Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
|
|
|
- Marcia Little
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (2010) 39, The British Institute of Radiology CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani 2 and T Koseki 2 1 Department of Oral Radiology, West China College of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China; 2 Department of Oral Radiology, Osaka Dental University, Osaka, Japan The purpose of this article is to report 20 cases of ossifying fibroma involving the jaw bone and to review the literature of this lesion. All the cases had adequate radiographs and clinical information. Varying shapes of the lesion including cystic lesion and mixed density lesion are presented, including two massive expansile lesions, which measured more than 10 cm. (2010) 39, doi: /dmfr/ Keywords: ossifying fibroma; plain X-ray; jaw bone; mandible; bone neoplasm Introduction Ossifying fibroma (OF) is classified as, and behaves like, a benign bone neoplasm. It is often considered to be a type of fibro-osseous lesion (FOL). It can affect both the mandible and the maxilla, particularly the mandible. This bone tumour consists of highly cellular, fibrous tissue that contains varying amounts of calcified tissue resembling bone, cementum or both. In 1968, Hamner et al 1 analysed 249 cases of fibroosseous jaw lesions of periodontal membrane origin and classified them. In 1973, Waldron and Giansanti 2 reported 65 cases (of which 43 cases had adequate clinical histories and radiographs) and concluded that this group of lesions was best considered as a spectrum of processes arising from cells in the periodontal ligament. In 1985, Eversole et al 3 described the radiographic characteristics of central ossifying fibroma, and two major patterns were noted, expansile unilocular radiolucencies and multilocular configuration. Although some cases of OF have been reported in the published literature, massive expansile lesions measuring more than 10 cm, like the cases in this study, were rare. The adequate radiographs of the cases of OF presented can further help us to understand the variable radiographic appearances of this lesion. Case reports 20 cases of OF were obtained from the Department of Oral Radiology, West China College of Stomatology, *Correspondence to: Hu Wang, Department of Oral Radiology, West China College of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, , PR China; wanghu200108@163.com Received 2 November 2008; revised 11 January 2009; accepted 6 February 2009 Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No and ) Sichuan University, from the years 1968 to The final diagnoses of all OF cases were confirmed by histopathological examination. The patient clinical data are shown in Table 1. The study was based on 20 patients, 9 males and 11 females. The mean age was 27.8 years, with a range of 6 57 years. 16 cases were located in the mandible and the other 4 cases in the maxilla. 12 patients showed obvious facial asymmetry and the other 8 patients showed only the affected side plumped up. 19 patients came to the hospital with a history of gradual swelling of the jaw, 1 of whom felt a little pain; the rest had no pain. One patient was admitted to hospital with cellulitis of submandibular space, and the mass was found inadvertently during the intraoral examination. Hard texture, immovability and a clear boundary line were present in all patients. The patient radiological data are shown in Table 2, and the radiological diagnosis in Table 3. Based on the radiographic appearances of the OF the lesions may occur at different positions on the jaw bone and present in varying shapes. There were eight cases showing cystic lesions, of which six were unicystic (75%) and two were multicystic (25%). The radiographic appearance of case 5 demonstrated a classic unilocular cyst-like lesion with an irregular high-density mass in it. The lesion was located at the apex region from the mandibular right canine to the left first premolar. A radiopaque line at the periphery separated the internal radiolucent portion from the surrounding normal bone, so the boundary between the lesion and normal mandibular bone was easy to distinguish (Figure 1). The other five cases (cases 1 4 and case 6) which presented as unicystic lesions had similar radiographic appearances involving
2 58 Y Liu et al Table 1 Clinical information on 20 cases of ossifying fibroma Case no. Gender Age (years) Chief complaint Oral examination 1 F 39 A painless swelling in the right mandible for 6 months A painless hard mass approximately cm 3 in the right mandibular angle region with the expansion of the right mandible well defined A hard and fixed mass with buccolingual expansion 2 F 6 Painless expansion of the left mandible for 25 days 3 F 45 A painless mass in the left A hard and immovable mass in the left mandible mandible for more than 2 years 4 F 30 Expansion of the mandible for A hard and fixed mass in the anterior teeth region, 6 months with buccolingual expansion of the bone 5 F 31 A swelling in the right mandible A painless mass in the lingual surface of the right mandible, for several days about 6 6 3cm 2 6 M 38 A painless swelling in the left A raised hard mass approximately 1.5 cm in diameter in the mandible for more than 10 years anterior teeth region of the left mandible, the second incisor and the canine shifting because of the mass 7 F 20 Expansion of the left face A swelling in the left hard palate from the first premolar to for 1.5 months the second molar 8 F 12 A symptomless mass for 2 weeks A hard mass with buccolingual expansion in the left mandible 9 F 12 An osteal swelling at the chin for Bulging in the anterior teeth area of the mandible 8 years 10 M 17 A swelling in the left face for A hard expansion in the premolar region of the left mandible 3 years, and recent rapid with the lingual displacement of the premolars development 11 M 30 A painless osteal mass in the right maxilla for 7 years 12 M 45 A painless swelling in the left mandible for more than 1 year, with recent pain 13 M 15 Right facial deformity for more than 8 years 14 M 12 A painless bulge in the right mandible for more than 4 years 15 M 35 Cellulitis of submandibular space for 5 days 16 M 33 Bulging in the mandible for more than 7 years, recurring 6 months after operation 17 F 20 A swelling in the right maxilla for 10 months 18 F 44 A symptomless mass in the right mandible for more than 2 months 19 F 57 A bulging in the right mandible for more than 10 years 20 M 15 A symptomless swelling mass for more than 6 months A hard and fixed mass in the right maxilla, about cm, with the absence of the maxillary right canine to the second molar A hard mass in the posterior teeth region with local mucosa erosion A giant mass in the right face with the expansion of the hard palate A fixed and well-defined mass, approximately 5 cm in diameter, with two soft and movable lymph nodes in the neck A hard mass in the right mandible, 3 cm in diameter Expansion of the whole mandible, about cm 3 A hard mass, about 2.5 cm in diameter with the absence of 7-4, first premolar to second molar A fixed osteal mass in the anterior region Buccal expansion of the right mandible with the absence of the second and third molars A round hard and smooth mass in the right mandible, about 5 cm in diameter, the first and second molars lingual displacing various ranges. The radiographic appearance of case 8 demonstrated an irregular multilocular lesion with the resorption of the affected teeth roots. Some honeycombed septa were scattered in the lesion. The lesion occupied almost the whole of the left mandibular ascending ramus and extended to the apex area of the left second premolar. The lesion was bulging and the cortex of mandibular bone was thinned (Figure 2). Case 7 also presented multicystic lesions but without obvious root resorption. Another 11 cases of OF chiefly revealed a mixeddensity mass, of which the internal structure was a mixture of radiolucent and radiopaque tissue. In four cases of this kind, a radiolucent band of capsule at the periphery separated the more mature internal radiopaque portion from the surrounding normal bone (Figure 3). However, in another seven cases, the radiographic border of the tumour appeared relatively defined and corticated (Figure 4). The tumours in two cases grew so large that the X-ray image showed a giant mass. The lesion of case 13 was located at the right side of the maxilla, occupying two-thirds of the face. The radiographic appearance revealed a round-like medium-density mass with cancellate dense lines in it (Figure 5). The tumour grew much larger and the neighbouring teeth had obviously migrated compared with 3 years previously (Figures 6 and 7). Another giant tumour, involving two sides of the mandible in case 16, was a recurrent case. The patient underwent local resection of the lesion at the left side of the mandible at the first presentation, and then underwent another resection of part of the jaw and bioceramic prosthesis implantation after 9 months because of the first recurrence. 5 years later, the tumour again recurred and involved the bilateral jaw bone. The left lateral position radiograph showed the rest of the bioceramic prosthesis (Figures 8 and 9).
3 Y Liu et al 59 Table 2 Radiological information on 20 cases of ossifying fibroma Case no. Radiographic appearance 1 Round-like, unicystic, obvious expansion, at the molar region of the right mandible 2 Oval, unicystic, with a tooth in it, at left mandibular ascending ramus 3 Round-like, small, unicystic, between the mandibular left premolars 4 Oval radiolucent cyst, at the apex area from the mandibular right canine to left first premolar 5 Round-like, radiolucent cyst, at the root of the second premolar and the first molar of the right mandible 6 Round, unicystic, at the chin from the right canine to the left canine 7 Irregular, multicystic, well defined, at the left premolar region of the maxilla 8 Irregular, well defined, multicystic, from the left molar region of the mandible to the mandibular ascending ramus 9 Round, well defined, medium-density, at the chin 10 Round-like, mixture of radiolucent and radiopaque tissue, at the left premolar region of the mandible 11 Round-like, honeycombed septum, at the premolar and canine region of the right maxilla with the expansion of maxillary antral lumen 12 Oval, radiopaque, pushing the adjacent teeth, between the first and second molars at the left mandible 13 Round, large, medium density, occupying two-thirds of the face 14 Round, large, medium density, obvious expansion, occupying the whole right part of the mandible 15 Round, mixed density, at the molar of the right mandible 16 Round and large, obvious expansion, involving two sides of the mandible 17 Irregular, high density, at the right premolar and maxillary sinus 18 Irregular, radiopaque, relatively well defined, at the region from the right first premolar to the left second premolar 19 Irregular, relatively radiopaque, obvious expansion, at the molar region of the right mandible 20 Oval, well defined, radiolucent, at right premolar region before operation; irregular, honeycombed septum, 5 years after operation; irregular, ill defined, radiopaque, bigger 20 years after operation The last special case was located at the apex of the canine and first premolar in the right mandible, featuring both the cystic and mixed-density features in different phases. The radiographic appearance revealed a unicystic view before the patient accepted local curettage of the tumour (Figure 10). Five years after the operation, the tumour presented as an irregular multicyst when it recurrenced (Figure 11). However, the X-ray image showed a high-density mass expanded downward, with the adjacent teeth leaning to the lesion area, 19 years after the first radiological examination (Figure 12). In nine cases (45%), the affected teeth roots were resorbed and the lamina dura was usually missing. Four cases (20%) revealed only that the lamina dura of Table 3 Radiological diagnosis Case no. Radiological diagnosis 1 Calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumour 2 Ossifying fibroma 3 Calcifying odontogenic cyst 4 Ossifying fibroma 5 Ossifying fibroma 6 Odontogenic cyst or tumour 7 Odontogenic cyst 8 Ameloblastoma 9 Ameloblastoma or fibro-osseous lesion 10 Fibro-osseous lesion 11 Fibro-osseous lesion 12 Odontogenic fibroma 13 Fibro-osseous fibroma 14 Fibro-osseous lesion 15 Fibro-osseous lesion or benign cementoblastoma 16 Ossifying fibroma 17 Complex odontoma or osteochondroma 18 Ossifying fibroma 19 Odontogenic benign tumour 20 Ameloblastoma or odontogenic cyst involved teeth was missing or obscure. Six cases (30%) showed displacement of the involved teeth and the lamina dura missing, but no root resorption. The relation between the lesions and the roots of the teeth in the last case (5%) was not clear because of the extraction of the affected teeth. Only nine cases that were treated surgically had operation reports (Table 4). The treatments included local curettage, local resection of the lesion, excision of jaw bone and reconstructive plate internal fixation, excision of jaw bone and rib graft, and excision of jaw bone and ceramic prosthesis reconstruction. There was follow-up on 11 patients, ranging from half a month to 20 years, and recurrences were found in 3 cases. Discussion The term ossifying fibroma has been used since 1927, and since 1968 cementum-containing tumours have been grouped together. 1 In 1971 the World Health Figure 1 Case 5. Panoramic radiograph showing a unicystic lesion at chin region. The image between the lesion and normal bone was easy to distinguish
4 60 Y Liu et al Figure 2 Case 8. Panoramic radiograph showing a multicystic lesion with the resorption of the affected teeth roots. Some honeycombed septa are scattered in the lesion. The lesion was bulging and the cortex of mandibular bone was thinned Organization (WHO) classified four types of cementum-containing lesions: fibrous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma, cementifying fibroma and cemento-ossifying fibroma. 4 According to the second WHO classification, benign fibro-osseous lesions in the oral and maxillofacial regions were divided into two categories, osteogenic neoplasm and non-neoplastic bone lesions; cementifying ossifying fibroma belonged to the former category. 5 However, the term cementifying ossifying fibroma was reduced to ossifying fibroma in the new WHO classification in The origin of OF is thought to be the periodontal membrane. 7 Some OFs do, in fact, contain prevalent cementum-like calcifications and others show only bony material, but a mixture of the two types of calcification is commonly seen in a single lesion. 4,5 It can occur at any age, however, many authors confirmed that OF of the jaw tended to occur middle-aged patients. 2,7 9 OF of the jaw bone shows a predilection Figure 4 Case 15. An oblique lateral projection showed that there was much high-density mass as cancellate dense lines in the lesion. The border between the lesion and the normal bone was relatively defined; there was often a dense bone line surrounding the lesion. The mesial root of the right second molar was resorbed for females. 2,8,9 In the cases shown in this report, females were also affected more than males. OF predominantly affects the craniofacial bone and rarely involves the long bones. Of the craniofacial bones, the Figure 3 Case 18. Lower occlusal film showing the border between the lesion and the normal bone as a low-density area, thus it is more indistinct than the cystic lesions Figure 5 Case 13. Posteroanterior cephalometric projection showing the lesion occupying two-thirds of the patient s face, located at the right side of the maxillary bone
5 Y Liu et al 61 Figure 6 Case 13. Lateral cephalometric projection, The maxillary lateral cephalometric projections revealed a round-like medium-density mass with cancellate dense lines in it mandible is the most commonly involved site, typically inferior to the premolars and molars. 10 Although MacDonald-Jankowski 11 considered that radiological diagnoses was not difficult for specialist radiologists, not all radiological diagnoses in the Figure 8 Case 16. Left lateral cephalometric projection. The radiographs in Figures 8 and 9 demonstrate that the tumour involved the bilateral jaw bone. The left mandible had been restored by bioceramic prosthesis reports were in accordance with the final histological diagnoses. However, for the early cases no CT scanning was available in the hospital and the similar radiological appearance of the tumour in the jaw bone may of confused the diagnosis of the radiologists. Here, in these reports, the radiographic characteristics of the tumour have two basic patterns: cystic lesion (unicystic or multicystic) and mixed-density lesion. The radiographic borders of the tumour appear relatively smooth, well defined and mostly corticated. The Figure 7 Case 13. Lateral cephalometric projection, The tumour has grown much larger and the affected teeth have obviously migrated, compared with 3 years previously Figure 9 Case 16. Right lateral cephalometric projection
6 62 Y Liu et al Figure 12 Case 20. Panoramic radiograph showed a high-density mass expanded downward and the affected teeth leaned toward the lesion area in 2000 Figure 10 Case 20. Right lateral oblique projection showing a single cystic view, 1981 contour is regular. The lesion tends to be concentric within the medullary part of the bone with outward expansion approximately equal in all directions. This can result in the expansion of the outer cortical plate of bone. A significant point is that the outer cortical plate, although displaced and thinned, remains intact, especially in those giant tumours. The density of the lesion is mixed. The internal structure may be a mixture of radiolucent and radiopaque tissue. The expansion of the tumour can result in displacement of teeth or the inferior alveolar canal. The lamina dura of involved teeth is usually missing and the affected teeth roots may be resorbed in some cases. Some lesions exhibited aggressive growth. Those massive expansile lesions can involve the whole jaw bone. This pattern lesion often Figure 11 Case 20. Right lateral oblique projection showing an irregular, honeycombed cyst, 1986 showed medium-density mass with cancellate dense lines in it. In his review MacDonald-Jankowski, 11 reported that the radiology of the OF in contrast to fibrous dysplasia is well defined and round or oval in shape. But, in fact OF may present as irregular in shape, especially if the tumour recurs or grows quickly in a short period. In these cases, the tumours always grow along the body of the jaws, even involving the whole jaw. This phenomenon suggests that OF may display aggressive local growth. There was a case of giant OF among the current sample, which was approximately 15 cm in diameter. The tumour not only involved the right maxilla, but also affected the hard palate, the right maxillary antrum, the right zygoma and even the inferior floor of the right orbit. Its histological diagnosis was OF, but not juvenile ossifying fibroma (JOF). JOF is another kind of benign lesion, which is similar to OF but more aggressive and of earlier onset. The case suggests that OF, particularly in children (below 15-years-old), could also exhibit rapid growth and erosion or invasion of the adjacent tissue. In this special case, it is unfortunate that the tumour became too large for surgical treatment. Resection of the tumour as early as possible is necessary. OF requires radical surgery because of the tendency for recurrence and possibility of malignant transformation. 8,12 All reported patients with partial or incomplete resection experienced recurrence. 13,14 The time of recurrence was always unpredictable, ranging from 6 months to 7 years after the operation in our reports. Therefore, there must be a long enough follow-up period of at least 10 years. In the recurrent cases in the study, the tumour often became much larger or the radiographic appearance changed extensively, especially in case 20. There were three different radiological appearances (from unicyst, multicyst to radiopaque mass) during this follow-up period. These appearances demonstrate that this group of lesions could be considered as a spectrum of processes arising from cells in the periodontal ligament. It is known, most OFs, once completely excised, do not recur. However, although the patient in case 16
7 Y Liu et al 63 Table 4 Operation reports and outcomes Case No. Operation Follow-up period Outcome 1 Local resection of the lesion 7 months No recurrence, pathological fracture 3 Local curettage None 6 Excision of jaw bone and reconstructive plate 5 months No recurrence, the implanted bone was OK internal fixation 8 Local resection of the lesion None 9 None 7 years The lesion became larger and the radiological appearance became more radiopaque 10 Excision of jaw bone and rib graft 7 years No recurrence 11 Local resection of the lesion 7 years Recurred, the lesion become larger, but symptomless 13 No 3 years The lesion became larger and the patient lost the opportunity for an operation 16 Excision of jaw bone and ceramic prosthesis 6 months Recurred, the tumour involved the whole of the mandible 19 Excision of jaw bone and reconstructive plate 2 weeks No recurrence internal fixation 20 Local curettage 20 years Recurred, the radiological appearance became more radiopaque accepted a radical resection, the tumour recurred, becoming larger and occupying the whole mandible. It seems that the operation may have stimulated the growth of the tumour. Some authors report that infection and dental extractions stimulate the periodontal membrane to produce and deposit cementum. 8 It is possible that trauma could serve as a factor in the proliferation of OF References 1. Hamner JE, Scofied HH, Cornyn J. Benign fibro-osseous jaw lesions of periodontal membrane origin. An analysis of 249 cases. Cancer 1968; 26: Waldron CA, Giansanti JS. Benign fibro-osseous lesions of the jaw: a clinical-radiologic review of sixty-five cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1973; 35: Eversole LR, Merrell PW, Strub D. Radiographic characteristics of central ossifying fibroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1985; 59: Pindborg JJ, Kramer IRH. Histological typing of odontogenic tumors, jaw cysts and allied lesions. In: International histological classification of tumors. Geneva: WHO, 1971, pp Kramer IRH, Pindborg JJ, Shear M. Neoplasm and other lesions related to bone. Histologic typing of odontogenic tumors, World Health Organization. Berlin, Springer-Verlag 1992: Reichart PA, Philipsen HP, Sciubba JJ. The new classification of Head and Neck Tumours (WHO) any changes? Oral Oncol 2006; 42: Krausen AS, Pullon PA, Gulmen S, Schenk NL, Ogura JH. Cementomas aggressive or innocuous neoplasm? Arch Otolaryngol 1977; 103: Hammer JE, Linghtbody PM, Ketcham AS, Swertlow H. Cemento-ossifying fibroma of the maxilla. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1968; 26: Longdon JD, Rapidis AD, Patel MF. Ossifying fibro-osseous lesions of the jaw. Br J Oral Surg 1976; 14: Eversole LR, Leider AS, Patel MF. Ossifying fibroma: a clinicopathologic study of sixty-four cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1985; 60: MacDonald-Jankowski DS. Fibro-osseous lesions of the face and jaws. Clin Radiol 2004; 59: Bertrand B, Eloy P, Cornelis JP, Gosseye S, Clotuche J, Gilliard C. Juvenile aggressive cemento-ossifying fibroma: case report and review of the literature. Laryngoscope 1993; 103: Margo CE, Ragsdate BD, Perman KI, Zinnerman LE, Sweet DE. Psammomatoid (juvenile) ossifying fibroma of the orbit. Ophthalmology 1985; 92: Margo CE, Weiss A, Habal MB. Psammomatoid ossifying fibroma. Arch Ophthalmol 1986; 104: Wenig BL, Sciubba JJ, Cohen A, Goldstein MN, Abramson AL. A destructive maxillary cemento-ossifying fibroma following maxillofacial trauma. Laryngoscope 1984; 94: Brademann G, Werner JA, Jänig U, Mehdorn HM, Rudert H. Cemento-ossifying fibroma of the petromastoid region: case report and review of the literature. J Laryngol Otol 1997; 111: Cheng C, Takahashi H, Yao K, Nakayama M, Makoshi T, Nagai H, et al. Cemento-ossifying fibroma of maxillary and sphenoid sinuses: case report and literature review. Acta Otolaryngol 2002; 547(Suppl):
Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle
 (2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
(2010) 39, 314 319 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Unusual radiographic appearance of ossifying fibroma in the left mandibular angle M Araki*,1,4, K Matsumoto
A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of. the ethmoid sinus
 Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible
 Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Case Report Aggressive Juvenile Ossifying Fibroma of the Anterior Mandible Dr.Ravikumar.R 1, Dr.Raghavendra.K 2, Dr.Santhosh Kumar 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Reader Department of Oral Surgery, Sri Siddhartha
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
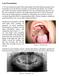 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth or a need. Case report and Extensive review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
Reconstruction of large mandibular defects
 Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN A CASE REPORT
 www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 18/May 05, 2014 Page 4859
 CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions.
 Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up
 OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
The concept of unicystic ameloblastoma (UA) was
 Publication Treatment of Giant Unicystic Ameloblastoma Suction Drainage and Secondary Curettage: a Case Report Bing LIU 1, Wen Feng ZHANG 1, Xin Ming CHEN 2, Zhi Jun SUN 3, Mohd Jamal Alsharif 1, Yi Fang
Publication Treatment of Giant Unicystic Ameloblastoma Suction Drainage and Secondary Curettage: a Case Report Bing LIU 1, Wen Feng ZHANG 1, Xin Ming CHEN 2, Zhi Jun SUN 3, Mohd Jamal Alsharif 1, Yi Fang
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth
 Oral Science International, November 2008, p.150 154 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth Hiroyuki
Oral Science International, November 2008, p.150 154 Copyright 2008, Japanese Stomatology Society. All Rights Reserved. Garré s Osteomyelitis of the Mandible Caused by an Infected Wisdom Tooth Hiroyuki
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report
 Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 212-216, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82185 A Case Report on Surgical Management of Odontogenic Keratocyst 1
Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference to their nature and interrelationship
 J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted Canines: Report of Five Cases Sulabha AN, Sachin Deshpande, Sameer C
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(3):56-60 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Intraosseous Transmigration of Impacted
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area. Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3. Objectives.
 Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary Intraoral examinations are the backbone of dental radiography.
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Lateral Area Carmen Elena Georgescu1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary Intraoral examinations are the backbone of dental radiography.
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Huge Central Ossifying Fibroma on the Anterior Mandible : A Case Report
 Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(4):243-250 하악전방부에발생한거대중심성골화성섬유종 문성용 1) *, 김수관 1), 김학균 2), 윤정훈 3) ** 조선대학교치과대학구강악안면외과학교실 1), 충남대학교의과대학치과학교실구강악안면외과 2) 원광대학교치과대학대전치과병원구강병리과 3) Huge Central
Kor J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2012;36(4):243-250 하악전방부에발생한거대중심성골화성섬유종 문성용 1) *, 김수관 1), 김학균 2), 윤정훈 3) ** 조선대학교치과대학구강악안면외과학교실 1), 충남대학교의과대학치과학교실구강악안면외과 2) 원광대학교치과대학대전치과병원구강병리과 3) Huge Central
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
Pleomorphic adenoma of palate: differential diagnosis and case report
 Case report Pleomorphic adenoma of palate: differential diagnosis and case report 1Dr. Jigna S. Shah, 2 Dr. MonaliPrajapati, 3 Dr. Utsav Bhatt 1Professor & Head, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Case report Pleomorphic adenoma of palate: differential diagnosis and case report 1Dr. Jigna S. Shah, 2 Dr. MonaliPrajapati, 3 Dr. Utsav Bhatt 1Professor & Head, Dept of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Govt.
Unusual Solitary Osteoma Coronoid Process And Aesthetic Facial Correction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Unusual Solitary Osteoma Coronoid Process And Aesthetic Facial Correction Z Núñez-Gil Citation Z Núñez-Gil.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Unusual Solitary Osteoma Coronoid Process And Aesthetic Facial Correction Z Núñez-Gil Citation Z Núñez-Gil.. The Internet Journal
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2015; 45: 49-54 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.49 Unusually large erupted complex odontoma: A rare case report Shivanand B. Bagewadi 1, *, Rahul Kukreja 1, Gundareddy
Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2016; 34(2): 123-8 Original Article Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report Sedigheh Bakhtiari 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas 2 Seyyed Hasan
Journal of Dental School 2016; 34(2): 123-8 Original Article Coincidence of Compound Odontoma and Cemento Ossifying Fibroma; A Rare Case Report Sedigheh Bakhtiari 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas 2 Seyyed Hasan
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
Key words: Third molar, Impacted tooth, Tooth Eruption, Molar, Mandible, Unerupted Tooth.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2014;4(2):286-290 OPG and CBCT Finding s of an Ectopic Third Molar in the Sub-condylar Region Tatu Joy E 1, Farakath Khan 1, Shameel Mohammed 2 From the Department of Oral Medicine
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
Case Report RESECTION OF AMELOBLASTOMA FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT
 Case Report FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT Tariq Javed 1, Waqar Jeelani 2, Qurat ul Ain 1 1 Senior Registrar, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
Case Report FOLLOWED BY RECONSTRUCTION WITH NONVASCULARISED ILIAC BONE GRAFT A CASE REPORT Tariq Javed 1, Waqar Jeelani 2, Qurat ul Ain 1 1 Senior Registrar, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,
