The surgical placement of dental implants has
|
|
|
- Amberlynn Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants placed with a flapless approach. Materials and Methods: Seven hundred seventy implants were placed in 359 patients to restore both completely edentulous and partially edentulous arches with fixed prostheses or removable complete dentures. Each patient was examined after 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, and then once every year. Prostheses were removed, if possible, and implant mobility was assessed, periapical radiographs were obtained, and periodontal probing was performed. Implants were considered failed if they had mobility or pain, had to be removed, or if they showed more than 0.5 mm of bone loss per year and signs of active peri-implantitis. Results: The cumulative success rate for implants placed using a flapless 1- stage surgical technique after a 10-year period varied from 74.1% for implants placed in 1990 to 100% at Discussion: Since flapless implant placement is a generally blind surgical technique, care must be taken when placing implants. Angulation of the implants affected by drilling is critcal to avoid perforation of the cortical plates, both lingual or buccal, especially on the lingual in the mandibular molar area and the anterior maxilla. There should be no problem if the patient has been appropriately selected and an appropriate width of bone is available for implant placement. There is a learning curve to every surgical procedure, after which it becomes routine. There are many advantages for the patient as well as for the surgeon, since the procedure is less time consuming, bleeding is minimal, implant placement is expedited, and there is no need to place and remove sutures. Conclusion: Flapless implant surgery is a predictable procedure if patient selection and surgical technique are appropriate. (INT J ORAL MAXILLOFAC IMPLANTS 2002;17: ) Key words: dental implants, implant surgery, soft tissue flaps The surgical placement of dental implants has undergone changes since the beginning of placement of root-form implants. Initially, using the Brånemark protocol, an incision in the mucosa or the mucobuccal fold was made, and then a flap was reflected to expose the underlying bone. The implants were placed and the flap was sutured back in place. 1 3 The rationale for this incision was to keep the incision line away from the implants, thereby possibly preventing infection. In a retrospective study, Scharf and Tarnow 4 demonstrated that there was no difference in the implant success rates when implants were placed with a midcrestal incision; however, they concluded that it was far more advantageous to use a midcrestal incision since the swelling and the postoperative pain were greatly minimized. 1 Private Practice, Madrid, Spain. 2 Maxillofacial Surgeon, Private Practice, Madrid, Spain. Reprint requests: Dr Luis Dominguez Campelo, Orense 22 A 8 B, Madrid, Spain. Fax: drluisdominguez@clinicadentaldrdominguez.com When dental implants are placed after reflecting soft tissue flaps, there generally is some bone resorption. During the initial phase of healing, bone resorption of varying degrees almost always occurs in the crestal area of the alveolar bone. 5 The extent of alveolar height reduction resulting from this resorption is related to the bone thickness at each specific site. 6 When teeth are present, blood supply to the bone comes from 3 different paths: from the periodontal ligament, from the connective tissue above the periosteum, and from inside the bone. When a tooth is lost, blood supply from the periodontal ligament disappears, so that blood now comes only from soft tissue and bone. Cortical bone is poorly vascularized and has very few blood vessels running through it, in contrast to marrow bone. When soft tissue flaps are reflected for implant placement, blood supply from the soft tissue to the bone (supraperiosteal blood supply) is removed, thus leaving poorly vascularized cortical bone without a part of its vascular supply, prompting bone resorption during the initial healing phase. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 271
2 Adequate bone width shown preopera- Fig 1a tively. Fig 1c There is some swelling, pain, and discomfort associated with every surgical procedure. With a flapless approach, surgical trauma is minimal because the circular incision is very small, usually 1 mm wider than the implant to be placed, so that postoperative pain, swelling, and discomfort related to soft tissue trauma are greatly minimized. MATERIALS AND METHODS In a retrospective clinical analysis dating to 1990, 359 patients were included in the investigation. These patients were provided with a total of 770 implants to replace missing teeth with either fixed partial dentures or implant-retained overdentures. The patient group comprised 126 men and 233 women with an age range from 27 to 83 at implant placement and a mean age of 54.7 years. Implants used were made of commercially pure grade III titanium with a sandblasted surface and a polished collar of 2 mm. The implants had an external hexagon of 1.7 mm in height. All implants placed were single-stage implants, so no secondstage surgery was performed. 272 Volume 17, Number 2, 2002 Implant placed with healing cap. Fig 1b Circular incisions made with the circumferential scalpel at low speed. Patient Selection All consecutive patients who had implants placed to restore either complete edentulism or partial edentulism since 1990 without the use of soft tissue flaps, and who have been followed to date (2000), have been included in this retrospective clinical analysis. Three hundred seventy-seven patients had 860 implants placed with a flapless approach. Patients were followed at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, and then once every year. Patients who had implants placed with this method and did not attend the yearly follow-up visit were not included in the study for statistical analysis (18 patients, 4.78% drop-out rate), which left a total of 359 patients with 770 implants placed. Periodontal probing, Gingival Index, and implant mobility were performed by the same clinicians, and implants were considered successful if they met the criteria of Albrektsson and coworkers. 7 Implants were examined at 3 months, 6 months, and then once every year. The restoration was removed, if possible, to check mobility at follow-up visits once a year. Since not all restorations could be removed, the success criteria were not met for every implant; however, they were considered successful if they had no pain while functioning and on percussion. Implants were recorded as failed if they were mobile or painful at any time following treatment, had to be removed because of pain, or showed bone loss of more than 0.5 mm per year for consecutive years after the first year of function. Periodontal probing and periapical radiography were obtained to assess changes in the bone and in peri-implant tissues. Surgical Technique Since no soft tissue flaps were going to be raised during implant placement, the quantity and morphology of the bone that would host the implants required preoperative assessment. At least 7 mm of bone width was required for placement using a noninvasive technique with no undercuts, since the direction of the bur would not be visible (Fig 1a). Bone anatomy and quantity were determined by means of a computed tomographic (CT) scan, digital palpation, or calipers. All patients who had
3 Fig 2a Improper bur angulation may lead to undesired results. implants placed in the maxilla routinely received a CT scan, while the number of mandibular implant patients who received a CT scan varied, depending on the quantity and morphology of the mandible. Under local anesthesia, a circumferential incision was made in the gingiva at the center of the implant site using a surgical template (Fig 1b). The cut was made with a circumferential rotary blade at low speed (100 rpm). The circumferential scalpel should be at least 1 mm wider than the implant to be placed. The incised gingival tissue was removed with a curette or mosquito hemostat. The thickness of the gingiva covering the bone was measured and the implants were placed as recommended by the manufacturer. Healing abutments were connected to the implants (Fig 1c). With the incision of the circumferential scalpel being 1 mm wider than the size of the implant to be placed, closure of the wound generally occurred between 3 or 4 days. Fenestration or dehiscence can occur when bur angulation is incorrect, so bur drilling is critical (Figs 2a and 2b). Fenestration occurred with 21 implants (2.73% of total implants placed), 12 in maxillary mids, 7 in maxillary left s, and 4 in the maxillary right. When fenestration occurred, a soft tissue flap was raised and the fenestration was covered with a xenograft and a resorbable membrane. Dehiscence occurred at 15 implants (2%), 6 in mandibular right s and 9 in mandibular mids. When dehiscence occurred, if the implant placed was to be used for a removable prosthesis, another implant site was chosen; if the implant s purpose was to support a fixed prosthesis, the site was left to heal for 3 months and then an implant was placed following a traditional soft tissue flap approach. Since surgical trauma is minimal, anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications were given to the patient as prophylactics and patients were advised not to take them in the absence of pain or swelling. Most patients did not require medication other than antibiotics and pain was minimal. Bone dehiscence after incorrect bur angu- Fig 2b lation. RESULTS The cumulative success rate for implants placed using a flapless, 1-stage surgical technique after a 10-year period varied from 74.1% for implants placed in 1990 to 100% in 2000 (Table 1). Of the 37 failed implants, 37.83% failed between placement and loading, 16.21% failed during the first year of function, and 45.94% failed after the first year of function (Table 1). Implant location was divided into 6 s, which were the maxillary right, maxillary mid, maxillary left, mandibular left, mandibular mid, and mandibular right (Table 2). The maxillary mid was the location that received the fewest implants, with 3.6% of the total; the remainder of the locations were similar in the quantity of implants placed. The cumulative success rate after a 10-year period was over 91% for any of the implant locations (Table 3). The failures were associated with a learning curve and patient selection, since most of the failures occurred in the early years of using this technique. During 1990, there were 8 failures among 31 implants (25%), which decreased to 0% in 2000 (Table 4 and Fig 3a). The results are associated with the learning curve and patient selection. As the patient selection and technique experience improved, the failure rate decreased, although the number of implants placed increased (Fig 3b). Every patient who had implants placed without flap reflection was queried. More than 90% of them indicated they had not taken any kind of pain medication and reported the procedure was totally painless. In fact, many patients were referred for treatment because of the reputation of being painless and which, to the patients, seemed simple and effective. Patients with complications during the surgical procedure were given pain medication and treated as if soft tissue flaps were reflected. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 273
4 274 Volume 17, Number 2, 2002 Table 1 Number of Implants Placed, Number of Implants Failed and Failing, Time to Failure, and Success Rate for Every Year Year Implants Failed Failed + Time to failure* Success placed placed implants Failing failing (% of failed implants) rate : 28.57% (2 implants) 74.1% 2: 14.28% (1 implant) 3: 57.14% (4 implants) : 66.66% (4 implants) 83.6% 3: 33.33% (2 implants) : 33.33% (2 implants) 87.1% 3: 66.66% (4 implants) : 20% (1 implant) 91.93% 2: 60% (3 implants) 3: 20% (1 implant) : 100% (3 implants) 92.64% : 100% (3 implants) 96.05% : 100% (2 implants) 94.1% : 100% (2 implants) 97.26% : 100% (2 implants) 96.55% : 100% (1 implant) 98.75% % Total *1 = between placement and loading; 2 = between loading and 1 year; 3 = after 1 year of function. Table 2 Table 3 Implants Failed by Location and Cumulative Success Rate After a 10-year Period Total implants failed One Two Cumulative implant implant success Location failure failure Total rate (%) Maxillary right Maxillary mid Maxillary left Mandibular left Mandibular mid Mandibular right Total Situation by Number of Implants Cumulative Location Frequency Percent percent Maxillary right Maxillary mid Maxillary left Mandibular left Mandibular mid Mandibular right Total Table 4 Total Number of Failed Implants per Year After a 10-year Period Cumulative Valid Frequency Percent percent Total
5 Fig 3a Total number of failed implants per year after a 10-year period. Fig 3b Number of implants per year. DISCUSSION Since flapless implant placement generally is a blind surgical technique, care must be taken when placing implants. Angulation of the implants affected by drilling is critical so as to avoid perforation of the cortical plates, both lingual and buccal, especially on the lingual in the mandibular molar area and the anterior maxilla. There should be no problem if the patient has been appropriately selected and an appropriate width of bone is available for implant placement. When the esthetic appearance of the soft tissue is critical, making a flap is far more advantageous, since the soft tissue can be manipulated to place it in a desirable position. Soft tissue augmentation can be predictably achieved around a healing abutment No. of implants No. of failures Year of implantation Year of implantation 85 at the time of implant placement or second-stage surgery. Today, with the use of stone or resin casts obtained from the patients CT scan and the use of computer software for implant guidance, it is possible to know preoperatively the exact direction of the implants to be placed, making it possible to fabricate surgical templates with guides that precisely orient the direction of the implant burs. 8 Existing literature concerning the desirability of keratinized tissue around endosseous implants shows conclusive results. While some studies show that the absence of keratinized tissue is not critical to the health of the gingival tissue and implant prognosis, 9,14 other studies suggest that the failure rate is higher when there is an absence or small amount of keratinized tissue The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants
6 After reviewing this literature, it is apparent that the presence or absence of keratinized tissue depends on the type of implant being used. The absence of keratinized tissue is not critical if machined implants or implants with a polished neck are used, while the presence of keratinized gingiva is critical if rough-surfaced implants (sand blasted, large grit, acid etched, resorbable blast media, acidetched, etc) are used. Consequently, implant companies have begun bringing the rough surface of their implants down to the second or third thread or providing hybrid designs in which the implants become rougher toward the apical end. Patient acceptance of this technique has been very high. Patients who have had implants placed with a flapless approach and also the conventional technique clearly prefer a flapless approach. Swelling and pain can be greatly avoided when there is no flap reflection, and patients also realize that there is no need to suture, which makes them believe that surgical trauma is lessened. Most patients, when having implants placed with flapless surgery, require minimal postoperative medication. There was no occurrence of hematoma compared to the conventional surgical approach, in which it is not rare to observe postoperative hemorrhage. Most patients can return to their normal lives the day following surgery. There is a learning curve with every surgical procedure, after which it becomes routine. There are many advantages for the patient as well as for the surgeon, since the procedure is less time consuming, bleeding is minimal, implant placement is expedited, and there is no need to place and remove sutures. CONCLUSIONS Flapless implant surgery is a predictable procedure when patient selection and surgical technique are appropriate. Correct bur angulation is critical in the procedure, where the chance of fenestration of dehiscence related to incorrect bur angulation must be minimized. As with every technique, there are some advantages and disadvantages associated with flapless surgical implant placement. It is the implant surgeon who should make the decision to place implants using a flapless approach, depending on the quantity and morphology of the bone that will receive the implants and based on his or her own surgical expertise and technique. 276 Volume 17, Number 2, 2002 REFERENCES 1. Brånemark P-I, Hansson BO, Adell R, et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand Plast Reconstr Surg 1977;16 (suppl): Albrektsson T, Brånemark P-I, Hansson HA, Lindström J. Osseointegrated titanium implants. Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting direct bone anchorage in man. Acta Orthop Scand 1981;52: Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark P-I. A 15-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg 1981;6: Scharf DR, Tarnow DP. The effect of crestal versus mucobuccal incisions on the success rate of implant osseointegration. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1993;8: Ramfjord SP, Costich ER. Healing after exposure of periosteum on the alveolar process. J Periodontol 1968;38: Wood DL, Hoag PM, Donnenfeld OW, Rosenfeld LD. Alveolar crest reduction following full and partial thickness flaps. J Periodontol 1972; 42: Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1986;1: Klein M, Abrams M. Computer-guided surgery utilizing a computer-milled surgical template. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 2001;13: Wennstrom JL, Bengazi F, Lekholm U. The influence of masticatory mucosa on the peri-implant soft tissue condition. Clin Oral Implants Res 1994;5: Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, et al. Marginal tissue reactions of osseointegrated titanium fixtures. I. A 3-year longitudinal prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1986;15: Krekeller G, Schilli W, Diemer J. Should the exit of the artificial abutment tooth be positioned in the region of the attached gingiva? Int J Oral Surg 1985;14: Lekholm U, Adell R, Lindhe J, et al. Marginal tissue reactions at osseointegrated titanium fixtures: A cross-sectional retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1986;15: Strub JR, Gabethuel TW, Grunder U. The role of attached gingiva in the health of peri-implant tissue in dogs. 1. Clinical findings. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1991;11: Van Steenberghe D. Periodontal aspects of osseointegrated oral implants ad modum Brånemark. Dent Clin North Am 1988;32: Block MS, Kent JN. Long-term follow-up on hydroxylapatite coated cylindrical dental implants: A comparison between developmental and recent periods. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1994;52: Block MS, Kent JN. Factors associated with soft- and hardtissue compromise of endosseous implans. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1990;48: Warrer K, Buser D, Lang NP, Karring T. Plaque-induced peri-implantitis in the presence or absence of keratinized mucosa. An experimental study in monkeys. Clin Oral Implants Res 1995;6: Kirsch A, Ackermann KC. The IMZ osteointegrated implant system. Dent Clin North Am 1989;33: Buser D, Weber HP, Lang NP. Tissue integration of nonsubmerged implants, 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-screw and hollow-cylinder implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1990;1: Buser DA, Schroeder A, Sutter F, Lang NP. The new concept of ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Part 2. Clinical aspects, indications, and early clincial results. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1988;3:
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report of two cases
 Case Report J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:194-200 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.4.194 A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report
Case Report J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:194-200 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.4.194 A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
A 1-year prospective clinical study of soft tissue conditions and marginal bone changes around dental implants after flapless implant surgery
 A 1-year prospective clinical study of soft tissue conditions and marginal bone changes around dental implants after flapless implant surgery Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD, a Byung-Ho Choi, DDS, PhD, b Jihun
A 1-year prospective clinical study of soft tissue conditions and marginal bone changes around dental implants after flapless implant surgery Seung-Mi Jeong, DDS, PhD, a Byung-Ho Choi, DDS, PhD, b Jihun
Much has been written about the success of various
 Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha
 Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha Bansal J, Bansal A, DK Suresh, Manocha A. Immediate loading of single stage implants with minimally invasive
Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha Bansal J, Bansal A, DK Suresh, Manocha A. Immediate loading of single stage implants with minimally invasive
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2018; 4(1): Dr. Renu gupta, Dr. RP Luthra, Suhani Kukreja
 2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants
 Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Richard P. Kinsel, DDS 1 /Mindy Liss, MSc 2
 Retrospective Analysis of 56 Edentulous Dental Arches Restored with 344 Single-Stage Implants Using an Immediate Loading Fixed Provisional Protocol: Statistical Predictors of Implant Failure Richard P.
Retrospective Analysis of 56 Edentulous Dental Arches Restored with 344 Single-Stage Implants Using an Immediate Loading Fixed Provisional Protocol: Statistical Predictors of Implant Failure Richard P.
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Successful osseointegration of implants has been
 Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
The clinical use of endosseous implants has
 A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
Replacement of missing teeth with
 A simple surgical technique to maximise prosthetic results Timothy Kosinski presents a technique to help minimise surgical risk, as well as helping the dentist to understand anatomy and proper implant
A simple surgical technique to maximise prosthetic results Timothy Kosinski presents a technique to help minimise surgical risk, as well as helping the dentist to understand anatomy and proper implant
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS
 DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Long-term Results of Implants Treated with Guided Bone Regeneration: A 5-year Prospective Study
 Long-term Results of Implants Treated with Guided Bone Regeneration: A 5-year Prospective Study Nicola Ursula Zitzmann, Dr Med Dent 1 /Peter Schärer, Prof Dr Med Dent, MS 2 / Carlo Paolo Marinello, Prof
Long-term Results of Implants Treated with Guided Bone Regeneration: A 5-year Prospective Study Nicola Ursula Zitzmann, Dr Med Dent 1 /Peter Schärer, Prof Dr Med Dent, MS 2 / Carlo Paolo Marinello, Prof
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework
 Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework Authors Dr. Aleksandar Lazarov Solunska Str. 3 BG-1000 Sofia Bulgaria Email: alex.lazarov@yahoo.co.uk
Case report: Replacement of failing 2 stage implants by basal implants and conventional bridgework Authors Dr. Aleksandar Lazarov Solunska Str. 3 BG-1000 Sofia Bulgaria Email: alex.lazarov@yahoo.co.uk
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally
 Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible
 Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report
 CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys
 The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
While the protocol for direct bone-to-implant
 Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Computer-guided minimally invasive
 CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible
 A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Initially, Brånemark System (Nobel Biocare AB,
 Clinical Application of Narrow Brånemark System Implants for Single-Tooth Restorations Giovanni Polizzi, MD, DDS*/Sandro Fabbro, MD**/Marco Furri, DDS**/ Irene Herrmann, DDS***/Sergio Squarzoni, MD****
Clinical Application of Narrow Brånemark System Implants for Single-Tooth Restorations Giovanni Polizzi, MD, DDS*/Sandro Fabbro, MD**/Marco Furri, DDS**/ Irene Herrmann, DDS***/Sergio Squarzoni, MD****
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants
 Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants Alan B. Carr, DMD, MS 1 /Yong-Geun Choi, DDS, MPH, MPH 2 / Steven E. Eckert, DDS, MS 1 /Ronald P. Desjardins, DMD, MS 3
Retrospective Cohort Study of the Clinical Performance of 1-Stage Dental Implants Alan B. Carr, DMD, MS 1 /Yong-Geun Choi, DDS, MPH, MPH 2 / Steven E. Eckert, DDS, MS 1 /Ronald P. Desjardins, DMD, MS 3
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Retrospective Clinical Study on Flapless Implant Placement
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Korean Dent Sci. 2012;5(2):54-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2012.5.2.54 ISSN 2005-4742 Retrospective Clinical Study on Flapless Implant Placement Jong-Hee Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE J Korean Dent Sci. 2012;5(2):54-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2012.5.2.54 ISSN 2005-4742 Retrospective Clinical Study on Flapless Implant Placement Jong-Hee Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1,
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
INTRODUCTION. General Information. Important Warning
 S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
Areview of recent studies concerning molar. Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report
 Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
The need for controlled clinical studies
 Factors Associated With Radiographic Vertical Bone Loss Around Implants Placed in a Clinical Study Michael C. Manz* * Previously, VA Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI; currently, Department of Cariology, Restorative
Factors Associated With Radiographic Vertical Bone Loss Around Implants Placed in a Clinical Study Michael C. Manz* * Previously, VA Medical Center, Ann Arbor, MI; currently, Department of Cariology, Restorative
Moderately to severely resorbed edentulous
 The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
Michael P. Hänggi,* Daniel C. Hänggi, John D. Schoolfield, Jürg Meyer,* David L. Cochran, and Joachim S. Hermann
 J Periodontol May 2005 Crestal Bone Changes Around Titanium Implants. Part I: A Retrospective Radiographic Evaluation in Humans Comparing Two Non-Submerged Implant Designs With Different Machined Collar
J Periodontol May 2005 Crestal Bone Changes Around Titanium Implants. Part I: A Retrospective Radiographic Evaluation in Humans Comparing Two Non-Submerged Implant Designs With Different Machined Collar
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants
 The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
CASE REPORT MEGAGEN IMPLANT. AnyRidge. CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP
 AnyRidge CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP AnyRidge Clinical Case Ⅰ. Dr. Davide Farronato Baseline - fractured tooth Baseline - fractured tooth #25 Rx view Atraumatic avulsion technique
AnyRidge CLINICAL CASE REPORT Davide Farronato, DDs, PhD, PD, AP AnyRidge Clinical Case Ⅰ. Dr. Davide Farronato Baseline - fractured tooth Baseline - fractured tooth #25 Rx view Atraumatic avulsion technique
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
 A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
INTRODUCTION. Jun-Won Hong 1, DDS, MS, Seung-Geun Ahn 1, DDS, PhD, Dae-Ho Leem 2, DDS, PhD, Jae-Min Seo 1 *, DDS, MS
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
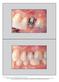
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
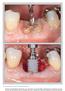 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Specialty Dentistry. Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association
 Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology
 Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
