographic findings for each group at follow up period are given in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. Among the 26 teeth included in this study, the following symptoms were observed: Enamel fractures, 4 teeth; non complicated crown fractures, 3 teeth; complicated crown fractures, 13 teeth; luxation injuries, 6 teeth; acute pain, 12 teeth; sensitivity to percussion, 19 teeth; sensitivity to palpation, 8 teeth; preoperative apical abscesses, 4 teeth; sinus tract, 6 teeth; preoperative radiographic periapical lesions, 17 teeth (8 teeth in MTA group and 9 teeth in BioAggregate group); the root formation at Stage 8, 19 teeth; (9 teeth in MTA group and 10 teeth in BioAggregate group) the root formation at Stage 9, 7 teeth (4 teeth in MTA group and 3 teeth in BioAggregate group). All teeth in both the MTA and BioAggregate groups were rated clinically and radiographically successful throughout c d Figure 3: Intraoral appearance of coronal discoloration of maxillary right central incisor treated with mineral trioxide aggregate the 24 month follow up period. This finding of the present study cannot be evaluated as statistically because of the success in all teeth [Figures 1 and 2]. Interestingly, the coronal discoloration was coincidentally observed in 2 teeth (15.39%) from the MTA group in the 6 month follow up [Figure 3], but no teeth in the BioAggregate group. No bleaching was performed to discolored teeth until the end of the study. Discussion The management of dental trauma to immature permanent teeth in young children can be challenging. As a result of dental trauma, these teeth may become nonvital, which leads to arrested root development. [22] Root canal treatment at this time is a significant challenge, because of the thin and Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1 55
5 fragile dentin walls, and the large open apex. [5] Apexification has long been the treatment of choice, enjoying considerable success in preserving traumatized nonvital immature teeth. [5] Ca(OH) 2 has been the material most frequently used to induce the formation of a calcified apical barrier in teeth with nonvital immature apices. [5] However, Ca(OH) 2 pastes have several disadvantages such as a prolonged treatment period, difficulties in managing patient recall, loss of temporary dressings and re infection, and treatment delays that increase the risk of tooth fracture following dressing with Ca(OH) 2 over extended periods. [2,5,7,25] Recently, regenerative endodontic procedures have become a viable treatment option for traumatized nonvital immature teeth. [2,6] Regenerative endodontics promotes a paradigm shift from performing apexification procedures to conserving any dental stem cells that might remain in the disinfected viable tissues to allow tissue regeneration and repair and achieve apexogenesis or maturogenesis. [2,6] Although regenerative endodontic seems promising, this procedure may have potential disadvantage such as the development of resistant bacterial strains, allergic reaction to the intracanal medication, increased number of appointments, and longer treatment times. [6,26,27] Unlike apexification and regenerative endodontic procedures, apical barrier technique entails closing the open apex with a biological material to permit immediate filling of the root canal. [5] Therefore, this clinical pilot study was preferred apical barrier technique for treatment of traumatized nonvital immature teeth. Although MTA has been the material most frequently used in apical barrier technique, [2 6] due to its disadvantages [7,8,12 14] necessitate more ideal apical barrier materials, with adequate biological and mechanical properties. Recently, a new calcium silicate based bioceramic material, BioAggregate has been introduced with the intention of preserving the properties and clinical applications of MTA without its negative characteristics. BioAggregate is composed of tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, tantalum pentoxide, calcium phosphate monobasic, hydroxyapatite, and amorphous silicon dioxide. [15,16] BioAggregate is also aluminum free content, a fact that contributes to its greater biocompatibility with a periradicular tissue. [16] Moreover, the various advantages of BioAggregate include ease of application and manipulation; working time is more than 5 min and convenient setting time; [15] higher fracture strength, [22] and better sealing ability [20,21] than MTA. Despite these advantages of BioAggregate, to our knowledge, there have not yet been any clinical researches examining the use of BioAggregate in apical barrier techniques. Therefore, this clinical pilot study aimed to evaluate and compare the clinical and radiographic success of MTA and BioAggregate when used as an apical barrier material in traumatized nonvital, immature permanent maxillary incisors. This clinical pilot study was carried out on a relatively small sample of nonvital, immature teeth (26 teeth in 20 children) over a relatively short follow up period (24 month). In this regard, the limitations in terms of collecting a sample of nonvital teeth with open apices that meet the inclusion criteria should be kept in mind. Moreover, whereas a larger sample size would allow for the identification of statistical differences between materials, the design of the present study (i.e. small sample size and relatively short follow up period) is consistent with other apexification studies in the literature. [4,7 9] Simon et al. [10] examined the radiographic success of MTA when used as an apical barrier material on 57 immature permanent incisors over a follow up period ranging from 6 to 36 months and reported reductions in preexisting periapical lesions in 81% of cases. Moore et al. [8] compared ProRoot MTA and MTA Angelus as an apical barrier material and found clinical and radiographic success rates of 95.5% for both materials. Another study evaluated apical barrier formation of 17 nonvital immature permanent incisors using MTA and found clinical and radiographic success rates of 94.1% and 76.5%, respectively. [7] A retrospective study by Mente et al. [11] assessing healing of immature teeth treated with MTA apical barriers found successful healing in 84% of cases. El Meligy and Avery [9] demonstrated a clinical and radiographic success rate of 100% with MTA, which was found to be a suitable replacement for Ca(OH) 2 in apexification treatment. Overall, a review of clinical studies indicates that clinical and radiographic success rates of apical barrier formation with MTA range from 81% to 100% and 76 95%, respectively. [4,7 11] In line with these findings, the present study showed that all teeth treated using MTA was clinically and radiographically successful over the course of 24 month of follow up. With regard to BioAggregate, given that the literature contains no previous reports on apical barrier formation using BioAggregate, no comparisons can be made with the clinical and radiographic success rates of apical barrier formation with this material found in the present study. Tooth discoloration is an important aesthetic concern in young patients. Studies by Sarris et al. [7] and Moore et al. [8] found coronal discoloration in 11.8% and 22.7% of cases, respectively, following the placement of MTA as an apical barrier material. In the present study, coronal discoloration was coincidentally observed in 2 teeth (15.39%) treated with MTA, whereas no coronal discoloration was observed among teeth treated with BioAggregate. Discoloration caused by MTA has been attributed to the metal oxides (e.g. Bi 2 O 3, Al 2 O 3, FeO) contained in the material. [28,29] Unlike MTA, BioAggregate contains no metal oxides, 16 which could explain the lack of coronal discoloration in the BioAggregate group in the present study. Additional in vitro and in vivo studies are needed to provide a more definitive determination of the cause of discoloration with MTA and BioAggregate. 56 Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1
6 Conclusions This study found excellent clinical and radiographic results when either MTA or BioAggregate is used as an apical barrier material in children with traumatized nonvital, immature permanent maxillary incisors. Within the limitation of this study, BioAggregate can be considered a possible alternative to the MTA. However, MTA still remains as one of the important materials used in apical barrier technique. Further clinical studies with larger sample sizes and longer follow up periods are required to find the best apical barrier material in dental practice. Acknowledgments This study was funded by the Ondokuz Mayis University Scientific Research and Development Support Program (PYO. DİS ). References 1. Melfi RC, Alley EK, editors. Permar s Oral Embryology and Microscopic Anatomy. 10 th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Co.; Jyothi M. Management of immature teeth A paradigm shift from apexification to apexogenesis. Ann Essences Dent 2012;IV: Nayak G, Hasan MF. Biodentine a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification. Restor Dent Endod 2014;39: Pradhan DP, Chawla HS, Gauba K, Goyal A. Comparative evaluation of endodontic management of teeth with unformed apices with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide. J Dent Child (Chic) 2006;73: Rafter M. Apexification: A review. Dent Traumatol 2005;21: Flanagan TA. What can cause the pulps of immature, permanent teeth with open apices to become necrotic and what treatment options are available for these teeth. Aust Endod J 2014;40: Sarris S, Tahmassebi JF, Duggal MS, Cross IA. A clinical evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate for root end closure of non vital immature permanent incisors in children a pilot study. Dent Traumatol 2008;24: Moore A, Howley MF, O Connell AC. Treatment of open apex teeth using two types of white mineral trioxide aggregate after initial dressing with calcium hydroxide in children. Dent Traumatol 2011;27: El Meligy OA, Avery DR. Comparison of apexification with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide. Pediatr Dent 2006;28: Simon S, Rilliard F, Berdal A, Machtou P. The use of mineral trioxide aggregate in one visit apexification treatment: A prospective study. Int Endod J 2007;40: Mente J, Hage N, Pfefferle T, Koch MJ, Dreyhaupt J, Staehle HJ, et al. Mineral trioxide aggregate apical plugs in teeth with open apical foramina: A retrospective analysis of treatment outcome. J Endod 2009;35: Torabinejad M, Hong CU, McDonald F, Pitt Ford TR. Physical and chemical properties of a new root end filling material. J Endod 1995;21: Santos AD, Moraes JC, Araújo EB, Yukimitu K, Valério Filho WV. Physico chemical properties of MTA and a novel experimental cement. Int Endod J 2005;38: Srinivasan V, Waterhouse P, Whitworth J. Mineral trioxide aggregate in paediatric dentistry. Int J Paediatr Dent 2009;19: Marwah N. The era of endodontic research. Root end filling materials. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2014;7:v vii. 16. Zhang H, Pappen FG, Haapasalo M. Dentin enhances the antibacterial effect of mineral trioxide aggregate and bioaggregate. J Endod 2009;35: Yan P, Yuan Z, Jiang H, Peng B, Bian Z. Effect of bioaggregate on differentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Int Endod J 2010;43: Yuan Z, Peng B, Jiang H, Bian Z, Yan P. Effect of bioaggregate on mineral associated gene expression in osteoblast cells. J Endod 2010;36: De Deus G, Canabarro A, Alves G, Linhares A, Senne MI, Granjeiro JM. Optimal cytocompatibility of a bioceramic nanoparticulate cement in primary human mesenchymal cells. J Endod 2009;35: Memis Özgül B, Bezgin T, Sahin C, Sari S. Resistance to leakage of various thicknesses of apical plugs of Bioaggregate using liquid filtration model. Dent Traumatol doi: /edt Leal F, De Deus G, Brandão C, Luna AS, Fidel SR, Souza EM. Comparison of the root end seal provided by bioceramic repair cements and White MTA. Int Endod J 2011;44: Tuna EB, Dinçol ME, Gençay K, Aktören O. Fracture resistance of immature teeth filled with BioAggregate, mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide. Dent Traumatol 2011;27: Hashem AA, Wanees Amin SA. The effect of acidity on dislodgment resistance of mineral trioxide aggregate and bioaggregate in furcation perforations: An in vitro comparative study. J Endod 2012;38: Nolla CM. The development of permanent teeth. J Dent Child 1960;27: Andreasen JO, Farik B, Munksgaard EC. Long term calcium hydroxide as a root canal dressing may increase risk of root fracture. Dent Traumatol 2002;18: Reynolds K, Johnson JD, Cohenca N. Pulp revascularization of necrotic bilateral bicuspids using a modified novel technique to eliminate potential coronal discolouration: A case report. Int Endod J 2009;42: Nosrat A, Homayounfar N, Oloomi K. Drawbacks and unfavorable outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatments of necrotic immature teeth: A literature review and report of a case. J Endod 2012;38: Akbari M, Rouhani A, Samiee S, Jafarzadeh H. Effect of dentin bonding agent on the prevention of tooth discoloration produced by mineral trioxide aggregate. Int J Dent 2012;2012: Vallés M, Mercadé M, Duran Sindreu F, Bourdelande JL, Roig M. Color stability of white mineral trioxide aggregate. Clin Oral Investig 2013;17: How to cite this article: Tuloglu N, Bayrak S. Comparative evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate and bioaggregate as apical barrier material in traumatized nonvital, immature teeth: A clinical pilot study. Niger J Clin Pract 2016;19:52-7. Source of Support: This study was funded by the Ondokuz Mayis University Scientific Research and Development Support Program (PYO. DİS ), Conflict of Interest: None declared. Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice Jan-Feb 2016 Vol 19 Issue 1 57
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures.
 Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
CONTENTS. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication. A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. B. Research C.
 CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report
 Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report Allison Clark, Anthony Pino, Danielle Attoe, Fatemeh Farzin, Keith Li, Malisa Gambacorta
Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report Allison Clark, Anthony Pino, Danielle Attoe, Fatemeh Farzin, Keith Li, Malisa Gambacorta
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018
 Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
DiaDent Group International DIA.DENT DiaRoot BioAggregate. Root Canal Repair Material
 DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
DiaDent Group International 1.877.DIA.DENT www.diadent.com DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material PRECISION. PURITY. RESULTS ABOUT DIAROOT... DiaRoot BioAggregate Root Canal Repair Material is
The traumatic injury of an immature permanent tooth can lead to the loss of pulp
 Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS
 CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA: A Case report
 International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research. Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016
 Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 The use of cone beam computed tomography in diagnosis and surgical management of a case of internal root resorption: A case report Samane
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 The use of cone beam computed tomography in diagnosis and surgical management of a case of internal root resorption: A case report Samane
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer
 Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24
 Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
Vijay Shekhar and K. Shashikala. 1. Introduction
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 714585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714585 Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of the Periapical Status of Nonvital Tooth with
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 714585, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/714585 Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of the Periapical Status of Nonvital Tooth with
The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open apices 1
 Dental Traumatology 2002; 18: 217 221 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600 4469 The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open
Dental Traumatology 2002; 18: 217 221 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600 4469 The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open
Intensive care for the immature pulp Maintaining pulp vitality after a traumatic injury
 Nine-year-old Josh is racing down a hill on his mountain bike. The bike hits a rock and Josh lands on the trail. His mouth is bloody. His front tooth feels funny. He gets up, dusts himself off and rides
Nine-year-old Josh is racing down a hill on his mountain bike. The bike hits a rock and Josh lands on the trail. His mouth is bloody. His front tooth feels funny. He gets up, dusts himself off and rides
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents
 Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010
 Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010 Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry Management and Root Canal Treatment of Non-Vital Immature
Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010 Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry Management and Root Canal Treatment of Non-Vital Immature
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide
 Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
MTA MIRACLE IN DENTISTRY Shikha Singh*,Rahul Maria**,AU Palekar***,Sweta Singh*.
 MTA MIRACLE IN DENTISTRY Shikha Singh*,Rahul Maria**,AU Palekar***,Sweta Singh*. Abstract MTA, is a new material developed for endodontics that appears to be a significant improvement over other materials
MTA MIRACLE IN DENTISTRY Shikha Singh*,Rahul Maria**,AU Palekar***,Sweta Singh*. Abstract MTA, is a new material developed for endodontics that appears to be a significant improvement over other materials
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Single-Step Apexification with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2016), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Single-Step Apexification with Mineral
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2016), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Single-Step Apexification with Mineral
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
Chronicles of Dental Research
 CASE REPORT Pulp Revascularization of Non vital Immature Young Permanent Tooth: A case report. Vikrant Kumar 1, Chhaya Sharma 1, Romana Nisar 1, Sheeba Hassan 1, Pooja Tiwari 1 Abstract Traumatic injuries
CASE REPORT Pulp Revascularization of Non vital Immature Young Permanent Tooth: A case report. Vikrant Kumar 1, Chhaya Sharma 1, Romana Nisar 1, Sheeba Hassan 1, Pooja Tiwari 1 Abstract Traumatic injuries
Bioactive Closure of Non Vital Immature Tooth with Open Apices - A Contemporary Approach
 Bioactive Closure of Non Vital Immature Tooth with Open Apices - A Contemporary Approach Shikha Jaiswal, Sachin Gupta, Shefali Sawani, Jatin Gupta Department of Conservative Dentisry & Endodontics, Subharti
Bioactive Closure of Non Vital Immature Tooth with Open Apices - A Contemporary Approach Shikha Jaiswal, Sachin Gupta, Shefali Sawani, Jatin Gupta Department of Conservative Dentisry & Endodontics, Subharti
MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
 MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS AUTHORS Dr. SHALINI.H, PG Student Dr. B. RAMAPRABHA, MDS Professor Dr. M. KAVITHA, MDS Professor and HOD DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS AUTHORS Dr. SHALINI.H, PG Student Dr. B. RAMAPRABHA, MDS Professor Dr. M. KAVITHA, MDS Professor and HOD DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports
 SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports with Authors ( Department of Conservative dentistry and Endodontics, TamilNadu Government Dental College, Chennai- 600 003):
SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports with Authors ( Department of Conservative dentistry and Endodontics, TamilNadu Government Dental College, Chennai- 600 003):
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
A combined approach with passive and active repositioning of a traumatically intruded immature permanent incisor
 H.-J. Kim*-**, Y.-I. Kim***, K.-S. Min**-**** *Department of Conservative Dentistry, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea **Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry and Institute
H.-J. Kim*-**, Y.-I. Kim***, K.-S. Min**-**** *Department of Conservative Dentistry, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea **Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry and Institute
Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis using triple antibiotic paste disinfection
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2016) 11, 196e201 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis
Journal of Dental Sciences (2016) 11, 196e201 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis
Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using Platelet-Rich Fibrin to Treat Traumatized Immature Permanent Tooth: a Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. VI (May. 2015), PP 36-40 www.iosrjournals.org Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. VI (May. 2015), PP 36-40 www.iosrjournals.org Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using
Case Report The Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate on the Periapical Tissues after Unintentional Extrusion beyond the Apical Foramen
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 3590680, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3590680 Case Report The Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate on the Periapical Tissues after Unintentional
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 3590680, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3590680 Case Report The Effect of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate on the Periapical Tissues after Unintentional
Received on Accepted on:
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Review Article www.ijptonline.com BIOCERAMICS IN ENDODONTICS Karthiga KS 1, Dr. Pradeep.S 2 1 Undergraduate, Saveetha Dental College, Chennai. 2 Department
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Review Article www.ijptonline.com BIOCERAMICS IN ENDODONTICS Karthiga KS 1, Dr. Pradeep.S 2 1 Undergraduate, Saveetha Dental College, Chennai. 2 Department
Intentional reimplantation - two case reports
 Case Report Intentional reimplantation - two case reports GURPREET SINGH * NIKHIL BAHUGUNA ** PARDEEP MAHAJAN *** ABSTRACT Intentional reimplantation is a procedure in which an intentional tooth extraction
Case Report Intentional reimplantation - two case reports GURPREET SINGH * NIKHIL BAHUGUNA ** PARDEEP MAHAJAN *** ABSTRACT Intentional reimplantation is a procedure in which an intentional tooth extraction
Examination of teeth and gingiva
 Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
MTA apical plug and clinical application of anatomic post and core for coronal restoration: A case report
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rahul Kumar1* BDS, Suvarna Patil2 MDS, Upendra Hoshing2 MDS, Ashish Medha2 MDS, Rushikesh Mahaparale1 BDS MTA apical plug and clinical application of anatomic post and core for coronal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rahul Kumar1* BDS, Suvarna Patil2 MDS, Upendra Hoshing2 MDS, Ashish Medha2 MDS, Rushikesh Mahaparale1 BDS MTA apical plug and clinical application of anatomic post and core for coronal
SINGLE VISIT MTA APEXIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR FORMATION OF ROOT-END BARRIER IN OPEN APICES- A CASE SERIES
 SINGLE VISIT MTA APEXIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR FORMATION OF ROOT-END BARRIER IN OPEN APICES- A CASE SERIES 1 2 3 4 Bhumika Kapoor, Osama Adeel Khan Sherwani, Rajendra K Tewari, Surendra K Mishra. 1,2 3,4
SINGLE VISIT MTA APEXIFICATION TECHNIQUE FOR FORMATION OF ROOT-END BARRIER IN OPEN APICES- A CASE SERIES 1 2 3 4 Bhumika Kapoor, Osama Adeel Khan Sherwani, Rajendra K Tewari, Surendra K Mishra. 1,2 3,4
Endodontic perforation repair with light-cured glass ionomer
 Clinical Endodontic perforation repair with light-cured glass ionomer Manal Farea, 1 Adam Husein, 2 Cornelis H Pameijer 3 The aim of endodontic therapy is for complete debridement of pulpal tissues, thorough
Clinical Endodontic perforation repair with light-cured glass ionomer Manal Farea, 1 Adam Husein, 2 Cornelis H Pameijer 3 The aim of endodontic therapy is for complete debridement of pulpal tissues, thorough
Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports
 Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
Pulpal treatment in young permanent teeth CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW
 Review CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW Anantharaj.A 1,Praveen.P 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3, Prathibha Rani.S 4, Sudhir.R 5,Murali Krishnan.B 6 1 Professor and Head, 2,3
Review CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW Anantharaj.A 1,Praveen.P 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3, Prathibha Rani.S 4, Sudhir.R 5,Murali Krishnan.B 6 1 Professor and Head, 2,3
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Case Report Single visit apexification technique by root end barrier formation with MTA
 Updat Dent. Coll.j 2015;5(1):21-25 Case Report Single visit apexification technique by root end barrier formation with MTA *Tazdik G. Chowdhury a, S. M Abdul Quader b, Tasnim-A-Jannat c, Shirin Sultana
Updat Dent. Coll.j 2015;5(1):21-25 Case Report Single visit apexification technique by root end barrier formation with MTA *Tazdik G. Chowdhury a, S. M Abdul Quader b, Tasnim-A-Jannat c, Shirin Sultana
Totalfill putty in action
 Totalfill putty in action Kazim Mahmood, Obyda Essam, Mike Dodd and Fadi Jarad present case studies that demonstrate the use of a new bioceramic material Recent advances in endodontics have seen an increase
Totalfill putty in action Kazim Mahmood, Obyda Essam, Mike Dodd and Fadi Jarad present case studies that demonstrate the use of a new bioceramic material Recent advances in endodontics have seen an increase
Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revascularization 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2438 of Teeth with Necrotic Pulp Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study 1 Padmaraj S Neelamurthy,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revascularization 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2438 of Teeth with Necrotic Pulp Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study 1 Padmaraj S Neelamurthy,
Mineral trioxide aggregate in endodontics
 2017; 3(1): 71-75 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2016; 3(1): 71-75 2016 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 13-11-2016 Accepted: 14-12-2016 Dr. B.S. Keshava Prasad Professor Dental
2017; 3(1): 71-75 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2016; 3(1): 71-75 2016 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 13-11-2016 Accepted: 14-12-2016 Dr. B.S. Keshava Prasad Professor Dental
Management of an extensive invasive root resorptive lesion with mineral trioxide aggregate: a case report
 397 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 53, No. 3, 397-401, 2011 Case Report Management of an extensive invasive root resorptive lesion with mineral trioxide aggregate: a case report Farzad Danesh 1), Kasra
397 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 53, No. 3, 397-401, 2011 Case Report Management of an extensive invasive root resorptive lesion with mineral trioxide aggregate: a case report Farzad Danesh 1), Kasra
ESTHETIC ENHANCEMENT BY NONVITAL BLEACHING PROCEDURE AND DIASTEMA CLOSURE WITH CERAMIC VENEER ON MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR
 Indian J.Sci.Res.10(1): 07-11, 2015 ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) ESTHETIC ENHANCEMENT BY NONVITAL BLEACHING PROCEDURE AND DIASTEMA CLOSURE WITH CERAMIC VENEER ON MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR SARITA SINGH 1a, NITIN
Indian J.Sci.Res.10(1): 07-11, 2015 ISSN: 2250-0138(Online) ESTHETIC ENHANCEMENT BY NONVITAL BLEACHING PROCEDURE AND DIASTEMA CLOSURE WITH CERAMIC VENEER ON MAXILLARY CENTRAL INCISOR SARITA SINGH 1a, NITIN
REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW
 REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW Marri Sai Archana 1 *, Varri Sujana 2, Bolla Nagesh 3, Polavarapu Jaya Krishna Babu 4 1. Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Sibar Institute of Dental
REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW Marri Sai Archana 1 *, Varri Sujana 2, Bolla Nagesh 3, Polavarapu Jaya Krishna Babu 4 1. Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Sibar Institute of Dental
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A."
 Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
Dental material for filling the root canals "AUREOSEAL M.T.A." Highly biocompatible root canal cement without eugenol. 1. Composition: Powder: Mineral-trioxide-agregat (М.Т.А.) based on Portland cement,
Emergency Management of Trauma
 Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS
 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
The use of mineral trioxide aggregate in one-visit apexification treatment: a prospective study
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01214.x The use of mineral trioxide aggregate in one-visit apexification treatment: a prospective study S. Simon 1,2, F. Rilliard 2, A. Berdal 1 & P. Machtou 2 1 Laboratory
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01214.x The use of mineral trioxide aggregate in one-visit apexification treatment: a prospective study S. Simon 1,2, F. Rilliard 2, A. Berdal 1 & P. Machtou 2 1 Laboratory
Current concepts in the management of dental trauma
 Current concepts in the management of dental trauma S ALBADRI BDS, PHD, MFDS, MPAEDENT, FDS (PAED DENT),FHES READER /HONORARY CONSULTANT IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Introduction ØAround one in ten children
Current concepts in the management of dental trauma S ALBADRI BDS, PHD, MFDS, MPAEDENT, FDS (PAED DENT),FHES READER /HONORARY CONSULTANT IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Introduction ØAround one in ten children
Trauma to the anterior teeth, commonly found among young children, accounts for
 Efficacy of Revascularization to Induce Apexification/Apexogensis in Infected, Nonvital, Immature Teeth: A Pilot Clinical Study Naseem Shah, MDS, Ajay Logani, MDS, Uday Bhaskar, MDS, and Vivek Aggarwal,
Efficacy of Revascularization to Induce Apexification/Apexogensis in Infected, Nonvital, Immature Teeth: A Pilot Clinical Study Naseem Shah, MDS, Ajay Logani, MDS, Uday Bhaskar, MDS, and Vivek Aggarwal,
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 120 127 doi: 10.1111/adj.12403 Life cycles of traumatized teeth: long-term
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 120 127 doi: 10.1111/adj.12403 Life cycles of traumatized teeth: long-term
Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach
 Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach Yuli Berlin-Broner 1 Ysidora Torrealba 2 Liran Levin 3 1 Division of Endodontics, Faculty of Medicine and
Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach Yuli Berlin-Broner 1 Ysidora Torrealba 2 Liran Levin 3 1 Division of Endodontics, Faculty of Medicine and
Endodontic treatment of mandibular incisors with two root canals: Report of two cases
 Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USAAEJAustralian Endodontic Journal1329-1947 2007 The Authors;? 2007 2731Case ReportMandibular Incisors with Two CanalsY. S. Kabak and P. V. Abbott Aust Endod J 2007; 33:
Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USAAEJAustralian Endodontic Journal1329-1947 2007 The Authors;? 2007 2731Case ReportMandibular Incisors with Two CanalsY. S. Kabak and P. V. Abbott Aust Endod J 2007; 33:
Management of Internal Resorption with Perforation
 Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Apexification of Immature Teeth Using Novel Apical Matrices and MTA Barrier: Report of Two Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III. (Mar. 2014), PP 27-31 Apexification of Immature Teeth Using Novel Apical Matrices
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III. (Mar. 2014), PP 27-31 Apexification of Immature Teeth Using Novel Apical Matrices
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
 Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Excellent results have been reported 1-4 with the use of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) (ProRoot MTA, Dentsply-Tulsa Dental, Tulsa, OK, USA) as a pulp capping agent. When compared
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Excellent results have been reported 1-4 with the use of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) (ProRoot MTA, Dentsply-Tulsa Dental, Tulsa, OK, USA) as a pulp capping agent. When compared
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
Pediatrics. Biodentine. Dentin Substitute
 Pediatrics Biodentine Dentin Substitute Biodentine : Therapeutic care for your younger patients teeth (5) 1 2 Maintain pulp vitality Biodentine is bioactive and promotes the pulp s self healing capacity
Pediatrics Biodentine Dentin Substitute Biodentine : Therapeutic care for your younger patients teeth (5) 1 2 Maintain pulp vitality Biodentine is bioactive and promotes the pulp s self healing capacity
SingleVisit Apexification Technique for Inducing Root-End Barrier Formation in Apical Closures: Report of Two Cases P. Jain, C. Rita, R.S.
 Case Report SingleVisit Apexification Technique for Inducing Root-End Barrier Formation in Apical Closures: Report of Two Cases P. Jain, C. Rita, R.S. Agarwal Department of Endodontics, Sri Aurobindo College
Case Report SingleVisit Apexification Technique for Inducing Root-End Barrier Formation in Apical Closures: Report of Two Cases P. Jain, C. Rita, R.S. Agarwal Department of Endodontics, Sri Aurobindo College
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report
 Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Pulp Vitality. in Pediatric Patients. Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth. 86 MAY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Jarod Johnson, DDS
 Pulp Vitality in Pediatric Patients Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth by Jarod Johnson, DDS Jarod Johnson, DDS, earned a bachelor s degree in biomedical engineering from the University
Pulp Vitality in Pediatric Patients Treating deep carious lesions in vital permanent teeth by Jarod Johnson, DDS Jarod Johnson, DDS, earned a bachelor s degree in biomedical engineering from the University
Chronic iatrogenic lateral root perforation with open apex
 CASE REPORT Chronic iatrogenic lateral root perforation with open apex Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 2, Srivastava MC 3 Quick Response Code doi: 10.5866/2015.7.10217 1 Associate Professor,
CASE REPORT Chronic iatrogenic lateral root perforation with open apex Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 2, Srivastava MC 3 Quick Response Code doi: 10.5866/2015.7.10217 1 Associate Professor,
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report
 Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Root canal therapy. Phase 1: Relief of pain
 Root canal therapy Root Canal therapy is required when the pulp becomes inflamed or infected. This can be caused by deep decay, recurring dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth.
Root canal therapy Root Canal therapy is required when the pulp becomes inflamed or infected. This can be caused by deep decay, recurring dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth.
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
MANAGEMENT OF OPEN APEX IN PERMANENT TEETH WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE PASTE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 01 MANAGEMENT OF OPEN APEX IN PERMANENT TEETH WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE PASTE Abu-Hussein Muhamad*, Jabareen Ayah, Abdulgani
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 01 MANAGEMENT OF OPEN APEX IN PERMANENT TEETH WITH CALCIUM HYDROXIDE PASTE Abu-Hussein Muhamad*, Jabareen Ayah, Abdulgani
The Endodontics Introduction. By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD
 The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes
 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad¹, Noushin Shokouhinejad 2, Salma Pirmoazen 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad¹, Noushin Shokouhinejad 2, Salma Pirmoazen 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 403045, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/403045 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 403045, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/403045 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam
The obturation of the prepared radicular space has been achieved by using a wide
 Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Obturation: A Review and Case Series George Bogen, DDS* and Sergio Kuttler, DDS Abstract Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) has emerged as a reliable bioactive material with extended
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Obturation: A Review and Case Series George Bogen, DDS* and Sergio Kuttler, DDS Abstract Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) has emerged as a reliable bioactive material with extended
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
Conservative Dentistry
 ISSN: 0972-0707 Journal of Conservative Dentistry Volume 18 Issue 6 Nov - Dec 2015 Official Publication of Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics Online full text at www.jcd.org.in
ISSN: 0972-0707 Journal of Conservative Dentistry Volume 18 Issue 6 Nov - Dec 2015 Official Publication of Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics Online full text at www.jcd.org.in
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions by means of Conventional Endodontic treatment a Report of Two Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2015), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2015), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics. Pain History. Patient Assessment. Examination. Examination 11/07/2014
 Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3.
 Case Report William Hu Non-Surgical Retreatment #3 36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3. Subjective Chief complaint: I was referred to see if you can do a new root
Case Report William Hu Non-Surgical Retreatment #3 36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3. Subjective Chief complaint: I was referred to see if you can do a new root
September 19. Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al.
 2012 September 19 Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al. Journal: Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 205-209 Reviewer: Arnav R. Mistry, DMD Purpose:
2012 September 19 Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al. Journal: Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 205-209 Reviewer: Arnav R. Mistry, DMD Purpose:
NON'SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' LARGE'PERIAPICAL'LESION'USING' MTA:'REPORT'OF'2'CASES)
 NOUSHAD,MC* NIYAZ,Mohammed* PEEDIKAYIL,FaizalC** PRADEEP,CV*** SEBASTIAN,Anish* ARAFATH,MuhammedYazar* NONSURGICALMANAGEMENTOF LARGEPERIAPICALLESIONUSING MTA:REPORTOF2CASES ABSTRACT Inthepast,caseswithopenapiceswereoftentreatedoverseveral
NOUSHAD,MC* NIYAZ,Mohammed* PEEDIKAYIL,FaizalC** PRADEEP,CV*** SEBASTIAN,Anish* ARAFATH,MuhammedYazar* NONSURGICALMANAGEMENTOF LARGEPERIAPICALLESIONUSING MTA:REPORTOF2CASES ABSTRACT Inthepast,caseswithopenapiceswereoftentreatedoverseveral
The Power of the Pulp
 The Power of the Pulp Part 1 Dr Kishan Sheth recently graduated from KCL as a runner-up for the prestigious Jose Souyave Prize and will embark on his vocational training in Central London. He has become
The Power of the Pulp Part 1 Dr Kishan Sheth recently graduated from KCL as a runner-up for the prestigious Jose Souyave Prize and will embark on his vocational training in Central London. He has become
See This presentation on Video. https://goo.gl/pmg3yg
 See This presentation on Video https://goo.gl/pmg3yg Coimbra Vienna INTRODUCTION Root resorption Pulp Capping Furcal repair Root end filling Repair of root perforation Apexification Parirokh M, Torabinejad
See This presentation on Video https://goo.gl/pmg3yg Coimbra Vienna INTRODUCTION Root resorption Pulp Capping Furcal repair Root end filling Repair of root perforation Apexification Parirokh M, Torabinejad
Apexification has traditionally formed an integral part of the treatment of teeth with
 Retrospective Analysis of Open Apex Teeth Obturated with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate David E. Witherspoon, BDSc, MS,* Joel C. Small, DDS,* John D. Regan, BDS, MS,* and Martha Nunn, DDS, PhD Abstract This
Retrospective Analysis of Open Apex Teeth Obturated with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate David E. Witherspoon, BDSc, MS,* Joel C. Small, DDS,* John D. Regan, BDS, MS,* and Martha Nunn, DDS, PhD Abstract This
Treatment of perforating internal root resorption with MTA: a case report
 127 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 54, No. 1, 127-131, 2012 Case Report Treatment of perforating internal root resorption with MTA: a case report Eduardo Nunes 1), Frank F. Silveira 1,2), Janir A. Soares
127 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 54, No. 1, 127-131, 2012 Case Report Treatment of perforating internal root resorption with MTA: a case report Eduardo Nunes 1), Frank F. Silveira 1,2), Janir A. Soares
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: , 2016
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 113-117, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Seal Ability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Nano Hydroxyapatite Retrograde Filling Material on Internal
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, March: 113-117, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Seal Ability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Nano Hydroxyapatite Retrograde Filling Material on Internal
Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching of Endodontically Treated Teeth
 0099-2399/90/1612-0570/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 12, DECEMBER 1990 Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching
0099-2399/90/1612-0570/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 12, DECEMBER 1990 Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University

